-
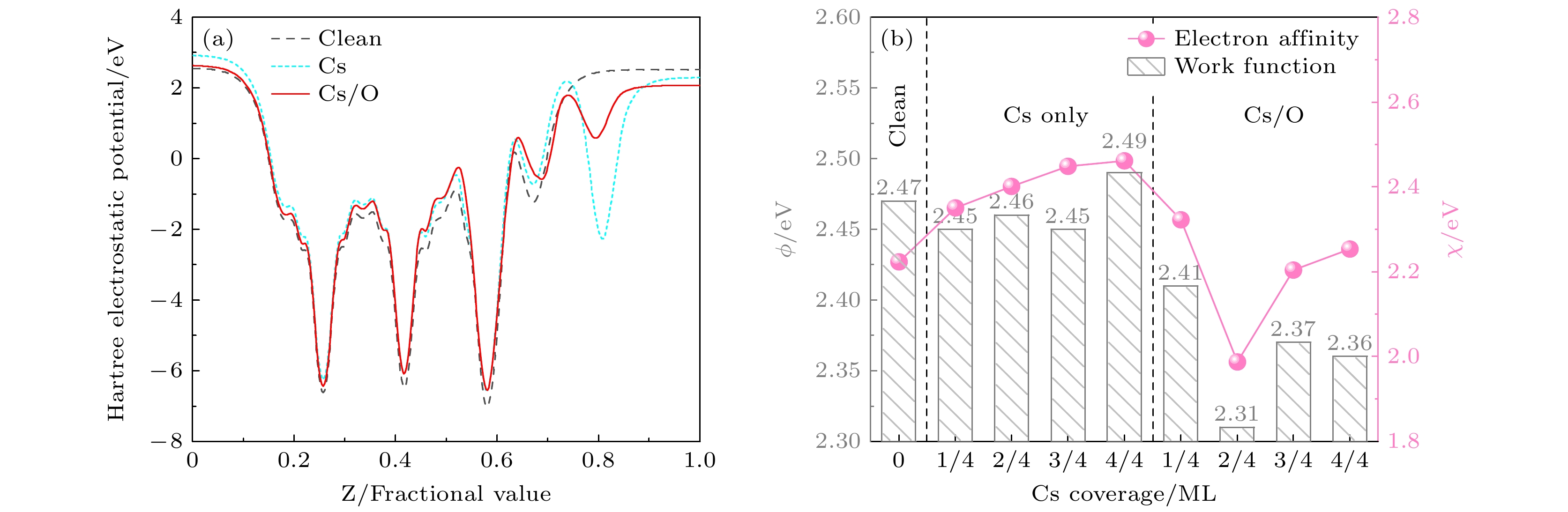
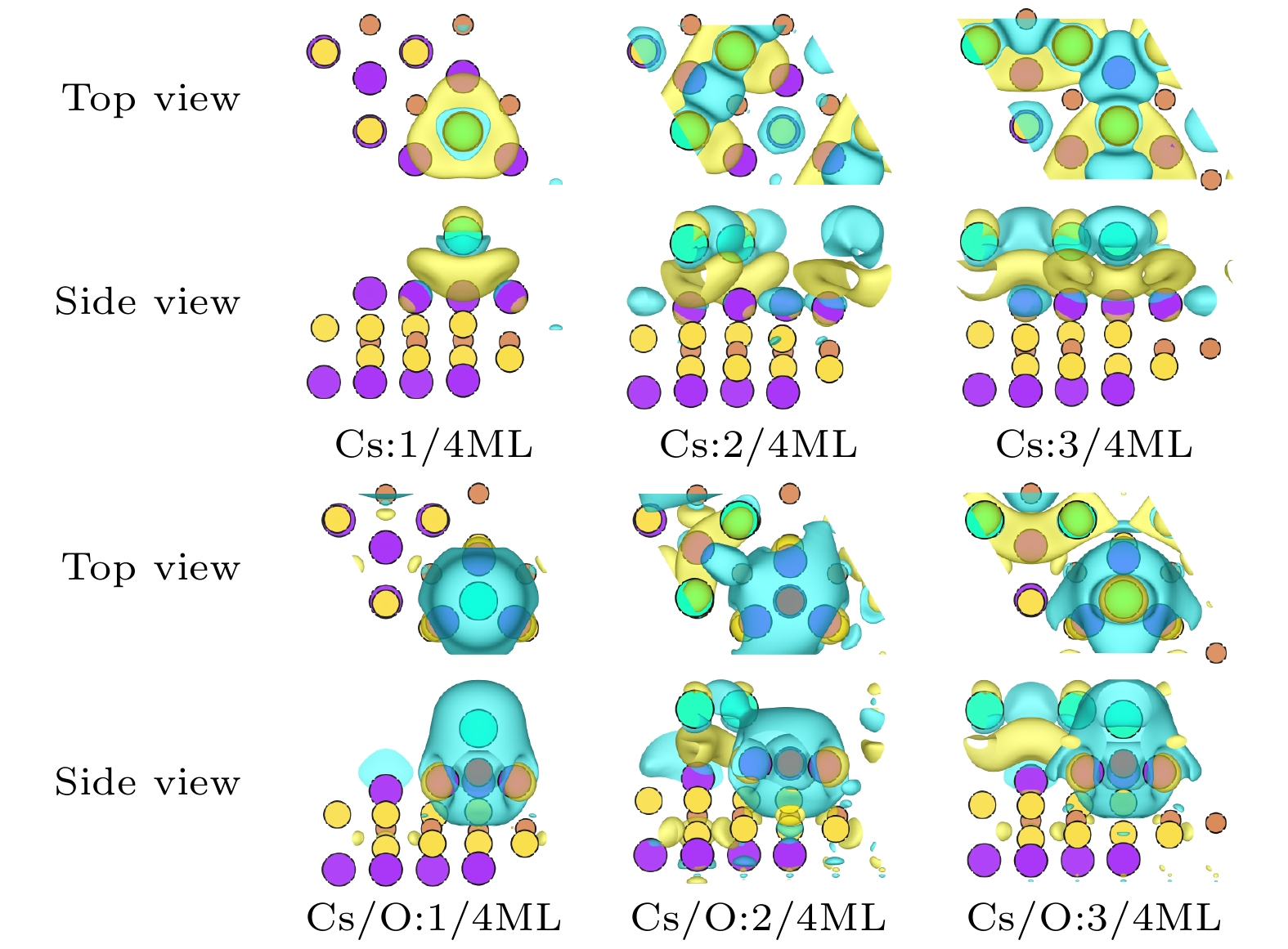
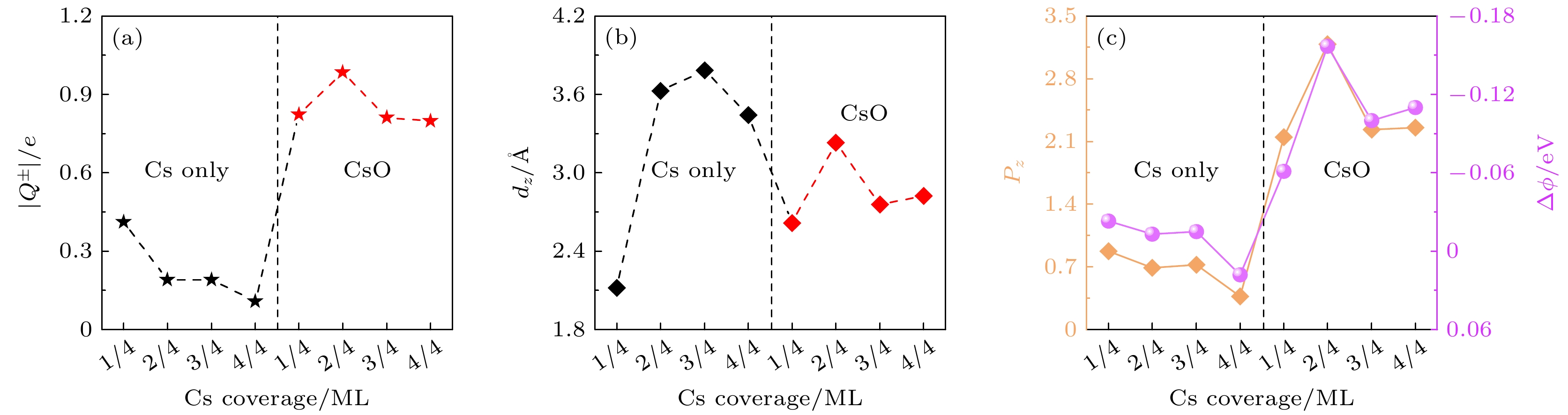
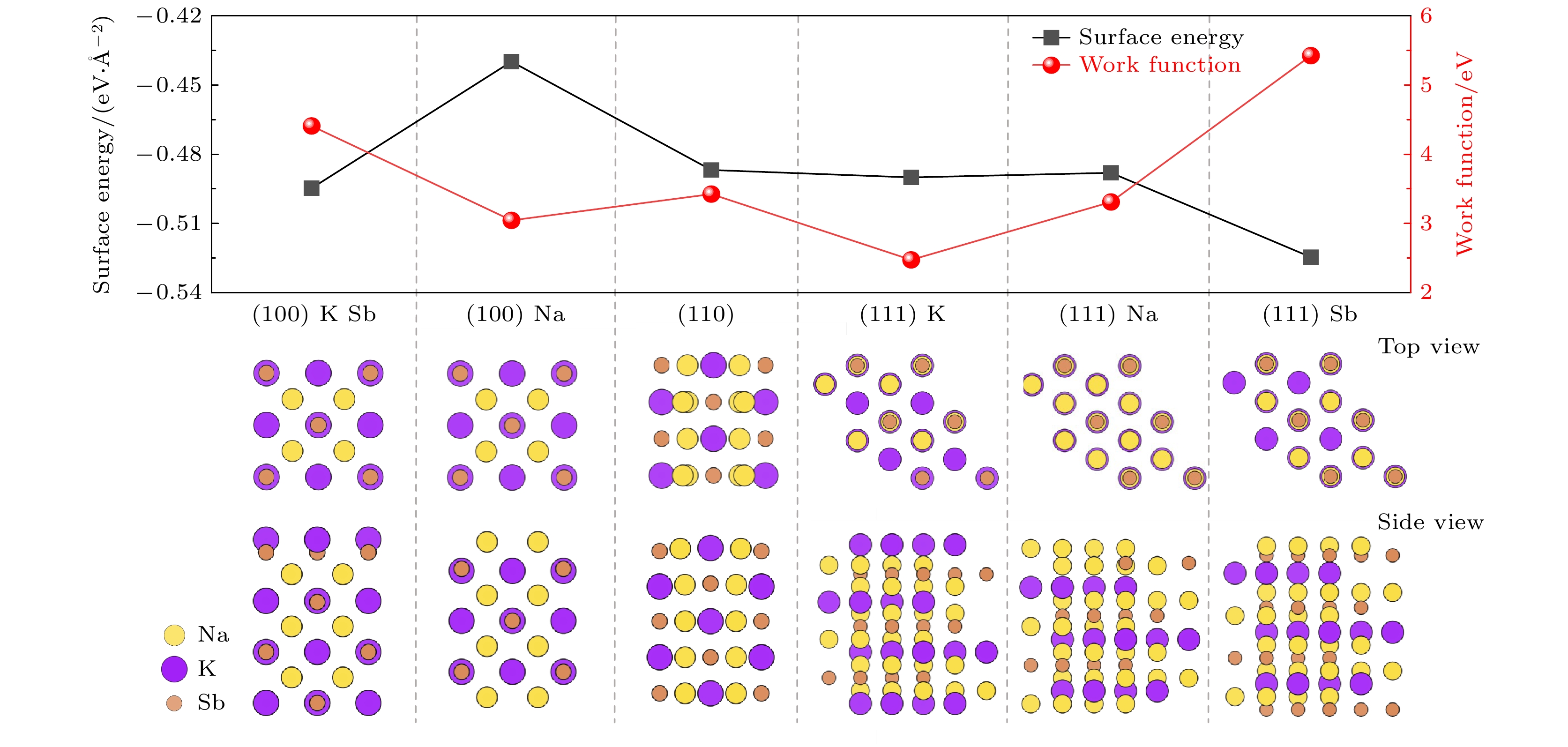
Na2KSb光电阴极在光电倍增管、图像增强器、真空电子源等领域具有重要应用. 为指导高灵敏度Na2KSb光电阴极的制备, 采用第一性原理计算方法, 研究不同表面取向和原子终止面的Na2KSb表面模型, 获得稳定且最有利于电子发射的表面结构. 基于该表面进一步研究了不同覆盖度下的Cs原子沉积和Cs/O原子共沉积对Na2KSb表面电子结构和光学性质的影响. 对比表面能、吸附能和吸附前后的功函数结果表明, Na2KSb (111) K表面具有优越的电子发射能力以及良好的稳定性. 当Na2KSb (111) K表面吸附2/4单层的Cs原子和1/4单层O原子时, 获得最大功函数下降量0.16 eV. 表面吸附Cs/O原子有利于电荷往表面上方转移, 并产生电荷累积, 能形成有效表面偶极矩. 通过分析能带结构和态密度, 发现吸附Cs原子对导带底存在额外的能带贡献, 且引入O原子吸附后价带发生上移. 此外, 吸附Cs/O原子有利于增强表面近红外光吸收, 但是会导致表面紫外和可见光吸收变差.
-
关键词:
- Na2KSb光电阴极 /
- Cs/O沉积 /
- 功函数 /
- 偶极矩
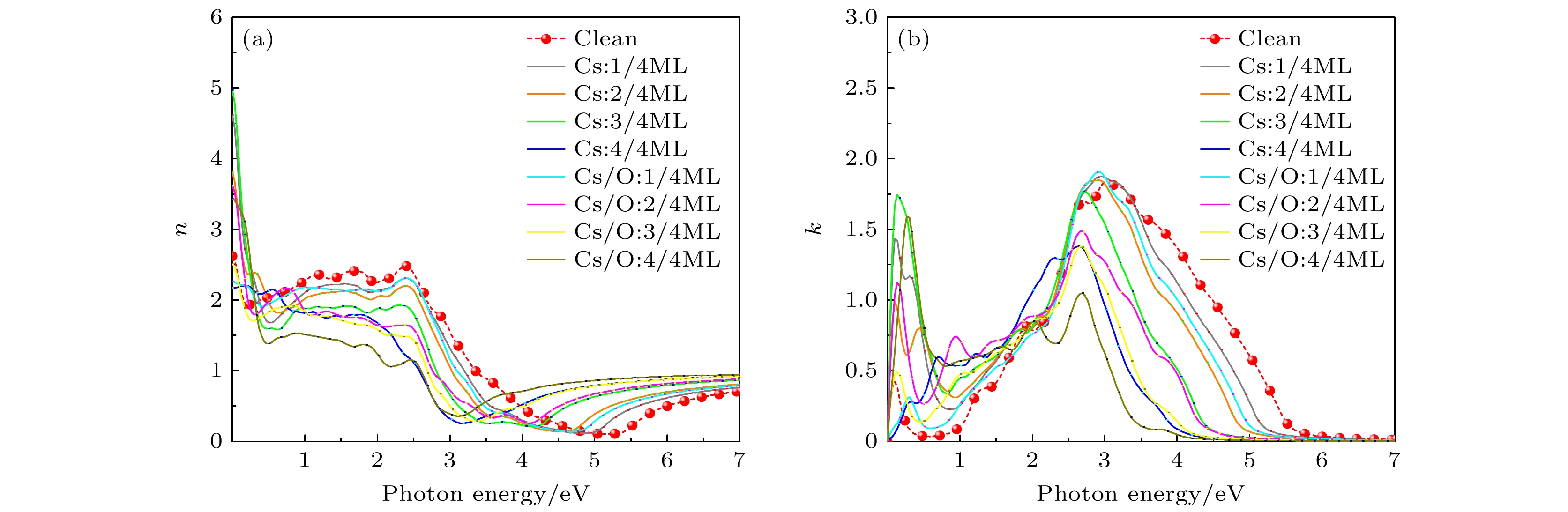
Na2KSb photocathodes have many applications in vacuum optoelectronic devices, such as photomultiplier tubes, image intensifiers, and streak image tubes for high-speed detection and imaging in extremely weak light environments, due to their advantages of high temperature resistance, small dark current, low vacuum requirement, low fabrication cost and high fabrication flexibility. In addition, this type of photocathode has important application prospect in high brightness accelerator photoinjectors. To guide the fabrication of high-sensitivity Na2KSb photocathodes, Na2KSb surfaces with different surface orientations and atom terminations are investigated by the first-principles calculation method based on the density functional theory to obtain the most stable and most favorable surface for electron emission. From the perspectives of surface energy, adsorption energy, and work function before and after Cs adsorption, it is revealed that the Na2KSb (111) K surface exhibits superior surface stability and electron emission capability. Furthermore, the electronic structure and optical properties of Cs adsorption and Cs/O co-adsorption on the Na2KSb (111) K surface under different Cs coverages are analyzed, and the mechanism of Cs/O deposition on Na2KSb surface is studied. The adsorption energy of Cs in the Cs/O adsorption model is much larger than that in the single Cs adsorption model, indicating that the adsorption of O atoms on the Na2KSb surface can make the adsorption of Cs atoms on the surface stronger, and thus increasing the adhesion of Cs atoms on the surface. After adsorption of Cs on the Na2KSb (111)K surface, the surface work function only decreases by 0.02 eV, while the maximum work function decrease for the Cs/O adsorbed surface is 0.16 eV, with the Cs coverage of 2/4 ML and the O coverage of 1/4 ML. The adsorption of Cs/O atoms on the surface facilitates the charge transfer above the surface and results in charge accumulation, which can form the effective surface dipole moment. The magnitude of the surface dipole moment is directly related to the change of work function. Furthermore, through the analysis of the electronic band structure and density of states, it is found that the adsorbed Cs atoms have additional contribution to the band structure near the conduction band minimum. After the introduction of O atoms, the valence band moves up, also the bottom of the conduction band and the top of the valence band become flat. The Cs/O deposition is beneficial to increasing the absorption of near-infrared light on the Na2KSb surface, but it will reduce the absorption of ultraviolet light and visible light, and the refractive index will also decrease. This work has a certain reference significance for understanding the optimal emission surface of Na2KSb photocathode and the mechanism of surface Cs/O deposition.-
Keywords:
- Na2KSb photocathode /
- Cs/O deposition /
- work function /
- dipole moment
[1] Hamamatsu Photonics K. K. https://www.hamamatsu.com/content/dam/hamamatsu-photonics/sites/documents/99_SALES_LIBRARY/etd/PMT_handbook_v4E.pdf [2023-6-1]
[2] Trucchi D M, Melosh N A 2017 MRS Bull. 42 488
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 田丽萍, 李立立, 温文龙, 王兴, 陈萍, 卢裕, 王俊锋, 赵卫, 田进寿 2018 67 188501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tian L P, Li L L, Wen W L, Wang X, Chen P, Lu Y, Wang J F, Zhao W, Tian J S 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 188501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Maxson J, Cultrera L, Gulliford C, Bazarov I 2015 Appl. Phys. Lett. 106 234102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wang Y, Mamun M A, Adderley P, et al. 2020 Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 23 103401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Cultrera L, Gulliford C, Bartnik A, Lee H, Bazarov I 2016 Appl. Phys Lett. 108 134105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yang B 1989 Appl. Phys Lett. 54 2548
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Rusetsky V S, Golyashov V A, Eremeev S V, et al. 2022 Phys. Rev. Lett. 129 166802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Erjavec B 1994 Vacuum 45 617
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Galan L, Bates Jr C W 1981 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 14 293
[11] Dolizy P 1980 Vacuum 30 489
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] McCarroll W H, Paff R J, Sommer A H 1971 J. Appl. Phys. 42 569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Erjavec B 1996 Appl. Surf. Sci. 103 343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Guo T L, Gao H R 1991 Appl. Phys. Lett. 58 1757
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Guo T L, Gao H R 1993 Appl. Surf. Sci. 70 355
[16] Guo T L 1996 Thin Solid Films 281 379
[17] Cultrera L, Karkare S, Lillard B, et al. 2013 Appl. Phys Lett. 103 103504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Cultrera L, Lee H, Bazarov I 2016 J. Vac. Sci. Technol. , B 34 011202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Ettema A R H F, Groot R A 2000 Phys. Rev. B 61 10035
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Murtaza G, Ullah M, Ullah N, Rani M, et al. 2016 Bull. Mater. Sci. 39 1581
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Amador R, Saßnick H D, Cocchi C 2021 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 33 365502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Schier R, Saßnick H D, Cocchi C 2022 Phys. Rev. Mater. 6 125001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Wang X C, Zhang K M, Jin M C, Ren L, Han Y F, Wang Q L, Zhang Y J 2022 Solid State Commun. 356 114960
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wang G X, Pandey R, Moody N A, Batista E R 2017 J. Phys. Chem. C 121 8399
[25] Shen Y, Yang X D, Bian Y, Chen L, Tang K, Wan J G, Zhang R, Zheng Y D, Gu S L 2018 Appl. Surf. Sci. 457 150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 向世明, 倪国强 1999 光电子成像器件原理 (北京: 国防工业出版社) 第291页
Xiang S M, Ni G Q 1999 The Principle of Optoelectronic Imaging Devices (Beijing: National Defense Industry Press) p291
[27] Karkare S, Boulet L, Singh A, Hennig R, Bazarov I 2015 Phys. Rev. B 91 035408
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Shaltaf R, Mete E, Ellialtioglu S, 2005 Phys. Rev. B 72 205415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Hogan C, Paget D, Garreau Y, Sauvage M, Onida G, Reining L, Chiaradia P, Corradini V 2003 Phys. Rev. B 68 205313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
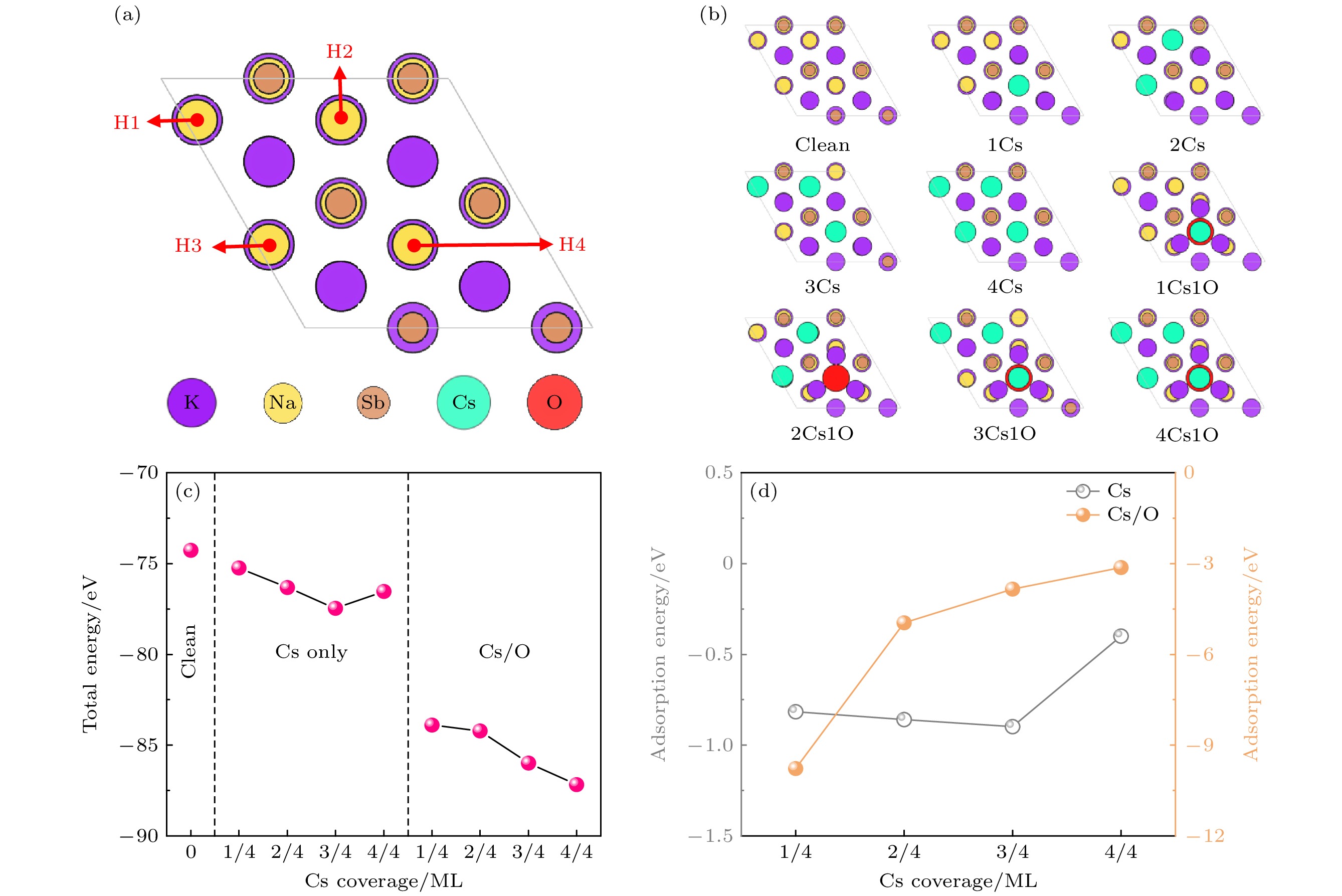
图 2 (a) Na2KSb (111) K表面的Cs, O原子吸附位; (b) 不同Cs/O覆盖度的吸附表面模型; (c) 不同吸附模型的总能量; (d) 不同吸附模型的Cs吸附能
Fig. 2. (a) Adsorption sites for Cs atoms and O atoms on Na2KSb (111) K surface; (b) adsorption surface models with different Cs/O coverages; (c) the total energies of different adsorption models; (d) the adsorption energies of isolated Cs atom of different adsorption models.
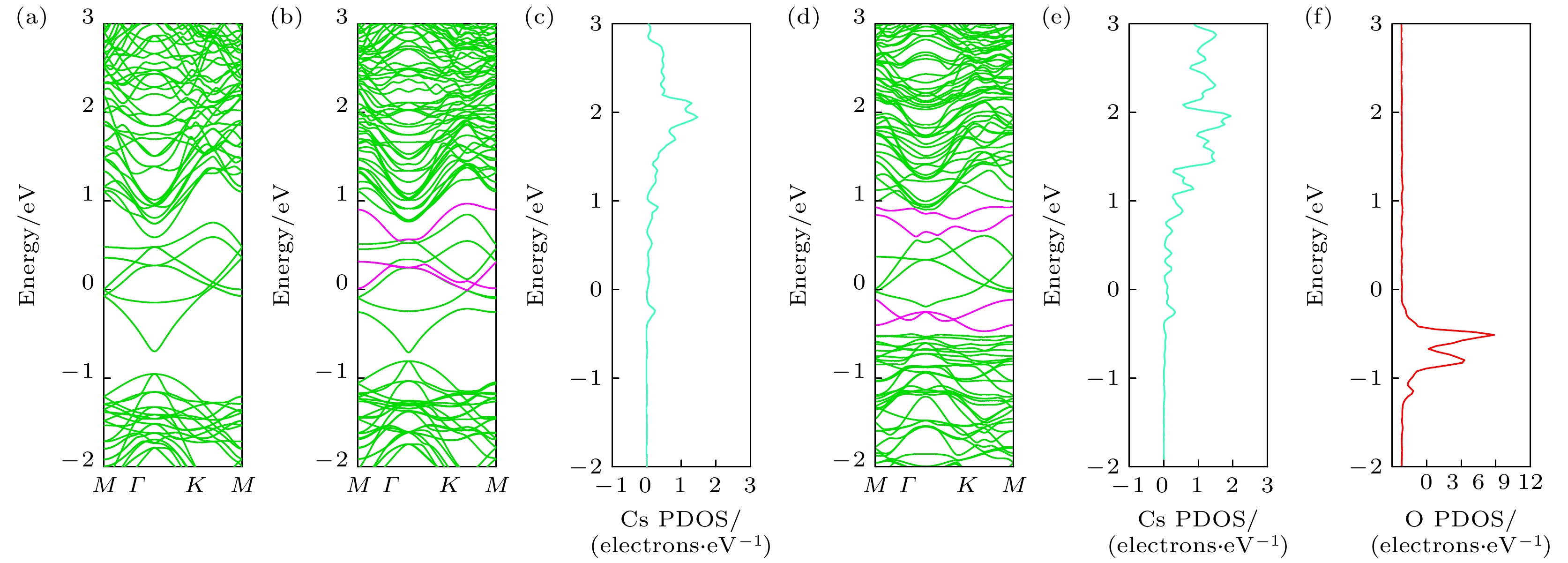
图 6 (a) 清洁表面能带结构; (b) Cs覆盖表面能带结构(Cs覆盖度: 2/4 ML, 紫红色曲线表示Cs吸附产生的能带贡献); (c) Cs覆盖表面的Cs原子6s轨道PDOS; (d) Cs/O覆盖表面能带结构(Cs覆盖度: 2/4 ML, O覆盖度: 1/4 ML, 紫红色曲线表示Cs/O吸附产生的能带贡献); (e) Cs/O覆盖表面的Cs原子6s轨道PDOS; (f) Cs/O覆盖表面的O原子2p轨道PDOS
Fig. 6. (a) Band structure for clean surface; (b) band structure for Cs-covered surface (Cs coverage: 2/4 ML, the magenta curve represents the energy band contribution from Cs adsorption); (c) PDOS of the 6s orbit of Cs atoms on the Cs-covered surface; (d) band structure for Cs/O-covered surface (Cs coverage: 2/4 ML, O coverage: 1/4 ML, the magenta curve represents the energy band contribution from Cs/O adsorption); (e) PDOS of the 6s orbit of Cs atoms on the Cs/O-covered surface; (f) PDOS of 2p orbit of O atom on the Cs/O-covered surface.
-
[1] Hamamatsu Photonics K. K. https://www.hamamatsu.com/content/dam/hamamatsu-photonics/sites/documents/99_SALES_LIBRARY/etd/PMT_handbook_v4E.pdf [2023-6-1]
[2] Trucchi D M, Melosh N A 2017 MRS Bull. 42 488
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 田丽萍, 李立立, 温文龙, 王兴, 陈萍, 卢裕, 王俊锋, 赵卫, 田进寿 2018 67 188501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tian L P, Li L L, Wen W L, Wang X, Chen P, Lu Y, Wang J F, Zhao W, Tian J S 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 188501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Maxson J, Cultrera L, Gulliford C, Bazarov I 2015 Appl. Phys. Lett. 106 234102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wang Y, Mamun M A, Adderley P, et al. 2020 Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 23 103401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Cultrera L, Gulliford C, Bartnik A, Lee H, Bazarov I 2016 Appl. Phys Lett. 108 134105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yang B 1989 Appl. Phys Lett. 54 2548
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Rusetsky V S, Golyashov V A, Eremeev S V, et al. 2022 Phys. Rev. Lett. 129 166802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Erjavec B 1994 Vacuum 45 617
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Galan L, Bates Jr C W 1981 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 14 293
[11] Dolizy P 1980 Vacuum 30 489
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] McCarroll W H, Paff R J, Sommer A H 1971 J. Appl. Phys. 42 569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Erjavec B 1996 Appl. Surf. Sci. 103 343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Guo T L, Gao H R 1991 Appl. Phys. Lett. 58 1757
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Guo T L, Gao H R 1993 Appl. Surf. Sci. 70 355
[16] Guo T L 1996 Thin Solid Films 281 379
[17] Cultrera L, Karkare S, Lillard B, et al. 2013 Appl. Phys Lett. 103 103504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Cultrera L, Lee H, Bazarov I 2016 J. Vac. Sci. Technol. , B 34 011202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Ettema A R H F, Groot R A 2000 Phys. Rev. B 61 10035
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Murtaza G, Ullah M, Ullah N, Rani M, et al. 2016 Bull. Mater. Sci. 39 1581
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Amador R, Saßnick H D, Cocchi C 2021 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 33 365502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Schier R, Saßnick H D, Cocchi C 2022 Phys. Rev. Mater. 6 125001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Wang X C, Zhang K M, Jin M C, Ren L, Han Y F, Wang Q L, Zhang Y J 2022 Solid State Commun. 356 114960
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wang G X, Pandey R, Moody N A, Batista E R 2017 J. Phys. Chem. C 121 8399
[25] Shen Y, Yang X D, Bian Y, Chen L, Tang K, Wan J G, Zhang R, Zheng Y D, Gu S L 2018 Appl. Surf. Sci. 457 150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 向世明, 倪国强 1999 光电子成像器件原理 (北京: 国防工业出版社) 第291页
Xiang S M, Ni G Q 1999 The Principle of Optoelectronic Imaging Devices (Beijing: National Defense Industry Press) p291
[27] Karkare S, Boulet L, Singh A, Hennig R, Bazarov I 2015 Phys. Rev. B 91 035408
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Shaltaf R, Mete E, Ellialtioglu S, 2005 Phys. Rev. B 72 205415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Hogan C, Paget D, Garreau Y, Sauvage M, Onida G, Reining L, Chiaradia P, Corradini V 2003 Phys. Rev. B 68 205313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 1556
- PDF下载量: 62
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: