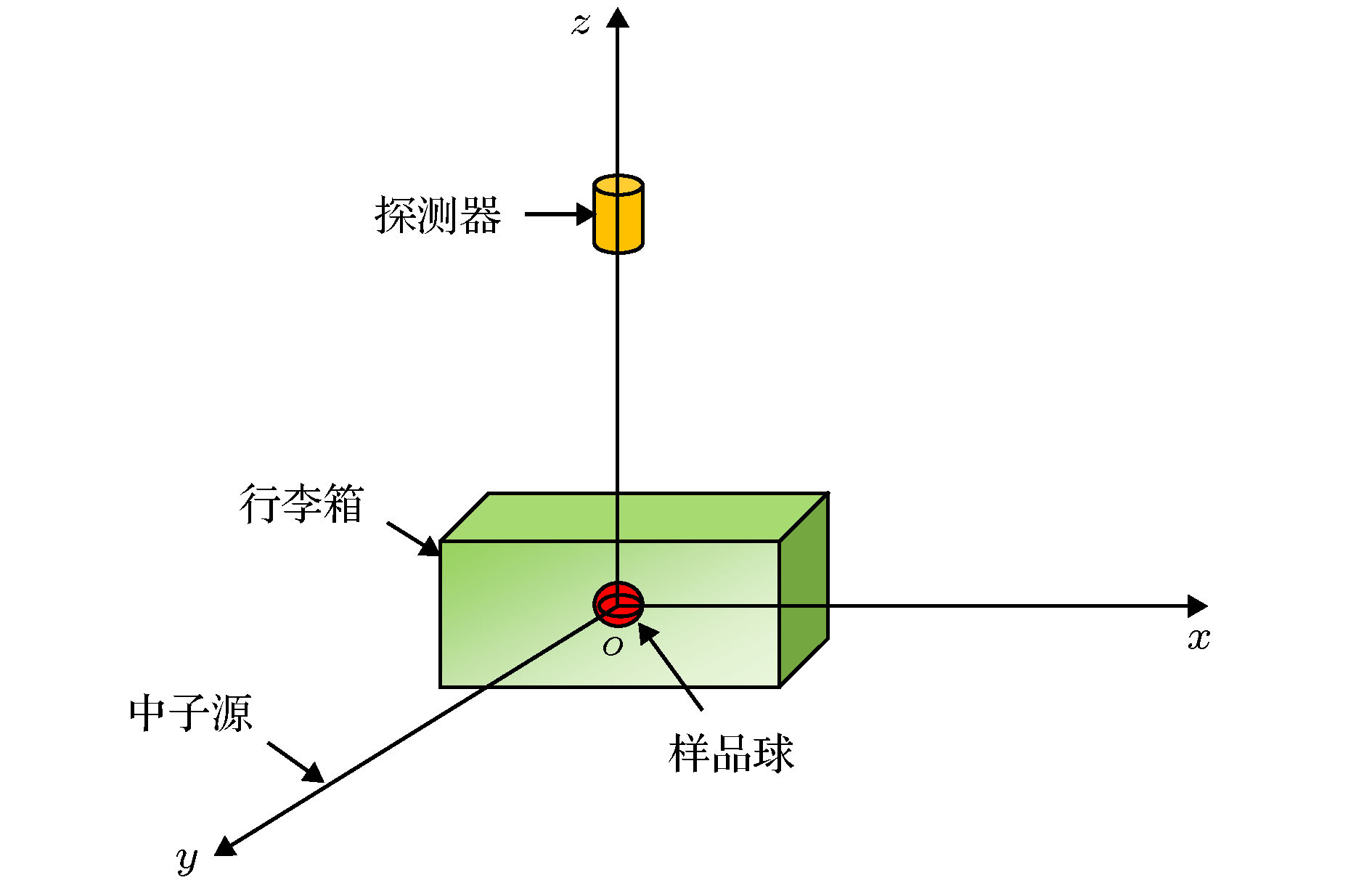
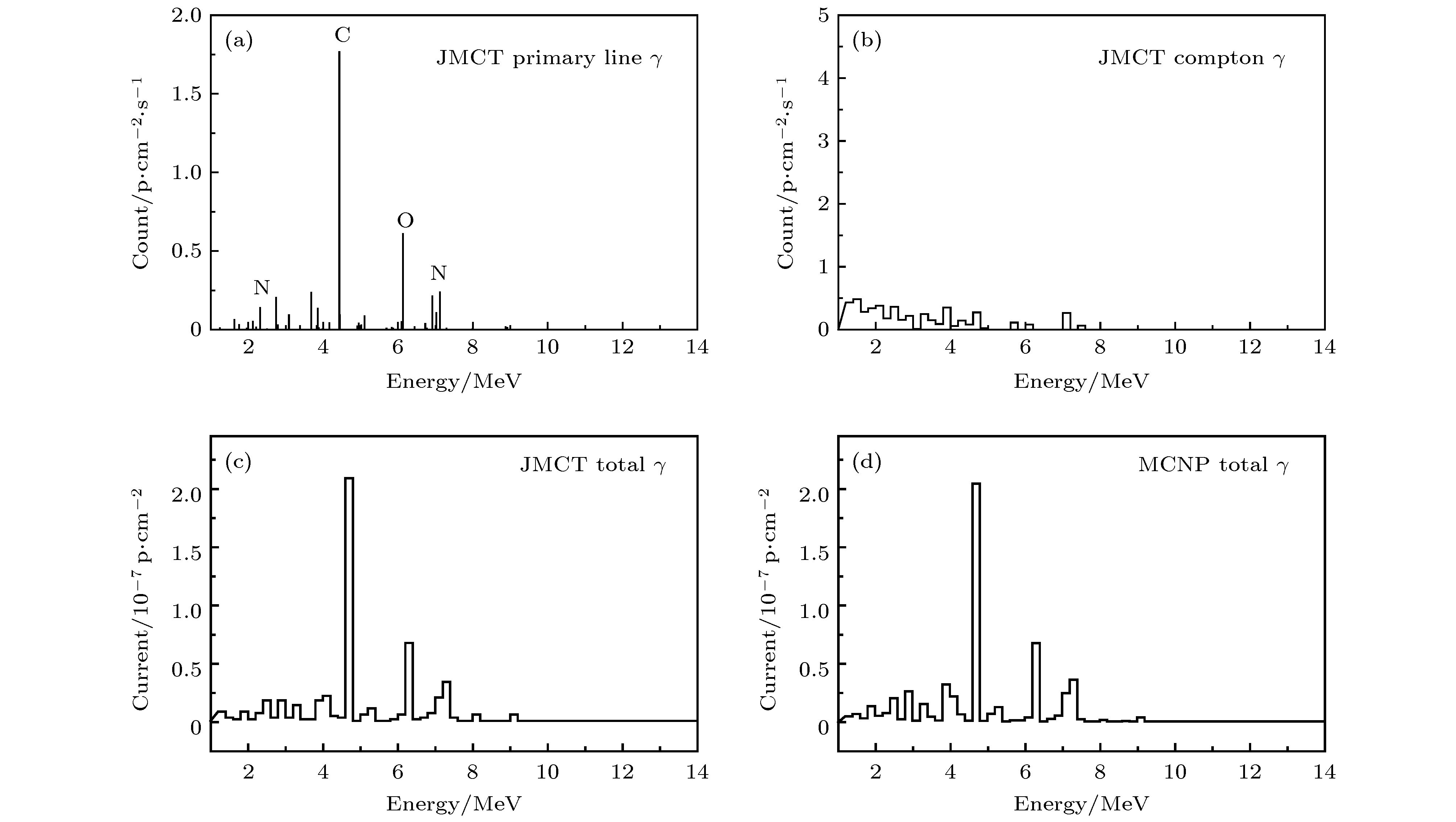
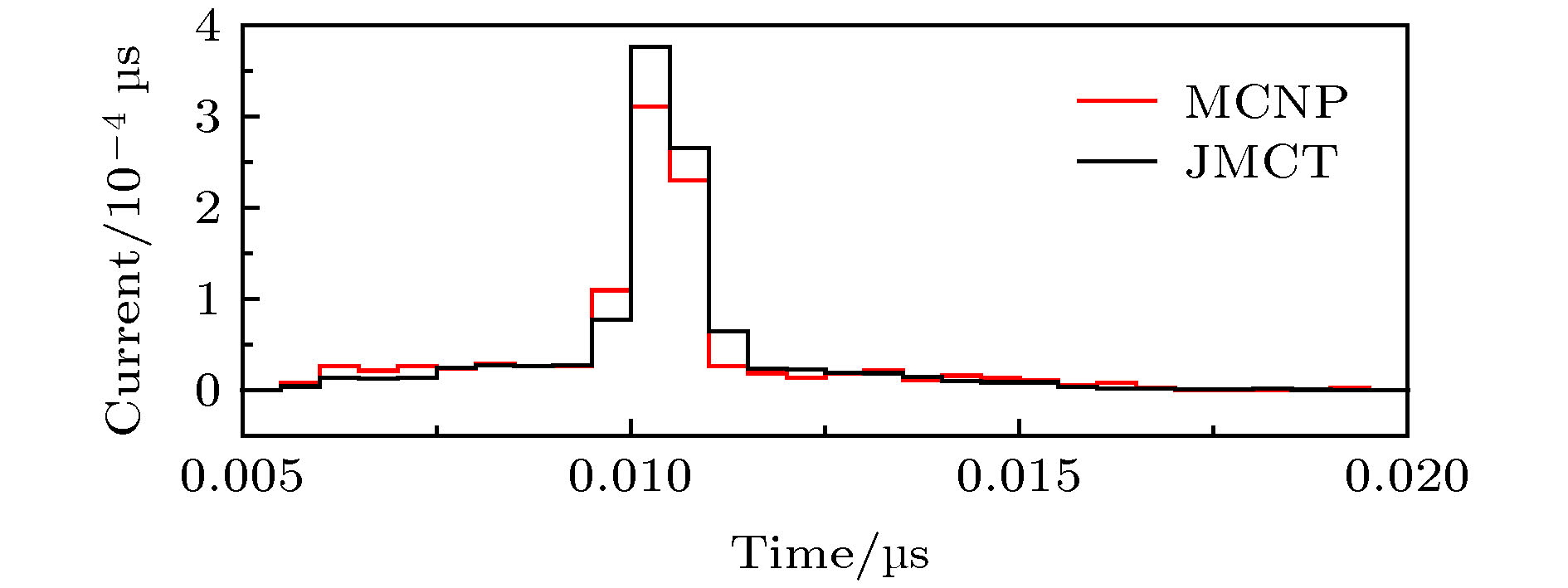
-
Monte Carlo method is an ideal way to simulate criticality, shielding and nuclear detection. JMCT is a multipurpose 3D Mont Carlo (MC) neutron-photon-electron and coupled neutron /photon /electron transport code which is developed by IAPCM. The program is developed based on the combinatorial geometry parallel infrastructure JCOGIN and has the most functions of general Monte Carlo particle transport code, including the various variance reduction techniques. In addition, some new algorithms, such as Doppler broadening on-the-fly (OTF), uniform tally density (UTD), consistent adjoint driven importance sampling (CADIS), fast criticality search of boron concentration (FCSBC), the domain decomposition (DD), the two-level parallel computation of MPI and OpenMP, etc. have been developed, where the number of geometry zones, materials, tallies, depletion zones, memories and period of random number are big enough to simulate various extremely complicated problems. Also the JMCT is hybrid the discrete ordinate SN program JSNT to generate source biasing factors and weight window parameters for deep-penetration shielding problems. The input is based on the CAD modeling, and the result is a visualized output. The JMCT can provide technology support for radiation shielding design, reactor physics and criticality safe analysis. Especially, the JMCT is coupled depletion and thermal-hydraulic code for simulating the reactor feedback effect, including depletion, thermal feedback. In recent years, new function of γ-ray spectrum analysis has been developed. In this paper, the working principles of timing measure are introduced. The advanced calibration count is developed for distinguishing between inelastic γ-ray and capture γ-ray based on time bin tally. On the other hand, when neutron collides with nuclide, the secondary photon is labeled into the primary line photon and primary continuous photon, where energy of primary line photon does not change with the incident neutron energy, such as carbon spectral-line at 4.43 MeV and oxygen spectral-line at 6.13 MeV. The element components of detected object can be determined by the primary line photon. On the other hand, expect value estimator (EVE) is used to produce the secondary photons. The advantage of EVE does not leak any event even with a small probability which is important for detecting the hide exploder. However the shortage of the EVE results in producing a great number of photons with small weight. If all of these small weight photons are simulated one by one, a great amount of computation time and memory will be consumed. For avoiding this case, a new algorithm is design by coupling EVE and DE (direct estimator). The all of secondary photons from EVE only make the direct tally take a little computing time, then end the photon history and return to the DE production photon model (one photon production at most). Final, the total tally is a summation of EVE direct tally and DE scattering tally. The use of new algorithm to realize the analysis of γ-ray spectrum will increase only a little computing time. The numerical tests are done by using own Monte Carlo code JMCT. The correctness and validity of the algorithm are shown preliminarily. -
Keywords:
- Monte Carlo method /
- nuclear detection /
- inelastic γ-ray /
- capture γ-ray /
- expect value estimator
[1] Briesmeister J F 1997 MCNP-a General Monte Carlo Code for n-particle Transport Code US LA-12625-M
[2] Gardner R P, Verghese K 1991 Nucl. Geophys. 5 4
[3] Ullo J J 1986 Nucl. Sci. Eng. 92 228
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Shyu C M, Gardner R P, Verghese K 1993 Nucl. Geophys. 7 241
[5] Verghese K, Gardner R P, Mickael M, et al. 1998 Nucl. Geophys 2 3
[6] Masayori I, Tooru K, Keiji K 2000 Nucl. Instrum. and Methods Phys. Res. 453 614
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Li D, Gang L, Baoyin Z, et al. 2018 PHYSOR2018, Cancun, Mexico, April 22–26 2018
[8] Li G, Zhang B Y, Deng L 2013 ANS Transactions 109 1425
[9] 李刚, 邓力, 张宝印, 等 2016 65 052801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li G, Deng L, Zhang B Y, et al. 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 052801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 刘雄国, 邓力, 胡泽华, 等 2016 65 092501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu X G, Deng L, Hu Z H, et al. 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 092501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Li D, Tao Y, Gang L, et al. 2014 PHYSOR2014, Kyoto, Japan, September 28–October 3 2014
[12] 付元光, 邓力, 李刚 2018 67 172802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fu Y G, Deng L, Li G 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 172802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 蔡少辉 1996 物理 25 12
Cai S H 1996 Physics 25 12
[14] 黄隆基 1985 放射性测井原理 (北京: 石油工业出版社)
Huang L J 1985 Principle of Radiation Oil Well-logging (Beijing: Oil Industry Press) (in Chinese)
[15] 朱达智, 栾士文, 程宗华等 1984 碳氧比能谱测井 (北京: 石油工业出版社)
Zhu Z D, Luan S W, Cheng Z H, et al. 1984 Energy Spectrum Well-logging Based on Ratio of Carbon and Oxygen (Beijing: Oil Industry Press) (in Chinese)
[16] 邓力 2001 博士学位论文 (西安: 西安交通大学)
Deng L 2001 Ph.D. Dissertation (Xian: Xian Jiaotong University) (in Chinese)
[17] Berger M J, Scltzer S M 1972 Nucl. Instrum. Methods 104 317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Jin Y, Gardner R P, Verghese K 1986 Nucl. Instrum. Methods 242 416
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Li D, Shao H C, Zheng F H 1996 J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 33 9
-
表 1 H, C, N, O等核素发射俘获γ谱线和非弹性散射γ谱线能量
Table 1. Energy of spectrum line from inelastic γ and capture γ about H, C, N, O, etc.
元素 反应类型 特征γ 谱线能量/MeV H 辐射俘获 2.2233 C 非弹性散射 4.433 N 辐射俘获非弹性散射 1.8848, 5.2692, 5.5534, 6.3224, 7.2991, 10.8290, 2.3128, 4.4444, 5.1059, 7.0280 O 非弹性散射 2.7419, 3.6841, 6.1310, 6.9170, 7.1190 F 非弹性散射 0.1090, 0.1971, 1.2358, 1.3480, 1.3565 P 辐射俘获非弹性散射 2.1542, 3.5228, 3.9003, 4.6713, 6.7853, 1.2661, 2.2334 S 辐射俘获 0.8411, 2.3797, 2.9311, 3.2208, 4.4308, 4.8698, 5.4205, Cl 辐射俘获 0.5167, 0.7884, 1.1647, 1.9509, 1.9591, 2.8639, 5.7153, 6.1109, 6.6195, 7.4138 As 辐射俘获非弹性散射 6.2941, 6.8094, 7.0192, 0.2646, 0.2795, 0.5725 Al 辐射俘获非弹性散射 0.9840, 2.9598, 4.1329, 4.2522, 7.7239, 0.8438, 1.0144, 2.2118 Fe 辐射俘获非弹性散射 0.3522, 1.7251, 5.9203, 6.0185, 7.6311, 7.6455, 8.8860, 9.2980, 0.8468,
1.2383, 1.4082, 1.8105, 2.1129, 2.5985表 2 烈性炸药(TNT)和某些化学武器中所含元素的重量百分比
Table 2. Weight percentage of elements in some spirited detonators (TNT) and chemical weapons.
元素 TNT 沙林/GB 神经性
毒气/VX芥子气/HD 孁烂性
毒气/L氢(H) 2.2 7.1 9.7 5.0 1.0 碳(C) 37.0 34.3 49.4 30.2 11.4 氮(N) 18.5 5.2 氧(O) 42.3 22.9 12.0 氟(F) 13.6 磷(P) 22.1 11.6 硫(S) 12.0 20.1 氯(Cl) 44.7 51.3 砷(As) 36.1 表 3 JMCT与MCNP次级γ流计算结果比较
Table 3. Comparison of calculated results about secondary γ between JMCT and MCNP.
程序 原级线
光子原级连续
光子散射光子 Jγ 总
光子流偏差/% JMCT 4.92519-7 0 4.34947-8 5.36014-7 0.4406 MCNP 无 无 无 5.38386-7 标准解 注: 偏差 = [Jγ(JMCT) – Jγ(MCNP)]/ Jγ(MCNP). 表 4 H, C, N, O瞬发γ计数及份额
Table 4. Count and percentage of prompt γ from H, C, N and O.
元素 计数 份额比/% 统计误差/% H 3.02643 × 10–11 0 0.56 C 1.77077 × 10–7 36 0.49 N 1.11146 × 10–7 23 0.12 O 2.03254 × 10–7 41 0.18 注: 偏差 = [Jγ(JMCT) – Jγ(MCNP)]/ Jγ(MCNP). -
[1] Briesmeister J F 1997 MCNP-a General Monte Carlo Code for n-particle Transport Code US LA-12625-M
[2] Gardner R P, Verghese K 1991 Nucl. Geophys. 5 4
[3] Ullo J J 1986 Nucl. Sci. Eng. 92 228
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Shyu C M, Gardner R P, Verghese K 1993 Nucl. Geophys. 7 241
[5] Verghese K, Gardner R P, Mickael M, et al. 1998 Nucl. Geophys 2 3
[6] Masayori I, Tooru K, Keiji K 2000 Nucl. Instrum. and Methods Phys. Res. 453 614
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Li D, Gang L, Baoyin Z, et al. 2018 PHYSOR2018, Cancun, Mexico, April 22–26 2018
[8] Li G, Zhang B Y, Deng L 2013 ANS Transactions 109 1425
[9] 李刚, 邓力, 张宝印, 等 2016 65 052801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li G, Deng L, Zhang B Y, et al. 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 052801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 刘雄国, 邓力, 胡泽华, 等 2016 65 092501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu X G, Deng L, Hu Z H, et al. 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 092501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Li D, Tao Y, Gang L, et al. 2014 PHYSOR2014, Kyoto, Japan, September 28–October 3 2014
[12] 付元光, 邓力, 李刚 2018 67 172802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fu Y G, Deng L, Li G 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 172802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 蔡少辉 1996 物理 25 12
Cai S H 1996 Physics 25 12
[14] 黄隆基 1985 放射性测井原理 (北京: 石油工业出版社)
Huang L J 1985 Principle of Radiation Oil Well-logging (Beijing: Oil Industry Press) (in Chinese)
[15] 朱达智, 栾士文, 程宗华等 1984 碳氧比能谱测井 (北京: 石油工业出版社)
Zhu Z D, Luan S W, Cheng Z H, et al. 1984 Energy Spectrum Well-logging Based on Ratio of Carbon and Oxygen (Beijing: Oil Industry Press) (in Chinese)
[16] 邓力 2001 博士学位论文 (西安: 西安交通大学)
Deng L 2001 Ph.D. Dissertation (Xian: Xian Jiaotong University) (in Chinese)
[17] Berger M J, Scltzer S M 1972 Nucl. Instrum. Methods 104 317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Jin Y, Gardner R P, Verghese K 1986 Nucl. Instrum. Methods 242 416
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Li D, Shao H C, Zheng F H 1996 J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 33 9
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 10798
- PDF Downloads: 177
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: