-
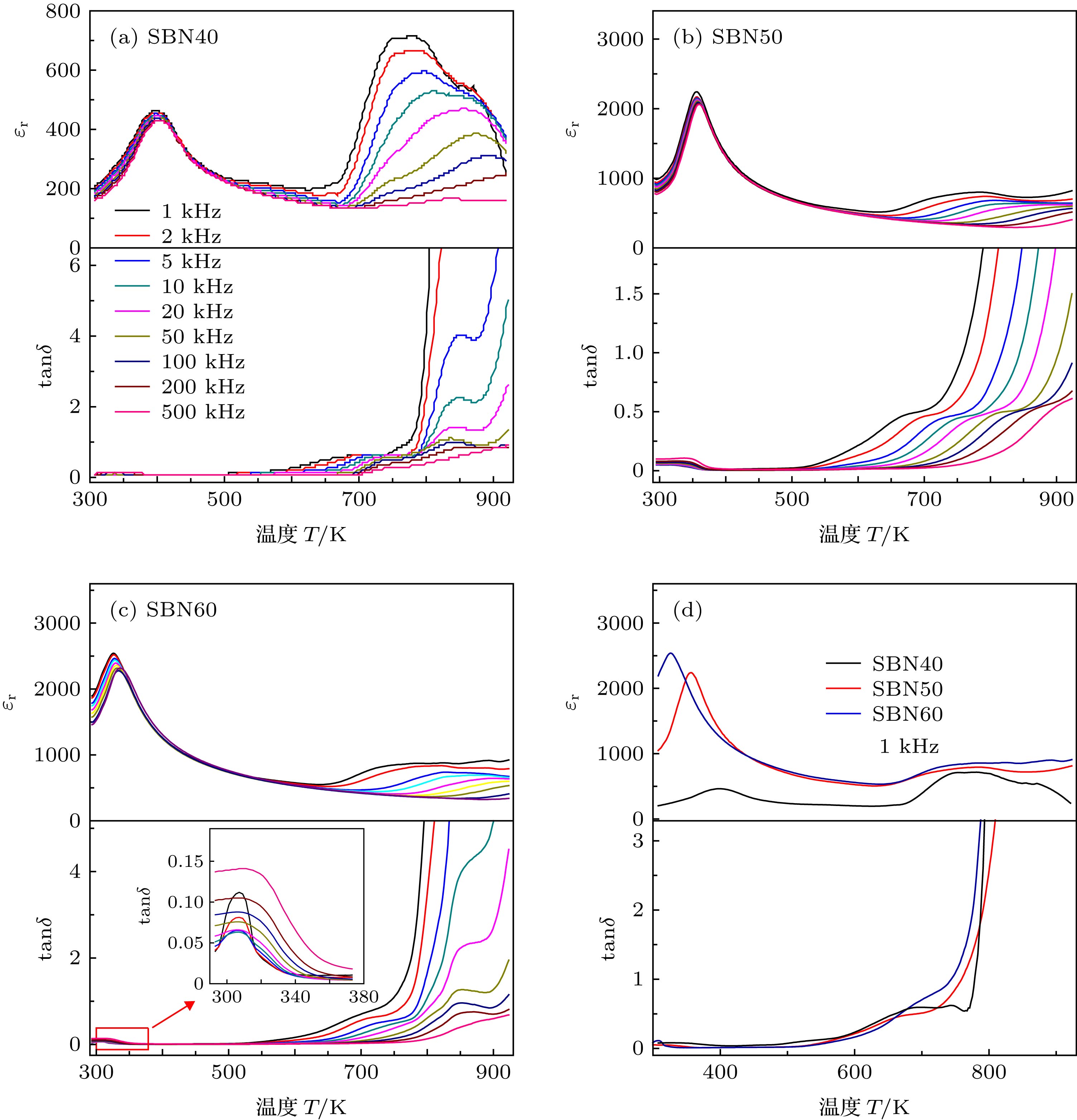
由于铅对环境存在各种危害, 无铅铁电功能陶瓷的研究是当前研究热点之一. 弛豫铁电体因具有较低的容温变化率和大的电致伸缩系数, 在陶瓷电容器材料中占据重要地位. 且无铅功能陶瓷在高温介电行为和阻抗的分析研究工作对功能陶瓷在高温下的适用具有重要的指导意义. SrxBa1–xNb2O6陶瓷采用传统的高温固相反应法制备而成, 并系统地研究了SrxBa1–xNb2O6陶瓷的介温特性和阻抗. 值得注意的是, 铌酸锶钡的高温弛豫尚未研究报导. 结果显示, 锶在陶瓷中组分比例的增加会使铁电相转变为顺电的相变温度降低. 此外, 通过计算, x = 0.6的铌酸锶钡陶瓷的弥散相变参数γ = 1.94, 表明x = 0.6的铌酸锶钡陶瓷在低温下接近理想的弛豫铁电体. 另外, 阻抗分析数据显示陶瓷存在热激活弛豫现象. 最后, 利用阿伦尼乌斯定律从阻抗和介电数据中计算出了电导活化能和弛豫活化能. 计算结果证明, 氧空位引起的离子跳跃在高温介电弛豫过程中发挥了关键作用.Due to the various risks caused by lead, the research of lead-free ferroelectric functional ceramics has been one of research hotspots recently. And relaxor ferroelectrics have an important position in materials for ceramic capacitor due to their low temperature change rate and large electrostrictive coefficient. However, the lead-free SrxBa1–xNb2O6 ceramic is a non-filled tungsten bronze structural material whose Curie temperature can be adjusted by changing the proportion of Sr composition. The increase of Sr concentration in ceramic can cause relaxor behavior and improve dielectric constant and ferroelectric properties. In this work, SrxBa1–xNb2O6 (x = 0.4, 0.5 and 0.6, abbreviated as SBN40, SBN50 and SBN60, respectively) ceramics are prepared by a high-temperature solid-state reaction process. The dielectric properties and the impedances of the SrxBa1–xNb2O6 ceramics are investigated in detail. It is worth noting that the high-temperature diffusion for the SrxBa1–xNb2O6 has not been studied before. Furthermore, the analysis of high-temperature dielectric behavior and impedance of lead-free functional ceramics is important for the application of functional ceramics in the high-temperature environment. The temperature of phase transition for SBN40, SBN50 and SBN60 are 401.15 K, 355.15 K, and 327.15 K, respectively, which are obtained from the modified Curie-Weiss law. The result shows that the increase of Sr composition leads the phase transition temperature from ferroelectric to paraelectric phase to decrease. In addition, the calculated value of diffusion phase transition parameter γ for SBN40, SBN50 and SBN60 are 1.53, 1.90 and 1.94, respectively, showing that it is close to an ideal relaxor ferroelectric with the Sr content increasing in SBN ceramics at low temperature. In addition, it is noticed that a similar diffusion appears in at high temperature. This phenomenon is unrelated to the phase transition, but it is corresponding to high temperature dielectric relaxation which is related to oxygen vacancy. As expected, the impedance spectroscopic data present a thermally activated relaxation phenomenon. Finally, activation energy for conduction and relaxation are calculated from the impedance and dielectric data through the Arrhenius law. Comparing the activation energy values for conduction and relaxation, it can be obviously concluded that the trap-controlled conduction process should be responsible for the relaxation process of sample. And the hopping of ions, caused by oxygen vacancies, plays a critical role in the dielectric relaxation process at high temperature.
-
Keywords:
- SrxBa1-xNb2O6 ceramic /
- diffusion phase transition /
- relaxor ferroelectric /
- oxygen vacancy
[1] Zhang Y, Xie M Y, Roscow J, Bao Y X, Zhou K C, Zhang D, Bowen C R 2017 J. Mater. Chem. A 5 6569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zhang S J, Li F 2012 J. Appl. Phys. 111 031301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhang S J, Li F, Jiang X N, Kim J, Luo J, Geng X C 2015 Prog. Mater. Sci. 68 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yang Q, Shi Z, Ma D, He Y, Wa ng 2018 J. Ceram. Int. 44 14850
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Qiao H M, He C, Wang Z J, Li X Z, Liu Y, Long X F 2018 J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38 3162
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhu L F, Zhang B P, Duan J Q, Xun B W, Wang N, Tang Y C, Zhao G L 2018 J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38 3463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Luo B C, Wang X H, Tian E K, Qu H M, Zhao Q C, Cai Z M, Wang H X, Feng W, Li B W, Li L T 2018 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 101 2976
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 曹万强, 刘培朝, 陈勇, 潘瑞琨, 祁亚军 2016 65 137701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao W Q, Liu P Z, Chen Y, Pan R K, Qi Y J 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 137701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Shvartsman V V, Kleemann W 2008 Phys. Rev. B 77 054105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang J, Wang G S, Gao F, Mao C L, Dong X L 2013 Ceram. Int. 39 1971
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ottini R, Tealdi C, Tomasi C, Tredici I G, Soffientini A, Anselmi-Tamburini U, Ghigna P, Spinolo G 2017 J. Appl. Phys. 121 085104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tagantsev A K, Sherman V O, Astafiev K F, Venkatesh J, Setter N 2003 J. Electroceram. 11 5
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Velayutham T, Salim N, Gan W 2016 J. Alloys Compd. 6 334
[14] Chen H, Guo S B, Yao C H, Dong X L, Mao C L, Wang G S 2017 Ceram. Int. 43 3610
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zheng J, Chen G H, Yuan C L, Zhou C R, Chen X, Feng Q, Li M 2016 Ceram. Int. 42 1827
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Chen F, Liu Q X, Tang X G, Jiang Y P, Yue J L, Li J K 2016 J. Elec. Mat. 45 3174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Fan H Q, Zhang L Y, Yao X 1998 J. Mater. Sci. 33 895
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Viehland D, Wu Z, Huang W H 1995 Philos. Mag. A 71 205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Hennings D, Schnell A, Simon G 1982 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 65 539
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhao Y Y, Wang J P, Zhang L X, Shi X J, Liu S J, Zhang D W 2016 Ceram. Int. 42 16697
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Bidault O, Goux P, Kchikech M, Belkaoumi M, Maglione M 1994 Phys. Rev. B 49 7868
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Cao Z Z, Liu X T, He W Y, Ruan X Z, Gao Y F, Liu J R 2015 Physica B 477 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Wang X, Lu X, Zhang C, Wu X, Cai W, Peng S, Bo H F, Kan Y, Huang F Z, Zhu J S 2010 J. Appl. Phys. 107 114101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Zhang T F, Tang X G, Liu Q X, Jiang Y P, Huang X X 2015 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 98 551
[25] Fang T T, Chung H Y 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 94 092905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 伍君博, 唐新桂, 贾振华, 陈东阁, 蒋艳平, 刘秋香 2012 61 207702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu J B, Tang X G, Jia Z H, Chen D G, Jiang Y P, Liu Q X 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 207702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Wang M J, Zhang Y, Liu X L, Wang X R 2013 Ceram. Int. 39 2069
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Morii K, Kawano H, Fujii I, Matsui T, Nakayama Y 1995 J. Appl. Phys. 78 1914
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhang T F, Tang X G, Liu Q X, Jiang Y P, Huang X X, Zhou Q F 2016 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 49 095302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Singh G, Tiwari V S, Gupta P K 2010 J. Appl. Phys. 107 064103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Jiang X P, Jiang Y L, Jiang X G, Chen C, Tu N, Chen Y J 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 077701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
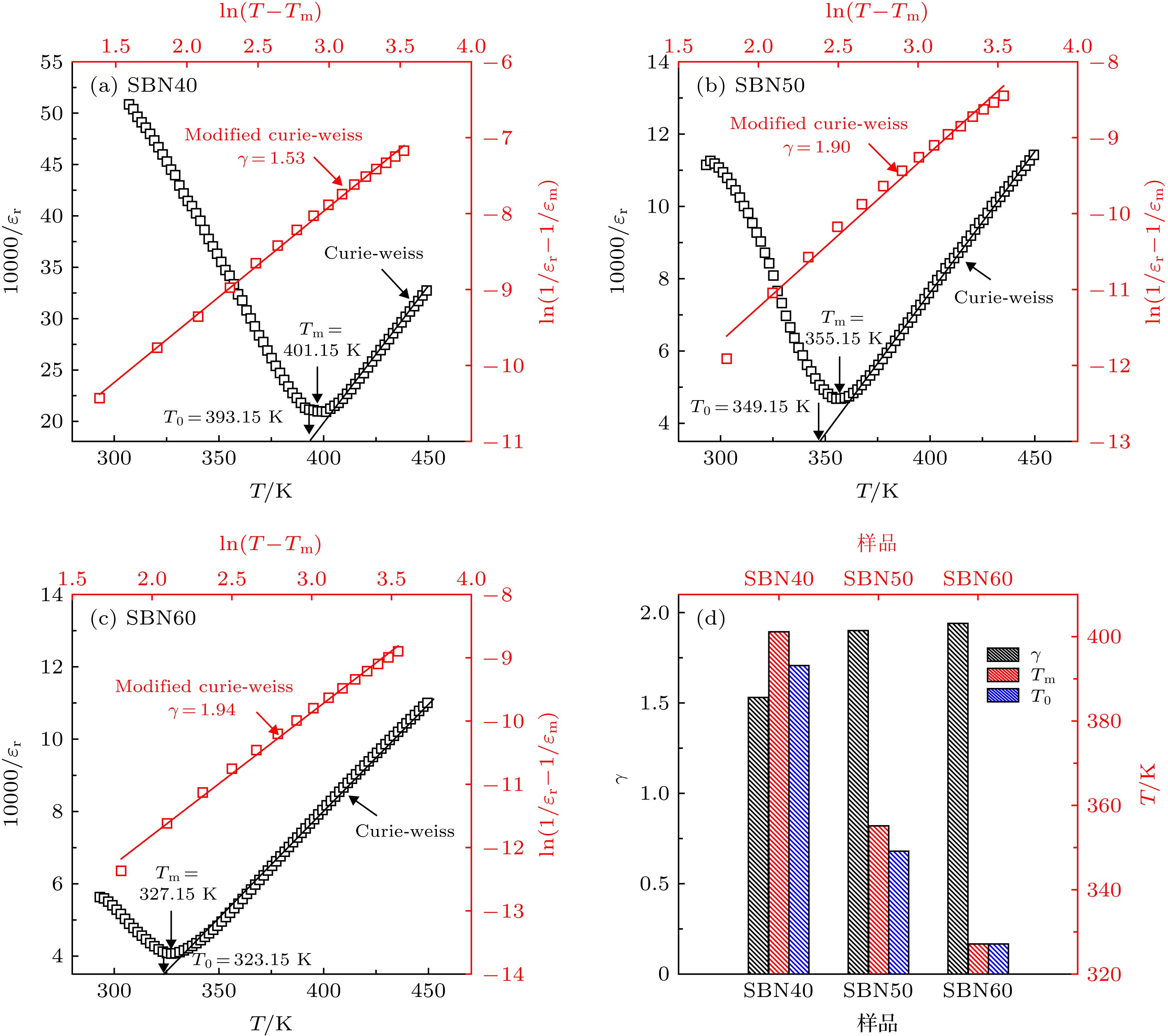
图 2 在1 kHz频率下, 介电常数与温度的函数关系(黑色实线是居里-外斯定律拟合, 红色实线是改进的居里-外斯定律的拟合) (a) SBN40; (b) SBN50; (c) SBN60; (d)在1 kHz下三个样品的γ, Tm和T0的值
Fig. 2. The inverse of dielectric permittivity as a function of temperature at 1 kHz (the black solid lines are used to fit the Curie-Weiss law, the red solid lines used to fit the modified Curie-Weiss law): (a) SBN40; (b) SBN50; (c) SBN60; (d) the value of γ, Tm and T0 for three samples at 1 kHz.
图 3 SBN陶瓷的Cole-Cole图(插图为阻抗虚部归一化 (Z''/Z''max)随频率的变化关系图) (a) SBN40; (b) SBN50; (c) SBN60; (d)在843 K下所有SBN陶瓷的Cole-Cole图
Fig. 3. Cole-Cole plots for SBN ceramics (the insets show the normalized imaginary parts of impedance (Z''/Z''max) with frequency): (a) SBN40; (b) SBN50; (c) SBN60; (d) Cole-Cole plots for SBN ceramics at 843 K.
-
[1] Zhang Y, Xie M Y, Roscow J, Bao Y X, Zhou K C, Zhang D, Bowen C R 2017 J. Mater. Chem. A 5 6569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zhang S J, Li F 2012 J. Appl. Phys. 111 031301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhang S J, Li F, Jiang X N, Kim J, Luo J, Geng X C 2015 Prog. Mater. Sci. 68 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yang Q, Shi Z, Ma D, He Y, Wa ng 2018 J. Ceram. Int. 44 14850
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Qiao H M, He C, Wang Z J, Li X Z, Liu Y, Long X F 2018 J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38 3162
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhu L F, Zhang B P, Duan J Q, Xun B W, Wang N, Tang Y C, Zhao G L 2018 J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38 3463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Luo B C, Wang X H, Tian E K, Qu H M, Zhao Q C, Cai Z M, Wang H X, Feng W, Li B W, Li L T 2018 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 101 2976
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 曹万强, 刘培朝, 陈勇, 潘瑞琨, 祁亚军 2016 65 137701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao W Q, Liu P Z, Chen Y, Pan R K, Qi Y J 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 137701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Shvartsman V V, Kleemann W 2008 Phys. Rev. B 77 054105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang J, Wang G S, Gao F, Mao C L, Dong X L 2013 Ceram. Int. 39 1971
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ottini R, Tealdi C, Tomasi C, Tredici I G, Soffientini A, Anselmi-Tamburini U, Ghigna P, Spinolo G 2017 J. Appl. Phys. 121 085104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tagantsev A K, Sherman V O, Astafiev K F, Venkatesh J, Setter N 2003 J. Electroceram. 11 5
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Velayutham T, Salim N, Gan W 2016 J. Alloys Compd. 6 334
[14] Chen H, Guo S B, Yao C H, Dong X L, Mao C L, Wang G S 2017 Ceram. Int. 43 3610
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zheng J, Chen G H, Yuan C L, Zhou C R, Chen X, Feng Q, Li M 2016 Ceram. Int. 42 1827
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Chen F, Liu Q X, Tang X G, Jiang Y P, Yue J L, Li J K 2016 J. Elec. Mat. 45 3174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Fan H Q, Zhang L Y, Yao X 1998 J. Mater. Sci. 33 895
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Viehland D, Wu Z, Huang W H 1995 Philos. Mag. A 71 205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Hennings D, Schnell A, Simon G 1982 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 65 539
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhao Y Y, Wang J P, Zhang L X, Shi X J, Liu S J, Zhang D W 2016 Ceram. Int. 42 16697
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Bidault O, Goux P, Kchikech M, Belkaoumi M, Maglione M 1994 Phys. Rev. B 49 7868
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Cao Z Z, Liu X T, He W Y, Ruan X Z, Gao Y F, Liu J R 2015 Physica B 477 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Wang X, Lu X, Zhang C, Wu X, Cai W, Peng S, Bo H F, Kan Y, Huang F Z, Zhu J S 2010 J. Appl. Phys. 107 114101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Zhang T F, Tang X G, Liu Q X, Jiang Y P, Huang X X 2015 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 98 551
[25] Fang T T, Chung H Y 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 94 092905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 伍君博, 唐新桂, 贾振华, 陈东阁, 蒋艳平, 刘秋香 2012 61 207702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu J B, Tang X G, Jia Z H, Chen D G, Jiang Y P, Liu Q X 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 207702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Wang M J, Zhang Y, Liu X L, Wang X R 2013 Ceram. Int. 39 2069
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Morii K, Kawano H, Fujii I, Matsui T, Nakayama Y 1995 J. Appl. Phys. 78 1914
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhang T F, Tang X G, Liu Q X, Jiang Y P, Huang X X, Zhou Q F 2016 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 49 095302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Singh G, Tiwari V S, Gupta P K 2010 J. Appl. Phys. 107 064103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Jiang X P, Jiang Y L, Jiang X G, Chen C, Tu N, Chen Y J 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 077701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 12732
- PDF下载量: 224
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: