-
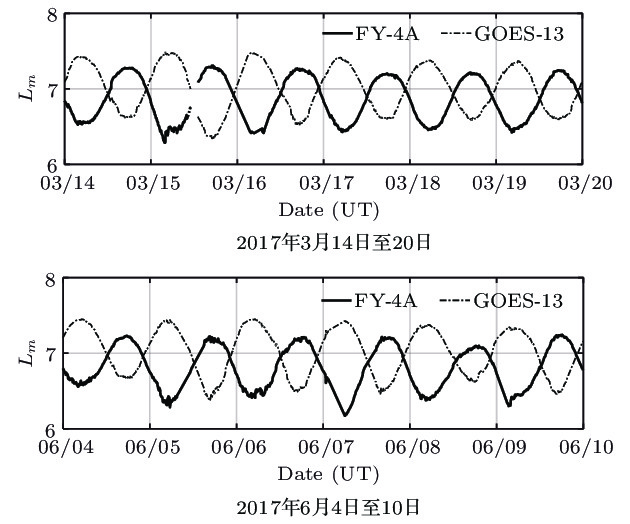
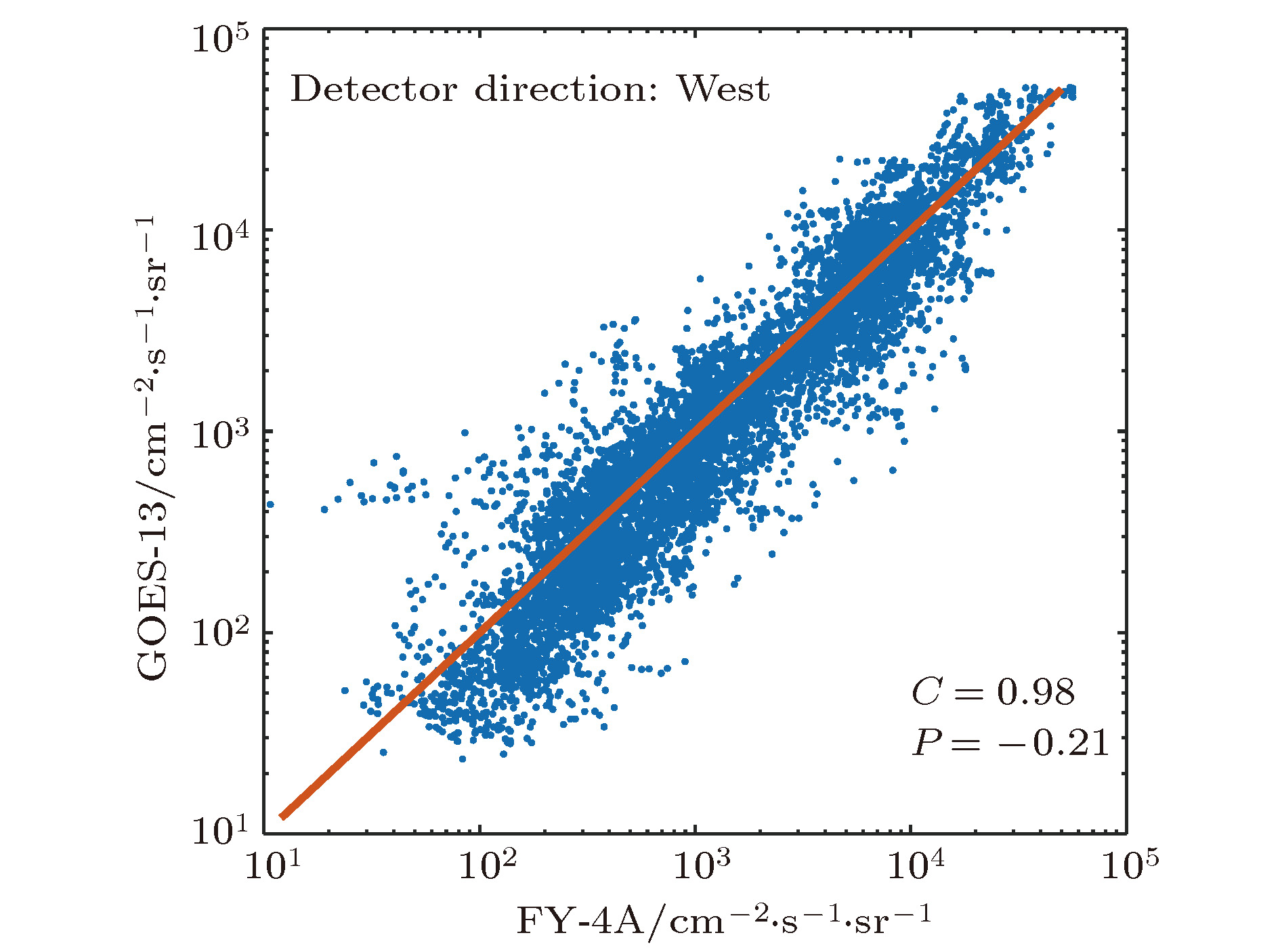
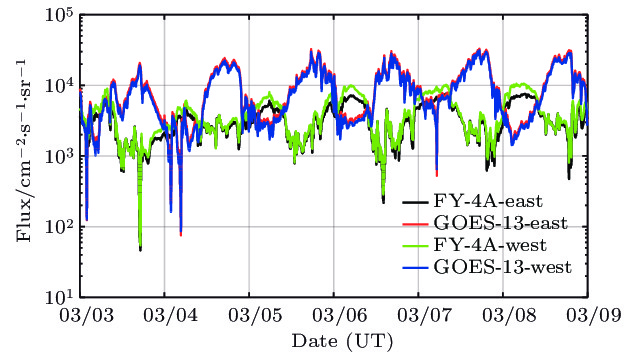
地球磁层空间的相对论电子通过内部充放电效应, 能够导致在轨航天器彻底失效. 由于对这种空间粒子的特性和物理机制仍不清楚, 磁层空间相对论电子一直是空间环境探测和空间科学研究的重要对象. 开展相关磁层空间环境特性的研究和粒子辐射环境建模等, 需要同时使用来自不同卫星、不同探测器的观测数据. 消除不同探测器之间的系统偏差, 实现不同来源数据的融合, 是开展相关研究的必要前提. 本文对我国最新的地球同步轨道卫星—风云四号A星(FY-4A)和同类轨道的美国GOES-13卫星相对论电子(> 2 MeV)观测数据, 开展在轨交叉定标及数据融合研究. 本文严格筛选出地磁宁静期(Kp < 2)的观测数据, 以保证研究对象是被地磁场稳定捕获的辐射带粒子. 根据辐射带粒子的物理特性, 即3个绝热不变量的基础之上, 以Liouville定理为依据, 在漂移壳Lm坐标下比较两颗卫星观测到的电子通量, 得到两颗卫星相对论电子观测之间的系统偏差. 依据该结果, 进行数据融合处理, 结果表明系统偏差得以很好地消除. 通过本项研究工作, 得到了国际上重要的两个地球同步轨道相对论电子观测系统之间的偏差, 并根据该研究成果, 成功实现两个探测系统观测数据之间的融合, 为后续的理论和应用研究工作打下了坚实的基础, 也为地球同步轨道其他能道高能电子观测数据的在轨交叉定标和数据融合提供了参考方法.Magnetospheric relativistic electrons can destroy on-orbit spacecrafts completely by internal charging and discharging effects. As the characteristics and physical mechanism of this space particle are still unclear, magnetospheric relativistic electrons have always been an important object of space environment exploration and space science research. For studying the physical mechanisms and developing models relating to magnetospheric relativistic electrons, it is necessary to use the observations from different satellites and detectors at the same time. Eliminating the systematic deviation between different detection systems to assimilate the observations from different sources is essentially required by such researches. In this work, the on-orbit cross-calibration and assimilation for relativistic electron (> 2 MeV) observations from FengYun 4A and GOES-13 are performed. In this work, only the observations obtained under very quiet geomagnetic conditions (Kp < 2) are adopted to ensure that the objects of study are the radiation belt particles, which are stably captured by the geomagnetic field. According to the physical characteristics of the radiation belt particles, that is, the three adiabatic invariants, and based on the Liouville theorem, the phase space density of the stably captured particles is unchanged. In this paper, the relativistic electron flux data of energy > 2 MeV and instrument pitch angle are in the east and west direction respectively. If the particles’ energy is the same, then their corresponding μ values are the same, and their particles’ directions are the same, then their corresponding J values are the same, and the Liouville theorem can be simplified as the drift shell Lm is the same, the fluxes are the same, and the electron fluxes observed by the two satellites are compared in the drift shell Lm coordinate. The systematic deviation between the two satellites’ relativistic electronic observations can be obtained. According to this result, the data assimilation is carried out, and the results show that the system deviation can be removed well. By this research work, the systematic deviation between two important relativistic electron detection systems in geosynchronous orbit is obtained. Based on the obtained systematic deviations, the assimilations for observations from the two detection systems are achieved. This work lays a solid foundation for the follow-up theoretical and applied researches, and also provides the methods for on-orbit cross-calibration and observation assimilation which could be referred to when other electronic observations on geosynchronous orbit are dealt with.
-
Keywords:
- relativistic electron /
- geosynchronous orbit /
- on-orbit cross-calibration /
- data assimilation /
- FengYun 4A
[1] 赵华, 朱光武, 王世金, 高玉芬, 刘振兴 2003 中国科学D辑 33 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao H, Zhu G W, Wang S J, Gao Y F, Liu Z X 2003 Sci. ChinaD 33 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 黄建国, 韩建伟 2010 59 2907
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang J G, Han J W 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 2907
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 宗秋刚, 袁憧憬, 王永福, 苏振鹏 2013 中国科学: 地球科学 43 951
Zong Q G, Yuan C J, Wang Y F, Su Z P 2013 Sci. China: Earth Sci. 43 951
[4] Friedel R H W, Reeves G, Belian D, Cayton T, Mouikis C, Korth A, Blake B, Fennel J, SelesnickR, Baker D, Onsagers T, Kaneka1 S 2000 Adv. Space Res. 26 93
[5] Chen Y, Friedel R H W, Reeves G D, Onsager T G, Thomsen M F 2005 J. Geophy. Res. 110 A10210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Chen Y, Friedel R H W, Reeves G D, Cayton T E, Christensen R 2007 J. Geophys. Res. 112 A11214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yang X C, Ni B B, Yu J, Zhang Y, Zhang X X, Sun Y Q 2017 J. Geophys. Res. 122 6255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Friedel R H W, Bourdarie S, Cayton T E 2005 Space Weather 3 S09B04
[9] Meredith Nigel P, Horne Richard B, Isles John D 2015 Space Weather 13 170
[10] Ganushkina N Yu, Sillanpää I, Welling D 2019 Space Weather 17 687
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 王馨悦, 王春琴, 杨晓超, 王世金 2008 地球 55 611
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X Y, Wang C Q, Yang X C, Wang S J 2008 Chin. J. Geophys. 55 611
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 于超, 李嘉巍, 张效信, 李传起, 王春琴, 王世金 2012 地球 55 2835
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu C, Li J W, Zhang X X, Li C Q, Wang C Q, Wang S J 2012 Chin. J. Geophys. 55 2835
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li X L, Temerin M A 2001 Space Sci. Rev. 95 569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 徐荣栏, 李磊 2005 磁层粒子动力学 (北京: 科学出版社) 第84—92页
Xu R L, Li L 2005 Magnetosphereic Partical Dynamics (Beijing: Science Press) pp84–92 (in Chinese)
[15] 涂传治 1988 日地空间物理学: 行星际与磁层(下册) (北京: 科学出版社) 第111—118页
Tu C Z 1988 Solar-Terrestrial Space Physics: Interplanetary and Magnetosphere (Vol.2) (Beijing: Science Press) pp111–118 (in Chinese)
[16] McCollough J P, Gannon J L, Baker D N, Gehmeyr M 2008 Space Weather 6 S10001
[17] Yang X C, Zhu G W, Zhang X X, Sun Y Q, Liang J B, Wei X H 2014 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 119 9038
-
表 1 FY-4A和GOES-13高能电子观测能谱
Table 1. Energy spectrum of FY-4A and GOES-13 energetic electron detector.
卫星 探测器 电子能量 FY-4A HET2 ≥ 1.5 MeV ≥ 2 MeV ≥ 3 Mev GOES-13 EPEAED > 0.6 MeV > 2 MeV -
[1] 赵华, 朱光武, 王世金, 高玉芬, 刘振兴 2003 中国科学D辑 33 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao H, Zhu G W, Wang S J, Gao Y F, Liu Z X 2003 Sci. ChinaD 33 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 黄建国, 韩建伟 2010 59 2907
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang J G, Han J W 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 2907
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 宗秋刚, 袁憧憬, 王永福, 苏振鹏 2013 中国科学: 地球科学 43 951
Zong Q G, Yuan C J, Wang Y F, Su Z P 2013 Sci. China: Earth Sci. 43 951
[4] Friedel R H W, Reeves G, Belian D, Cayton T, Mouikis C, Korth A, Blake B, Fennel J, SelesnickR, Baker D, Onsagers T, Kaneka1 S 2000 Adv. Space Res. 26 93
[5] Chen Y, Friedel R H W, Reeves G D, Onsager T G, Thomsen M F 2005 J. Geophy. Res. 110 A10210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Chen Y, Friedel R H W, Reeves G D, Cayton T E, Christensen R 2007 J. Geophys. Res. 112 A11214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yang X C, Ni B B, Yu J, Zhang Y, Zhang X X, Sun Y Q 2017 J. Geophys. Res. 122 6255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Friedel R H W, Bourdarie S, Cayton T E 2005 Space Weather 3 S09B04
[9] Meredith Nigel P, Horne Richard B, Isles John D 2015 Space Weather 13 170
[10] Ganushkina N Yu, Sillanpää I, Welling D 2019 Space Weather 17 687
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 王馨悦, 王春琴, 杨晓超, 王世金 2008 地球 55 611
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X Y, Wang C Q, Yang X C, Wang S J 2008 Chin. J. Geophys. 55 611
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 于超, 李嘉巍, 张效信, 李传起, 王春琴, 王世金 2012 地球 55 2835
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu C, Li J W, Zhang X X, Li C Q, Wang C Q, Wang S J 2012 Chin. J. Geophys. 55 2835
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li X L, Temerin M A 2001 Space Sci. Rev. 95 569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 徐荣栏, 李磊 2005 磁层粒子动力学 (北京: 科学出版社) 第84—92页
Xu R L, Li L 2005 Magnetosphereic Partical Dynamics (Beijing: Science Press) pp84–92 (in Chinese)
[15] 涂传治 1988 日地空间物理学: 行星际与磁层(下册) (北京: 科学出版社) 第111—118页
Tu C Z 1988 Solar-Terrestrial Space Physics: Interplanetary and Magnetosphere (Vol.2) (Beijing: Science Press) pp111–118 (in Chinese)
[16] McCollough J P, Gannon J L, Baker D N, Gehmeyr M 2008 Space Weather 6 S10001
[17] Yang X C, Zhu G W, Zhang X X, Sun Y Q, Liang J B, Wei X H 2014 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 119 9038
计量
- 文章访问数: 9051
- PDF下载量: 73
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: