-
Amorphous FeSiB ribbons with nominal composition of Fe78Si9B13 are prepared by single roll rapid quenching technique. In order to enhance the giant magneto-impedance (GMI) effect of FeSiB ribbons, interlaminar gluing method is used to produce FeSiB/Cu/FeSiB sandwiched structure in which the FeSiB ribbons act as external soft magnetic layers and the Cu foil acts as internal conductive layer. The variation characteristics of GMI with angle
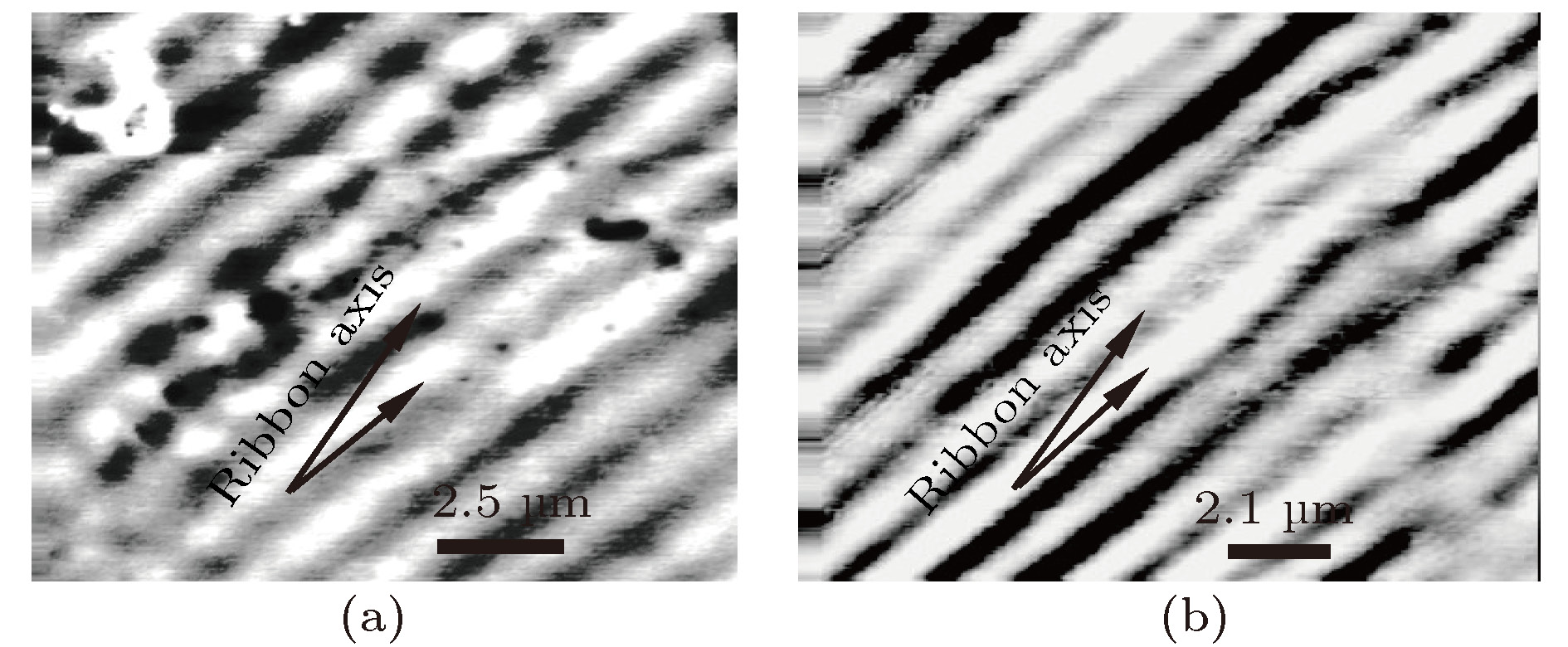
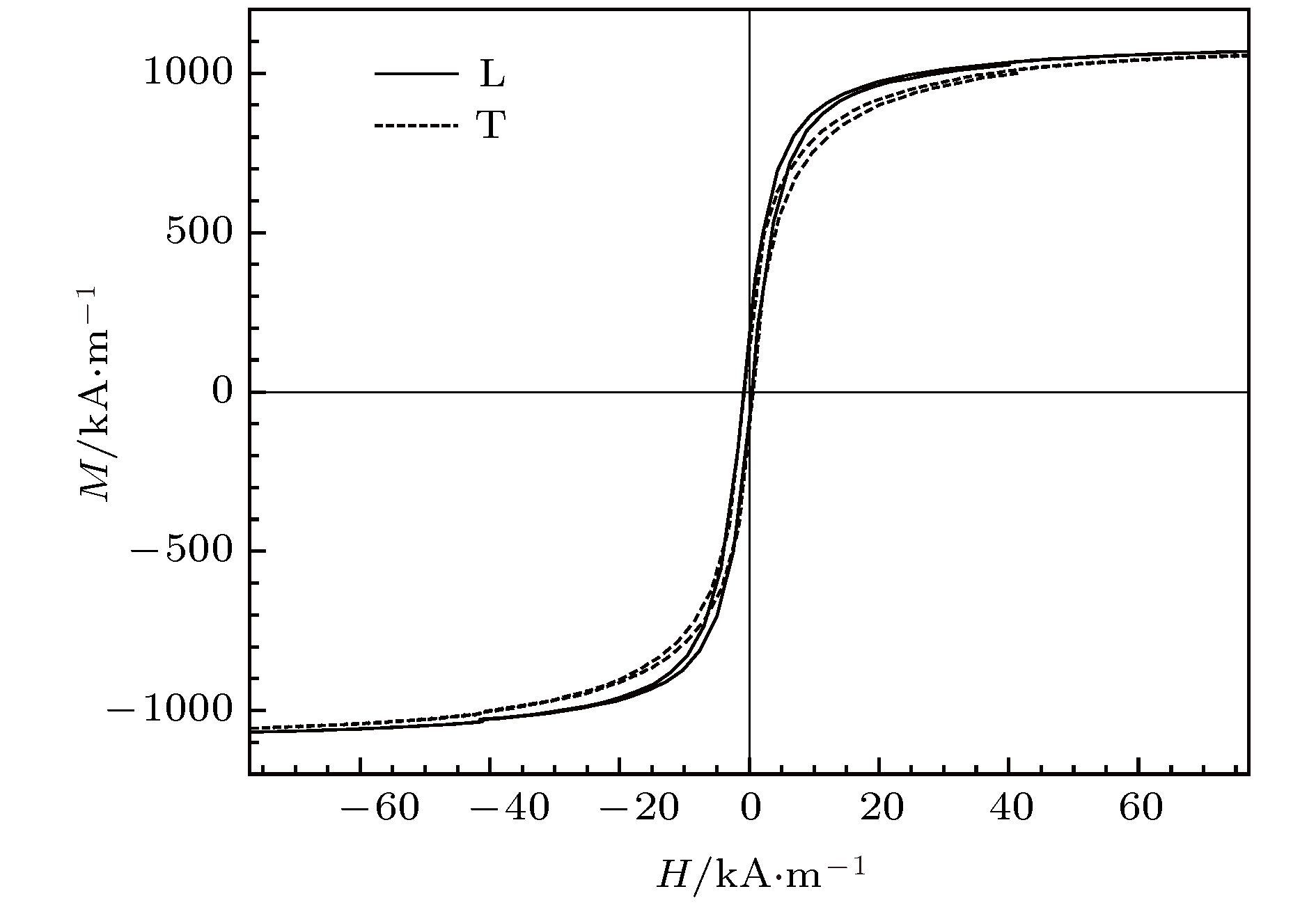
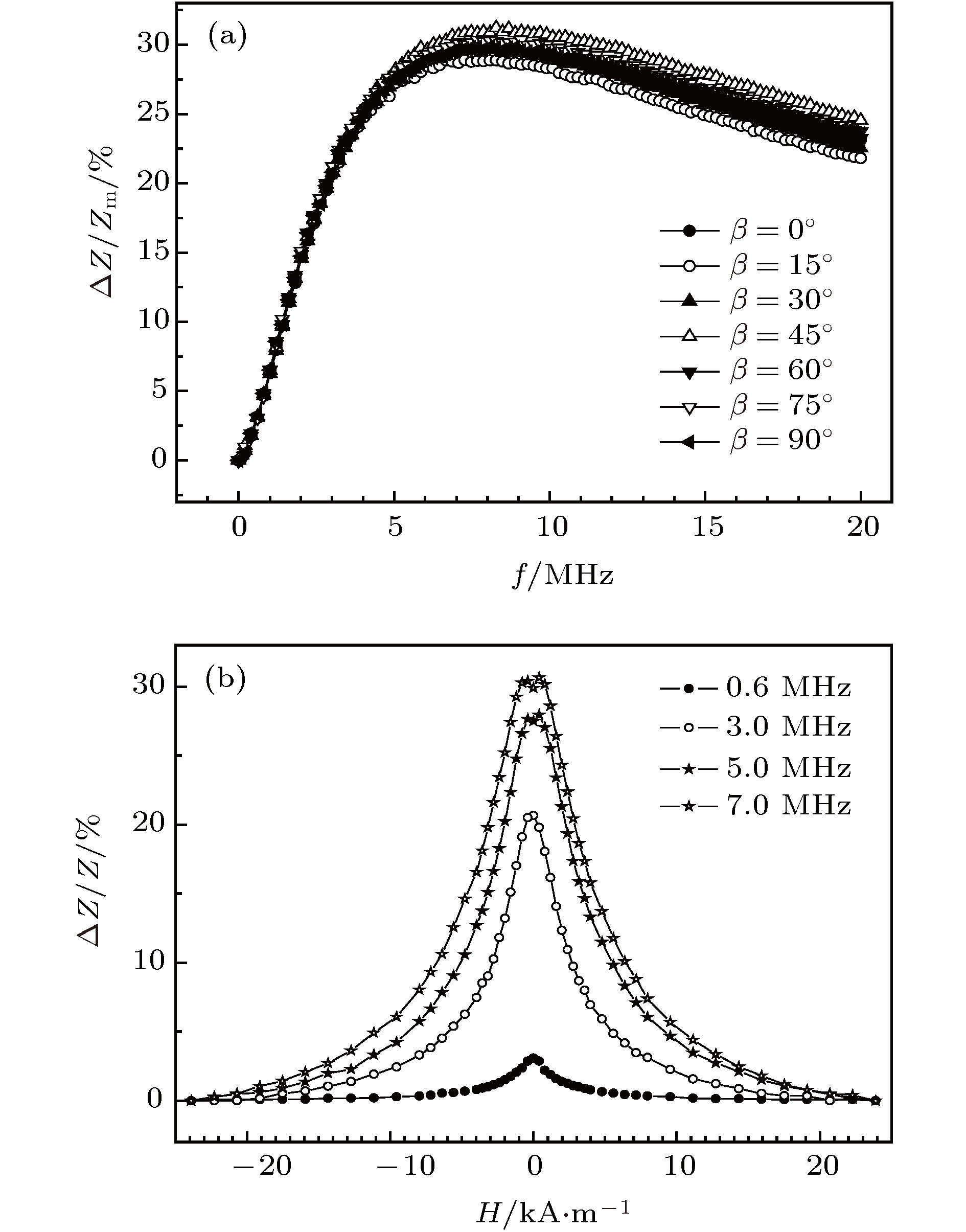
$\beta$ between the external magnetic field and the ribbon axis for the single layer FeSiB ribbon and the sandwiched ribbon are studied by a rotating device placed in magnetic field which can drive the sample to rotate, to obtain a variable angle$\beta$ from 0° to 90° with 15° degree angle interval. Magnetic domain structure detection shows that the amorphous FeSiB ribbons have near-axial magnetic anisotropy, and the angle between easy axis and ribbon axis is about 15°. In this work, in the case without considering the effects of shape anisotropy, the functional relationship among magnetic field at anisotropic peak of permeability, transverse permeability ratio and angle$\beta$ is obtained according to the expression of the transverse permeability of ribbon derived from a domain rotation model. The results display that anisotropic peak appears in the transverse permeability for each of all testing values of angle$\beta$ . Moreover, the transverse permeability ratio increases with$\beta$ increasing. The magneto-impedance testing results indicate that the maximum GMI ratio of single layer ribbon is only about 30% at an optimum response frequency of 7.0 MHz, and angle$\beta$ has almost no influence on the GMI. In contrast, the GMI of sandwiched ribbon presents a significant enhancement, the maximum value of the longitudinal GMI ratio and that of transverse GMI ratio reach 272% and 464%, respectively at an optimum response frequency of 0.6 MHz, the GMI of sandwiched ribbon is sensitive to the variation of angle$\beta$ , and with increase of$\beta$ the GMI increases accordingly. In addition, for all testing values of angle$\beta$ , the GMI profiles of sandwiched ribbon show anisotropic peaks, due to the influence of transverse demagnetization field, and the anisotropic peak broadens with the increase of angle$\beta$ . By comparing the theoretical and experimental results, it can be concluded that for the sandwiched ribbon, the characteristics of GMI changing with angle$\beta$ agree better with the theoretical transverse permeability, which but is not for single layer ribbon. Besides, whether the anisotropic peak of GMI appears is independent of the orientation of the external magnetic field. As the transverse permeability ratio increases with the increase of angle$\beta$ , the GMI effect of sandwiched ribbon is enhanced accordingly. The study results also demonstrate that the domain rotation model can be used to explicate the variation of GMI properties of sandwiched ribbon with the angle between magnetic field and ribbon axis qualitatively when the domain rotation magnetization is dominant.-
Keywords:
- giant magneto-impadence effect /
- FeSiB /
- sandwiched ribbon
[1] 张树玲, 陈炜晔, 张勇 2015 64 167501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang S L, Chen W Y, Zhang Y 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 167501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 王文静, 袁慧敏, 李娟, 姬长建, 代由勇, 萧淑琴 2013 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 43 852
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang W J, Yuan H M, Li J, Ji C J, Dai Y Y, Xiao S Q 2013 Sci. Chin: Phys. Mech. Astron. 43 852
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Phan M H, Peng H X 2008 Prog. Mater. Sci. 53 323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] He J, Guo H Q, Shen B G, He K Y, Zhang H W 2001 Mater. Sci. Eng. A 304–306 988
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Phan M H, Peng H X, Wisnom M R, Yu S C, Kim C G, Nghi N H 2006 Sensor. Actuat. A: Phys. 129 62
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Hika K, Panina L V, Mohri K 1996 IEEE Trans. Magn. 32 4594
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Xiao S Q, Liu Y H, Yan S S, Dai Y Y, Zhang L, Mei L M 2000 Phys. Rev. B 61 5734
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Le A T, Tung M T, Phan M H 2012 J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 25 1133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 周勇, 丁文, 陈吉安, 杨春生, 高孝裕, 王明军, 张亚民 2004 磁性材料及器件 35 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou Y, Ding W, Chen J A, Yang C S, Gao X Y, Wang M J, Zhang Y M 2004 J. Magn. Mater. Dev. 35 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhong Z Y, Zhang H W, Jing Y L, Tang X L, Liu S 2008 Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 141 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Amalou F, Gijs M A M 2004 J. Appl. Phys. 95 1364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Alves F, Moutoussamy J, Coillot C, Abirached L, Kaviraj B 2008 Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 145–146 241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 邵先亦, 陈卫平, 钟彬荃, 谢佳文 2018 稀有金属材料与工程 47 1160
Shao X Y, Chen W P, Zhong B Q, Xie J W 2018 Rare Metal Mat. Eng. 47 1160
[14] Zhao C B, Zhang X L, Liu Q F, Wang J B 2016 J. Phys. D 49 065006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Sommer R L, Chien C L 1996 Phys. Rev. B 53 R5982
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Pirota K R, Kraus L, Knobel M, Pagliuso P G, Rettori C 1999 Phys. Rev. B 60 6685
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yu J Q, Yu A B, Zhou Y, Cai B C, Zhao X L 2000 Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Thin Film Physics and Applications Shanghai, China, May 8–11, 2000 p514
[18] Mardani R, Amirabadizadeh A 2014 Mod. Phys. Lett. B 28 1450197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 王艾玲, 刘江涛, 周云松, 姜宏伟, 郑鹉 2004 53 905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang A L, Liu J T, Zhou Y S, Jiang H W, Zheng W 2004 Acta Phys. Sin. 53 905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Panina L V, Mohri K, Uchiyama T, Noda M 1995 IEEE Trans. Magn. 31 1249
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Reichl L E 1998 A Modern Course in Statistical Physics (2nd Ed.) (New York: Wiley-VCH) p376
[22] Atkinson D, Squire P T 1998 J. Appl. Phys. 83 6569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 张建强, 叶慧群, 郑建龙, 李通银, 李文忠, 马云, 方允樟 2010 浙江师范大学学报(自然科学版) 33 150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang J Q, Ye H Q, Zheng J L, Li T Y, Li W Z, Ma Y, Fang Y Z 2010 J. Zheiiang Normal Univ. (Nat. Sci.)
33 150  Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Makhnovskiy D P, Panina L V, Mapps D J 2001 J. Appl. Phys. 89 7224
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Betancourt I 2011 Materials 4 37
[26] Kurlyandskaya G V, Barandiarán J M, Vázquez M, Garcı́A D, Dmitrieva N V 2000 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 215–216 740
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Franco C S, Ribas G P, Bruno A C 2006 Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 132 85
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Sommer R L, Chien C L 1995 J. Appl. Phys. Lett. 67 3346
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhao C B, Pan L N, Ma X Q, Li J N, Liu Q F, Wang J B 2017 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 444 198
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] 张树玲, 陈炜晔, 张勇 2015 64 167501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang S L, Chen W Y, Zhang Y 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 167501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 王文静, 袁慧敏, 李娟, 姬长建, 代由勇, 萧淑琴 2013 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 43 852
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang W J, Yuan H M, Li J, Ji C J, Dai Y Y, Xiao S Q 2013 Sci. Chin: Phys. Mech. Astron. 43 852
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Phan M H, Peng H X 2008 Prog. Mater. Sci. 53 323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] He J, Guo H Q, Shen B G, He K Y, Zhang H W 2001 Mater. Sci. Eng. A 304–306 988
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Phan M H, Peng H X, Wisnom M R, Yu S C, Kim C G, Nghi N H 2006 Sensor. Actuat. A: Phys. 129 62
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Hika K, Panina L V, Mohri K 1996 IEEE Trans. Magn. 32 4594
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Xiao S Q, Liu Y H, Yan S S, Dai Y Y, Zhang L, Mei L M 2000 Phys. Rev. B 61 5734
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Le A T, Tung M T, Phan M H 2012 J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 25 1133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 周勇, 丁文, 陈吉安, 杨春生, 高孝裕, 王明军, 张亚民 2004 磁性材料及器件 35 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou Y, Ding W, Chen J A, Yang C S, Gao X Y, Wang M J, Zhang Y M 2004 J. Magn. Mater. Dev. 35 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhong Z Y, Zhang H W, Jing Y L, Tang X L, Liu S 2008 Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 141 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Amalou F, Gijs M A M 2004 J. Appl. Phys. 95 1364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Alves F, Moutoussamy J, Coillot C, Abirached L, Kaviraj B 2008 Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 145–146 241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 邵先亦, 陈卫平, 钟彬荃, 谢佳文 2018 稀有金属材料与工程 47 1160
Shao X Y, Chen W P, Zhong B Q, Xie J W 2018 Rare Metal Mat. Eng. 47 1160
[14] Zhao C B, Zhang X L, Liu Q F, Wang J B 2016 J. Phys. D 49 065006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Sommer R L, Chien C L 1996 Phys. Rev. B 53 R5982
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Pirota K R, Kraus L, Knobel M, Pagliuso P G, Rettori C 1999 Phys. Rev. B 60 6685
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yu J Q, Yu A B, Zhou Y, Cai B C, Zhao X L 2000 Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Thin Film Physics and Applications Shanghai, China, May 8–11, 2000 p514
[18] Mardani R, Amirabadizadeh A 2014 Mod. Phys. Lett. B 28 1450197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 王艾玲, 刘江涛, 周云松, 姜宏伟, 郑鹉 2004 53 905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang A L, Liu J T, Zhou Y S, Jiang H W, Zheng W 2004 Acta Phys. Sin. 53 905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Panina L V, Mohri K, Uchiyama T, Noda M 1995 IEEE Trans. Magn. 31 1249
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Reichl L E 1998 A Modern Course in Statistical Physics (2nd Ed.) (New York: Wiley-VCH) p376
[22] Atkinson D, Squire P T 1998 J. Appl. Phys. 83 6569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 张建强, 叶慧群, 郑建龙, 李通银, 李文忠, 马云, 方允樟 2010 浙江师范大学学报(自然科学版) 33 150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang J Q, Ye H Q, Zheng J L, Li T Y, Li W Z, Ma Y, Fang Y Z 2010 J. Zheiiang Normal Univ. (Nat. Sci.)
33 150  Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Makhnovskiy D P, Panina L V, Mapps D J 2001 J. Appl. Phys. 89 7224
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Betancourt I 2011 Materials 4 37
[26] Kurlyandskaya G V, Barandiarán J M, Vázquez M, Garcı́A D, Dmitrieva N V 2000 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 215–216 740
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Franco C S, Ribas G P, Bruno A C 2006 Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 132 85
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Sommer R L, Chien C L 1995 J. Appl. Phys. Lett. 67 3346
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhao C B, Pan L N, Ma X Q, Li J N, Liu Q F, Wang J B 2017 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 444 198
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 9044
- PDF Downloads: 60
- Cited By: 0
















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: