-
针对传统鬼成像目标重建算法在低测量次数下重建质量较差的问题, 本文提出了一种结合盲噪声估计与迭代滤波降噪的目标重建方法, 旨在优化低测量数据条件下的鬼成像效果, 提升目标重建质量. 为解决噪声和欠采样带来的不准确重建, 首先通过伪逆运算和单位矩阵提高测量矩阵的稳定性, 然后计算修正项以优化桶探测器的观测数据. 使用平衡的全一列向量作为初始值, 以加速收敛. 在迭代过程中, 引入一种新的目标图像降噪算法, 该算法结合了盲噪声估计、块匹配三维滤波和导向滤波. 这种动态滤波有效保留了每次迭代中的重要细节, 即便在测量次数较低的情况下, 仍能实现高质量的目标重建. 仿真和实验结果表明, 该方法在边缘保留和纹理细节质量上优于传统方法, 为鬼成像技术在遥感和医学成像等领域的应用提供重要的技术支持.This paper introduces an adaptive blind noise dynamic filtering for ghost imaging reconstruction (ABNDF-GIR), a novel method of optimizing ghost imaging data with a limited number of measurements, significantly improving image quality and peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR). To address the challenges of noise and undersampling, we first enhance the stability of the measurement matrix by using pseudoinversion and a unit matrix, and calculate correction terms for bucket detector observations to optimize the reconstruction process. A balanced all-one column vector is used as the initial value to accelerate convergence. For iterative computation, we propose a novel filtering and denoising technique, the adaptive denoising window-based guided filtering with BM3D (ADW-BG), which integrates blind noise estimation, block matching and 3D filtering, and guided filtering. This dynamic filtering method effectively preserves important details during each iteration, and can achieve high-quality target reconstruction even with fewer measurements. Extensive simulations and experimental results verify that our method is significantly superior to traditional filtering methods and various compressiv sensing algorithms, especially in edge preservation and texture detail enhancement. The proposed technique provides a key technical advancement for the application of ghost imaging in fields such as remote sensing and medical imaging, showing significant advantages in real-world imaging scenarios.
-
Keywords:
- ghost imaging /
- blind noise estimation /
- iterative operation /
- low measurement number
[1] Klyshko D N 1988 Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 94 82
[2] Pittman T B, Shih Y, Strekalov D, Sergienko A V 1995 Phys. Rev. A 52 R3429
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Cheng J, Han S 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 92 093903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Cao D Z, Xiong J, Wang K 2005 Phys. Rev. A 71 013801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhao C, Gong W, Chen M, Li E, Wang H, Xu W, Han S 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 101 141123
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Deng C, Gong W, Han S 2016 Opt. Express 24 25983
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wang C, Mei X, Pan L, Wang P, Li W, Gao X, Bo Z, Chen M, Gong W, Han S 2018 Remote Sens. 10 732
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Huang X, Xu Y, Bai Y, Fu X 2023 Opt. Lett. 48 5543
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhang L, Wang X, Zhou Q, Xue J, Xu B 2024 Opt. Express 32 4242
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Ma J, Li Z, Zhao S, Wang L 2023 Opt. Express 31 11717
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Huang W, Tan W, Qin H, Wang J, Huang Z, Huang X, Fu X, Bai Y 2023 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 40 1696
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang Y, Wang X, Gao C, Yu Z, Wang H, Zhao H, Yao Z 2024 Sensors 24 4197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Ferri F, Magatti D, Lugiato L, Gatti A 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 253603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Sun B, Welsh S S, Edgar M P, Shapiro J H, Padgett M J 2012 Opt. Express 20 16892
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Li M, Zhang Y, Luo K, Wu L, Fan H 2013 Phys. Rev. A 87 033813
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhang J, Zhao D, Li Y, Liu Y, Sun M, Li X, Yu Z, Zhou X 2023 Appl. Opt. 62 7678
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 白旭, 李永强, 赵生妹 2013 62 044209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bai X, Li Y Q, Zhao S M 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 044209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wang L, Zhao S M 2020 Chin. Phys. B 29 024204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhang C, Guo S, Cao J, Guan J, Gao F 2014 Opt. Express 22 30063
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Gong W 2015 Photonics Res. 3 234
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Yao X, Yu W, Liu X, Li L, Li M, Wu L, Zhai G 2014 Opt. Express 22 24268
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Li G, Yang Z, Zhao Y, Yan R, Liu X, Liu B 2017 Laser Phys. Lett. 14 025207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 张海鹏, 赵昌哲, 鞠晓璐, 汤杰, 肖体乔 2022 71 074201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang H P, Zhao C Z, Ju X L, Tang J, Xiao T Q 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 074201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Chen L, Wang C, Xiao X, Ren C, Zhang D, Li Z, Cao D 2022 Opt. Express 30 6248
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wu H, Wang C, Gong W 2018 Opt. Express 26 4183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Xu C, Li D, Fan X, Lin B, Guo K, Yin Z, Guo Z 2023 Phys. Scr. 98 065011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Kataoka S, Mizutani Y, Uenohara T, Takaya Y, Matoba O 2022 Appl. Opt. 61 10126
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zhou C, Liu X, Feng Y, Li X, Wang G, Sun H, Huang H, Song L 2022 Opt. Lasers Eng. 156 107101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Fan Y, Bai Y, Fu Q, Zhang R, Zhou L, Zhu X, Zou X, Fu X 2024 Opt. Commun. 566 130684
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Katkovnik V, Astola J 2012 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 29 1556
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Zhou C, Feng D, Wang G, Huang J, Huang H, Liu X, Li X, Feng Y, Sun H, Song L 2023 Opt. Express 31 25013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Tomasi C, Manduchi R 1998 Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Computer Vision Bombay, India, January 7, 1998 p839
[33] Buades A, Coll B, Morel J M 2005 Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition San Diego, CA, USA, June 20–25, 2005 p60
[34] Dabov K, Foi A, Katkovnik V, Egiazarian K 2007 IEEE Trans. Image Process. 16 2080
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] He K, Sun J, Tang X 2012 IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 35 1397
[36] Liu X, Jing X Y, Tang G, Wu F, Ge Q 2017 Signal Process. 135 239
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Izadi S, Sutton D, Hamarneh G 2023 Artif. Intell. Rev. 56 5929
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Liu X, Tanaka M, Okutomi M 2013 IEEE Trans. Image Process. 22 5226
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Lei T, Zhang R, Ma Y, Ding X, Wu Y, Shiyong W 2024 Opt. Commun. 550 130023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] 李龙珍, 姚旭日, 刘雪峰, 俞文凯, 翟光杰 2014 63 224201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li L Z, Yao X R, Liu X F, Yu W K, Zhai G J 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 224201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
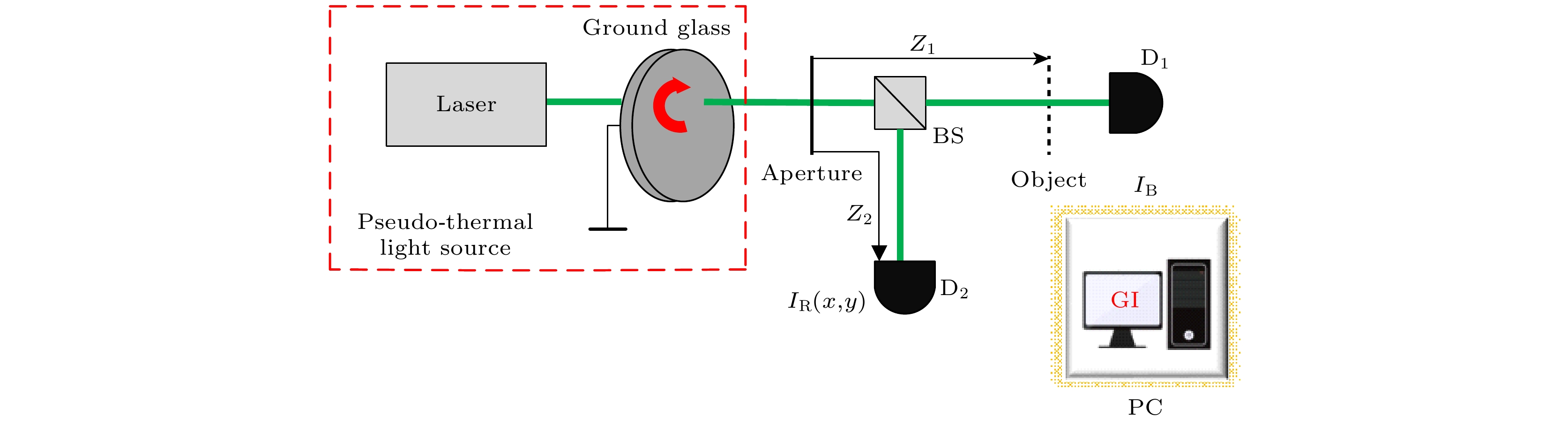
图 1 基于赝热光源的鬼成像原理示意图. BS表示分束棱镜, PC表示计算机, $ {z}_{1} $表示目标与光源之间的距离, $ {z}_{2} $表示CCD与光源之间的距离
Fig. 1. Principle of ghost imaging using pseudo-thermal light source. BS represents the beam splitter, PC represents the computer, $ {z}_{1} $ denotes the distance between the target and the light source, $ {z}_{2} $ denotes the distance between the CCD and the light source.
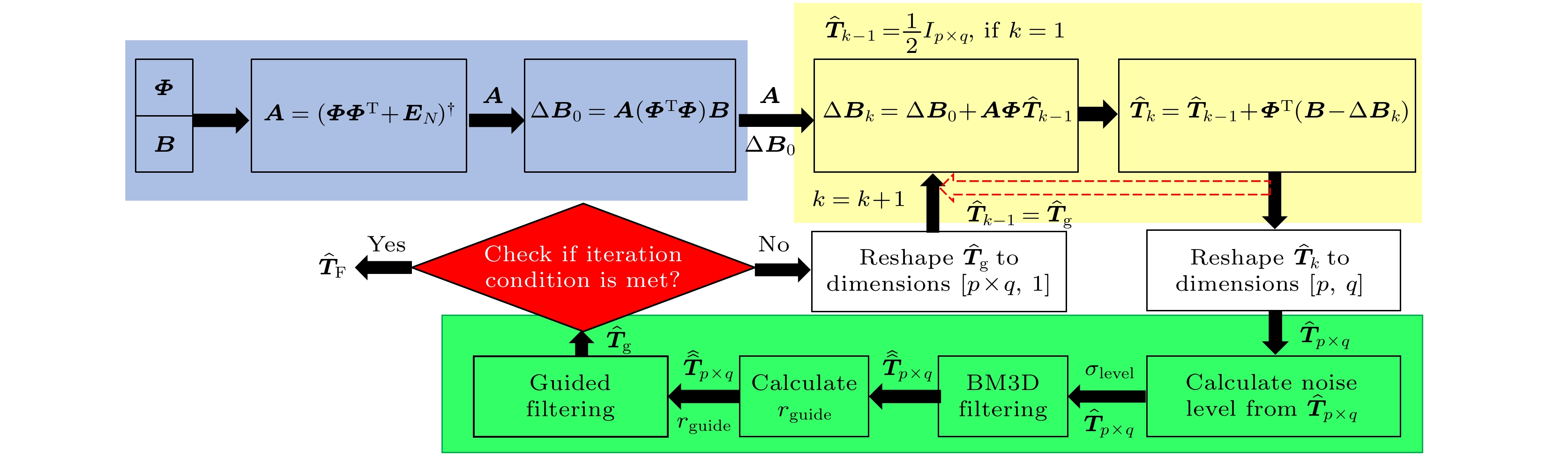
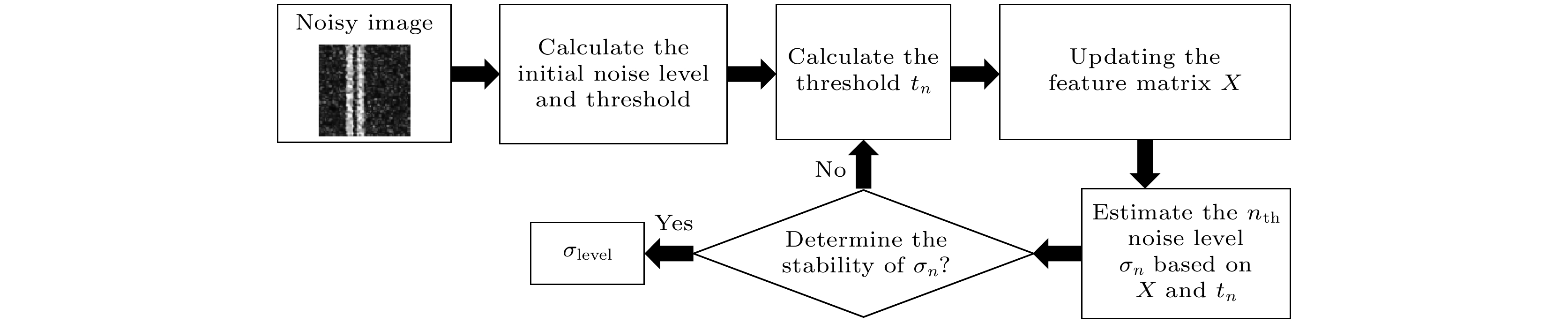
图 2 ABNDF-GIR方法的示意图. 蓝色部分计算桶探测器观测值的修正项, 黄色部分涵盖了目标重建的迭代计算过程, 绿色部分展示了用于目标重建和噪声抑制的ADW-BG方法, 红色部分为迭代停止准则
Fig. 2. Schematic diagram of the ABNDF-GIR method. The blue section calculates correction terms for bucket detector observations, the yellow section covers the iterative computation process of compressed sensing ghost imaging, the green section presents the proposed ADW-BG method for target reconstruction and noise reduction, and the red section assesses the iterative stopping condition.
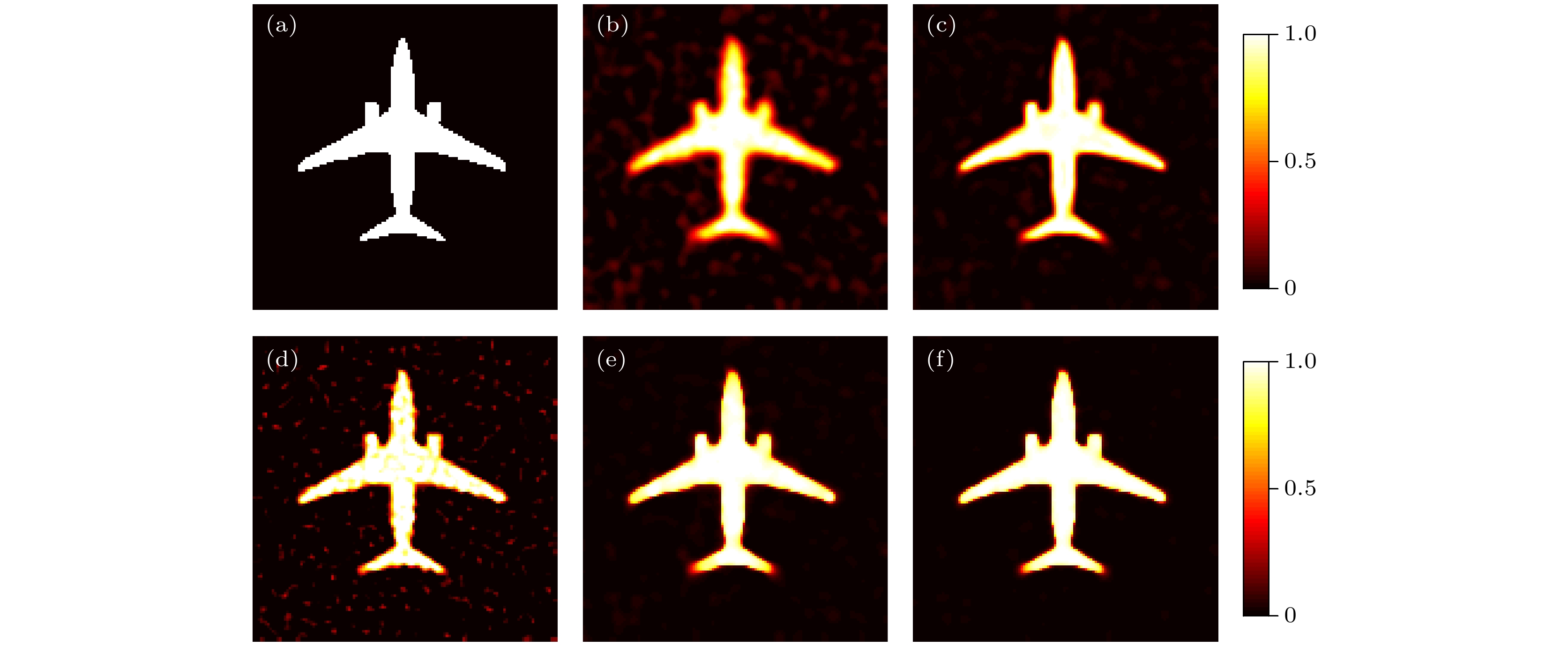
图 4 不同滤波方法的迭代重建“Airplane”二值图像结果 (a)原始图像; (b)—(f)分别为采用BF, NLF, BM3D, GF和ADW-BG方法在迭代算法中得到的重建图像
Fig. 4. Iterative reconstruction results of the “Airplane” binary image using different filtering methods: (a) Original image; (b)–(f) the reconstructed images obtained using BF, NLF, BM3D, GF, and ADW-BG methods, respectively, in the iterative algorithm.
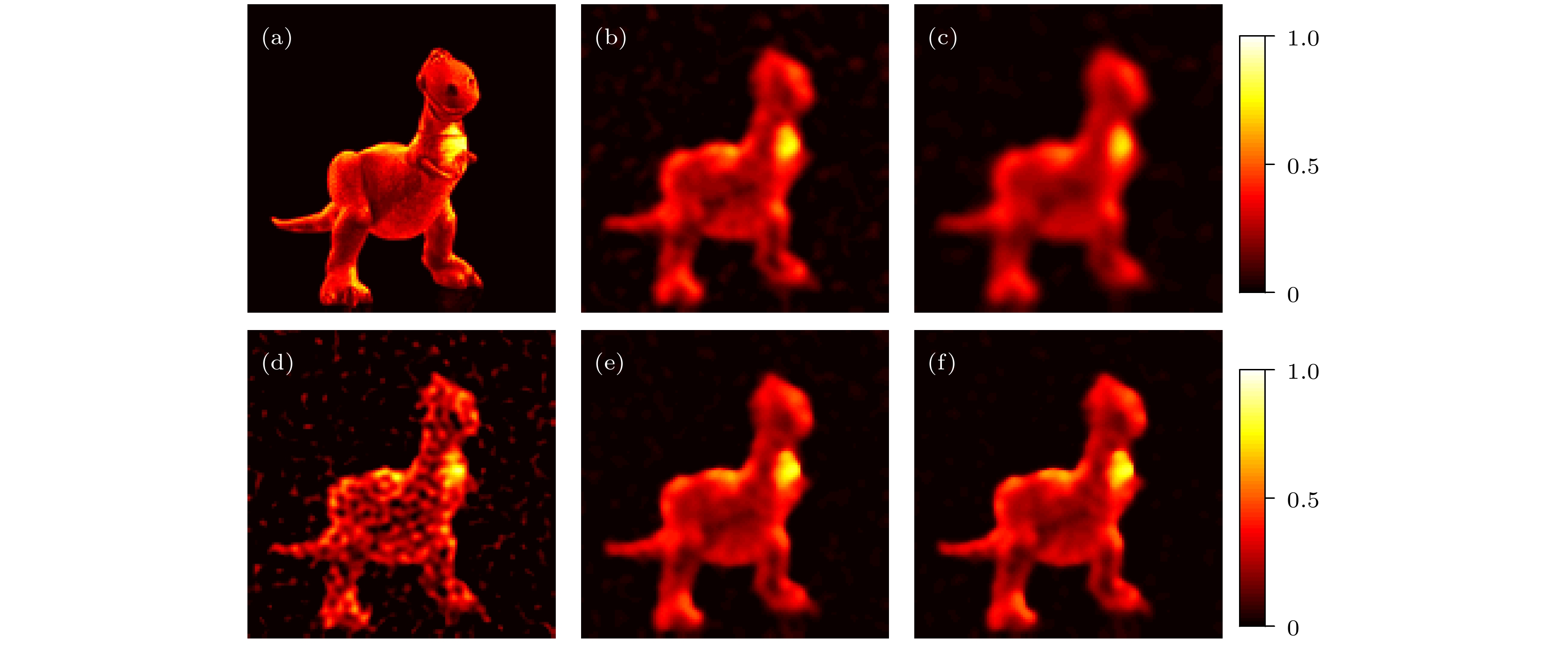
图 5 不同滤波方法下“Dinosaur”灰度图像的迭代重建结果 (a)原始图像; (b)—(f)分别为采用BF, NLF, BM3D, GF和ADW-BG方法重建的图像
Fig. 5. Iterative reconstruction results of the grayscale target “Dinosaur” using different filtering methods: (a) Original image; (b)–(f) the images reconstructed using the BF, NLF, BM3D, GF, and ADW-BG methods, respectively.
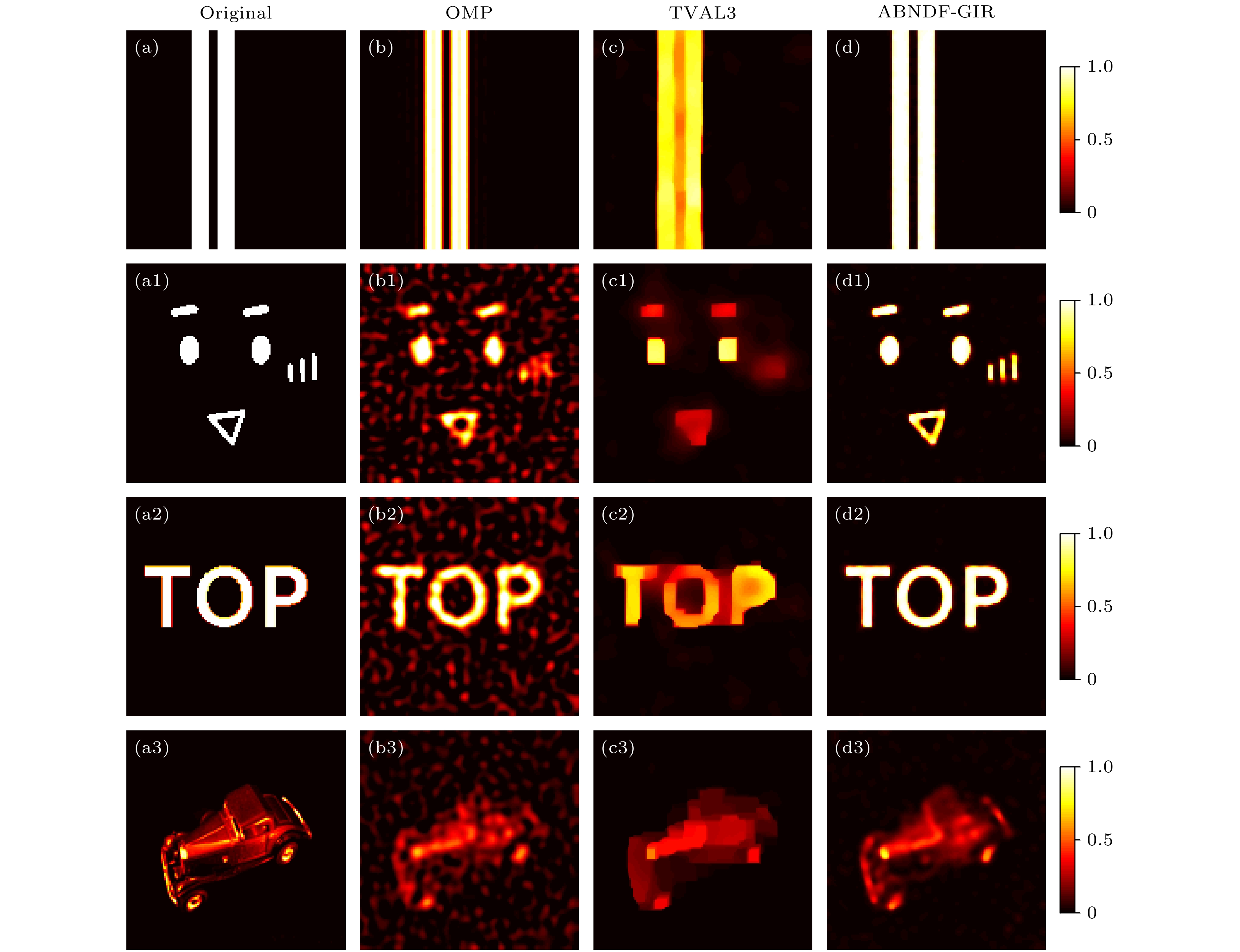
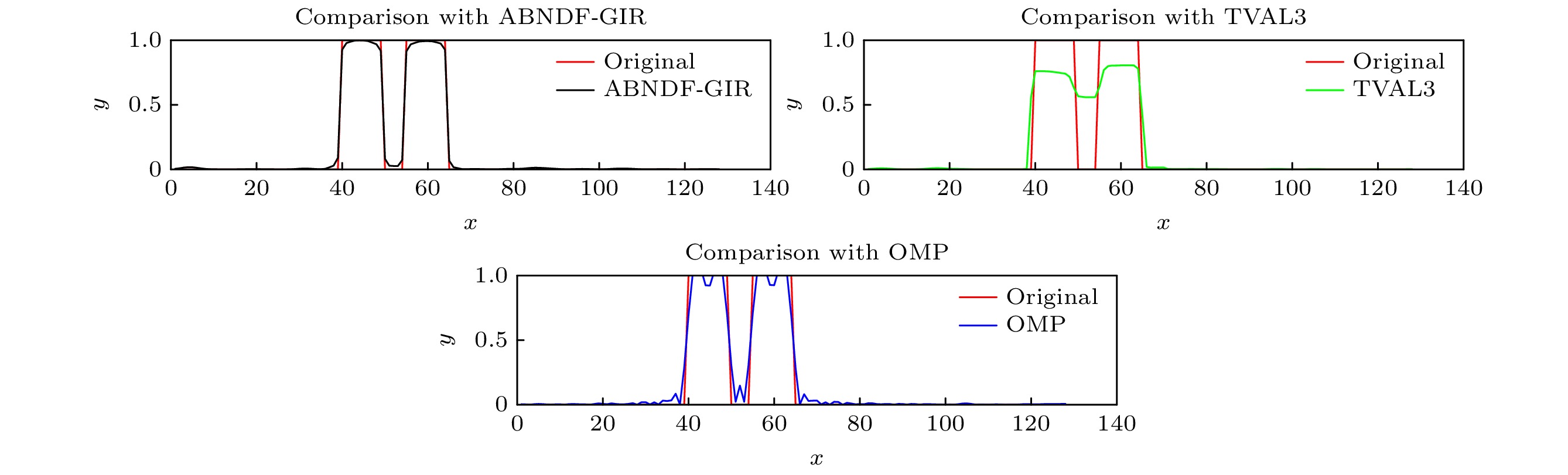
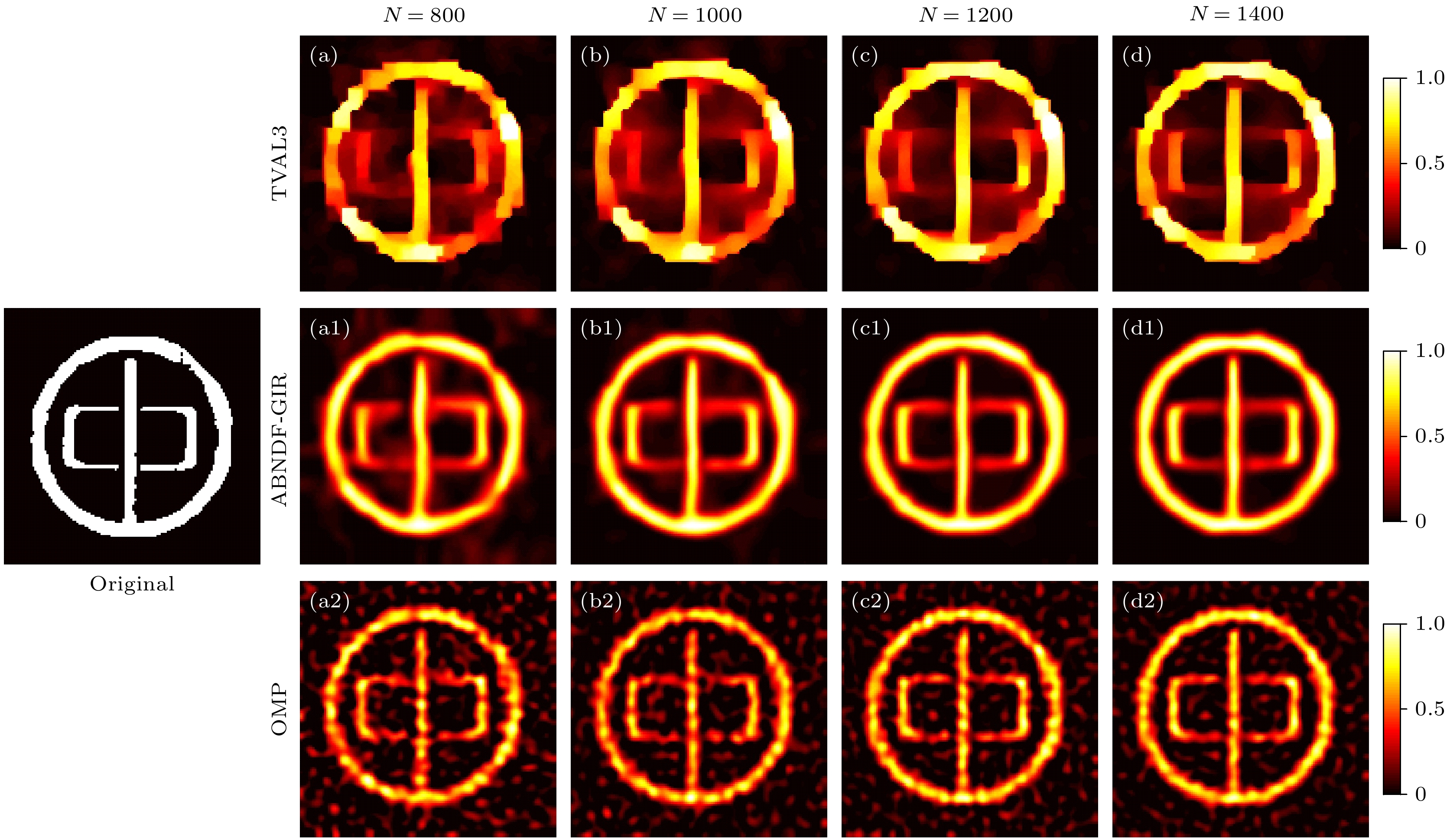
图 7 使用不同鬼成像目标重建方法的重建结果比较 (a), (a1), (a2)和(a3)分别展示了原始目标: “Double Slit”, “Expression”, “TOP”和“Car”; (b), (b1), (b2)和(b3)展示了使用OMP方法的重建结果; (c), (c1), (c2)和(c3)展示了使用TVAL3方法的重建结果; 图(d), (d1), (d2)和(d3)展示了本文方法的重建结果
Fig. 7. Comparison of reconstruction results using different ghost imaging target reconstruction methods. Panels (a), (a1), (a2), and (a3) display the original targets: “Double Slit,” “Expression,” “TOP,” and “Car,” respectively. Panels (b), (b1), (b2), and (b3) present the reconstruction results using OMP; panels (c), (c1), (c2), and (c3) showcase the reconstruction results using TVAL3; and panels (d), (d1), (d2), and (d3) demonstrate the reconstruction results of our method.
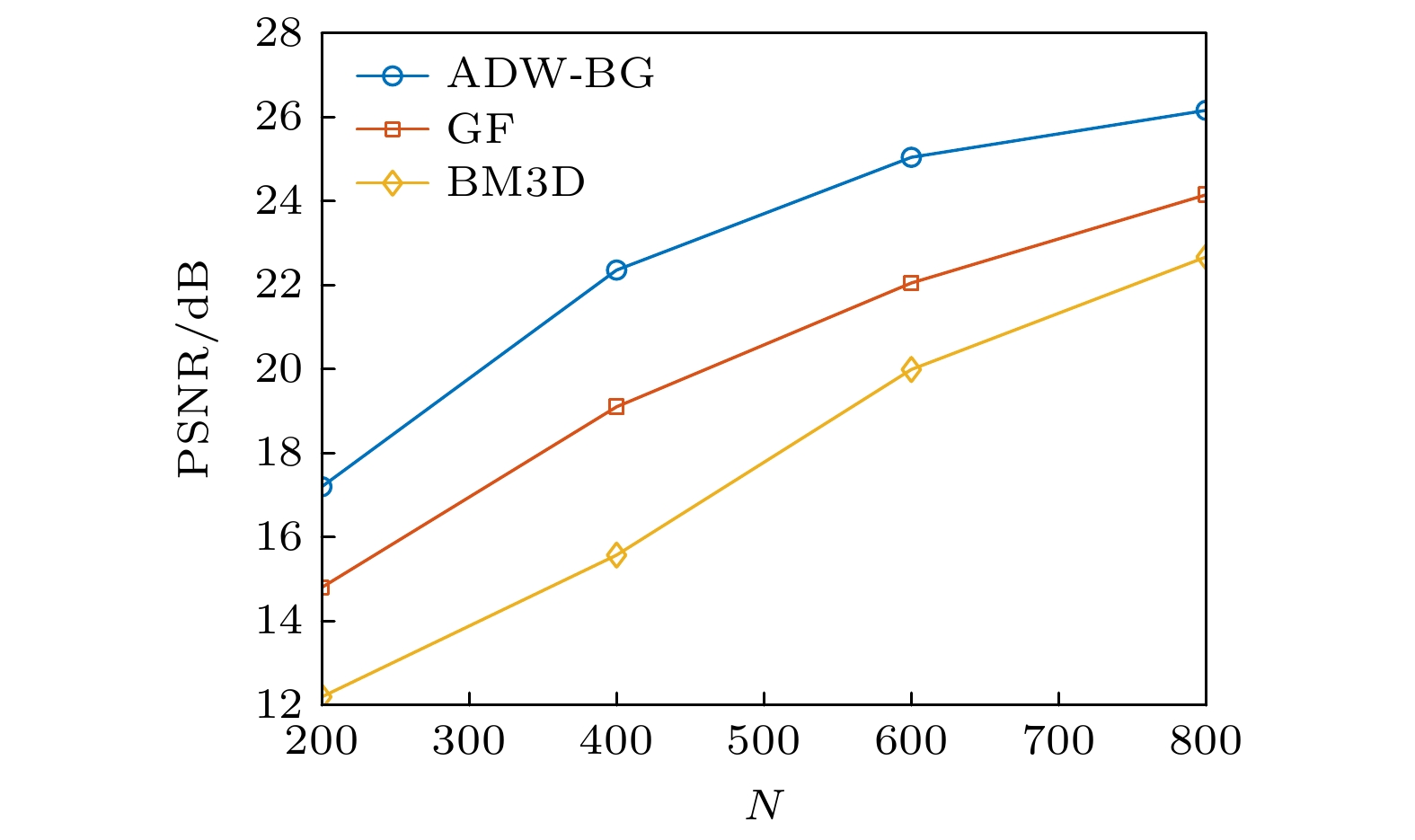
表 1 不同目标重建中不同滤波方法的PSNR值对比
Table 1. PSNR values for different filtering methods in the reconstruction of various targets.
BF/dB NLF/dB BM3D/dB GF/dB ADW-BG/dB “Airplane” 19.23 21.58 22.67 24.15 26.16 “Dinosaur” 25.69 25.90 25.98 26.42 27.56 表 2 不同方法的重建结果PSNR值
Table 2. Reconstruction results in PSNR for different methods.
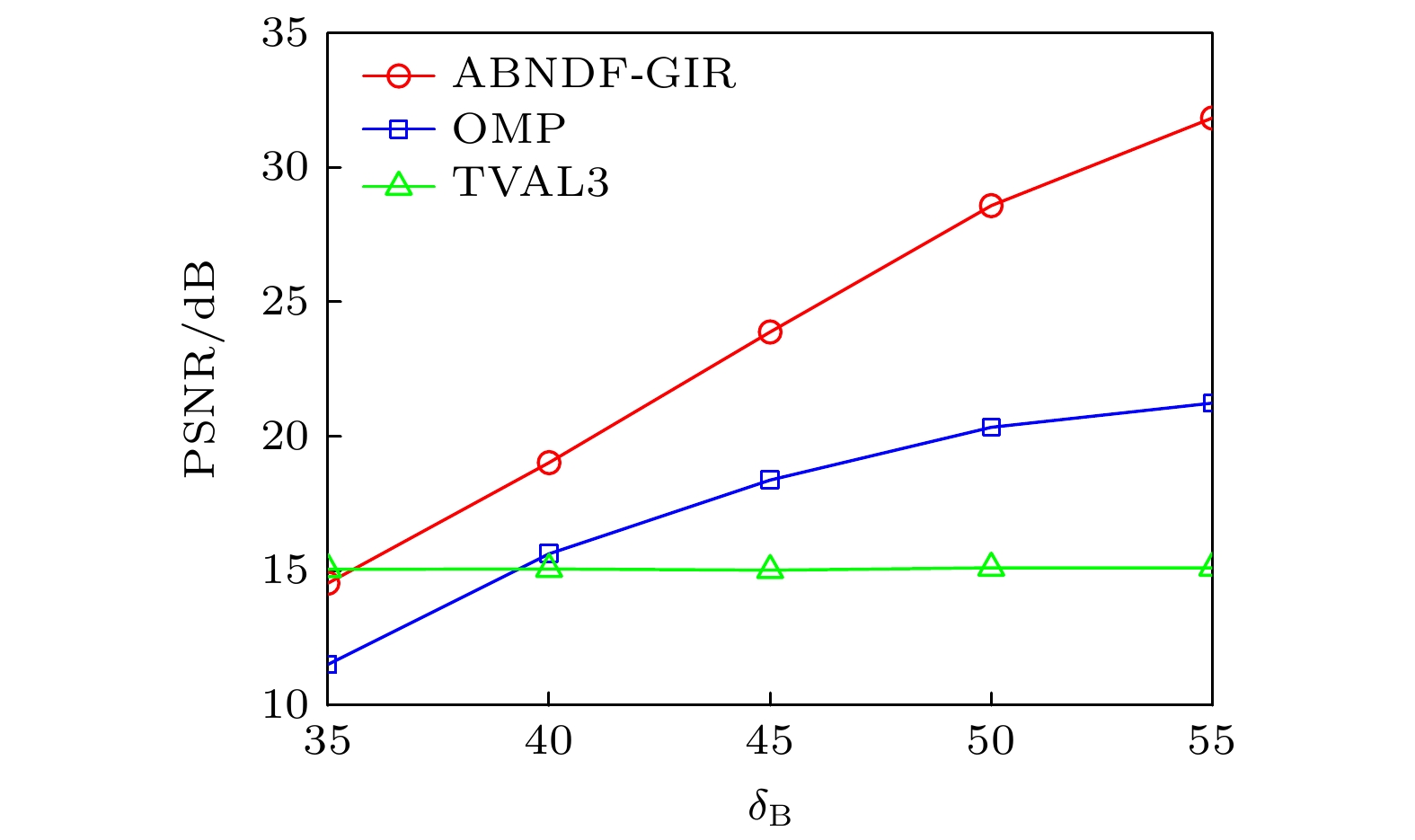
OMP/dB TVAL3/dB ABNDF-GIR/dB (a) 21.78 15.89 34.12 (a1) 16.17 17.37 25.41 (a2) 18.25 17.63 30.95 (a3) 22.27 24.38 26.94 -
[1] Klyshko D N 1988 Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 94 82
[2] Pittman T B, Shih Y, Strekalov D, Sergienko A V 1995 Phys. Rev. A 52 R3429
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Cheng J, Han S 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 92 093903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Cao D Z, Xiong J, Wang K 2005 Phys. Rev. A 71 013801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhao C, Gong W, Chen M, Li E, Wang H, Xu W, Han S 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 101 141123
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Deng C, Gong W, Han S 2016 Opt. Express 24 25983
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wang C, Mei X, Pan L, Wang P, Li W, Gao X, Bo Z, Chen M, Gong W, Han S 2018 Remote Sens. 10 732
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Huang X, Xu Y, Bai Y, Fu X 2023 Opt. Lett. 48 5543
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhang L, Wang X, Zhou Q, Xue J, Xu B 2024 Opt. Express 32 4242
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Ma J, Li Z, Zhao S, Wang L 2023 Opt. Express 31 11717
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Huang W, Tan W, Qin H, Wang J, Huang Z, Huang X, Fu X, Bai Y 2023 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 40 1696
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang Y, Wang X, Gao C, Yu Z, Wang H, Zhao H, Yao Z 2024 Sensors 24 4197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Ferri F, Magatti D, Lugiato L, Gatti A 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 253603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Sun B, Welsh S S, Edgar M P, Shapiro J H, Padgett M J 2012 Opt. Express 20 16892
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Li M, Zhang Y, Luo K, Wu L, Fan H 2013 Phys. Rev. A 87 033813
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhang J, Zhao D, Li Y, Liu Y, Sun M, Li X, Yu Z, Zhou X 2023 Appl. Opt. 62 7678
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 白旭, 李永强, 赵生妹 2013 62 044209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bai X, Li Y Q, Zhao S M 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 044209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wang L, Zhao S M 2020 Chin. Phys. B 29 024204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhang C, Guo S, Cao J, Guan J, Gao F 2014 Opt. Express 22 30063
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Gong W 2015 Photonics Res. 3 234
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Yao X, Yu W, Liu X, Li L, Li M, Wu L, Zhai G 2014 Opt. Express 22 24268
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Li G, Yang Z, Zhao Y, Yan R, Liu X, Liu B 2017 Laser Phys. Lett. 14 025207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 张海鹏, 赵昌哲, 鞠晓璐, 汤杰, 肖体乔 2022 71 074201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang H P, Zhao C Z, Ju X L, Tang J, Xiao T Q 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 074201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Chen L, Wang C, Xiao X, Ren C, Zhang D, Li Z, Cao D 2022 Opt. Express 30 6248
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wu H, Wang C, Gong W 2018 Opt. Express 26 4183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Xu C, Li D, Fan X, Lin B, Guo K, Yin Z, Guo Z 2023 Phys. Scr. 98 065011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Kataoka S, Mizutani Y, Uenohara T, Takaya Y, Matoba O 2022 Appl. Opt. 61 10126
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zhou C, Liu X, Feng Y, Li X, Wang G, Sun H, Huang H, Song L 2022 Opt. Lasers Eng. 156 107101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Fan Y, Bai Y, Fu Q, Zhang R, Zhou L, Zhu X, Zou X, Fu X 2024 Opt. Commun. 566 130684
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Katkovnik V, Astola J 2012 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 29 1556
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Zhou C, Feng D, Wang G, Huang J, Huang H, Liu X, Li X, Feng Y, Sun H, Song L 2023 Opt. Express 31 25013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Tomasi C, Manduchi R 1998 Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Computer Vision Bombay, India, January 7, 1998 p839
[33] Buades A, Coll B, Morel J M 2005 Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition San Diego, CA, USA, June 20–25, 2005 p60
[34] Dabov K, Foi A, Katkovnik V, Egiazarian K 2007 IEEE Trans. Image Process. 16 2080
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] He K, Sun J, Tang X 2012 IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 35 1397
[36] Liu X, Jing X Y, Tang G, Wu F, Ge Q 2017 Signal Process. 135 239
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Izadi S, Sutton D, Hamarneh G 2023 Artif. Intell. Rev. 56 5929
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Liu X, Tanaka M, Okutomi M 2013 IEEE Trans. Image Process. 22 5226
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Lei T, Zhang R, Ma Y, Ding X, Wu Y, Shiyong W 2024 Opt. Commun. 550 130023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] 李龙珍, 姚旭日, 刘雪峰, 俞文凯, 翟光杰 2014 63 224201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li L Z, Yao X R, Liu X F, Yu W K, Zhai G J 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 224201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 520
- PDF下载量: 8
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: