-
Uniformity of magnetic field is an important parameter of magnetic resonance system. Improving the uniformity of magnetic field is helpful for detecting the magnetic resonance time domain signal and improving the resolution of magnetic resonance frequency domain signal. Based on the idea of continuous current density distribution in an active shimming field, the shimming coil is designed by combining the target field point method with the current function method. That is to say, the relationship between magnetic field distribution and current density is determined by Biot-Savart law. After confining the coil radius and setting the constraint point, the current density distribution on the coil plane is inversely solved according to the target field distribution. Then the current density distribution is discretized by the current function, and the winding position distribution of the uniform field coil is obtained. According to the results of electromagnetic simulation, the first-order and second-order shimming coils are fabricated and applied to the magnetic resonance analyzer. The experimental results show that the shimming coils can effectively improve the magnetic field uniformity of the permanent magnet in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) system.
[1] 白烨, 王秋良, 余运佳 2004 中国电机工程学报 24 132
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bai Y, Wang Q L, Yu Y J 2004 Proc. CSEE 24 132
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Hu G, Ni Z, Wang Q 2014 IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 24 1
[3] Kong X 2016 J. Magn. Reson. 263 122
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 丁守谦 1985 CN 1061486 A
Ding S Q 1985 CN 1061486 A
[5] Turner R 1986 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 19 L147
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Moon S, Hatano M 2000 J. Phys. 88 4994
[7] Forbes L K, Crozier S 2002 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 35 839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Harvey P R, Smink J S, Peeren G N, Jacob A D 2004 US Patent 7 412 278
[9] 李霞, 谢德馨 2005 电工理论与新技术学术年会论文集
Li X, Xie D X 2005 Annual Conference Papers on Electrical Theory and New Technologies
[10] Liu W, Tang X, Zu D 2010 Concepts Magn. Reson. Part B 37B 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Liu W T, Zu D L, Tang X 2010 Chin. Phys. B 19 018701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Poole M S 2007 Ph. D. Dissertation (Nottingham: The University of Nottingham)
[13] Liu W T, Zu D L, Tang X 2007 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 40 4418
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Forbes L K, Crozier S 2003 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 36 68
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Chen S S, Xia T, Miao Z Y 2017 Meas. Sci. Technol. 28 055902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhang R, Xu J, Fu Y 2011 Meas. Sci. Technol. 22 25505
[17] You X F, Hu L L, Yang W H 2010 IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 20 1045
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Tian X, Miao Z Y, Chen S S 2017 PLoS One 12 e0181552
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Xiao C, Cai C, Chen Z 2008 IEEE International Symposium on IT in Medicine and Education
[20] 李杰森, 陈应书 1983 分析仪器 27
Li J S, Chen Y S 1983 Anal. Instrum. 27
[21] Forbes L K, Brideson M A, Crozier S 2005 IEEE Trans. Magn. 41 2134
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Li C L, Guo J, Zhang P 2014 Chin. Phys. Express: Engl. Ed. 31 184
[23] 汪红志, 蔡筱云, 王鹤 2011 60 090204
Wang H Z, Cai X Y, Wang H 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 090204
[24] 周玉淑, 曹洁 2010 59 2898
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou Y S, Cao J 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 2898
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 沈杰, 宁瑞鹏, 刘颖 2006 55 3060
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shen J, Ning R P, Liu Y 2006 Acta Phys. Sin. 55 3060
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Pan H, Jia F, Liu Z Y 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 50201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
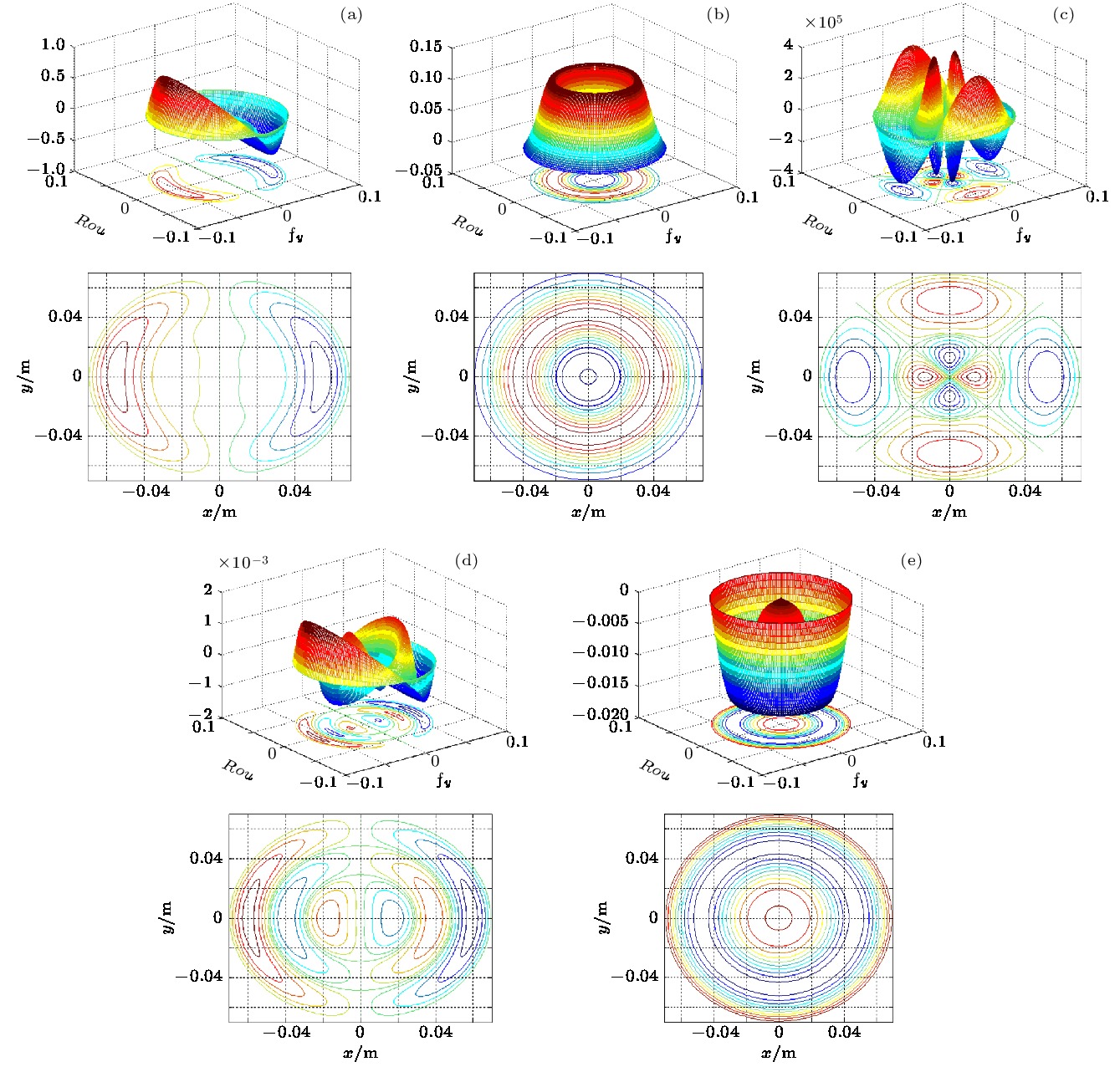
图 2 各阶次线圈的流函数和绕线分布 (a) X, Y线圈的流函数和绕线分布; (b) Z线圈的流函数和绕线分布; (c) XY线圈的流函数和绕线分布; (d) XZ, YZ线圈的流函数和绕线分布; (e) Z2线圈的流函数和绕线分布
Fig. 2. Flow function distribution and coil winding of each order coils: (a) Flow function distribution and coil winding of X and Y coil; (b) flow function distribution and coil winding of Z coil; (c) flow function distribution and coil winding of XY coil; (d) flow function distribution and coil winding of XZ and YZ coil; (e) flow function distribution and coil winding of Z2 coil
图 3 采用有源匀场线圈匀场前后磁共振检测的FID信号和频谱的FWHM (a)有源匀场线圈应用于磁共振系统的实验平台; (b)匀场前FID信号; (c)匀场前频谱的FWHM; (d)二阶匀场线圈匀场后的FID信号; (e)二阶匀场线圈匀场后频谱的FWHM
Fig. 3. FID signal detected by magnetic resonance before and after shimming with active shimming coil: (a) Experimental platform of active shimming coil applied to magnetic resonance system; (b) FID signal before shimming; (c) FWHM of the pre-shimming spectrum; (d) FID signal after the second-order shimming coil shimming; (e) FWHM of after the second-order shimming coil shimming
表 1
${B_z}$ 在直角坐标系和球坐标系下的分量表示Table 1. Component representation of
${B_z}$ in Cartesian and spherical coordinates.阶次 次序 分量 系数 球坐标系 直角坐标系 ($r,\;\,\theta,\;\,\phi $) ($x,\;\,y,\;\,z$) 0 0 Z0 A01 1 1 1 0 Z 2A02 rcosθ z 1 1 X 3A12 rsinθ cosϕ x 1 1 Y 3B12 rsinθ sinϕ y 2 0 Z2 3A03 r2 (3cos2θ–1)/2 z2–(x2+y2)/2 2 1 XZ 12A13 r2 cos θ sinθcosϕ xz 2 1 YZ 12B13 ${r^2}\cos \theta {\rm{sin}}\theta {\rm{sin}}\phi $ yz 2 2 X2–Y2 15A23 ${r^2}{\rm{si}}{{\rm{n}}^2}\theta {\rm{cos}}2\phi $ x2–y2 2 2 2XY 15B23 ${r^2}{\rm{si}}{{\rm{n}}^2}\theta {\rm{sin}}2\phi $ 2xy 3 0 Z3 4A04 ${r^3}\cos \theta (5{\cos ^2}\theta - 3)/2$ $z[{z^2} - 3\left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right)/2]$ 3 1 XZ2 15A14 ${r^3}\sin \theta \cos \phi (5{\cos ^2}\theta - 1)/2$ $x[4{z^2} - \left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right)]$ 3 1 YZ2 15B14 ${r^3}\sin \theta \sin \phi (5{\cos ^2}\theta - 1)/2$ $y[4{z^2} - \left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right)]$ 3 2 Z(X2–Y2) 90A24 ${r^3}{\rm{cos}}\theta {\rm{si}}{{\rm{n}}^2}\theta {\rm{cos}}2\phi $ z(x2–y2) 3 2 XYZ 90B24 ${r^3}{\rm{cos}}\theta {\rm{si}}{{\rm{n}}^2}\theta {\rm{sin}}2\phi $ 2xyz 3 3 X3 105A34 ${r^3}{\rm{si}}{{\rm{n}}^3}\theta {\rm{cos}}3\phi $ ${x^3} - 3x{y^2}$ 3 3 Y3 105B34 ${r^3}{\rm{si}}{{\rm{n}}^3}\theta {\rm{sin}}3\phi $ $3{x^2}y - {y^3}$ 4 0 Z4 5A05/8 ${r^4}(35{\cos ^4}\theta - 30{\rm{co}}{{\rm{s}}^2}\theta + 3)$ $8{z^4} - 24{z^2}\left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right) + 3{\left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right)^2}$ … … 表 2 有源匀场线圈匀场效果评价技术指标对比
Table 2. Comparison of technical indicators for evaluating shimming effect of active shimming coil.
有源匀场线圈 FID信号(积分区域) 频谱半高宽/Hz 磁场均匀性/ppm 匀场前 1270683 338 19.17 一阶线圈匀场 3937325 98 18.23 二阶线圈匀场 4866520 48 1.98 -
[1] 白烨, 王秋良, 余运佳 2004 中国电机工程学报 24 132
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bai Y, Wang Q L, Yu Y J 2004 Proc. CSEE 24 132
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Hu G, Ni Z, Wang Q 2014 IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 24 1
[3] Kong X 2016 J. Magn. Reson. 263 122
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 丁守谦 1985 CN 1061486 A
Ding S Q 1985 CN 1061486 A
[5] Turner R 1986 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 19 L147
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Moon S, Hatano M 2000 J. Phys. 88 4994
[7] Forbes L K, Crozier S 2002 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 35 839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Harvey P R, Smink J S, Peeren G N, Jacob A D 2004 US Patent 7 412 278
[9] 李霞, 谢德馨 2005 电工理论与新技术学术年会论文集
Li X, Xie D X 2005 Annual Conference Papers on Electrical Theory and New Technologies
[10] Liu W, Tang X, Zu D 2010 Concepts Magn. Reson. Part B 37B 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Liu W T, Zu D L, Tang X 2010 Chin. Phys. B 19 018701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Poole M S 2007 Ph. D. Dissertation (Nottingham: The University of Nottingham)
[13] Liu W T, Zu D L, Tang X 2007 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 40 4418
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Forbes L K, Crozier S 2003 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 36 68
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Chen S S, Xia T, Miao Z Y 2017 Meas. Sci. Technol. 28 055902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhang R, Xu J, Fu Y 2011 Meas. Sci. Technol. 22 25505
[17] You X F, Hu L L, Yang W H 2010 IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 20 1045
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Tian X, Miao Z Y, Chen S S 2017 PLoS One 12 e0181552
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Xiao C, Cai C, Chen Z 2008 IEEE International Symposium on IT in Medicine and Education
[20] 李杰森, 陈应书 1983 分析仪器 27
Li J S, Chen Y S 1983 Anal. Instrum. 27
[21] Forbes L K, Brideson M A, Crozier S 2005 IEEE Trans. Magn. 41 2134
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Li C L, Guo J, Zhang P 2014 Chin. Phys. Express: Engl. Ed. 31 184
[23] 汪红志, 蔡筱云, 王鹤 2011 60 090204
Wang H Z, Cai X Y, Wang H 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 090204
[24] 周玉淑, 曹洁 2010 59 2898
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou Y S, Cao J 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 2898
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 沈杰, 宁瑞鹏, 刘颖 2006 55 3060
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shen J, Ning R P, Liu Y 2006 Acta Phys. Sin. 55 3060
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Pan H, Jia F, Liu Z Y 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 50201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 12821
- PDF下载量: 184
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: