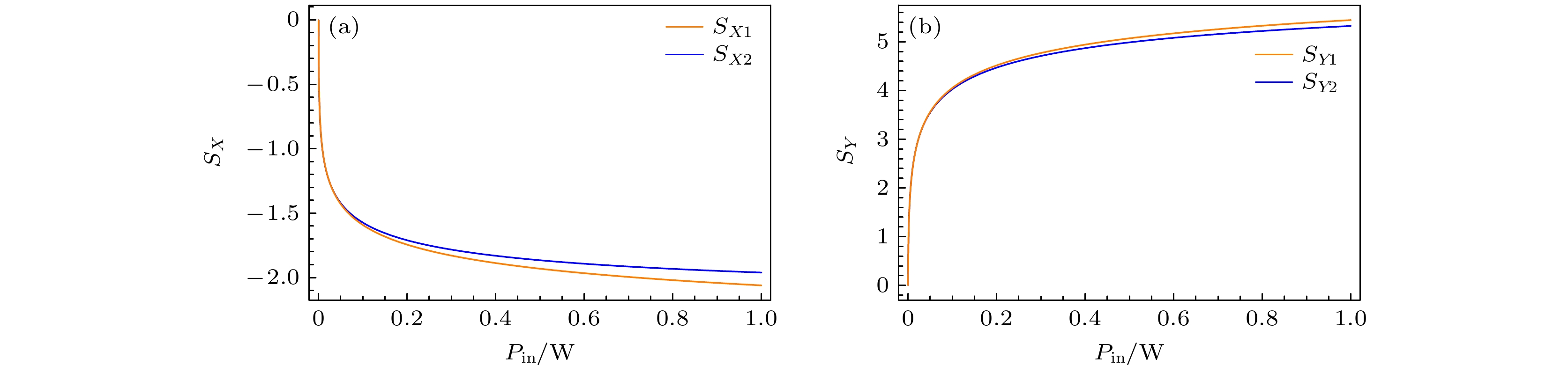
-
量子纠缠是执行量子计算和构建量子通信网络的关键资源, 制备与操控纠缠态光场是实现量子信息处理的基础要素. 本文提出了利用双端光学腔倍频产生四组份纠缠态的理论模型, 从耦合波方程出发得到Ⅱ类倍频过程的传输矩阵, 通过腔内自再现方程和输入输出传输矩阵理论研究了输出的两束倍频光的噪声特性; 对于两束倍频光和两束基频泵浦场, 利用多组份纠缠光场的充分必要判据PPT方法(positivity under partial transposition criterion)分析了最小辛本征值与泵浦功率及分析频率之间的关系, 研究结果表明基频泵浦光与倍频光之间存在四组份纠缠.Quantum entanglement is a crucial resource for performing quantum computing and constructing quantum communication networks. The preparation and manipulation of entangled light field are the basic elements of quantum communication. With the development of science and technology, multicolor multipartite entanglement is becoming a kind of special resource for quantum information, quantum networks, and quantum memory. In this paper, we propose a scheme of generating quadripartite entanglement among four output beams from a two-port frequency doubling resonator, in which a type-II phase matching nonlinear crystal is placed. We make two fundamental-frequency pump beams with the same frequency and vertical polarization pass through the nonlinear crystal to produce two frequency-doubling beams. There is a quadripartite entanglement between the frequency-doubling beams, which are output at two ports of the optical resonator, and the incident fundamental beams. Based on the transmission matrix from the coupled wave equation, the self-consistent equations of the intracavity modes and the corresponding noise properties of the output modes can be obtained. Then, the quadripartite entanglement produced from two second harmonic beams and two reflected fundamental-frequency pump beams, is verified by using the positive partial transposition criterion, in a wide range of pumping power and analysis frequency. The setup proposed in this work is compact and experimentally feasible. It is also convenient to separate the four entangled beams spatially, with different wavelengths and polarizations. When the beam wavelengths are matched with 1560 nm (low loss window of fiber) and 780 nm (atomic absorption line of Rb), this scheme can be more useful in both quantum communication and quantum memory.
-
Keywords:
- quantum entanglement /
- two-port frequency doubling resonator /
- positive partial transposition criterion
[1] Tang J F, Hou Z B, Shang J W, Zhu H J, Xiang G Y, Li C F, Guo G C 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 124 060502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Xie B Y, Feng S 2021 Chin. Opt. Lett. 19 072701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Brendel J, Gisin N, Tittel W, Zbinden H 1999 Phys. Rev. Lett. 82 2594
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Giovannetti V, Lloyd S, Maccone L 2004 Science 306 1330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Avis G, Rozpędek F, Wehner S 2023 Phys. Rev. A 107 012609
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Bugalho L, Coutinho B C, Monteiro F A, Omar Y 2023 Quantum 7 920
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Karpow E, Navez P, Gerf N J 2004 Phys. Rev. A 69 040301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wang X W, Yang G J 2009 Phys. Rev. A 79 062315
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Das S, Halder P, Banerjee R, Sen A 2023 Phys. Rev. A 107 042414
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Jing J T, Zhang J, Yan Y, Zhao F G, Xie C D, Peng K C 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 90 167903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Navascues M, Wolfe E, Rosset D, Pozas-Kerstjens A 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 125 240505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Menicucc N C, van Loock P, Gu M, Weedbrook C, Ralph T C, Nielsen M A 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 97 110501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Bruß D, Macchiavello C 2011 Phys. Rev. A 83 052313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Su X L, Hao S H, Deng X W, Ma L Y, Wang M H, Jia X J, Xie C D, Peng K P 2013 Nat. Commun. 4 2828
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 余胜, 刘焕章, 刘胜帅, 荆杰泰 2020 69 090303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu S, Liu H Z, Liu S S, Jing J T 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 090303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Du P L, Wang Y, Liu K, Yang R G, Zhang J 2023 Opt. Express 31 7535
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 何英秋, 丁东, 彭涛, 闫凤利, 高亭 2018 67 060302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
He Y Q, Ding D, Peng T, Yan F L, Gao T 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 060302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 丁东, 何英秋, 闫凤利, 高亭 2015 64 160301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ding D, He Y Q, Yan F L, Gao T 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 160301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 张越, 侯飞雁, 刘涛, 张晓斐, 张首刚, 董瑞芳 2018 67 144204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y, Hou F Y, Liu T, Zhang X F, Zhang S G, Dong R F 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 144204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Leng H Y, Wang J F, Yu Y B, Yu X Q, Xu P, Xie Z D, Zhao J S, Zhu S N 2009 Phys. Rev. A 79 032337
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Lim O K, Saffman M 2006 Phys. Rev. A 74 023816
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhai S Q, Yang R G, Liu K, Zhang H L, Zhang J X, Gao J R 2009 Opt. Express 17 9851
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Yang R G, Zhai S Q, Liu K, Zhang J X, Gao J R 2010 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 27 2721
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Xue X X, Leo F, Xuan Y, Jaramillo-Villegas J A, Wang P H, Leaird D E, Erkintalo M, Qi M H, Weiner Andrew M 2017 Light: Sci. Appl. 6 e16253
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Barral D, Bencheikh K, Belabas N, Levenson J A 2019 Phys. Rev. A 99 051801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Armstrong J A, Bloembergen N, Ducuing J, Pershan P S 1962 Phys. Rev. 127 1918
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Li R D, Kumar P 1994 Phys. Rev. A 49 2157
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Simón R 2000 Phys. Rev. Lett. 84 2726
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Bohnet-Waldraff F, Braun D, Giraud O 2016 Phy. Rev. A 94 042343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 冯晋霞 2008 博士学位论文 (太原: 山西大学)
Feng J X 2008 Ph. D. Dissertation (Shanxi: Shanxi University
[31] Villar A S, Cruz L S, Cassemiro K N, Martinelli M, Nussenzveig P 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 95 243603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
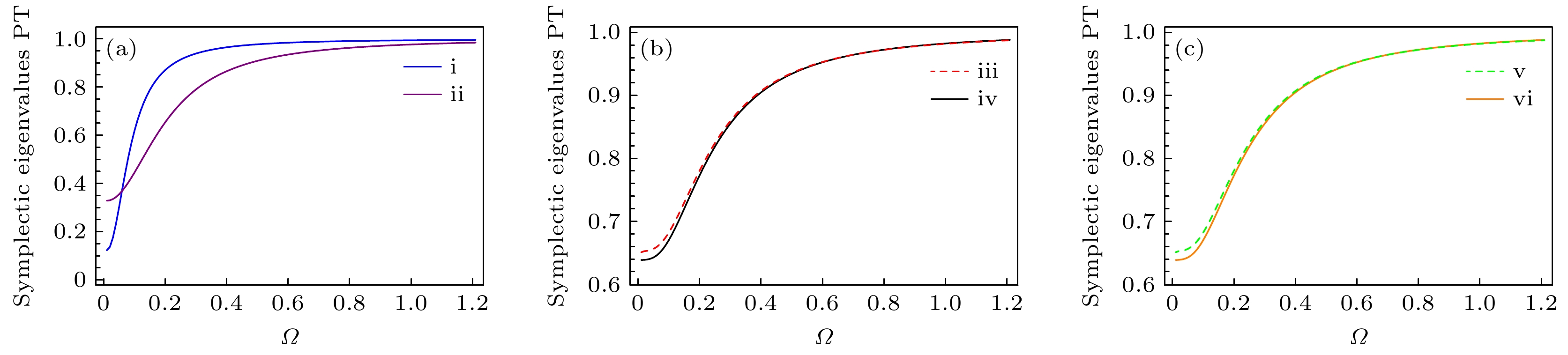
图 3 最小辛本征值与泵浦功率${P_{{\text{in}}}}$的关系图 (a) i表示两束基频光的纠缠, ii表示两束倍频光的纠缠; (b) iii表示基频光1与倍频光1的纠缠, iv表示基频光1与倍频光2的纠缠; (c) v表示基频光2与倍频光1的纠缠, vi表示基频光2与倍频光2的纠缠
Fig. 3. Lines about symplectic eigenvalues are plotted as functions of ${P_{{\text{in}}}}$ when $\varOmega = 0$: (a) i represents the entanglement of two fundamental beams, ii represents the entanglement of two frequency-doubling beams; (b) iii represents the entanglement of fundamental beam1 and frequency-doubling beam1, iv represents the entanglement of fundamental beam1 and frequency-doubling beam2; (c) v represents the entanglement of fundamental beam2 and frequency-doubling beam1, vi represents the entanglement of fundamental beam2 and frequency-doubling beam2.
图 4 最小辛本征值与归一化到腔带宽频率$\varOmega $的关系图 (a) i表示两束基频光的纠缠, ii表示两束倍频光的纠缠; (b) iii表示基频光1与倍频光1的纠缠, iv表示基频光1与倍频光2的纠缠; (c) v表示基频光2与倍频光1的纠缠, vi表示基频光2与倍频光2的纠缠
Fig. 4. Lines about symplectic eigenvalues are plotted as functions of $\varOmega $ when ${P_{{\text{in}}}} = 2{\text{ W}}$: (a) i represents the entanglement of two fundamental beams, ii represents the entanglement of two frequency-doubling beams; (b) iii represents the entanglement of fundamental beam1 and frequency-doubling beam1, iv represents the entanglement of fundamental beam1 and frequency-doubling beam2; (c) v represents the entanglement of fundamental beam2 and frequency-doubling beam1, vi represents the entanglement of fundamental beam2 and frequency-doubling beam2.
-
[1] Tang J F, Hou Z B, Shang J W, Zhu H J, Xiang G Y, Li C F, Guo G C 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 124 060502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Xie B Y, Feng S 2021 Chin. Opt. Lett. 19 072701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Brendel J, Gisin N, Tittel W, Zbinden H 1999 Phys. Rev. Lett. 82 2594
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Giovannetti V, Lloyd S, Maccone L 2004 Science 306 1330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Avis G, Rozpędek F, Wehner S 2023 Phys. Rev. A 107 012609
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Bugalho L, Coutinho B C, Monteiro F A, Omar Y 2023 Quantum 7 920
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Karpow E, Navez P, Gerf N J 2004 Phys. Rev. A 69 040301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wang X W, Yang G J 2009 Phys. Rev. A 79 062315
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Das S, Halder P, Banerjee R, Sen A 2023 Phys. Rev. A 107 042414
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Jing J T, Zhang J, Yan Y, Zhao F G, Xie C D, Peng K C 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 90 167903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Navascues M, Wolfe E, Rosset D, Pozas-Kerstjens A 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 125 240505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Menicucc N C, van Loock P, Gu M, Weedbrook C, Ralph T C, Nielsen M A 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 97 110501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Bruß D, Macchiavello C 2011 Phys. Rev. A 83 052313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Su X L, Hao S H, Deng X W, Ma L Y, Wang M H, Jia X J, Xie C D, Peng K P 2013 Nat. Commun. 4 2828
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 余胜, 刘焕章, 刘胜帅, 荆杰泰 2020 69 090303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu S, Liu H Z, Liu S S, Jing J T 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 090303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Du P L, Wang Y, Liu K, Yang R G, Zhang J 2023 Opt. Express 31 7535
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 何英秋, 丁东, 彭涛, 闫凤利, 高亭 2018 67 060302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
He Y Q, Ding D, Peng T, Yan F L, Gao T 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 060302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 丁东, 何英秋, 闫凤利, 高亭 2015 64 160301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ding D, He Y Q, Yan F L, Gao T 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 160301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 张越, 侯飞雁, 刘涛, 张晓斐, 张首刚, 董瑞芳 2018 67 144204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y, Hou F Y, Liu T, Zhang X F, Zhang S G, Dong R F 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 144204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Leng H Y, Wang J F, Yu Y B, Yu X Q, Xu P, Xie Z D, Zhao J S, Zhu S N 2009 Phys. Rev. A 79 032337
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Lim O K, Saffman M 2006 Phys. Rev. A 74 023816
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhai S Q, Yang R G, Liu K, Zhang H L, Zhang J X, Gao J R 2009 Opt. Express 17 9851
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Yang R G, Zhai S Q, Liu K, Zhang J X, Gao J R 2010 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 27 2721
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Xue X X, Leo F, Xuan Y, Jaramillo-Villegas J A, Wang P H, Leaird D E, Erkintalo M, Qi M H, Weiner Andrew M 2017 Light: Sci. Appl. 6 e16253
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Barral D, Bencheikh K, Belabas N, Levenson J A 2019 Phys. Rev. A 99 051801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Armstrong J A, Bloembergen N, Ducuing J, Pershan P S 1962 Phys. Rev. 127 1918
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Li R D, Kumar P 1994 Phys. Rev. A 49 2157
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Simón R 2000 Phys. Rev. Lett. 84 2726
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Bohnet-Waldraff F, Braun D, Giraud O 2016 Phy. Rev. A 94 042343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 冯晋霞 2008 博士学位论文 (太原: 山西大学)
Feng J X 2008 Ph. D. Dissertation (Shanxi: Shanxi University
[31] Villar A S, Cruz L S, Cassemiro K N, Martinelli M, Nussenzveig P 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 95 243603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 3397
- PDF下载量: 57
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: