-
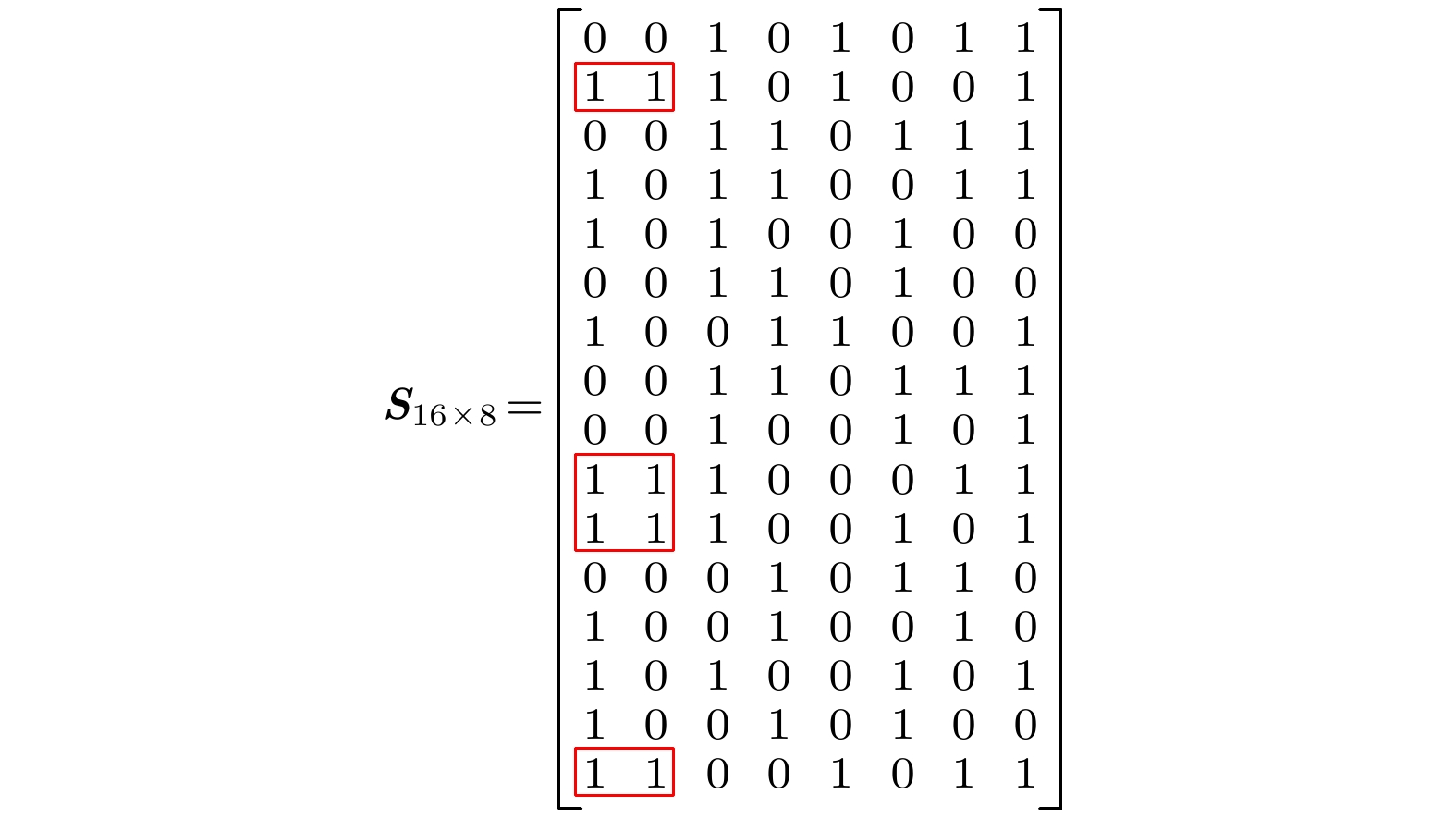
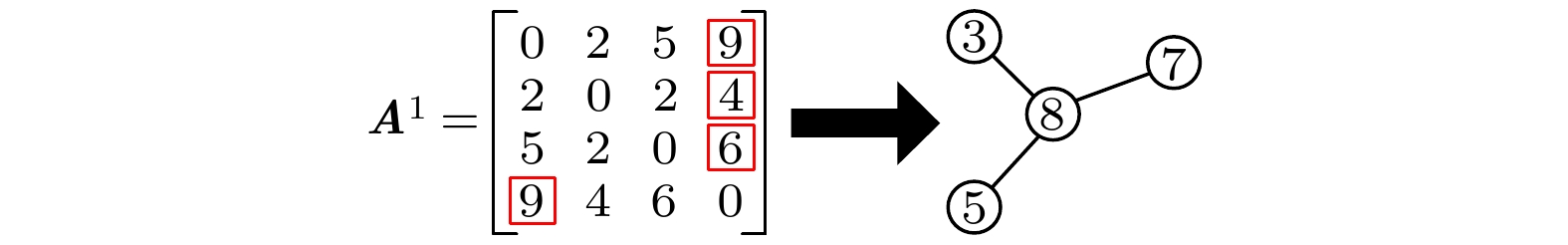
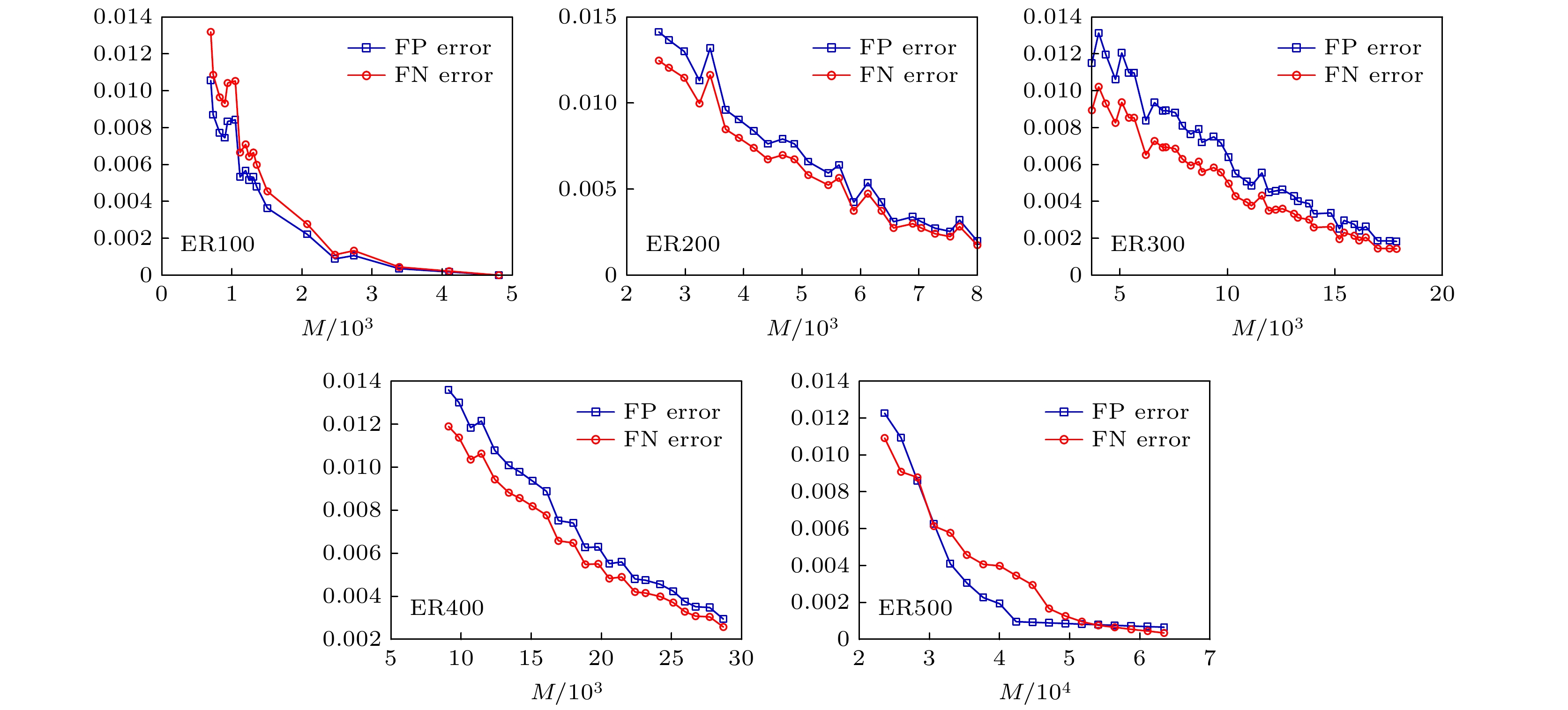
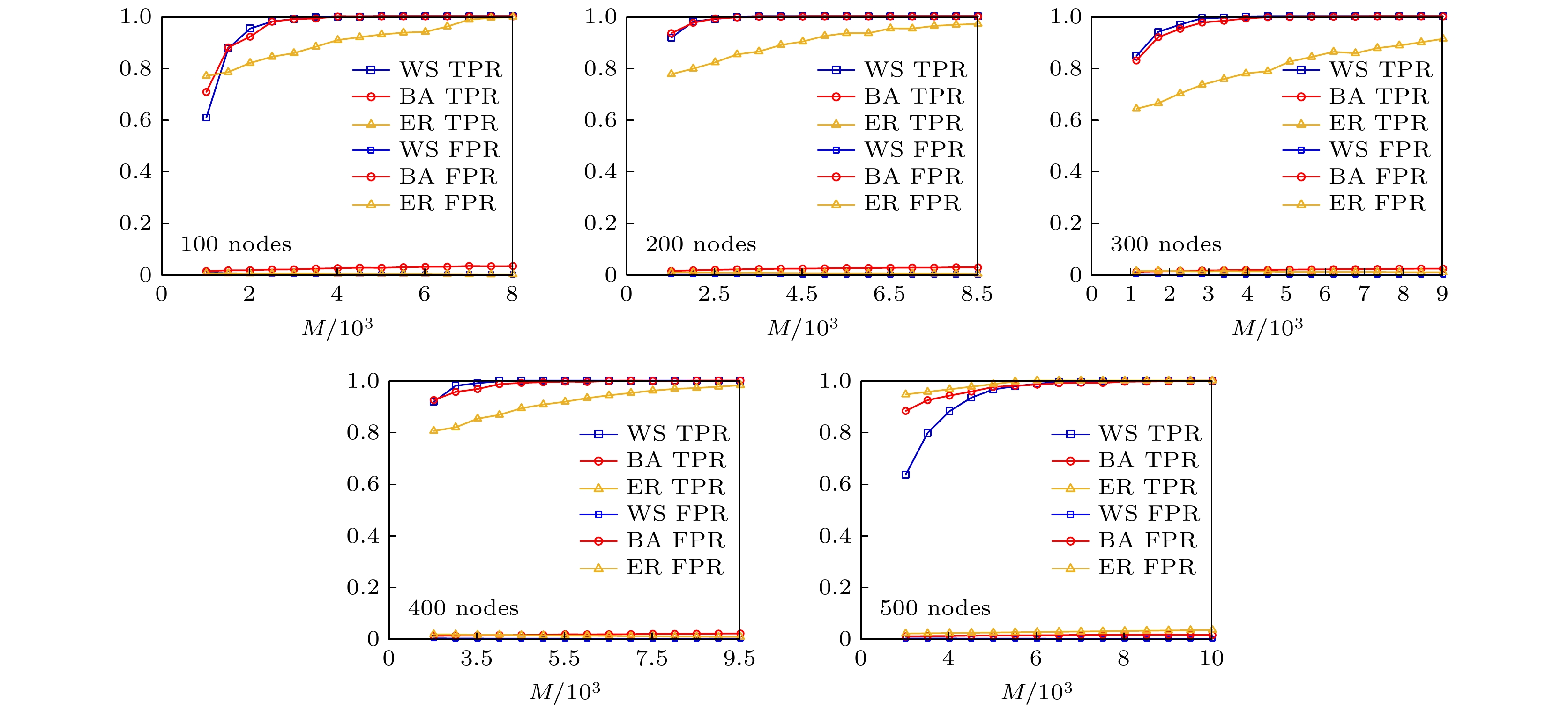
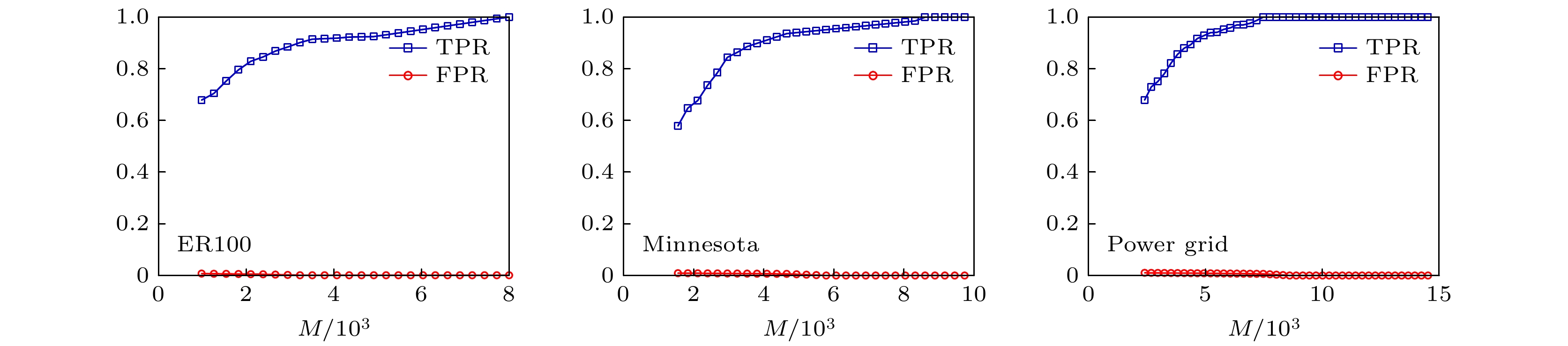
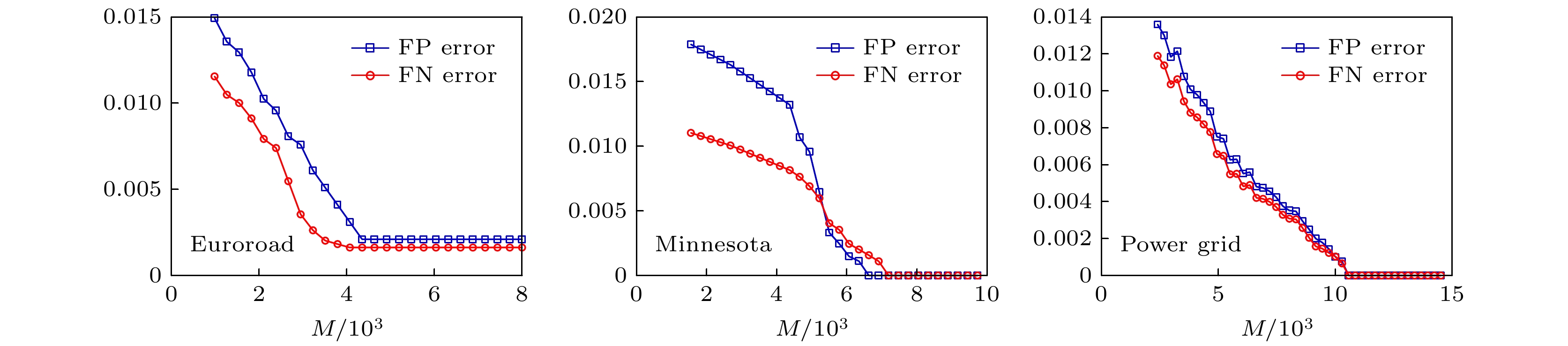
The structure and the function of network interact with each other. The function of network is often reflected as the dynamic process on the network. The dynamic process on the network is reflected by the behavior data in the network. Therefore, it is possible to reconstruct the network structure according to the observed data. This paper aims to solve the problem of how to restore the network topology according to the observable discrete data on the network. In this paper, an algorithm to infer the possibility of edge connection between nodes is proposed by using the similarity degree of each node corresponding to each discrete datum, and by reconstructing each local topology of the network through multiple discrete data, and by superposing the local topology obtained from multiple data, the global topology of the whole network is reconstructed finally. The data in the network are generated by SIR (Susceptible Infective Removed) model with infection probability of 0.2 and recovery probability of 1. Each time, a single node is selected as the infected node, and the final infection state of the network is counted as a network datum. In order to verify the feasibility and accuracy of the algorithm, the network reconfiguration experiments are carried out in small world, scale-free and random networks. Through the network reconstruction experiments in the networks of three different types and different scales, we can see that the performances of network reconstruction algorithm in different types of networks are different, and the average degree of network will affect the requirements for data of the network reconstruction algorithm. In order to verify the applicability of the algorithm, network reconstruction experiments are carried out on three practical networks. The results show that the algorithm can be applied to the reconstruction of large-scale networks. In order to show the accuracy of the algorithm more intuitively, we analyze the network reconstruction error after each network reconstruction experiment. The experiment shows that with the gradual increase of network data, the network reconstruction error gradually decreases and finally approaches to 0. In a nutshell, the algorithm we proposed in this work has good applicability and accuracy, and is suitable for different types of network topology reconstructions.
-
Keywords:
- network reconstruction /
- complex networks /
- dynamics /
- discrete data
[1] Martinez N D 1991 Ecol. Monogr. 61 367
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Oh S W, Harris J A, Ng L 2014 Nature 508 207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Watts D J, Strogatz S H 1998 Nature 393 440
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Faloutsos M, Faloutsos P, Faloutsos C 1999 Sigcomm. Comput. Commun. Rev. 29 251
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Scott J 1994 Sociology 22 109
[6] 丁香园新型冠状病毒肺炎数据 https://ncov.dxy.cn/ncovh5/view/pneumonia?from=timeline&isappinstalled=0 [2020-11-16]
Ding Xiang Yuan COVID-19 data https://ncov.dxy.cn/ncovh5/view/pneumonia?from=timeline&isappinstalled=0. [2020-11-16] (in Chinese)
[7] Bongard J, Lipson H 2007 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104 9943
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Sugihara G, May R, Ye H 2012 Science 338 496
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Marbach D, Costello J C, Küffner R 2012 Nat. Methods 9 796
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wang W X, Lai Y C, Grebogi C 2016 Phys. Rep. 644 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Casadiego J, Nitzan M, Hallerberg S, Timme M 2017 Nat. Commun. 8 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Nitzan M, Casadiego J, Timme M 2017 Sci. Adv. 3 e1600396
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhao H, Li L, Peng H, Xiao J, Yang Y, Zheng M 2017 Neurocomputing 219 5
[14] Granger C W 1969 Econometrica 37 424
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Runge J, Bathiany S, Bollt E 2019 Nat. Commun. 10 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Maziarz M 2015 J. Phil. Econ. 8 86
[17] Zhou D, Xiao Y, Zhang Y, Xu Z, Cai D 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 111 054102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wang W X, Yang R, Lai Y C 2011 EPL 94 48006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Shen Z, Wang W X, Fan Y, Di Z, Lai Y C 2014 Nat. Commun. 5 1
[20] Li L, Xu D, Peng H, Kurths J, Yang Y 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zhang Z, Chen Y, Mi Y, Hu G 2019 Phys. Rev. E 99 042311
[22] Hempel S, Koseska A, Kurths J, Nikoloski Z 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 107 3214
[23] Akaike H 1973 Information Theory and an Extension of the Maximum Likelihood Principle (New York: Springer) pp199−213
[24] Donges J F, Zou Y, Marwan N, Kurths J 2009 EPL 87 48007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Stetter O, Battaglia D, Soriano J, Geisel T 2012 PloS Comput. Biol. 8 e1002653
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Sun J, Bollt E M 2014 Physica D 267 49
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Sun J, Taylor D, Bollt E M 2015 SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst. 14 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Sharma P, Bucci D J, Brahma S K, Varshney P K 2019 IEEE T. Netw. Sci. Eng. 7 562
[29] 张海峰, 王文旭 2020 69 088906
Zhang H F, Wang W X 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 088906
[30] 张朝阳, 陈阳, 弭元元, 胡岗 2020 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 1 3
Zhang Z Y, Chen Y, Mi Y Y, Hu G 2020 Sci. Sin.: Phys. Mech. Astron. 1 3
[31] Ma C, Zhang H F, Lai Y C 2017 Phys. Rev. E 96 022320
[32] Wagner A 2000 Nat. Genet. 24 355
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Levnajić Z 2012 arXiv: 1209.0219
[34] Eagle N, Pentland A S, Lazer D 2009 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106 15274
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Lü L, Jin C H, Zhou T 2009 Phys. Rev. E 80 046122
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Clauset A, Moore C, Newman M E 2008 Nature 453 98
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Taskar B, Wong M F, Abbeel P, Koller D 2004 NIPS 16 659
[38] Liu W, Lü L 2010 EPL 89 58007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Ma C, Chen H S, Li X, Lai Y C, Zhang H F 2020 SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst. 19 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Pastor-Satorras R, Castellano C, Van Mieghem P, Vespignani A 2015 Rev. Mod. Phys. 87 120
[41] Zhang H F, Xu F, Bao Z K, Ma C 2018 IEEE T. Circuits-I 66 4
[42] Hempel S, Koseska A, Kurths J, Nikoloski Z 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 107 054101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Han X, Shen Z, Wang W X, Di Z 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 028701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Barabási A L, Albert R 1999 Science 286 509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Erdős P, Rényi A 1960 Publ. Math. Inst. Hung. Acad. Sci. 5 17
-
表 1 三类网络的基本拓扑特征
Table 1. Basic topological features of the three types of networks.
WS networks N E $ \langle k\rangle $ C $ \langle l\rangle $ WS100 100 200 4 0.099 3.61 WS200 200 400 4 0.078 4.17 WS300 300 600 4 0.057 4.51 WS400 400 800 4 0.052 4.74 WS500 500 1000 4 0.082 4.96 WS600 600 1200 4 0.062 5.12 WS700 700 1400 4 0.071 5.25 WS800 800 1600 4 0.079 5.43 WS900 900 1800 4 0.068 5.48 WS1000 1000 2000 4 0.068 5.58 BA networks N E $ \langle k\rangle $ C $ \langle l\rangle $ BA100 100 196 3.92 0.155 3.11 BA200 200 396 3.96 0.075 3.41 BA300 300 596 3.97 0.073 3.53 BA400 400 796 3.98 0.068 3.62 BA500 500 996 3.98 0.037 3.81 BA600 600 1196 3.98 0.044 3.77 BA700 700 1396 3.98 0.034 3.95 BA800 800 1596 3.99 0.023 3.93 BA900 900 1796 3.99 0.020 4.06 BA1000 1000 1996 3.99 0.027 4.14 ER networks N E $ \langle k\rangle $ C $ \langle l\rangle $ ER100 100 487 9.74 0.117 2.249 ER200 200 2056 20.56 0.103 2.004 ER300 300 4579 30.65 0.103 1.936 ER400 400 7936 39.68 0.099 1.917 ER500 500 12284 49.14 0.098 1.909 表 2 三个实际网络的基本拓扑特征
Table 2. Basic topological characteristics of three practical networks.
实际网络 N E $\langle k \rangle$ C $ \langle l \rangle $ Euroroad 1174 1417 2.414 0.020 18.371 Minnesota 2642 3303 2.500 0.017 35.349 Power Grid 4941 6594 2.669 0.107 18.989 -
[1] Martinez N D 1991 Ecol. Monogr. 61 367
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Oh S W, Harris J A, Ng L 2014 Nature 508 207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Watts D J, Strogatz S H 1998 Nature 393 440
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Faloutsos M, Faloutsos P, Faloutsos C 1999 Sigcomm. Comput. Commun. Rev. 29 251
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Scott J 1994 Sociology 22 109
[6] 丁香园新型冠状病毒肺炎数据 https://ncov.dxy.cn/ncovh5/view/pneumonia?from=timeline&isappinstalled=0 [2020-11-16]
Ding Xiang Yuan COVID-19 data https://ncov.dxy.cn/ncovh5/view/pneumonia?from=timeline&isappinstalled=0. [2020-11-16] (in Chinese)
[7] Bongard J, Lipson H 2007 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104 9943
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Sugihara G, May R, Ye H 2012 Science 338 496
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Marbach D, Costello J C, Küffner R 2012 Nat. Methods 9 796
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wang W X, Lai Y C, Grebogi C 2016 Phys. Rep. 644 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Casadiego J, Nitzan M, Hallerberg S, Timme M 2017 Nat. Commun. 8 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Nitzan M, Casadiego J, Timme M 2017 Sci. Adv. 3 e1600396
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhao H, Li L, Peng H, Xiao J, Yang Y, Zheng M 2017 Neurocomputing 219 5
[14] Granger C W 1969 Econometrica 37 424
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Runge J, Bathiany S, Bollt E 2019 Nat. Commun. 10 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Maziarz M 2015 J. Phil. Econ. 8 86
[17] Zhou D, Xiao Y, Zhang Y, Xu Z, Cai D 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 111 054102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wang W X, Yang R, Lai Y C 2011 EPL 94 48006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Shen Z, Wang W X, Fan Y, Di Z, Lai Y C 2014 Nat. Commun. 5 1
[20] Li L, Xu D, Peng H, Kurths J, Yang Y 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zhang Z, Chen Y, Mi Y, Hu G 2019 Phys. Rev. E 99 042311
[22] Hempel S, Koseska A, Kurths J, Nikoloski Z 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 107 3214
[23] Akaike H 1973 Information Theory and an Extension of the Maximum Likelihood Principle (New York: Springer) pp199−213
[24] Donges J F, Zou Y, Marwan N, Kurths J 2009 EPL 87 48007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Stetter O, Battaglia D, Soriano J, Geisel T 2012 PloS Comput. Biol. 8 e1002653
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Sun J, Bollt E M 2014 Physica D 267 49
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Sun J, Taylor D, Bollt E M 2015 SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst. 14 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Sharma P, Bucci D J, Brahma S K, Varshney P K 2019 IEEE T. Netw. Sci. Eng. 7 562
[29] 张海峰, 王文旭 2020 69 088906
Zhang H F, Wang W X 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 088906
[30] 张朝阳, 陈阳, 弭元元, 胡岗 2020 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 1 3
Zhang Z Y, Chen Y, Mi Y Y, Hu G 2020 Sci. Sin.: Phys. Mech. Astron. 1 3
[31] Ma C, Zhang H F, Lai Y C 2017 Phys. Rev. E 96 022320
[32] Wagner A 2000 Nat. Genet. 24 355
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Levnajić Z 2012 arXiv: 1209.0219
[34] Eagle N, Pentland A S, Lazer D 2009 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106 15274
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Lü L, Jin C H, Zhou T 2009 Phys. Rev. E 80 046122
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Clauset A, Moore C, Newman M E 2008 Nature 453 98
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Taskar B, Wong M F, Abbeel P, Koller D 2004 NIPS 16 659
[38] Liu W, Lü L 2010 EPL 89 58007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Ma C, Chen H S, Li X, Lai Y C, Zhang H F 2020 SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst. 19 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Pastor-Satorras R, Castellano C, Van Mieghem P, Vespignani A 2015 Rev. Mod. Phys. 87 120
[41] Zhang H F, Xu F, Bao Z K, Ma C 2018 IEEE T. Circuits-I 66 4
[42] Hempel S, Koseska A, Kurths J, Nikoloski Z 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 107 054101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Han X, Shen Z, Wang W X, Di Z 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 028701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Barabási A L, Albert R 1999 Science 286 509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Erdős P, Rényi A 1960 Publ. Math. Inst. Hung. Acad. Sci. 5 17
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 7956
- PDF Downloads: 139
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: