-
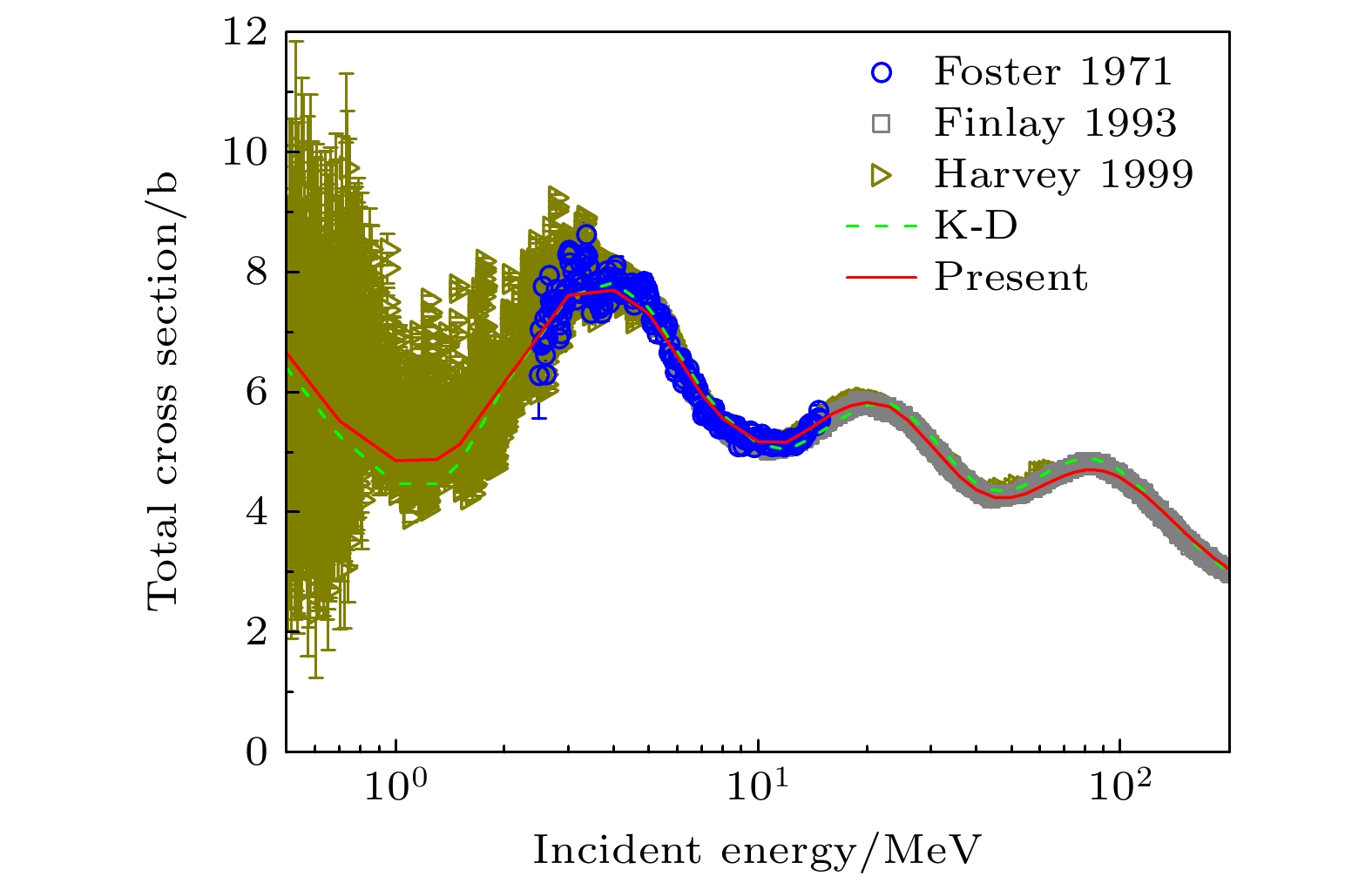
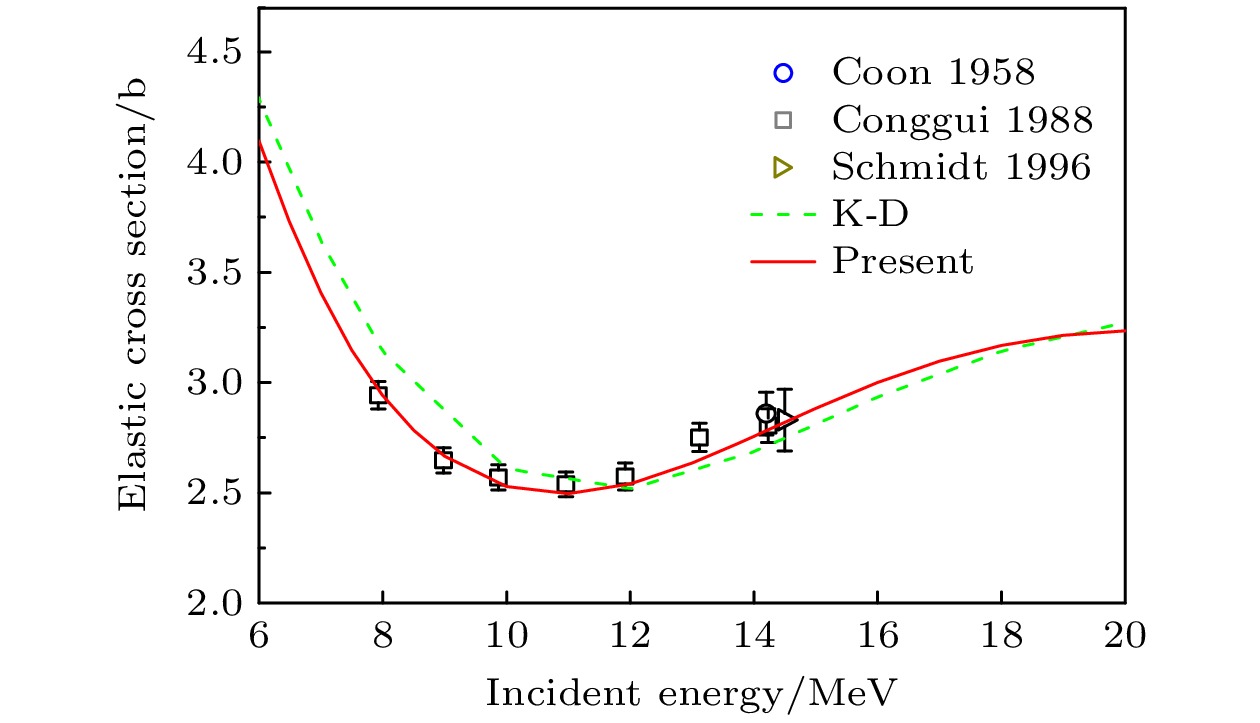
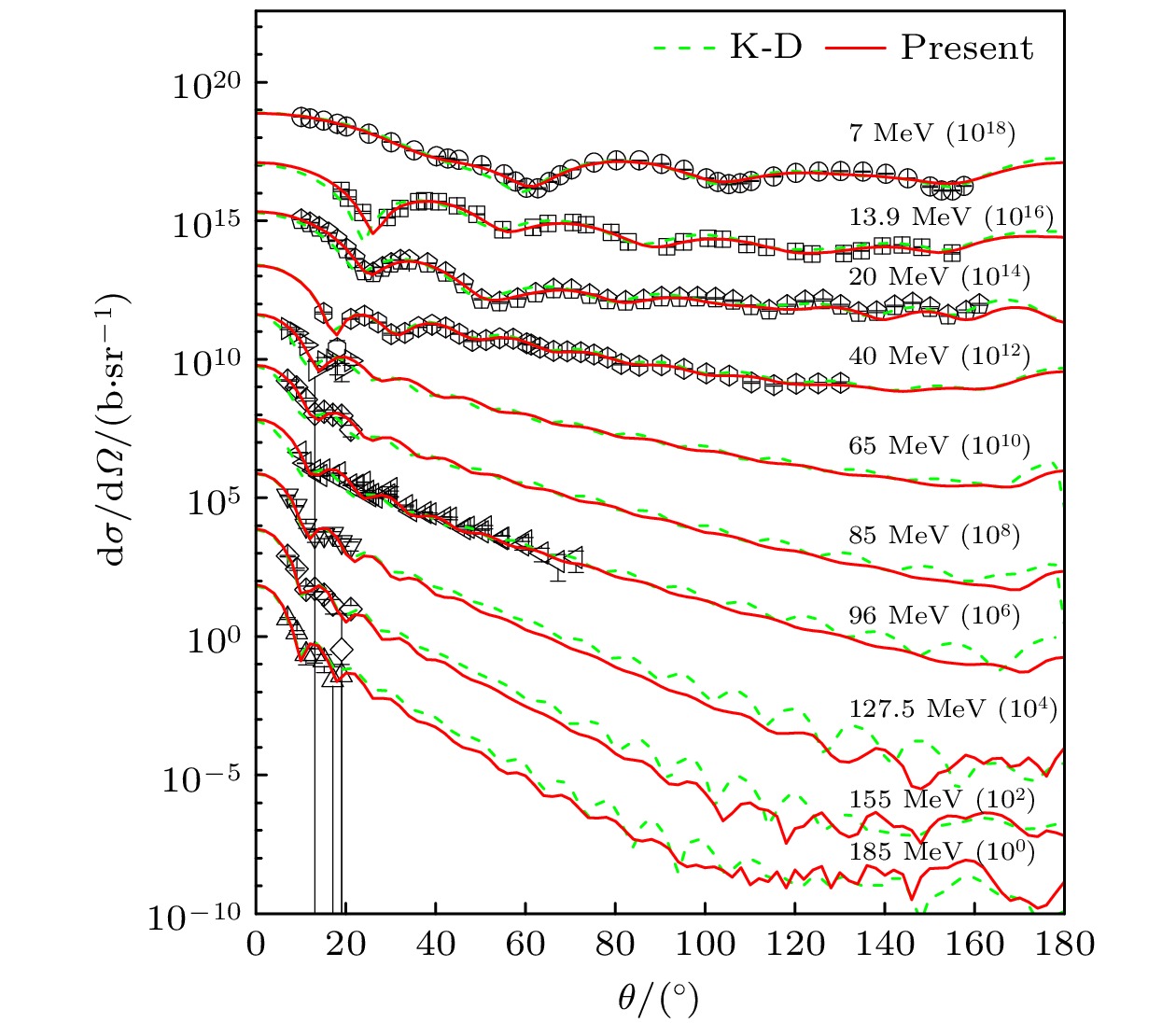
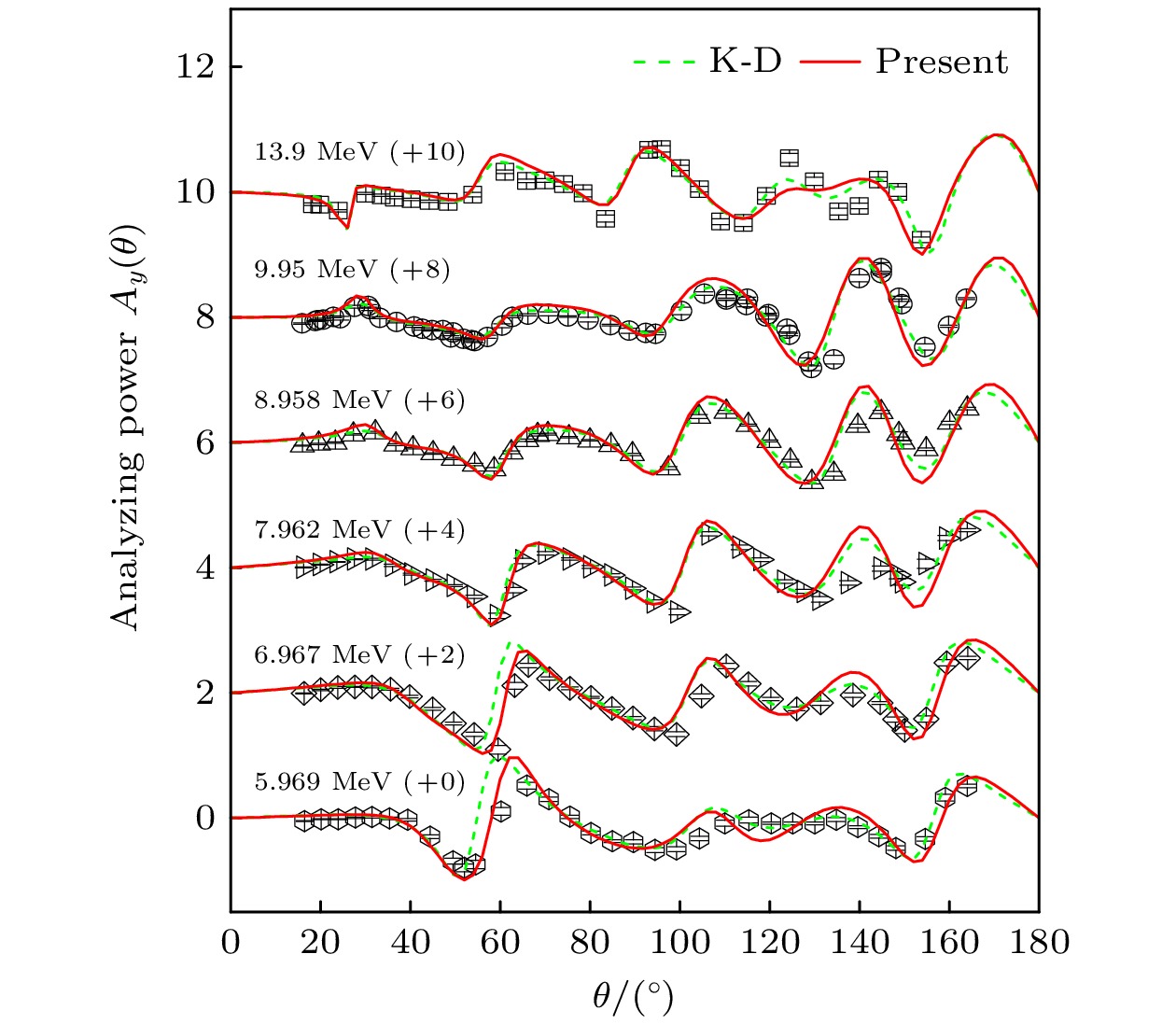
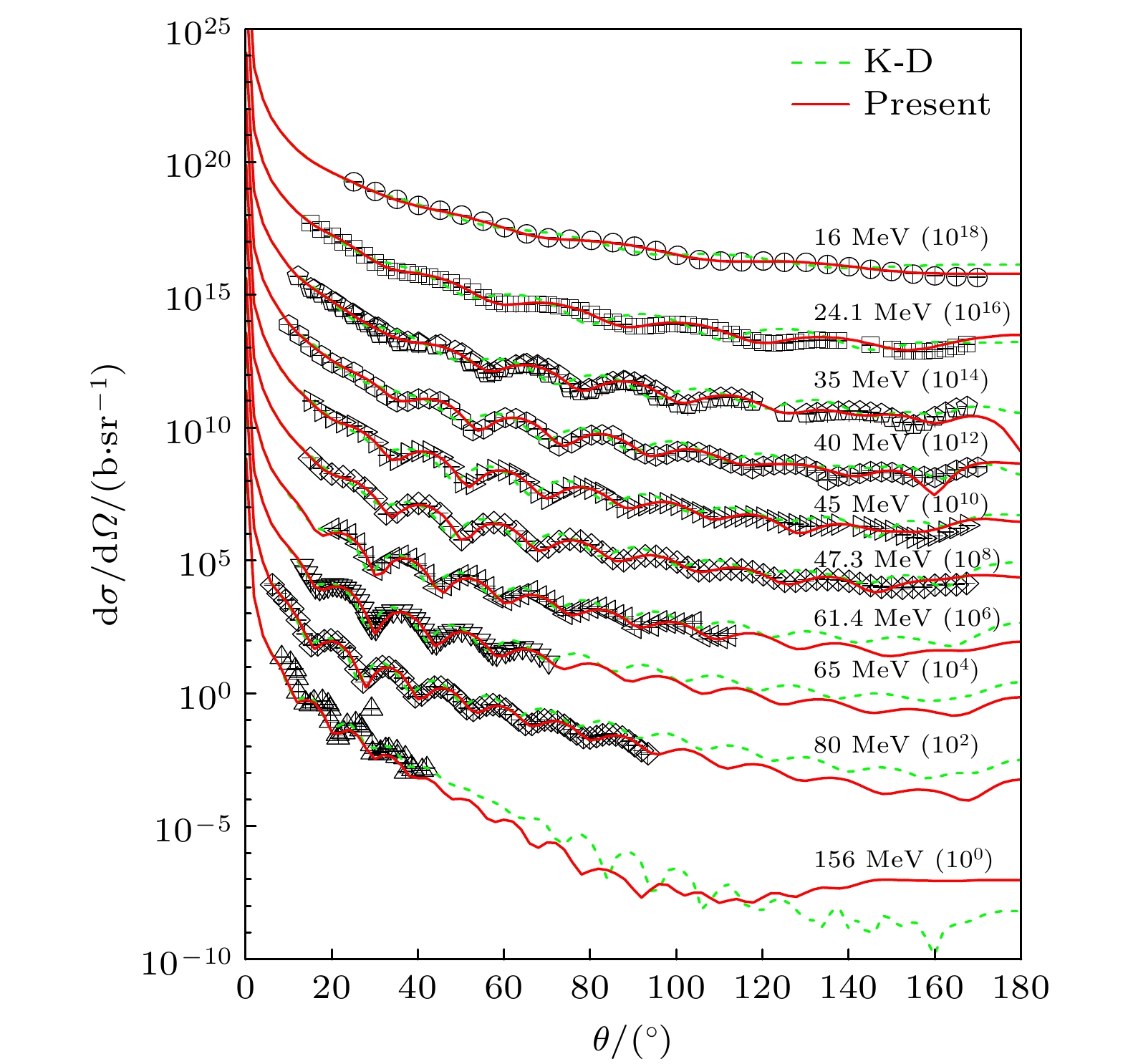
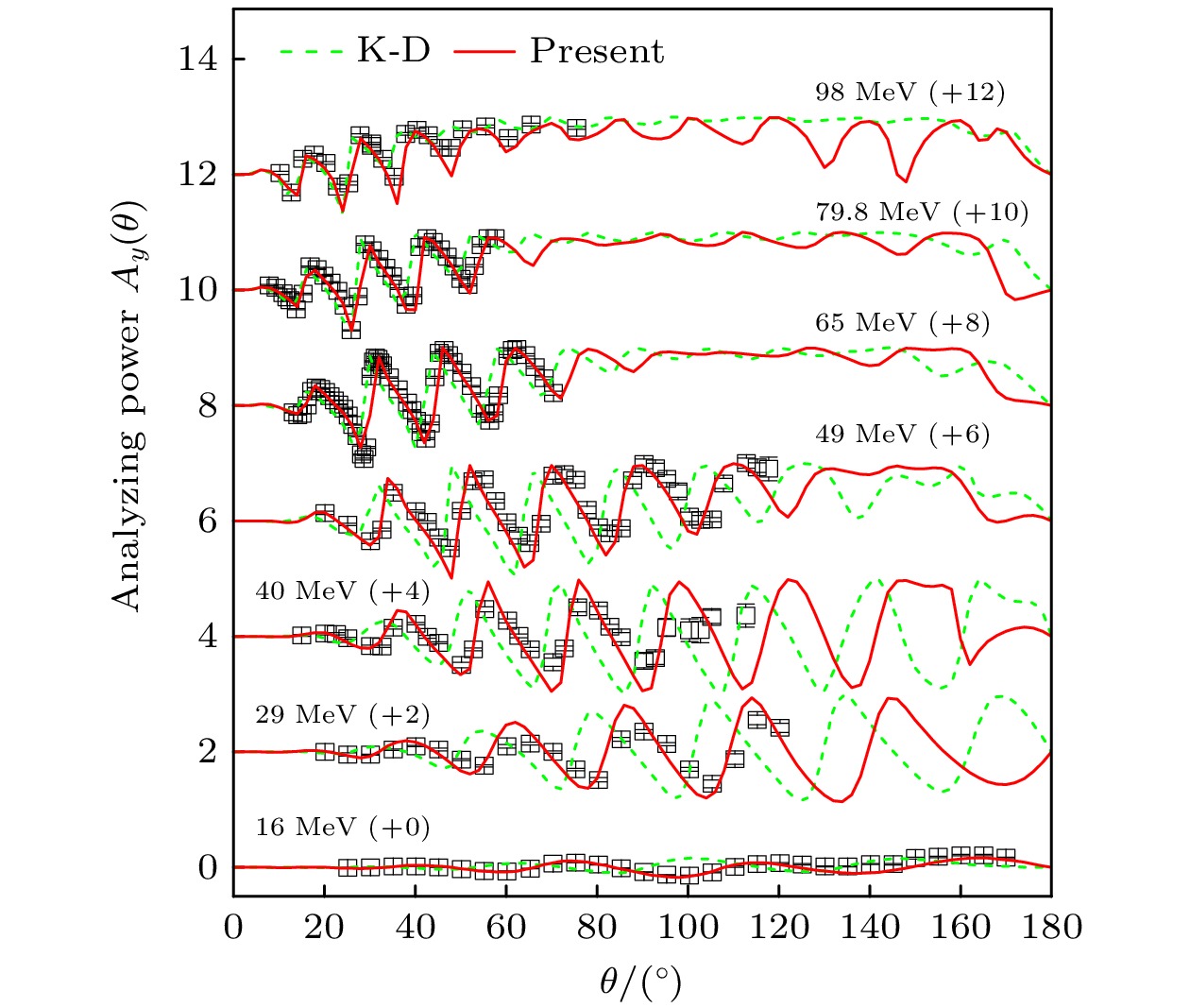
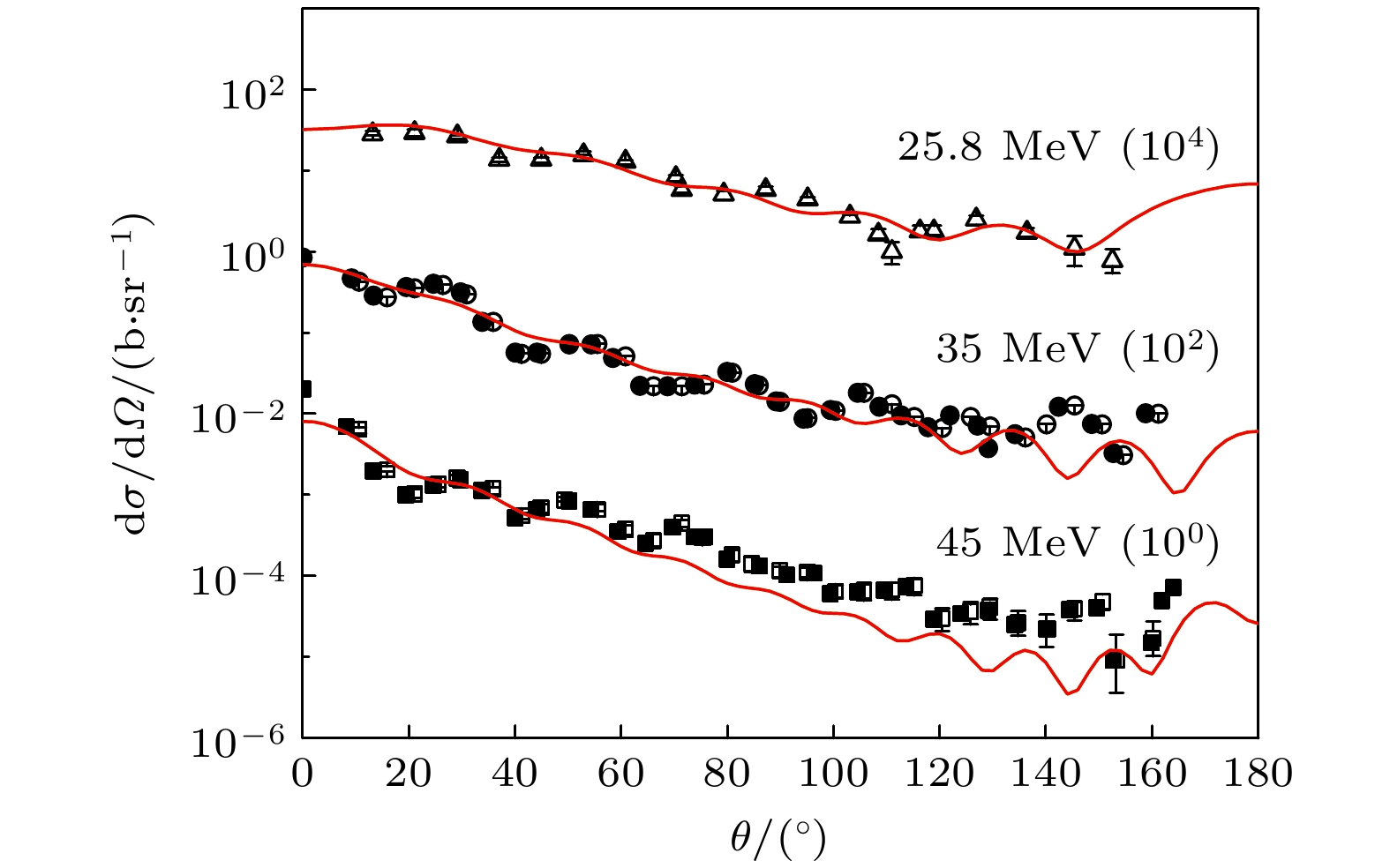
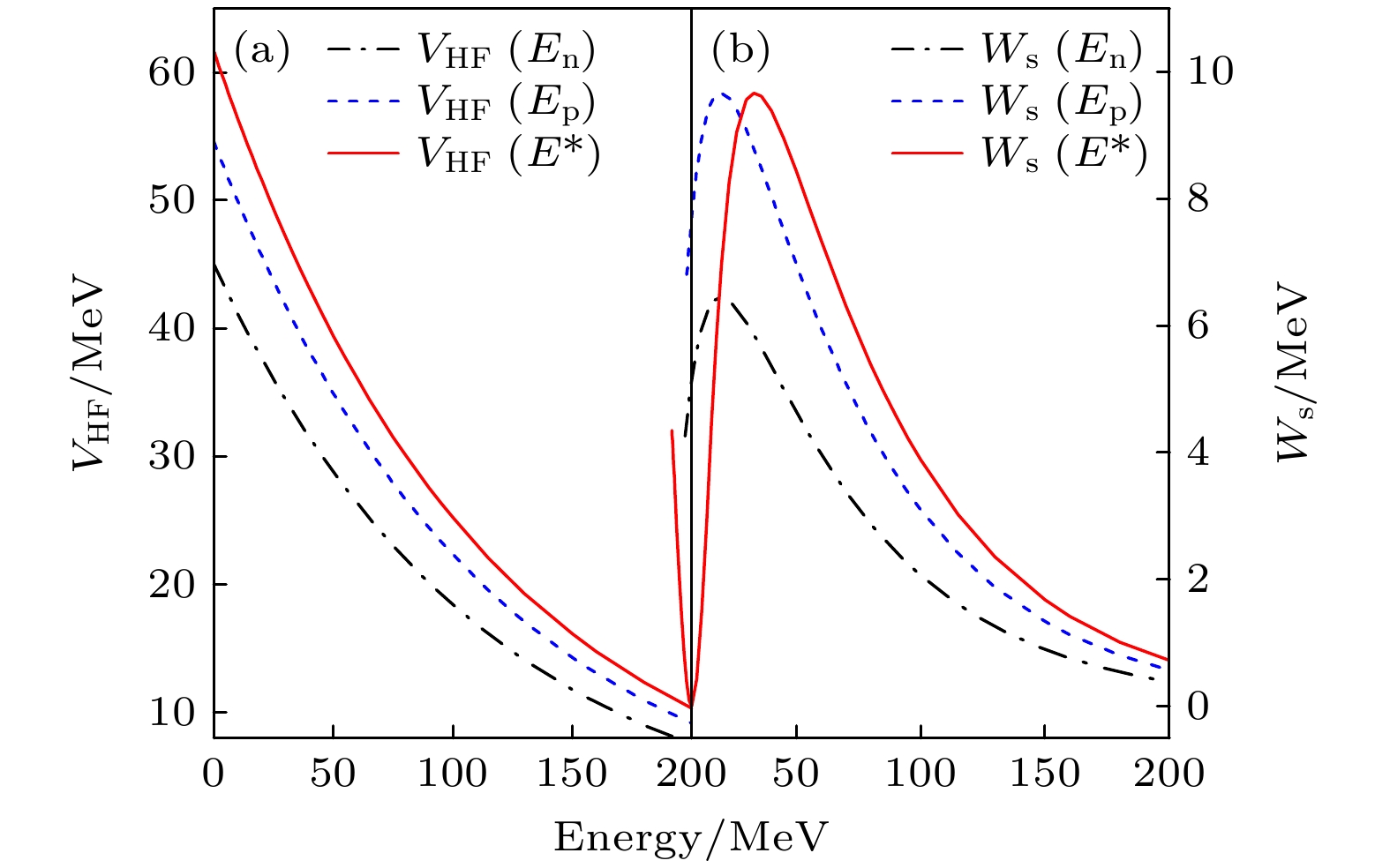
Lead is an important alloy material and nuclear fuel component. Lead-based eutectic alloys serve as important coolants and have been extensively utilized in the construction of lead-cooled fast reactor, such as the European lead-cooled System (ELSY) and the China lead-based Research reactor (CLEAR-I). These materials also play a significant role in research related to Generation-IV reactors. The study and calculation of lead nuclear data have important theoretical value and application prospects. 208Pb is the most stable and abundant isotope in lead nuclei, and high-quality description of 208Pb nuclear scattering data is important in achieving accurate theoretical calculations of nuclear reaction cross-sections in lead-based nuclear systems Based on the dispersive optical model, the nucleon scattering on 208Pb is described through the implementation of a dispersive optical potential in this work. The dispersive optical model potential is defined as energy-dependent real potential and imaginary potential. The dispersive contribution corresponding to the real potential is calculated analytically from the corresponding imaginary potential by using a dispersion relation, and the isospin dependence is reasonably considered by introducing an isovector component (i.e. Lane term) into the real part and the imaginary part of potential: the depth constant of the real Hartree-Fock potential $ V_{\rm{HF}}$ and the depth constant of surface imaginary potential $ W_{\rm{s}}$. Unlike K-D potential, which requires two different sets of parameters to describe neutron and proton induced scattering data. This optical potential uses the same set of parameters to simultaneously describe nucleon-nucleus scattering data. The derived potential in this work shows a very good description of nucleon-nucleus scattering data on 208Pb with energies up to 200 MeV. The calculated neutron total cross sections, neutron and proton elastic scattering angular distributions, and neutron and proton elastic analyzing powers are shown to be in good agreement with experimental data. Additionally, the difference in potential between neutrons and protons induced is described by an isovector term, achieving the reasonable and good prediction of quasielastic (p, n) scattering data.
[1] 吴宜灿, 柏云清, 宋勇, 黄群英, 刘超, 王明煌, 周涛, 金鸣, 吴庆生, 汪建业, 蒋洁琼, 胡丽琴, 李春京, 高胜, 李亚洲, 龙鹏程, 赵柱民, 郁杰, FDS团队 2014 核科学与工程 34 201
Wu Y C, Bai Y Q, Song Y, Huang Q Y, Liu C, Wang M H, Zhou T, Jin M, Wu Q S, Wang J Y, Jang J Q, Hu L Q, Li C J, Gao S, Li Y Z, Long P C, Zhao Z M, Yu J, FDS Team 2014 Nucl. Sci. and Eng. 34 201
[2] Nifenecker H, David S, Loiseaux J M, Meplan O 2001 Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 463 505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Gudowski W 2000 Nucl. Phys. A 663-664 169c
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Qaim S M 2001 Radiochim. Acta 89 189
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Stankovskiy A, Malambu E, Eynde G V D, Diez C J 2014 Nucl. Data Sheets 118 513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Yang W S, Khalil H S 1999 Trans. Am. Nucl. Soc. 81 273
[7] Martin M J 2007 Nucl. Data Sheets 108 1583
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Koning A J, Delaroche J P 2003 Nucl. Phys. A 713 231
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Soukhovitskiĩ E Sh, Capote R, Quesada J M, Chiba S 2005 Phys. Rev. C 72 024604
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Capote R, Chiba S, Soukhovitskiĩ E Sh, Quesada J M, Bauge E 2008 J. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 45 333
[11] Zhao X N, Sun W L, Soukhovitskiĩ E Sh, Martyanov D S, Quesada J M, Capote R 2021 J. Phys. G: Nucl. Part. Phys. 48 075101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhao X N, Du W Q, Capote R, Soukhovitskiĩ E Sh 2023 Phys. Rev. C 107 064606
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Mahaux C, Sartor R 1986 Phys. Rev. Lett. 57 3015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 赵岫鸟, 杜文青 2023 72 222401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao X N, Du W Q 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 222401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Quesada J M, Capote R, Soukhovitskiĩ E Sh, Chiba S 2007 Phys. Rev. C 76 057602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Lipperheide R 1967 Z. Phys. 202 58
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Mahaux C, Sartor R 1991 Nucl. Phys. A 528 253
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Brown G E, Rho M 1981 Nucl. Phys. A 372 397
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Delaroche J P, Wang Y, Rapaport J 1989 Phys. Rev. C 39 391
[20] Quesada J M, Capote R, Molina A, Lozano M, Raynal J 2003 Phys. Rev. C 67 067601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Chiba S, Iwamoto O, Yamanouti Y, Sugimoto M, Mizumoto M, Hasegawa K, Soukhovitskiĩ E Sh, Porodzinskiĩ Y V, Watanabe Y 1997 Nucl. Phys. A 624 305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Lane A M 1962 Phys. Rev. Lett. 8 171
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Lane A M 1962 Nucl. Phys. 35 676
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] EXchange FORmat database (EXFOR) is maintained by the Network of Nuclear Reaction Data Centers (see www-nds.iaea.org/nrdc/). Data available online (e.g., at www-nds.iaea.org/exfor/
[25] Capote R, Herman M, Obložinský P, Young P G, Goriely S, Belgya T, Ignatyuk A V, Koning A J, Hilaire S, Plujko V A, Avrigeanu M, Bersillon O, Chadwick M B, Fukahori T, Ge Z G, Han Y L, Kailas S, Kopecky J, Maslov V M, Reffo G, Sin M, Soukhovitskiĩ E Sh, Talou P 2009 Nucl. Data Sheets 110 3107
-
表 1 $^{208}{\rm{Pb}}$的色散光学模型势参数
Table 1. Dispersive optical-model potential parameters for nucleon induced reactions on $^{208}{\rm{Pb}}$.
$V_{{\mathrm{HF}}}$ Volume Surface Spin-orbit Coulomb Potential $V_{0}$ = 52.4 MeV $A_{\rm{v}}$ = 12.47 MeV $W_{0}$ = 15.82 MeV $ V_{\rm{SO}} $ = 8.1 MeV $C_{\rm{Coul}}$ = 1.0 MeV $\lambda_{\rm{HF}}$ = 0.009 MeV–1 $B_{\rm{v}}$ = 81.67 MeV $B_{\rm{s}}$ = 13.31 MeV $\lambda_{\rm{so}}$ = 0.005 MeV–1 $C_{\rm{viso}}$ = 23.85 MeV $E_{\rm{a}}$ = 56 MeV $C_{\rm{s}}$ = 0.02 MeV–1 $W_{\rm{SO}}$ = –3.1 MeV $C_{\rm{wiso}}$ = 14.98 MeV $B_{\rm{so}}$ = 160 MeV Geometry $r_{\rm{HF}}$ = 1.24 fm $r_{\rm{v}}$ = 1.25 fm $r_{\rm{s}}$ = 1.18 fm $r_{\rm{so}}$ = 1.08 fm $r_{\rm{c}}$ = 1.03 fm $a_{\rm{HF}}$ = 0.63 fm $a_{\rm{v}}$ = 0.69 fm $a_{\rm{s}}$ = 0.63 fm $a_{\rm{so}}$ = 0.59 fm $a_{\rm{c}}$ = 0.61 fm -
[1] 吴宜灿, 柏云清, 宋勇, 黄群英, 刘超, 王明煌, 周涛, 金鸣, 吴庆生, 汪建业, 蒋洁琼, 胡丽琴, 李春京, 高胜, 李亚洲, 龙鹏程, 赵柱民, 郁杰, FDS团队 2014 核科学与工程 34 201
Wu Y C, Bai Y Q, Song Y, Huang Q Y, Liu C, Wang M H, Zhou T, Jin M, Wu Q S, Wang J Y, Jang J Q, Hu L Q, Li C J, Gao S, Li Y Z, Long P C, Zhao Z M, Yu J, FDS Team 2014 Nucl. Sci. and Eng. 34 201
[2] Nifenecker H, David S, Loiseaux J M, Meplan O 2001 Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 463 505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Gudowski W 2000 Nucl. Phys. A 663-664 169c
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Qaim S M 2001 Radiochim. Acta 89 189
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Stankovskiy A, Malambu E, Eynde G V D, Diez C J 2014 Nucl. Data Sheets 118 513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Yang W S, Khalil H S 1999 Trans. Am. Nucl. Soc. 81 273
[7] Martin M J 2007 Nucl. Data Sheets 108 1583
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Koning A J, Delaroche J P 2003 Nucl. Phys. A 713 231
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Soukhovitskiĩ E Sh, Capote R, Quesada J M, Chiba S 2005 Phys. Rev. C 72 024604
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Capote R, Chiba S, Soukhovitskiĩ E Sh, Quesada J M, Bauge E 2008 J. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 45 333
[11] Zhao X N, Sun W L, Soukhovitskiĩ E Sh, Martyanov D S, Quesada J M, Capote R 2021 J. Phys. G: Nucl. Part. Phys. 48 075101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhao X N, Du W Q, Capote R, Soukhovitskiĩ E Sh 2023 Phys. Rev. C 107 064606
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Mahaux C, Sartor R 1986 Phys. Rev. Lett. 57 3015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 赵岫鸟, 杜文青 2023 72 222401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao X N, Du W Q 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 222401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Quesada J M, Capote R, Soukhovitskiĩ E Sh, Chiba S 2007 Phys. Rev. C 76 057602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Lipperheide R 1967 Z. Phys. 202 58
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Mahaux C, Sartor R 1991 Nucl. Phys. A 528 253
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Brown G E, Rho M 1981 Nucl. Phys. A 372 397
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Delaroche J P, Wang Y, Rapaport J 1989 Phys. Rev. C 39 391
[20] Quesada J M, Capote R, Molina A, Lozano M, Raynal J 2003 Phys. Rev. C 67 067601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Chiba S, Iwamoto O, Yamanouti Y, Sugimoto M, Mizumoto M, Hasegawa K, Soukhovitskiĩ E Sh, Porodzinskiĩ Y V, Watanabe Y 1997 Nucl. Phys. A 624 305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Lane A M 1962 Phys. Rev. Lett. 8 171
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Lane A M 1962 Nucl. Phys. 35 676
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] EXchange FORmat database (EXFOR) is maintained by the Network of Nuclear Reaction Data Centers (see www-nds.iaea.org/nrdc/). Data available online (e.g., at www-nds.iaea.org/exfor/
[25] Capote R, Herman M, Obložinský P, Young P G, Goriely S, Belgya T, Ignatyuk A V, Koning A J, Hilaire S, Plujko V A, Avrigeanu M, Bersillon O, Chadwick M B, Fukahori T, Ge Z G, Han Y L, Kailas S, Kopecky J, Maslov V M, Reffo G, Sin M, Soukhovitskiĩ E Sh, Talou P 2009 Nucl. Data Sheets 110 3107
计量
- 文章访问数: 2285
- PDF下载量: 84
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: