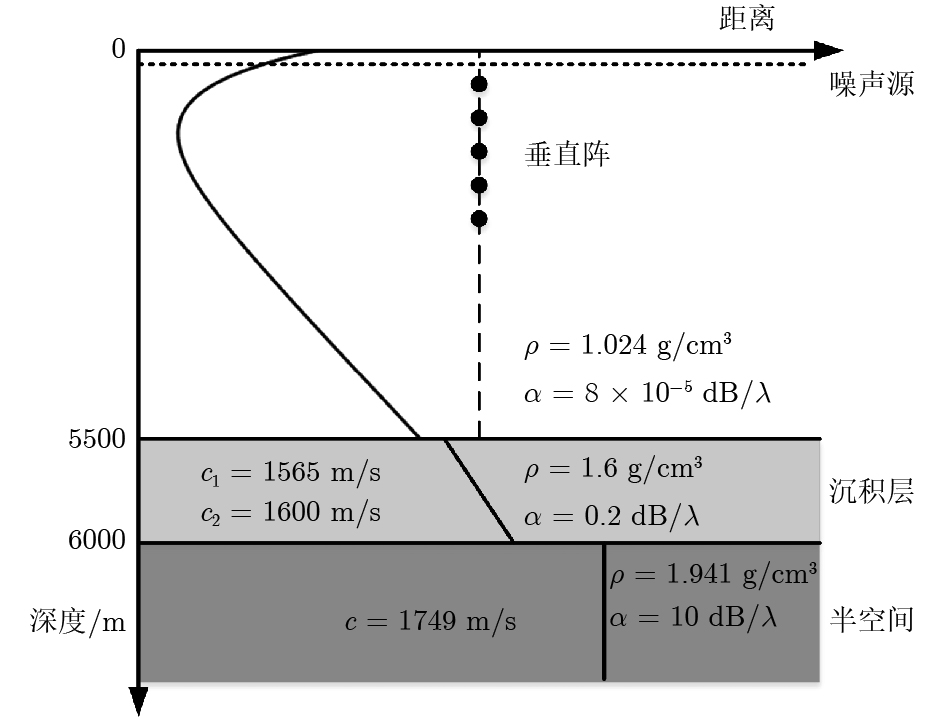
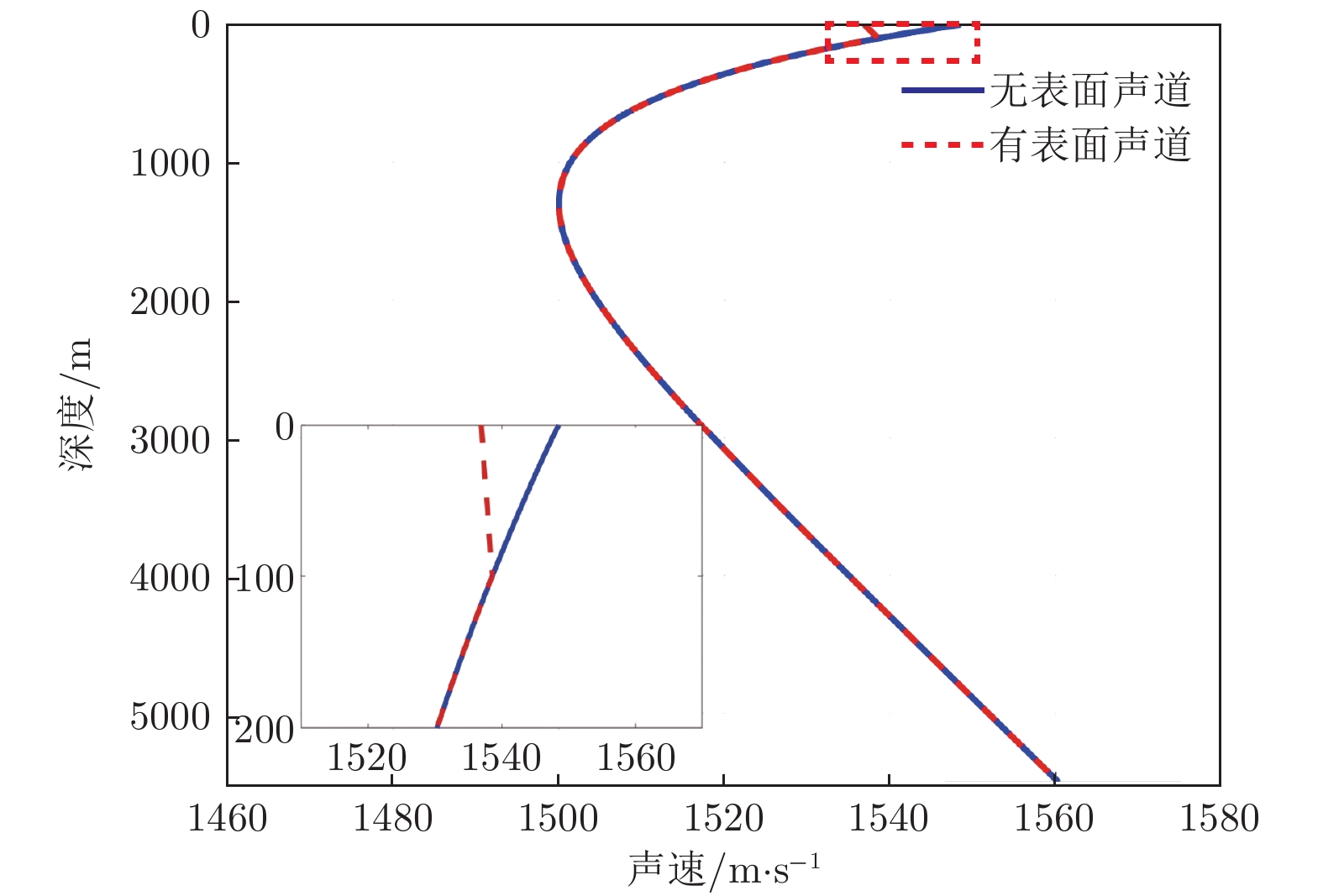
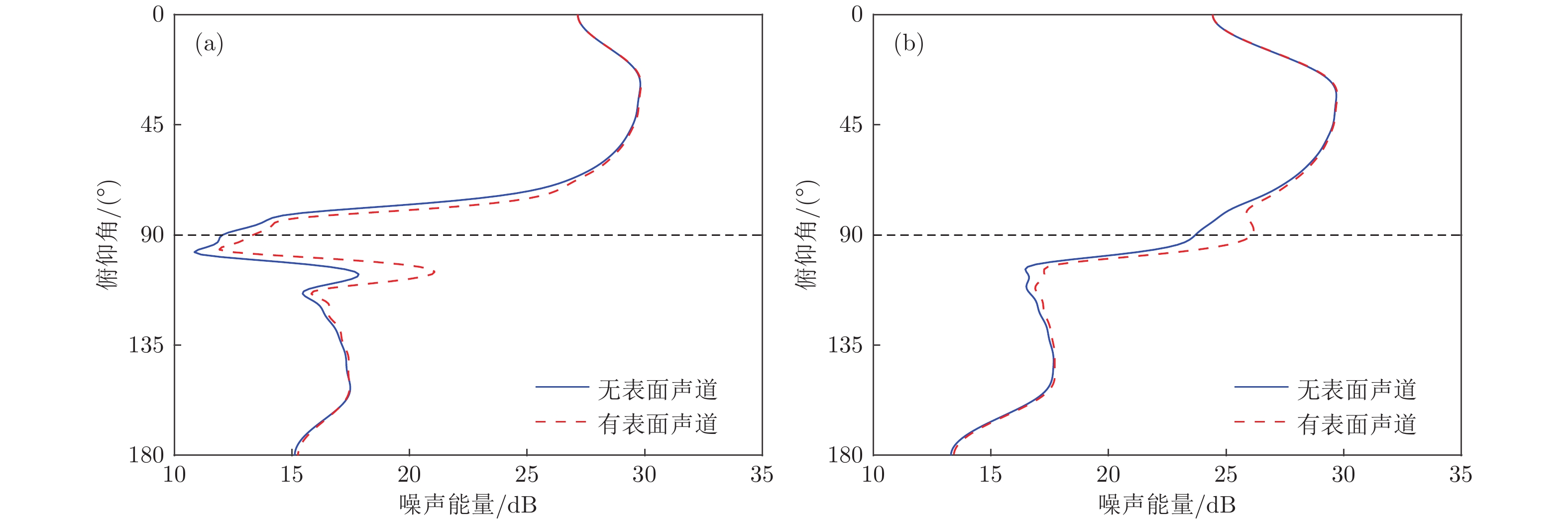
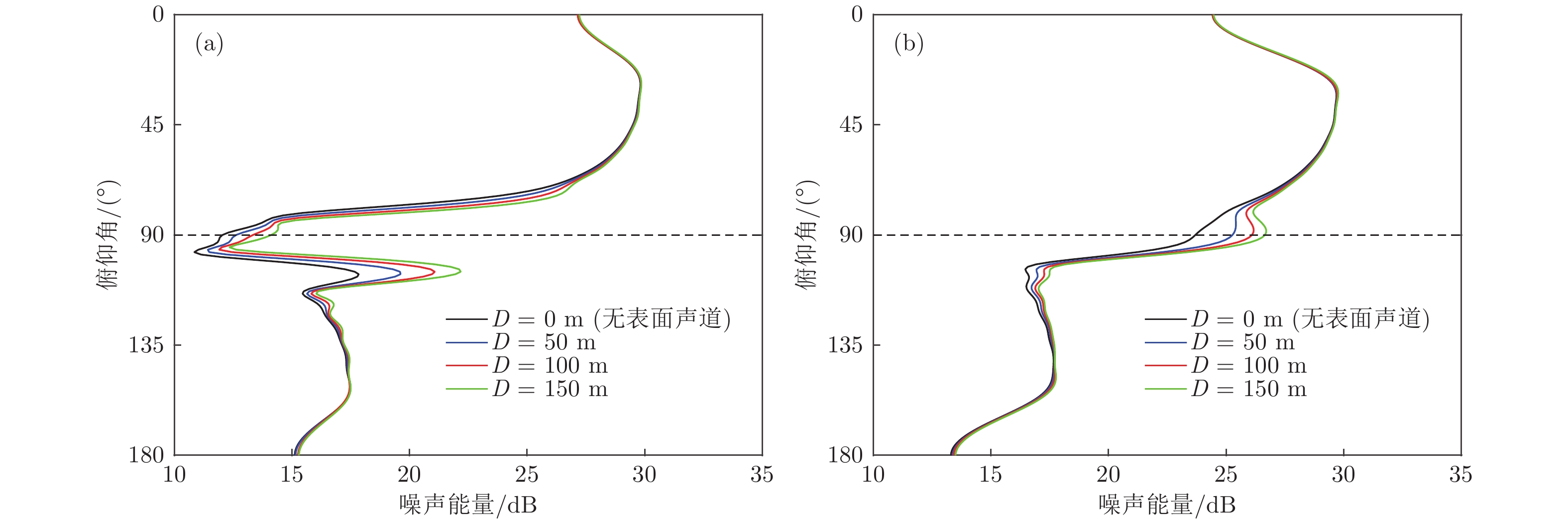
-
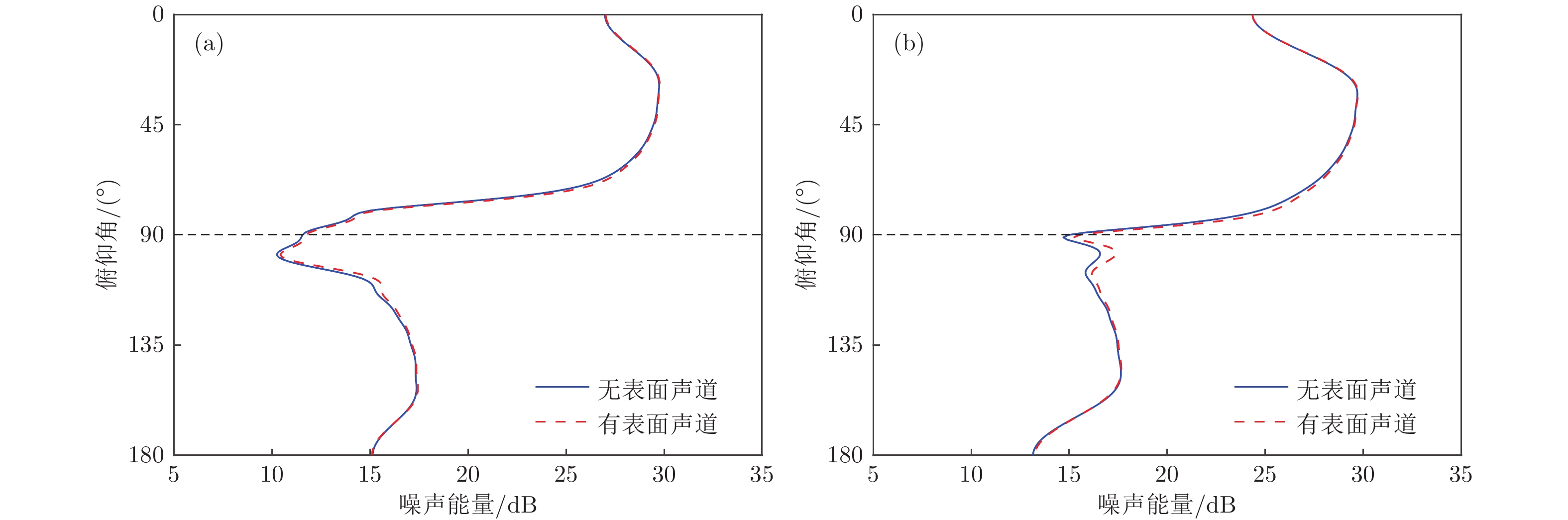
水下风成噪声的垂直空间特性包括噪声垂直方向性和垂直相关性, 研究海洋环境对其影响规律对提升声呐性能、增加海洋环境参数反演的准确性具有重要意义. 本文利用Pekeris割线下的简正波理论描述噪声的传播过程, 研究了深海环境下存在表面声道时, 表面声道以下噪声垂直空间特性的变化规律及其原因. 研究表明, 在临界深度以上, 表面声道的存在导致噪声垂直方向性在水平凹槽边缘靠近海底方向上的峰值升高, 噪声垂直相关性随垂直距离增加先后周期地向正相干和负相干方向偏移; 在临界深度以下, 表面声道的存在导致水平方向上的噪声能量增强, 噪声垂直相关性整体向正相干方向偏移. 当表面声道的参数变化时, 表面声道的厚度变化对噪声垂直空间特性影响较大, 而表面声道内的声速梯度变化对噪声垂直空间特性几乎没有影响. 结合各类简正波的变化分析表明, 存在表面声道时, 噪声源激发的折射简正波阶数增加, 强度增强, 是表面声道引起噪声垂直空间特性变化的主要原因.Vertical spatial characteristics of the wind-generated noise include the noise vertical directionality and the noise vertical coherence, which seriously affect the performance of sonar devices and play an important role in ocean environment parameters inversion. In this paper, we investigate the influence of surface duct on the noise vertical spatial characteristics at the depths below the duct. The Kuperman-Ingenito (K/I) model is employed to describe the distribution of the noise sources, and Pekeris-branch-cut-based normal modes are used to represent the Green's functions between the noise sources and the receivers. Both the noise vertical directionality and the noise vertical coherence are expressed as a function of the normal modes, so that we can investigate the physical reason for the variance of the noise vertical spatial characteristics by analyzing the variance of the normal modes. The numerical simulations on the noise vertical spatial characteristics show that the influence of surface duct above the critical depth is different from that below the critical depth. Above the critical depth, there exists a peak in the noise vertical directionality at the edge of the horizontal notch close to the bottom side. In the presence of surface duct, this peak significantly rises up, and the noise vertical coherence deviates from that in the absence of surface duct and tends to be perfect positive coherence and perfect negative coherence periodically as the vertical distance between the two receivers increases. On the other hand, below the critical depth, the noise power comes from the horizontal direction becomes stronger and the noise vertical coherence tends to be perfect positive coherence in the presence of surface duct as compared with the case in the absence of surface duct. Moreover, the influence will become severer as the thickness of the surface duct increases, while almost keep unchanged when the sound speed gradient in the surface duct varies. The modal analysis indicates that the noise source excites more refracted normal modes with stronger modal intensity in the presence of surface duct, and the excited refracted normal modes become more and stronger if the surface duct is thicker. As the result, the increase of the refracted mode number and the enhancement of their modal intensity cause the vertical spatial characteristics of noise to change.
-
Keywords:
- wind-generated noise /
- surface duct /
- noise vertical directionality /
- noise vertical coherence /
- normal modes
[1] Carey W M, Evans R B 2011 Ocean Ambient Noise (New York: Springer) pp1−7
[2] Waite A D 2002 Sonar for Practising Engineer (Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons) pp 86−89
[3] 殷宝友, 马力, 林建恒 2012 声学学报 37 424
Yin B Y, Ma L, Lin J H 2012 Acta Acustia 37 424
[4] 江鹏飞, 林建恒, 孙军平, 衣雪娟 2017 66 014306
Jiang P F, Lin J H, Sun J P, Yi X J 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 014306
[5] Chapman N R, Cornish J W 1993 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 93 782
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 林建恒, 常道庆, 马力, 李学军, 蒋国健 2001 声学学报 26 217
Lin J H, Chang D Q, Ma L, Li X J, Jiang G J 2001 Acta Acustia 26 217
[7] Cron B F, Sherman C H 1962 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 34 1732
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kuperman W A, Ingenito F 1980 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 67 1988
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Carey W M, Evans R B, Davis J A, Botseas G 1990 IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 15 324
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Perkins J S, Kuperman W A, Ingenito F, Fialkows L T, Glattere J 1993 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 93 739
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Hamson R M 1985 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 78 1702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Yang T C, Yoo K 1997 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 101 2541
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Rouseff D, Tang D 2006 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 120 1284
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 江鹏飞, 林建恒, 马力, 蒋国健 2013 声学学报 38 724
Jiang P F, Lin J H, Ma L, Jiang G J 2013 Acta Acustia 38 724
[15] 周建波, 朴胜春, 刘亚琴, 祝捍皓 2017 66 014301
Zhou J B, Piao S C, Liu Y Q, Zhu H H 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 014301
[16] Buckingham M J 2013 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 134 950
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 刘姗琪, 李风华 2015 声学技术 34 143
Liu S Q, Li F H 2015 Tech. Acoust. 34 143
[18] 王璟琰, 李风华 2016 声学技术 35 109
Wang J Y, Li F H 2016 Tech. Acoust. 35 109
[19] 刘伯胜, 雷家煜 2010 水声学原理(哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学出版社)第26−27页
Liu B S, Lei J Y 2010 Principle of Underwater Acoustics (Haerbin: Harbin Engineering University Press) pp26−27(in Chinese)
[20] 汪德昭, 尚尔昌 2013 水声学(北京: 科学出版社)第24−25页
Wang D Z, Shang E C 2013 Underwater Acousitcs (Beijing: Science Press) pp24−25(in Chinese)
[21] Labianca F M 1973 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 53 1137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Urick R J 1975 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 58 S121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Pekeris C L 1948 Geol. Soc. Am. Mem. 27 1
[24] Jensen F B, Kuperman W A, Porter M B, Schmidt H 2011 Computational Ocean Acoustics (New York: Springer) pp25−26
[25] Ewing W M, Jardetzkey W S, Press F 1957 Elastic Waves in Layered Media (New York: McGraw-Hill) pp 126−137
[26] Bartberger C L 1977 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 61 1643
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Jiang G Y, Sun C, Liu X H, Xie L, Shao X, Kong D Z 2017 OCEANS Aberdeen, UK, June 19−22 2017 pp1−6
[28] Munk W H 1974 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 55 220
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 段睿 2016 博士学位论文(西安: 西北工业大学)
Duan R 2016 Ph. D. Dissertation (Xi'an: Northwestern Polytechnical University) (in Chinese)
[30] Cox H 1973 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 54 1289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 张旭, 张永刚, 张胜军, 吴世华 2009 热带海洋学报 28 23
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X, Zhang Y G, Zhang S J, Wu S H 2009 J. Trop. Oceanograph. 28 23
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
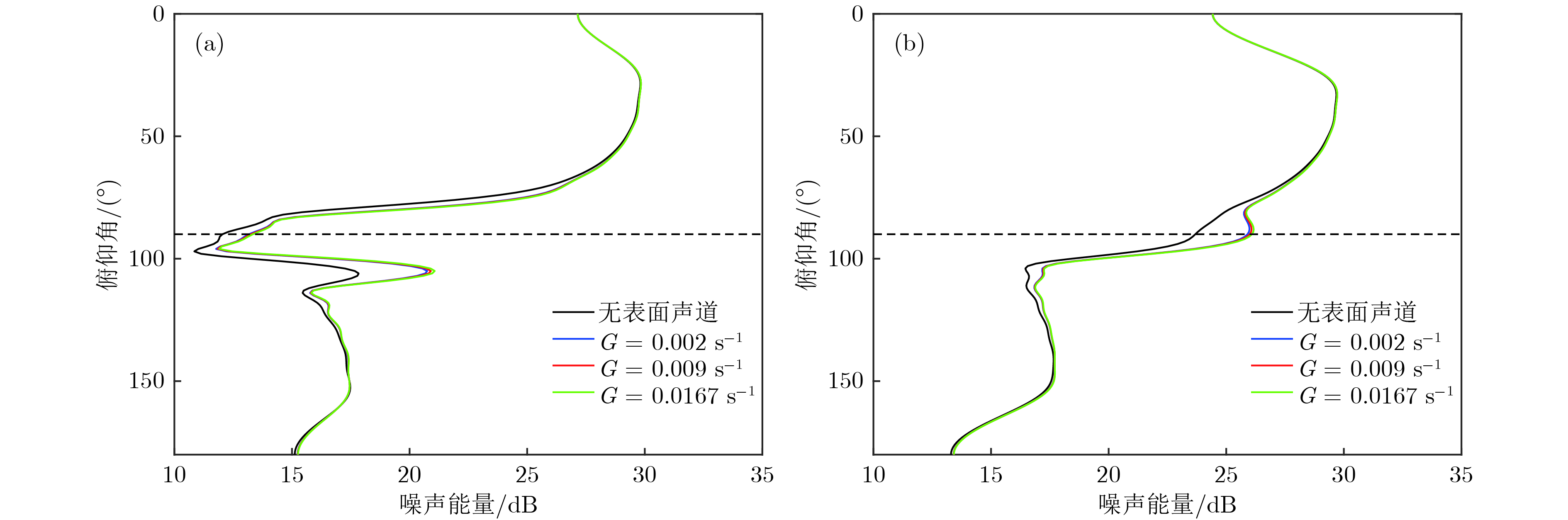
图 9 无表面声道及表面声道内的声速梯度为0.002, 0.009和0.0167 s−1时, 1300和5000 m 深度上的噪声垂直方向性 (a) 1300 m; (b) 5000 m
Fig. 9. Vertical directionality of the noise at 1300 and 5000 m in absence of surface duct and with the sound speed gradient in the 100 m-thick surface duct varying from 0.002 to 0.009 and 0.0167 s−1: (a) 1300 m; (b) 5000 m.
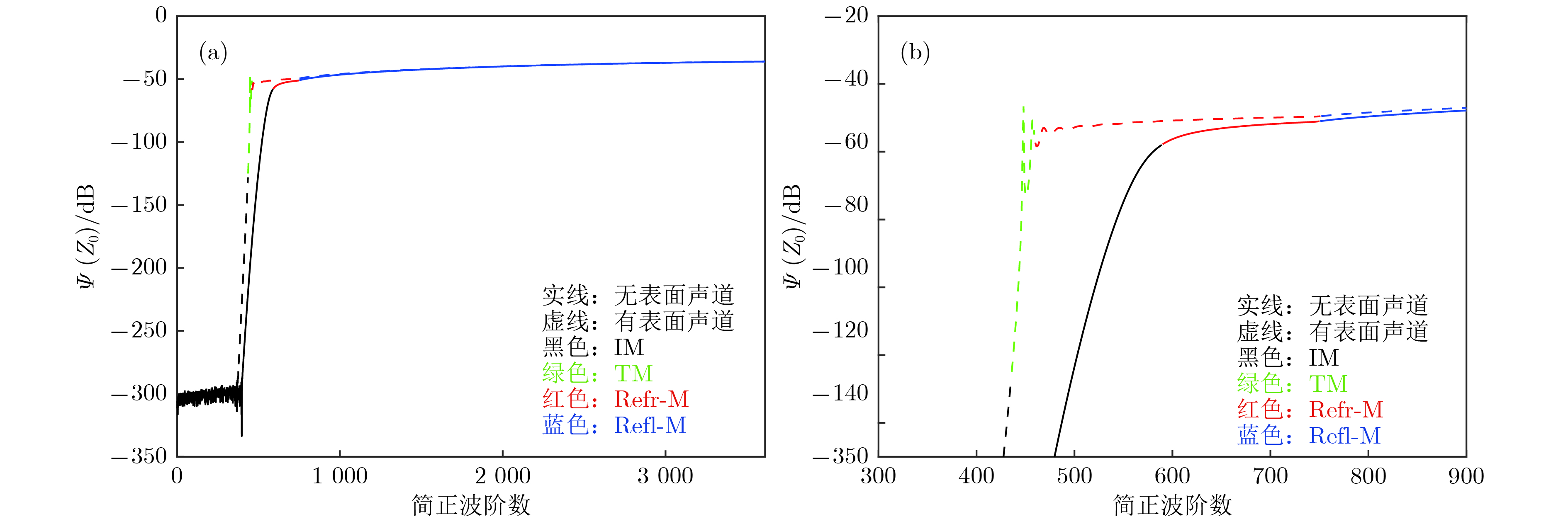
图 11 有无表面声道时各阶简正波的简正波强度
$\scriptstyle \varPsi(z_0) $ (a) 整体图; (b) 局部放大图Fig. 11. Modal intensity
$\scriptstyle \varPsi(z_0) $ of noise-sources-generated normal modes in absence and in presence of surface duct: (a) The overall plot ; (b) zoom in Fig. (a).图 12
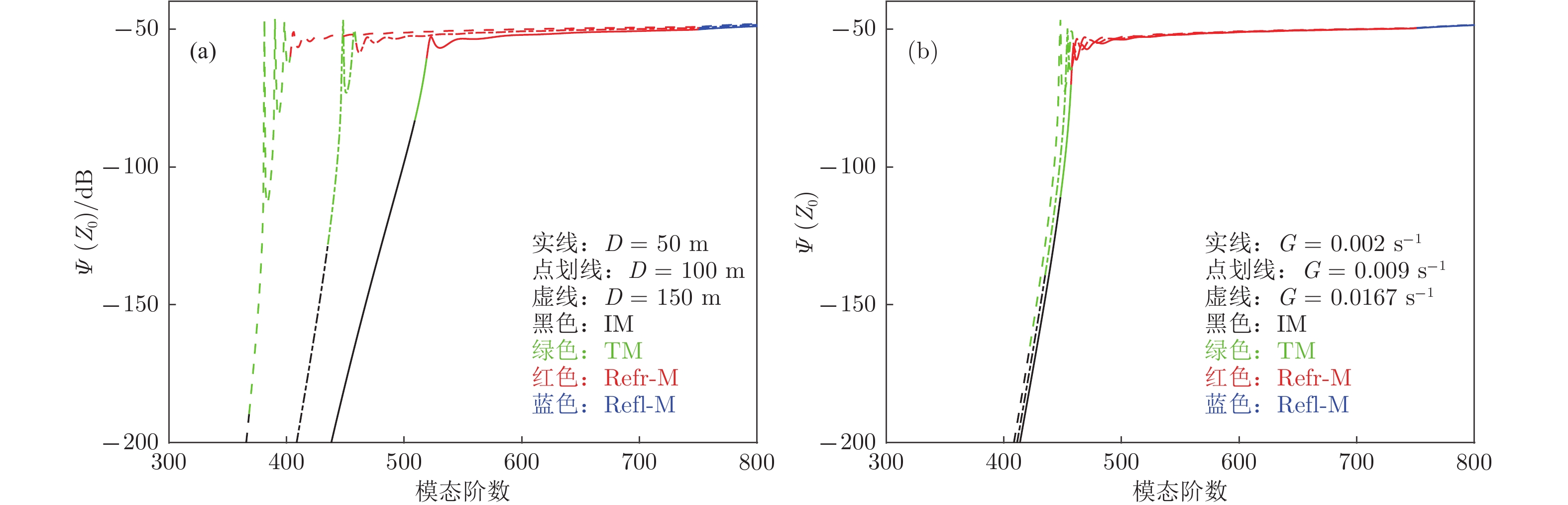
$\scriptstyle D $ 和$\scriptstyle G $ 取不同值时各阶简正波的简正波强度$\scriptstyle \varPsi(z_0) $ (a)$\scriptstyle D $ 取不同值; (b)$\scriptstyle G $ 取不同值Fig. 12. Modal intensity
$\scriptstyle \varPsi(z_0) $ of noise-sources-excited normal modes with different$\scriptstyle D $ and different$\scriptstyle G $ : (a) Different$\scriptstyle D $ ; (b) different$\scriptstyle G $ .图 17 有无表面声道时, 1300和5000 m深度上的
$\scriptstyle \varGamma(d) $ ,$\scriptstyle \varGamma(d)_{\rm Refr{\text{-}} M} $ 和$\scriptstyle \varGamma(d)_{\rm Refl{\text{-}} M} $ (a) 1300 m; (b) 5000 mFig. 17.
$\scriptstyle \varGamma(d) $ ,$\scriptstyle \varGamma(d)_{\rm Refr{\text{-}} M} $ and$\scriptstyle \varGamma(d)_{\rm Refl{\text{-}} M} $ in absence and in presence of surface duct at 1300 and 5000 m: (a) 1300 m; (b) 5000 m.表 1 有无表面声道时各类简正波的水平波数
$\scriptstyle k_{{\rm rm}} $ 所处区间Table 1. The intervals of
$\scriptstyle k_{{\rm rm}} $ for different kinds of normal modes in absence and in presence of surface duct.简正波类型 Refl-M Refr-M TM IM 无表面声道 ${\scriptstyle {k_{\rm rm}} < }\frac{\omega }{c_{\rm N{\text{-}}SD{\text{-}}b}} $ $ \frac{\omega}{c_{\rm N{\text{-}}SD{\text{-}}b}}{\scriptstyle < {k_{\rm rm}} < }\frac{\omega }{c_{\rm N{\text{-}}SD{\text{-}}s}} $ — $ \frac{\omega }{c_{\rm N{\text{-}}SD{\text{-}}s}}{\scriptstyle < {k_{\rm rm}} }$ 有表面声道 ${\scriptstyle {k_{\rm rm}} <} \frac{\omega }{c_{\rm SD{\text{-}}b}} $ $ \frac{\omega}{c_{\rm SD{\text{-}}b}} {\scriptstyle < {k_{\rm rm}} <} \frac{\omega }{c_{\rm SD{\text{-}}i}} $ $ \frac{\omega}{c_{\rm SD{\text{-}}i}} {\scriptstyle < {k_{\rm rm}} <} \frac{\omega }{c_{\rm SD{\text{-}}s}} $ $ \frac{\omega }{c_{\rm SD{\text{-}}s}} {\scriptstyle < {k_{\rm rm}}} $ $\scriptstyle k_{\rm rm} $区间大小变化 不变 增大 — 减小 表 2 仿真条件下有无表面声道时各类简正波的阶数
Table 2. The indexes of different kinds of normal modes in absence and in presence of surface duct under the simulation environment.
简正波类型 Refl-M Refr-M TM IM 无表面声道 751—3611阶(共2861) 590—750阶(共161阶) — 1—589 阶(共589阶) 有表面声道 752—3611阶(共2860阶) 460—751阶(共292阶) 436—459 阶(共24阶) 1—435 阶(共435阶) -
[1] Carey W M, Evans R B 2011 Ocean Ambient Noise (New York: Springer) pp1−7
[2] Waite A D 2002 Sonar for Practising Engineer (Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons) pp 86−89
[3] 殷宝友, 马力, 林建恒 2012 声学学报 37 424
Yin B Y, Ma L, Lin J H 2012 Acta Acustia 37 424
[4] 江鹏飞, 林建恒, 孙军平, 衣雪娟 2017 66 014306
Jiang P F, Lin J H, Sun J P, Yi X J 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 014306
[5] Chapman N R, Cornish J W 1993 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 93 782
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 林建恒, 常道庆, 马力, 李学军, 蒋国健 2001 声学学报 26 217
Lin J H, Chang D Q, Ma L, Li X J, Jiang G J 2001 Acta Acustia 26 217
[7] Cron B F, Sherman C H 1962 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 34 1732
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kuperman W A, Ingenito F 1980 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 67 1988
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Carey W M, Evans R B, Davis J A, Botseas G 1990 IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 15 324
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Perkins J S, Kuperman W A, Ingenito F, Fialkows L T, Glattere J 1993 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 93 739
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Hamson R M 1985 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 78 1702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Yang T C, Yoo K 1997 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 101 2541
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Rouseff D, Tang D 2006 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 120 1284
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 江鹏飞, 林建恒, 马力, 蒋国健 2013 声学学报 38 724
Jiang P F, Lin J H, Ma L, Jiang G J 2013 Acta Acustia 38 724
[15] 周建波, 朴胜春, 刘亚琴, 祝捍皓 2017 66 014301
Zhou J B, Piao S C, Liu Y Q, Zhu H H 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 014301
[16] Buckingham M J 2013 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 134 950
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 刘姗琪, 李风华 2015 声学技术 34 143
Liu S Q, Li F H 2015 Tech. Acoust. 34 143
[18] 王璟琰, 李风华 2016 声学技术 35 109
Wang J Y, Li F H 2016 Tech. Acoust. 35 109
[19] 刘伯胜, 雷家煜 2010 水声学原理(哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学出版社)第26−27页
Liu B S, Lei J Y 2010 Principle of Underwater Acoustics (Haerbin: Harbin Engineering University Press) pp26−27(in Chinese)
[20] 汪德昭, 尚尔昌 2013 水声学(北京: 科学出版社)第24−25页
Wang D Z, Shang E C 2013 Underwater Acousitcs (Beijing: Science Press) pp24−25(in Chinese)
[21] Labianca F M 1973 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 53 1137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Urick R J 1975 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 58 S121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Pekeris C L 1948 Geol. Soc. Am. Mem. 27 1
[24] Jensen F B, Kuperman W A, Porter M B, Schmidt H 2011 Computational Ocean Acoustics (New York: Springer) pp25−26
[25] Ewing W M, Jardetzkey W S, Press F 1957 Elastic Waves in Layered Media (New York: McGraw-Hill) pp 126−137
[26] Bartberger C L 1977 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 61 1643
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Jiang G Y, Sun C, Liu X H, Xie L, Shao X, Kong D Z 2017 OCEANS Aberdeen, UK, June 19−22 2017 pp1−6
[28] Munk W H 1974 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 55 220
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 段睿 2016 博士学位论文(西安: 西北工业大学)
Duan R 2016 Ph. D. Dissertation (Xi'an: Northwestern Polytechnical University) (in Chinese)
[30] Cox H 1973 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 54 1289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 张旭, 张永刚, 张胜军, 吴世华 2009 热带海洋学报 28 23
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X, Zhang Y G, Zhang S J, Wu S H 2009 J. Trop. Oceanograph. 28 23
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 11748
- PDF下载量: 114
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: