-
Magnetometry has already been widely used in mineral exploration, medical exploration and precision measurement physics. One is trying to improve the sensitivity of the magnetometer. One of the most widely used magnetometers is based on the Bell-Bloom structure, which can be realized by modulating the pump light. The sensitivity of the Bell-Bloom magnetometer is determined by the magnetic resonance linewidth (MRL) and the signal-to-noise under the condition of magnetic resonance (SNR). Both are affected by the pump intensity and the relaxation rate of the atoms. In order to achieve a higher sensitivity, how these factors affect the magnetic field measurement should be analyzed. In this paper, the influence of the pump light on the sensitivity of the linearly polarized Bell-Bloom magnetometer is investigated based on the Bloch equation with amplitude modulated pump beam and the rate equations with spin relaxation. The rate equations are obtained from the Liouville equation, and the theoretical analysis is based on the cesium. The pump beam is linearly polarized and is resonant to D1 transition of cesium. Both the direct pump (pump frequency is resonant to
${6^2}{{\rm{S}}_{1/2}}\;F = 4$ −${6^2}{{\rm{P}}_{1/2}}\;F' = 3$ transition) and the indirect pump (pump frequency is resonant to${6^2}{{\rm{S}}_{1/2}}\;F = 3 $ −${6^2}{{\rm{P}}_{1/2}}\;F' = 4$ transition) are analyzed. The experiment is performed based on a 20-mm cube cesium vapour cell with 20-Torr helium as buffer gas. The linearly polarized probe beam is tuned to resonance to cesium D2 transition${6^2}{{\rm{S}}_{1/2}}\;F = 4$ −$ {6^2}{{\rm{P}}_{3/2}}\;F' = 5$ , and the intensity of the probe is 0.2 W/m2. The spectra of magnetic resonance are measured by using the lock-in detection with a scanning of the modulation frequency. Then the sensitivity can be obtained by measuring MRL and SNR. The experimental results show that the sensitivity and the pump intensity are related nonlinearly, which is coincident with theoretical result. Higher sensitivity can be obtained under the condition of indirect pump. In addition, the effect of atomic spin relaxation on sensitivity is also analyzed with the indirect pump beam. This work clarifies the dynamics of the Bell-Bloom magnetometer to some extent. The highest sensitivity obtained is$31.7\;{\rm{pT}}/\sqrt {{\rm{Hz}}} $ in our experiment, which can be optimized by using other kinds of vapour cells and different measuring methods.[1] Budker D, Romalis M V 2007 Nat. Phys. 3 227
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Allred J C, Lyman R N, Kornack T W, Romalis M V 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 130801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Dang H B, Maloof A C, Romalis M V 2010 Appl. Phys. Lett. 97 151110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Bell W E, Bloom A L 1961 Phys. Rev. Lett. 6 623
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Bell W E, Bloom A L 1961 Phys. Rev. Lett. 6 280
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wang M L, Wang M B, Zhang G Y, Zhao K F 2016 Chin. Phys. B 25 060701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Jiménez-Martínez R, Griffith W C, Knappe S, Kitching J, Prouty M 2012 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 29 3398
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Grujić Z D, Weis A 2013 Phys. Rev. A 88 012508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Mateos I, Patton B, Zhivun E, Budker D, Wurm D, Ramos-Castro J 2015 Sensors and Actuators A: Physical 224 147
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Liu G, Li X, Sun X, Feng J, Ye C, Zhou X 2013 J. Magn. Reson. 237 158
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Pustelny S, Wojciechowski A, Gring M, Kotyrba M, Zachorowski J, Gawlik W 2008 J. Appl. Phys. 103 063108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhang J H, Liu Q, Zeng X J, Li J X, Sun W M 2012 Chin. Phys. Lett. 29 068501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 董海峰, 郝慧杰, 黄海超, 胡旭阳, 周斌权 2014 仪器仪表学报 35 2783
Dong H F, Hao H J, Huang H C, Hu X Y, Zhou B Q 2014 Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 35 2783
[14] Huang H C, Dong H F, Hao H J, Hu X Y 2015 Chin. Phys. Lett. 32 098503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Wang M B, Zhao D F, Zhang G Y, Zhao K F 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 100701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Lucivero V G, Anielski P, Gawlik W, Mitchell M W 2014 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85 113108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Li W H, Peng X, Li S J, Liu C F, Guo H 2016 IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium (IFCS) New Orleans, USA, May 9−12, 2016 p1
[18] Julsgaard B, Sherson J, Sørensen J L, Polzik E S 2004 J. Opt. B 6 5
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Avila G, Giordano V, Candelier V, de Clercq E, Theobald G, Cerez P 1987 Phys. Rev. A 36 3719
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 张军海, 向康, 梅红松, 赵文辉, 黄宗军, 孙伟民 2015 光电子•激光 26 211
Zhang J H, Xiang K, Mei H S, Zhao W H, Huang Z J, Sun W M 2015 J. Optoelectron. Laser 26 211
[21] Ledbetter M P, Savukov I M, Acosta V M, Budker D, Romalis M V 2008 Phys. Rev. A 77 033408
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Yang G Q, Zhang H B, Geng X X, Liang S Q, Zhu Y F, Mao J T, Huang G M, Li G X 2018 Opt. Express 26 30313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Rochester S M 2010 Ph. D. Dissertation (Berkeley: University of California
[24] Bloch F 1946 Phys. Rev. 70 460
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Harris M L, Adams C S, Cornish S L, McLeod I C, Tarleton E, Hughes I G 2006 Phys. Rev. A 73 062509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 薛佳, 秦际良, 张玉驰, 李刚, 张鹏飞, 张天才, 彭堃墀 2016 65 044211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xue J, Qin J L, Zhang Y C, Li G, Zhang P F, Zhang T C, Peng K C 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 044211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Castagna N, Bison G, Di Domenico G, Hofer A, Knowles P, Macchione C, Saudan H, Weis A 2009 Appl. Phys. B 96 763
[28] Li W H, Balabas M, Peng X, Pustelny S, Wickenbrock A, Guo H, Budker D 2017 J. Appl. Phys. 121 063104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Graf M T, Kimball D F, Rochester S M, Kerner K, Wong C, Budker D, Alexandrov E B, Balabas M V, Yashchuk V V 2005 Phys. Rev. A 72 023401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Cates G D, Schaefer S R, Happer W 1988 Phys. Rev. A 37 2877
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Hasson K C, Cates G D, Lerman K, Bogorad P, Happer W 1990 Phys. Rev. A 41 3672
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Seltzer S J, Romalis M V 2009 J. Appl. Phys. 106 114905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Dressel J, Malik M, Miatto F M, Jordan A N, Boyd R W 2014 Rev. Mod. Phys. 86 307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] 黄江 2016 量子光学学报 22 121
Huang J 2016 J. Quantum Opt. 22 121
[35] Auzinsh M, Budker D, Kimball D F, Rochester S M, Stalnaker J E, Sushkov A O, Yashchuk V V 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 93 173002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Koschorreck M, Napolitano M, Dubost B, Mitchell M W 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 105 093602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 3 铯原子基态
${6^2}{{\rm{S}}_{1/2}}\;F = 4$ 和${6^2}{{\rm{S}}_{1/2}}\;F = 3$ 各个磁子能级的布居数随时间的演化 (a)${I_0} = 0.5\;{\rm{ W/}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}}$ 时, 直接抽运的情况; (b)${I_0} = 10\;{\rm{ W/}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}}$ 时, 间接抽运的情况Figure 3. Evolution of the populations in each Zeeman sublevels with time of cesium atoms’s ground state
${6^2}{{\rm{S}}_{1/2}}\;F = 4$ and${6^2}{{\rm{S}}_{1/2}}\;F = 3$ : (a) Results of direct pump with the pump intensity${I_0} = 0.5\;{\rm{ W/}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}}$ ; (b) results of indirect pump with the pump intensity${I_0} = 10\;{\rm{ W/}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}}$ 图 4 磁共振时, 信号幅度
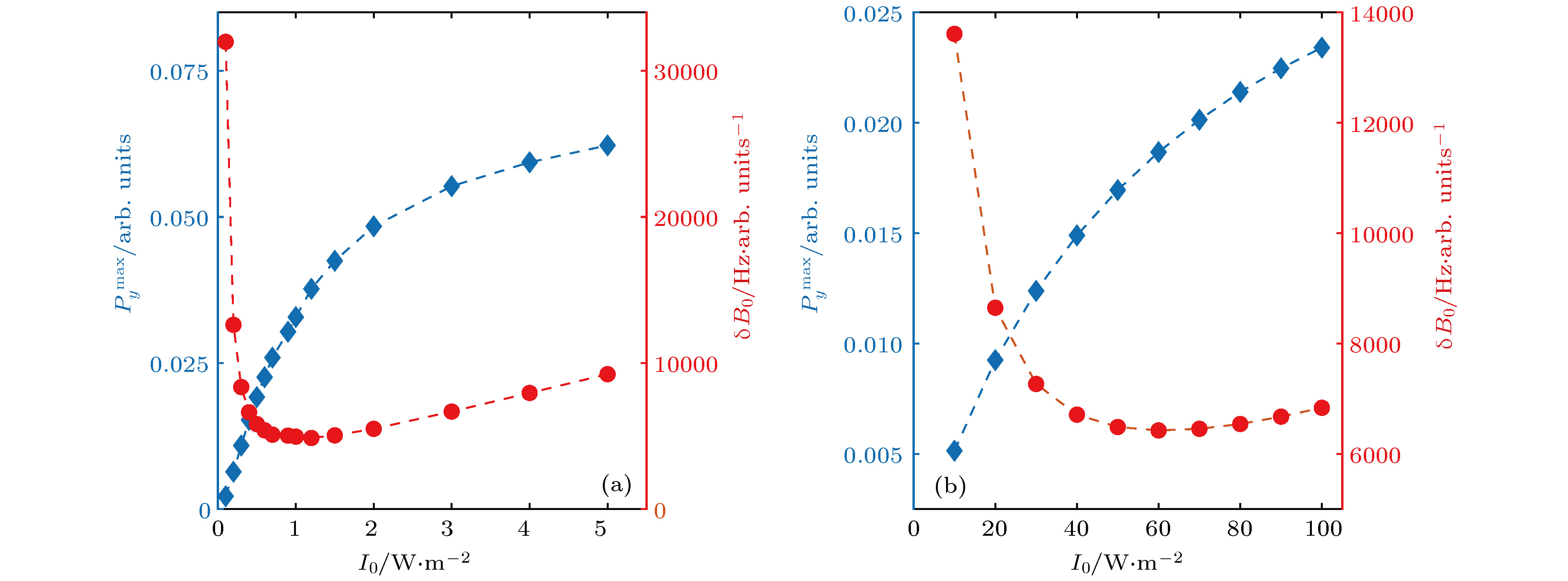
$P_y^{\max }$ 与约化磁场灵敏度${\text{δ}}{B_0}$ 随抽运光光强${I_0}$ 的变化 (a)直接抽运,$ \alpha =2{\text{π}} \times 103\; {\rm{ Hz}} \times {{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}}{\rm{/W}} $ ; (b)间接抽运,$ \alpha =2{\text{π}} \times 1 \; {\rm{ Hz}} \times {{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}}{\rm{/W}} $ Figure 4. Signal amplitude
$P_y^{\max }$ and relative sensitivity${\text{δ}}{B_0}$ change along with the pump intensity${I_0}$ under the condition of magnetic resonance: (a) Direct pump with$ \alpha =2{\text{π}} \times 103 \; {\rm{ Hz}} \times {{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}}{\rm{/W}} $ ; (b) indirect pump with$ \alpha = 2{\text{π}} \times1 \; {\rm{ Hz}} \times {{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}}{\rm{/W}} $ 图 5 实验装置图(SAS, 饱和吸收谱; VNDF, 连续可变衰减片; HWP, 半波片; PBS, 偏振分束器; HR, 高反镜; GTP, 格兰泰勒棱镜; WP, 渥拉斯顿棱镜; EO-AM, 电光振幅调制器; BPD, 平衡探测器; LIA, 锁相放大器; AC, 交流电源; DC, 直流电源; HC, 亥姆霍兹线圈; OSC, 示波器; SA, 频谱分析仪; P, 光的偏振方向)
Figure 5. Experimental setup. SAS, saturated absorption spectrum; VNDF, variable neutral density filter; HWP, half wave plate; PBS, polarization beam splitter; HR, high reflectivity mirror; GTP, Glan-Tylor prism; WP, Wollaston prism; EO-AM, electro-optical amplitude modulator; BPD, balanced photodetector; LIA, lock-in amplifier; AC, alternating current power supply; DC, direct current power supply; HC, Helmholtz coils; OSC, oscilloscope; SA, spectrum analyzer; P, direction of light polarization
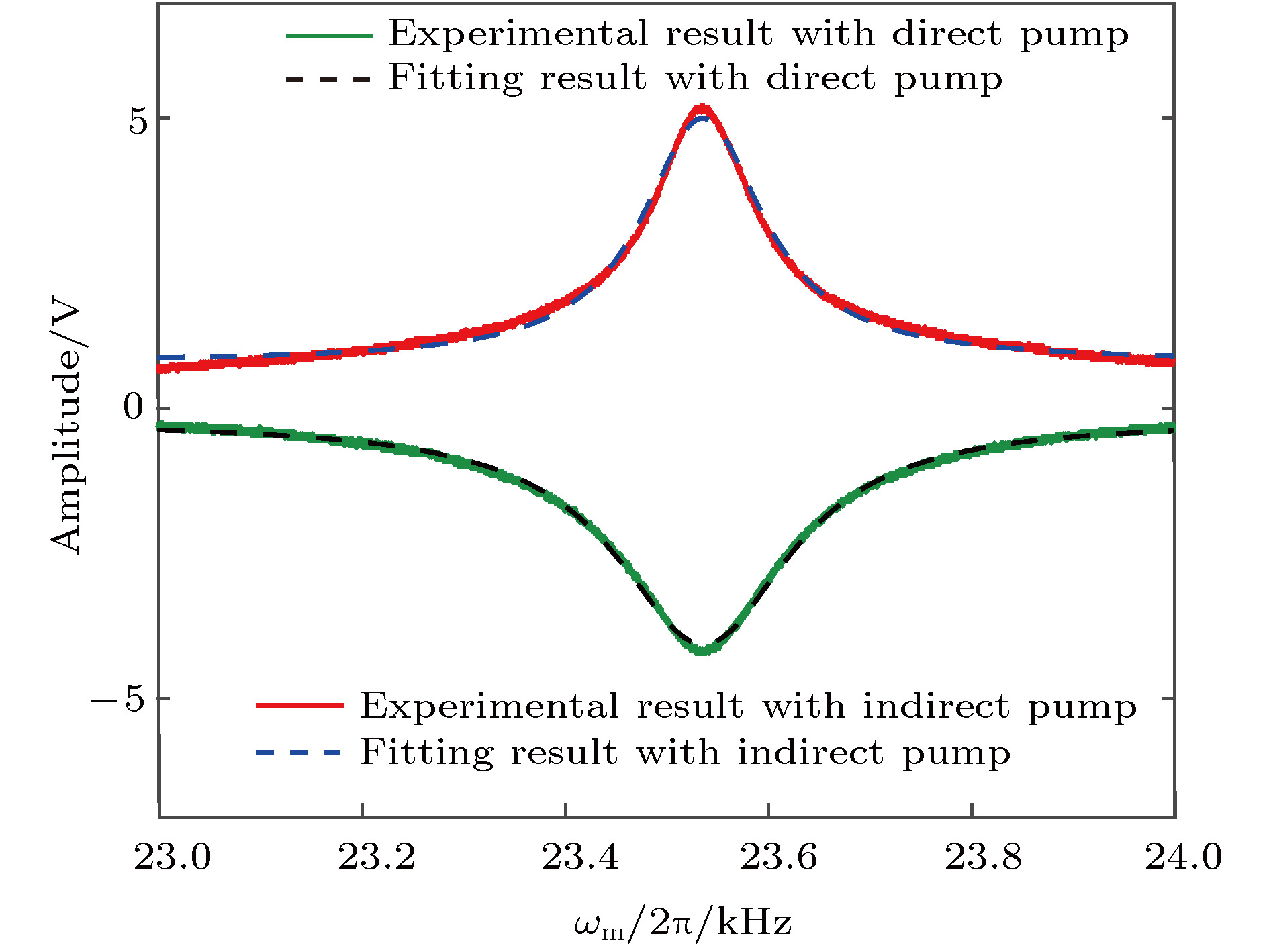
图 7 磁共振线宽
$\Delta \omega $ 随抽运光光强${I_0}$ 的变化 (a)直接抽运,$ \alpha =2{\text{π}} \times (103.2 \pm 14.3)\;{\rm{ Hz}} \times {{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}}{\rm{/W}} $ ; (b)间接抽运,$ \alpha =2{\text{π}} \;\times $ $ (0.6907 \;\pm 0.1318)\;{\rm{ Hz}} \times {{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}}{\rm{/W}} $ Figure 7. Variation of magnetic resonance linewidth
$\Delta \omega $ with pump intensity${I_0}$ : (a) Direct pump,$ \alpha = 2{\text{π}}\times (103.2 \pm 14.3)\;{\rm{ Hz}} \;\times$ $ {{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}}{\rm{W}} $ ; (b) indirect pump,$ \alpha = 2{\text{π}} \times (0.6907 \pm 0.1318)\;{\rm{ Hz}} \times {{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}}$ /W -
[1] Budker D, Romalis M V 2007 Nat. Phys. 3 227
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Allred J C, Lyman R N, Kornack T W, Romalis M V 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 130801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Dang H B, Maloof A C, Romalis M V 2010 Appl. Phys. Lett. 97 151110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Bell W E, Bloom A L 1961 Phys. Rev. Lett. 6 623
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Bell W E, Bloom A L 1961 Phys. Rev. Lett. 6 280
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wang M L, Wang M B, Zhang G Y, Zhao K F 2016 Chin. Phys. B 25 060701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Jiménez-Martínez R, Griffith W C, Knappe S, Kitching J, Prouty M 2012 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 29 3398
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Grujić Z D, Weis A 2013 Phys. Rev. A 88 012508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Mateos I, Patton B, Zhivun E, Budker D, Wurm D, Ramos-Castro J 2015 Sensors and Actuators A: Physical 224 147
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Liu G, Li X, Sun X, Feng J, Ye C, Zhou X 2013 J. Magn. Reson. 237 158
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Pustelny S, Wojciechowski A, Gring M, Kotyrba M, Zachorowski J, Gawlik W 2008 J. Appl. Phys. 103 063108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhang J H, Liu Q, Zeng X J, Li J X, Sun W M 2012 Chin. Phys. Lett. 29 068501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 董海峰, 郝慧杰, 黄海超, 胡旭阳, 周斌权 2014 仪器仪表学报 35 2783
Dong H F, Hao H J, Huang H C, Hu X Y, Zhou B Q 2014 Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 35 2783
[14] Huang H C, Dong H F, Hao H J, Hu X Y 2015 Chin. Phys. Lett. 32 098503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Wang M B, Zhao D F, Zhang G Y, Zhao K F 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 100701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Lucivero V G, Anielski P, Gawlik W, Mitchell M W 2014 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85 113108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Li W H, Peng X, Li S J, Liu C F, Guo H 2016 IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium (IFCS) New Orleans, USA, May 9−12, 2016 p1
[18] Julsgaard B, Sherson J, Sørensen J L, Polzik E S 2004 J. Opt. B 6 5
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Avila G, Giordano V, Candelier V, de Clercq E, Theobald G, Cerez P 1987 Phys. Rev. A 36 3719
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 张军海, 向康, 梅红松, 赵文辉, 黄宗军, 孙伟民 2015 光电子•激光 26 211
Zhang J H, Xiang K, Mei H S, Zhao W H, Huang Z J, Sun W M 2015 J. Optoelectron. Laser 26 211
[21] Ledbetter M P, Savukov I M, Acosta V M, Budker D, Romalis M V 2008 Phys. Rev. A 77 033408
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Yang G Q, Zhang H B, Geng X X, Liang S Q, Zhu Y F, Mao J T, Huang G M, Li G X 2018 Opt. Express 26 30313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Rochester S M 2010 Ph. D. Dissertation (Berkeley: University of California
[24] Bloch F 1946 Phys. Rev. 70 460
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Harris M L, Adams C S, Cornish S L, McLeod I C, Tarleton E, Hughes I G 2006 Phys. Rev. A 73 062509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 薛佳, 秦际良, 张玉驰, 李刚, 张鹏飞, 张天才, 彭堃墀 2016 65 044211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xue J, Qin J L, Zhang Y C, Li G, Zhang P F, Zhang T C, Peng K C 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 044211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Castagna N, Bison G, Di Domenico G, Hofer A, Knowles P, Macchione C, Saudan H, Weis A 2009 Appl. Phys. B 96 763
[28] Li W H, Balabas M, Peng X, Pustelny S, Wickenbrock A, Guo H, Budker D 2017 J. Appl. Phys. 121 063104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Graf M T, Kimball D F, Rochester S M, Kerner K, Wong C, Budker D, Alexandrov E B, Balabas M V, Yashchuk V V 2005 Phys. Rev. A 72 023401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Cates G D, Schaefer S R, Happer W 1988 Phys. Rev. A 37 2877
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Hasson K C, Cates G D, Lerman K, Bogorad P, Happer W 1990 Phys. Rev. A 41 3672
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Seltzer S J, Romalis M V 2009 J. Appl. Phys. 106 114905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Dressel J, Malik M, Miatto F M, Jordan A N, Boyd R W 2014 Rev. Mod. Phys. 86 307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] 黄江 2016 量子光学学报 22 121
Huang J 2016 J. Quantum Opt. 22 121
[35] Auzinsh M, Budker D, Kimball D F, Rochester S M, Stalnaker J E, Sushkov A O, Yashchuk V V 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 93 173002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Koschorreck M, Napolitano M, Dubost B, Mitchell M W 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 105 093602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 12540
- PDF Downloads: 106
- Cited By: 0





















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: