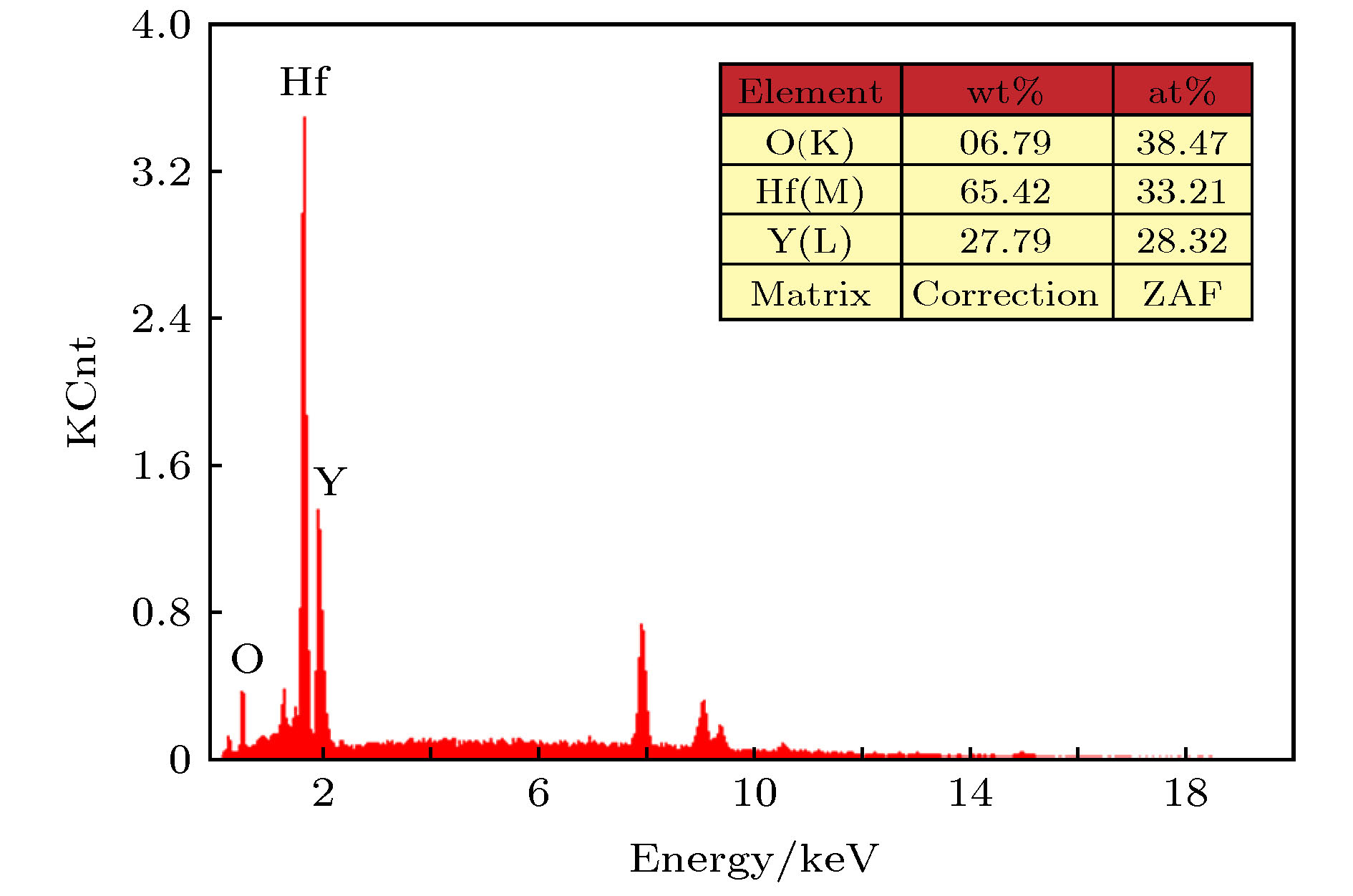
-
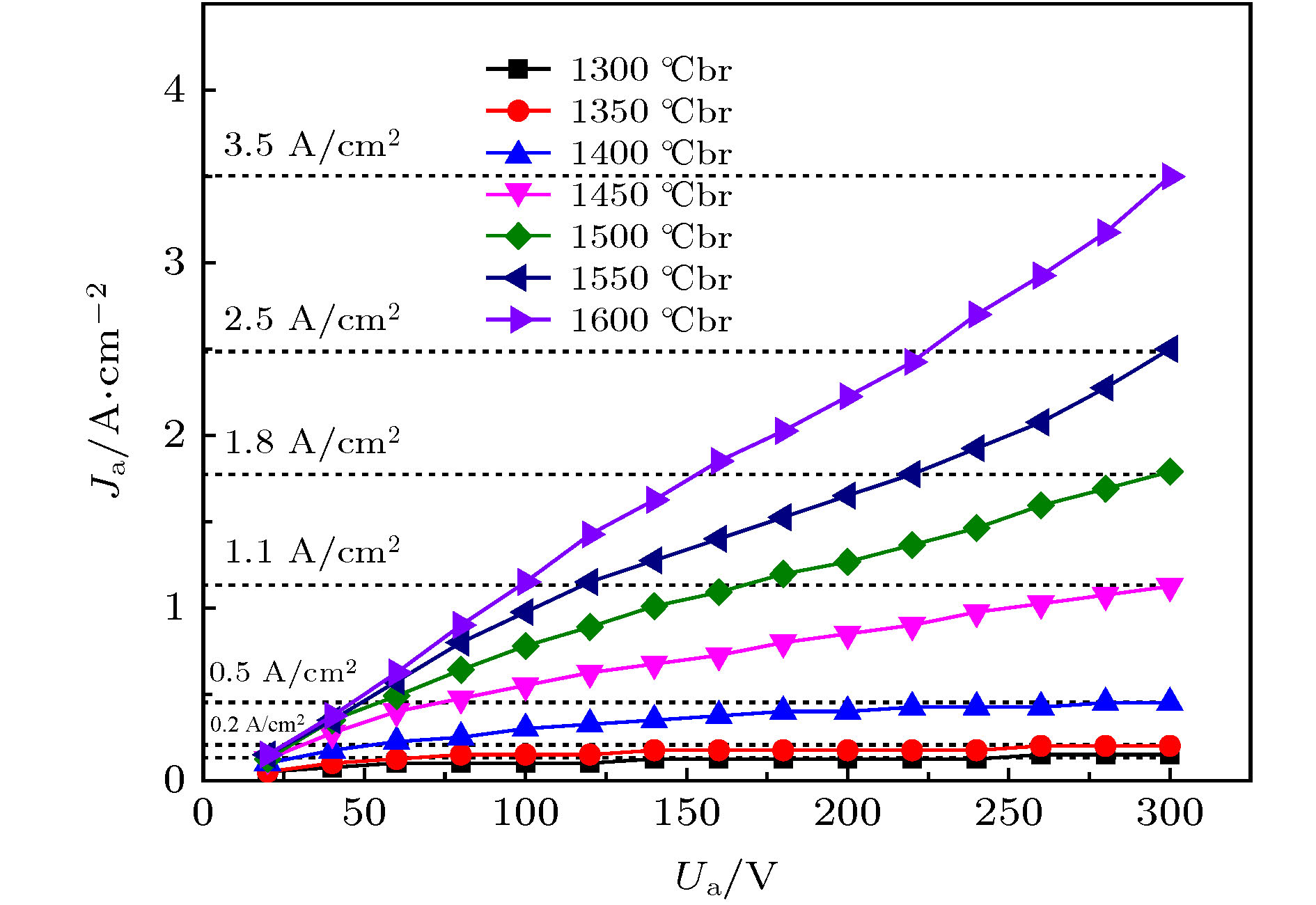
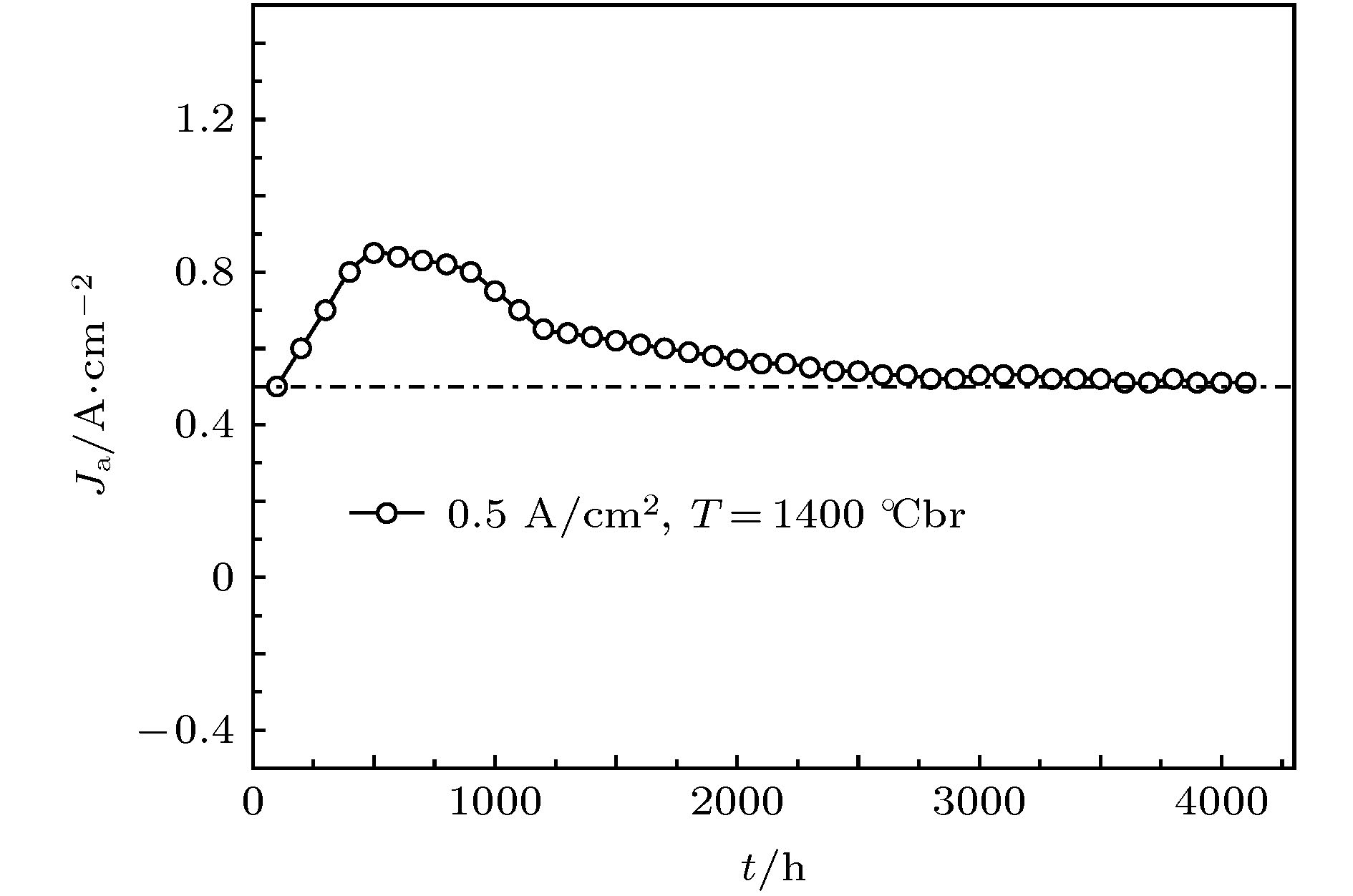
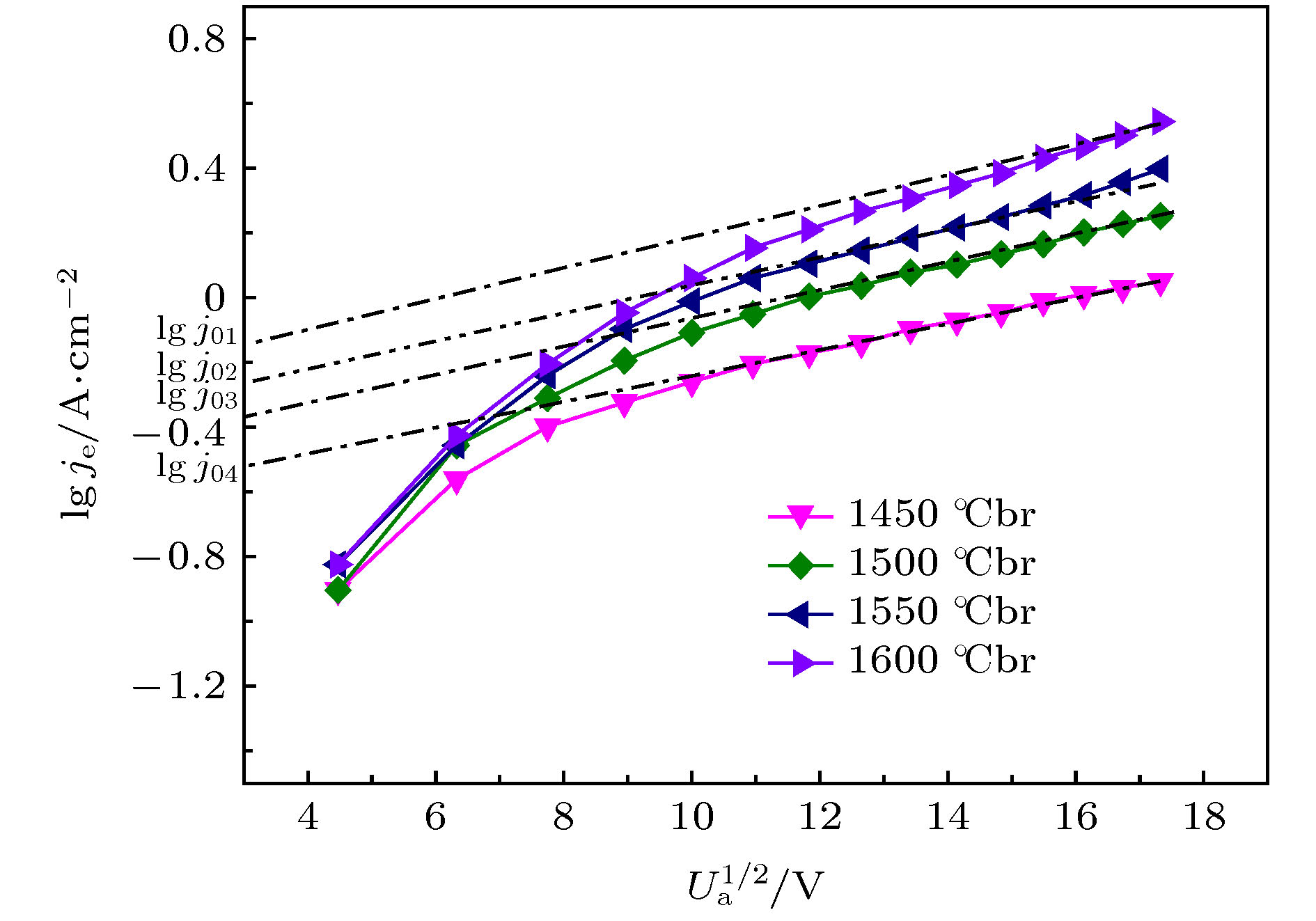
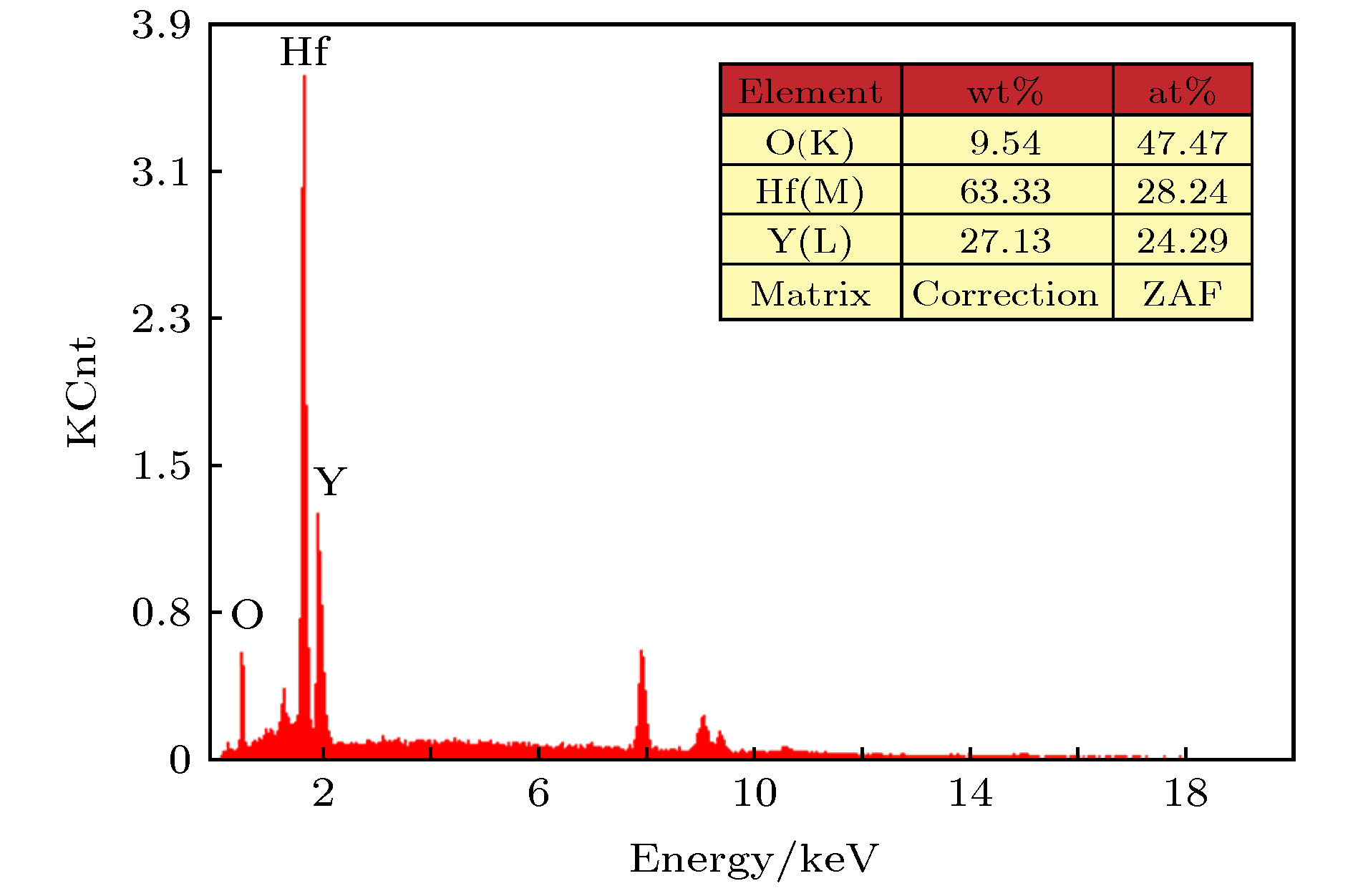
为了提高大功率磁控管的输出功率, 延长其使用寿命, 首次采用稀土氧化物Y2O3和过渡金属氧化物HfO2制备大功率磁控管用Y2Hf2O7 (铪酸钇)陶瓷阴极, 并对该阴极的热发射特性和寿命特性等进行了测试, 热发射测试结果显示该阴极在1300, 1350, 1400, 1450, 1500, 1550, 1600 ℃br亮度温度, 300 V阳极电压下即可分别提供0.15, 0.2, 0.5, 1.1, 1.8, 2.5, 3.5 A/cm2的发射电流密度. 利用理查森直线法求得该阴极的绝对零度逸出功为1.26 eV, 理查森-道舒曼公式法求得该阴极在1450, 1500, 1550, 1600 ℃br亮度温度下的有效逸出功分别为3.10, 3.15, 3.21, 3.26 eV. 寿命实验结果显示, 该阴极在工作温度为1400 ℃br, 直流负载为0.5 A/cm2的条件下, 寿命超过4000 h. 最后, 利用X射线衍射仪、扫描电子显微镜、X射线能谱分析仪、俄歇电子能谱仪以及结合氩离子刻蚀技术的深度俄歇能谱仪等分别对该阴极活性物质的分子结构, 阴极表面微观形貌、元素成分及含量等进行了研究. 结果表明, 高温烧结合成了单一的铪酸钇物相, 高温烧结过程中当一种Y3+价稀土氧化物Y2O3掺入Hf4+价的过渡金属氧化物HfO2时, 会发生离子置换固溶, 为了保持铪酸钇晶格的电中性, 晶格中就会产生一个氧空位. 当阴极在激活、老练、热发射测试时, 会加速氧空位的生成, 产生的氧空位越多, 阴极表面导电性就会越好, 这间接降低了逸出功, 从而提高了阴极的热发射能力.Nowadays, the output power and lifetime of a single magnetron are far from the requirements of industrial applications. So the new materials and methods are urgently needed to enhance the output power and prolong the lifetime of the magnetron. As the heart of a magnetron, cathode, whose quality directly affects the output power and lifetime of the magnetron, plays an important role. In order to enhance the output power and prolong the lifetime of the high power magnetron, a method of doping rare earth oxide Y2O3 into transition metal oxide HfO2 is used to prepare Y2Hf2O7 ceramic cathode. The thermionic emission and lifetime characteristics of the Y2Hf2O7 cathode are measured. The results show that the cathode can provide 0.15, 0.2, 0.5, 1.1, 1.8, 2.5, 3.5 A/cm2 current density for the space charge limitation at 1300, 1350, 1400, 1450, 1500, 1550, 1600 ℃br under 300 V anode voltage, respectively. Absolute zero work function of the cathode is only 1.26 eV obtained by the Richardson line method. The effective work function of the cathode is 3.10, 3.15, 3.21, 3.26 eV obtained by the Richardson-Dushman formula at 1450, 1500, 1550, 1600 ℃br respectively. The lifetime of the cathode is more than 4000 h under an initial load of 0.5 A/cm2 at 1400 ℃br, the lifetime which is much longer than the 2000 h average life span for the 2450 MHz continuous wave magnetron cathode used in production. Finally, the molecular structure, surface microstructure, element composition and content of the Y2Hf2O7 ceramic cathode are analyzed by the X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscope, energy dispersive spectrometer, Auger electron spectroscopy with argon ion etching respectively. The analysis results show that the single Y2Hf2O7 phase forms under the high sintering temperature. When the Y3+ valence Y2O3 is doped into the Hf4+ valence HfO2, the substitutional solid solution will form. An oxygen vacancy is generated in the lattice, thus maintaining the electrical neutrality of the Y2Hf2O7 lattice. During the cathode activating, aging, and thermally testing, the oxygen vacancy is generated fast. The more the obtained oxygen vacancies, the higher the conductivity of the cathode surface will be. Besides, due to the improvement of the electro-conductivity thus enhancing the thermionic emission capability of the cathode, the work function of the cathode can be reduced.
-
Keywords:
- magnetron /
- cathode /
- thermionic emission /
- lifetime /
- emission mechanism
[1] Jacqueline M R B, Paré J R J 2007 J. Microwave Power EE. 42 24
[2] Lester E, Kingman S, Dodds C 2005 Fuel 84 423
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 岳松, 张兆传, 高东平 2013 62 178401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yue S, Zhang Z C, Gao D P 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 178401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 杨宋寒, 刘友春, 袁正勇 2014 中国专利ZL 201410193925.2
Yang S H, Liu Y C, Yuan Z Y 2014 CN Patent ZL 201410193925.2
[5] Zhang E Q 1980 IEEETrans. Elec. Dev. 27 1280
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 电子管设计手册编辑委员会 1979 磁控管设计手册 (北京: 国防工业出版社) 第193, 211, 420页
Electronic tube design handbook editorial Committee 1979 Magnetron Design Handbook (Beijing: National Defence Industry Press) pp193, 211, 420 (in Chinese)
[7] Li SG, Yan T C, Li F L, Yang J S, Shi W 2016 IEEE Trans. Plasma. Sci. 44 1386
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Huang H P, Huang K M, Liu C J 2018 IEEE Microw Wirel Co. 28 509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Buxbaum C, Gessinger G 1978 US Patent 4083811
[10] Goebel D M, Hirooka Y, Campbell G A 1985 Rev. Sci. Instrum 56 1888
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Frank B, Gartner G 1985 US Patent 4533852
[12] Tadashi S, Kiyosaki M 1990 JP Patent 59179754
[13] Rao G S, Dharmadhikari C V, Nigavekar A S 1989 J Vac Sci Technol 7 3269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang J S, Zhou M L, Ma S Y J, Zuo T Y 2006 J. Alloys Compd. 419 172
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhang J X, Zhou M L, Zhou W Y, Wang J S, Nie Z R, Zuo T Y 2002 Trans: Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 12 43
[16] Nie Z R, Zuo T Y, Zhou M L, Wang Y M, Wang J S 2000 J. Rare Earth 18 110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Bruining D H 1954 Physics and Application of Secondary Electron Emission (Oxford: Pergamon Press LTD) p19
[18] 刘学悫 1980 阴极电子学 (北京: 科学出版社) 第95, 97, 149, 211页
Liu X Q 1980 Cathode Electronics (Beijing: Science Press) pp95, 149, 184, 211 (in Chinese)
[19] 漆世锴, 王小霞, 罗积润, 赵青兰, 李云, 2016 65 057901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi S K, Wang X X, Luo J R, Zhao Q L, Li Y 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 057901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Qi S K, Wang X X, Luo J R, Zhao S K, Zhao Q L, Li Y, Zhang Q Proceedings of IVESC Saint-Petersburg, Russia, June 30–July 4, 2014 p18
[21] Qi S K, Wang X X, Luo J R, Hu M W, Li Y 2015 Proceedings of IRMMW-THz Hong Kong, China, August 23–28, 2015 p12
[22] 漆世锴, 王小霞, 罗积润, 赵青兰, 张琪, 李云 2018 稀有金属材料与工程 473 784
Qi S K, Wang X X, Luo J R, Zhao S K, Zhao Q L, Li Y, Zhang Q 2018 Rare Metal Mat. Eng. 473 784
[23] 漆世锴, 王小霞, 罗积润, 胡明玮, 李云 2016 无机材料学报 31 987
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi S K, Wang X X, Luo J R, Hu M W, Li Y 2016 J. Inorg. Mater. 31 987
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Hu M W, Wang X X, Qi S K 2019 IEEE Trans. Elec. Dev. 66 3592
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wang X X, Liao X H, Luo J R, Zhao Q L, Zhang M, Wang Q F, Li Y 2012 IEEETrans. Elec. Dev. 59 491
[26] 常铁军, 祁欣 1999 材料近代分析测试方法 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学出版社) 第124, 125页
Chang T J, Qi X 1999 Modern Analysis Methods of Materials (Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press) pp124, 125
-
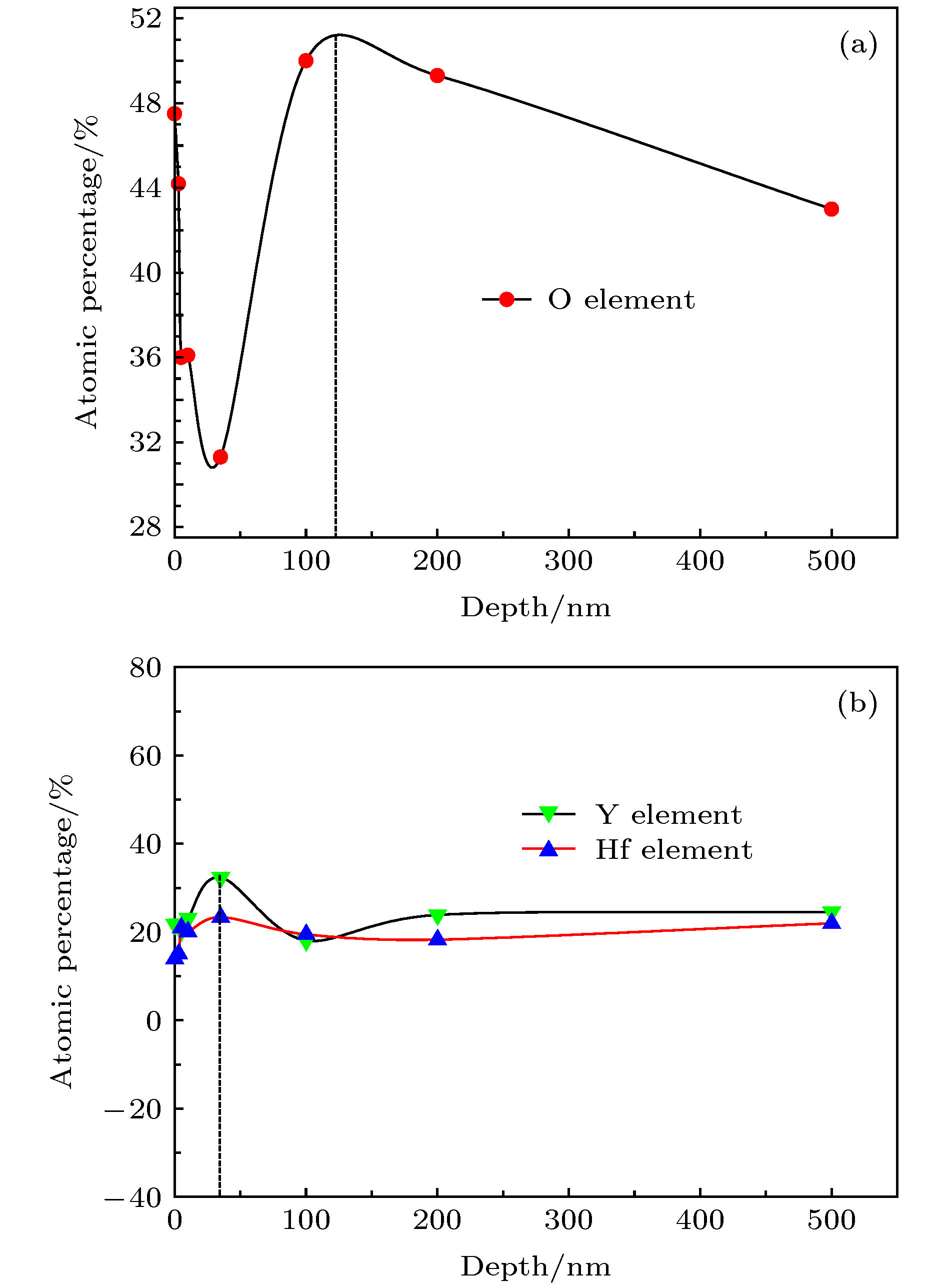
表 1 O, Y, Hf, C元素原子百分数与氩离子蚀刻深度的关系
Table 1. O, Y, Hf, C element content as a function of the depth using argon ion etching method.
Depth/nm Element content/at% O Y Hf C 0 47.5 21.7 13.9 17.0 3 44.2 21.8 15.0 19.0 5 36.0 20.2 20.9 22.9 10 36.1 23.0 20.0 20.9 35 31.3 32.3 23.3 13.4 100 50.0 18.0 19.4 12.5 200 49.3 23.8 18.2 8.7 500 43.0 24.5 21.9 10.6 -
[1] Jacqueline M R B, Paré J R J 2007 J. Microwave Power EE. 42 24
[2] Lester E, Kingman S, Dodds C 2005 Fuel 84 423
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 岳松, 张兆传, 高东平 2013 62 178401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yue S, Zhang Z C, Gao D P 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 178401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 杨宋寒, 刘友春, 袁正勇 2014 中国专利ZL 201410193925.2
Yang S H, Liu Y C, Yuan Z Y 2014 CN Patent ZL 201410193925.2
[5] Zhang E Q 1980 IEEETrans. Elec. Dev. 27 1280
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 电子管设计手册编辑委员会 1979 磁控管设计手册 (北京: 国防工业出版社) 第193, 211, 420页
Electronic tube design handbook editorial Committee 1979 Magnetron Design Handbook (Beijing: National Defence Industry Press) pp193, 211, 420 (in Chinese)
[7] Li SG, Yan T C, Li F L, Yang J S, Shi W 2016 IEEE Trans. Plasma. Sci. 44 1386
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Huang H P, Huang K M, Liu C J 2018 IEEE Microw Wirel Co. 28 509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Buxbaum C, Gessinger G 1978 US Patent 4083811
[10] Goebel D M, Hirooka Y, Campbell G A 1985 Rev. Sci. Instrum 56 1888
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Frank B, Gartner G 1985 US Patent 4533852
[12] Tadashi S, Kiyosaki M 1990 JP Patent 59179754
[13] Rao G S, Dharmadhikari C V, Nigavekar A S 1989 J Vac Sci Technol 7 3269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang J S, Zhou M L, Ma S Y J, Zuo T Y 2006 J. Alloys Compd. 419 172
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhang J X, Zhou M L, Zhou W Y, Wang J S, Nie Z R, Zuo T Y 2002 Trans: Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 12 43
[16] Nie Z R, Zuo T Y, Zhou M L, Wang Y M, Wang J S 2000 J. Rare Earth 18 110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Bruining D H 1954 Physics and Application of Secondary Electron Emission (Oxford: Pergamon Press LTD) p19
[18] 刘学悫 1980 阴极电子学 (北京: 科学出版社) 第95, 97, 149, 211页
Liu X Q 1980 Cathode Electronics (Beijing: Science Press) pp95, 149, 184, 211 (in Chinese)
[19] 漆世锴, 王小霞, 罗积润, 赵青兰, 李云, 2016 65 057901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi S K, Wang X X, Luo J R, Zhao Q L, Li Y 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 057901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Qi S K, Wang X X, Luo J R, Zhao S K, Zhao Q L, Li Y, Zhang Q Proceedings of IVESC Saint-Petersburg, Russia, June 30–July 4, 2014 p18
[21] Qi S K, Wang X X, Luo J R, Hu M W, Li Y 2015 Proceedings of IRMMW-THz Hong Kong, China, August 23–28, 2015 p12
[22] 漆世锴, 王小霞, 罗积润, 赵青兰, 张琪, 李云 2018 稀有金属材料与工程 473 784
Qi S K, Wang X X, Luo J R, Zhao S K, Zhao Q L, Li Y, Zhang Q 2018 Rare Metal Mat. Eng. 473 784
[23] 漆世锴, 王小霞, 罗积润, 胡明玮, 李云 2016 无机材料学报 31 987
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi S K, Wang X X, Luo J R, Hu M W, Li Y 2016 J. Inorg. Mater. 31 987
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Hu M W, Wang X X, Qi S K 2019 IEEE Trans. Elec. Dev. 66 3592
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wang X X, Liao X H, Luo J R, Zhao Q L, Zhang M, Wang Q F, Li Y 2012 IEEETrans. Elec. Dev. 59 491
[26] 常铁军, 祁欣 1999 材料近代分析测试方法 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学出版社) 第124, 125页
Chang T J, Qi X 1999 Modern Analysis Methods of Materials (Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press) pp124, 125
计量
- 文章访问数: 10728
- PDF下载量: 77
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: