-
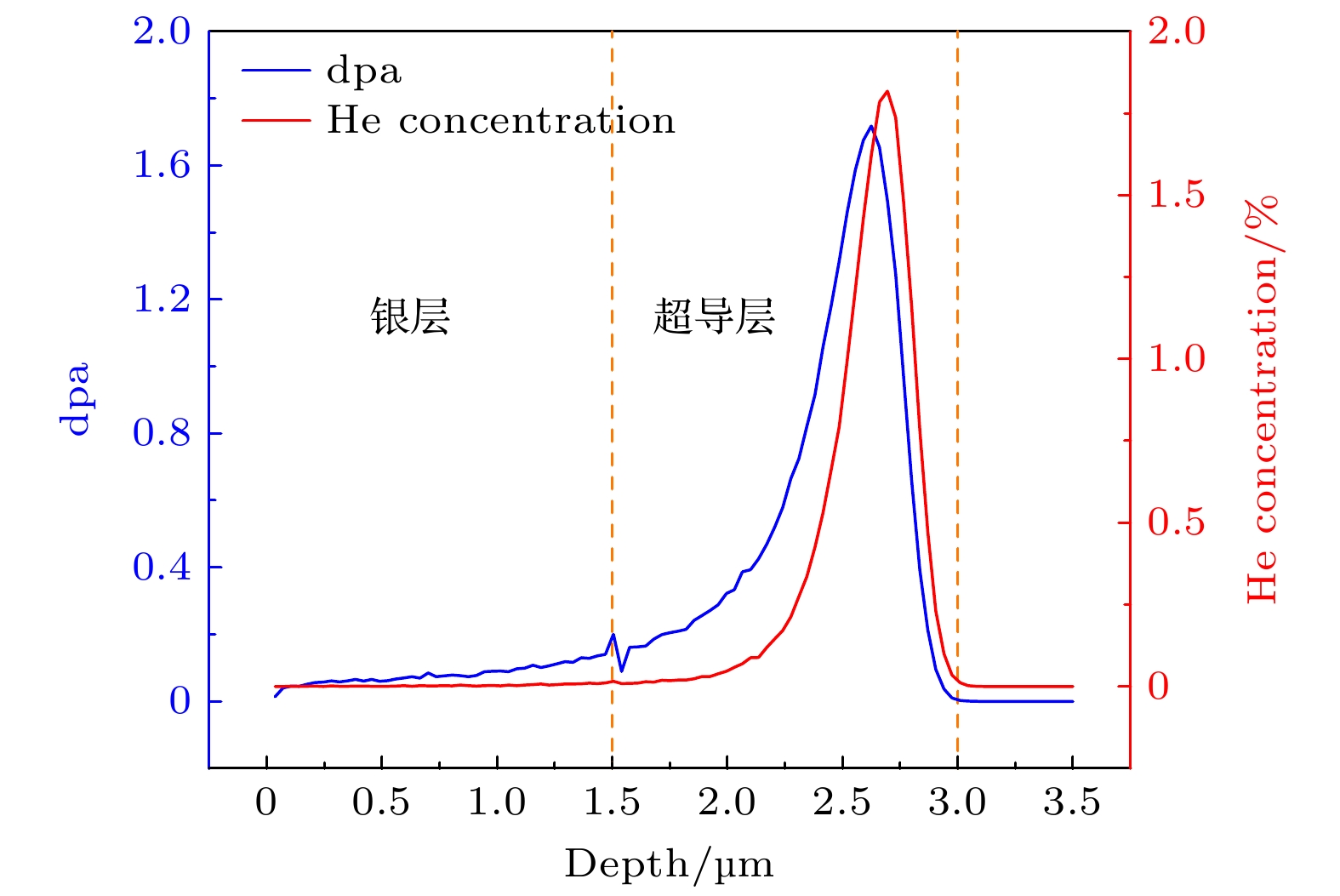
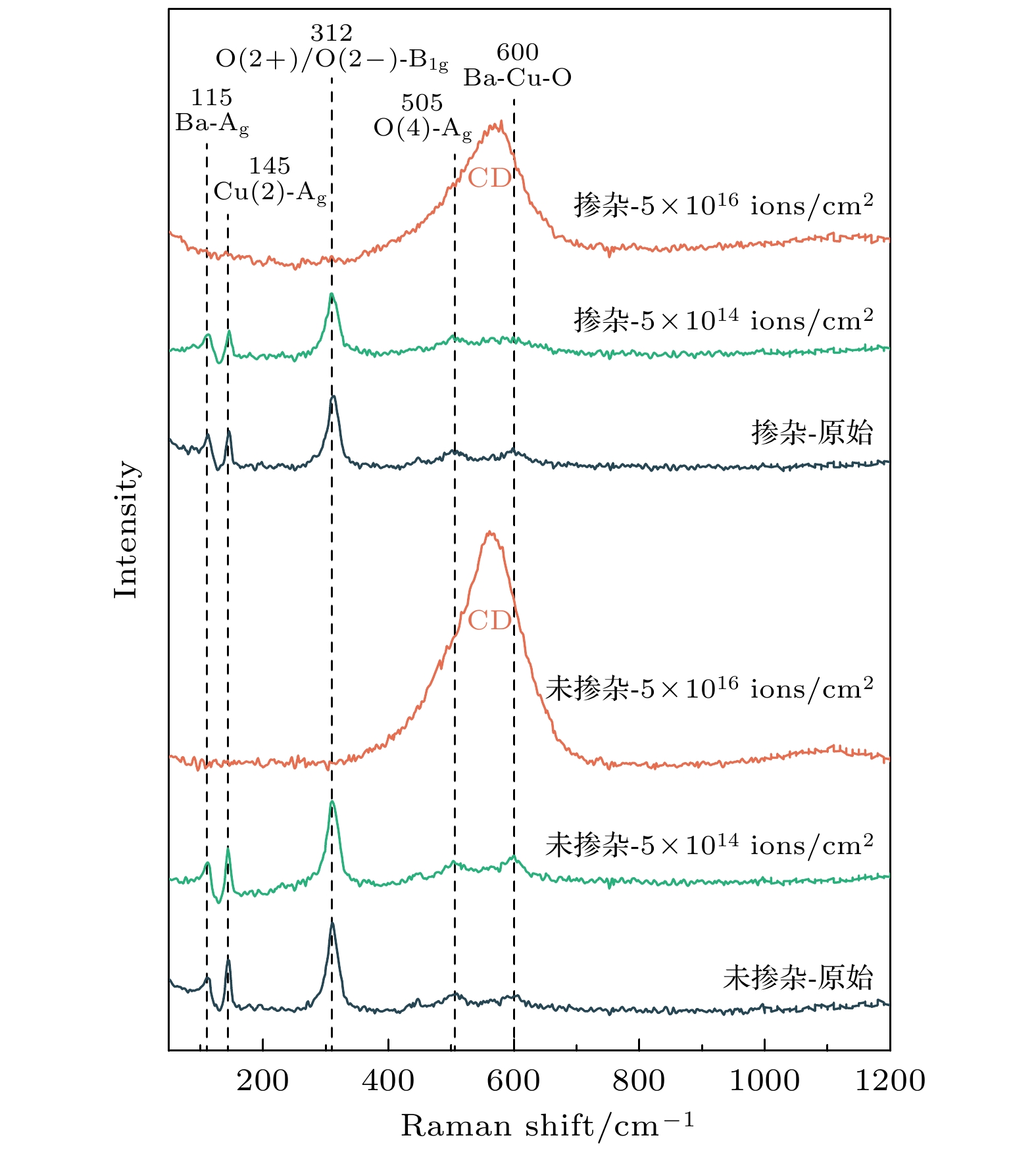
为探究稀土钡铜氧化物(REBCO)第二代高温超导带材中掺杂相对离子辐照缺陷演化及超导电性的影响机理, 本文采用能量为1.4 MeV的He+离子对国产化未掺杂和掺杂摩尔分数3.5% BaHfO3(BHO)的EuBa2Cu3O7–δ带材进行三种不同剂量的室温辐照实验并退火. 电学性能测试表明, 随着辐照剂量的增加, 掺杂带材的临界电流密度仍均高于未掺杂带材并且下降程度更小. 透射电镜表征结果证明, 超导层中通过掺杂BHO纳米相引入局域应变改变了辐照He缺陷的迁移行为, 在一定范围内修复了损伤的超导结构, 提高了带材载流能力的辐照耐受性. 同时BHO纳米柱作为强钉扎中心使得掺杂带材临界电流密度的磁场依赖性和温度依赖性受辐照影响更小. 不同于中子或重离子辐照后, 通过退火可以恢复材料一定程度的超导电性, 本文中大剂量He +离子辐照的两种带材经氧气氛退火后, 其电学性能继续恶化. 相比于未掺杂带材, 掺杂带材中BHO产生的局域应变在高温下抑制了辐照He缺陷在三维方向上的尺寸增长, 改变了磁通钉扎特性, 延缓了因氦泡长大而造成的超导层结构无序和非晶化. 本研究为评估REBCO超导带材在辐照环境下的工况服役行为提供了参考依据.Rare-earth barium copper oxide (REBCO) as a representative of the second-generation high-temperature superconducting materials possesses superior physical advantages such as high critical magnetic field, elevated critical temperature, and superior current density, which has been applied to many domains. Although the introduction of non-superconducting nanoscale particle dopants, as a critical method, can enhance the magnetic flux pinning capability of REBCO strips, the effect of the doping on the performance change and microstructure evolution of the strips under irradiation is ignored. In this work, undoped and 3.5% BaHfO3 (BHO) doped EuBa2Cu3O7–δ strips are investigated in the room-temperature irradiation experiments (1.4 MeV He+ ions) with three distinct doses of 5×1014, 5×1015, and 5×1016 ions/cm2, respectively. Electrical performance tests reveal that the undoped strips exhibit a slight increase in Jc after the low-dose irradiation. However, with dose increasing, Jc decreases by over 60%. In contrast, doped strips experience a significantly smaller decline in Jc, ranging only between 30% and 40% at high-dose irradiation. Raman spectroscopy and transmission electron microscopy characterizations confirm that the defects induced by He+ ion irradiation lead to amorphization and structural disorder within the superconducting layers, which is the primary reason for the decline in the superconducting properties of the strips. The results show that the introduction of localized strain through BHO nanophase in the superconducting layer changes the migration and aggregation behavior of irradiation-induced defects, repairing the damaged superconductor structure. Furthermore, the field dependence and temperature dependence of Jc of doped strips are irradiation-resistant due to BHO nanocrystals as strong pinning centers. Additionally, unlike the superconducting properties of the REBCO strips that can be repaired through oxygen annealing after neutron or heavy ion irradiation, the electrical properties of the two types of strips irradiated with high doses of He+ ions in this work are further deteriorated after being annealed. It is worth noting that compared with the undoped strip, the localized strain generated by BHO in the doped strip inhibits the size growth of helium defects in the three-dimensional direction at high temperatures, which changes the magnetic flux pinning characteristics and delays the disorder and amorphization of the superconducting layer structure caused by the severe growth of helium bubbles. This study provides a reference for the application of REBCO superconducting strips in the irradiation environment.
-
Keywords:
- REBCO superconducting strips /
- irradiation damage /
- critical current density /
- characterization of microstructure
[1] Gurevich A 2011 Nat. Mater. 10 255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Li X G, Kobayashi R, Kotaka Y, Shimoyama J I, Kishio K 1994 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. , Part 1 33 L843
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 蔡传兵, 池长鑫, 李敏娟, 刘志勇, 鲁玉明, 郭艳群, 白传易, 陆齐, 豆文芝 2018 科学通报 64 827
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cai C B, Chi C X, Li M J, Liu Z Y, Lu Y M, Guo Y Q, Bai C Y, Lu Q, Dou W Z 2018 Chin. Sci. Bull. 64 827
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Bruzzone P, Fietz W H, Minervini J V, Novikov M, Yanagi N, Zhai Y, Zheng J 2018 Nucl. Fusion 58 103001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Humphry-Baker S A, Smith G D W 2019 Philos. Trans. Royal Soc. A 377 0443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Creely A J, Greenwald M J, Ballinger S B, et al. 2020 J. Plasma Phys. 86 6
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Mitchell N, Zheng J, Vorpahl C, et al. 2021 Supercond. Sci. Technol. 34 103001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Coleman M, McIntosh S 2019 Fusion Eng. Des. 139 26
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Fischer D X, Prokopec R, Emhofer J, Eisterer M 2018 Supercond. Sci. Technol. 31 044006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Torsello D, Gambino D, Gozzelino L, Trotta A, Laviano F 2023 Supercond. Sci. Technol. 36 014003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Kwok W K, Welp U, Glatz A, Koshelev A E, Kihlstrom K J, Crabtree G W 2016 Rep. Prog. Phys. 79 116501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Jia Y, LeRoux M, Miller D J, Wen J G, Kwok W K, Welp U, Rupich M W, Li X, Sathyamurthy S, Fleshler S, Malozemoff A P, Kayani A, Ayala-Valenzuela O, Civale L 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 103 122601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Shao B L, Liu A S, Ren H T, He Q, Xiao L, Tajeyana T 1991 Mater. Res. Bull. 27 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Sauerzopf F M, Werner M, Weber H W, Suris R A, Kulikov D V, Kharlamov V S, Trushin Y V 1997 Physica C 282-287 1333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Veterníková J, Chudý M, Slugeň V, Eisterer M, Weber H W, Sojak S, Petriska M, Hinca R, Degmová J, Sabelová V 2011 J. Fusion Energy 31 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 朱红梅, 李佐光, 邱长军, 毛哲华, 秦经刚 2020 材料导报 34 15116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu H M, Li Z G, Qiu C J, Mao Z H, Qin J G 2020 Mater. Rep. 34 15116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 张振闯, 周海山, 秦经刚, 罗广南 2019 材料热处理学报 40 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Z C, Zhou H S, Qin J G, Luo G N 2019 Trans. Mater. Heat Treat. 40 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Adams K, Iliffe W, Nicholls R J, He G, Diaz-Moreno S, Mosselmans F, Fischer D, Eisterer M, Grovenor C R M, Speller S C 2023 Supercond. Sci. Technol. 36 10LT01
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Iliffe W, Peng N, Brittles G, Bateman R, Webb R, Grovenor C, Speller S 2021 Supercond. Sci. Technol. 34 09LT01
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Huang D X, Gu H W, Shang H J, Li T G, Xie B W, Zou Q, Chen D, Chu W k, Ding F Z 2021 Supercond. Sci. Technol. 34 045001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Matsui H, Yamaguchi I 2022 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 61 043001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhang Y, Rupich M W, Solovyov V, Li Q, Goyal A 2020 Sci. Rep. 10 14848
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Unterrainer R, Fischer D X, Lorenz A, Eisterer M 2022 Supercond. Sci. Technol. 35 04LT01
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Strickland N M, Wimbush S C, Kluth P, Mota-Santiago P, Ridgway M C, Kennedy J V, Long N J 2017 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 409 351
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 马衍伟 2022 超导材料科学与技术 (北京: 科学出版社) 第398—399页
Ma Y W 2022 Superconducting Materials Science and Technology (Beijing: Science Press) pp398–399
[26] Jha A K, Matsumoto K 2019 Front. Phys. 7 82
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Wu J, Shi J 2017 Supercond. Sci. Technol. 30 103002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wang M, Beyerlein I J, Zhang J, Han W Z 2018 Acta Mater. 160 211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Gao R, Jin M M, Han F, Wang B M, Wang X P, Fang Q F, Dong Y H, Sun C, Shao L, Li M D, Li J 2020 Acta Mater. 197 212
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Llordés A, Palau A, Gázquez J, Coll M, Vlad R, Pomar A, Arbiol J, Guzmán R, Ye S, Rouco V, Sandiumenge F, Ricart S, Puig T, Varela M, Chateigner D, Vanacken J, Gutiérrez J, Moshchalkov V, Deutscher G, Magen C, Obradors X 2012 Nat. Mater. 11 329
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Kwon J H, Meng Y, Wu L, Zhu Y, Zhang Y, Selvamanickam V, Welp U, Kwok W K, Zuo J M 2018 Supercond. Sci. Technol. 31 105006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Cui X M, Liu G Q, Wang J, Huang Z C, Zhao Y T, Tao B W, Li Y R 2007 Physica C 466 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Eisterer M, Fuger R, Chudy M, Hengstberger F, Weber H W 2010 Supercond. Sci. Technol. 23 014009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Higuchi T, Yoo S I, Murakami M 1999 Phys. Rev. B 59 1514
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] 谷裕, 蔡传兵, 刘志勇, 刘杰, 刘丽, 黄荣铁 2021 科学通报 66 3965
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gu Y, Cai C B, Liu Z Y, Liu J, Liu L, Huang R T 2021 Chin. Sci. Bull. 66 3965
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Krusin-Elbaum L, Civale L, Thompson J R, Feild C 1996 Phys. Rev. B 53 11744
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Teral T, Masegi T, Kusagaya K, Takahashi Y, Kishio K, Motohira N, Nakatanl K 1991 Physica C 185-189 2383
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Feighan J P F, Kursumovic A, MacManus-Driscoll J L 2017 Supercond. Sci. Technol. 30 123001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Khalfinand I B, Shapiro B Y 1993 Physica C 207 359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Thomsen C, Kaczmarczyk G 2006 Vibrational Raman Spectroscopy of High-temperature Superconductors (Hoboken: Wiley
[41] 刘丽, 刘杰, 曾健, 翟鹏飞, 张胜霞, 徐丽君, 胡培培, 李宗臻, 艾文思 2020 69 077401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu L, Liu J, Zeng J, Zhai P F, Zhang S X, Xu L J, Hu P P, Li Z Z, Ai W S 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 077401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Venkataraman K, Baurceanu R, Maroni V A 2005 Appl. Spectrosc. 59 639
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Gibson G, MacManus-Driscoll J L, Cohen L F 1997 IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 7 2130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] 但敏, 陈伦江, 贺岩斌, 吕兴旺, 万俊豪, 张虹, 张珂嘉, 杨莹, 金凡亚 2022 71 237401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dan M, Chen L J, He Y B, Lü X W, Wan J H, Zhang H, Zhang K J, Yang Y, Jin F Y 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 237401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Trinkaus H, Singh B N 2003 J. Nucl. Mater. 323 229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] 王玉珍 马颖 周益春 2014 63 246101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y Z, Ma Y, Zhou Y C 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 246101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] 刘思冕 韩卫忠 2019 68 137901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu S M, Han W Z 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 137901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[48] Li S H, Li J T, Han W Z 2019 Materials 12 1036
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
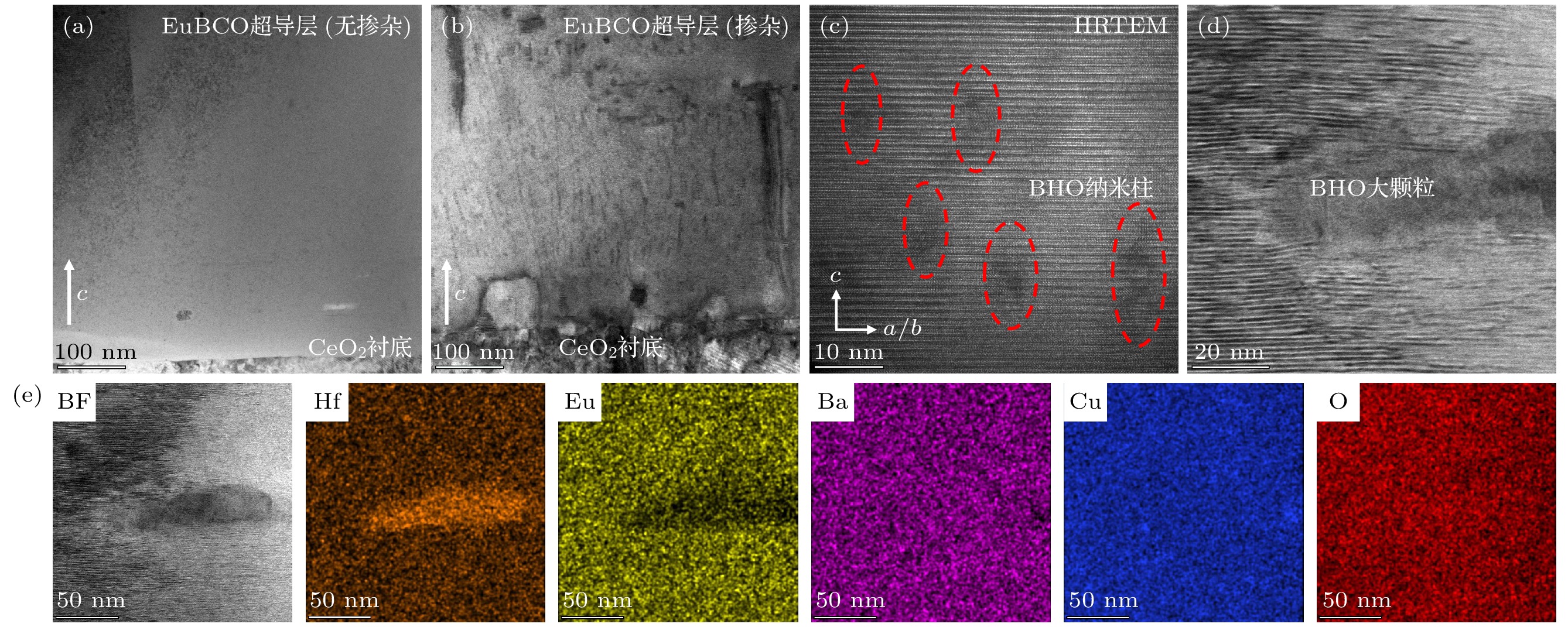
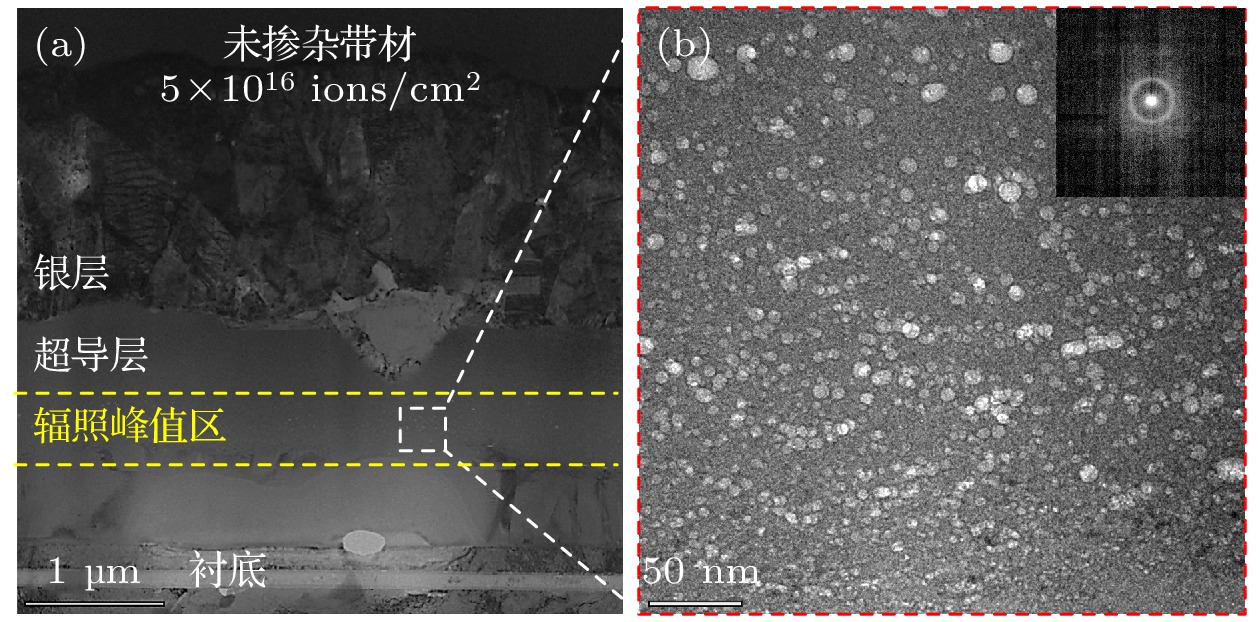
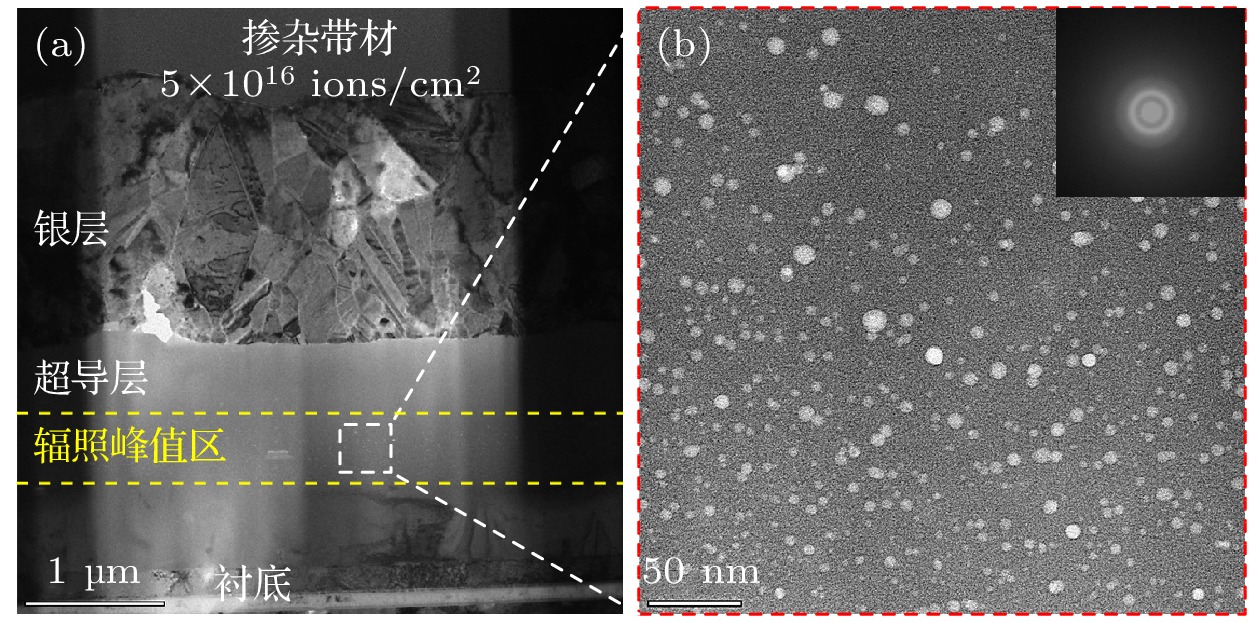
图 3 未掺杂/掺杂EuBCO带材的微观结构 (a) 未掺杂带材超导层的TEM图像; (b) 掺杂带材超导层的TEM图像; (c) 掺杂带材超导层中BHO纳米柱的高分辨图像; (d) 掺杂带材中BHO大颗粒周围的大幅局域弯曲应变和大量层错; (e) 图(d)中BHO大颗粒的EDS-mapping图像
Fig. 3. Microscopic structure of undoped/doped EuBCO strips: (a) TEM image of the superconducting layer of undoped strip; (b) TEM image of superconducting layer of doped strip; (c) high-resolution image of BHO nanocolumns in the superconducting layer of doped strip; (d) large localized bending strain and numerous stacking faults around BHO large particle in doped strip; (e) EDS-mapping images of the large BHO particle in Figure (d).
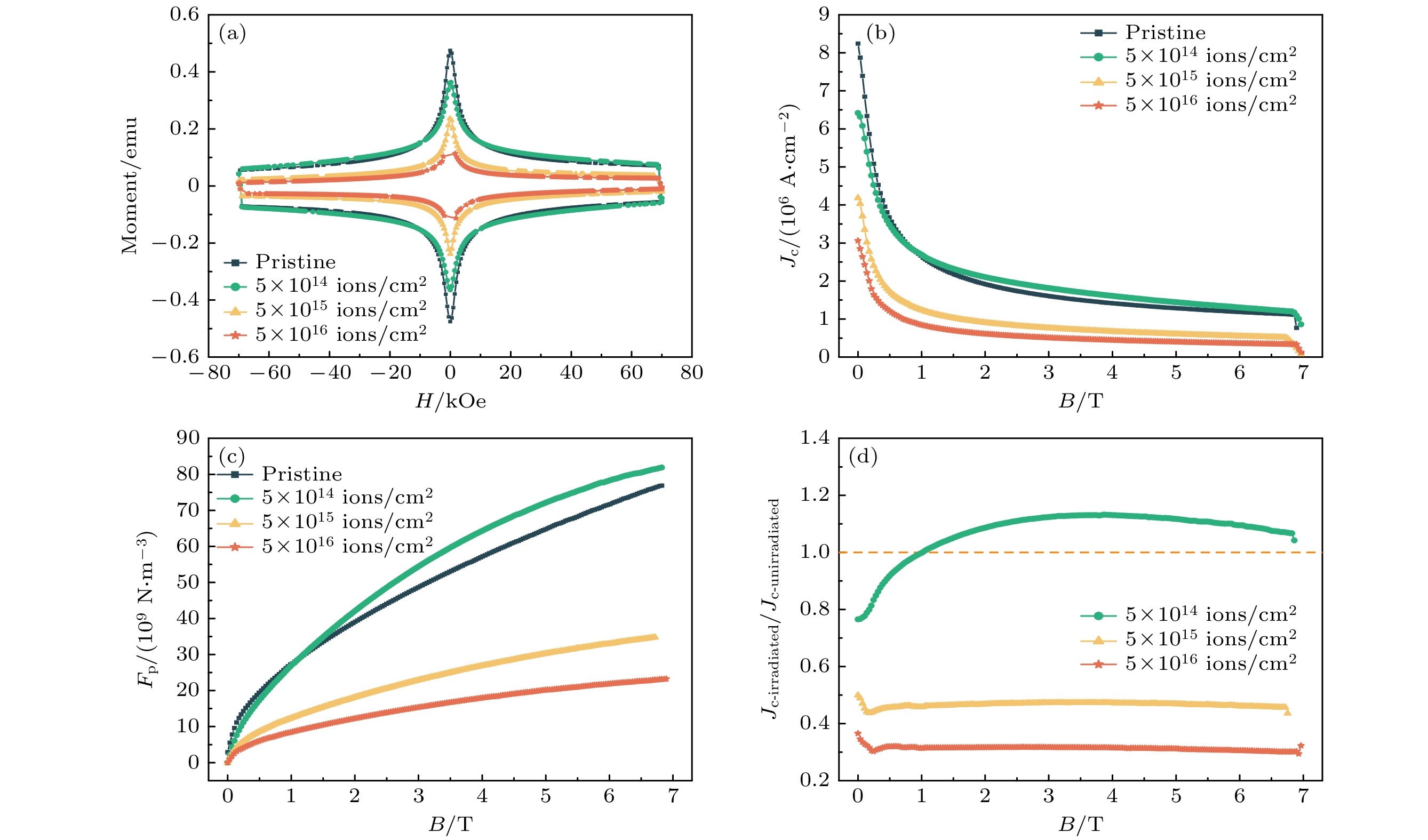
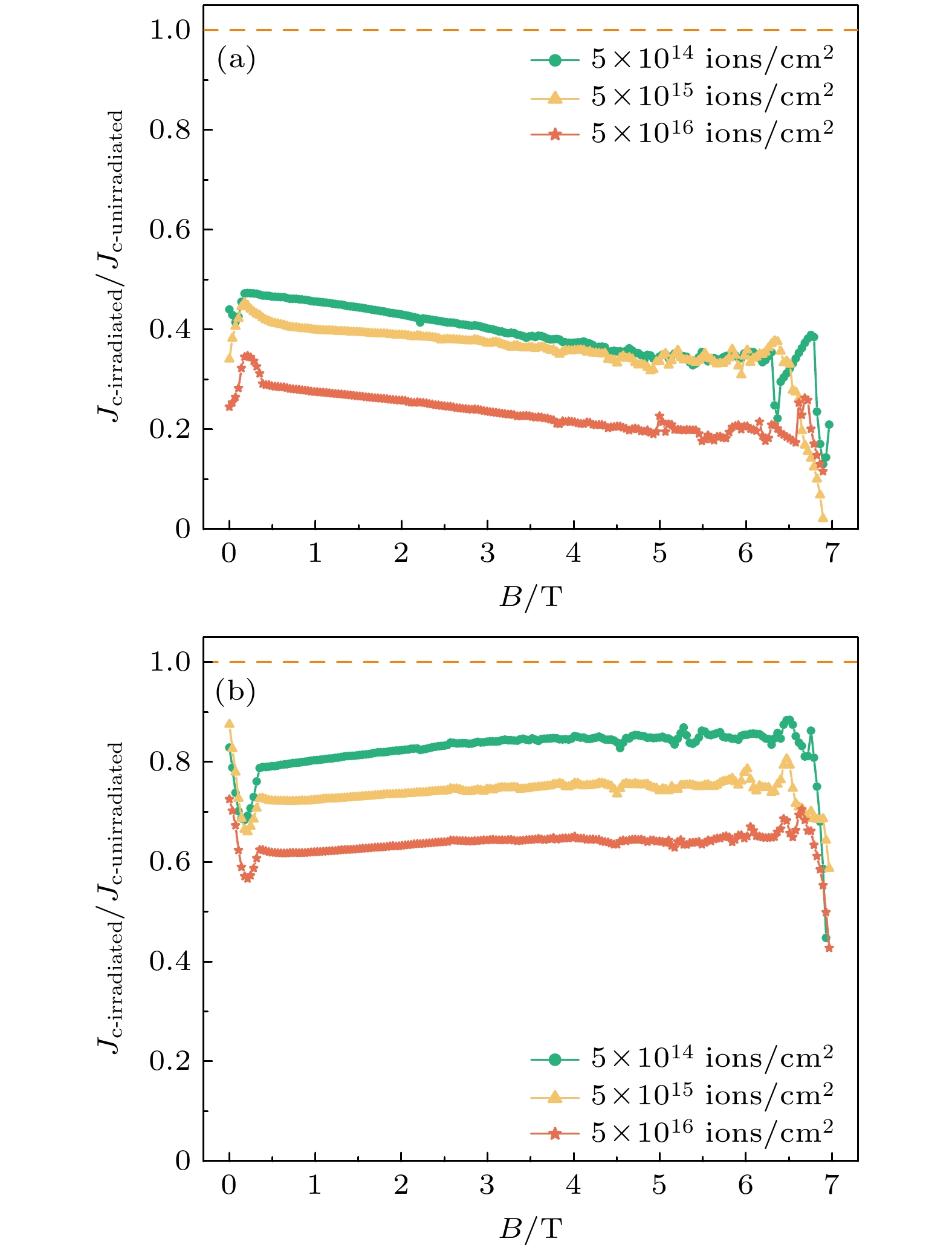
图 4 未掺杂EuBCO带材不同剂量辐照后的电学性能 (a) 33 K下的M-H曲线; (b) 33 K下的Jc-B曲线; (c) 33 K下的Fp-B曲线; (d) 辐照后相比辐照前的归一化Jc-B曲线
Fig. 4. Electrical properties of undoped EuBCO strip with different irradiation doses: (a) M-H curves at 33 K; (b) Jc-B curves at 33 K; (c) Fp-B curves at 33 K; (d) normalized Jc-B curves for before and after irradiation.
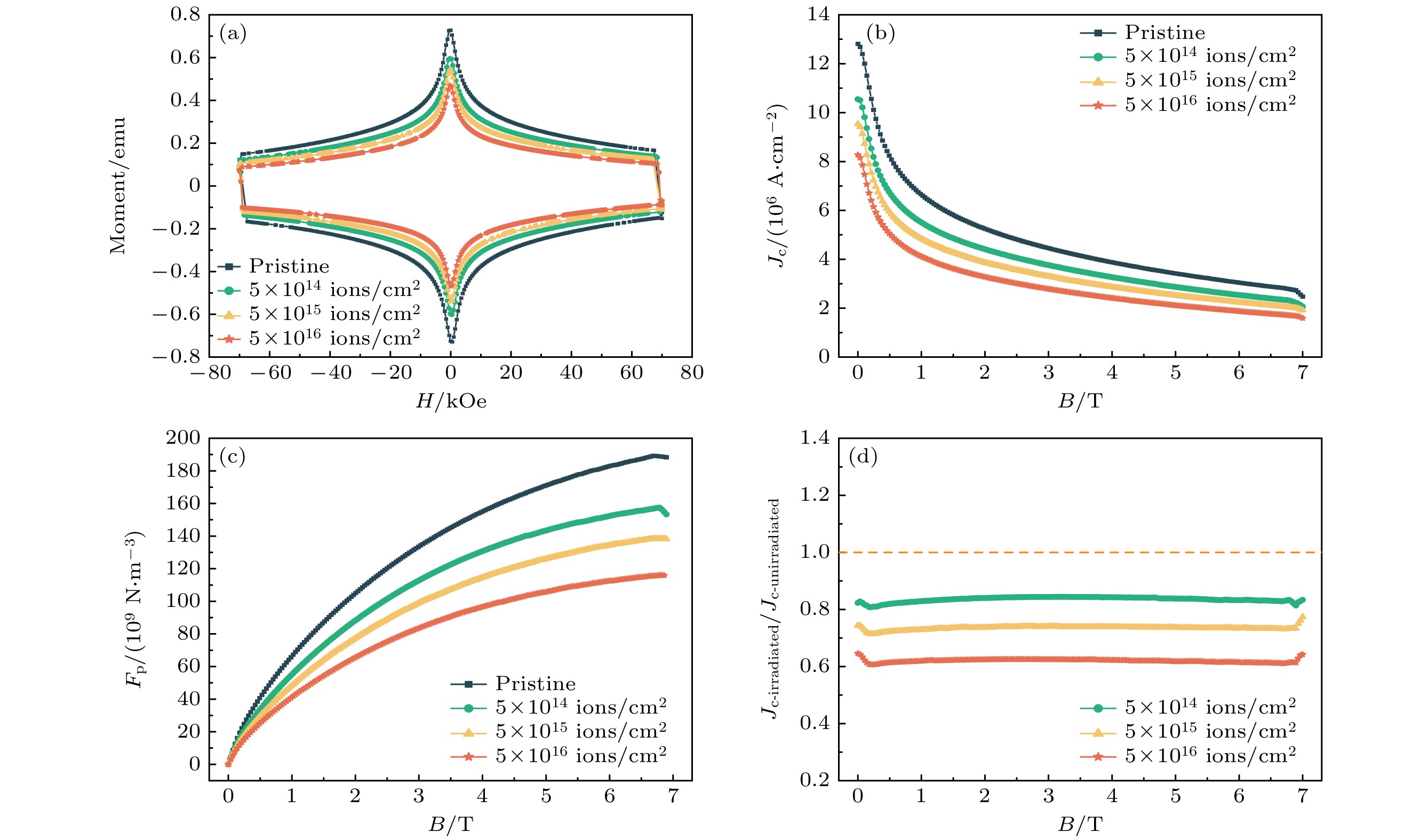
图 5 掺杂EuBCO带材不同剂量辐照后的电学性能 (a) 33 K下的M-H曲线; (b) 33 K下的Jc-B曲线; (c) 33 K下的Fp-B曲线; (d) 辐照后相比辐照前的归一化Jc-B曲线
Fig. 5. Electrical properties of doped EuBCO strip with different irradiation doses: (a) M-H curves at 33 K; (b) Jc-B curves at 33 K; (c) Fp-B curves at 33 K; (d) normalized Jc-B curves for before and after irradiation.
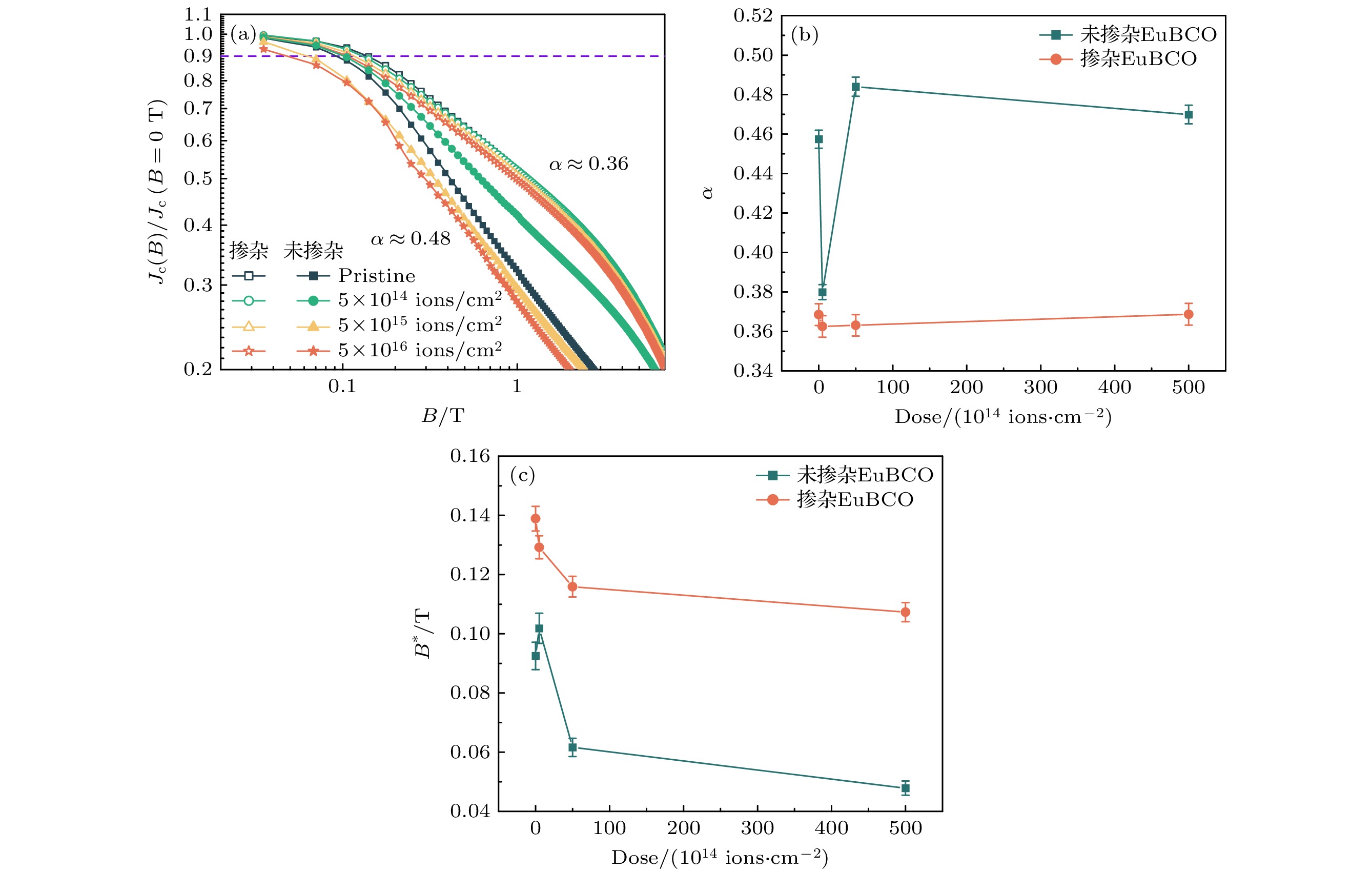
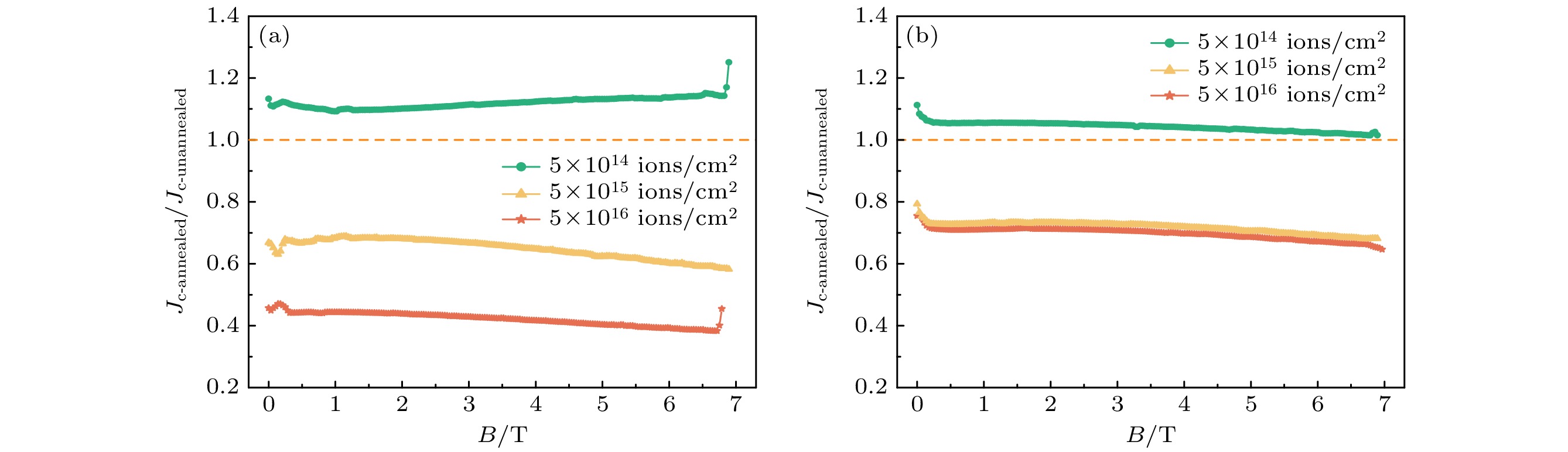
图 6 两种带材Jc随磁场衰减的对数曲线, 以及幂参数α和过渡场B*随辐照剂量的变化 (a) Jc(B)/Jc (B=0 T)-B曲线; (b) α的变化; (c) $B^* $的变化
Fig. 6. Logarithmic curves of Jc attenuating with magnetic field for two types of strips, and changes of power parameter α and characteristic field with irradiation doses: (a) Jc(B)/Jc (B = 0 T)-B curves; (b) changes in α; (c) changes in $B^* $.
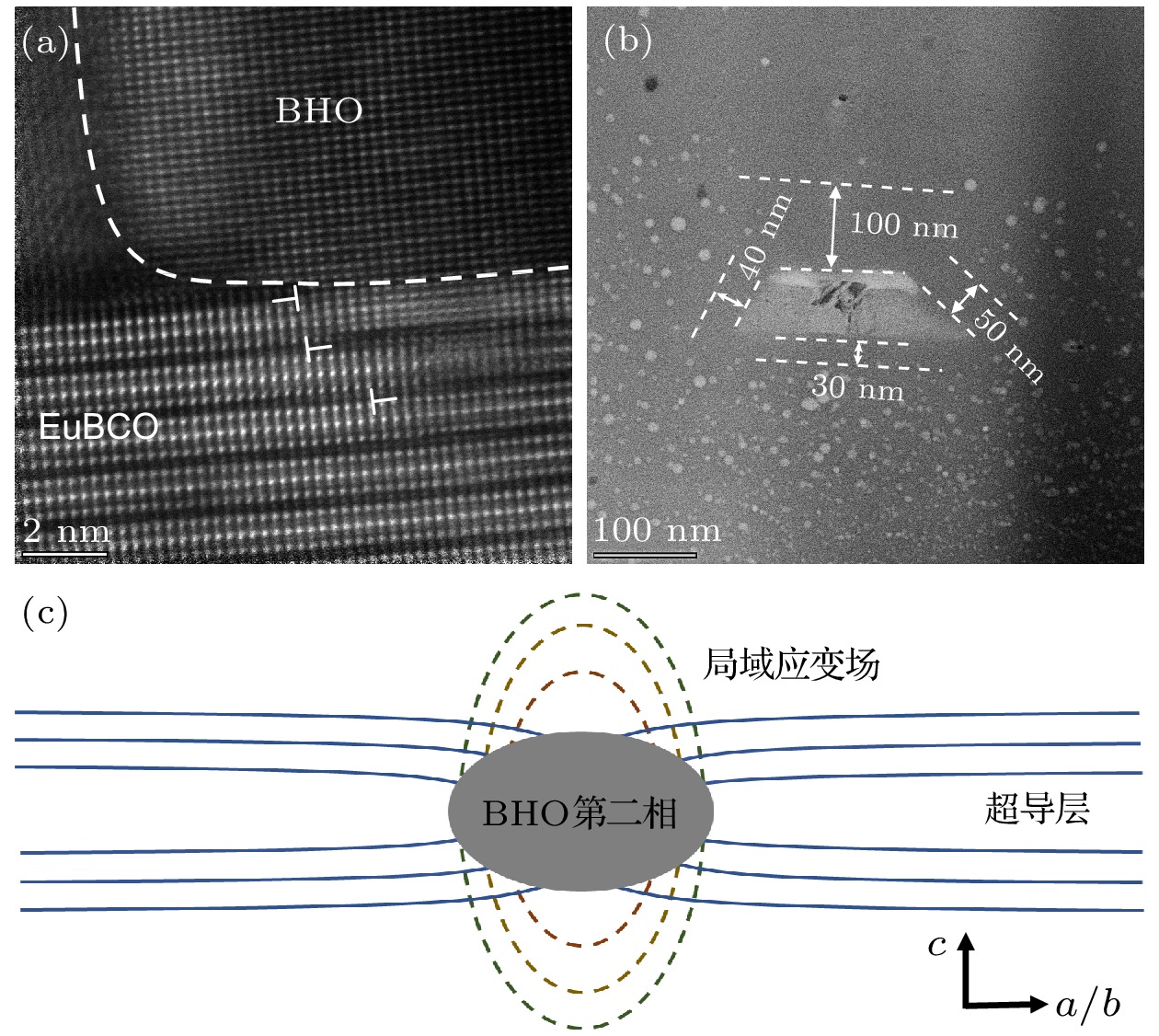
图 11 BHO掺杂对氦泡演化行为的影响 (a) 球差电镜下BHO颗粒与EuBCO基体的高分辨原子像; (b) BHO相界面对氦泡的吸附; (c) 超导层中BHO第二相诱导局域应变的示意图
Fig. 11. The effect of BHO doping on the evolution behavior of helium bubbles: (a) High-resolution atomic image of BHO particles and EuBCO matrix under aberration transmission electron microscopy; (b) the adsorption of helium bubbles on the BHO interface; (c) schematic diagram of localized strain induced by the second phase of BHO in the superconducting layer.
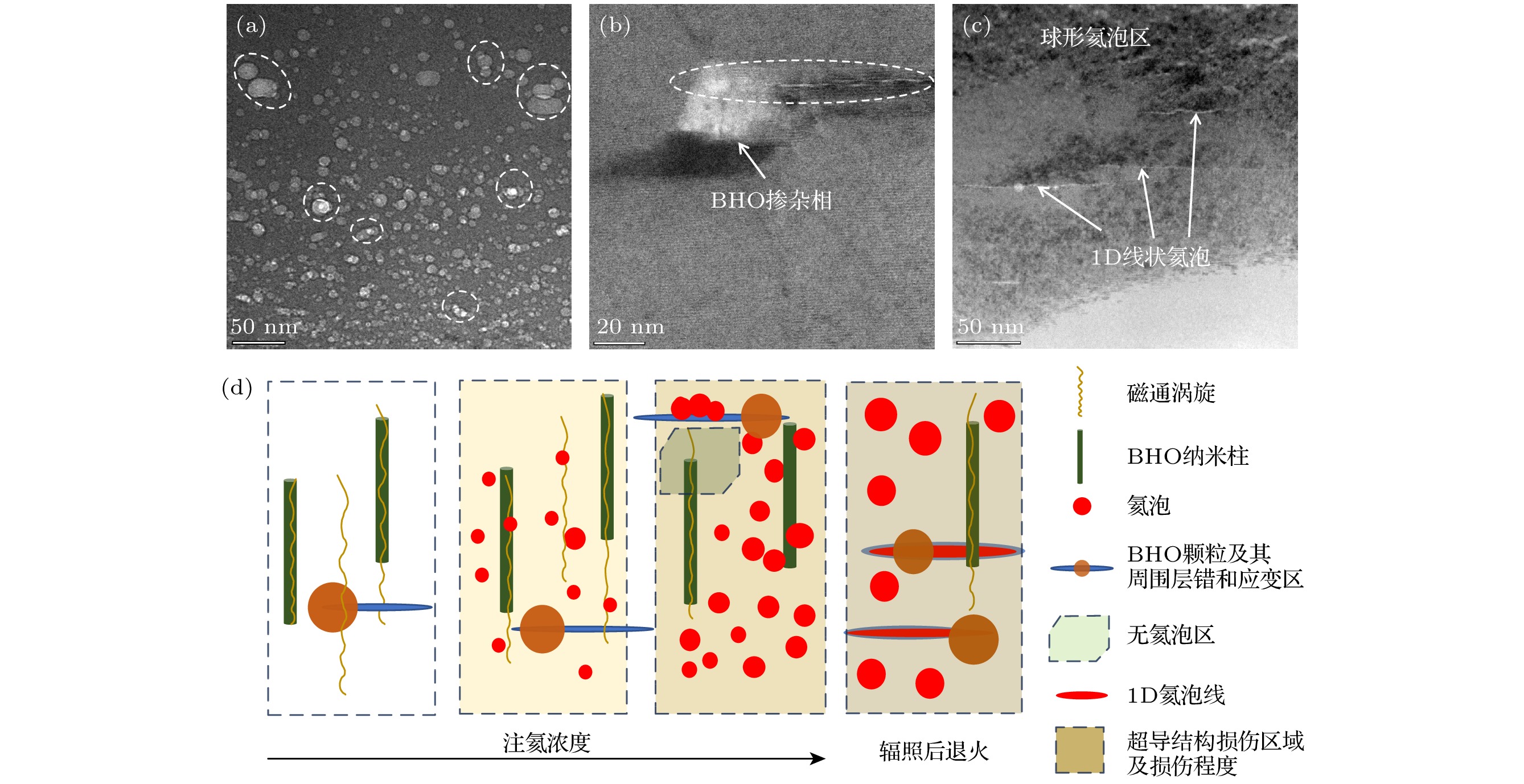
图 13 退火后未掺杂带材和掺杂带材的辐照缺陷演化 (a) 未掺杂带材5×1016 ions/cm2辐照并退火后峰值区的氦泡分布; (b) BHO掺杂相附近的氦泡形貌; (c) 氦泡沿层错形成一维线状氦泡; (d) 辐照及退火过程中的磁通钉扎演变示意图
Fig. 13. Evolution of irradiation defects in undoped and doped strips after annealing: (a) Distribution of helium bubbles in the peak region after annealing of undoped strip irradiated with 5×1016 ions/cm2; (b) morphology of helium bubbles around BHO doping phase; (c) 1D linear helium bubbles formed along stacking faults; (d) schematic diagram of magnetic flux pinning evolution during irradiation and annealing processes.
-
[1] Gurevich A 2011 Nat. Mater. 10 255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Li X G, Kobayashi R, Kotaka Y, Shimoyama J I, Kishio K 1994 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. , Part 1 33 L843
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 蔡传兵, 池长鑫, 李敏娟, 刘志勇, 鲁玉明, 郭艳群, 白传易, 陆齐, 豆文芝 2018 科学通报 64 827
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cai C B, Chi C X, Li M J, Liu Z Y, Lu Y M, Guo Y Q, Bai C Y, Lu Q, Dou W Z 2018 Chin. Sci. Bull. 64 827
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Bruzzone P, Fietz W H, Minervini J V, Novikov M, Yanagi N, Zhai Y, Zheng J 2018 Nucl. Fusion 58 103001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Humphry-Baker S A, Smith G D W 2019 Philos. Trans. Royal Soc. A 377 0443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Creely A J, Greenwald M J, Ballinger S B, et al. 2020 J. Plasma Phys. 86 6
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Mitchell N, Zheng J, Vorpahl C, et al. 2021 Supercond. Sci. Technol. 34 103001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Coleman M, McIntosh S 2019 Fusion Eng. Des. 139 26
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Fischer D X, Prokopec R, Emhofer J, Eisterer M 2018 Supercond. Sci. Technol. 31 044006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Torsello D, Gambino D, Gozzelino L, Trotta A, Laviano F 2023 Supercond. Sci. Technol. 36 014003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Kwok W K, Welp U, Glatz A, Koshelev A E, Kihlstrom K J, Crabtree G W 2016 Rep. Prog. Phys. 79 116501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Jia Y, LeRoux M, Miller D J, Wen J G, Kwok W K, Welp U, Rupich M W, Li X, Sathyamurthy S, Fleshler S, Malozemoff A P, Kayani A, Ayala-Valenzuela O, Civale L 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 103 122601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Shao B L, Liu A S, Ren H T, He Q, Xiao L, Tajeyana T 1991 Mater. Res. Bull. 27 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Sauerzopf F M, Werner M, Weber H W, Suris R A, Kulikov D V, Kharlamov V S, Trushin Y V 1997 Physica C 282-287 1333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Veterníková J, Chudý M, Slugeň V, Eisterer M, Weber H W, Sojak S, Petriska M, Hinca R, Degmová J, Sabelová V 2011 J. Fusion Energy 31 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 朱红梅, 李佐光, 邱长军, 毛哲华, 秦经刚 2020 材料导报 34 15116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu H M, Li Z G, Qiu C J, Mao Z H, Qin J G 2020 Mater. Rep. 34 15116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 张振闯, 周海山, 秦经刚, 罗广南 2019 材料热处理学报 40 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Z C, Zhou H S, Qin J G, Luo G N 2019 Trans. Mater. Heat Treat. 40 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Adams K, Iliffe W, Nicholls R J, He G, Diaz-Moreno S, Mosselmans F, Fischer D, Eisterer M, Grovenor C R M, Speller S C 2023 Supercond. Sci. Technol. 36 10LT01
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Iliffe W, Peng N, Brittles G, Bateman R, Webb R, Grovenor C, Speller S 2021 Supercond. Sci. Technol. 34 09LT01
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Huang D X, Gu H W, Shang H J, Li T G, Xie B W, Zou Q, Chen D, Chu W k, Ding F Z 2021 Supercond. Sci. Technol. 34 045001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Matsui H, Yamaguchi I 2022 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 61 043001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhang Y, Rupich M W, Solovyov V, Li Q, Goyal A 2020 Sci. Rep. 10 14848
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Unterrainer R, Fischer D X, Lorenz A, Eisterer M 2022 Supercond. Sci. Technol. 35 04LT01
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Strickland N M, Wimbush S C, Kluth P, Mota-Santiago P, Ridgway M C, Kennedy J V, Long N J 2017 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 409 351
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 马衍伟 2022 超导材料科学与技术 (北京: 科学出版社) 第398—399页
Ma Y W 2022 Superconducting Materials Science and Technology (Beijing: Science Press) pp398–399
[26] Jha A K, Matsumoto K 2019 Front. Phys. 7 82
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Wu J, Shi J 2017 Supercond. Sci. Technol. 30 103002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wang M, Beyerlein I J, Zhang J, Han W Z 2018 Acta Mater. 160 211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Gao R, Jin M M, Han F, Wang B M, Wang X P, Fang Q F, Dong Y H, Sun C, Shao L, Li M D, Li J 2020 Acta Mater. 197 212
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Llordés A, Palau A, Gázquez J, Coll M, Vlad R, Pomar A, Arbiol J, Guzmán R, Ye S, Rouco V, Sandiumenge F, Ricart S, Puig T, Varela M, Chateigner D, Vanacken J, Gutiérrez J, Moshchalkov V, Deutscher G, Magen C, Obradors X 2012 Nat. Mater. 11 329
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Kwon J H, Meng Y, Wu L, Zhu Y, Zhang Y, Selvamanickam V, Welp U, Kwok W K, Zuo J M 2018 Supercond. Sci. Technol. 31 105006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Cui X M, Liu G Q, Wang J, Huang Z C, Zhao Y T, Tao B W, Li Y R 2007 Physica C 466 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Eisterer M, Fuger R, Chudy M, Hengstberger F, Weber H W 2010 Supercond. Sci. Technol. 23 014009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Higuchi T, Yoo S I, Murakami M 1999 Phys. Rev. B 59 1514
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] 谷裕, 蔡传兵, 刘志勇, 刘杰, 刘丽, 黄荣铁 2021 科学通报 66 3965
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gu Y, Cai C B, Liu Z Y, Liu J, Liu L, Huang R T 2021 Chin. Sci. Bull. 66 3965
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Krusin-Elbaum L, Civale L, Thompson J R, Feild C 1996 Phys. Rev. B 53 11744
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Teral T, Masegi T, Kusagaya K, Takahashi Y, Kishio K, Motohira N, Nakatanl K 1991 Physica C 185-189 2383
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Feighan J P F, Kursumovic A, MacManus-Driscoll J L 2017 Supercond. Sci. Technol. 30 123001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Khalfinand I B, Shapiro B Y 1993 Physica C 207 359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Thomsen C, Kaczmarczyk G 2006 Vibrational Raman Spectroscopy of High-temperature Superconductors (Hoboken: Wiley
[41] 刘丽, 刘杰, 曾健, 翟鹏飞, 张胜霞, 徐丽君, 胡培培, 李宗臻, 艾文思 2020 69 077401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu L, Liu J, Zeng J, Zhai P F, Zhang S X, Xu L J, Hu P P, Li Z Z, Ai W S 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 077401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Venkataraman K, Baurceanu R, Maroni V A 2005 Appl. Spectrosc. 59 639
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Gibson G, MacManus-Driscoll J L, Cohen L F 1997 IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 7 2130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] 但敏, 陈伦江, 贺岩斌, 吕兴旺, 万俊豪, 张虹, 张珂嘉, 杨莹, 金凡亚 2022 71 237401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dan M, Chen L J, He Y B, Lü X W, Wan J H, Zhang H, Zhang K J, Yang Y, Jin F Y 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 237401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Trinkaus H, Singh B N 2003 J. Nucl. Mater. 323 229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] 王玉珍 马颖 周益春 2014 63 246101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y Z, Ma Y, Zhou Y C 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 246101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] 刘思冕 韩卫忠 2019 68 137901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu S M, Han W Z 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 137901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[48] Li S H, Li J T, Han W Z 2019 Materials 12 1036
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 4197
- PDF下载量: 113
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: