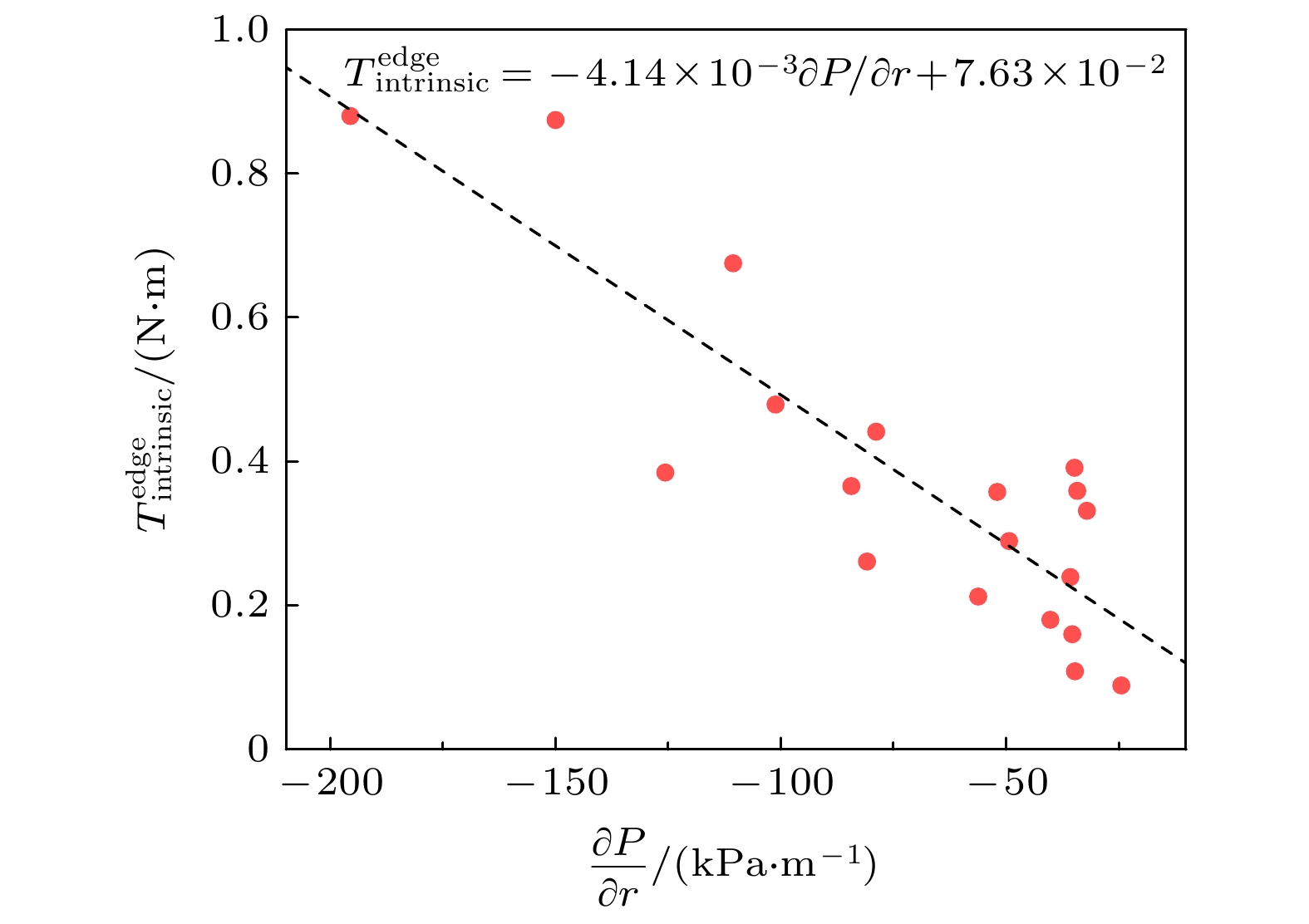
-
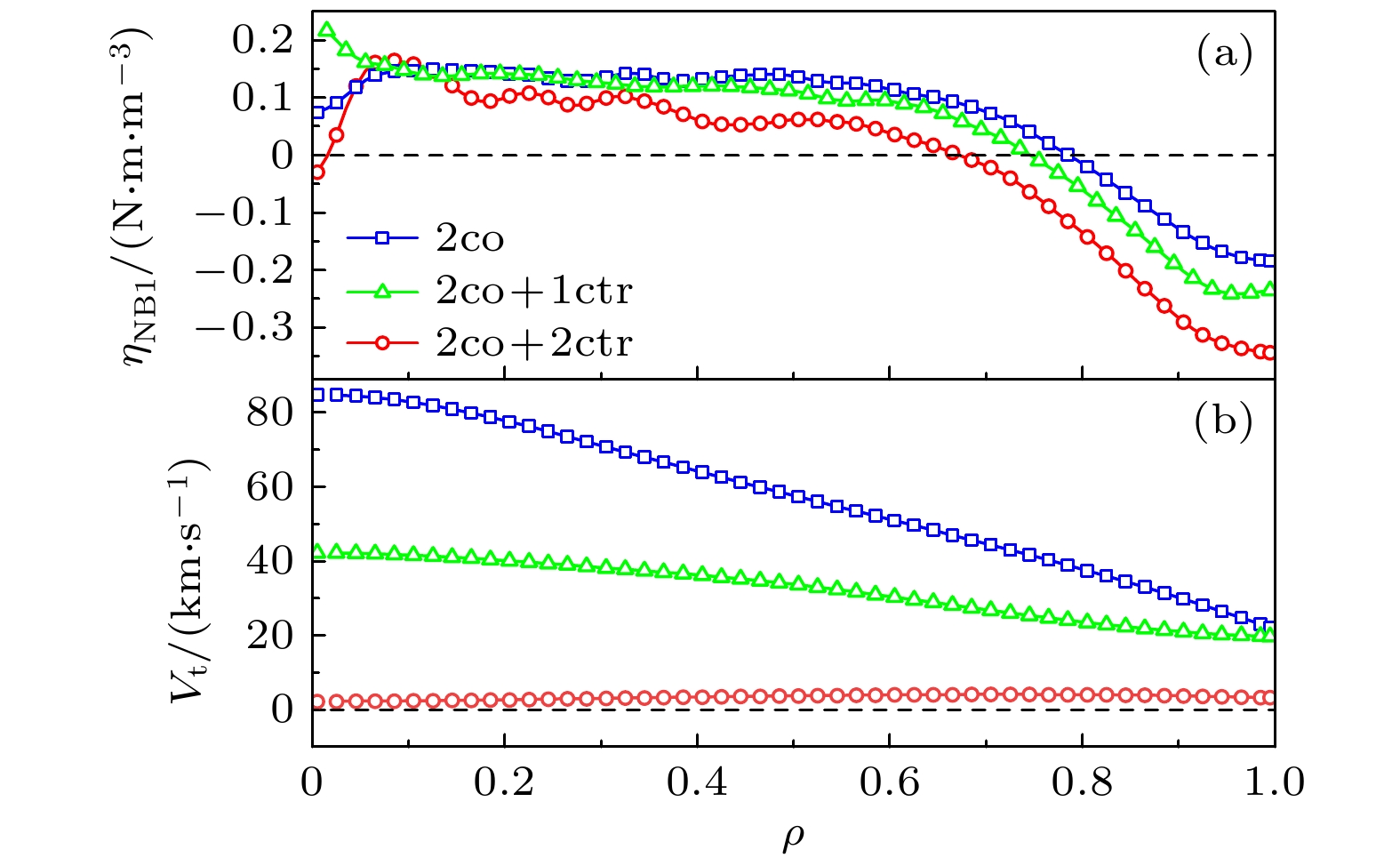
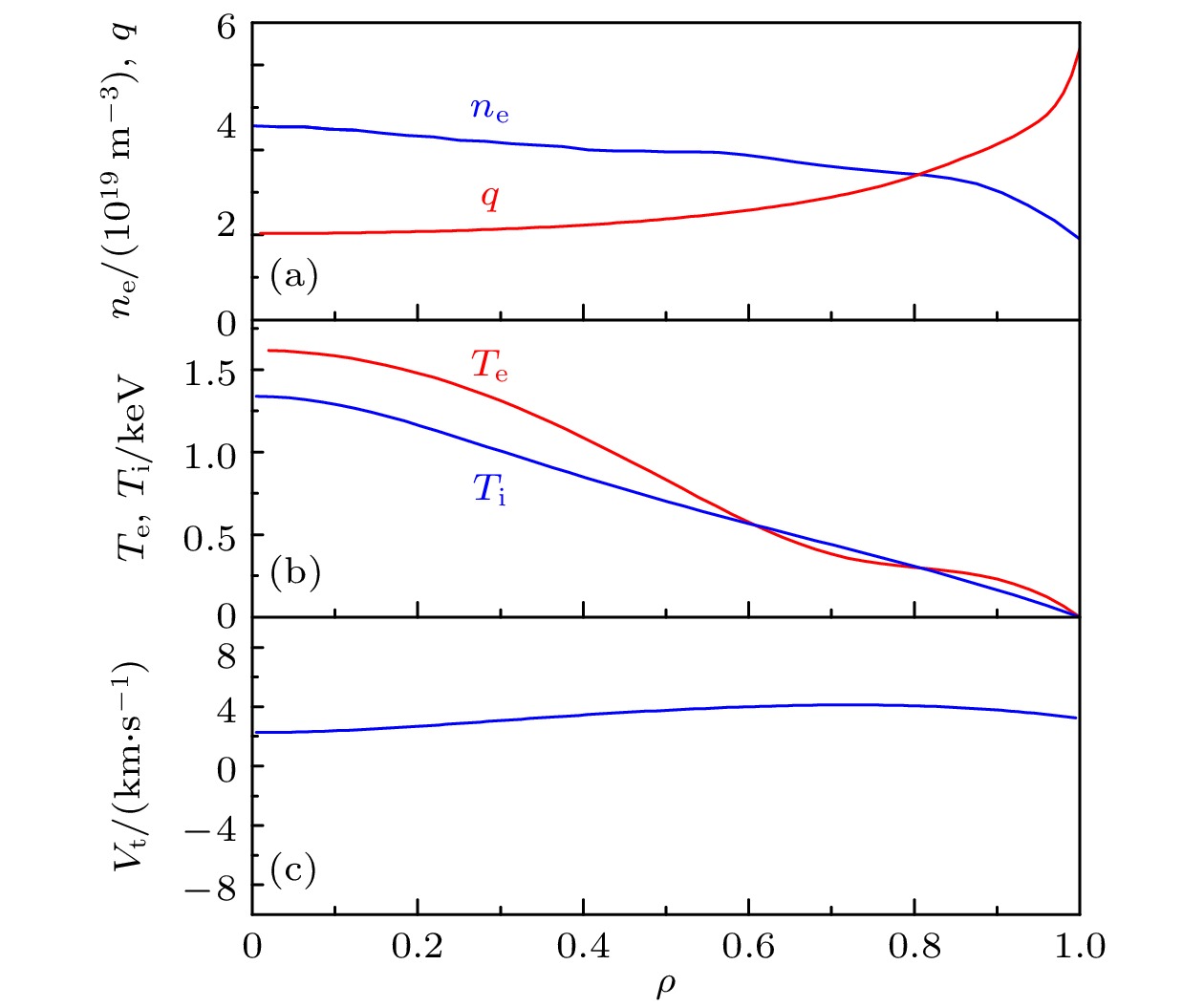
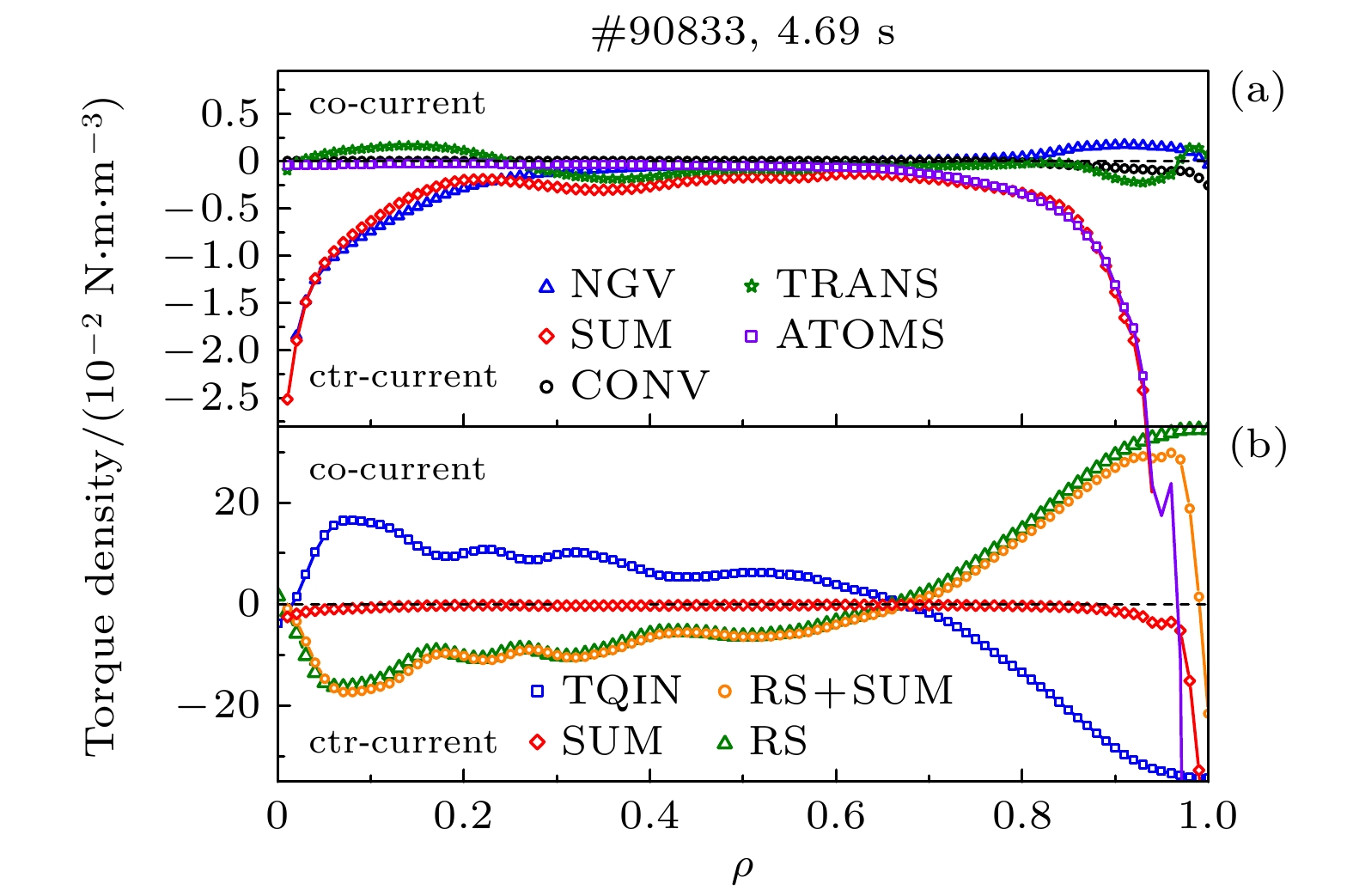
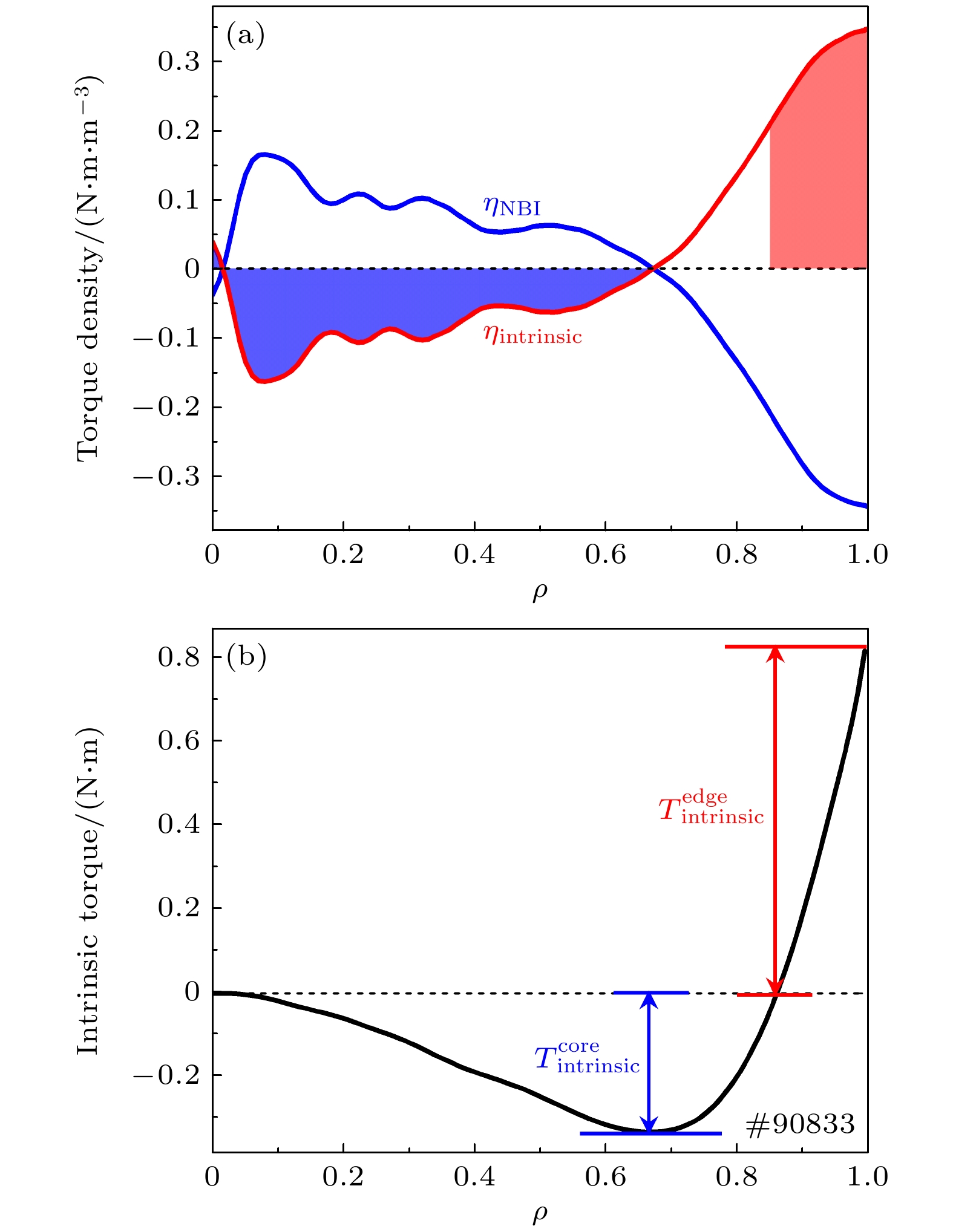
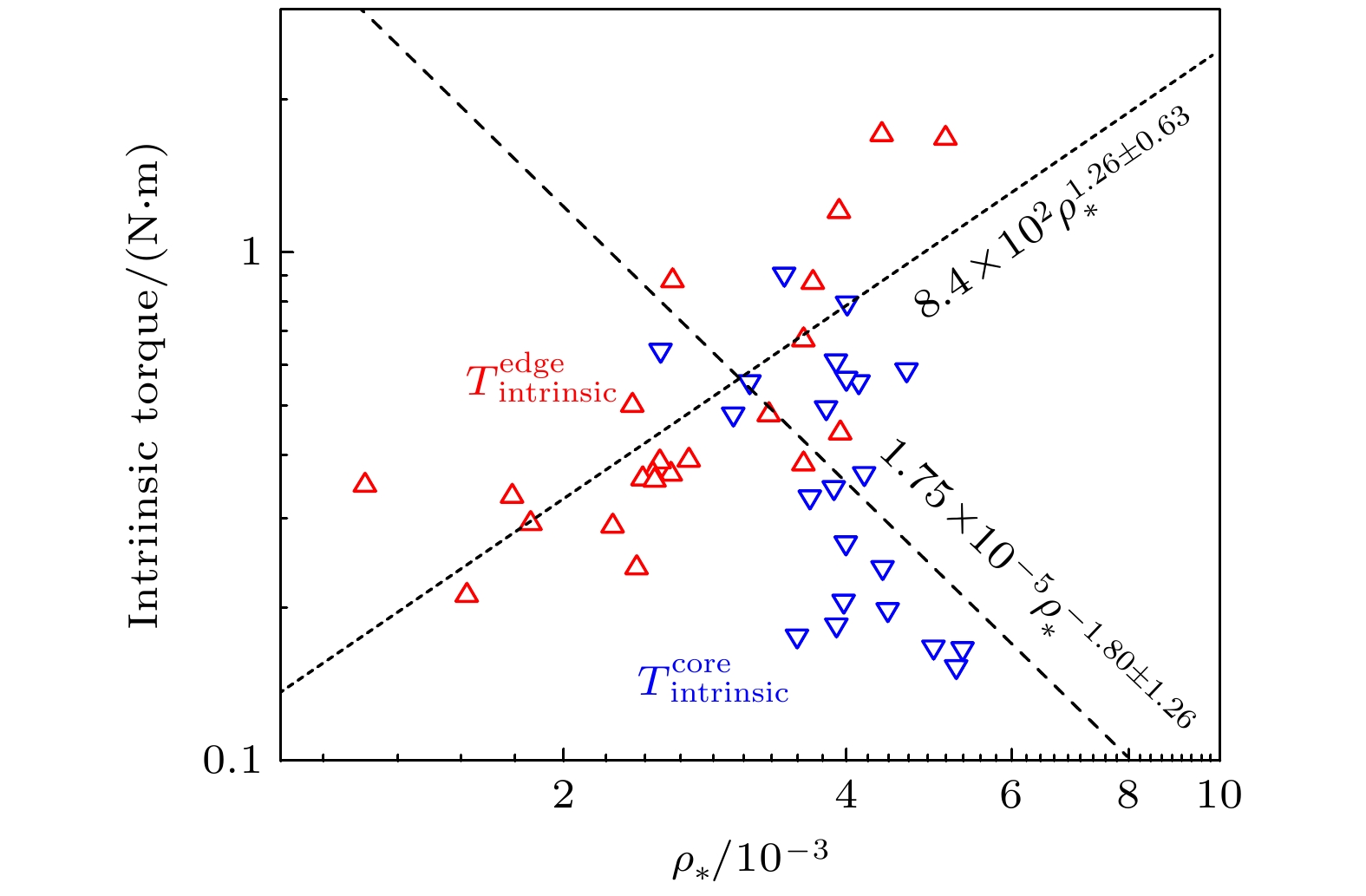
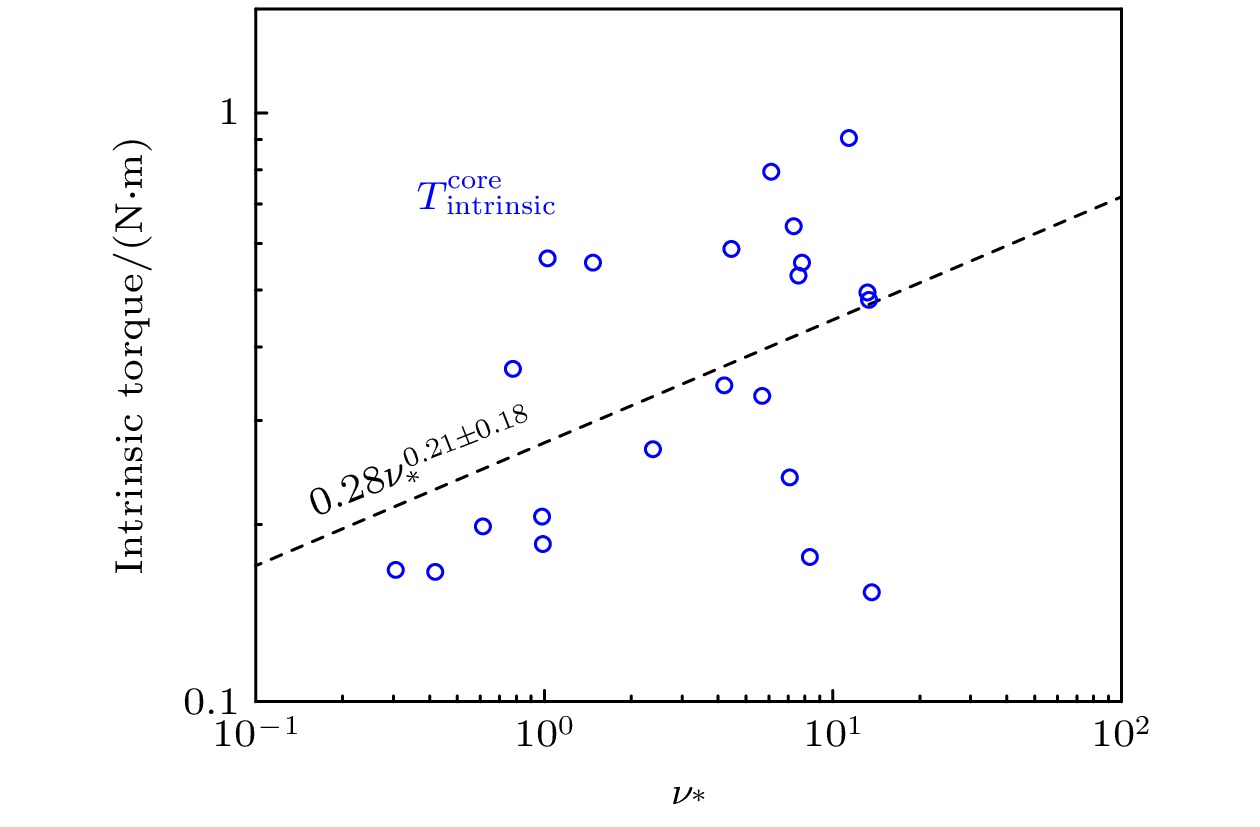
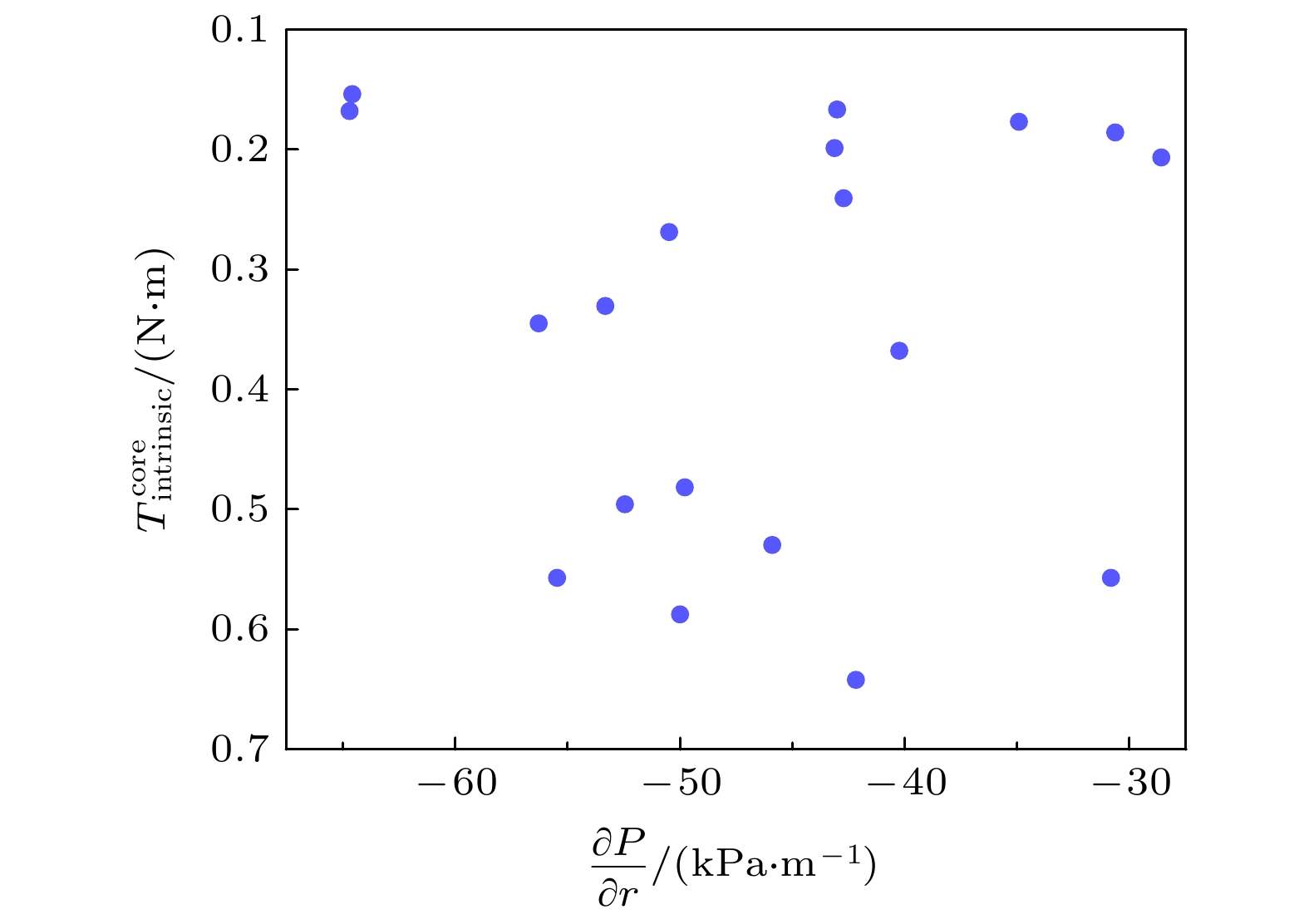
等离子体旋转及其剪切是影响聚变装置的关键参数之一, 等离子体旋转的驱动和控制对未来聚变堆的稳定运行和约束改善都具有很大意义. 目前靠外部动量注入的方式不足以在满足Q大于5的同时抑制电阻壁模不稳定性. 因此, 有必要对不依赖外部动量注入的等离子体自发旋转展开实验研究. 为了更好地预测未来聚变装置中自发旋转速度的大小, 本文在东方超环托卡马克(EAST)上开展了残余应力与无量纲参数的定标研究, 利用平衡中性束的方法进行了多次自发扭矩的实验测量, 为未来托卡马克装置中等离子体自发旋转的预测提供实验依据. 实验定标结果表明, 芯部残余应力与$\rho _{\ast }^{-1.80\pm1.26}$相关, 而边界残余应力的定标则显示出对$\rho _{\ast }^{1.26\pm0.63}$的依赖性, 这表明随着装置尺寸的增大, 未来托卡马克聚变堆中芯部的残余应力可能会增大, 而边界残余应力则减小. 芯部与边界残余应力的定标结果差异表明, 在边界区域刮削层区残余应力的产生过程中, 有$\boldsymbol{E}\times\boldsymbol{B}$流剪切以外的对称性破坏机制起主导作用. 在自发扭矩与$\nu _{\ast }$的定标之间发现芯部自发扭矩依赖于$\nu _{\ast }^{0.21\pm0.18}$. 结合芯部自发扭矩与归一化旋转半径、归一化碰撞率的定标结果, 得到芯部自发扭矩的定标律为$\rho _{\ast }^{-1.39\pm0.71}\nu _{\ast }^{-0.11\pm0.10}$. 使用ITER氘-氚混合运行方案中的等离子体参数预测得到芯部自发扭矩大小为$(1.0\pm6.3)$ N$\cdot$m, 远小于之前DIII-D预测结果.Plasma rotation and its shear are key parameters influencing the performance of fusion devices. The prediction and control of plasma rotation velocity are of great significance for improving the stable operation and confinement of future fusion reactors. External momentum injection methods are insufficient to suppress resistive wall mode instability while achieving Q greater than 5 in international thermonuclear experimental reactor (ITER). Therefore, it is necessary to conduct experimental research on intrinsic plasma rotation that does not rely on external momentum injection. To better predict the magnitude of intrinsic rotation velocity in future fusion devices, we conduct an experimental study on the scaling of residual stress and dimensionless parameters on EAST. Using the balanced neutral beam, multiple measurements of intrinsic torque are performed, providing experimental basis for predicting the intrinsic rotation in future tokamak devices. The scaling results indicate that the core residual stress is dependent on $\rho_{\ast}^{-1.80\pm1.26}$, while the scaling of edge residual stress shows an opposite trend with $\rho _{\ast }^{1.26\pm0.63}$. This suggests that as the device size increases, the core residual stress in future large devices can increase, while the edge residual stress can decrease. The difference in scaling results between the core and edge residual stress indicates that in the edge region, the symmetry-breaking mechanism other than $\boldsymbol{E}\times\boldsymbol{B}$ flow shear dominates the generation of residual stress in the scrape-off layer. A relationship is found between intrinsic torque and $\nu _{\ast }$, revealing that the core intrinsic torque depends on $\nu _{\ast }^{-0.21\pm0.18}$. Combining the scaling results of core intrinsic torque with the gyroradius and normalized collisionality, the scaling law for core intrinsic torque is obtained to be $\rho _{\ast }^{-1.39\pm0.71}\nu _{\ast }^{0.11\pm0.10}$. Using plasma parameters of ITER operation scenario 1, the core intrinsic torque in future ITER plasma is predicted to be $(1.0\pm6.3)~{\mathrm{N}}{\cdot} {\mathrm{m}}$, which is much smaller than the predicted magnitude at DIII-D.
-
Keywords:
- tokamak /
- momentum transport /
- intrinsic rotation /
- scaling law
[1] Peeters A, Angioni C, Bortolon A, Camenen Y, Casson F, Duval B, Fiederspiel L, Hornsby W, Idomura Y, Hein T, Kluy N, Mantica P, Parra F, Snodin A, Szepesi G, Strintzi D, Tala T, Tardini G, De Vries P, Weiland J 2011 Nucl. Fusion 51 094027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Diamond P, Kosuga Y, Gürcan Ö, McDevitt C, Hahm T, Fedorczak N, Rice J, Wang W, Ku S, Kwon J, Dif-Pradalier G, Abiteboul J, Wang L, Ko W, Shi Y, Ida K, Solomon W, Jhang H, Kim S, Yi S, Ko S, Sarazin Y, Singh R, Chang C 2013 Nucl. Fusion 53 104019
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ida K, Rice J 2014 Nucl. Fusion 54 045001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Rice J E 2016 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 58 083001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Stoltzfus-Dueck T 2019 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 61 124003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Garofalo A M, Strait E J, Johnson L C, La Haye R J, Lazarus E A, Navratil G A, Okabayashi M, Scoville J T, Taylor T S, Turnbull A D 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 235001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Chapman I T, Liu Y Q, Asunta O, Graves J P, Johnson T, Jucker M 2012 Phys. Plasmas 19 052502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ida K, Miura Y, Matsuda T, Itoh K, Hidekuma S, Itoh S I, Jft-2M Group 1995 Phys. Rev. Lett. 74 1990
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Rice J, Ince-Cushman A, deGrassie J, Eriksson L G, Sakamoto Y, Scarabosio A, Bortolon A, Burrell K, Duval B, Fenzi-Bonizec C, Greenwald M, Groebner R, Hoang G, Koide Y, Marmar E, Pochelon A, Podpaly Y 2007 Nucl. Fusion 47 1618
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Yoshida M, Kamada Y, Takenaga H, Sakamoto Y, Urano H, Oyama N, Matsunaga G 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 105002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Solomon W M, Burrell K H, deGrassie J S, Budny R, Groebner R J, Kinsey J E, Kramer G J, Luce T C, Makowski M A, Mikkelsen D, Nazikian R, Petty C C, Politzer P A, Scott S D, Van Zeeland M A, Zarnstorff M C 2007 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 49 B313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Solomon W M, Burrell K H, Garofalo A M, Kaye S M, Bell R E, Cole A J, deGrassie J S, Diamond P H, Hahm T S, Jackson G L, Lanctot M J, Petty C C, Reimerdes H, Sabbagh S A, Strait E J, Tala T, Waltz R E 2010 Phys. Plasmas 17 056108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Chrystal C, Grierson B A, Solomon W M, Tala T, deGrassie J S, Petty C C, Salmi A, Burrell K H 2017 Phys. Plasmas 24 042501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Rice J, Cao N, Tala T, Chrystal C, Greenwald M, Hughes J, Marmar E, Reinke M, Rodriguez Fernandez P, Salmi A 2021 Nucl. Fusion 61 026013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zimmermann C, McDermott R, Angioni C, Duval B, Dux R, Fable E, Salmi A, Stroth U, Tala T, Tardini G, Pütterich T, the ASDEX Upgrade Team 2023 Nucl. Fusion 63 126006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Rice J, Duval B, Reinke M, Podpaly Y, Bortolon A, Churchill R, Cziegler I, Diamond P, Dominguez A, Ennever P, Fiore C, Granetz R, Greenwald M, Hubbard A, Hughes J, Irby J, Ma Y, Marmar E, McDermott R, Porkolab M, Tsujii N, Wolfe S 2011 Nucl. Fusion 51 083005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang X, Lyu B, Lu X, Li Y, Solomon W M, Hao B, Chen J, Wang F, Fu J, Zhang H, Yang J, Bin B, He L, Li Y, Wan S, Gong X, Wan B, Ye M 2020 Plasma Sci. Technol. 22 065104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Bae C, Jin Y, Lyu B, Hao B, Li Y, Zhang X, Liu H, Zhang H, Wang F, Fu J, Fu J, Huang J, Zeng L, Zang Q, Li Y, He L, Lu D 2024 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 66 045020
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yang S, Na Y S, Na D, Park J K, Shi Y, Ko W, Lee S, Hahm T 2018 Nucl. Fusion 58 066008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zimmermann C F B, McDermott R M, Fable E, Angioni C, Duval B P, Dux R, Salmi A, Stroth U, Tala T, Tardini G, Pütterich T 2022 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 64 055020
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ohtani Y, Yoshida M, Honda M, Narita E 2021 AIP Adv. 11 085306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Wan B, Gong X, Liang Y, Xiang N, Xu G, Sun Y, Wang L, Qian J, Liu H, Zhang B, Xia T, Huang J, Ding R, Zhang T, Zuo G, Sun Z, Zeng L, Zhang X, Zang Q, Lyu B, Garofalo A, Li G, Li K, Yang Q, For The East Team And Collaborators 2022 Nucl. Fusion 62 042010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Liu H, Jie Y, Ding W, Brower D, Zou Z, Qian J, Li W, Yang Y, Zeng L, Zhang S, Lan T, Wang S, Hanada K, Wei X, Hu L, Wan B 2016 JINST 11 C01049
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Zang Q, Zhao J, Yang L, Hu Q, Xi X, Dai X, Yang J, Han X, Li M, Hsieh C L 2011 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 82 063502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhao H, Zhou T, Liu Y, Ti A, Ling B, Austin M E, Houshmandyar S, Huang H, Rowan W L, Hu L 2018 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 89 10H111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Li Y Y, Fu J, Lyu B, Du X W, Li C Y, Zhang Y, Yin X H, Yu Y, Wang Q P, von Hellermann M, Shi Y J, Ye M Y, Wan B N 2014 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85 11E428
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Yin X H, Li Y Y, Fu J, Jiang D, Feng S Y, Gu Y Q, Cheng Y, Lyu B, Shi Y J, Ye M Y, Wan B N 2016 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 87 11E539
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Yin X, Li Y, Fu J, Jiang D, Lyu B, Shi Y, Ye M, Wan B 2019 Fusion Eng. Des. 148 111282
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Yoshida M, Koide Y, Takenaga H, Urano H, Oyama N, Kamiya K, Sakamoto Y, Kamada Y, Team T J 2006 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 48 1673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Tala T, Crombé K, De Vries P C, Ferreira J, Mantica P, Peeters A G, Andrew Y, Budny R, Corrigan G, Eriksson A, Garbet X, Giroud C, Hua M D, Nordman H, Naulin V, Nave M F F, Parail V, Rantamäki K, Scott B D, Strand P, Tardini G, Thyagaraja A, Weiland J, Zastrow K D, JET-EFDA Contributors 2007 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 49 B291
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Ryter F, Dux R, Mantica P, Tala T 2010 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 52 124043
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 杨进, 陈俊, 王福地, 李颖颖, 吕波, 向东, 尹相辉, 张洪明, 符佳, 刘海庆, 臧庆, 储宇奇, 刘建文, 王勋禺, 宾斌, 何梁, 万顺宽, 龚学余, 叶民友 2020 69 055201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang J, Chen J, Wang F D, Li Y Y, Lyu B, Xiang D, Yin X H, Zhang H M, Fu J, Liu H Q, Zang Q, Chu Y Q, Liu J W, Wang X Y, Bin B, He L, Wan S K, Gong X Y, Ye M Y 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 055201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Bae C, Stacey W, Solomon W 2013 Nucl. Fusion 53 043011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Bae C, Jin Y, Lyu B, Fu J, Wang F, Zhang H 2024 Comput. Phys. Commun. 296 108992
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Goldston R J 1981 J. Comput. Phys. 43 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Pankin A, McCune D, Andre R, Bateman G, Kritz A 2004 Comput. Phys. Commun. 159 157
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Solomon W, Burrell K, deGrassie J, Boedo J, Garofalo A, Moyer R, Muller S, Petty C, Reimerdes H 2011 Nucl. Fusion 51 073010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Rice J E, Ince-Cushman A C, Reinke M L, Podpaly Y, Greenwald M J, LaBombard B, Marmar E S 2008 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 50 124042
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Kosuga Y, Diamond P H, Gürcan ff D 2010 Phys. Plasmas 17 102313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Green B J, Team I I, Teams P 2003 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 45 687
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] III R W B, Stoltzfus-Dueck T 2024 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 66 065011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Parra F I, Barnes M 2015 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusionn 57 045002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
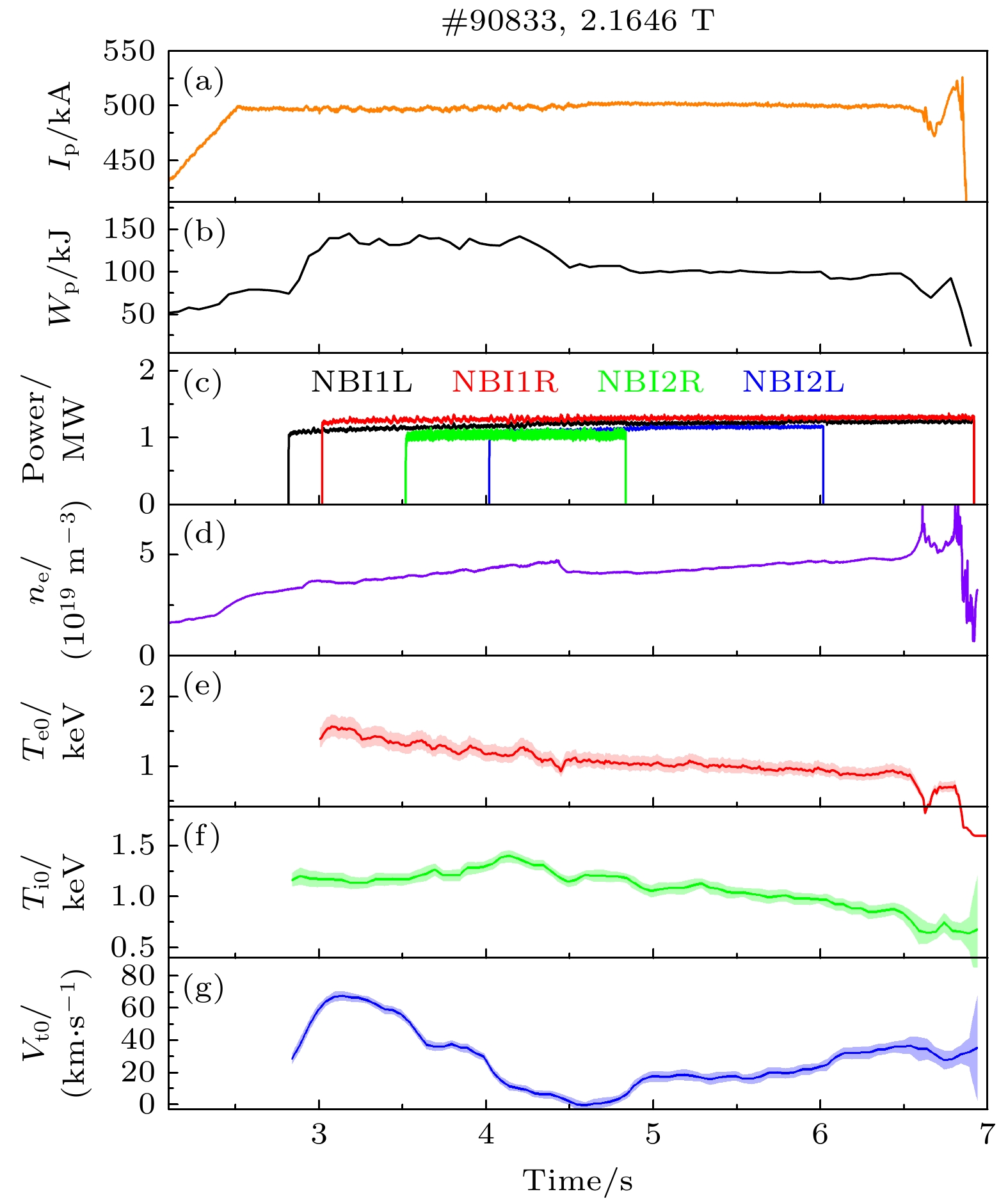
图 2 (a)等离子体电流、(b)等离子体储能、(c)中性束功率、(d)平均电子密度、(e)芯部电子温度、(f)芯部离子温度和(g)芯部环向旋转速度随时间演化
Fig. 2. Time evolutions of (a) plasma current, (b) stored energy, (c) neutral beam source power, (d) line-averaged electron density, (e) central electron temperature, (f) central ion temperature, and (g) central toroidal rotation velocity.
-
[1] Peeters A, Angioni C, Bortolon A, Camenen Y, Casson F, Duval B, Fiederspiel L, Hornsby W, Idomura Y, Hein T, Kluy N, Mantica P, Parra F, Snodin A, Szepesi G, Strintzi D, Tala T, Tardini G, De Vries P, Weiland J 2011 Nucl. Fusion 51 094027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Diamond P, Kosuga Y, Gürcan Ö, McDevitt C, Hahm T, Fedorczak N, Rice J, Wang W, Ku S, Kwon J, Dif-Pradalier G, Abiteboul J, Wang L, Ko W, Shi Y, Ida K, Solomon W, Jhang H, Kim S, Yi S, Ko S, Sarazin Y, Singh R, Chang C 2013 Nucl. Fusion 53 104019
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ida K, Rice J 2014 Nucl. Fusion 54 045001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Rice J E 2016 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 58 083001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Stoltzfus-Dueck T 2019 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 61 124003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Garofalo A M, Strait E J, Johnson L C, La Haye R J, Lazarus E A, Navratil G A, Okabayashi M, Scoville J T, Taylor T S, Turnbull A D 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 235001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Chapman I T, Liu Y Q, Asunta O, Graves J P, Johnson T, Jucker M 2012 Phys. Plasmas 19 052502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ida K, Miura Y, Matsuda T, Itoh K, Hidekuma S, Itoh S I, Jft-2M Group 1995 Phys. Rev. Lett. 74 1990
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Rice J, Ince-Cushman A, deGrassie J, Eriksson L G, Sakamoto Y, Scarabosio A, Bortolon A, Burrell K, Duval B, Fenzi-Bonizec C, Greenwald M, Groebner R, Hoang G, Koide Y, Marmar E, Pochelon A, Podpaly Y 2007 Nucl. Fusion 47 1618
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Yoshida M, Kamada Y, Takenaga H, Sakamoto Y, Urano H, Oyama N, Matsunaga G 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 105002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Solomon W M, Burrell K H, deGrassie J S, Budny R, Groebner R J, Kinsey J E, Kramer G J, Luce T C, Makowski M A, Mikkelsen D, Nazikian R, Petty C C, Politzer P A, Scott S D, Van Zeeland M A, Zarnstorff M C 2007 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 49 B313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Solomon W M, Burrell K H, Garofalo A M, Kaye S M, Bell R E, Cole A J, deGrassie J S, Diamond P H, Hahm T S, Jackson G L, Lanctot M J, Petty C C, Reimerdes H, Sabbagh S A, Strait E J, Tala T, Waltz R E 2010 Phys. Plasmas 17 056108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Chrystal C, Grierson B A, Solomon W M, Tala T, deGrassie J S, Petty C C, Salmi A, Burrell K H 2017 Phys. Plasmas 24 042501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Rice J, Cao N, Tala T, Chrystal C, Greenwald M, Hughes J, Marmar E, Reinke M, Rodriguez Fernandez P, Salmi A 2021 Nucl. Fusion 61 026013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zimmermann C, McDermott R, Angioni C, Duval B, Dux R, Fable E, Salmi A, Stroth U, Tala T, Tardini G, Pütterich T, the ASDEX Upgrade Team 2023 Nucl. Fusion 63 126006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Rice J, Duval B, Reinke M, Podpaly Y, Bortolon A, Churchill R, Cziegler I, Diamond P, Dominguez A, Ennever P, Fiore C, Granetz R, Greenwald M, Hubbard A, Hughes J, Irby J, Ma Y, Marmar E, McDermott R, Porkolab M, Tsujii N, Wolfe S 2011 Nucl. Fusion 51 083005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang X, Lyu B, Lu X, Li Y, Solomon W M, Hao B, Chen J, Wang F, Fu J, Zhang H, Yang J, Bin B, He L, Li Y, Wan S, Gong X, Wan B, Ye M 2020 Plasma Sci. Technol. 22 065104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Bae C, Jin Y, Lyu B, Hao B, Li Y, Zhang X, Liu H, Zhang H, Wang F, Fu J, Fu J, Huang J, Zeng L, Zang Q, Li Y, He L, Lu D 2024 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 66 045020
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yang S, Na Y S, Na D, Park J K, Shi Y, Ko W, Lee S, Hahm T 2018 Nucl. Fusion 58 066008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zimmermann C F B, McDermott R M, Fable E, Angioni C, Duval B P, Dux R, Salmi A, Stroth U, Tala T, Tardini G, Pütterich T 2022 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 64 055020
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ohtani Y, Yoshida M, Honda M, Narita E 2021 AIP Adv. 11 085306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Wan B, Gong X, Liang Y, Xiang N, Xu G, Sun Y, Wang L, Qian J, Liu H, Zhang B, Xia T, Huang J, Ding R, Zhang T, Zuo G, Sun Z, Zeng L, Zhang X, Zang Q, Lyu B, Garofalo A, Li G, Li K, Yang Q, For The East Team And Collaborators 2022 Nucl. Fusion 62 042010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Liu H, Jie Y, Ding W, Brower D, Zou Z, Qian J, Li W, Yang Y, Zeng L, Zhang S, Lan T, Wang S, Hanada K, Wei X, Hu L, Wan B 2016 JINST 11 C01049
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Zang Q, Zhao J, Yang L, Hu Q, Xi X, Dai X, Yang J, Han X, Li M, Hsieh C L 2011 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 82 063502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhao H, Zhou T, Liu Y, Ti A, Ling B, Austin M E, Houshmandyar S, Huang H, Rowan W L, Hu L 2018 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 89 10H111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Li Y Y, Fu J, Lyu B, Du X W, Li C Y, Zhang Y, Yin X H, Yu Y, Wang Q P, von Hellermann M, Shi Y J, Ye M Y, Wan B N 2014 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85 11E428
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Yin X H, Li Y Y, Fu J, Jiang D, Feng S Y, Gu Y Q, Cheng Y, Lyu B, Shi Y J, Ye M Y, Wan B N 2016 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 87 11E539
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Yin X, Li Y, Fu J, Jiang D, Lyu B, Shi Y, Ye M, Wan B 2019 Fusion Eng. Des. 148 111282
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Yoshida M, Koide Y, Takenaga H, Urano H, Oyama N, Kamiya K, Sakamoto Y, Kamada Y, Team T J 2006 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 48 1673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Tala T, Crombé K, De Vries P C, Ferreira J, Mantica P, Peeters A G, Andrew Y, Budny R, Corrigan G, Eriksson A, Garbet X, Giroud C, Hua M D, Nordman H, Naulin V, Nave M F F, Parail V, Rantamäki K, Scott B D, Strand P, Tardini G, Thyagaraja A, Weiland J, Zastrow K D, JET-EFDA Contributors 2007 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 49 B291
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Ryter F, Dux R, Mantica P, Tala T 2010 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 52 124043
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 杨进, 陈俊, 王福地, 李颖颖, 吕波, 向东, 尹相辉, 张洪明, 符佳, 刘海庆, 臧庆, 储宇奇, 刘建文, 王勋禺, 宾斌, 何梁, 万顺宽, 龚学余, 叶民友 2020 69 055201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang J, Chen J, Wang F D, Li Y Y, Lyu B, Xiang D, Yin X H, Zhang H M, Fu J, Liu H Q, Zang Q, Chu Y Q, Liu J W, Wang X Y, Bin B, He L, Wan S K, Gong X Y, Ye M Y 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 055201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Bae C, Stacey W, Solomon W 2013 Nucl. Fusion 53 043011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Bae C, Jin Y, Lyu B, Fu J, Wang F, Zhang H 2024 Comput. Phys. Commun. 296 108992
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Goldston R J 1981 J. Comput. Phys. 43 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Pankin A, McCune D, Andre R, Bateman G, Kritz A 2004 Comput. Phys. Commun. 159 157
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Solomon W, Burrell K, deGrassie J, Boedo J, Garofalo A, Moyer R, Muller S, Petty C, Reimerdes H 2011 Nucl. Fusion 51 073010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Rice J E, Ince-Cushman A C, Reinke M L, Podpaly Y, Greenwald M J, LaBombard B, Marmar E S 2008 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 50 124042
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Kosuga Y, Diamond P H, Gürcan ff D 2010 Phys. Plasmas 17 102313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Green B J, Team I I, Teams P 2003 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 45 687
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] III R W B, Stoltzfus-Dueck T 2024 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 66 065011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Parra F I, Barnes M 2015 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusionn 57 045002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 825
- PDF下载量: 31
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: