-
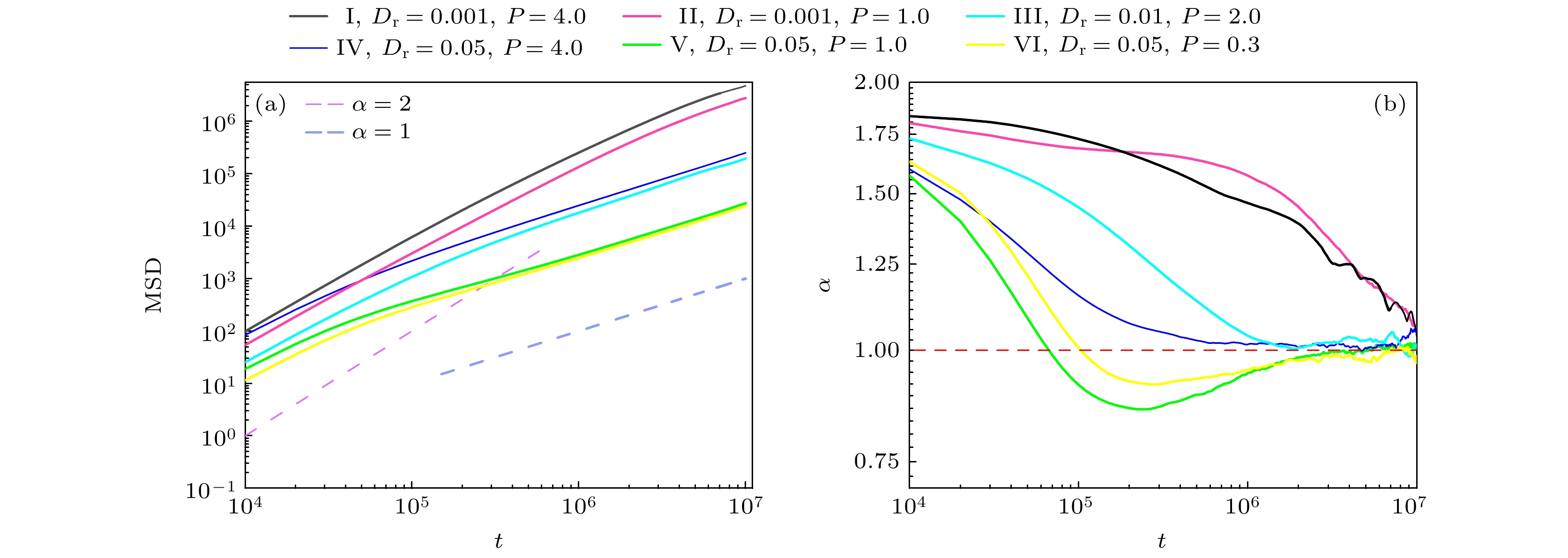
Active particle systems are nonequilibrium systems composed of self-propelled Brownian particles, where interactions between particles can give rise to various collective behaviors. This study, based on Brownian dynamics simulations, explores the effects of light intensity, rotational diffusion coefficient, and the width and spacing of illuminated regions on the aggregation structures of the system. First, this study examines the influence of light intensity on aggregation structures under different rotational diffusion coefficients, finding that as the rotational diffusion coefficient increases, the system gradually stabilizes. This stabilization is attributed to the reduced collision effects among particles at higher diffusion coefficients. Under suitable rotational diffusion coefficients, gradually increasing the ratio of longitudinal to transverse light-induced self-propulsion forces leads to a transition in the system’s aggregation structure from a transverse stripe structure configuration to a tic-tac-toe structure, ultimately resulting in a longitudinal stripe structure. This indicates that the system’s aggregation structure can be effectively controlled by changing the relative light intensity of the longitudinal and transverse illumination. From a dynamical perspective, an unstable structure consistently exhibits a super-diffusive behavior throughout the simulations, while stable structure transitions from initial super-diffusion to normal diffusion, indicating that under steady state conditions, particles aggregate in the shaded regions, exhibiting Brownian motion. To further investigate the influence of light field on collective particle behavior, in this study the width of the illuminated region and the spacing between adjacent illuminated regions are systematically varied, finding that the overall trends are consistent with previous conclusions. It is also observed that wider illumination regions with narrower spacing contribute to the formation of tic-tac-toe structures, while narrower illumination regions with wider spacing give rise to a novel structure—checkerboard structures. This study investigates the phase separation behavior of particles in complex optical field environments, providing some valuable ideas for controlling aggregation states in active particle systems.
-
Keywords:
- light field regulation /
- active particle /
- ordered structure
[1] Ramaswamy S 2017 J. Stat. Mech. 5 054002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ramaswamy S 2010 Annu. Rev. Condens. Mater Phys. 1 323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Tailleur J, Cates M E 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 218103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Martinez R, Alarcon F, Rodriguez D R, Aragones J L, Valeriani C 2018 Eur. Phys. J. E 41 91
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Vladescu I D, Marsden E J, Schwarz-Linek J, Martinez V A, Arlt J, Morozov A N, Marenduzzo D, Cates M E, Poon W C 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 113 268101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Schweitzer F, Tilch B, Ebeling W 2000 Eur. Phys. J. B 14 157
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Erdmann U, Ebeling W, Schimansky-Geier L, Schweitzer F 2000 Eur. Phys. J. B 15 105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Schweitzer F, Ebeling W, Tilch B 1998 Phys. Rev. Lett. 80 5044
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Yang X, Manning M L, Marchetti M C 2014 Soft Matter 10 6477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Stenhammar J, Tiribocchi A, Allen R J, Marenduzzo D, Cates M E 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 111 145702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Stenhammar J, Wittkowski R, Marenduzzo D, Cates M E 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 018301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Dolai P, Simha A, Mishra S 2017 Soft Matter 14 6137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 高艺雯, 王影, 田文得, 陈康 2022 71 240501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao Y W, Wang Y, Tian W D, Chen K 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 240501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Fernandez-Rodriguez M A, Grillo F, Alvarez L, Rathlef M, Buttinoni L, Volpe G, Isa L 2020 Nat. Commun. 11 4223
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Vutukuri H R, Lisicki M, Lauga E, Vermant J 2020 Nat. Commun. 11 2628
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Hernández R J, Sevilla F J, Mazzulla A, Pagliusi P, Pellizzi N, Cipparrone G 2020 Soft Matter 16 7704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zhang J H, Guo J J, Mou F Z, Guan J G 2018 Micromachines 9 88
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Bäuerle T, Fischer A, Speck T, Bechinger C 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 3232
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wang G, Phan T V, Li S, Wombacher M, Qu J, Peng Y, Chen G, Goldman D I, Levin S A, Austin R H, Liu L Y 2021 Phys. Rev. Lett. 126 108002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Liu Y P, Wang G, Wang P L, Yuan D M, Hou S X, Jin Y K, Wang J, Liu L Y 2023 Chin. Phys. B 32 068701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K 1996 J. Mol. Graphics 14 33
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Ning H P, Zhang Y, Zhu H, Ingham A, Huang G S, Mei Y F, Solovev A A 2018 Micromachines 9 75
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chen H X, Zhao Q L, Du X M 2018 Micromachines 9 41
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Xu L L, Mou F Z, Gong H T, Luo M, Guan J G 2017 Chem. Soc. Rev. 46 6905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wang W, Duan W T, Ahmed S, Sen A, Mallouk T E 2015 Acc. Chem. Res. 48 1938
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Chen C R, Mou F Z, Xu L L, Wang S F, Guan J G, Feng Z P, Wang Q W, Kong L, Li W, Wang J, Zhang Q J 2017 Adv. Mater. 29 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Tang S S, Zhang F Y, Zhao J, Talaat W, Soto F, Karshalev E, Chen C R, Hu Z H, Lu X L, Li J X, Lin Z H, Dong H F, Zhang X J, Nourhani A, Wang J 2019 Adv. Funct. Mater. 29 1809003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Sun Y Y, Liu Y, Zhang D M, Zhang H, Jiang J W, Duan R M, Xiao J J, Xing J, Zhang D F, Dong B 2019 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11 40533
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Singh D P, Choudhury U, Fischer P, Mark A G 2017 Adv Mater. 29 32
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Lin Z, Si T, Wu Z, Gao C, Lin X, He Q 2017 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56 13517
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Wang Y, Shen Z L, Xia Y Q, Feng G Q, Tian W D 2020 Chin. Phys. B 29 053103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Pan J X, Wei H, Qi M J, Wang H F, Zhang J J, Tian W D, Chen K 2020 Soft Matter 16 5545
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Ye S M, Liu P, Wei Z X, Ye F F, Yang M C, Chen K 2020 Chin. Phys. B 29 058201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Zhou X L, Wang Y Z, Xu B J, Liu Y P, Lu D, Luo J, Yang Z Y 2023 AIP Adv. 13 065332
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Chen J M, Zhou X L, Zhang L X 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 118701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Quillen A C, Smucker J P, Peshkov A 2020 Phys. Rev. E 101 052618
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Liu P, Ye S M, Ye F F, Chen K, Yang M C 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 124 158001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Das S, Ghosh S, Chelakkot R 2020 Phys. Rev. E 102 032619
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Das S, Chelakkot R 2020 Soft Matter 16 7250
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Knežević M, Stark H 2020 New J. Phys 22 113025
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Chen X G, Lin L H, Li Z C, Sun H J 2022 Adv. Funct. Mater. 32 2104649
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Volpe G, Buttinoni I, Vogt D, Kuemmerer H J, Bechinger C 2011 Soft Matter. 7 8810
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Jahanshahi S, Lozano C, Liebchen B, Löwen H, Bechinger C 2020 Commun. Phys. 3 127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Palacci J, Sacanna S, Steinberg A P, Pine D J, Chaikin P M 2013 Science 339 936
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Xia Y Q, Shen Z L, Tian W D, Chen K 2019 J. Chem. Phys. 150 154903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Wang C, Li H S, Ma Y Q, Tian W D, Chen K 2018 J. Chem. Phys. 149 164902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] Shan W J, Zhang F, Tian W D, Chen K 2019 Soft Matter 15 4761
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[48] 石子璇, 金燕, 金奕扬, 田文得, 张天辉, 陈康 2024 73 170501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shi Z X, Jin Y, Jin Y Y, Tian W D, Zhang T H, Chen K 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 170501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[49] 王晶, 焦阳, 田文得, 陈康 2023 72 190501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J, Jiao Y, Tian W D, Chen K 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 190501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[50] Tiwari C, Singh P S 2024 Soft Matter 20 4816
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[51] Shen Y F, Hu H X, Luo M B 2024 Soft Matter 20 621
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[52] Cates M E, Tailleur J 2015 Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys. 6 219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[53] Gomez-Solano J R, Samin S, Lozano C, Ruedas-Batuecas P, van Roij R, Bechinger C 2017 Sci Rep. 7 14891
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[54] Caprini L, Marini Bettolo Marconi U, Wittmann R, Löwen H 2022 Soft Matter 8 1412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[55] Takatori S C, Yan W, Brady J F 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 113 028103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[56] Bechinger C, Di Leonardo R, Löwen H, Reichhardt C, Volpe G, Volpe G 2016 Rev. Mod. Phys. 88 045006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
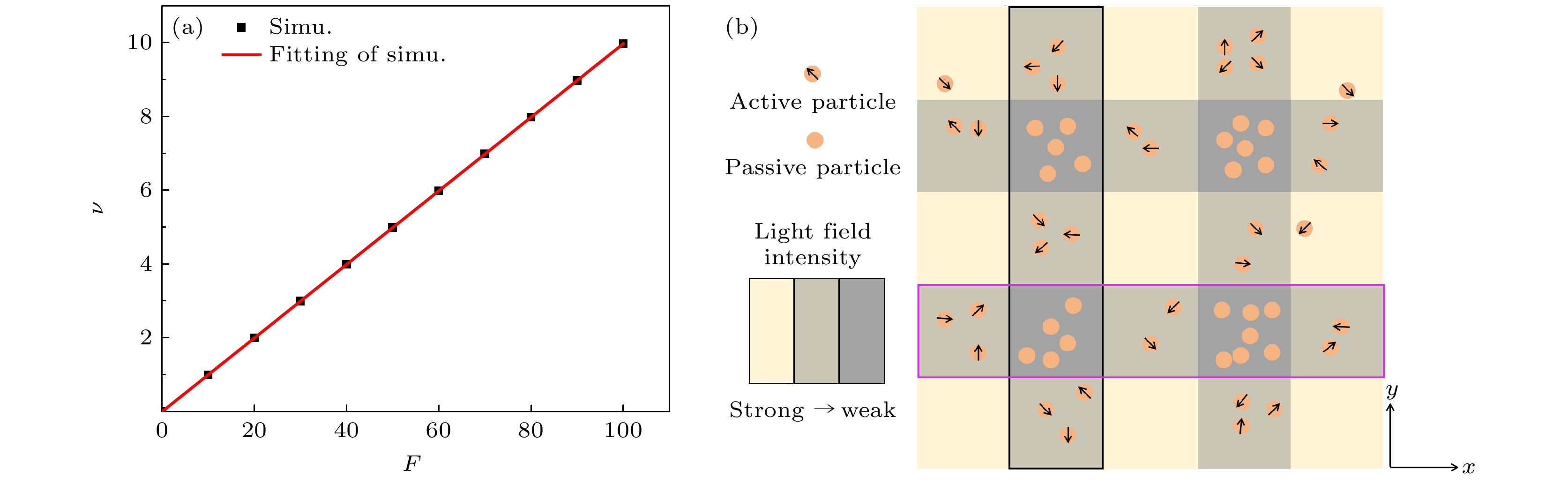
图 1 (a)均匀光场中活性粒子速度v与自驱力F关系; (b)周期性条形光场驱动活性粒子模型示意图; 黑色方框标注的区域为I区, 代表一个纵向遮光区; 紫色方框标注的区域为II区, 代表一个横向遮光区
Fig. 1. (a) Relationship between the velocity v of active particles and the self-propulsive force F in a uniform light field; (b) model schematic of active particles driven by the periodic striped light field. The region marked by the black box is Zone I, representing a longitudinal shaded region, while the region marked by the purple box is Zone II, representing a transverse shaded region.
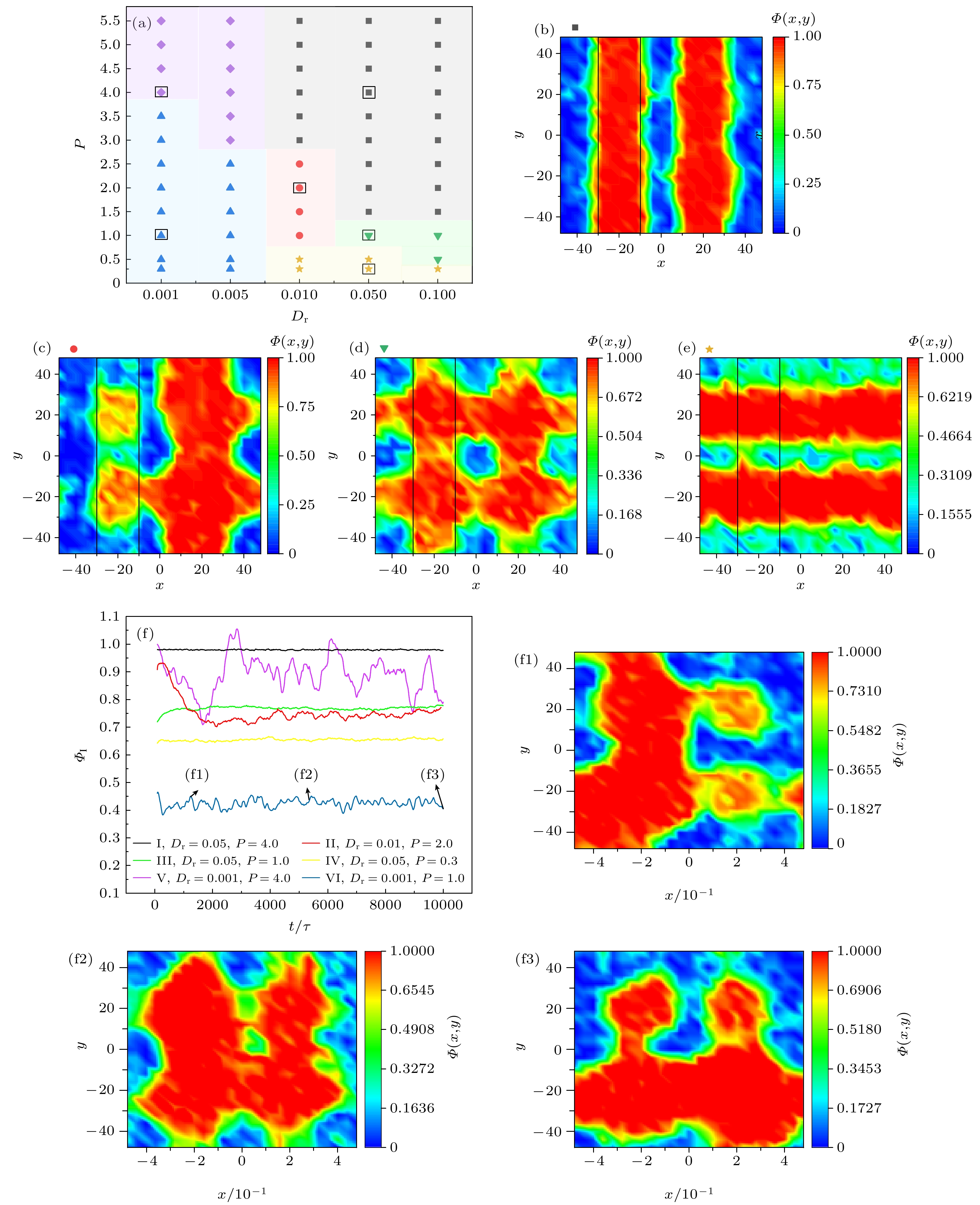
图 2 (a)体系聚集结构相图分布, 其中◆代表振荡结构; ▲代表不稳定团簇结构; ■代表纵向条形结构; ●代表条形格状混合结构; ▼代表井字结构; ★代表横向条形结构; (b), (c), (d), (e)为代表性结构的密度分布图, 图中黑色方框代表纵向遮光区I; (f)不同结构下纵向遮光区I粒子数密度随时间的演化
Fig. 2. (a) Phase diagram of the system’s aggregation structures. ◆ represents an oscillatory structure; ▲ represents an unstable cluster structure; ■ represents a longitudinal stripe structure; ● represents a mixed striped block-like hybrid structure; ▼ represents a tic-tac-toe structure; ★ represents a transverse stripe structure. (b), (c), (d), and (e) The density distribution of representative structures, with the black boxes indicating the longitudinal shading region I. (f) Temporal evolution of particle number density in region I for different structures.
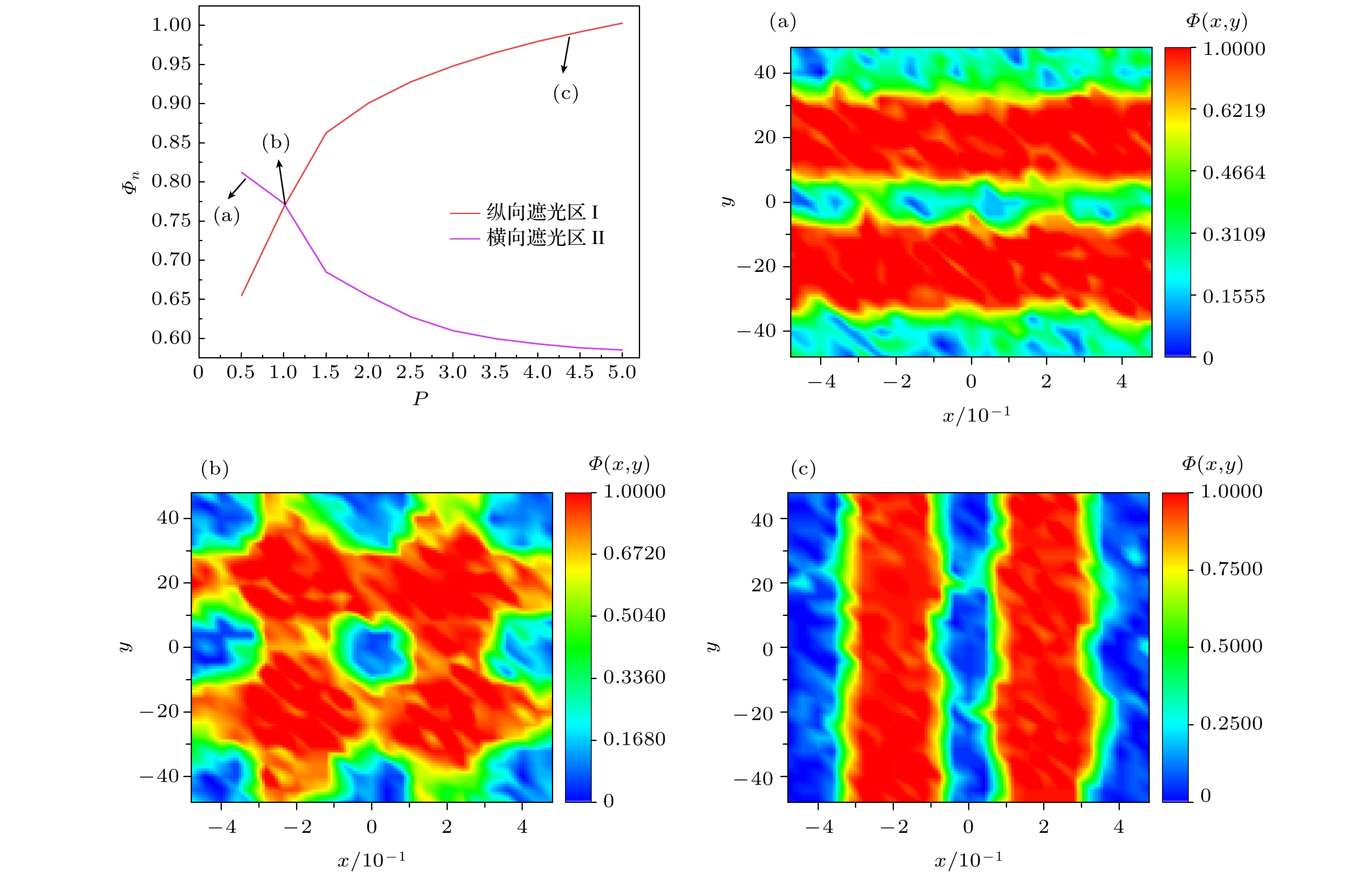
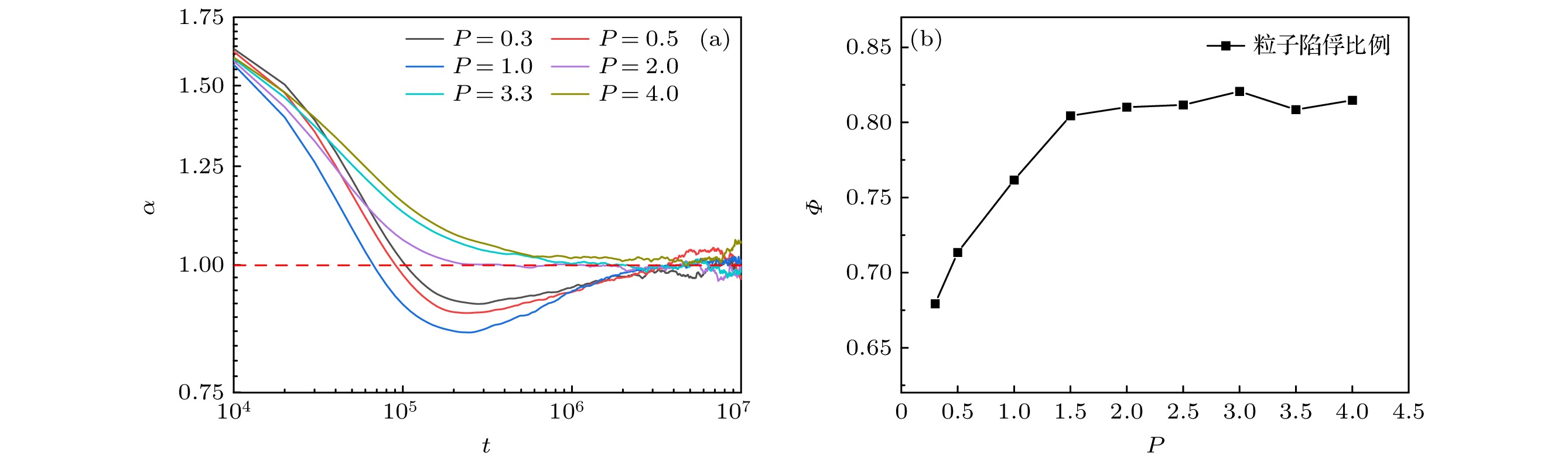
图 3 ${D_{\text{r}}} = 0.05$时纵向遮光区I、横向遮光区II中粒子数密度$ {\varPhi _{\text{n}}} $随纵向与横向光场自驱力比值P的变化
Fig. 3. Relationship between particle number density ($ {\varPhi _{\text{n}}} $) and the ratio P of longitudinal to transverse light-induced self-propulsion forces in the longitudinal shading region I and the transverse shaded region II at ${D_{\text{r}}} = 0.05$.
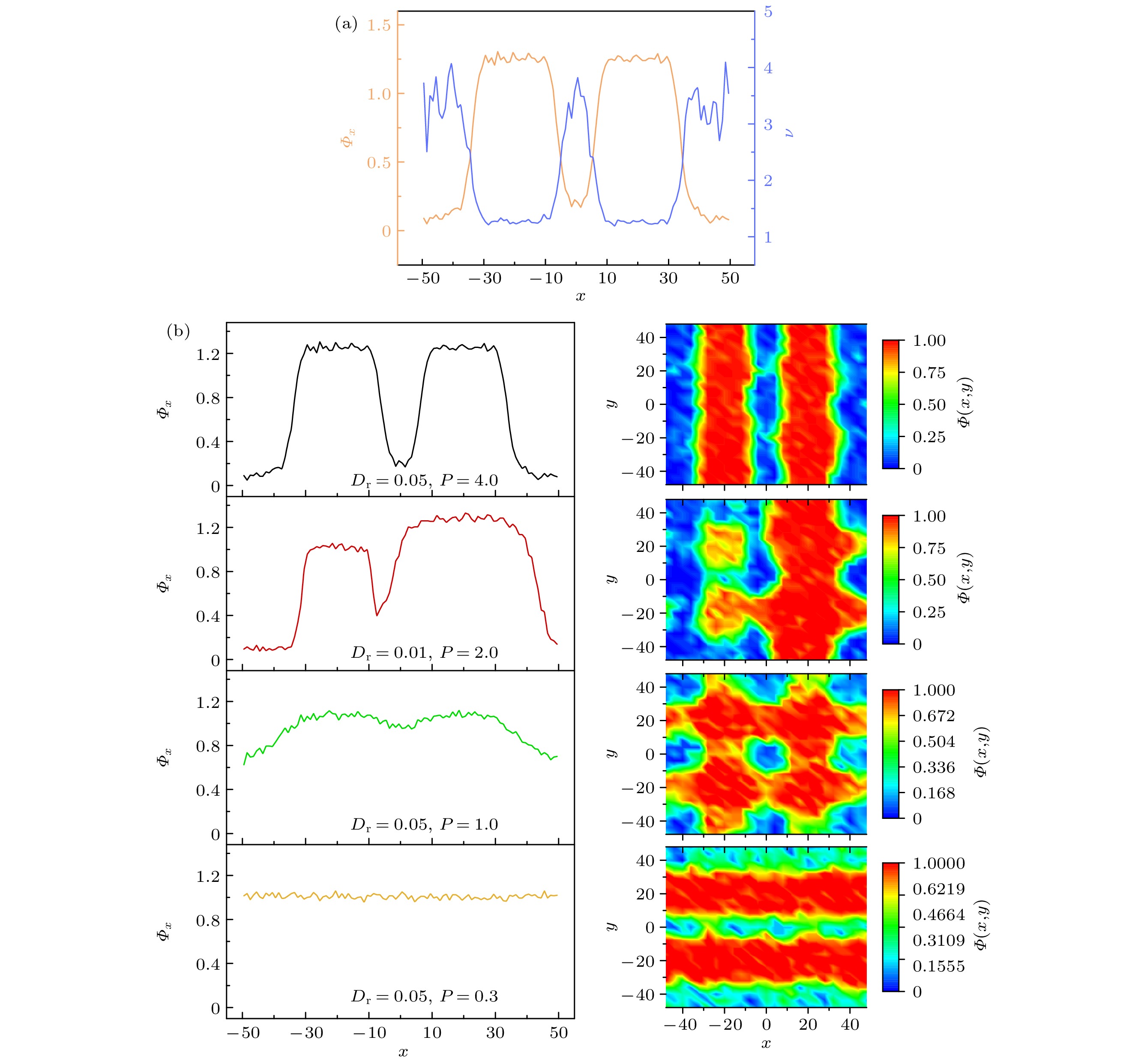
图 4 (a)纵向条形结构在横向遮光区(II)内沿x轴方向的粒子数密度和速度分布图; (b)四种稳定状态在横向遮光区(II)内沿x轴方向的粒子数密度分布图
Fig. 4. (a) Distributions of particle number density and velocity along the x-axis within the transverse shaded region (II) of the longitudinal stripe structure; (b) distributions of particle number density along the x-axis in the transverse shaded region (II) for four steady states.
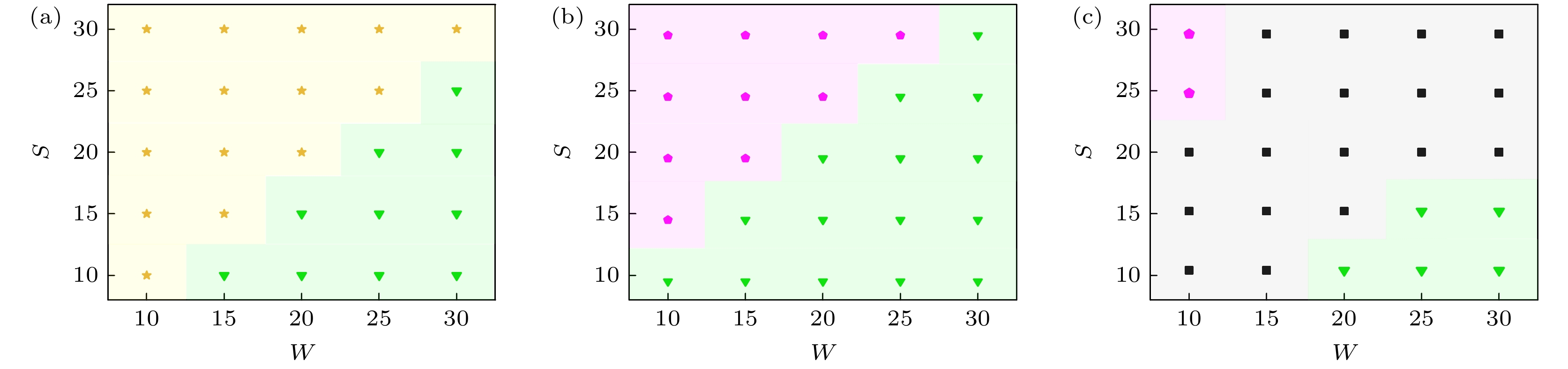
图 7 改变光照区域的宽度W和相邻光照区域间距S对体系聚集结构影响的相图(★代表横向条形结构; ▼代表井字结构; ●代表棋盘状结构; ■代表纵向条形结构) (a) Dr = 0.05, P = 0.5; (b) Dr = 0.05, P = 1.0; (c) Dr = 0.05, P = 1.5
Fig. 7. Phase diagrams showing the effect of varying the illumination region width W and the spacing S between adjacent illuminated regions on the aggregation structure of the system: (a) Dr = 0.05, P = 0.5; (b) Dr = 0.05, P = 1.0; (c) Dr = 0.05, P =1.5. ★ represents the transverse stripe structure; ▼ represents the tic-tac-toe structure; ● represents the checkerboard-like structure; ■ represents the longitudinal stripe structure.
-
[1] Ramaswamy S 2017 J. Stat. Mech. 5 054002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ramaswamy S 2010 Annu. Rev. Condens. Mater Phys. 1 323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Tailleur J, Cates M E 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 218103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Martinez R, Alarcon F, Rodriguez D R, Aragones J L, Valeriani C 2018 Eur. Phys. J. E 41 91
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Vladescu I D, Marsden E J, Schwarz-Linek J, Martinez V A, Arlt J, Morozov A N, Marenduzzo D, Cates M E, Poon W C 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 113 268101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Schweitzer F, Tilch B, Ebeling W 2000 Eur. Phys. J. B 14 157
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Erdmann U, Ebeling W, Schimansky-Geier L, Schweitzer F 2000 Eur. Phys. J. B 15 105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Schweitzer F, Ebeling W, Tilch B 1998 Phys. Rev. Lett. 80 5044
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Yang X, Manning M L, Marchetti M C 2014 Soft Matter 10 6477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Stenhammar J, Tiribocchi A, Allen R J, Marenduzzo D, Cates M E 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 111 145702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Stenhammar J, Wittkowski R, Marenduzzo D, Cates M E 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 018301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Dolai P, Simha A, Mishra S 2017 Soft Matter 14 6137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 高艺雯, 王影, 田文得, 陈康 2022 71 240501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao Y W, Wang Y, Tian W D, Chen K 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 240501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Fernandez-Rodriguez M A, Grillo F, Alvarez L, Rathlef M, Buttinoni L, Volpe G, Isa L 2020 Nat. Commun. 11 4223
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Vutukuri H R, Lisicki M, Lauga E, Vermant J 2020 Nat. Commun. 11 2628
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Hernández R J, Sevilla F J, Mazzulla A, Pagliusi P, Pellizzi N, Cipparrone G 2020 Soft Matter 16 7704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zhang J H, Guo J J, Mou F Z, Guan J G 2018 Micromachines 9 88
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Bäuerle T, Fischer A, Speck T, Bechinger C 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 3232
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wang G, Phan T V, Li S, Wombacher M, Qu J, Peng Y, Chen G, Goldman D I, Levin S A, Austin R H, Liu L Y 2021 Phys. Rev. Lett. 126 108002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Liu Y P, Wang G, Wang P L, Yuan D M, Hou S X, Jin Y K, Wang J, Liu L Y 2023 Chin. Phys. B 32 068701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K 1996 J. Mol. Graphics 14 33
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Ning H P, Zhang Y, Zhu H, Ingham A, Huang G S, Mei Y F, Solovev A A 2018 Micromachines 9 75
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chen H X, Zhao Q L, Du X M 2018 Micromachines 9 41
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Xu L L, Mou F Z, Gong H T, Luo M, Guan J G 2017 Chem. Soc. Rev. 46 6905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wang W, Duan W T, Ahmed S, Sen A, Mallouk T E 2015 Acc. Chem. Res. 48 1938
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Chen C R, Mou F Z, Xu L L, Wang S F, Guan J G, Feng Z P, Wang Q W, Kong L, Li W, Wang J, Zhang Q J 2017 Adv. Mater. 29 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Tang S S, Zhang F Y, Zhao J, Talaat W, Soto F, Karshalev E, Chen C R, Hu Z H, Lu X L, Li J X, Lin Z H, Dong H F, Zhang X J, Nourhani A, Wang J 2019 Adv. Funct. Mater. 29 1809003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Sun Y Y, Liu Y, Zhang D M, Zhang H, Jiang J W, Duan R M, Xiao J J, Xing J, Zhang D F, Dong B 2019 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11 40533
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Singh D P, Choudhury U, Fischer P, Mark A G 2017 Adv Mater. 29 32
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Lin Z, Si T, Wu Z, Gao C, Lin X, He Q 2017 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56 13517
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Wang Y, Shen Z L, Xia Y Q, Feng G Q, Tian W D 2020 Chin. Phys. B 29 053103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Pan J X, Wei H, Qi M J, Wang H F, Zhang J J, Tian W D, Chen K 2020 Soft Matter 16 5545
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Ye S M, Liu P, Wei Z X, Ye F F, Yang M C, Chen K 2020 Chin. Phys. B 29 058201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Zhou X L, Wang Y Z, Xu B J, Liu Y P, Lu D, Luo J, Yang Z Y 2023 AIP Adv. 13 065332
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Chen J M, Zhou X L, Zhang L X 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 118701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Quillen A C, Smucker J P, Peshkov A 2020 Phys. Rev. E 101 052618
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Liu P, Ye S M, Ye F F, Chen K, Yang M C 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 124 158001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Das S, Ghosh S, Chelakkot R 2020 Phys. Rev. E 102 032619
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Das S, Chelakkot R 2020 Soft Matter 16 7250
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Knežević M, Stark H 2020 New J. Phys 22 113025
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Chen X G, Lin L H, Li Z C, Sun H J 2022 Adv. Funct. Mater. 32 2104649
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Volpe G, Buttinoni I, Vogt D, Kuemmerer H J, Bechinger C 2011 Soft Matter. 7 8810
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Jahanshahi S, Lozano C, Liebchen B, Löwen H, Bechinger C 2020 Commun. Phys. 3 127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Palacci J, Sacanna S, Steinberg A P, Pine D J, Chaikin P M 2013 Science 339 936
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Xia Y Q, Shen Z L, Tian W D, Chen K 2019 J. Chem. Phys. 150 154903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Wang C, Li H S, Ma Y Q, Tian W D, Chen K 2018 J. Chem. Phys. 149 164902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] Shan W J, Zhang F, Tian W D, Chen K 2019 Soft Matter 15 4761
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[48] 石子璇, 金燕, 金奕扬, 田文得, 张天辉, 陈康 2024 73 170501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shi Z X, Jin Y, Jin Y Y, Tian W D, Zhang T H, Chen K 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 170501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[49] 王晶, 焦阳, 田文得, 陈康 2023 72 190501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J, Jiao Y, Tian W D, Chen K 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 190501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[50] Tiwari C, Singh P S 2024 Soft Matter 20 4816
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[51] Shen Y F, Hu H X, Luo M B 2024 Soft Matter 20 621
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[52] Cates M E, Tailleur J 2015 Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys. 6 219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[53] Gomez-Solano J R, Samin S, Lozano C, Ruedas-Batuecas P, van Roij R, Bechinger C 2017 Sci Rep. 7 14891
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[54] Caprini L, Marini Bettolo Marconi U, Wittmann R, Löwen H 2022 Soft Matter 8 1412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[55] Takatori S C, Yan W, Brady J F 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 113 028103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[56] Bechinger C, Di Leonardo R, Löwen H, Reichhardt C, Volpe G, Volpe G 2016 Rev. Mod. Phys. 88 045006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 920
- PDF下载量: 44
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: