-
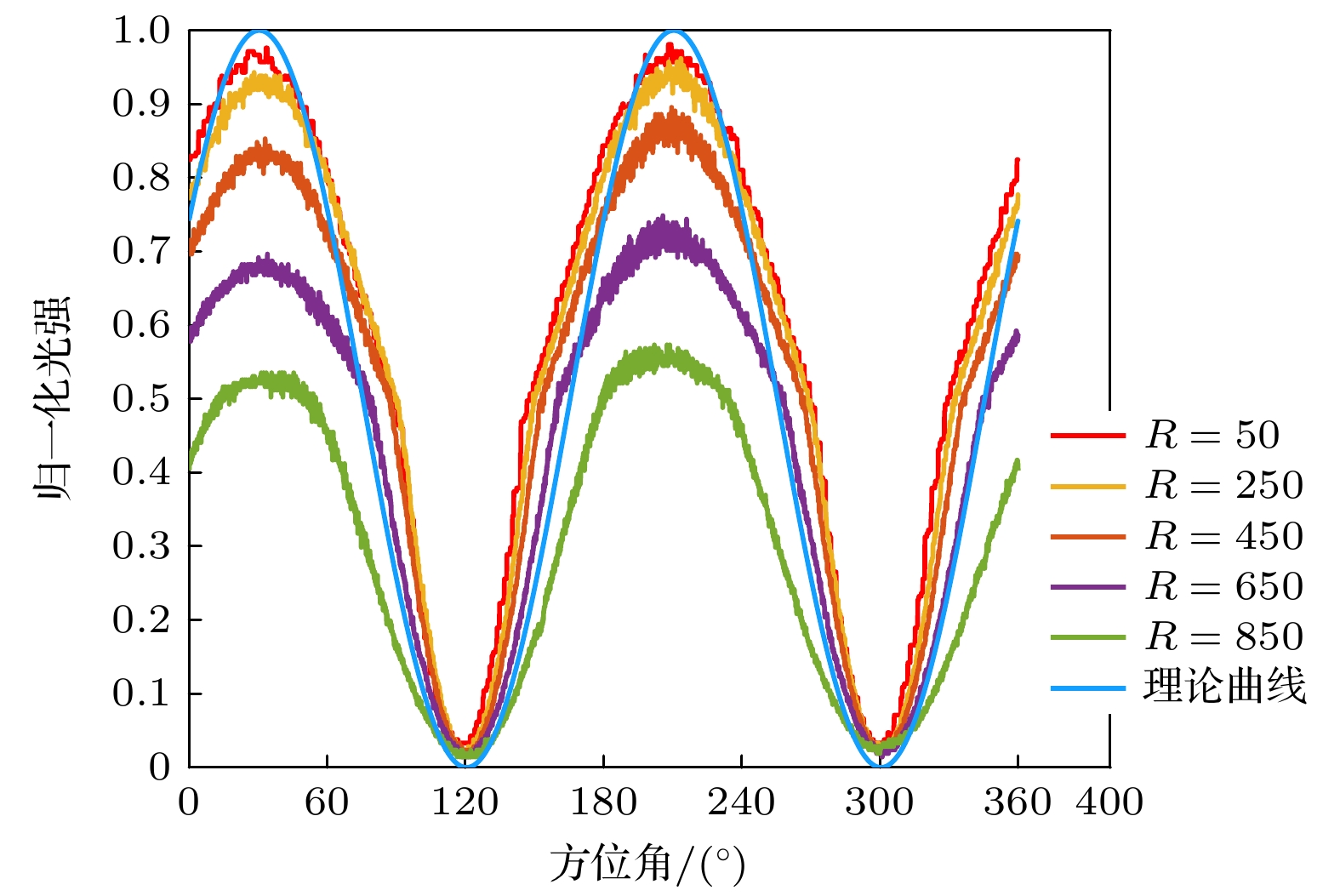
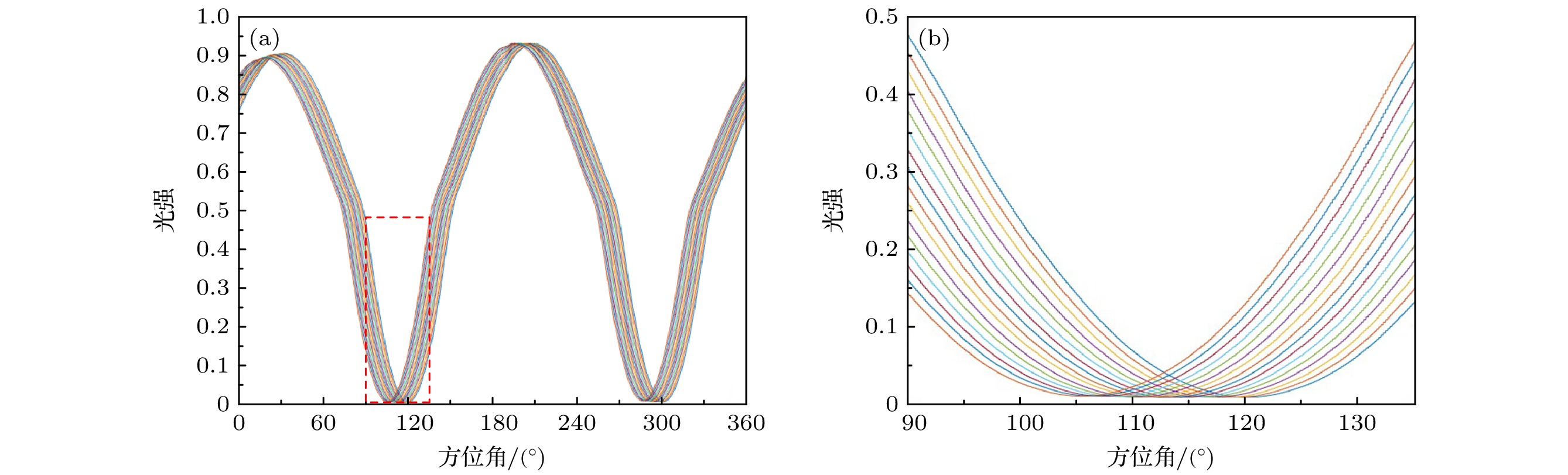
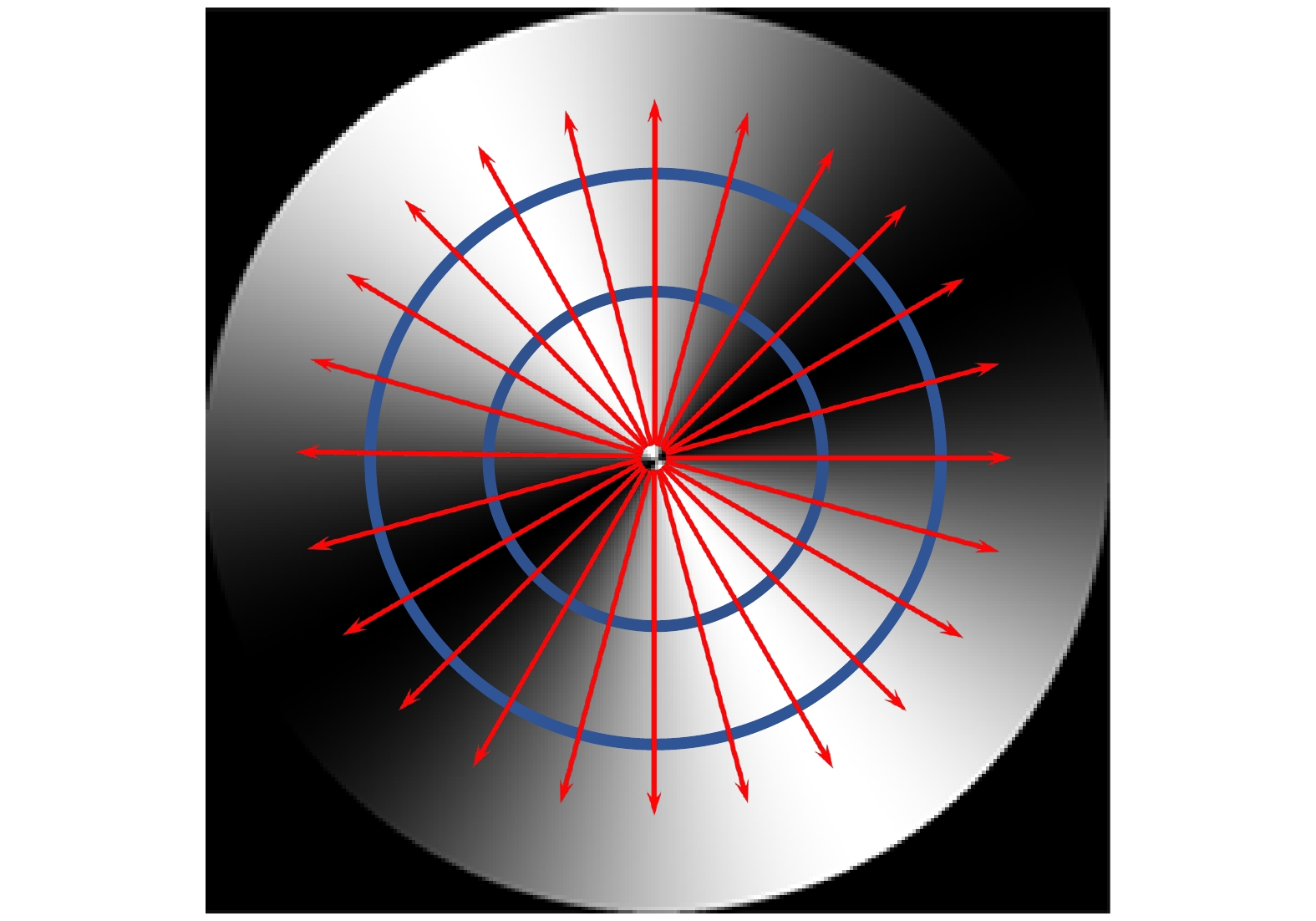
基于矢量光场调制与图像处理的偏振测量技术是一种新型的空间调制型偏振检测技术, 快速高精度的偏振解算方法是该技术走向实用的关键. 为探索快速高精度的偏振方向解算方法, 在简要介绍基于矢量光场空间调制的偏振方向检测技术原理的基础上, 分析了空间偏振调制型光强分布图像的基本特征, 设计并实现了Radon变换、光强调制曲线检测、径向积分和图像相关检测四种偏振方向解算方法, 详细阐述了他们的工作原理和物理思想. 为进行算法性能对比, 搭建实验系统并采集图像进行了实验验证, 分别对四种解算方法的稳定性、速度和精度等进行了对比研究, 结果表明, 四种方法均可实现稳定可靠的偏振方向检测, 光强调制曲线检测、径向积分和图像相关检测三种方法可获得优于0.01度的角度检测精度, 光强调制曲线检测和径向积分法的检测速度较快, 综合性能最优, 是最有潜力实现实时高精度偏振方向检测的两种方法.Polarization is an important property of electromagnetic waves, and measuring their polarization properties fast and precisely is a very important issue in many applications, such as skylight polarization navigation, optical activity measurement, imaging polarimetry, spectroscopic ellipsometry, and fluorescence polarization immunoassay . The polarization measurement method based on vector optical field modulation and image processing is a new type of spatial modulation polarization detection technology. The key step of this technique moving to practical application is determined by effective polarization measuring algorithms with high speed and accuracy. In order to find out the method of fast and precisely calculating polarization direction, the principle of polarization direction measurement based on vector optical field and spatial modulation is introduced briefly, and the basic characteristics of the spatially modulated intensity distribution images are analyzed. According to the properties of spatially modulated image, we propose and implement four different polarization direction calculation methods, which are the Radon transform, intensity modulation curve detection, radial integration, and image correlation detection, and also introduce their working principles and physical thoughts elaborately. To compare the detailed performances of these four algorithms, an experimental setup is constructed to collect the images and perform the algorithm verification, and the stabilities, speeds and accuracies of the four algorithms are compared. The research results indicate that all the four methods can achieve their stable and reliable polarization direction detections. The three methods, intensity modulation curve detection, radial integration and image correlation detection, can achieve the polarization direction measuring accuracy better than 0.01° . The intensity modulation curve detection and radial integration have relatively fast calculation speed and the best comprehensive performances , and are the most promising methods to realize real-time and high-precision polarization measurement.
-
Keywords:
- polarization direction measurement /
- vector optical field /
- spatial modulation /
- image processing
[1] Zhang W J, Zhang X Z, Cao Y, Liu H B, Liu Z J 2016 Appl. Opt. 55 3518
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Tang J, Zhang N, Li D L, Wang F, Zhang B Z, Wang C G, Shen C, Ren J B, Xue C Y, Liu J 2016 Opt. Express 24 15834
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 王成, 范之国, 金海红, 汪先球, 华豆 2021 70 104201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang C, Fan Z G, Jing H H, Wang X Q, Hua D 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 104201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 康健, 马伟, 李沅 2022 科学技术与工程 22 02696
Kang J, Ma W, Li Y 2022 Sci. Technol. Eng. 22 02696
[5] Qiu X D, Xie L G, Liu X, Luo L, Zhang Z Y, Du J L 2011 Opt. Lett. 41 4032
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Eom I, Ahn S H, Rhee H J, Cho M H 2011 Opt. Express 19 10017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 章慧, 齐爱华, 李丹, 李荣兴 2022 大学化学 37 2105009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang H, Qi A H, Li D, Li R X 2022 Univ. Chem. 37 2105009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 李子骏, 贾宏志 2016 光学仪器 38 288
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Z J, Jia H Z 2016 Opt. Instrum. 38 288
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 汪杰君, 刘少晖, 李树, 叶松, 王新强, 王方原 2021 光子学报 50 0228001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J J, Liu S H, Li S, Ye S, Wang X Q, Wang F Y 2021 Acta Photonica Sin. 50 0228001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 王宇瑶, 麻金继, 李婧晗, 洪津, 李正强 2022 遥感学报 26 0852
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y Y, Ma J J, Li J H, Hong J, Li Z Q 2022 J. Remote Sens. 26 0852
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Jiang S X, Jia H Z, Lei Y, Shen X R, Cao J J, Wang N 2017 Opt. Express 25 7445
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Vishnyakov G N, Levin G G, Lomakin A G 2011 J. Opt. Technol. 78 124
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 李荣华, 朴俊峰, 唐智超, 褚清清 2020 传感器与微系统 39 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li R H, Piao J F, Tang Z C, Chu Q Q 2020 Transducer Microsys. Technol. 39 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 简小华, 张淳民, 赵葆常, 张霖, 朱兰艳 2009 58 2286
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jian X H, Zhang C M, Zhao B C, Zhang L, Zhu L Y 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 2286
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 陈强华, 周胜, 丁锦红, 韩文远, 孔祥悦, 罗会甫 2022 光学学报 42 0712004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen Q H, Zhou S, Ding J H, Han W Y, Kong X Y, Luo H F 2022 Acta Opt. Sin. 42 0712004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 2020-11-06] [刘振, 葛惊寰, 高桂爱, 解学军, 刘莉, 杨孟杰 2020 中国专利 CN 111896489 A [2020-11-06
Liu Z, Ge J H, Gao G A, Xie X J, Liu L, Yang M J 2020 Chin. Patent CN 111896489 A (in Chinese)
[17] 张伟, 朱秋东, 张旭升 2018 光学学报 38 0426001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang W, Zhu Q D, Zhang X S 2018 Acta Opt. Sin. 38 0426001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Liu X, Yang J L, Geng Z H, Jia H Z 2020 Chirality 32 1072
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Ma X 2019 Sens. Actuators, B 283 857
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 2021-09-28] [李艳秋, 宁天磊, 周国栋 2021 中国专利 CN 113447126 A [2021-09-28
Li Y Q, Ning T L, Zhou G D 2021 Chin. Patent CN 113447126 A (in Chinese)
[21] 曹奇志, 张晶, 爱德华·德霍格, 卢远, 胡宝清, 李武刚, 李建映, 樊东鑫, 邓婷, 闫妍 2016 65 050702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cao Q Z, Zhang J, Edward D H, Lu Y, Hu B Q, Li W G, Li J Y, Fan D X, Deng T, Yan Y 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 050702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Lei B, Liu S G 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 2969
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Gao C, Lei B 2021 Chin. Opt. Lett. 19 21201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wang F J, Lei B, Gao C, Wen X K, Lei Y 2022 Appl. Opt. 61 1965
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhan Q W 2013 Vectorial Optical Fields: Fundamentals and Application (Singapore: World Scientific Publishing Co Pte. Ltd.) pp28–74
[26] 2014-07-07] [齐晓岩, 单旭晨, 马宇, 曹远 2014 中国专利 CN 203705145 U [2014-07-07
Qi X Y, Shan X C, Ma Y, Cao Y, Liu S G 2014 Chin. Patent CN 203705145 U (in Chinese)
[27] Zhang W J, Zhang Z W 2019 Sens. Actuators, B 286 119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 拉斐尔·C. 冈萨雷斯, 理查德·E. 伍兹 著 (阮秋琦, 阮宇智 译) 2020 数字图像处理 (第4版) (北京: 电子工业出版社) 第206—263页
Gonzalez R C, Woods R E (translated by Ruan Q Q, Ruan Y Z) 2020 Digital Image Processing (4th Ed.) (Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry) pp260–263 (in Chinese)
-
表 1 四种解算方法对同一位置数据处理结果的对比
Table 1. Comparison of the calculation results by using four algorithms with the data in the same location.
解算方法 平均值/(°) 最大误差/(°) 平均误差/(°) 误差标准差/(°) 耗费时间/s Radon变换 128.9380 0.0085 0.0026 0.0036 69.6582 光强调制曲线 129.1450 0.0060 0.0048 0.0015 0.2997 径向积分 129.0090 0.0080 0.0032 0.0040 0.4783 图像相关检测 129.0310 0.0050 0.0050 0.0050 0.8909 表 2 四种解算方法对15个旋转角数据处理结果的对比
Table 2. Comparison of the calculation results by using four algorithms in 15 rotation angles.
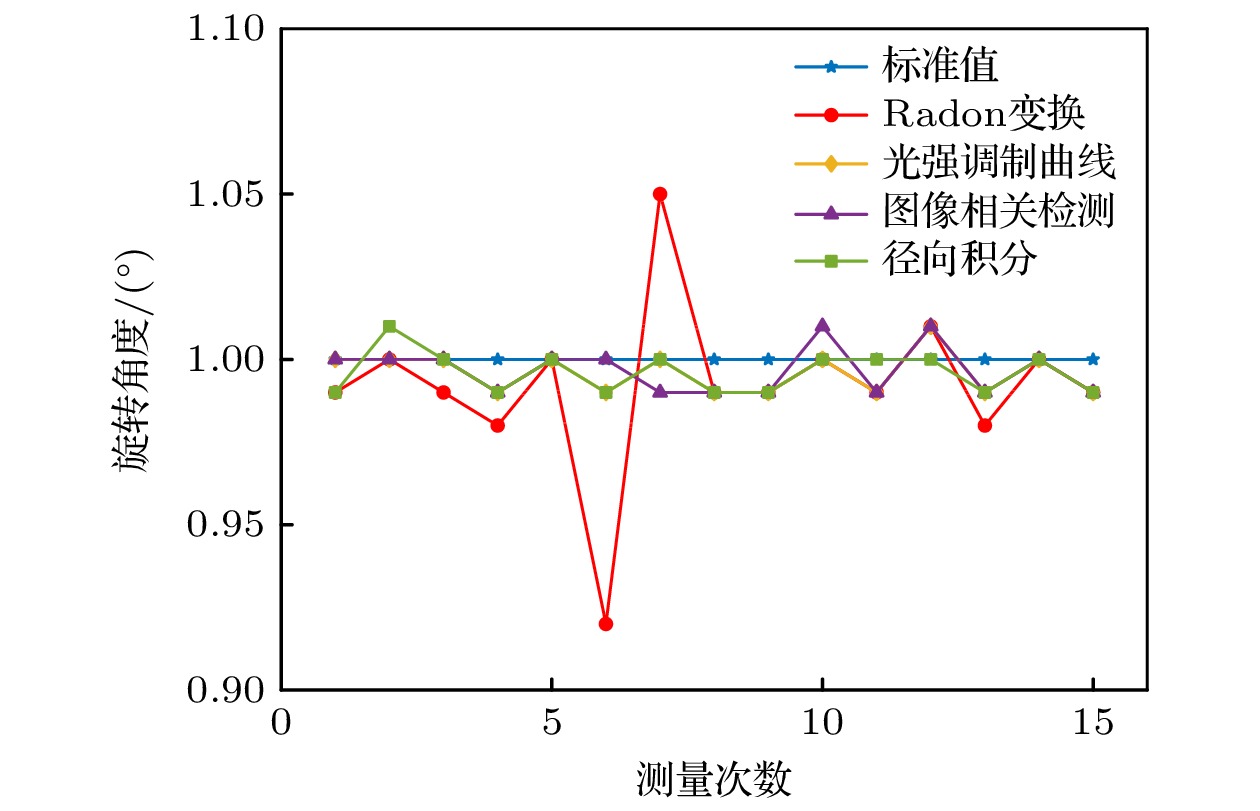
解算方法 平均转角/(°) 最大误差/(°) 平均误差/(°) 标准差/(°) 平均耗时/s Radon变换 0.9920 0.0800 0.0160 0.0228 67.1860 光强调制曲线 0.9960 0.0100 0.0040 0.0063 0.3019 径向积分 0.9960 0.0100 0.0040 0.0063 0.4335 图像相关检测 0.9967 0.0100 0.0045 0.0067 0.8810 -
[1] Zhang W J, Zhang X Z, Cao Y, Liu H B, Liu Z J 2016 Appl. Opt. 55 3518
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Tang J, Zhang N, Li D L, Wang F, Zhang B Z, Wang C G, Shen C, Ren J B, Xue C Y, Liu J 2016 Opt. Express 24 15834
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 王成, 范之国, 金海红, 汪先球, 华豆 2021 70 104201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang C, Fan Z G, Jing H H, Wang X Q, Hua D 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 104201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 康健, 马伟, 李沅 2022 科学技术与工程 22 02696
Kang J, Ma W, Li Y 2022 Sci. Technol. Eng. 22 02696
[5] Qiu X D, Xie L G, Liu X, Luo L, Zhang Z Y, Du J L 2011 Opt. Lett. 41 4032
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Eom I, Ahn S H, Rhee H J, Cho M H 2011 Opt. Express 19 10017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 章慧, 齐爱华, 李丹, 李荣兴 2022 大学化学 37 2105009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang H, Qi A H, Li D, Li R X 2022 Univ. Chem. 37 2105009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 李子骏, 贾宏志 2016 光学仪器 38 288
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Z J, Jia H Z 2016 Opt. Instrum. 38 288
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 汪杰君, 刘少晖, 李树, 叶松, 王新强, 王方原 2021 光子学报 50 0228001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J J, Liu S H, Li S, Ye S, Wang X Q, Wang F Y 2021 Acta Photonica Sin. 50 0228001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 王宇瑶, 麻金继, 李婧晗, 洪津, 李正强 2022 遥感学报 26 0852
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y Y, Ma J J, Li J H, Hong J, Li Z Q 2022 J. Remote Sens. 26 0852
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Jiang S X, Jia H Z, Lei Y, Shen X R, Cao J J, Wang N 2017 Opt. Express 25 7445
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Vishnyakov G N, Levin G G, Lomakin A G 2011 J. Opt. Technol. 78 124
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 李荣华, 朴俊峰, 唐智超, 褚清清 2020 传感器与微系统 39 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li R H, Piao J F, Tang Z C, Chu Q Q 2020 Transducer Microsys. Technol. 39 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 简小华, 张淳民, 赵葆常, 张霖, 朱兰艳 2009 58 2286
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jian X H, Zhang C M, Zhao B C, Zhang L, Zhu L Y 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 2286
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 陈强华, 周胜, 丁锦红, 韩文远, 孔祥悦, 罗会甫 2022 光学学报 42 0712004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen Q H, Zhou S, Ding J H, Han W Y, Kong X Y, Luo H F 2022 Acta Opt. Sin. 42 0712004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 2020-11-06] [刘振, 葛惊寰, 高桂爱, 解学军, 刘莉, 杨孟杰 2020 中国专利 CN 111896489 A [2020-11-06
Liu Z, Ge J H, Gao G A, Xie X J, Liu L, Yang M J 2020 Chin. Patent CN 111896489 A (in Chinese)
[17] 张伟, 朱秋东, 张旭升 2018 光学学报 38 0426001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang W, Zhu Q D, Zhang X S 2018 Acta Opt. Sin. 38 0426001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Liu X, Yang J L, Geng Z H, Jia H Z 2020 Chirality 32 1072
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Ma X 2019 Sens. Actuators, B 283 857
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 2021-09-28] [李艳秋, 宁天磊, 周国栋 2021 中国专利 CN 113447126 A [2021-09-28
Li Y Q, Ning T L, Zhou G D 2021 Chin. Patent CN 113447126 A (in Chinese)
[21] 曹奇志, 张晶, 爱德华·德霍格, 卢远, 胡宝清, 李武刚, 李建映, 樊东鑫, 邓婷, 闫妍 2016 65 050702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cao Q Z, Zhang J, Edward D H, Lu Y, Hu B Q, Li W G, Li J Y, Fan D X, Deng T, Yan Y 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 050702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Lei B, Liu S G 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 2969
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Gao C, Lei B 2021 Chin. Opt. Lett. 19 21201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wang F J, Lei B, Gao C, Wen X K, Lei Y 2022 Appl. Opt. 61 1965
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhan Q W 2013 Vectorial Optical Fields: Fundamentals and Application (Singapore: World Scientific Publishing Co Pte. Ltd.) pp28–74
[26] 2014-07-07] [齐晓岩, 单旭晨, 马宇, 曹远 2014 中国专利 CN 203705145 U [2014-07-07
Qi X Y, Shan X C, Ma Y, Cao Y, Liu S G 2014 Chin. Patent CN 203705145 U (in Chinese)
[27] Zhang W J, Zhang Z W 2019 Sens. Actuators, B 286 119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 拉斐尔·C. 冈萨雷斯, 理查德·E. 伍兹 著 (阮秋琦, 阮宇智 译) 2020 数字图像处理 (第4版) (北京: 电子工业出版社) 第206—263页
Gonzalez R C, Woods R E (translated by Ruan Q Q, Ruan Y Z) 2020 Digital Image Processing (4th Ed.) (Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry) pp260–263 (in Chinese)
计量
- 文章访问数: 5500
- PDF下载量: 124
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: