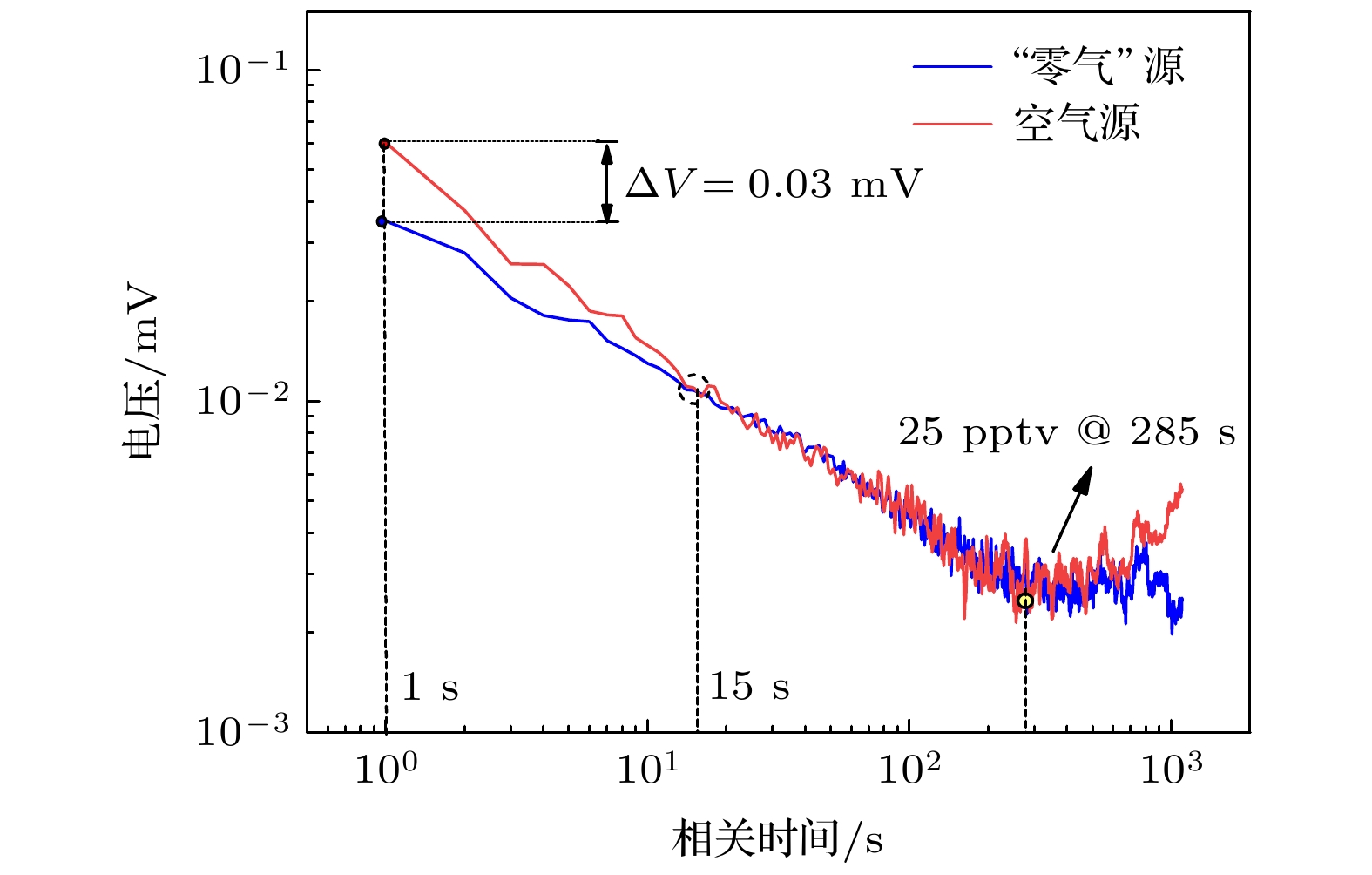
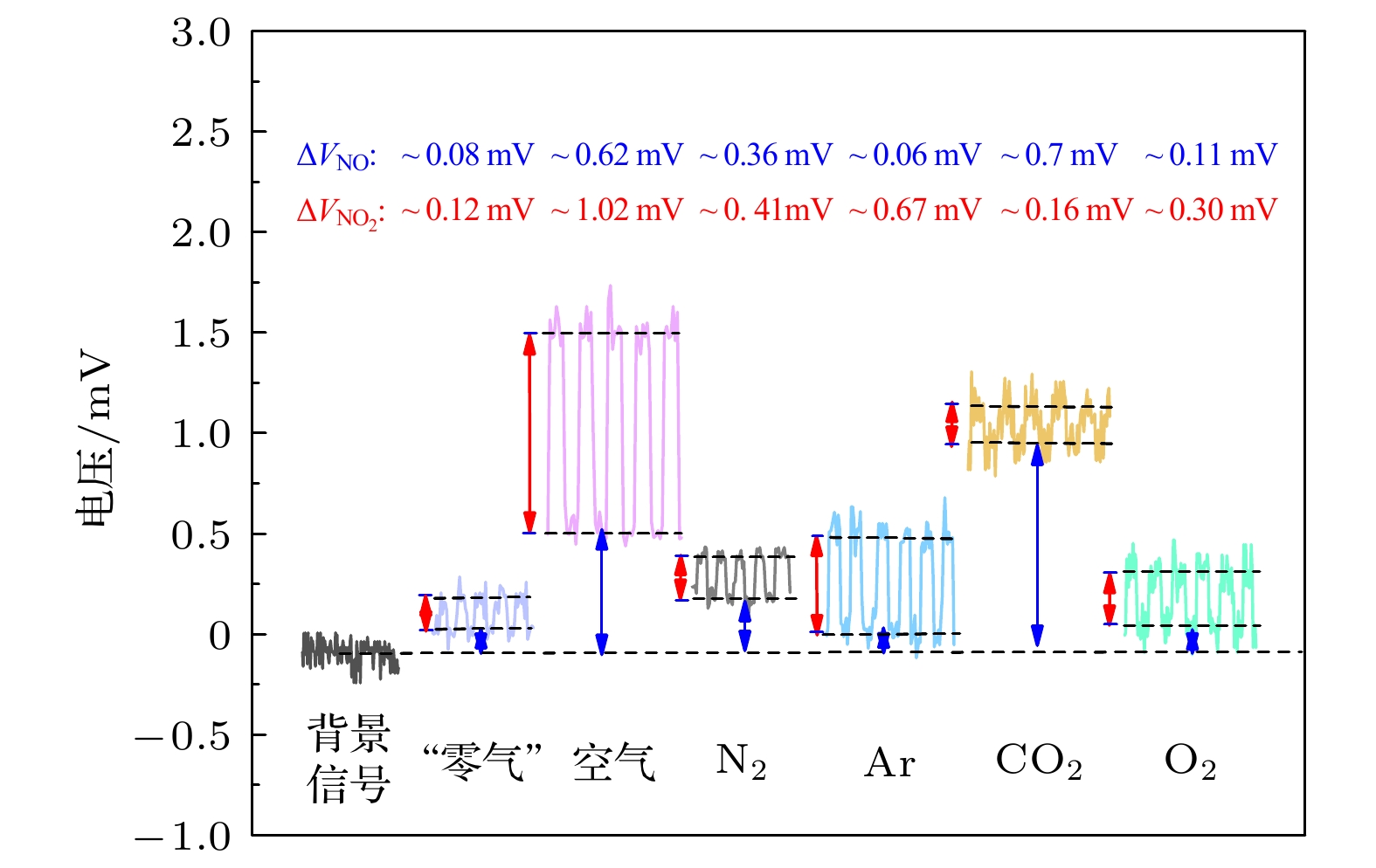
-
高纯气体在半导体器件制作及燃料电池等行业应用广泛, 但其杂质气体直接对加工精度及效果产生显著影响, 因此对关键痕量杂质气体进行浓度诊断尤为必要. 本文基于化学发光光谱理论和氮氧化物催化转化机理, 设计了一套痕量NO/NOx同步高精度测量系统, 通过标定实验可知, 该测量系统具有高线性度(R2 = 0.99967)、高灵敏度、低检测下限(约25 ppt, 1 ppt = 10–12)、易操作性等优势; 同时, 综合考虑不同背景气体对荧光、磷光的淬灭效应, 建立不同高纯气体中NOx测量方法, 并利用该探测系统对实验室常用4种高纯气体(Ar, O2, CO2, N2)中ppb量级的氮氧化物进行测量, 结果表示CO2中的NO含量最高, 约为9 ppb (1 ppb = 10–9), 其他高纯气体中的NO含量较低, 仅有0—4 ppb, 4种高纯气体的NO2含量均较低(<6 ppb); 最后结合气体制备及提纯方式对高纯气体中杂质NOx含量进行评价及分析, 旨在为燃料电池、半导体器件制备等尖端科技领域提供可靠的杂质气体成分诊断方法和数据基础.High-purity gases are widely used in semiconductor device manufacturing and fuel cell industries. However, the impurities have a significant influence on the processing accuracy directly. Thus, it is particularly necessary to carry out the concentration diagnosis of key trace impurity gases. In this work, an integrated system for the simultaneous detection of trace NO/NOx is designed based on the chemiluminescence spectrum theory and the catalytic conversion mechanism of nitrogen oxides. The test experiments reveal that the measurement system has the advantages of high linearity (R2 = 0.99967), high sensitivity, low detection limit (~25 ppt), and easy operation. Subsequently, the measurement method for NOx with different high-purity gases are established considering the quenching effects of different background gases on fluorescence and phosphorescent. The detection system is then used to measure the ppb-level NOx impurities in four commonly used high-purity gases (Ar, O2, CO2, N2) in the laboratory. The results show that the NO impurity in CO2 gas is the highest, approximately 9 ppb,but relatively low, 0–4 ppb, in the other high-purity gases. The NO2 impurities in all four high-purity gases are very low (< 6 ppb). Finally, the NOx impurity content values in high-purity gases are evaluated and analyzed based on the gas preparation and purification approach. The aim of the work is to provide a reliable diagnostic approach and data basis of the impurity composition for the fuel cell, semiconductor and other cutting-edge technological fields.
-
Keywords:
- chemiluminescence /
- high-purity gas /
- trace gas /
- quenching
[1] Funke H H, Grissom B L, McGrew C E, Raynor M W 2003 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 74 3909
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 单静, 王莹, 王杰, 靳鹏杰, 吉雪霞 2020 低温与特气 38 32
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shan J, Wang Y, Wang J, Jin P J, Ji X X 2020 Low Temper. Speci. Gas. 38 32
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Z 2021 Nat. Gas Ind. 41 115 (in Chinese) [潘义, 邓凡锋, 王维康, 杨嘉伟, 张婷, 林俊杰, 龙舟, 姚伟民, 方正 2021 天然气工业 41 115]
Pan Y, Deng F F, Wang W K, Yang J W, Zhang T, Lin J J, Long Z, Yao W M, Fang
[4] Sethuraman V A, Weidner J W 2010 Electrochim. Acta 55 5683
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Myrberg T, Jacob A P, Nur O, Friesel M, Willander M, Patel C J, Campidelli Y, Hernandez C, Kermarrec O, Bensahel D 2004 J. Mater Sci. Mater. Electron. 15 411
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 牛丽红, 李胜, 于世林 2017 广东化工 44 117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Niu L H, Li S, Yu S L 2017 Guangzhou Chem. Indust. 44 117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Engel G S, Moyer E J 2007 Opt. Lett. 32 704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Chao X, Jeffries J B, Hanson R K 2011 Appl. Phys. B 106 987
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 孙逊运 1988 色谱 6 334
Sun X Y 1988 Chin. J. Chromatogr. 6 334
[10] Li H, Liu W Q, Kan R F 2019 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 90 046103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Dickerson R R, Delany A C, Wartburg A F 1984 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 55 1995
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Delany A C, Dickerson R R, Melchior F L, Wartburg A F 1982 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 53 1899
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Johnston H S, Crosby H J 1954 J. Phys. Chem. C 22 689
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Douglas A E, Huber K P 1965 Can. J. Phys. 43 74
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Clough P N, Thrush B A 1967 J. Chem. Soc. , Faraday trans. 63 915
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Steffenson D M, Stedman D H 1974 Anal. Chem. 46 1704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Ridley B A, Grahek F E 1990 J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech. 7 307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Kliner D A V, Daube B C, Burley J D, Wofsy S C 1997 J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 102 10759
[19] Day D A, Dillon M B, Wooldridge P J, Thornton J A, Rosen R S, Wood E C, Cohen R C 2003 J. Geophys. Res. 108 4501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] McClenny W A, Williams E J, Cohen R C, Stutz J 2002 J. Air. Waste Manag. Assoc. 52 542
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Putluru S S R, Schill L, Jensen A D, Fehrmann R S N 2015 Appl Catal. B 165 628
[22] Bollinger M J, Sievers R E, Fahey D W, Fehsenfeld F C 1983 Anal. Chem. 55 1980
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Yagi S, Tanaka M 1979 J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 12 1509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Thrush B A 1973 J. Phys. Chem. C 58 5191
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Smith W H, Liszt H S 1971 J. Quant. Spectrosc. Ra. 11 45
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Fereja T H, Hymete A, Gunasekaran T 2013 ISRN Spectroscopy 2013 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Zabielski M F, Seery D J, Dodge L G 1984 Environ. Sci. Technol. 18 88
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Fontijn A, Meyer C B, Schiff H I 1964 J. Chem. Phys. 40 64
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Moonen P C, Cape J N, Storeton-West R L, McColm R 1998 J. Atmos. Chem. 29 299
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Mehrabzadeh A A, O'Brien R J, Hard T M 1983 Anal. Chem. 55 1660
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Tidona R J, Nizami A A, Cernansky N P 1988 JAPCA 38 806
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Nakayama T, Ide T, Taketani F, Kawai M, Takahashi K, Matsumi Y 2008 Atmospheric Environ. 42 1995
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 2 化学发光测量系统装置示意图. V为可调节脉冲型高压电源; MFC为流量控制计; CL为化学发光; PMT为光电倍增管; T0为NO测量模式通道; T1为NO2测量模式通道
Fig. 2. Schematic diagram of chemiluminescence measurement system. V is adjustable pulse high voltage power supply; MFC is flow control meter; CL is chemiluminescence; PMT is photomultiplier tube, T0 is NO measurement mode channel; T1 is NO2 measurement mode channel.
图 4 不同NO2标气浓度测量结果 (a)不同NO2浓度下对应5个周期的原始测量信号; (b)不同NO2标气浓度的电压信号及其线性拟合曲线
Fig. 4. Different NO2 standard gas concentration measurement: (a) Original measurement signals corresponding to 5 cycles at different NO2 concentrations; (b) voltage signals of different NO2 gas concentrations and their linear fitting curves.
表 1 不同组分高纯气体的NOx转换系数及其测量结果修正值
Table 1. NOx conversion coefficient of different high-purity gas components and modification of measurement results.
高纯气体
组分线性
系数(m)$I_{\rm N_2}/I_{\rm M}$ 浓度修正值
(ppb, 高纯气体)NO NO2 O2 0.115 1.115 ~1.4 ~2.9 CO2 1.047 2.047 ~ 8.9 ~2.3 Ar –0.48 0.73 ~0.5 ~5.2 N2 0 1 ~3.9 ~4.4 注: 相对淬灭系数Rm可以用公式Rm = 1+ m*d{M}描述, 式中m为线性拟合系数, {M}为M的物质的量的比. 具体公式推导见文献[31]. -
[1] Funke H H, Grissom B L, McGrew C E, Raynor M W 2003 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 74 3909
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 单静, 王莹, 王杰, 靳鹏杰, 吉雪霞 2020 低温与特气 38 32
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shan J, Wang Y, Wang J, Jin P J, Ji X X 2020 Low Temper. Speci. Gas. 38 32
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Z 2021 Nat. Gas Ind. 41 115 (in Chinese) [潘义, 邓凡锋, 王维康, 杨嘉伟, 张婷, 林俊杰, 龙舟, 姚伟民, 方正 2021 天然气工业 41 115]
Pan Y, Deng F F, Wang W K, Yang J W, Zhang T, Lin J J, Long Z, Yao W M, Fang
[4] Sethuraman V A, Weidner J W 2010 Electrochim. Acta 55 5683
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Myrberg T, Jacob A P, Nur O, Friesel M, Willander M, Patel C J, Campidelli Y, Hernandez C, Kermarrec O, Bensahel D 2004 J. Mater Sci. Mater. Electron. 15 411
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 牛丽红, 李胜, 于世林 2017 广东化工 44 117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Niu L H, Li S, Yu S L 2017 Guangzhou Chem. Indust. 44 117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Engel G S, Moyer E J 2007 Opt. Lett. 32 704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Chao X, Jeffries J B, Hanson R K 2011 Appl. Phys. B 106 987
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 孙逊运 1988 色谱 6 334
Sun X Y 1988 Chin. J. Chromatogr. 6 334
[10] Li H, Liu W Q, Kan R F 2019 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 90 046103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Dickerson R R, Delany A C, Wartburg A F 1984 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 55 1995
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Delany A C, Dickerson R R, Melchior F L, Wartburg A F 1982 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 53 1899
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Johnston H S, Crosby H J 1954 J. Phys. Chem. C 22 689
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Douglas A E, Huber K P 1965 Can. J. Phys. 43 74
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Clough P N, Thrush B A 1967 J. Chem. Soc. , Faraday trans. 63 915
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Steffenson D M, Stedman D H 1974 Anal. Chem. 46 1704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Ridley B A, Grahek F E 1990 J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech. 7 307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Kliner D A V, Daube B C, Burley J D, Wofsy S C 1997 J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 102 10759
[19] Day D A, Dillon M B, Wooldridge P J, Thornton J A, Rosen R S, Wood E C, Cohen R C 2003 J. Geophys. Res. 108 4501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] McClenny W A, Williams E J, Cohen R C, Stutz J 2002 J. Air. Waste Manag. Assoc. 52 542
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Putluru S S R, Schill L, Jensen A D, Fehrmann R S N 2015 Appl Catal. B 165 628
[22] Bollinger M J, Sievers R E, Fahey D W, Fehsenfeld F C 1983 Anal. Chem. 55 1980
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Yagi S, Tanaka M 1979 J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 12 1509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Thrush B A 1973 J. Phys. Chem. C 58 5191
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Smith W H, Liszt H S 1971 J. Quant. Spectrosc. Ra. 11 45
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Fereja T H, Hymete A, Gunasekaran T 2013 ISRN Spectroscopy 2013 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Zabielski M F, Seery D J, Dodge L G 1984 Environ. Sci. Technol. 18 88
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Fontijn A, Meyer C B, Schiff H I 1964 J. Chem. Phys. 40 64
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Moonen P C, Cape J N, Storeton-West R L, McColm R 1998 J. Atmos. Chem. 29 299
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Mehrabzadeh A A, O'Brien R J, Hard T M 1983 Anal. Chem. 55 1660
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Tidona R J, Nizami A A, Cernansky N P 1988 JAPCA 38 806
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Nakayama T, Ide T, Taketani F, Kawai M, Takahashi K, Matsumi Y 2008 Atmospheric Environ. 42 1995
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 6957
- PDF下载量: 94
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: