-
颗粒-流体界面处的耦合传热以及颗粒间的碰撞在颗粒沉降过程中起着至关重要的作用. 本文基于热颗粒流体积格子Boltzmann方法对流固耦合传热作用下封闭通道中两颗粒沉降过程拖曳-接触-翻滚运动开展了数值模拟研究, 探究了颗粒与流体比热容比${R_{{c_{\text{v}}}}}$、Grashof数$Gr$、颗粒初始温度对拖曳-接触-翻滚运动的影响. 结果表明, 随着比热容比${R_{{c_{\text{v}}}}}$的增加, 两冷颗粒沉降过程拖曳-接触-翻滚运动的拖曳时长和翻滚时长均减小, 而接触时长则相应增加. 随着Grashof数$Gr$的增加, 两冷颗粒沉降过程拖曳-接触-翻滚运动的拖曳时长显著减小, 但接触时长和翻滚时长则近似保持不变. 两冷颗粒沉降过程拖曳-接触-翻滚运动发生的时刻最早, 一冷一热颗粒次之, 两热颗粒最晚; 颗粒初始温度低于流体温度对拖曳-接触-翻滚运动的促进作用主要体现在拖曳阶段和接触阶段, 颗粒初始温度对翻滚时长则近似无影响.The conjugate heat transfer at the particle-fluid interface and the collision between particles play a crucial role in the sedimentation process of particles. In this work, the recent volumetric lattice Boltzmann method for thermal particulate flows with conjugate heat transfer is adopted to investigate the drafting-kissing-tumbling movement in the sedimentation process of two particles in a closed channel. This volumetric lattice Boltzmann method is based on double distribution functions, with the density distribution function used for the velocity field and the internal energy distribution function used for the temperature field. It is a single-domain approach, and the nonslip velocity condition within the solid domain can be strictly ensured. The difference in thermophysical properties between the solid and fluid can be correctly handled, and the conjugate heat transfer condition can be automatically achieved without any additional treatments. Based on this particle-resolved simulation, the influences of the solid-to-fluid specific heat ratio, the Grashof number, and the particle’s initial temperature on the drafting-kissing-tumbling movement are discussed in detail. It is found that the fluid cooled by the particle and thus subjected to the downward buoyancy force can promote particle sedimentation. As the specific heat ratio increases, the particle’s temperature rises relatively slowly. In the sedimentation of two cold particles, the drafting duration and tumbling duration of the drafting-kissing-tumbling movement decrease when the heat capacity ratio increases. In contrast, the kissing duration increases as the heat capacity ratio increases. When the Grashof number increases, the heat transfer between the particle and fluid is enhanced, and the drafting duration significantly decreases while the kissing duration and tumbling duration remain almost unchanged in the sedimentation of two cold particles. The particle’s initial temperature greatly affects the occurrence moment of the drafting-kissing-tumbling movement. To be specific, the drafting-kissing-tumbling movement occurs at the earliest moment for the sedimentation of two cold particles, followed by the sedimentation of one cold and one hot particle, and the latest for the sedimentation of two hot particles. The promoting effect of the low particle’s initial temperature on the drafting-kissing-tumbling movement mainly takes place in the dragging stage and kissing stage. The particle’s initial temperature has almost no influence on the tumbling duration.
[1] Yang G C, Jing L, Kwok C Y, Sobral Y D 2019 Comput. Geotech. 114 103100
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 王尤富 2005 特种油气藏 12 91
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y F 2005 Special Oil Gas Reservoirs 12 91
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Li H Y, Xue H R, Zhang J Y, Zhang G J 2023 Processes 11 2573
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Nie D M, Lin J Z 2010 Commun. Comput. Phys. 7 544
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Uhlmann M 2005 J. Comput. Phys. 209 448
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Fortes A F, Joseph D D, Lundgren T S 1987 J. Fluid Mech. 177 467
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wang Z, Fan J, Luo K 2008 Int. J. Multiphase Flow 34 283
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Feng J, Hu H H, Joseph D D 1994 J. Fluid Mech. 261 95
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wang L, Guo Z, Mi J 2014 Comput. Fluids 96 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Gan H, Chang J, Feng J J, Hu H H 2003 J. Fluid Mech. 481 385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 仝志辉 2010 59 1884
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tong Z H 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 1884
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 毛威, 郭照立, 王亮 2013 62 084703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mao W, Guo Z L, Wang L 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 084703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 刘汉涛, 常建忠, 安康, 苏铁熊 2010 59 1877
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu H T, Chang J Z, An K, Su T X 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 1877
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Yang B, Chen S, Cao C, Liu Z, Zheng C 2016 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 93 477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ström H, Sasic S 2015 Procedia Eng. 102 1563
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Feng Z G, Michaelides E E 2004 J. Comput. Phys. 195 602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Liu J, Huang C, Chai Z, Shi B 2022 Comput. Fluids 233 105240
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 史冬岩, 王志凯, 张阿漫 2014 63 074703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shi D Y, Wang Z K, Zhang A M 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 074703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 孙东科, 项楠, 陈科, 倪中华 2013 62 024703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun D K, Xiang N, Chen K, Ni Z H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 024703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] He X, Chen S, Doolen G D 1998 J. Comput. Phys. 146 282
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zhang X, Wang D, Li Q, Huang R 2024 arXiv: 2410.23802 [physics. comp-ph]
[22] Qian Y H, d’Humières D, Lallemand P 1992 Europhys. Lett. 17 479
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chai Z, Shi B 2020 Phys. Rev. E 102 023306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Lallemand P, Luo L S 2000 Phys. Rev. E 61 6546
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Huang R, Wu H 2016 J. Comput. Phys. 315 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Huang H, Yang X, Krafczyk M, Lu X Y 2012 J. Fluid Mech. 692 369
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Suzuki K, Inamuro T 2011 Comput. Fluids 49 173
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Glowinski R, Pan T W, Hesla T I, Joseph D D, Periaux J 2001 J. Comput. Phys. 169 363
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
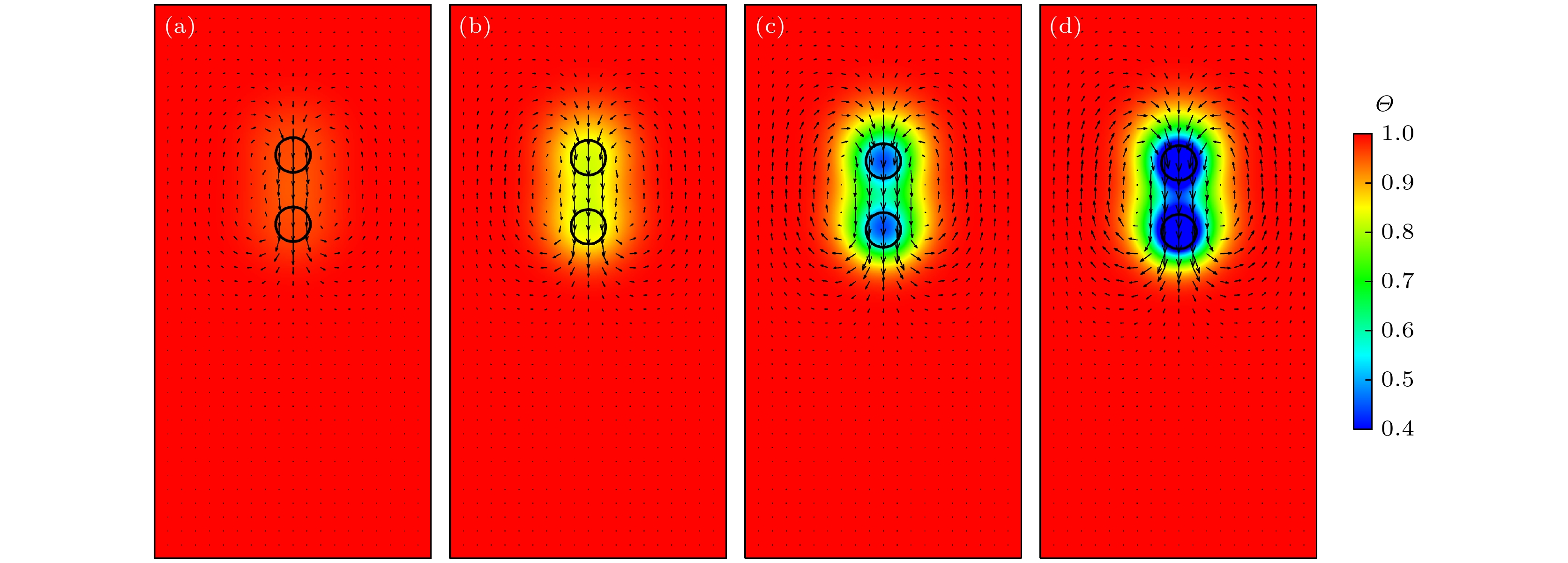
图 2 不同${R_{{c_{\text{v}}}}}$时, 两颗粒沉降过程在$t = 0.084{\text{ s}}$时刻的无量纲温度场、速度矢量和颗粒位置 (a) ${R_{{c_{\text{v}}}}} = 0.25$; (b) ${R_{{c_{\text{v}}}}} = 1$; (c) ${R_{{c_{\text{v}}}}} = 4$; (d) ${R_{{c_{\text{v}}}}} = 16$
Fig. 2. Dimensionless temperature field, velocity vectors, and particle positions in the sedimentation process of two particles at time $t = 0.084{\text{ s}}$ for different ${R_{{c_{\text{v}}}}}$: (a) ${R_{{c_{\text{v}}}}} = 0.25$; (b) ${R_{{c_{\text{v}}}}} = 1$; (c) ${R_{{c_{\text{v}}}}} = 4$; (d) ${R_{{c_{\text{v}}}}} = 16$.
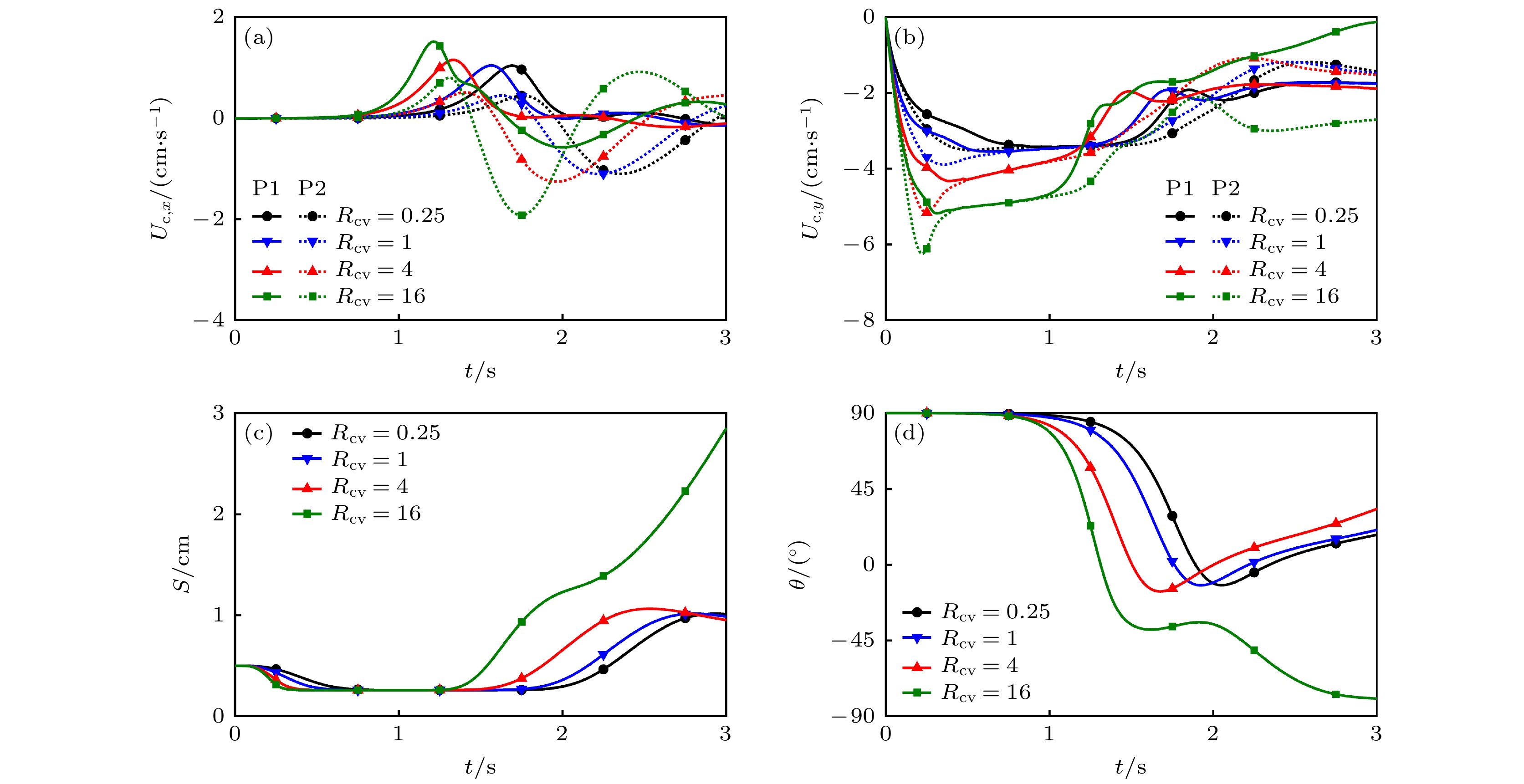
图 3 不同${R_{{c_{\text{v}}}}}$时, 两颗粒沉降过程不同因素随时间的变化 (a) 质心水平速度${U_{{\text{c}}, x}}$; (b) 质心竖直速度${U_{{\text{c}}, y}}$; (c) 质心距离$S$; (d) 质心水平夹角$\theta $
Fig. 3. Variations of different factors with time in the sedimentation process of two particles for different ${R_{{c_{\text{v}}}}}$: (a) The horizontal velocity of mass center ${U_{{\text{c}}, x}}$; (b) the vertical velocity of mass center ${U_{{\text{c}}, y}}$; (c) the distance between mass center $S$; (d) the horizontal angle of mass center $\theta $.
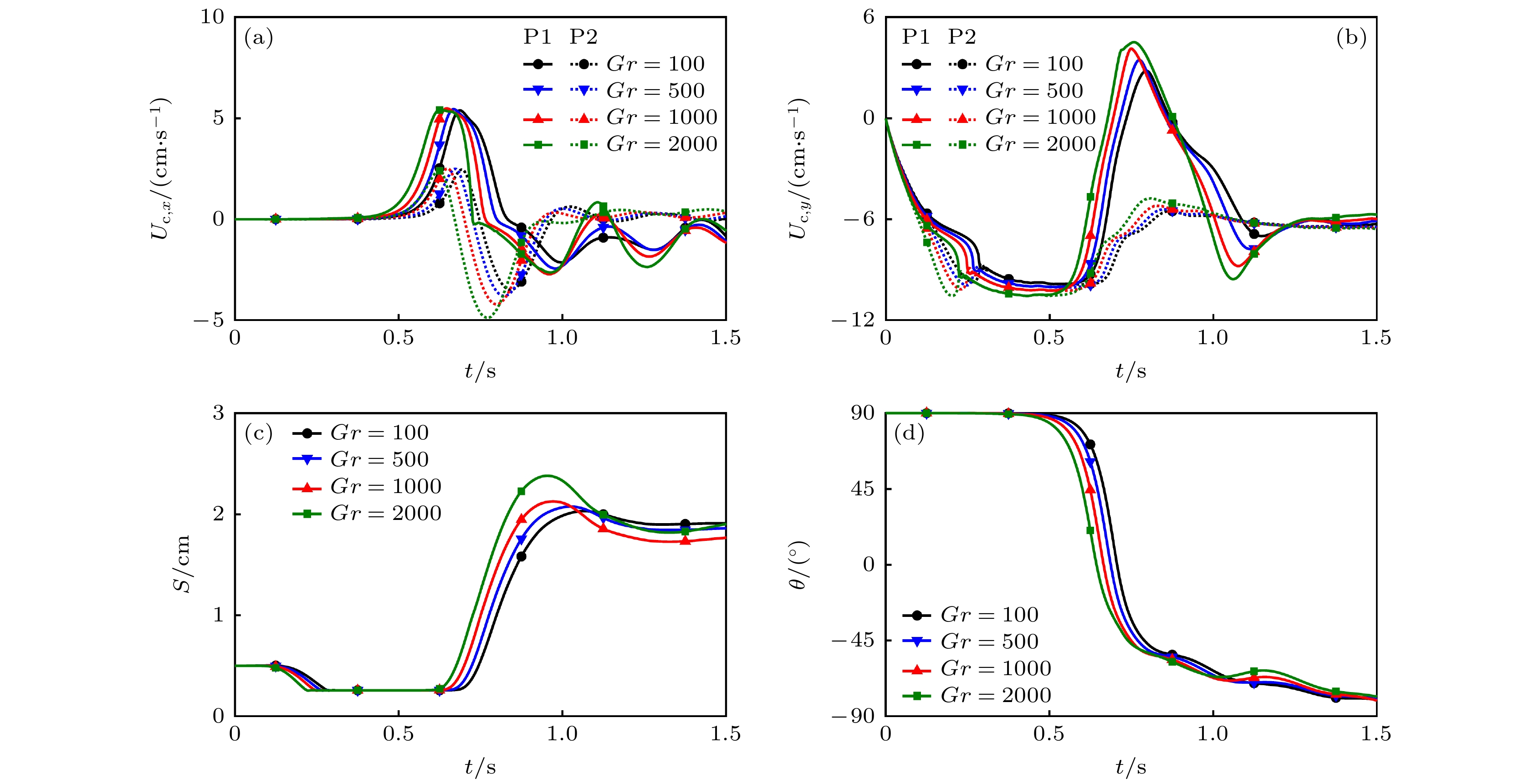
图 4 不同$Gr$时, 两颗粒沉降过程不同因素随时间的变化 (a) 质心水平速度${U_{{\text{c}}, x}}$; (b) 质心竖直速度${U_{{\text{c}}, y}}$; (c) 质心距离$S$; (d) 质心水平夹角$\theta $
Fig. 4. Variations of different factors with time in the sedimentation process of two particles for different $Gr$: (a) The horizontal velocity of mass center ${U_{{\text{c}}, x}}$; (b) the vertical velocity of mass center ${U_{{\text{c}}, y}}$; (c) the distance between mass center $S$; (d) the horizontal angle of mass center $\theta $.
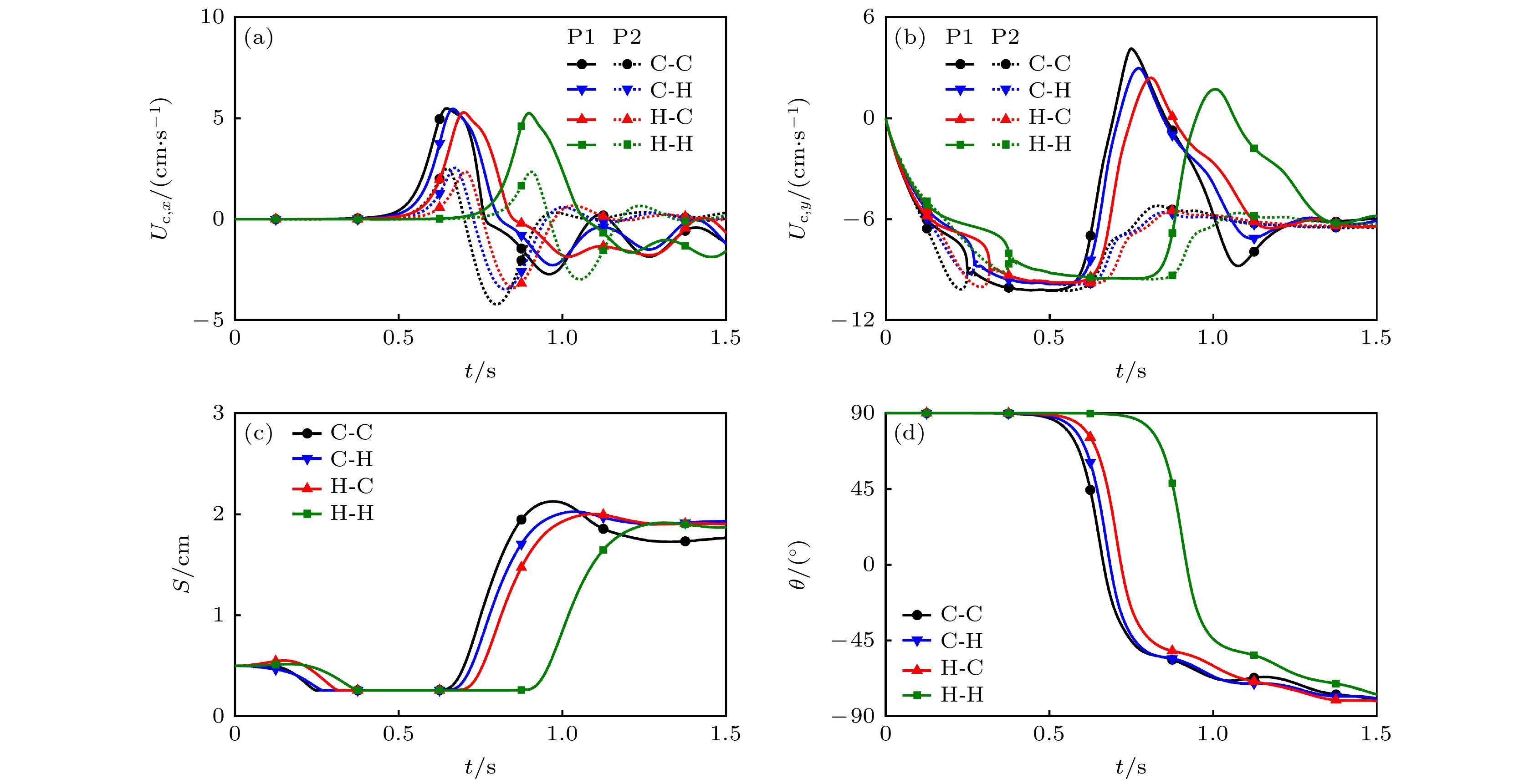
图 5 不同颗粒初始温度时, 两颗粒沉降过程不同因素随时间的变化 (a) 质心水平速度${U_{{\text{c}}, x}}$; (b) 质心竖直速度${U_{{\text{c}}, y}}$; (c) 质心距离$S$; (d) 质心水平夹角$\theta $
Fig. 5. Variations of different factors with time in the sedimentation process of two particles for different particle’s initial temperatures: (a) The horizontal velocity of mass center ${U_{{\text{c}}, x}}$; (b) the vertical velocity of mass center ${U_{{\text{c}}, y}}$; (c) the distance between mass center $S$; (d) the horizontal angle of mass center $\theta $.
表 1 不同${R_{{c_{\text{v}}}}}$时, 两颗粒沉降过程的接触时刻${t_{{\text{kiss}}}}$、翻滚时刻${t_{{\text{tumble}}}}$、分离时刻${t_{{\text{detach}}}}$、拖曳时长$\Delta {t_{{\text{draft}}}}$、接触时长$\Delta {t_{{\text{kiss}}}}$、翻滚时长$\Delta {t_{{\text{tumble}}}}$
Table 1. The kissing, tumbling, and detaching moments (${t_{{\text{kiss}}}}$, ${t_{{\text{tumble}}}}$, and ${t_{{\text{detach}}}}$) and the drafting, kissing, and tumbling durations ($\Delta {t_{{\text{draft}}}}$, $\Delta {t_{{\text{kiss}}}}$, and $\Delta {t_{{\text{tumble}}}}$) in the sedimentation process of two particles for different ${R_{{c_{\text{v}}}}}$.
${R_{{c_{\text{v}}}}}$ ${t_{{\text{kiss}}}}$/s ${t_{{\text{tumble}}}}$/s ${t_{{\text{detach}}}}$/s $\Delta {t_{{\text{draft}}}}$/s $\Delta {t_{{\text{kiss}}}}$/s $\Delta {t_{{\text{tumble}}}}$/s 0.25 0.707 0.938 1.890 0.707 0.231 0.952 1 0.561 0.821 1.761 0.561 0.260 0.940 4 0.387 0.689 1.510 0.387 0.303 0.821 16 0.314 0.686 1.314 0.314 0.372 0.628 表 2 不同$Gr$时, 两颗粒沉降过程的接触时刻${t_{{\text{kiss}}}}$、翻滚时刻${t_{{\text{tumble}}}}$、分离时刻${t_{{\text{detach}}}}$、拖曳时长$\Delta {t_{{\text{draft}}}}$、接触时长$\Delta {t_{{\text{kiss}}}}$、翻滚时长$\Delta {t_{{\text{tumble}}}}$
Table 2. The kissing, tumbling, and detaching moments (${t_{{\text{kiss}}}}$, ${t_{{\text{tumble}}}}$, and ${t_{{\text{detach}}}}$) and the drafting, kissing, and tumbling durations ($\Delta {t_{{\text{draft}}}}$, $\Delta {t_{{\text{kiss}}}}$, and $\Delta {t_{{\text{tumble}}}}$) in the sedimentation process of two particles for different $Gr$.
$Gr$ ${t_{{\text{kiss}}}}$/s ${t_{{\text{tumble}}}}$/s ${t_{{\text{detach}}}}$/s $\Delta {t_{{\text{draft}}}}$/s $\Delta {t_{{\text{kiss}}}}$/s $\Delta {t_{{\text{tumble}}}}$/s 100 0.275 0.489 0.689 0.275 0.214 0.200 500 0.257 0.468 0.669 0.257 0.211 0.201 1000 0.239 0.444 0.647 0.239 0.205 0.203 2000 0.214 0.413 0.623 0.214 0.199 0.210 表 3 不同颗粒初始温度时, 两颗粒沉降过程的接触时刻${t_{{\text{kiss}}}}$、翻滚时刻${t_{{\text{tumble}}}}$、分离时刻${t_{{\text{detach}}}}$、拖曳时长$\Delta {t_{{\text{draft}}}}$、接触时长$\Delta {t_{{\text{kiss}}}}$、翻滚时长$\Delta {t_{{\text{tumble}}}}$
Table 3. The kissing, tumbling, and detaching moments (${t_{{\text{kiss}}}}$, ${t_{{\text{tumble}}}}$, and ${t_{{\text{detach}}}}$) and the drafting, kissing, and tumbling durations ($\Delta {t_{{\text{draft}}}}$, $\Delta {t_{{\text{kiss}}}}$, and $\Delta {t_{{\text{tumble}}}}$) in the sedimentation process of two particles for different particle’s initial temperatures.
Case ${t_{{\text{kiss}}}}$/s ${t_{{\text{tumble}}}}$/s ${t_{{\text{detach}}}}$/s $\Delta {t_{{\text{draft}}}}$/s $\Delta {t_{{\text{kiss}}}}$/s $\Delta {t_{{\text{tumble}}}}$/s C-C 0.239 0.444 0.647 0.239 0.205 0.203 C-H 0.258 0.469 0.669 0.258 0.211 0.200 H-C 0.307 0.501 0.701 0.307 0.194 0.200 H-H 0.365 0.703 0.902 0.365 0.338 0.199 -
[1] Yang G C, Jing L, Kwok C Y, Sobral Y D 2019 Comput. Geotech. 114 103100
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 王尤富 2005 特种油气藏 12 91
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y F 2005 Special Oil Gas Reservoirs 12 91
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Li H Y, Xue H R, Zhang J Y, Zhang G J 2023 Processes 11 2573
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Nie D M, Lin J Z 2010 Commun. Comput. Phys. 7 544
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Uhlmann M 2005 J. Comput. Phys. 209 448
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Fortes A F, Joseph D D, Lundgren T S 1987 J. Fluid Mech. 177 467
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wang Z, Fan J, Luo K 2008 Int. J. Multiphase Flow 34 283
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Feng J, Hu H H, Joseph D D 1994 J. Fluid Mech. 261 95
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wang L, Guo Z, Mi J 2014 Comput. Fluids 96 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Gan H, Chang J, Feng J J, Hu H H 2003 J. Fluid Mech. 481 385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 仝志辉 2010 59 1884
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tong Z H 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 1884
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 毛威, 郭照立, 王亮 2013 62 084703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mao W, Guo Z L, Wang L 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 084703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 刘汉涛, 常建忠, 安康, 苏铁熊 2010 59 1877
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu H T, Chang J Z, An K, Su T X 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 1877
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Yang B, Chen S, Cao C, Liu Z, Zheng C 2016 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 93 477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ström H, Sasic S 2015 Procedia Eng. 102 1563
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Feng Z G, Michaelides E E 2004 J. Comput. Phys. 195 602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Liu J, Huang C, Chai Z, Shi B 2022 Comput. Fluids 233 105240
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 史冬岩, 王志凯, 张阿漫 2014 63 074703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shi D Y, Wang Z K, Zhang A M 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 074703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 孙东科, 项楠, 陈科, 倪中华 2013 62 024703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun D K, Xiang N, Chen K, Ni Z H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 024703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] He X, Chen S, Doolen G D 1998 J. Comput. Phys. 146 282
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zhang X, Wang D, Li Q, Huang R 2024 arXiv: 2410.23802 [physics. comp-ph]
[22] Qian Y H, d’Humières D, Lallemand P 1992 Europhys. Lett. 17 479
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chai Z, Shi B 2020 Phys. Rev. E 102 023306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Lallemand P, Luo L S 2000 Phys. Rev. E 61 6546
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Huang R, Wu H 2016 J. Comput. Phys. 315 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Huang H, Yang X, Krafczyk M, Lu X Y 2012 J. Fluid Mech. 692 369
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Suzuki K, Inamuro T 2011 Comput. Fluids 49 173
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Glowinski R, Pan T W, Hesla T I, Joseph D D, Periaux J 2001 J. Comput. Phys. 169 363
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 1543
- PDF下载量: 49
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: