-
本文数值研究了自旋
$ S=1/2,1,2 $ 的各向异性量子XXZD模型的Luttinger液体参数K. 首先, 利用$ U(1) $ 对称的无限矩阵乘积态算法(iMPS)得到在Luttinger液体相中的基态波函数. 通过二分量子涨落F和有限纠缠标度指数$ \kappa $ 的关系可以提取出Luttinger液体参数K. 对于自旋$ S=1/2, D=0 $ 的量子XXZD模型, 本文利用$ U(1) $ 对称的iMPS的算法得到的数值结果与精确解符合得很好. 在参数$ D\leqslant -2 $ 的区域, 自旋$ S=1 $ 的XXZD模型的哈密顿量可以被映射到一个自旋$ S=1/2 $ 的有效XXZ模型, 本文计算了在这个区域内的Luttinger液体参数K与精确解基本是一致的, 相对误差小于$ 1\% $ . 此外, 在参数$ \varDelta=-0.5, D=0 $ 处, 本文数值计算的Luttinger液体参数与密度矩阵重整化群(DMRG)的结果也是一致的. 这些研究结果表明: 当系统具有$ U(1) $ 对称性时, 利用$ U(1) $ 对称的iMPS的方法可以提取无能隙相中的Luttinger液体参数. 本文利用此方法还研究了自旋$ S=1 $ 的XXZD模型在其他参数下的Luttinger液体参数, 以及自旋$ S=2 $ 的XXZD模型的Luttinger液体参数.-
关键词:
- 无限矩阵乘积态 /
- Luttinger液体参数 /
- 二分量子涨落
We numerically calculate Luttinger liquid parameter K in the anisotropic spin XXZD models with spin$s = 1/2$ , 1, and 2. In order to obtain groundstate wavefunctions in Luttinger liquid phases, we employ the$U(1)$ symmetric infinite matrix product states algorithm (iMPS). By using relation between the bipartite quantum fluctuations F and the so-called finite-entanglement scaling exponents$\kappa$ , the Luttinger liquid parameter K can be extracted. For$s = 1/2$ and$D=0$ , the numerically extracted Luttinger liquid parameter K is shown to be good agreement with the exact value. On using the fact that the spin-1 XXZD Hamiltonian with$ D \leqslant - 2$ can be mapped to an effective spin-1/2 XXZ model, we calculate the Luttinger liquid parameter for the region of$ D \leqslant - 2$ . It is shown that our numerical value of the Luttinger liquid parameter agree well with the exact values, here, the relative error less than$1\%$ . Also, our Luttinger liquid parameter at$\Delta = - 0.5$ and$ D = 0$ is shown to be consistent with the result form the density matrix renormalization group (DMRG) method. These results suggest that the$U(1)$ symmetric iMPS method can be applicable to calculate Luttinger liquid parameters if any system has a$U(1)$ symmetry for gapless phases. For instance, we present our Luttinger liquid parameters for the first time for the spin-1 XXZD model under the other parameters and the spin-2 XXZD model with$D = 1.5$ .-
Keywords:
- infinite matrix product state /
- Luttinger liquid parameter /
- bipartite quantum fluctuations
[1] Sachdev S 1999 Quantum Phase Transitions (Cambridge: Cambridge University)pp3—5
[2] White S R 1992 Phys. Rev. Lett. 69 2863
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Landau D P, Binder K 2011 A Guide to Monte-Carlo Simulatios in Statistical Physics (Cambridge: Cambridge University)pp70-73
[4] Evenbly G, Vidal G 2009 Phys. Rev. B 79 144108.
[5] Jordan J, Orus R, Vidal G, Verstraete F, Cirac J I 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 250602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Singh S, Zhou H Q, Vidal G 2010 New J. Phys. 12 033029
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Jiang H C, Weng Z Y, Xiang T 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 090603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Czarnik P, Dziarmaga J 2015 Phys. Rev. B 92 035120.
[9] Li W, Ran S J, Gong S S, Zhao Y, Xi B, Ye F, Su G 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 106 127202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chen B B, Chen L, Chen Z Y, Li W, Weichselbaum A 2018 Phys. Rev. X 8 031082
[11] Corboz P, Czarnik P, Kapteijns G, Tagliacozzo L 2018 Phys. Rev. X 8 031031
[12] Singh S, Pfeifer R N C, Vidal G 2010 Phys. Rev. A 82 050301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Haghshenas R, Sheng D N 2017 arXiv: 1711.07584v1 [cond-mat.str-el]
[14] Singh S, Pfeifer R N C, Vidal G 2011 Phys. Rev. B 83 115125
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Song H F, Rachel S, Hur K Le 2010 Phys. Rev. B 82 012405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Song H F, Rachel S, Flindt C,Klich I, Laflorencie N, Hur K Le 2012 Phys. Rev. B 85 035409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yang M F 2007 Phys. Rev. B 76 180403(R).
[18] Boschi C D E, Ercolessi E, Ortolani F, Roncaglia M 2003 Eur. Phys. J. B 35 465
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Pollmann F, Mukerjee S, Turner A, Moore J E 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 102 255701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 苏耀恒, 陈爱民, 王洪雷, 相春环 2017 66 120301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Su Y H, Chen A M, Wang H L, Xiang C H 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 120301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Yang C N, Yang C P 1966 Phys. Rev. 150 321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Chen W, Hida K, Sanctuary B C 2003 Phys. Rev. B 67 104401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Kjall J A, Zaletel M P, Mong R S K, Bardarson J H, Pollmann F 2013 Phys. Rev. B 87 235106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
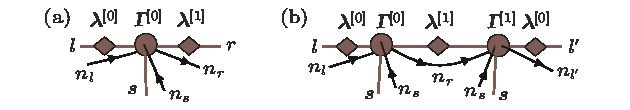
图 2 更新具有
$U(1)$ 对称的MPS的过程(a)把U门作用在具有$U(1)$ 对称的MPS上; (b)吸收U门缩并(a)中的张量使之成为一个两指标张量${ {\varTheta}}$ ;(c)对张量${ {\varTheta}}$ 进行奇异值分解(SVD), 得到新的张量X, Y和$\tilde{{ {\lambda}}_{\rm B}}$ , 同时得到新的粒子数$\tilde{n_r}$ ;(d)插入逆矩阵, 还原原来的原胞结构; (e)得到更新的张量$\tilde{ {\varGamma}}^{\rm A}$ ,$\tilde{ {\varGamma}}^{\rm B}$ 和$\tilde{ {\lambda}}^{\rm B}$ 及粒子数$\tilde{n_r}$ Fig. 2. The process of update the U(1) symmetric MPS (a) applied gate U on the U(1) symmetric MPS, then contract the tensor network (a) into a single tensor
${ {\varTheta}}$ . We compute the singular value decomposition of tensor${ {\varTheta}}$ , and get the new tensor X, Y和$\tilde{{ {\lambda}}_{\rm B}}$ and particle number$\tilde{n_r}$ as in (c). (d) Insert inverse matrix and restore the original tensor structure, we obtain the new tensor$\tilde{ {\varGamma}}^{\rm A}$ ,$\tilde{ {\varGamma}}^{\rm B}$ ,$\tilde{ {\lambda}}^{\rm B}$ and particle number$\tilde{n_r}$ as in (e).表 1 自旋S = 1/2的XXZD模型在临界区的Luttinger液体参数K, 其中参数D = 0
Table 1. Estimates for Luttinger liquid parameter K in the critical phase of spin S = 1/2 XXZD model with the parameter D = 0.
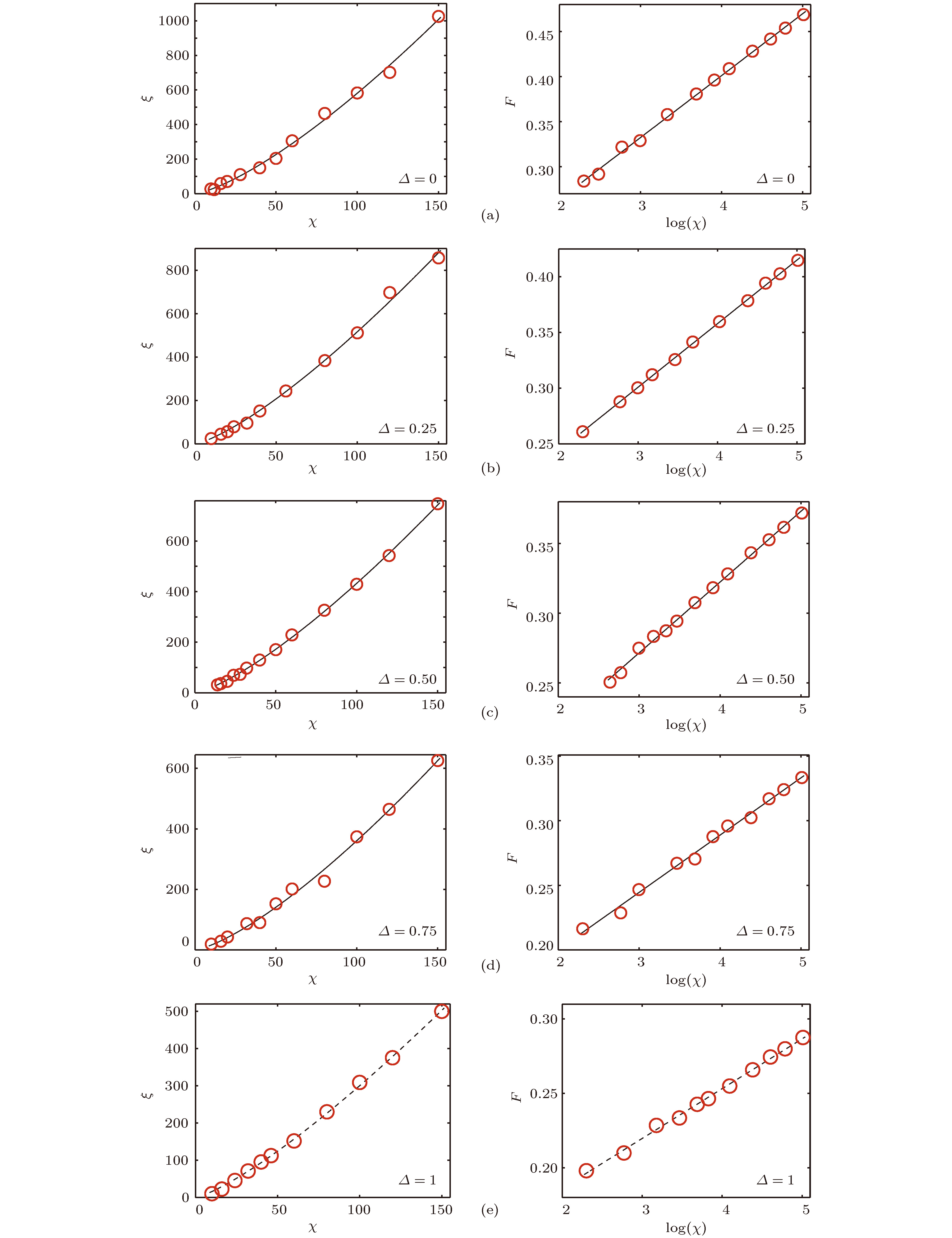
Δ 0 0.25 0.5 0.75 1 K[精确] 1.0 0.8614... 0.75 0.6493... 0.5 K[数值] 0.999 0.856 0.7529 0.6457 0.5198 相对误差 0.001 0.0063 0.0039 0.0053 0.0396 表 2 自旋
$S = 1$ 的XXZD模型在临界区的Luttinger液体参数K, 固定参数$\varDelta = -0.5$ Table 2. Estimates for Luttinger liquid parameter K in the critical phase of spin
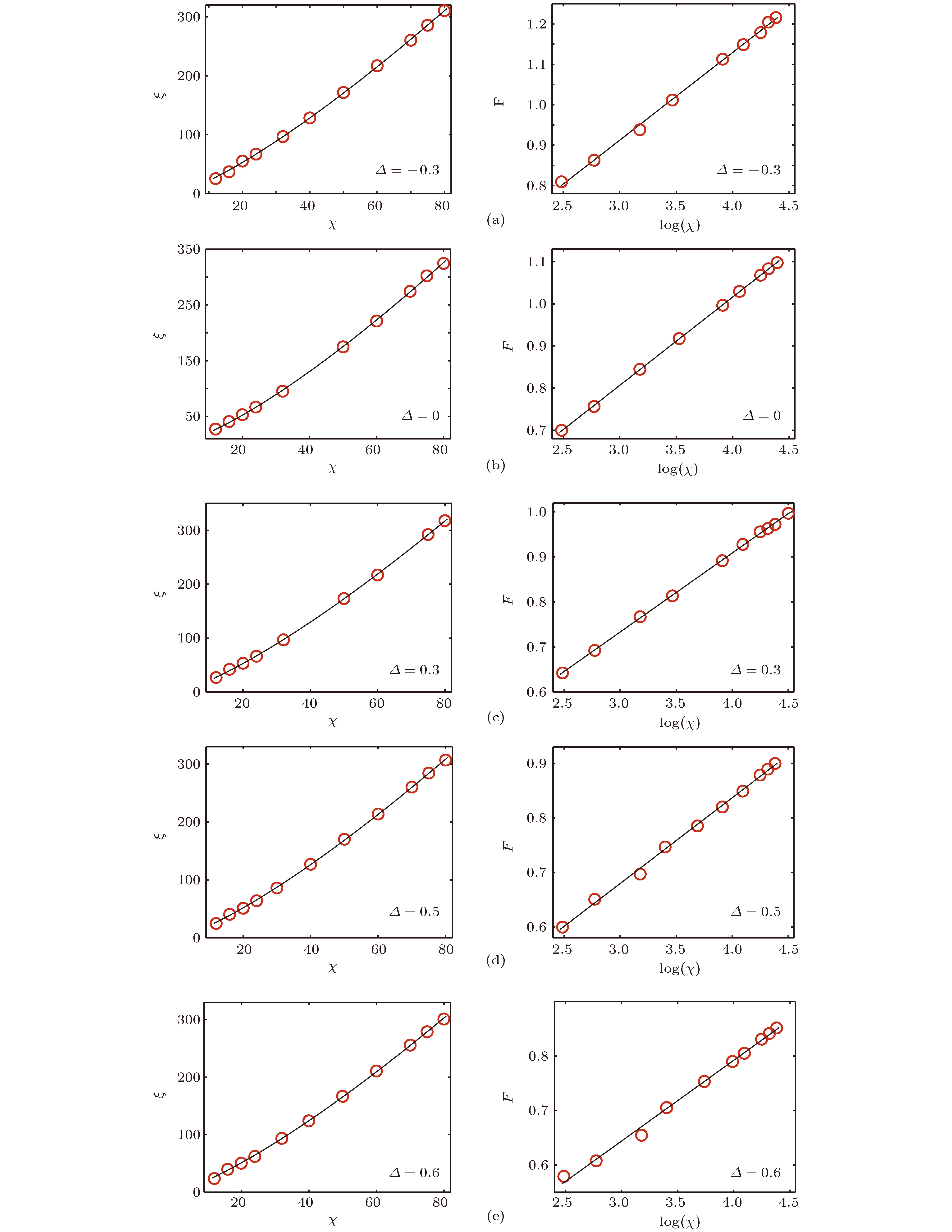
$S = 1$ XXZD model with the parameter$\varDelta = -0.5$ .D –0.3 0 0.3 0.5 0.6 K[数值] 3.3679 3.1275 2.6834 2.4126 2.2745 表 3 自旋S = 2的XXZD模型在临界区的Luttinger液体参数K, 固定参数
$D = 1.5$ Table 3. Estimates for Luttinger liquid parameter K in the critical phase of spin S = 2 XXZD model with the parameter
$D = 1.5$ .Δ 0.4 0.8 1 1.2 1.6 K[数值] 1.652 2.5227 2.4096 2.3546 2.1107 -
[1] Sachdev S 1999 Quantum Phase Transitions (Cambridge: Cambridge University)pp3—5
[2] White S R 1992 Phys. Rev. Lett. 69 2863
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Landau D P, Binder K 2011 A Guide to Monte-Carlo Simulatios in Statistical Physics (Cambridge: Cambridge University)pp70-73
[4] Evenbly G, Vidal G 2009 Phys. Rev. B 79 144108.
[5] Jordan J, Orus R, Vidal G, Verstraete F, Cirac J I 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 250602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Singh S, Zhou H Q, Vidal G 2010 New J. Phys. 12 033029
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Jiang H C, Weng Z Y, Xiang T 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 090603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Czarnik P, Dziarmaga J 2015 Phys. Rev. B 92 035120.
[9] Li W, Ran S J, Gong S S, Zhao Y, Xi B, Ye F, Su G 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 106 127202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chen B B, Chen L, Chen Z Y, Li W, Weichselbaum A 2018 Phys. Rev. X 8 031082
[11] Corboz P, Czarnik P, Kapteijns G, Tagliacozzo L 2018 Phys. Rev. X 8 031031
[12] Singh S, Pfeifer R N C, Vidal G 2010 Phys. Rev. A 82 050301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Haghshenas R, Sheng D N 2017 arXiv: 1711.07584v1 [cond-mat.str-el]
[14] Singh S, Pfeifer R N C, Vidal G 2011 Phys. Rev. B 83 115125
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Song H F, Rachel S, Hur K Le 2010 Phys. Rev. B 82 012405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Song H F, Rachel S, Flindt C,Klich I, Laflorencie N, Hur K Le 2012 Phys. Rev. B 85 035409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yang M F 2007 Phys. Rev. B 76 180403(R).
[18] Boschi C D E, Ercolessi E, Ortolani F, Roncaglia M 2003 Eur. Phys. J. B 35 465
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Pollmann F, Mukerjee S, Turner A, Moore J E 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 102 255701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 苏耀恒, 陈爱民, 王洪雷, 相春环 2017 66 120301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Su Y H, Chen A M, Wang H L, Xiang C H 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 120301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Yang C N, Yang C P 1966 Phys. Rev. 150 321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Chen W, Hida K, Sanctuary B C 2003 Phys. Rev. B 67 104401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Kjall J A, Zaletel M P, Mong R S K, Bardarson J H, Pollmann F 2013 Phys. Rev. B 87 235106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 13110
- PDF下载量: 98
- 被引次数: 0





































 下载:
下载: