-
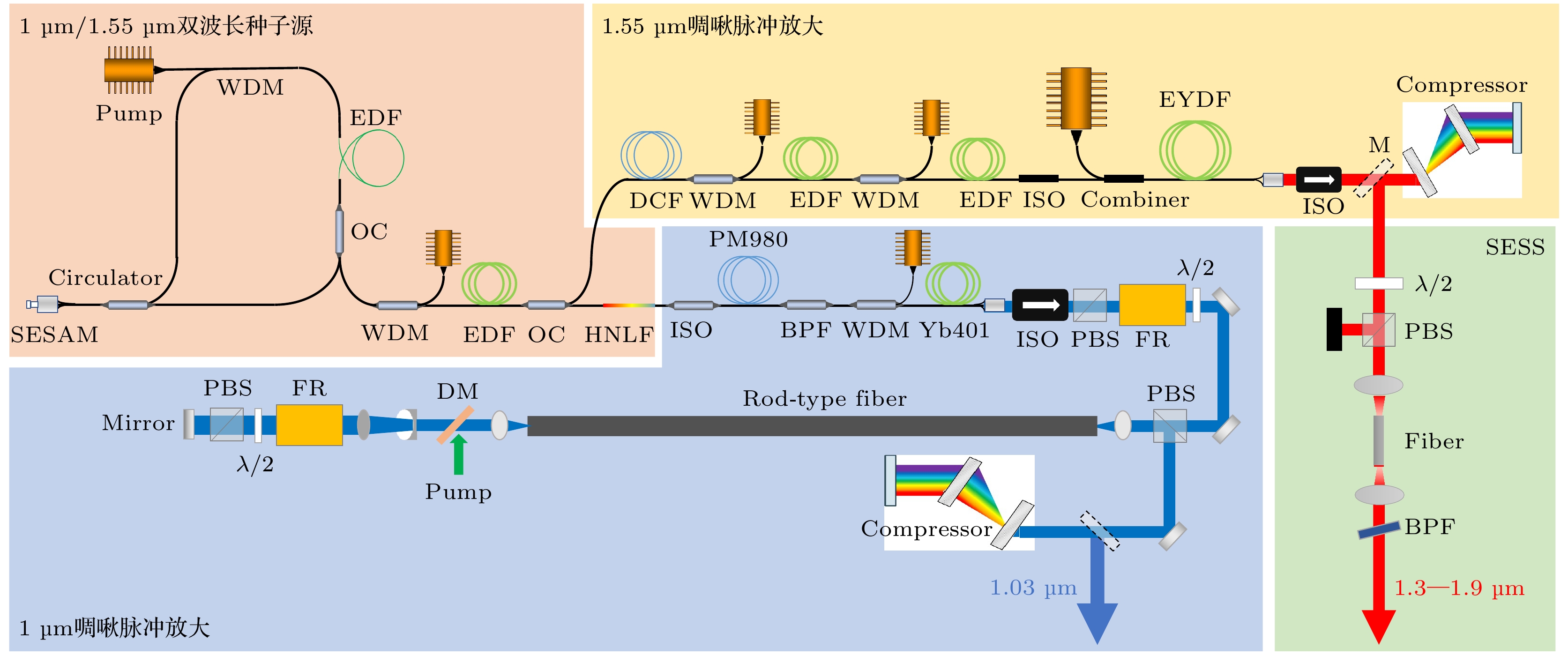
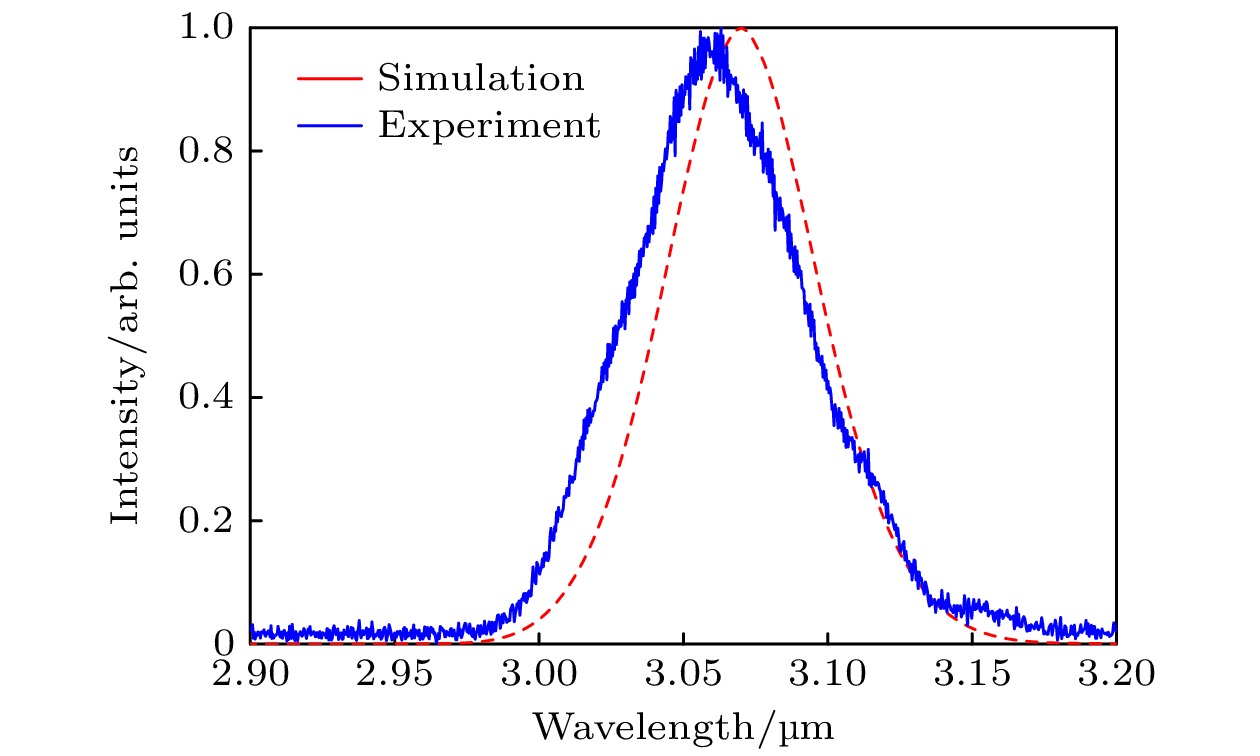
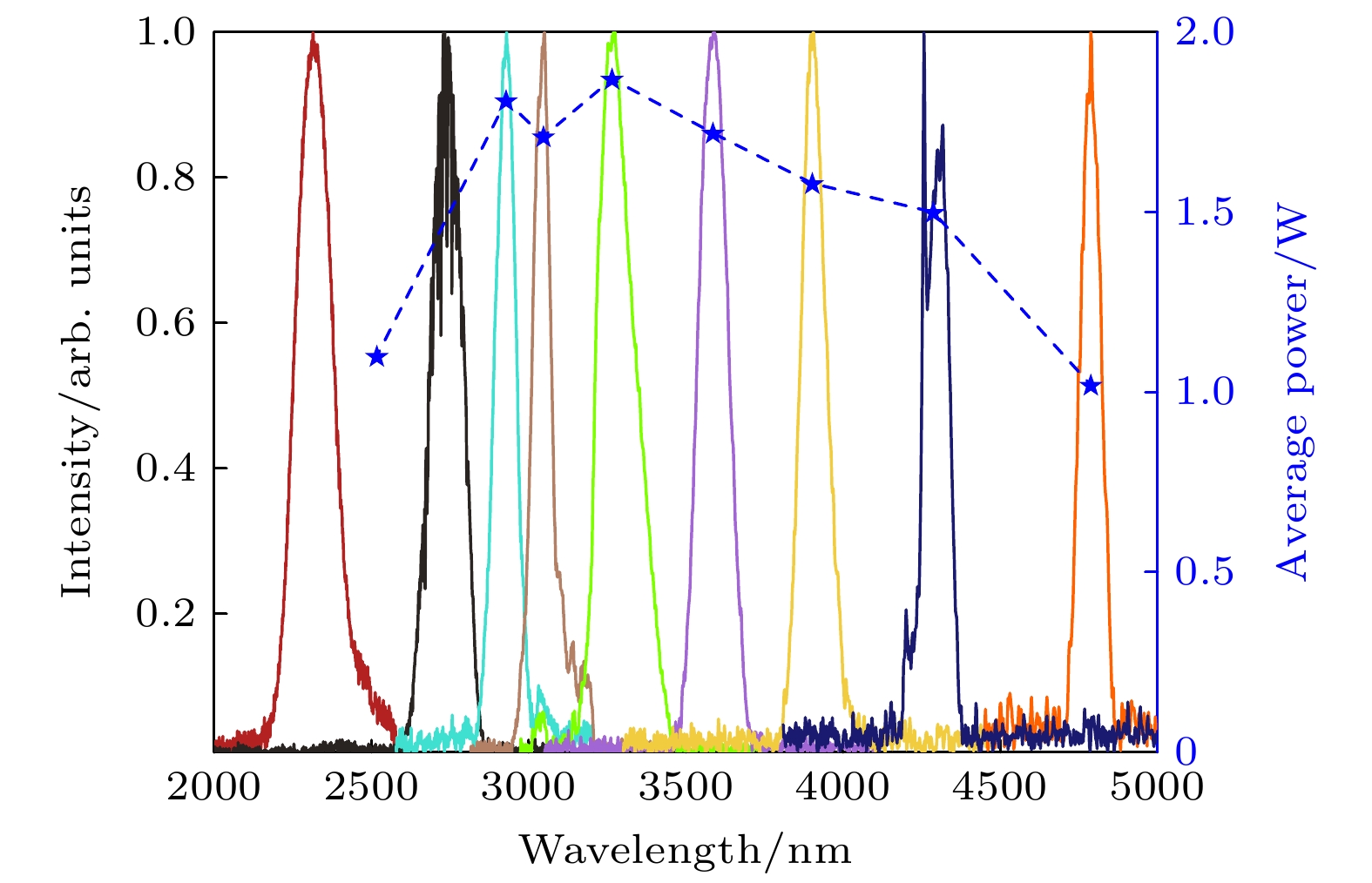
波长位于2—5 μm的中红外超快光源在众多领域具有重要应用价值, 如分子检测、空间通信、非线性光学和生物医疗等, 但目前实现该波段激光的方法存在局限性. 本研究采用差频产生技术, 利用高功率双波长超快光纤激光系统, 结合3 mm周期极化铌酸锂晶体, 通过调节泵浦脉冲与信号脉冲之间的延时, 优化了输出闲频光的能量. 本研究成功生成了中心波长为3.06 μm的中红外超快激光, 平均功率达到3.06 W, 脉冲能量为90 nJ. 此外, 还实现了波长在2—5 μm范围内可调的中红外超快激光, 平均功率均超过1 W, 为当前该波段可实现的最高平均功率水平.
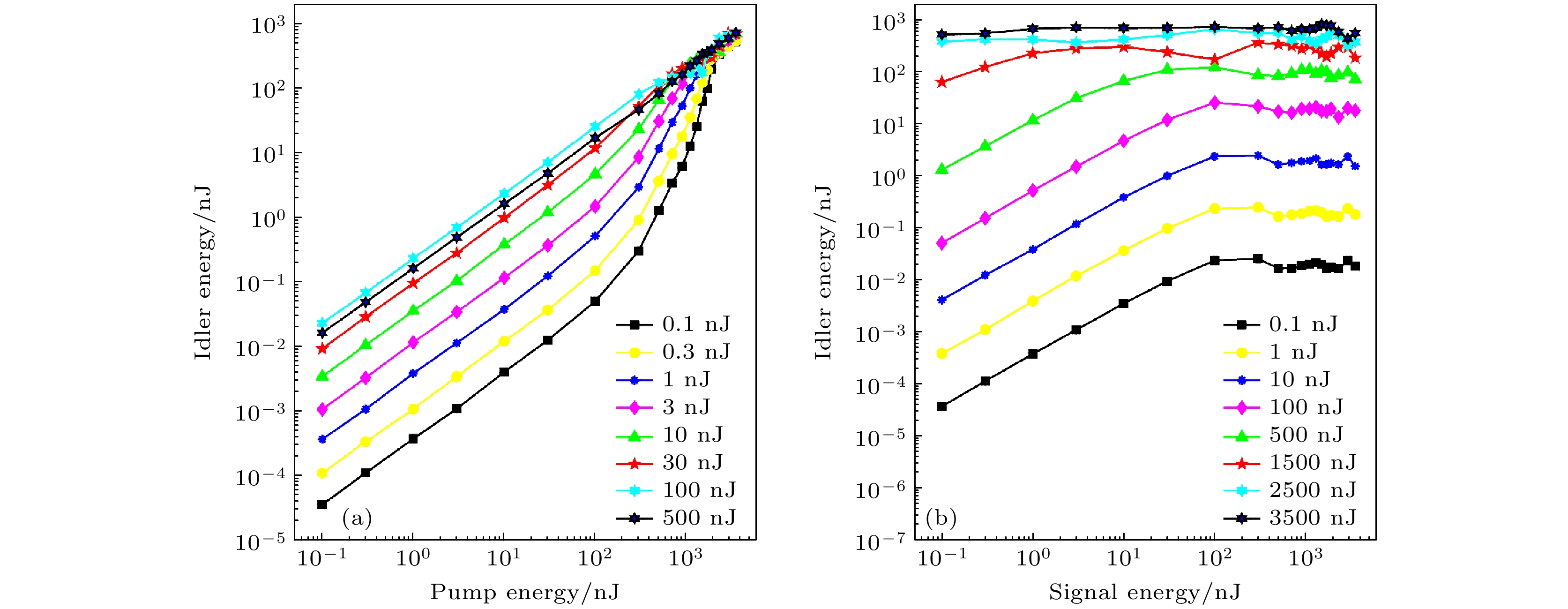
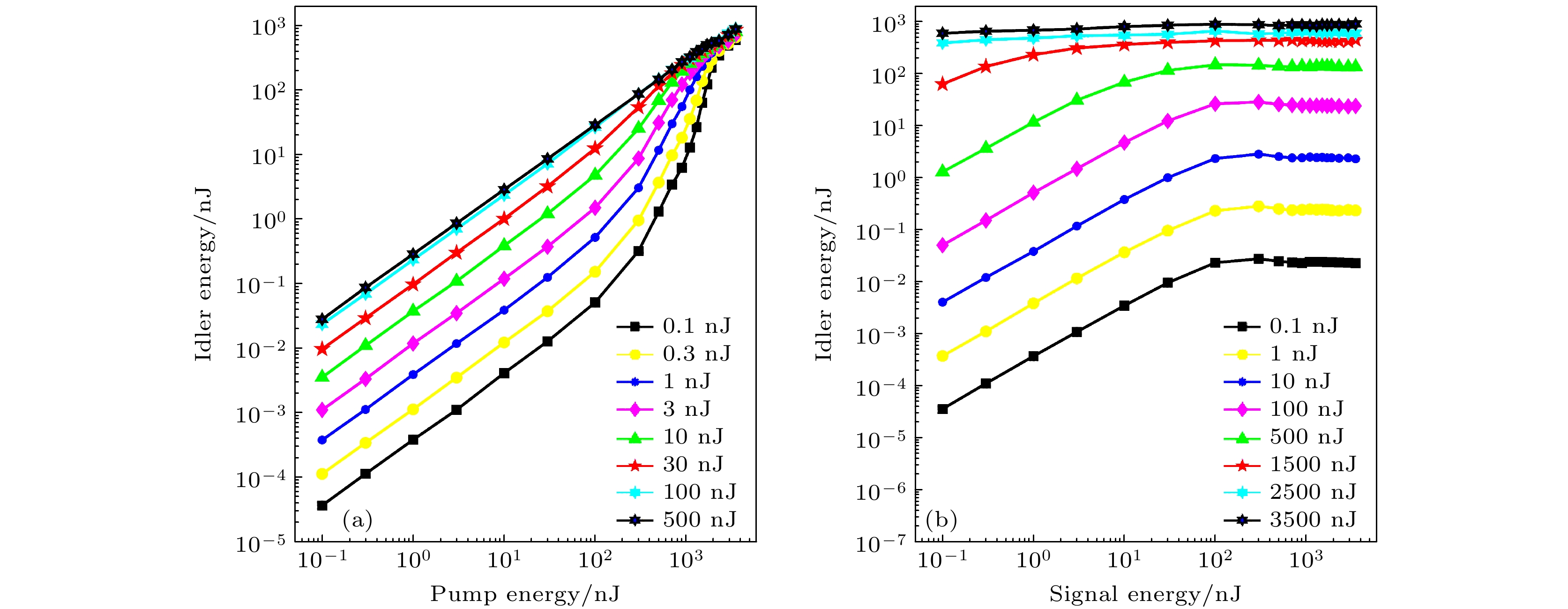
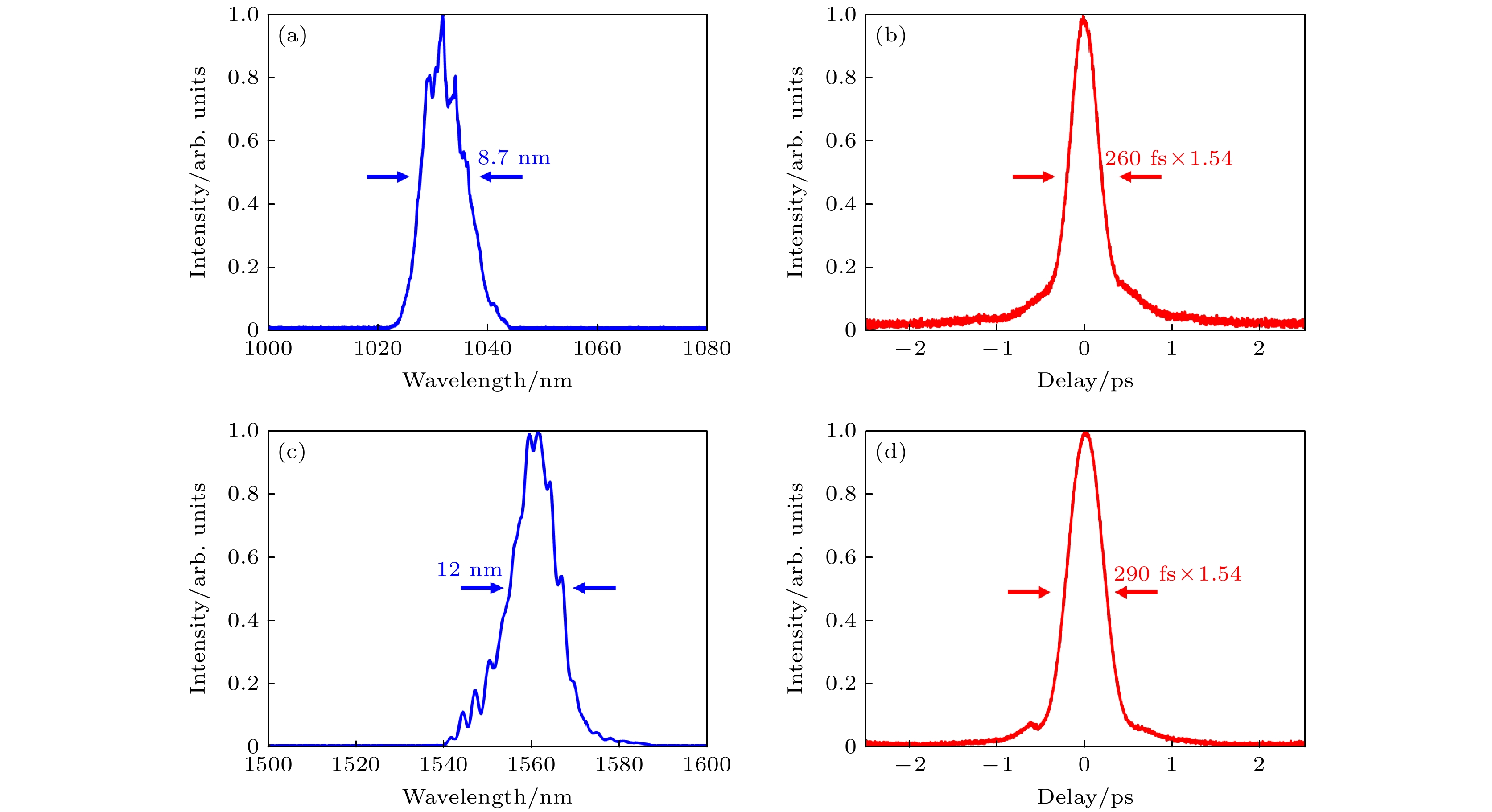
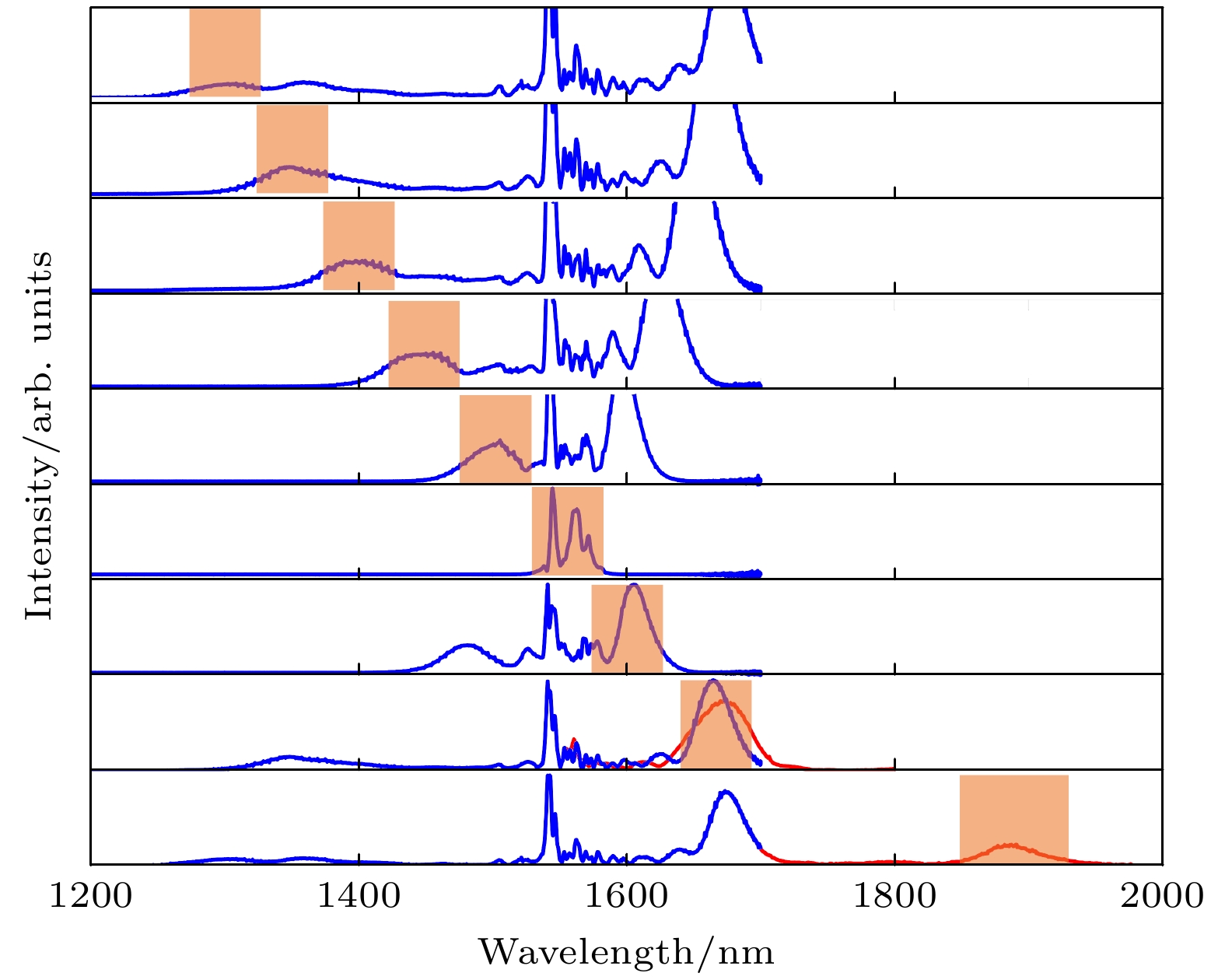
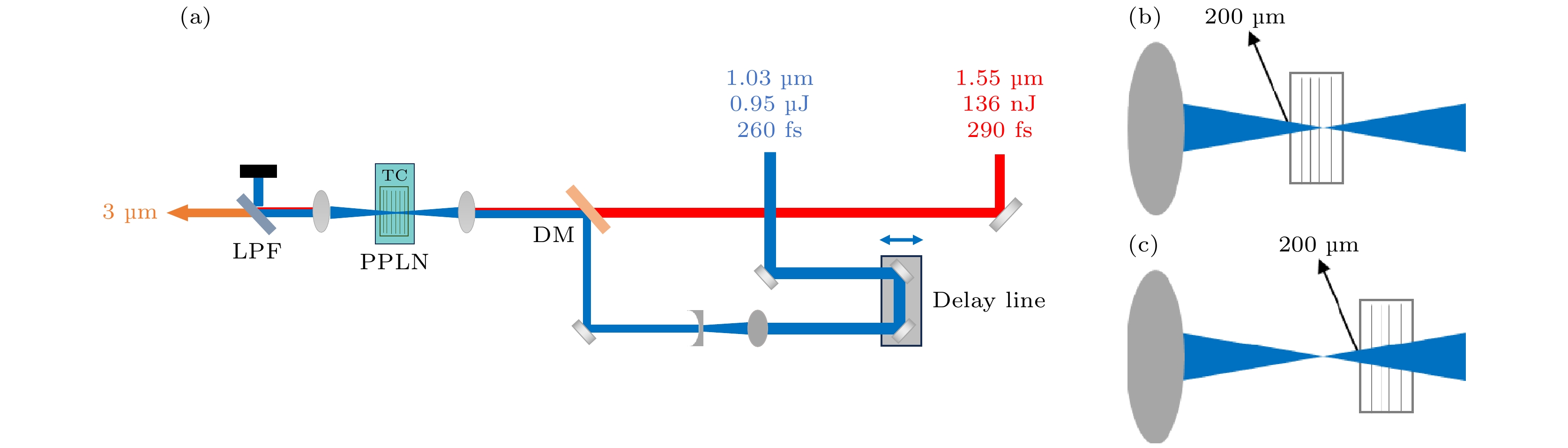
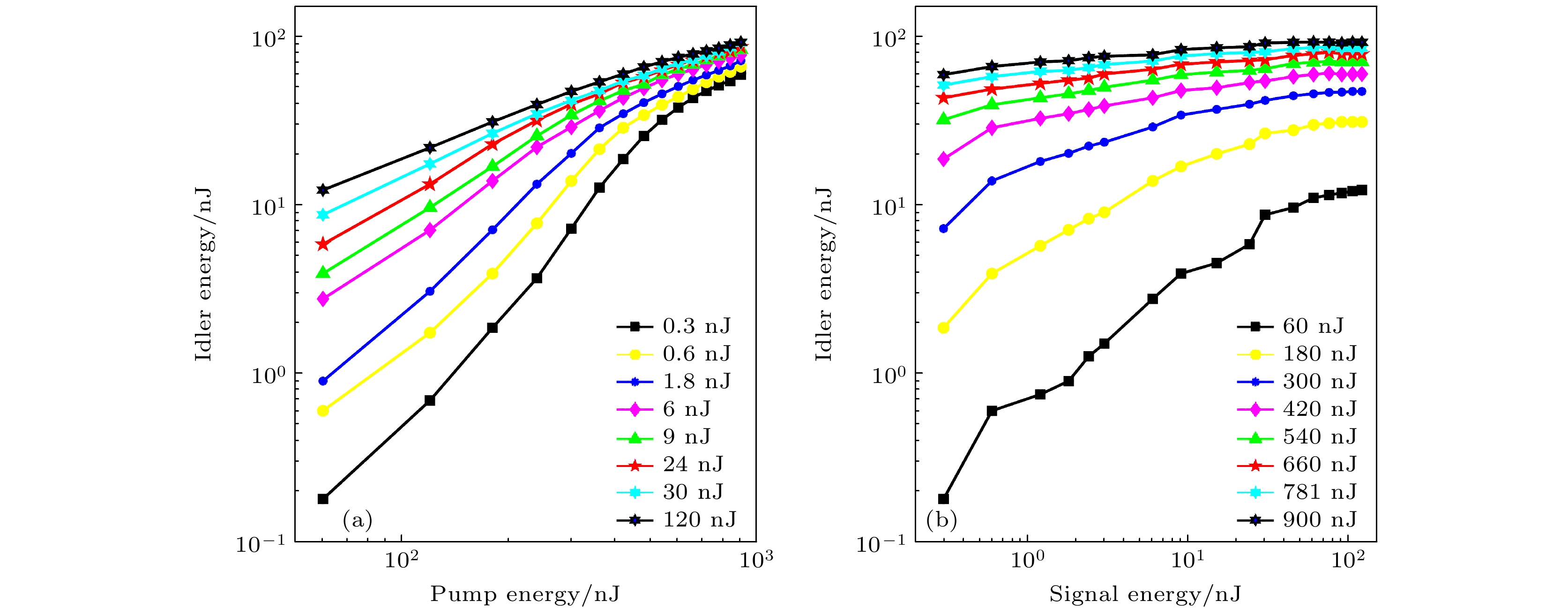
In the mid-infrared spectral range of 2–5 μm, ultrafast laser sources are indispensable for a number of scientific and industrial applications. In these applications, some unique properties of mid-infrared light are utilized, such as molecular overtone and combined tone absorption for sensitive gas detection, minimal atmospheric attenuation for efficient free-space optical communication, phase-matching extension in nonlinear optical processes for high-order harmonic generation, and non-invasive molecular vibration spectroscopy for biomedical imaging. However, the generation of high-power, tunable mid-infrared lasers is hindered by the complex spectral phase of supercontinuum sources, the demanding resonator design of optical parametric oscillators, the limited tuning range of rare-earth-doped fiber lasers, and the power limitations of intrapulse difference-frequency generation. To cope with these challenges, this study employs a difference-frequency generation (DFG) scheme in which a high-power dual-wavelength ultrafast fiber laser system is utilized. The system comprises an Er-doped fiber laser operating at 1556 nm and a Yb-doped fiber amplifier extending the spectrum to 1030 nm. The 1.03-μm pump pulses are amplified to 31.5 W with a pulse energy value of 0.95 μJ and a duration of 260 fs, while the 1.55-μm signal pulses are amplified to 4.6 W, featuring 136 nJ in energy and 290 fs in width. A key innovation is the spectral broadening of the signal pulses via the SESS (SPM-Enabled Spectral Selection) technique in dispersion-shifted fiber, achieving tunable sidebands from 1.3 to 1.9 μm with average power values of 200–400 mW. The DFG process occurs in a 3-mm fan-out PPLN crystal, where the pump and signal pulses are temporally synchronized and focused into 200-μm spots. By solving the three-wave coupling equations with the split-step Fourier method, we reveal that the idle light energy exhibits linear, exponential, and saturation regimes with respect to pump energy and signal energy. Experimental optimization of the pulse delay between the pump beam and signal beam enhances the idle light energy, achieving a central wavelength of 3.06 μm with 3.06-W average power and 92-nJ pulse energy at a 33.3-MHz repetition rate. Moreover, by tuning the signal wavelength from 1.3 to 1.9 μm and adjusting the PPLN poling period, we generate tunable mid-infrared radiation across 2–5 μm, maintaining average power above 1 W throughout the range. At a specific wavelength like 3.28 μm, the output power reaches 1.87 W, with the power gradually decreasing towards longer wavelengths due to crystal phase-matching limitations. The physical significance of these results is profound. The high-power, broadly tunable mid-infrared source can realize high-sensitivity gas detection with an accuracy of a few parts per billion. Real-time combustion diagnostics can be carried out through simultaneous multi-species monitoring, and desktop harmonics can be generated for attosecond pulse synthesis. Furthermore, this study elucidates the nonlinear energy transfer mechanisms in PPLN crystals, providing some rules for designing future high-power mid-infrared systems. The experimental demonstration not only advances the power frontier of this spectral region but also establishes a robust platform for exploring various cutting-edge scientific and industrial applications. -
Keywords:
- mid-infrared ultrashort laser /
- difference-frequency generation /
- high average power /
- wavelength tuning
[1] Zhang Z T, Cheng C F, Sun Y R, Li M, Wang X M 2020 Opt. Express 28 27600
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Foltynowicz A, Masłowski P, Fleisher A J, Merer A J, O'Keefe A, Toon G C 2013 Appl. Phys. B 110 163
[3] Zhu Z, Wu G, Li H, Zhang L, Wang Y F 2018 Enging 4 772
[4] Prasad N S 2005 J. Opt. Fiber Commun. Rep. 2 558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lin P, Wang T, Ma W, Zhao X X, Chen X 2020 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 32 223
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Walsh S M, Karpathakis S F E, McCann A S, Liao A, Leaird D E, Weiner A M 2022 Sci. Rep. 12 18345
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Popmintchev T, Chen M C, Popmintchev D, Arpin P, Murnane M M, Kapteyn H C 2012 Science 336 1287
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Rutledge J, Catanese A, Hickstein D D, Dollar F, Kapteyn H C, Murnane M M 2021 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 38 2252
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Vampa G, Vasilyev S, Liu H, Popmintchev T, Murnane M M, Kapteyn H C 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 259
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Seddon A B 2011 Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 2 177
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Aebischer D, Bartusik D, Tabarkiewicz J 2017 Biomed. Pharmacother. 85 434
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Seddon A B, Napier B, Lindsay I, Rennick T, Meldrum A, MacGregor A 2018 Analyst 143 5874
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Marandi A, Rudy C W, Plotnichenko V G, Kieu K, Boyer A G, Fejer M M 2012 Opt. Express 20 24218
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Liu K, Liu J, Shi H, Wang Y, Zhang X, Li H 2014 Opt. Express 22 24384
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Woyessa G, Kwarkye K, Dasa M K, Tadesse Y, Debbarma S, Dudley J M, Agger C, Bang O 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 1129
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Von Grafenstein L, Bock M, Ueberschaer D, Karpowicz N, Filsinger F, Küpper J 2017 Opt. Lett. 42 3796
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 胡明列, 王珏, 范锦涛 2021 中国激光 48 1901001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu M L, Wang J, Fan J T 2021 Chin. J. Lasers 48 1901001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Smolski V O, Vasilyev S, Schunemann P G, Kuleshov N V, Klimov V V, Kozlov V A 2015 Opt. Lett. 40 2906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhou Y, Qin Z, Yuan P, Li H, Wang X, Zhang Y 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 5104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Yu L, Liang J, Huang S, Wang Y, Zhang X, Li H 2022 Opt. Lett. 47 2562
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Duval S, Bernier M, Fortin V, Chagnon M, Taillon J, Boudreau J 2015 Optica 2 623
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Cui Y, Chen M, Du W, Li H, Zhang Y, Wang X 2021 Opt. Express 29 42924
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Wang Q, Zhang J, Kessel A, Zeng X, Li H, Zhang Y 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 2566
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Krogen P, Suchowski H, Liang H, Wang Z, Steinleitner P, Nagl N, Kowalczyk M 2017 Nat. Photonics 11 222
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Liang H, Krogen P, Wang Z, Steinleitner P, Nagl N, Kowalczyk M 2017 Nat. Commun. 8 141
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Elu U, Maidment L, Vamos L, Tani F, Novoa D, Frosz M H, Badikov V, Petrov V, Steinle T, Haberstroh F 2021 Nat. Photonics 15 277
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Zhou L, Qin X, Di Y, Xie G, Deng Z, Gu C, Luo D, Li W 2023 Opt. Lett. 48 4673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zhu F, Hundertmark H, Kolomenskii A A, et al. 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 2360
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Liu Y, Zhao J, Wei Z, Zhang X, Li H, Zhang Y 2023 Opt. Lett. 48 1052
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Zhou L, Liu Y, Lou H, Di Y, Xie G, Zhu Z, Deng Z, Luo D, Gu C, Chen H, Li W 2020 Opt. Lett. 45 6458
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Catanese A, Rutledge J, Silfies M C, et al. 2020 Opt. Lett. 45 1248
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Boyd R W 2008 Nonlinear Optics (3rd Ed) (San Diego: Academic Press) p132
-
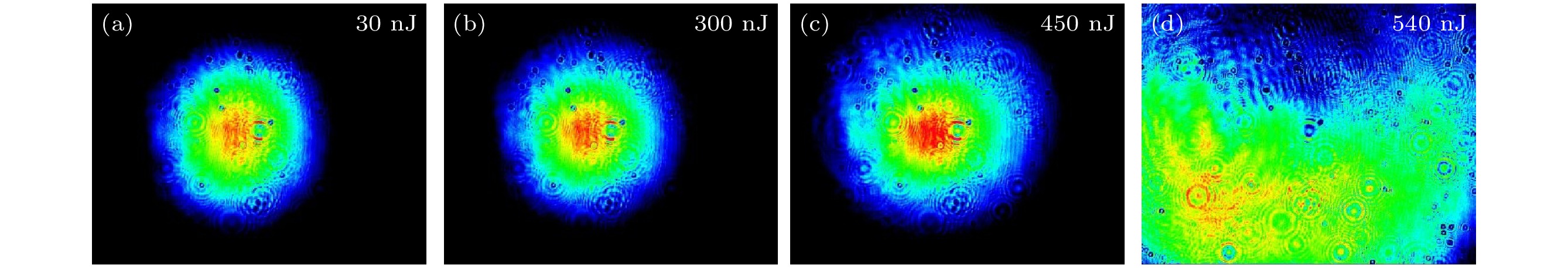
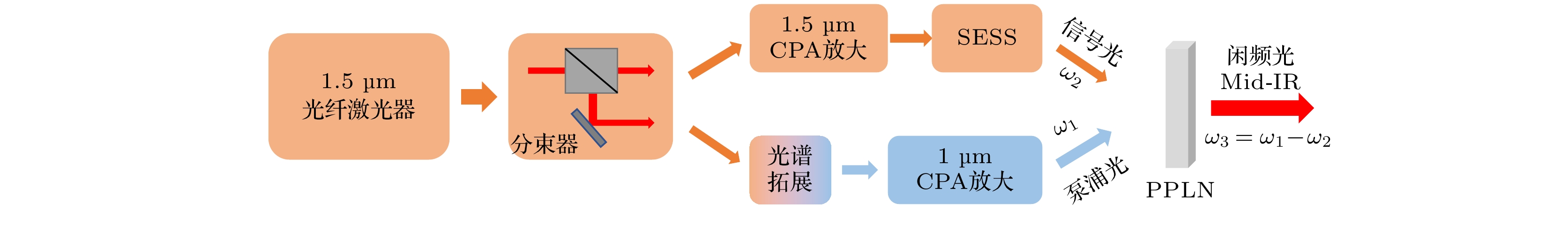
图 7 差频产生3 μm高功率中红外激光 (a)实验装置图; (b)焦点位于晶体前表面之后; (c)焦点位于晶体前表面之前
Fig. 7. The DFG-based 3μm high-power mid-infrared laser: (a) Drawings of experimental installations; (b) the focal point located behind the front surface of the crystal; (c) the focal point located before the front surface of the crystal.
-
[1] Zhang Z T, Cheng C F, Sun Y R, Li M, Wang X M 2020 Opt. Express 28 27600
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Foltynowicz A, Masłowski P, Fleisher A J, Merer A J, O'Keefe A, Toon G C 2013 Appl. Phys. B 110 163
[3] Zhu Z, Wu G, Li H, Zhang L, Wang Y F 2018 Enging 4 772
[4] Prasad N S 2005 J. Opt. Fiber Commun. Rep. 2 558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lin P, Wang T, Ma W, Zhao X X, Chen X 2020 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 32 223
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Walsh S M, Karpathakis S F E, McCann A S, Liao A, Leaird D E, Weiner A M 2022 Sci. Rep. 12 18345
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Popmintchev T, Chen M C, Popmintchev D, Arpin P, Murnane M M, Kapteyn H C 2012 Science 336 1287
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Rutledge J, Catanese A, Hickstein D D, Dollar F, Kapteyn H C, Murnane M M 2021 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 38 2252
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Vampa G, Vasilyev S, Liu H, Popmintchev T, Murnane M M, Kapteyn H C 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 259
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Seddon A B 2011 Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 2 177
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Aebischer D, Bartusik D, Tabarkiewicz J 2017 Biomed. Pharmacother. 85 434
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Seddon A B, Napier B, Lindsay I, Rennick T, Meldrum A, MacGregor A 2018 Analyst 143 5874
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Marandi A, Rudy C W, Plotnichenko V G, Kieu K, Boyer A G, Fejer M M 2012 Opt. Express 20 24218
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Liu K, Liu J, Shi H, Wang Y, Zhang X, Li H 2014 Opt. Express 22 24384
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Woyessa G, Kwarkye K, Dasa M K, Tadesse Y, Debbarma S, Dudley J M, Agger C, Bang O 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 1129
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Von Grafenstein L, Bock M, Ueberschaer D, Karpowicz N, Filsinger F, Küpper J 2017 Opt. Lett. 42 3796
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 胡明列, 王珏, 范锦涛 2021 中国激光 48 1901001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu M L, Wang J, Fan J T 2021 Chin. J. Lasers 48 1901001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Smolski V O, Vasilyev S, Schunemann P G, Kuleshov N V, Klimov V V, Kozlov V A 2015 Opt. Lett. 40 2906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhou Y, Qin Z, Yuan P, Li H, Wang X, Zhang Y 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 5104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Yu L, Liang J, Huang S, Wang Y, Zhang X, Li H 2022 Opt. Lett. 47 2562
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Duval S, Bernier M, Fortin V, Chagnon M, Taillon J, Boudreau J 2015 Optica 2 623
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Cui Y, Chen M, Du W, Li H, Zhang Y, Wang X 2021 Opt. Express 29 42924
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Wang Q, Zhang J, Kessel A, Zeng X, Li H, Zhang Y 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 2566
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Krogen P, Suchowski H, Liang H, Wang Z, Steinleitner P, Nagl N, Kowalczyk M 2017 Nat. Photonics 11 222
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Liang H, Krogen P, Wang Z, Steinleitner P, Nagl N, Kowalczyk M 2017 Nat. Commun. 8 141
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Elu U, Maidment L, Vamos L, Tani F, Novoa D, Frosz M H, Badikov V, Petrov V, Steinle T, Haberstroh F 2021 Nat. Photonics 15 277
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Zhou L, Qin X, Di Y, Xie G, Deng Z, Gu C, Luo D, Li W 2023 Opt. Lett. 48 4673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zhu F, Hundertmark H, Kolomenskii A A, et al. 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 2360
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Liu Y, Zhao J, Wei Z, Zhang X, Li H, Zhang Y 2023 Opt. Lett. 48 1052
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Zhou L, Liu Y, Lou H, Di Y, Xie G, Zhu Z, Deng Z, Luo D, Gu C, Chen H, Li W 2020 Opt. Lett. 45 6458
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Catanese A, Rutledge J, Silfies M C, et al. 2020 Opt. Lett. 45 1248
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Boyd R W 2008 Nonlinear Optics (3rd Ed) (San Diego: Academic Press) p132
计量
- 文章访问数: 666
- PDF下载量: 39
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: