-
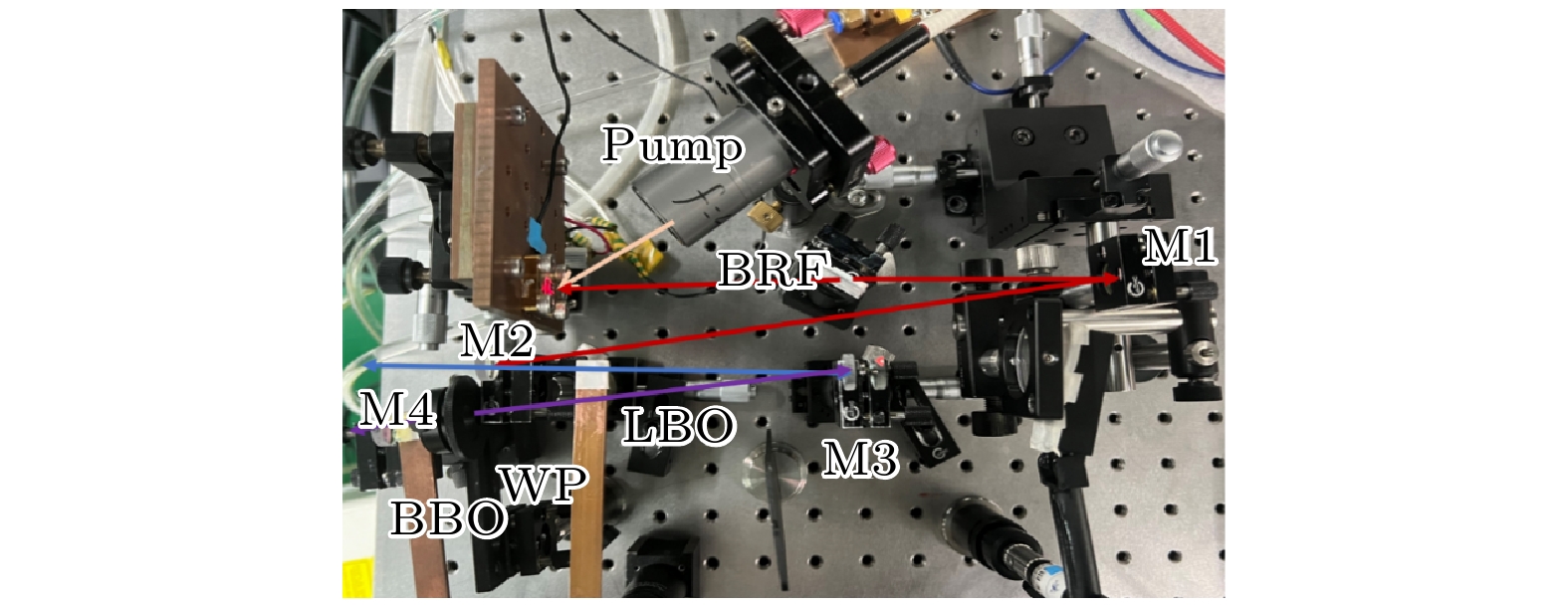
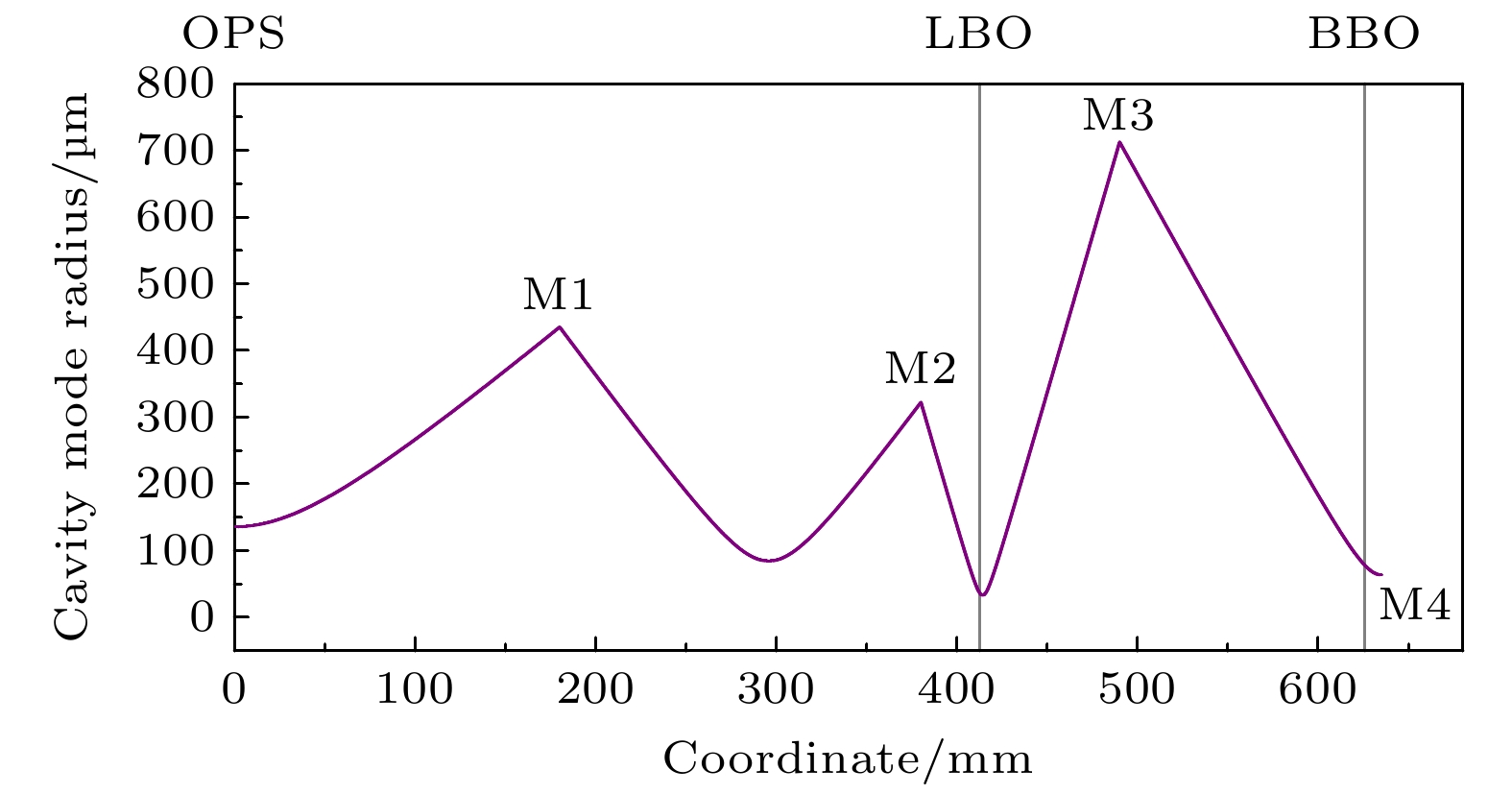
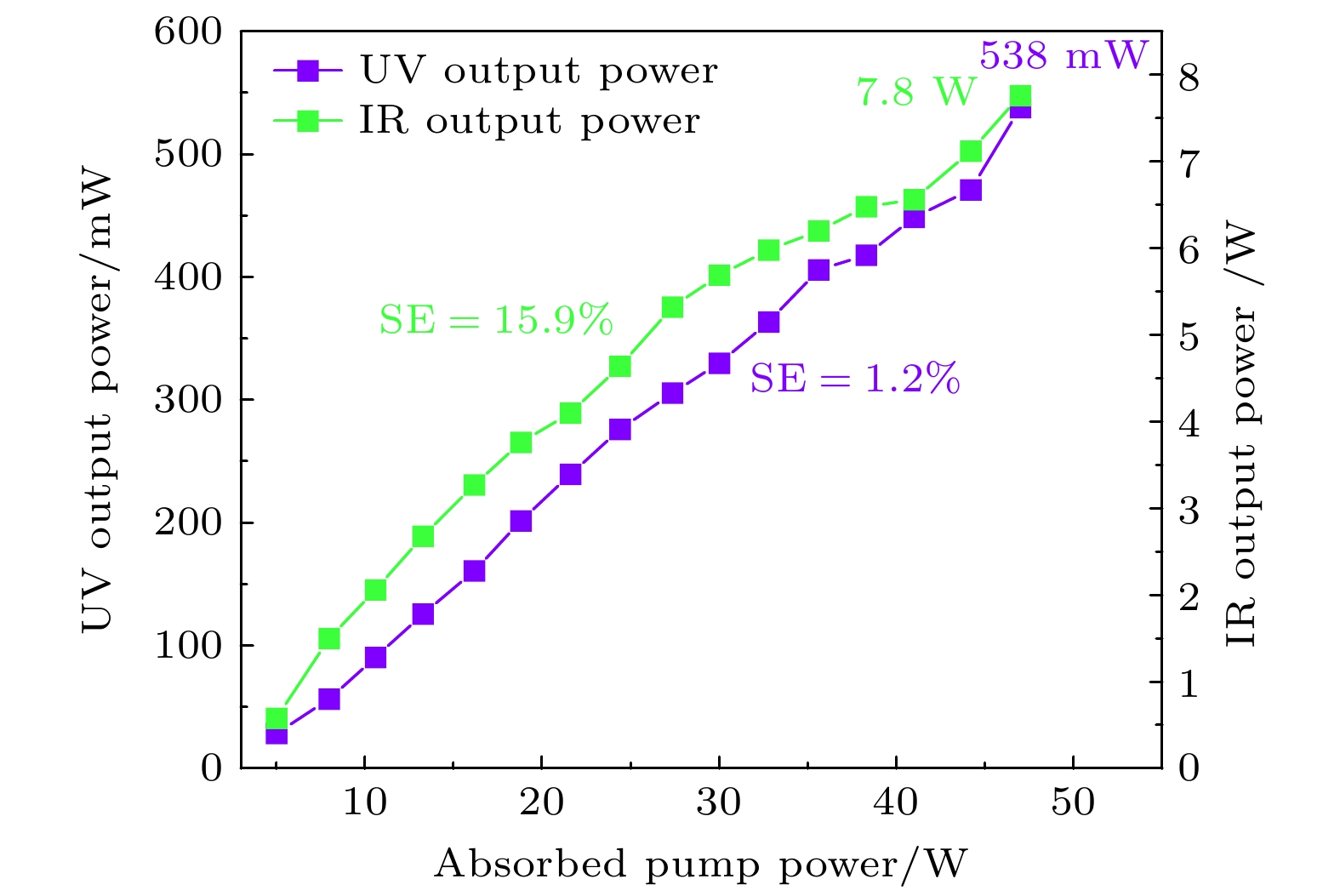
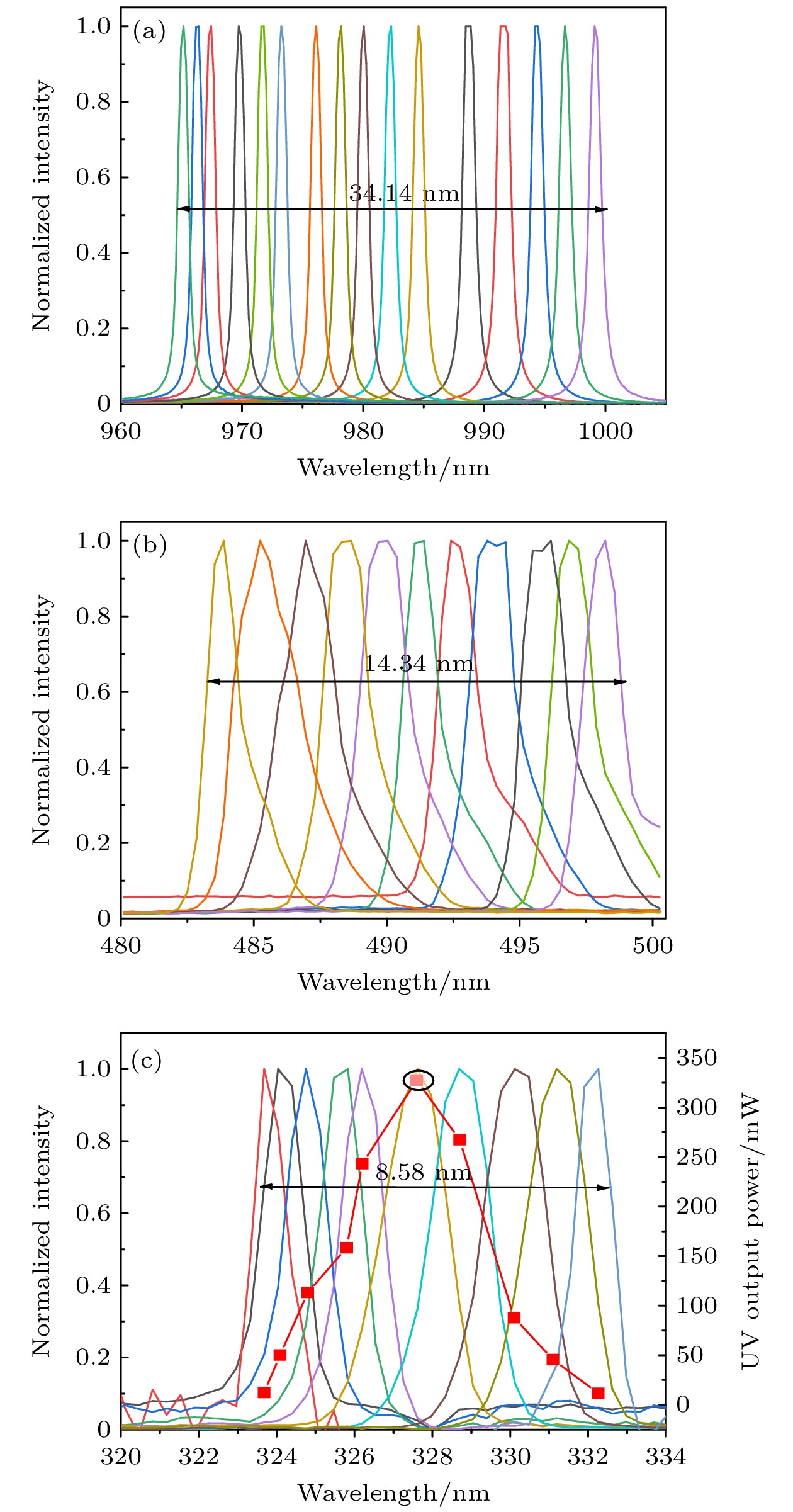
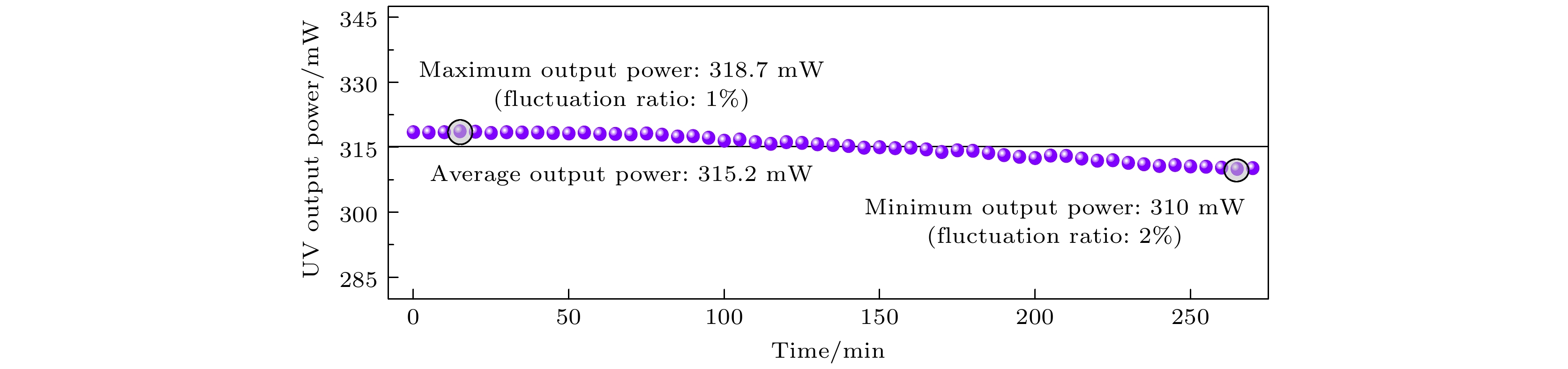
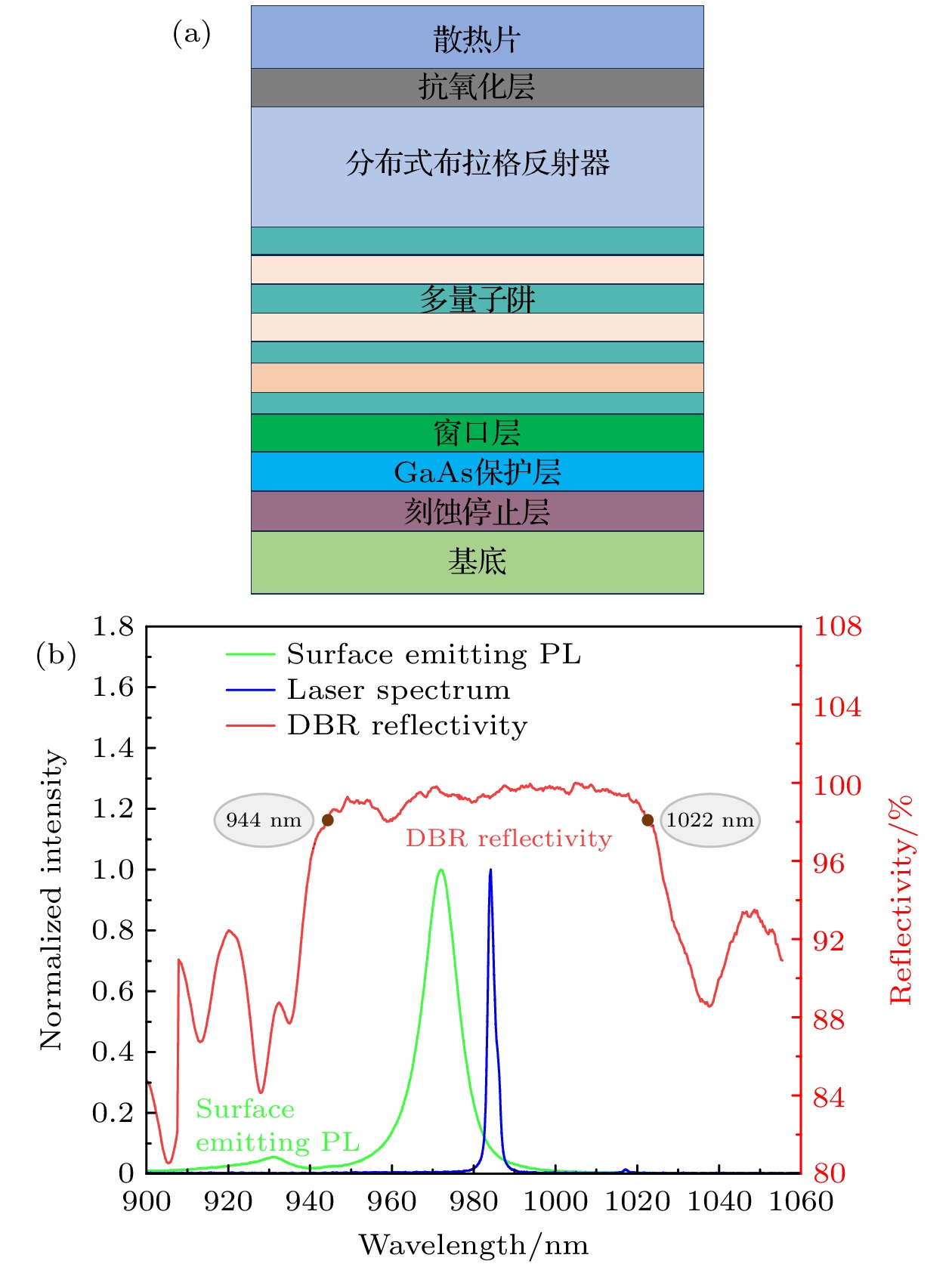
紫外激光器具有频率高、波长短、单光子能量大以及空间分辨率高等特点, 在精细加工、生命科学、光谱学等许多方面应用前景广阔. 本文报道了一种基于外腔面发射激光器腔内三倍频的可调谐紫外激光器. 该激光器采用了W型谐振腔, 并插入双折射滤波片作为偏振和波长调谐元件, 通过I类相位匹配的LBO晶体对980 nm基频光进行倍频产生490 nm蓝光, 再通过I类相位匹配的BBO晶体对980 nm基频光和490 nm倍频光进行和频获得327 nm紫外输出. 当LBO和BBO晶体的长度都为5 mm时, 在环境温度为15 ℃, 泵浦功率为47 W的条件下, 实验输出的327 nm紫外激光功率达到538 mW. 选择厚度为2 mm的双折射滤波片作为调谐元件, 可获得的紫外激光器输出波长的连续调谐范围为8.6 nm. 该紫外激光器同时显示了良好的光束质量和较好的功率稳定性.Ultraviolet laser has high frequency, short wavelength, large single-photon energy, and high spatial resolution, and has wide applications in many fields such as fine processing, life sciences, and spectroscopy. In this work, a wavelength tunable ultraviolet laser based on intracavity third harmonic generation from an external-cavity surface-emitting laser is reported. The W-type resonant cavity of the laser is composed of a distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) at the bottom of the gain chip, three plane-concave mirrors, and a rear plane mirror. On the arm containing the gain chip, a birefringent filter is inserted at the Brewster angle as the polarization and wavelength tuning element, which can also narrow the linewidth of the fundamental laser to a certain extent. A type-I phase-matched LBO crystal is placed on the beam waist between the folding mirrors M2 and M3 to convert the 980 nm fundamental laser into 490 nm blue light, and a type-I phase-matched BBO crystal is inserted in the beam waist near the rear mirror to produce a 327 nm ultraviolet output from the remained 980 nm fundamental laser and the frequency-doubled 490 nm second harmonic. Before the BBO crystal, a half-wave plate at 980 nm is employed to change the polarization of the fundamental laser, so as to meet the type-I phase-matching condition of the used BBO crystal. Owing to the larger nonlinear coefficient of the type-I phase-matched BBO crystal, and its obviously higher transmittance at 327 nm wavelength than the usually used LBO crystal, the output power is obtained to be 538 mW at 327 nm ultraviolet wavelength, corresponding to a conversion efficiency of 1.1% from pump light to ultraviolet laser. The experiment is performed under conditions of 15 ℃ temperature, 47 W absorbed pump power, 5 mm-length LBO and 5 mm-length BBO crystals. By using a 2 mm-thick birefringent filter as the tuning element, 34.1 nm tuning range of the 980 nm fundamental laser, 14.3 nm tuning range of the 490 nm second harmonic, and 8.6 nm tuning range of the 327 nm third harmonic are obtained. The ultraviolet laser exhibits good beam quality as well as acceptable power stability with the maximum power fluctuation less than 2% within 4.5 h.
-
Keywords:
- tunable /
- external-cavity surface-emitting laser /
- nonlinear frequency conversion /
- third harmonic generation
[1] 唐娟, 廖健宏, 蒙红云 2007 激光与光电子学进展 44 52
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang J, Liao J H, Meng H Y 2007 Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 44 52
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 俞君, 曾智江, 朱三根 2008 红外 29 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu J, Zeng Z J, Zhu S G 2008 Infrared 29 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 李林, 李正佳, 何艳艳 2005 激光杂志 6 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li L, Li Z J, He Y Y 2005 Laser J. 6 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Sasaki T, Mori Y, Yoshimura M 2000 Mat. Sci. Eng. R. 30 54
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wang C X, Wang G Y, Hicks A V 2006 Proc. SPIE 6100 19
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Hodgson N, Li M, Held A 2003 Proc. SPIE 4977 281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Basov N G, Danilychev V A, Popov Y M 1970 JETP Lett. 12 329
[8] Rhodes C K 1979 Mol. Phys. 1 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Oka M, Liu L Y, Wiechmann W 1995 IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. 1 859
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Yap Y K, Inagaki M, Nakajima S 1996 Opt. Lett. 21 1348
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Deyra L, Martial I 2014 Opt. Lett. 39 2236
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Jewell J L, Harbison J P, Scherer A 1991 IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 27 1332
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Crump P, Wenzel H, Erbert G 2012 Proc. SPIE 8241 222
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Rahimi-Iman A 2016 J. Optics-UK 18 093003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Guina M, Rantamäki A, Härkönen A 2017 J. Phy. D Appl. Phys. 50 383001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Hastie J E, Morton L G, Dawson M D 2006 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1 109
[17] Jennifer E H, Morton L G, Kemp A J 2006 Appl. Phys. Lett. 89 061114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Schwarzbäck T, Kahle H, Eichfelder M 2011 J. Opt. Soc. Korea 1 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Shu Q Z, Caprara A L, Berger J D 2009 Proc. SPIE 7193 339
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Polanik M, Hirlinger A J 2016 Annu. Rep. 8 140
[21] Kaneda Y, Yarborough J M, Li L 2008 Opt. Lett. 33 1705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Meyer J T, Lukowski M L, Hessenius C 2021 Opt. Commun. 499 127255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zondy J J 1991 Opt. Commun. 81 427
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Nightingale J L,Becker R A, Willis P C 1987 Appl. Phys. Lett. 51 716
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Smith A V, Armstrong D J, Alford W J 1998 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 15 122
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
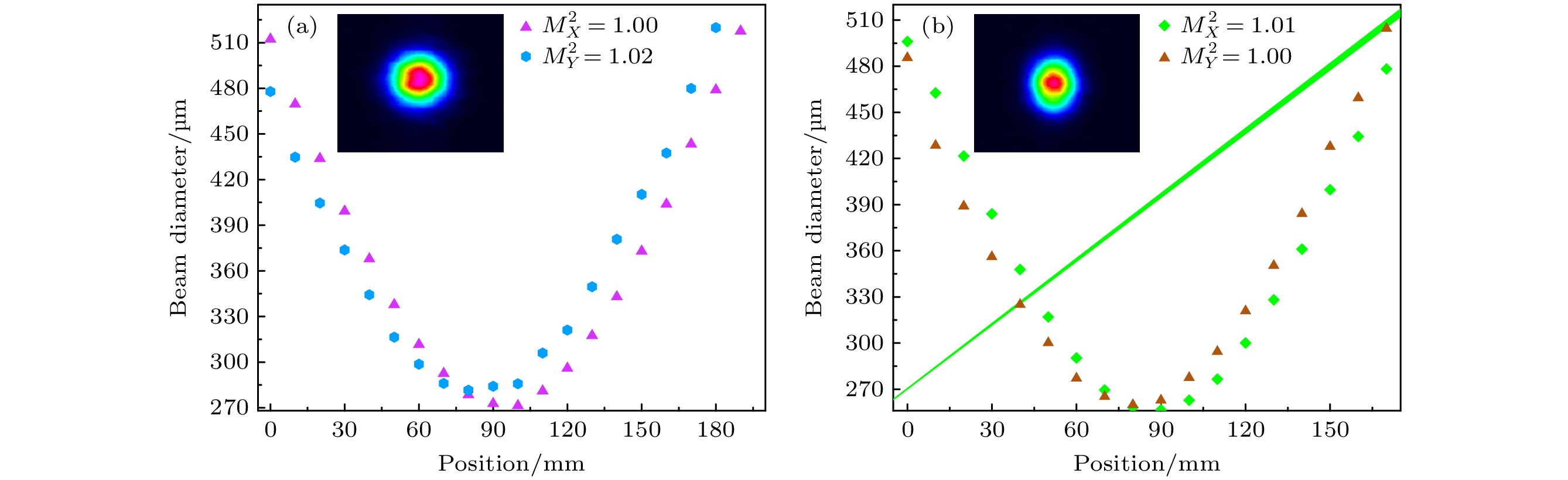
图 6 (a)基频激光的光束质量M2因子, 插图为光强的二维分布图; (b)倍频激光的光束质量M2 因子, 插图为对应的二维光强分布图
Fig. 6. (a) Beam quality M2 factor of the fundamental laser, the inset shows a 2-dimension distribution of the laser spot; (b) M2 factor of the frequency-doubled laser, and the 2-dimension distribution of the laser intensity is also shown as an inset.
-
[1] 唐娟, 廖健宏, 蒙红云 2007 激光与光电子学进展 44 52
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang J, Liao J H, Meng H Y 2007 Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 44 52
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 俞君, 曾智江, 朱三根 2008 红外 29 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu J, Zeng Z J, Zhu S G 2008 Infrared 29 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 李林, 李正佳, 何艳艳 2005 激光杂志 6 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li L, Li Z J, He Y Y 2005 Laser J. 6 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Sasaki T, Mori Y, Yoshimura M 2000 Mat. Sci. Eng. R. 30 54
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wang C X, Wang G Y, Hicks A V 2006 Proc. SPIE 6100 19
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Hodgson N, Li M, Held A 2003 Proc. SPIE 4977 281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Basov N G, Danilychev V A, Popov Y M 1970 JETP Lett. 12 329
[8] Rhodes C K 1979 Mol. Phys. 1 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Oka M, Liu L Y, Wiechmann W 1995 IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. 1 859
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Yap Y K, Inagaki M, Nakajima S 1996 Opt. Lett. 21 1348
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Deyra L, Martial I 2014 Opt. Lett. 39 2236
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Jewell J L, Harbison J P, Scherer A 1991 IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 27 1332
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Crump P, Wenzel H, Erbert G 2012 Proc. SPIE 8241 222
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Rahimi-Iman A 2016 J. Optics-UK 18 093003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Guina M, Rantamäki A, Härkönen A 2017 J. Phy. D Appl. Phys. 50 383001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Hastie J E, Morton L G, Dawson M D 2006 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1 109
[17] Jennifer E H, Morton L G, Kemp A J 2006 Appl. Phys. Lett. 89 061114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Schwarzbäck T, Kahle H, Eichfelder M 2011 J. Opt. Soc. Korea 1 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Shu Q Z, Caprara A L, Berger J D 2009 Proc. SPIE 7193 339
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Polanik M, Hirlinger A J 2016 Annu. Rep. 8 140
[21] Kaneda Y, Yarborough J M, Li L 2008 Opt. Lett. 33 1705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Meyer J T, Lukowski M L, Hessenius C 2021 Opt. Commun. 499 127255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zondy J J 1991 Opt. Commun. 81 427
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Nightingale J L,Becker R A, Willis P C 1987 Appl. Phys. Lett. 51 716
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Smith A V, Armstrong D J, Alford W J 1998 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 15 122
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 3580
- PDF下载量: 75
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: