-
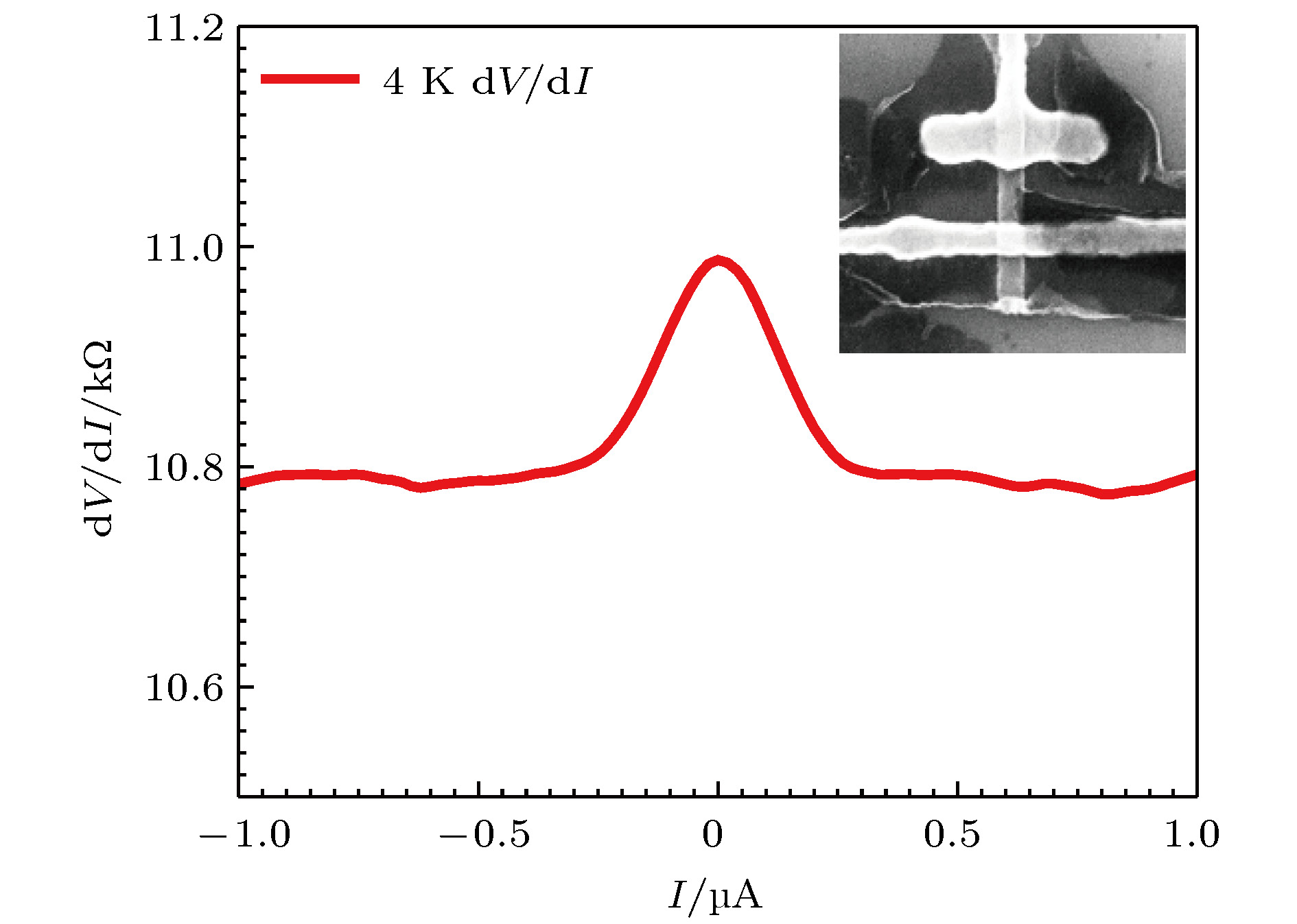
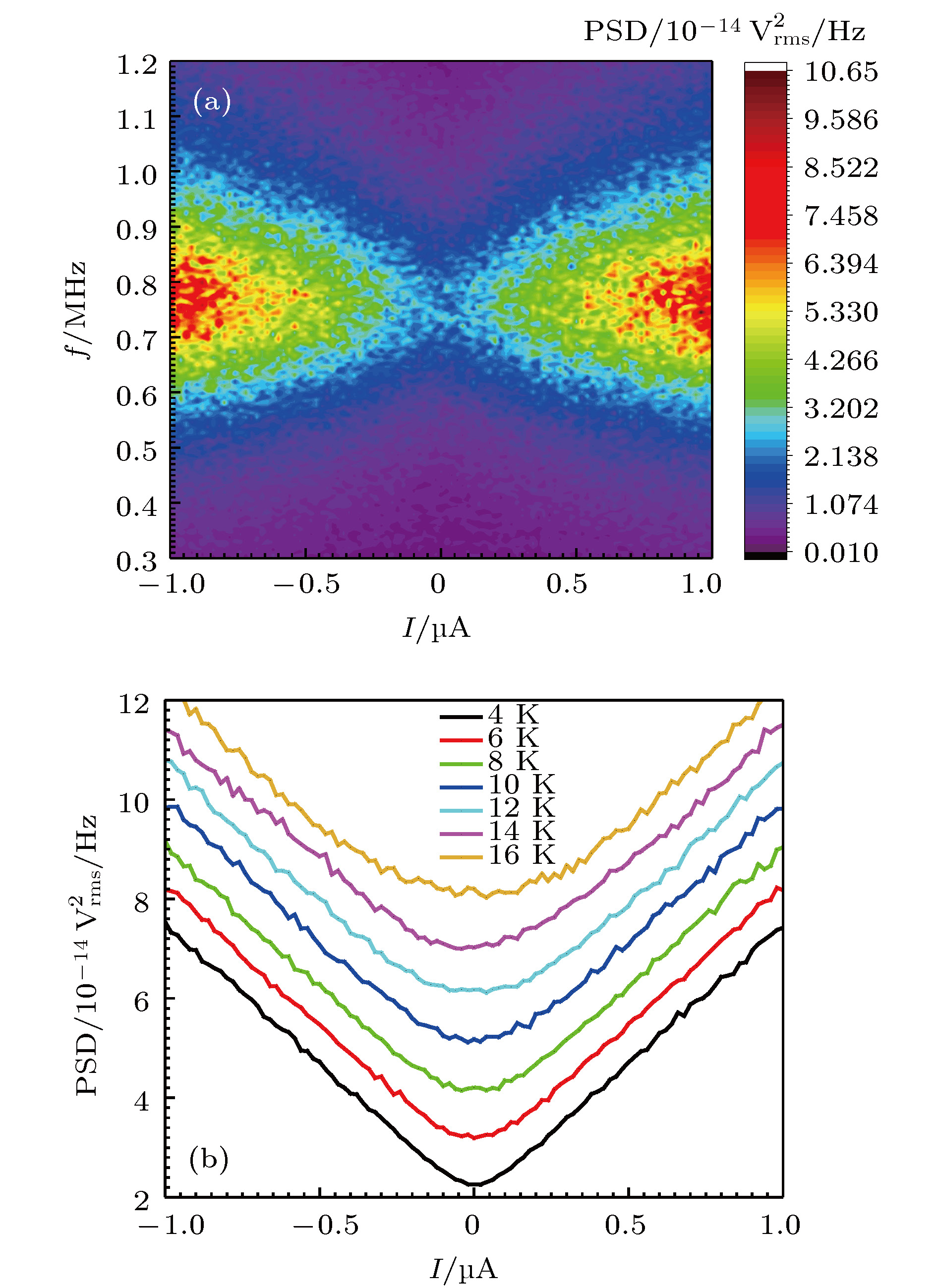
介观体系输运过程中载流子的离散性导致了散粒噪声. 通过测量散粒噪声可以得到传统的基于时间平均值的电导测量无法得到的随时间涨落信息, 因而作为一种重要手段在极低温量子输运研究中得到了一定的应用. 极低温环境下的噪声测量是一种难度很大的极端条件下的微弱信号测量, 通常需要在低温端安装前置放大器并且尽量靠近待测器件以提高测量信噪比和带宽, 因此对放大器的噪声水平和功耗都有严格的要求. 提出了在稀释制冷机内搭建的散粒噪声测量系统, 以及利用此套系统得到了在mK温区超导隧道结散粒噪声的测量结果. 自行研制的高电子迁移率晶体管低温前置放大器采用整体封装, 便于安装在商用干式稀释制冷机的4 K温区, 本底电压噪声为0.25 nV/√Hz, 功耗仅为0.754 mW. 通过对隧道结进行散粒噪声测量, 得到的Fano因子和理论计算吻合.Traditionally, electrical noise is considered as an interference source for low level measurements. Shot noise is the current fluctuation caused by the discreteness of electrons. In a mesoscopic system, shot noise is sensitive to the interaction of charge carriers. Since the 20th century, it has been found that the shot noise measurement can provide the information about quantum fluctuations, which cannot be measured with traditional transport measurement method. It is usually difficult to measure weak noise signal at ultra- low temperature due to technical difficulties. It is necessary to mount a cryogenic preamplifier close to the sample to improve signal-to-noise ratio and to increase the bandwidth. Therefore, the ultra-low background noise and the power consumption of the amplifier should be used. In this report we present a shot noise measurement system at dilution refrigerator temperatures. We also introduce and analyze the noise model of our shot noise measurement system. With customized high electron mobility transistors, we make a series of ultra-low noise cryogenic preamplifiers. All the electronic components of the amplifier are packed into a shielding box, which makes the installation of the cryogenic amplifier more convenient. The amplifier is mounted on the 4 K stage of a dry dilution refrigerator and the total power consumption is less than 0.754 mW. The gains and the background noises of the amplifiers are calibrated with the Johnson-Nyquist noise of the combination of a superconducting resistor and a normal resistor at various temperatures. The measured input referred noise voltage can be as low as 0.25 nV/√Hz. In this report, the performance of the system is demonstrated by the shot noise measurement of an Al/AlOx/Al tunnel junction at various temperatures. Above the superconducting transition temperature of aluminum, the measured Fano factor of the system is very close to 1, which is in a good agreement with the theory prediction.
-
Keywords:
- dilution refrigerator /
- low noise amplifier /
- shot noise /
- tunneling junction
[1] Landauer R 1998 Nature 392 658
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Schottky W 1918 Ann. Phys. 57 541
[3] Beenakker C, Schönenberger C 2003 Phys. Today 56 37
[4] Blanter Y M, Büttiker M 2000 Phys. Rep. 336 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lesovik G B 1989 JETP Lett. 49 513
[6] Buttiker M 1990 Phys. Rev. Lett. 65 2901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Beenakker C W J, Büttiker M 1992 Phys. Rev. B 46 1889
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Reznikov M, Heiblum M, Shtrikman H, Mahalu D 1995 Phys. Rev. Lett. 75 3340
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Kumar A, Saminadayar L, Glattli D C 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 76 2778
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Picciotto R D, Reznikov M, Heiblum M, Umansky V, Bunin G, Mahalu D 1997 Nature 389 162
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Saminadayar L, Glattli D C, Jin Y, Etienne B 1997 Phys. Rev. Lett. 79 2526
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Reznikov M, de Picciotto R, Griffiths T G, Heiblum M, Umansky V 1999 Nature 399 238
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Hasan M Z, Kane C L 2010 Rev. Mod. Phys. 82 3045
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Nayak C, Simon S H, Stern A, Freedman M, Das Sarma S 2008 Rev. Mod. Phys. 80 1083
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhang H, Liu C X, Gazibegovic S, Xu D, Logan J A, Wang G, van Loo N, Bommer J D S, de Moor M W A, Car D, Op Het Veld R L M, van Veldhoven P J, Koelling S, Verheijen M A, Pendharkar M, Pennachio D J, Shojaei B, Lee J S, Palmstrom C J, Bakkers E, Sarma S D, Kouwenhoven L P 2018 Nature 556 74
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Armitage N P, Mele E J, Vishwanath A 2018 Rev. Mod. Phys. 90 015001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Sbierski B, Pohl G, Bergholtz E J, Brouwer P W 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 113 026602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Trescher M, Sbierski B, Brouwer P W, Bergholtz E J 2015 Phys. Rev. B 91 115135
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Matveeva P G, Aristov D N, Meidan D, Gutman D B 2017 Phys. Rev. B 96 165406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Yang Y L, Bai C X, Xu X G, Jiang Y 2018 Nanotechnology 29 074002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Golub A, Horovitz B 2011 Phys. Rev. B 83 153415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Bolech C J, Demler E 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 237002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Soller H, Komnik A 2014 Physica E 63 99
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Bolech C J, Demler E 2008 Physica B 403 994
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Akhmerov A R, Dahlhaus J P, Hassler F, Wimmer M, Beenakker C W 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 106 057001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Lü H F, Guo Z, Ke S S, Guo Y, Zhang H W 2015 J. Appl. Phys. 117 164312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] DiCarlo L, Zhang Y, McClure D T, Marcus C M, Pfeiffer L N, West K W 2006 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 77 073906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Hashisaka M, Nakamura S, Yamauchi Y, Kasai S, Kobayashi K, Ono T 2008 Phys. Status Solidi C 5 182
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Arakawa T, Nishihara Y, Maeda M, Norimoto S, Kobayashi K 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 103 172104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Robinson A M, Talyanskii V I 2004 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 75 3169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Ronen Y, Cohen Y, Kang J H, Haim A, Rieder M T, Heiblum M, Mahalu D, Shtrikman H 2016 Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 113 1743
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 陈文豪, 杜磊, 庄奕琪, 包军林, 何亮, 陈华, 孙鹏, 王婷岚 2011 60 050704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen W H, Du L, Zhuang Y Q, Bao J L, He L, Chen H, Sun P, Wang T L 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 050704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Yang W H, Wei J 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 060702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Dong Q, Liang Y X, Ferry D, Cavanna A, Gennser U, Couraud L, Jin Y 2014 Appl. Phys. Lett. 105 013504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Hashisaka M, Yamauchi Y, Nakamura S, Kasai S, Kobayashi K, Ono T 2008 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 109 012013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Dicarlo L, Williams J R, Zhang Y, McClure D T, Marcus C M 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 156801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 不同课题组及公司的低温放大器功耗和本底电压噪声对比
Table 1. Comparison of power consumption and background noises of different cryogenic amplifiers made by different groups and companies.
表 2 不同架构的低温放大器参数对比
Table 2. Comparison of our home-made cryogenic amplifiers.
放大器架构 HEMT类型 增益/倍 功耗/mW 带宽 1/f噪声的拐角 等效输入电压噪声/nV·Hz–1/2 共源极 + 源极跟随 ATF33143 15.8 3.568 10 Hz—20 MHz 300 kHz 0.45 共源极 定制* 10 0.754 10 Hz—1 MHz 3 kHz 0.25 共源共栅 + 源极跟随 定制* 25 3 500 Hz—20 MHz 30 kHz 0.17 注: *表示由法国国家科学院纳米科学与技术中心金勇课题组提供的HEMT 表 3 不同温度下, 拟合得到的Fano因子
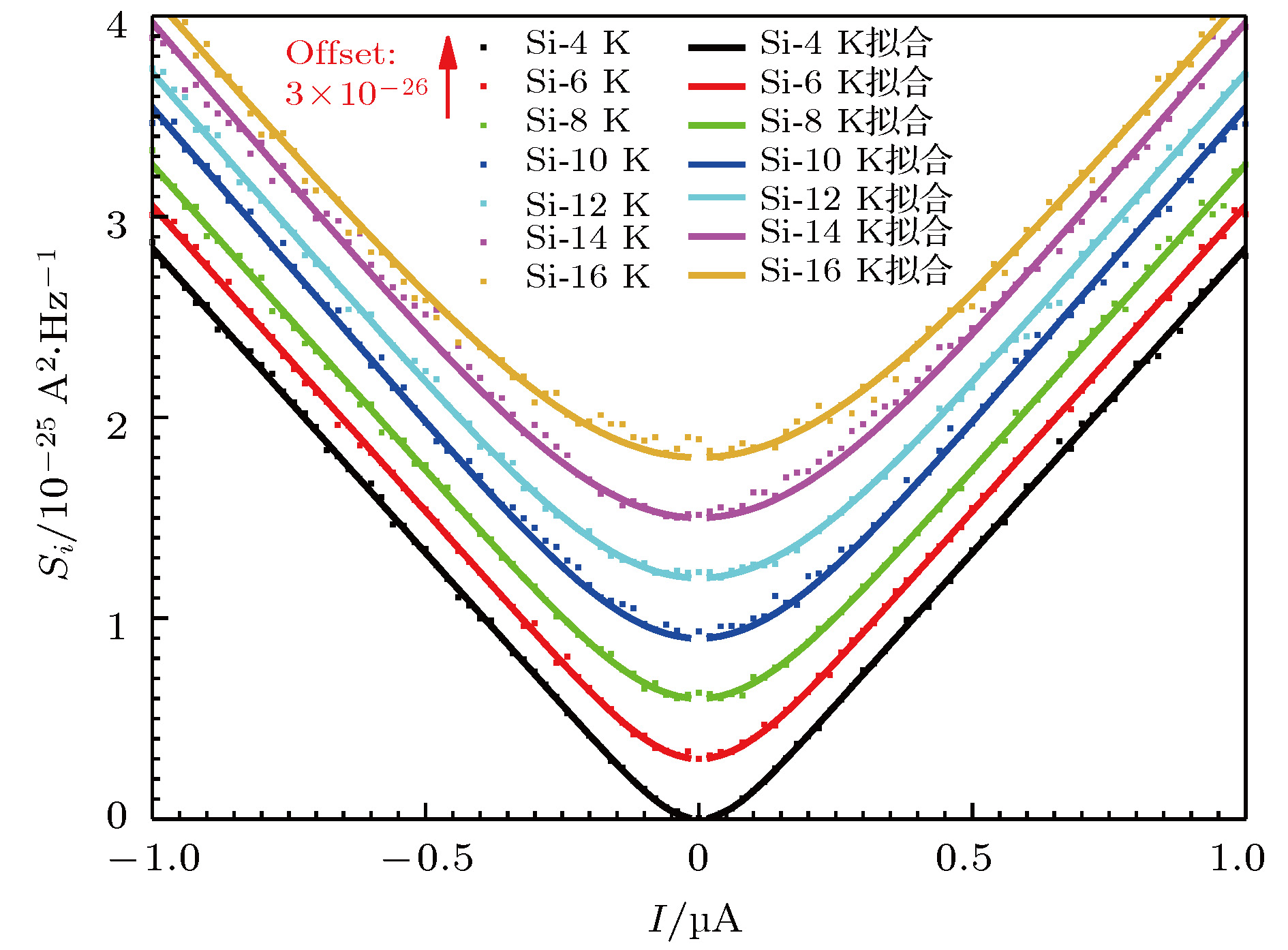
Table 3. Fano factors are obtained by fitting the test data at different temperature.
T/K 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 F 0.94827 0.95085 0.95115 0.98194 0.97113 0.99088 0.96408 -
[1] Landauer R 1998 Nature 392 658
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Schottky W 1918 Ann. Phys. 57 541
[3] Beenakker C, Schönenberger C 2003 Phys. Today 56 37
[4] Blanter Y M, Büttiker M 2000 Phys. Rep. 336 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lesovik G B 1989 JETP Lett. 49 513
[6] Buttiker M 1990 Phys. Rev. Lett. 65 2901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Beenakker C W J, Büttiker M 1992 Phys. Rev. B 46 1889
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Reznikov M, Heiblum M, Shtrikman H, Mahalu D 1995 Phys. Rev. Lett. 75 3340
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Kumar A, Saminadayar L, Glattli D C 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 76 2778
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Picciotto R D, Reznikov M, Heiblum M, Umansky V, Bunin G, Mahalu D 1997 Nature 389 162
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Saminadayar L, Glattli D C, Jin Y, Etienne B 1997 Phys. Rev. Lett. 79 2526
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Reznikov M, de Picciotto R, Griffiths T G, Heiblum M, Umansky V 1999 Nature 399 238
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Hasan M Z, Kane C L 2010 Rev. Mod. Phys. 82 3045
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Nayak C, Simon S H, Stern A, Freedman M, Das Sarma S 2008 Rev. Mod. Phys. 80 1083
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhang H, Liu C X, Gazibegovic S, Xu D, Logan J A, Wang G, van Loo N, Bommer J D S, de Moor M W A, Car D, Op Het Veld R L M, van Veldhoven P J, Koelling S, Verheijen M A, Pendharkar M, Pennachio D J, Shojaei B, Lee J S, Palmstrom C J, Bakkers E, Sarma S D, Kouwenhoven L P 2018 Nature 556 74
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Armitage N P, Mele E J, Vishwanath A 2018 Rev. Mod. Phys. 90 015001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Sbierski B, Pohl G, Bergholtz E J, Brouwer P W 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 113 026602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Trescher M, Sbierski B, Brouwer P W, Bergholtz E J 2015 Phys. Rev. B 91 115135
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Matveeva P G, Aristov D N, Meidan D, Gutman D B 2017 Phys. Rev. B 96 165406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Yang Y L, Bai C X, Xu X G, Jiang Y 2018 Nanotechnology 29 074002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Golub A, Horovitz B 2011 Phys. Rev. B 83 153415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Bolech C J, Demler E 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 237002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Soller H, Komnik A 2014 Physica E 63 99
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Bolech C J, Demler E 2008 Physica B 403 994
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Akhmerov A R, Dahlhaus J P, Hassler F, Wimmer M, Beenakker C W 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 106 057001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Lü H F, Guo Z, Ke S S, Guo Y, Zhang H W 2015 J. Appl. Phys. 117 164312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] DiCarlo L, Zhang Y, McClure D T, Marcus C M, Pfeiffer L N, West K W 2006 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 77 073906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Hashisaka M, Nakamura S, Yamauchi Y, Kasai S, Kobayashi K, Ono T 2008 Phys. Status Solidi C 5 182
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Arakawa T, Nishihara Y, Maeda M, Norimoto S, Kobayashi K 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 103 172104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Robinson A M, Talyanskii V I 2004 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 75 3169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Ronen Y, Cohen Y, Kang J H, Haim A, Rieder M T, Heiblum M, Mahalu D, Shtrikman H 2016 Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 113 1743
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 陈文豪, 杜磊, 庄奕琪, 包军林, 何亮, 陈华, 孙鹏, 王婷岚 2011 60 050704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen W H, Du L, Zhuang Y Q, Bao J L, He L, Chen H, Sun P, Wang T L 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 050704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Yang W H, Wei J 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 060702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Dong Q, Liang Y X, Ferry D, Cavanna A, Gennser U, Couraud L, Jin Y 2014 Appl. Phys. Lett. 105 013504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Hashisaka M, Yamauchi Y, Nakamura S, Kasai S, Kobayashi K, Ono T 2008 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 109 012013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Dicarlo L, Williams J R, Zhang Y, McClure D T, Marcus C M 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 156801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 12149
- PDF下载量: 223
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: