-
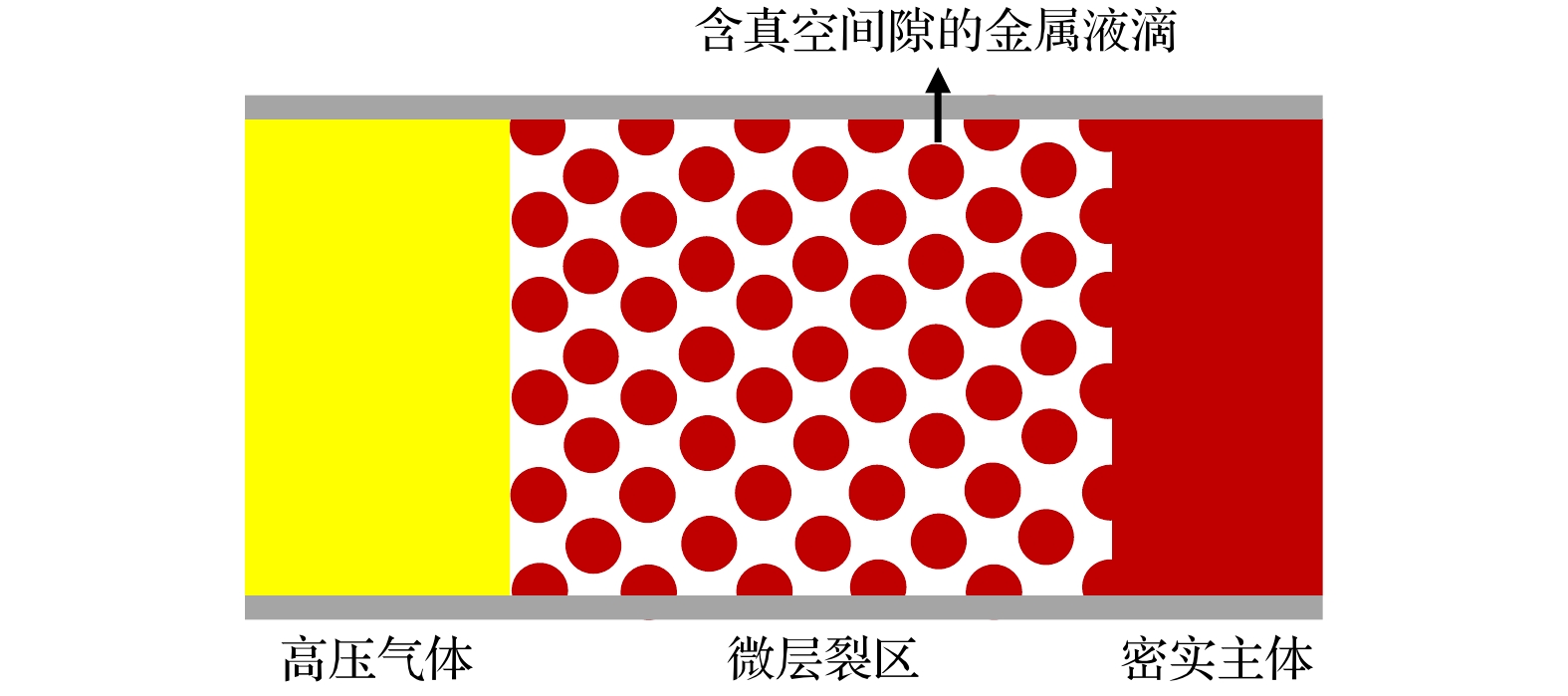
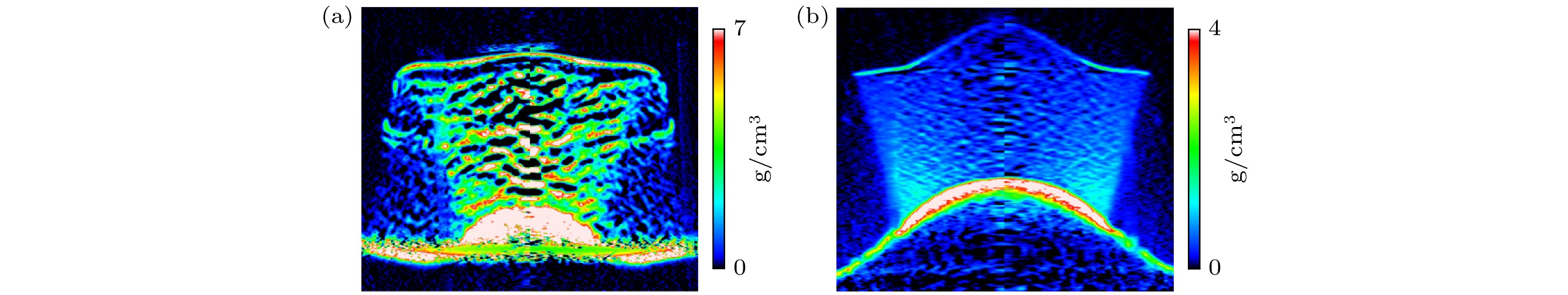
After high pressure shock, the shock wave in the metal is unloaded at the metal-gas interface, and micro spallation occurs when the metal melts. When the micro spallation develops to a certain extent, the high pressure gas penetrates the zero pressure vacuum gap between the metal melt droplets. In this paper, the phenomenon of gas penetrating metal micro spallation zone is analyzed theoretically. Based on the regular hexahedron periodic arrangement of metal droplets, the calculation formulas of the maximum penetration depth, the sealing time of the penetration channel and the maximum mass of the gas penetrating the metal micro spallation zone are given through theoretical analysis under the quasi-static and semi-dynamic conditions. The quasi-static process is considered to be the gas penetration process that can be approximated as the escape process of gas into the vacuum, and the gap in the metal micro spallation zone will be filled with gas. The semi-dynamic analysis is based on two basic assumptions: one is the equal droplet size and spacing in the micro spallation zone and the other is the critical sealing condition of gas penetration. In the process of semi-dynamic analysis it is demonstrated that the initial critical sealing distance is independent of the shape factor of the droplet single control volume. The semi-dynamic analysis can give various critical sealing information when the gas stops penetrating the metal micro spallation zone. The results of quasi-static analysis can be used as the upper limit of gas penetration, and the semi-dynamic analysis results can be used as the lower limit of gas penetration. From the sensitivity analysis, it can be seen that the change law of physical phenomena given by theoretical analysis accords with the basic physical understanding of the problem. Through this study, the upper and lower limit of the mixed state of gas penetrating the metal micro spallation zone can be estimated, which can provide more accurate initial metal-gas mixed state for subsequent research of the evolution of mixed state. The theoretical analyses given in this paper are based on a lot of uncertain assumptions, and the in-depth study of this phenomenon is still needed based on the law summary and mutual confirmation of experiment and simulation.
-
Keywords:
- metal micro spallation /
- gas penetration /
- penetration depth /
- penetration quality
[1] Johnson J N 1981 J. Appl. Phys. 52 2812
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Tonks D L, Thissell W R, Schwartz D S 2014 AIP Conf. Proc. 706 507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 裴晓阳, 彭辉, 贺红亮, 李平 2015 64 054601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pei X Y, Peng H, He H L, Li P 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 054601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 张凤国, 周洪强 2013 62 164601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang F G, Zhou H Q 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 164601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Holtkamp D B, Clark D A, Ferm E N, Gallegos R A, Stacy H L 2004 AIP Conf. Proc. 706 477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Andriot P, Chapron P, Lambert V, Olive F 1983 Shock Waves in Condensed Matter North-Holland Physics, Santa Fe, 1983 p277
[7] Holtkamp D B, Clark D A, Crain M D, Furnish M D, Thomas K A 2004 AIP Conf. Proc. 706 473
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] De Resseguier T, Signor L, Dragon A, Boustie M, Roy G, Llorca F 2007 J. Appl. Phys. 101 013506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 陈永涛, 任国武, 汤铁钢 2013 62 116202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen Y T, Ren G W, Tang T G 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 116202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chen Y T, Ren G W, Tang T G 2016 Shock Waves 26 221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 陈永涛, 洪仁楷, 陈浩玉 2017 爆炸与冲击 37 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen Y T, Ren G W, Chen H Y 2017 Explosion and Shock Waves 37 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 邵建立, 王裴, 何安民, 秦承森, 辛建婷, 谷渝秋 2013 62 076201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shao J L, Wang P, He A M, Qin C S, Xin J T, Gu Y Q 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 076201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Shao J L, Wang P, He A M, Zhang R, Qin C S 2013 J. Appl. Phys. 114 173501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Xiang M Z, Hu H B, Chen J 2013 J. Appl. Phys. 113 163507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 王裴, 邵建立, 秦承森 2012 61 234701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang P, Shao J L, Qin C S 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 234701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Lescoute E, De Resseguier T, Chevalier J M, Loison D, Cuq-Lelandais J P, Boustie M, Breil J, Maire P H, Schurtz G 2010 J. Appl. Phys. 108 093510
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yaziv D, Bless S J, Rosenberg Z 1985 J. Appl. Phys. 58 3415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Becker R , Leblanc M M , Cazamias J U 2007 J. Appl. Phys. 102 093512
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Turley W D, Stevens G, Hixson R S, Cerreta E 2016 J. Appl. Phys. 120 085904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Jones D R, Fensin S J, Morrow B M, Hixson R S 2020 J. Appl. Phys. 127 245901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Hawkins M C, Thomas S A, Fensin S J, Hixson R S 2020 J. Appl. Phys. 128 045902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Buttler W T, Hixson R S, King N, Olson R T 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett. 90 113508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Buttler W T, Oro D M, Olson R T, Cherne F J 2014 J. Appl. Phys. 116 103519
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Karkhanis V, Ramaprabhu P, Buttler W T, Hammerberg J E, Cherne F J, Andrews M J 2017 J. Dynamic Behavior Mater. 3 265
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
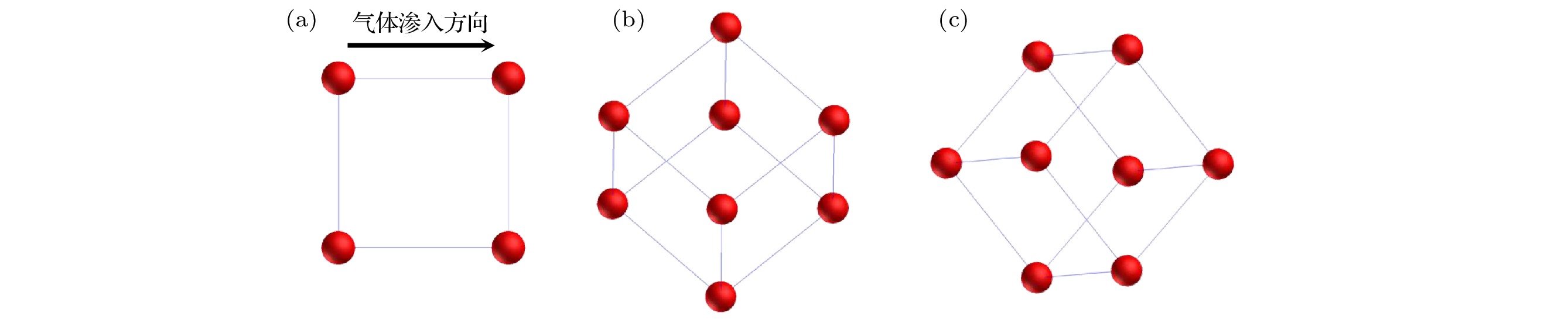
图 6 微层裂区球形液滴单控制体沿气体渗入方向的三种典型形态 (a)
$ \beta =1 $ ; (b)$ \beta =- \sqrt {\rm{2}} $ ; (c)$\beta = {{\sqrt {\rm{3}} }}/{{\rm{3}}}$ Fig. 6. Three forms of single control volume of spherical droplet in micro spallation zone along gas infiltration direction: (a)
$ \beta =1 $ ; (b)$ \beta =- \sqrt {\rm{2}} $ ; (c)$\beta = {{\sqrt {\rm{3}} }}/{{\rm{3}}}$ . -
[1] Johnson J N 1981 J. Appl. Phys. 52 2812
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Tonks D L, Thissell W R, Schwartz D S 2014 AIP Conf. Proc. 706 507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 裴晓阳, 彭辉, 贺红亮, 李平 2015 64 054601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pei X Y, Peng H, He H L, Li P 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 054601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 张凤国, 周洪强 2013 62 164601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang F G, Zhou H Q 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 164601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Holtkamp D B, Clark D A, Ferm E N, Gallegos R A, Stacy H L 2004 AIP Conf. Proc. 706 477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Andriot P, Chapron P, Lambert V, Olive F 1983 Shock Waves in Condensed Matter North-Holland Physics, Santa Fe, 1983 p277
[7] Holtkamp D B, Clark D A, Crain M D, Furnish M D, Thomas K A 2004 AIP Conf. Proc. 706 473
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] De Resseguier T, Signor L, Dragon A, Boustie M, Roy G, Llorca F 2007 J. Appl. Phys. 101 013506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 陈永涛, 任国武, 汤铁钢 2013 62 116202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen Y T, Ren G W, Tang T G 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 116202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chen Y T, Ren G W, Tang T G 2016 Shock Waves 26 221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 陈永涛, 洪仁楷, 陈浩玉 2017 爆炸与冲击 37 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen Y T, Ren G W, Chen H Y 2017 Explosion and Shock Waves 37 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 邵建立, 王裴, 何安民, 秦承森, 辛建婷, 谷渝秋 2013 62 076201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shao J L, Wang P, He A M, Qin C S, Xin J T, Gu Y Q 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 076201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Shao J L, Wang P, He A M, Zhang R, Qin C S 2013 J. Appl. Phys. 114 173501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Xiang M Z, Hu H B, Chen J 2013 J. Appl. Phys. 113 163507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 王裴, 邵建立, 秦承森 2012 61 234701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang P, Shao J L, Qin C S 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 234701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Lescoute E, De Resseguier T, Chevalier J M, Loison D, Cuq-Lelandais J P, Boustie M, Breil J, Maire P H, Schurtz G 2010 J. Appl. Phys. 108 093510
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yaziv D, Bless S J, Rosenberg Z 1985 J. Appl. Phys. 58 3415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Becker R , Leblanc M M , Cazamias J U 2007 J. Appl. Phys. 102 093512
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Turley W D, Stevens G, Hixson R S, Cerreta E 2016 J. Appl. Phys. 120 085904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Jones D R, Fensin S J, Morrow B M, Hixson R S 2020 J. Appl. Phys. 127 245901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Hawkins M C, Thomas S A, Fensin S J, Hixson R S 2020 J. Appl. Phys. 128 045902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Buttler W T, Hixson R S, King N, Olson R T 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett. 90 113508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Buttler W T, Oro D M, Olson R T, Cherne F J 2014 J. Appl. Phys. 116 103519
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Karkhanis V, Ramaprabhu P, Buttler W T, Hammerberg J E, Cherne F J, Andrews M J 2017 J. Dynamic Behavior Mater. 3 265
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 5664
- PDF下载量: 67
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: