-
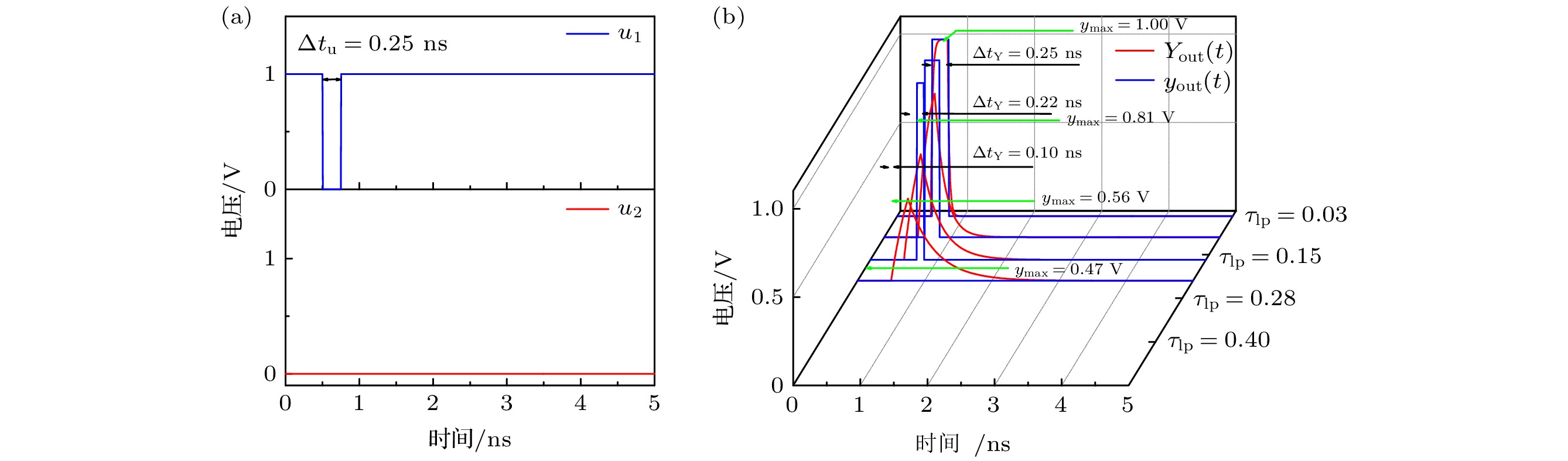
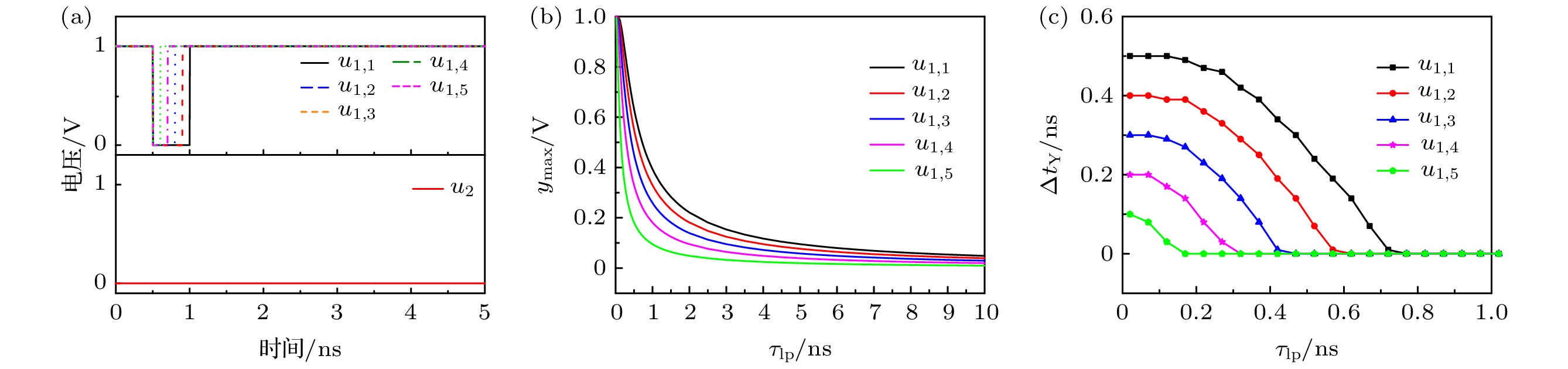
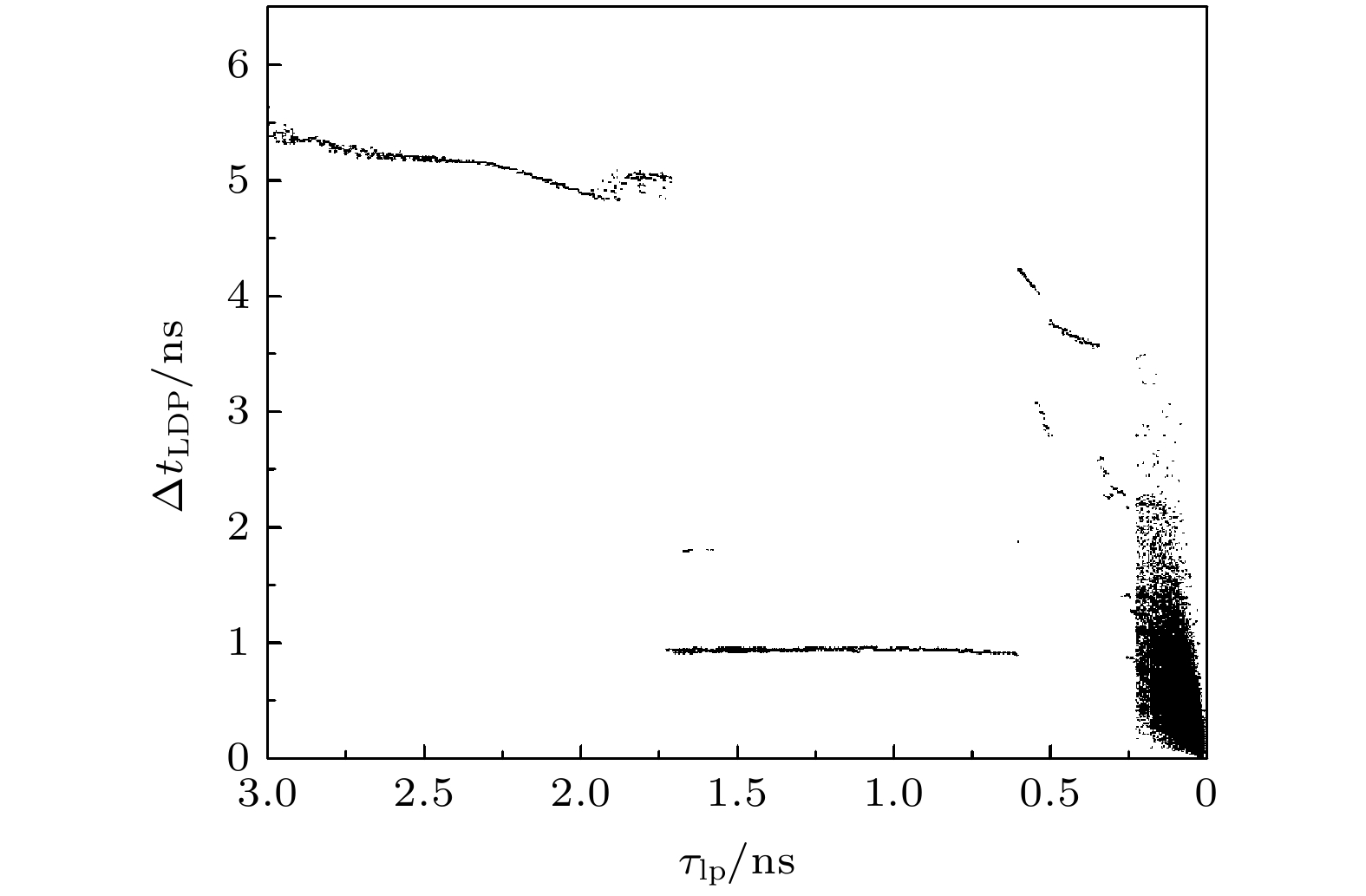
Boolean networks (BNs) are nonlinear systems and each BN has a simple structure, thus it is easy to construct large networks. The BNs are becoming increasingly important as they have been widely used in many fields like random number generation, gene regulation, and reservoir computing. In recent years, autonomous Boolean networks (ABNs) have been proposed and realized by actual digital logic circuit. The BNs each have a clock or selection device to determine the update time of each node. Unlike BNs, ABNs have no device to control the update mechanism, and the update of each node is determined by response characteristics of the logic gate that make up the node, which leads to continuous and complicated outputs. Time series with different complexities including periodic and chaotic sequences can be generated by the ABNs, which is very meaningful in different applications.Research on the regulation of ABNs’ output is of big significance. Non-ideal response characteristics of the logic gates and time delay on the link are two major factors which can regulate the output state. Many studies focus on time delay on the link and indicate that the large delay inconsistency leads to complex outputs.In this paper, in order to study the regulation of ABNs’ output, it is demonstrated that the response characteristics of the logic gate can be continuously adjusted by the parameters in the ABNs’ equations. Then the effects of logic gates’ response characteristics on ABNs’ outputs are studied by simulation. The simulation results indicate that the ABNs’ outputs can transform between periodic and chaotic state with the change of logic gates’ response characteristics. Moreover, the interrelationship between logic gates’ response characteristics and propagation delays along the links is reinvestigated. The results show that the high complexity series space is extended by the fast logic gates’ response characteristics. Also the effects of different logic gates’ response characteristics on the ABNs’ output are compared, and the results indicate that node 2 has a good performance on the regulation of ABNs’ output while node 1 and node 3 show small effect on the ABNs’ output.It is concluded that the complexity of the ABNs’ output can be regulated by the logic gates’ response characteristics, and the high complexity series’ generation can be promoted by the fast logic gates’ response characteristics. This conclusion is conducive to the logic gates’ selection in random number generation, gene regulation, reservoir computing and other applications.
-
Keywords:
- autonomous Boolean network /
- chaos /
- logic gates’ response characteristics /
- permutation entropy
[1] Gaucherel C, Thero H, Puiseux A, Bonhomme V 2017 Ecol. Complex 31 104114
[2] Albert R, Barabasi A L 2000 Phys. Rev. Lett. 84 5660
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ghil M, Zaliapin I, Coluzzi B 2008 Physica D 237 2967
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Kauffman S A 1969 J. Theor. Biol. 22 437
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Bornholdt S 2008 Jr. Soc. Nterface 5 S85
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Tran V, Mccall M N, Mcmurray H R, Almudevar A 2013 Front. Genet. 4 263
[7] Chaves M, Albert R, Sontag E D 2005 J. Theor. Biol. 235 431
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Farrow C L, Heidel J, Maloney J, Rogers J 2004 IEEE T. Neural. Networ. 15 348
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Darby M S, Mysak L A 1993 Clim. Dyn. 8 241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang R, Cavalcante H L D D S, Gao Z, Gauthier D J, Socolar J E S, Adams M M, Lathrop D P 2009 Phys. Rev. E 80 045202
[11] Rosin D P, Rontani D, Gauthier D J 2013 Phys. Rev. E 87 040902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Dong LH, Yang H, Zeng Y 2017 13th International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security, Hong Kong, China, DEC 15
[13] Park M, Rodgers J C, Lathrop D P 2015 Microelectr. J. 46 1364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 马荔, 张建国, 李璞, 徐航, 王云才 2018 中南大学学报 49 888
Ma L, Zhang J G, Li P, Xu H, Wang Y C 2018 J. Cent. South. Univ. (Sci. Tech.) 49 888
[15] 张琪琪, 张建国, 李璞, 郭龑强, 王云才 2019 通信学报 40 2019014
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Q Q, Zhang J G, Li P, Guo Y Q, Wang Y C 2019 J. Commun. 40 2019014
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Canaday D, Griffith A, Gauthier D J 2018 Chaos 28 123119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Haynes N D, Soriano M C, Rosin D P, Fischer I, Gauthier D J 2014 Phys. Rev. E 91 020801
[18] Cheng X R, Sun M Y, Socolar J E S 2012 J. R. Soc. Interface 10 20120574
[19] Sun M Y 2013 Ph. D. Dissertation (Berlin: Duke University).
[20] Charlot N, Canaday D, Pomerance A, Gauthier D J 2020 arXiv: 1907.12542 v2 [cs. CR.]
[21] Cavalcante H L D D S, Gauthier D J, Socolar J E S, Zhang R 2010 Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 368 495
[22] Rosin D P, Rontani D, Gauthier D J 2014 Phys. Rev. E 89 042907
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Rosin D P, Rontani D, Haynes N D, Scholl E, Gauthier D J 2014 Phys. Rev. E 90 030902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] D'Huys O, Lohmann J, Haynes N D, Gauthier D J 2016 Chaos 26 094810
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 龚利爽, 侯二林, 刘海芳, 李凯凯, 王云才 2019 通信学报 40 2019048
Gong L S, Hou E L, Liu H F, Li K K, Wang Y C 2019 J. Commun. 40 2019048
[26] Rosin D 2014 Ph. D. Dissertation (Berlin: Duke University).
[27] Xiang S Y, Pan W, Li N Q, Zhang L Y, Zhu H N 2013 Opt. Commun. 311 294
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Toker D, Sommer F T, D'Esposito M 2020 Commun. Biol. 3 11
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Ghil M, Mullhaupt A 1985 J. Stat. Phys. 41 125
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
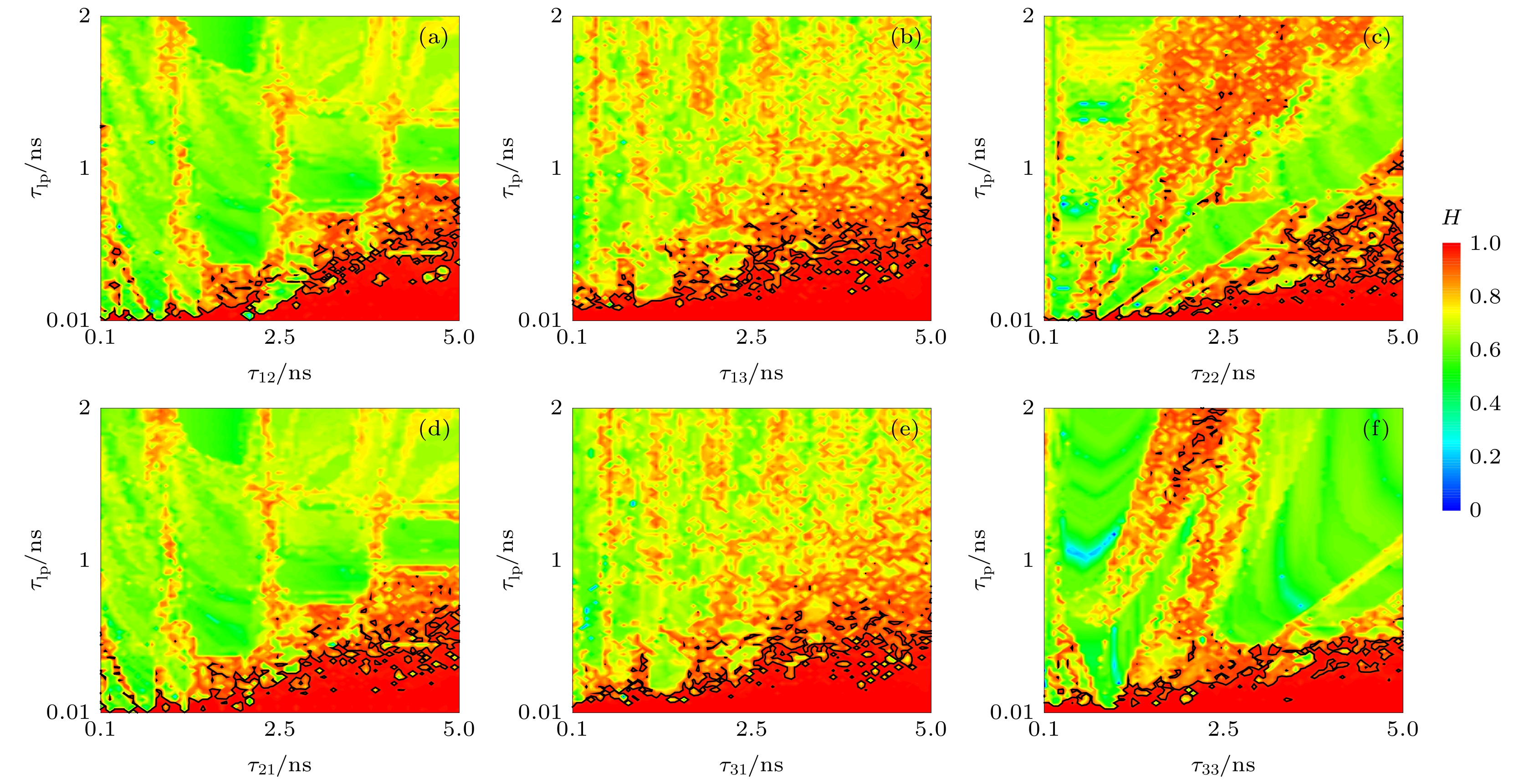
图 9 排序熵值在二维参数空间(τlp,i, τlp,j)上的分布图 (a1)−(a3) τlp,1 = 0.1, 0.3, 0.5 ns且(τlp,i, τlp,j) = (τlp,2, τlp,3); (b1)−(b3) τlp,2 = 0.1, 0.3, 0.5 ns且(τlp,i, τlp,j) = (τlp,1, τlp,3); (c1)−(c3) τlp,3 = 0.1, 0.3, 0.5 ns且(τlp,i, τlp, j) = (τlp,1, τlp,2)
Figure 9. Two dimensional maps of H in the parameter space of (τlp,i, τlp,j): (a1)−(a3) τlp,1 = 0.1, 0.3, 0.5 ns and (τlp,i, τlp,j) = (τlp,2, τlp,3); (b1)−(b3) τlp,2 = 0.1, 0.3, 0.5 ns and (τlp,i, τlp,j) = (τlp,1, τlp,3); (c1)−(c3) τlp,3 = 0.1, 0.3, 0.5 ns and (τlp,i, τlp,j) = (τlp,1, τlp,2).
-
[1] Gaucherel C, Thero H, Puiseux A, Bonhomme V 2017 Ecol. Complex 31 104114
[2] Albert R, Barabasi A L 2000 Phys. Rev. Lett. 84 5660
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ghil M, Zaliapin I, Coluzzi B 2008 Physica D 237 2967
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Kauffman S A 1969 J. Theor. Biol. 22 437
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Bornholdt S 2008 Jr. Soc. Nterface 5 S85
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Tran V, Mccall M N, Mcmurray H R, Almudevar A 2013 Front. Genet. 4 263
[7] Chaves M, Albert R, Sontag E D 2005 J. Theor. Biol. 235 431
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Farrow C L, Heidel J, Maloney J, Rogers J 2004 IEEE T. Neural. Networ. 15 348
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Darby M S, Mysak L A 1993 Clim. Dyn. 8 241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang R, Cavalcante H L D D S, Gao Z, Gauthier D J, Socolar J E S, Adams M M, Lathrop D P 2009 Phys. Rev. E 80 045202
[11] Rosin D P, Rontani D, Gauthier D J 2013 Phys. Rev. E 87 040902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Dong LH, Yang H, Zeng Y 2017 13th International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security, Hong Kong, China, DEC 15
[13] Park M, Rodgers J C, Lathrop D P 2015 Microelectr. J. 46 1364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 马荔, 张建国, 李璞, 徐航, 王云才 2018 中南大学学报 49 888
Ma L, Zhang J G, Li P, Xu H, Wang Y C 2018 J. Cent. South. Univ. (Sci. Tech.) 49 888
[15] 张琪琪, 张建国, 李璞, 郭龑强, 王云才 2019 通信学报 40 2019014
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Q Q, Zhang J G, Li P, Guo Y Q, Wang Y C 2019 J. Commun. 40 2019014
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Canaday D, Griffith A, Gauthier D J 2018 Chaos 28 123119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Haynes N D, Soriano M C, Rosin D P, Fischer I, Gauthier D J 2014 Phys. Rev. E 91 020801
[18] Cheng X R, Sun M Y, Socolar J E S 2012 J. R. Soc. Interface 10 20120574
[19] Sun M Y 2013 Ph. D. Dissertation (Berlin: Duke University).
[20] Charlot N, Canaday D, Pomerance A, Gauthier D J 2020 arXiv: 1907.12542 v2 [cs. CR.]
[21] Cavalcante H L D D S, Gauthier D J, Socolar J E S, Zhang R 2010 Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 368 495
[22] Rosin D P, Rontani D, Gauthier D J 2014 Phys. Rev. E 89 042907
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Rosin D P, Rontani D, Haynes N D, Scholl E, Gauthier D J 2014 Phys. Rev. E 90 030902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] D'Huys O, Lohmann J, Haynes N D, Gauthier D J 2016 Chaos 26 094810
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 龚利爽, 侯二林, 刘海芳, 李凯凯, 王云才 2019 通信学报 40 2019048
Gong L S, Hou E L, Liu H F, Li K K, Wang Y C 2019 J. Commun. 40 2019048
[26] Rosin D 2014 Ph. D. Dissertation (Berlin: Duke University).
[27] Xiang S Y, Pan W, Li N Q, Zhang L Y, Zhu H N 2013 Opt. Commun. 311 294
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Toker D, Sommer F T, D'Esposito M 2020 Commun. Biol. 3 11
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Ghil M, Mullhaupt A 1985 J. Stat. Phys. 41 125
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 6092
- PDF Downloads: 70
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: