-
在研究量子态的演化问题时, 量子演化速率往往定义为量子初态与其演化态之间的态距离随时间的变化率. 本文将量子演化的基本理论与线性代数方法相结合, 通过量子态演化的路径距离来研究量子系统的演化. 量子幺正演化系统中, 量子演化算符包含了量子演化的路径信息, 路径距离的大小则决定于演化算符本征值的幅角主值分布. 由量子态演化的路径距离随时间的变化率而得到的量子瞬时演化速率则正比于系统哈密顿量的最大与最小本征值之差. 作为应用之一, 利用量子演化的路径距离及哈密顿量诱导的瞬时演化速率, 可以给出量子演化新的时间下限. 此时间下限只与系统的演化算符及哈密顿量有关, 而与量子初态的具体形式无关, 这与量子系统真实演化时间所具有的性质一致. 严格的理论证明以及两个演化实例的数值结果均表明, 在
$ [0,\ \pi/(2\omega_{\mathrm{H}})]$ 时间范围内, 本文给出的演化时间下限与真实演化时间重合, 是真实演化时间的准确预测. 通过量子演化的路径距离及相应演化速率来研究量子系统的演化, 为相关问题的解答提供了新的思路和方法.In the issue of quantum evolution, quantum evolution speed is usually quantified by the time rate of change of state distance between the initial sate and its time evolution. In this paper, the path distance of quantum evolution is introduced to study the evolution of a quantum system, through the approach combined with basic theory of quantum evolution and the linear algebra. In a quantum unitary system, the quantum evolution operator contains the path information of the quantum evolution, where the path distance is determined by the principal argument of the eigenvalues of the unitary operator. Accordingly, the instantaneous quantum evolution speed is proportional to the distance between the maximum and minimum eigenvalues of the Hamiltonian. As one of the applications, the path distance and the instantaneous quantum evolution speed could be used to form a new lower bound of the real evolution time, which depends on the evolution operator and Hamiltonian, and is independent of the initial state. It is found that the lower bound presented here is exactly equal to the real evolution time in the range$ \left[ {0, {\pi }/({{2{\omega _{\rm{H}}}}}}) \right]$ . The tool of path distance and instantaneous quantum evolution speed introduced here provides new method for the related researches.-
Keywords:
- quantum evolution /
- path distance /
- quantum evolution speed
[1] Mandelstam L, Tamm I 1945 J. Phys. (USSR) 9 249
[2] Vaidman L 1992 American J. Phys. 60 182
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Margolus N and Levitin L B 1998 Physica D 120 188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Lloyd S 2000 Nature 406 1047
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lloyd S 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 88 237901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Bekenstein J D 1981 Phys. Rev. Lett. 46 623
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Murphy M, Montangero S, Giovannetti V, Calarco T 2010 Phys. Rev. A 82 022318
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Mohan B, Das S, Pati A K 2022 New J. Phys. 24 065003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Giovannetti V, Lloyd S, Maccone L 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 96 010401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Giovannetti V, Lloyd S, Maccone L 2011 Nat. Photonics 5 222
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Chin A W, Huelga S F, Plenio M B 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 233601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Binder F C, Vinjanampathy S, Modi K, Goold J 2015 New J. Phys. 17 075015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Campaioli F, Pollock F A, Binder F C, Céleri L, Goold J, Vinjanampathy S, Modi K 2017 Phys. Rev. Lett. 118 150601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Scully M O, Zubairy M S 1997 Quantum Optics (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) pp204–205
[15] Bures D 1969 Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 135 199
[16] Wootters W K 1981 Phys. Rev. D 23 357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Uhlmann A 1992 Groups and Related Topics (New York: Kluwer Academic) pp267–274
[18] Uhlmann A 1976 Rep. Math. Phys. 9 273
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bhattacharyya K 1983 J. Phys. A 16 2993
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Huang J H, Hu L Y, Liu F Y 2020 Phys. Rev. A 102 062221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Campaioli F, Pollock F A, Binder F C, Modi K 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 120 060409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Huang J H, Qin L G, Chen G L, Hu L Y, Liu F Y 2022 Chin. Phys. B 31 110307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Levitin L B, Toffoli T 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 160502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Pires D P, Cianciaruso M, Celeri L C, Adesso G, Soares-Pinto D O 2016 Phys. Rev. X 6 021031
[25] Alberti A, Ness G, Sagi Y 2022 Phys. Rev. Lett. 129 140403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Shiraishi N, Funo K, Saito K 2019 New J. Phys. 21 013006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Hörnedal N, Allan D, Sönnerborn O 2022 New J. Phys. 24 055004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 田聪, 鹿翔, 张英杰, 夏云杰 2019 68 150301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tian C, Lu X, Zhang Y J, Xia Y J 2019 Acta. Phys. Sin. 68 150301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 刘天, 李宗良, 张延惠, 蓝康 2023 72 047301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu T, Li Z L, Zhang Y H, Lan K 2023 Acta. Phys. Sin. 72 047301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Ma Y J, Gao X C, Wu S X, Yu C S 2023 Chin. Phys. B 32 040308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
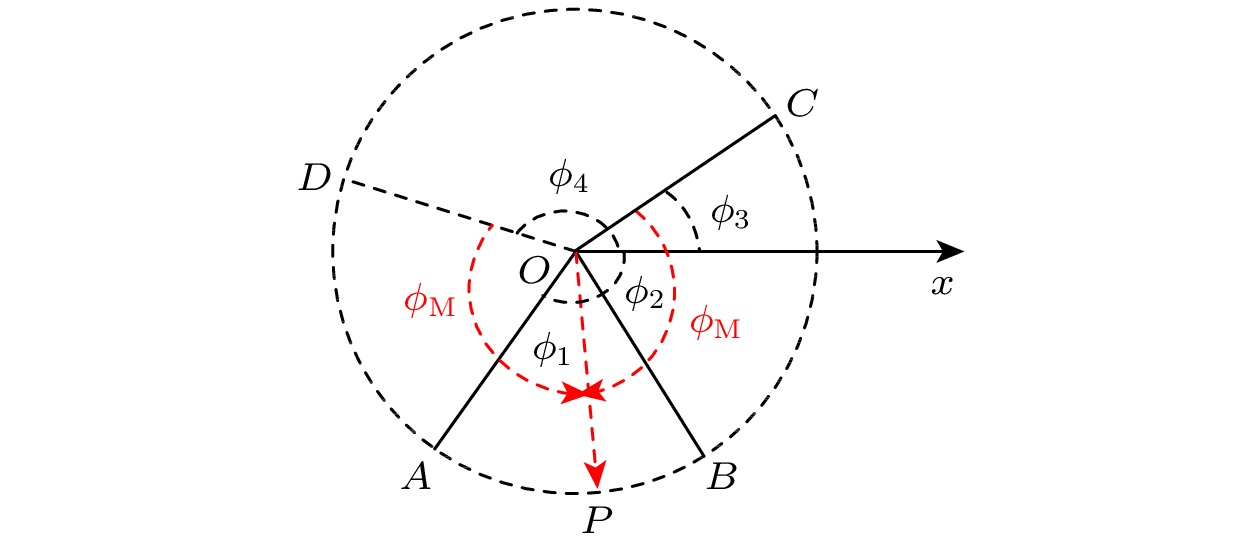
图 1 在极坐标系的单位圆中, 不同半径的极角与演化算符本征值的辐角主值相对应. 具有最大夹角的两相邻半径, 其夹角平分线的反向延长线的极角即为
$ \phi_0 $ 取值, 而$ \phi_{\rm{M}} $ 则为此反向延长线与前述两相邻半径的夹角.$ \phi_{\rm{M}} $ 也有如下等效理解: 演化算符本征值的每个辐角主值与一个半径对应, 找到能覆盖所有半径的最小扇形, 此最小扇形的圆心角的一半即为目标$ \phi_{\rm{M}} $ 值Fig. 1. In the polar coordinate system, the polar angle of a radius in the unit circle corresponds to the principal argument of an eigenvalue of the evolution operator. The angular bisector of two neighboring radii, which form the largest included angle among all neighboring radii, is the reverse extension line of the radius with polar angle
$ \phi_0 $ , and$ \phi_{\rm{M}} $ is equal to half the largest included angle among all neighboring radii. Equivalently speaking, the principal argument of each eigenvalue of the evolution operator corresponds to a radius in the unit circle. If we find out the smallest sector in this unit circle to cover all radii mentioned above,$ \phi_{\rm{M}} $ is then equal to half the sector angle.图 2 三能级量子纯态
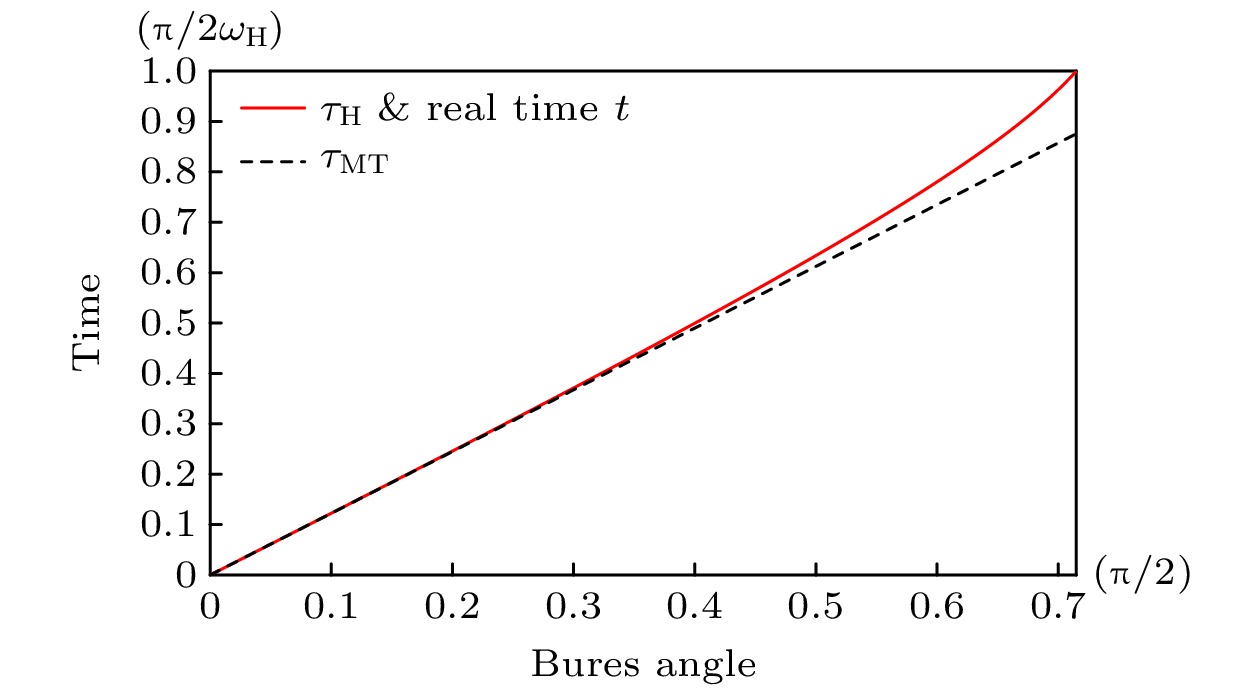
$ |\psi_0\rangle $ 在$ t\in\left[0,\frac {\pi}{2\omega_{\mathrm{H}}}\right]$ 时间范围内的自由演化过程中, 本文提出的演化时间下限$ \tau_{\mathrm{H}} $ 始终与真实演化时间t重合, 见红色实线. 而Mandelstam-Tamm时间下限位于真实演化时间曲线的下方, 见黑色短划线Fig. 2. During the evolution of a qutrit prepared in a pure state
$ |\psi_0\rangle $ , the lower bound of the evolution time proposed here meets the real evolution time perfectly in the range$ t\in\left[0,\frac {\pi}{2\omega_{\mathrm{H}}}\right]$ . The curve of the Mandelstam-Tamm bound is below the curve of the real evolution time, see the black dashed line.图 3 在相同的哈密顿量作用下, 三能级量子纯态
$ |\psi_0\rangle $ 和混合态$ \rho_0 $ 在演化过程中, 依据本文提出的时间下限$ \tau_{{\rm{H}}} $ 在$ \left[0, {\pi}/({2\omega_{\rm{H}}})\right] $ 范围内与真实演化时间相等, 见红色实线. 量子纯态$ |\psi_0\rangle $ 演化过程中的Mandelstam-Tamm时间下限小于真实演化时间, 见黑色短划线. 对混合态$ \rho_0 $ 的演化而言, 其Mandelstam-Tamm时间下限与真实演化时间的偏差最大, 见蓝色点线Fig. 3. During the evolution of a qutrit prepared in a pure state
$ |\psi_0\rangle $ and in a mixed state$ \rho_0 $ , governed by the same Hamiltonian, the lower bound of the evolution time proposed here meets the real evolution time perfectly in the range$ t\in \left[0, {\pi}/({2\omega_{\rm{{\rm{H}}}}})\right] $ , see the black dashed line. In the evolution of the mixed state$ \rho_0 $ , the Mandelstam-Tamm bound is deviated from the real evolution time substantially, see the blue dotted line. -
[1] Mandelstam L, Tamm I 1945 J. Phys. (USSR) 9 249
[2] Vaidman L 1992 American J. Phys. 60 182
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Margolus N and Levitin L B 1998 Physica D 120 188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Lloyd S 2000 Nature 406 1047
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lloyd S 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 88 237901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Bekenstein J D 1981 Phys. Rev. Lett. 46 623
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Murphy M, Montangero S, Giovannetti V, Calarco T 2010 Phys. Rev. A 82 022318
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Mohan B, Das S, Pati A K 2022 New J. Phys. 24 065003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Giovannetti V, Lloyd S, Maccone L 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 96 010401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Giovannetti V, Lloyd S, Maccone L 2011 Nat. Photonics 5 222
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Chin A W, Huelga S F, Plenio M B 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 233601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Binder F C, Vinjanampathy S, Modi K, Goold J 2015 New J. Phys. 17 075015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Campaioli F, Pollock F A, Binder F C, Céleri L, Goold J, Vinjanampathy S, Modi K 2017 Phys. Rev. Lett. 118 150601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Scully M O, Zubairy M S 1997 Quantum Optics (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) pp204–205
[15] Bures D 1969 Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 135 199
[16] Wootters W K 1981 Phys. Rev. D 23 357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Uhlmann A 1992 Groups and Related Topics (New York: Kluwer Academic) pp267–274
[18] Uhlmann A 1976 Rep. Math. Phys. 9 273
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bhattacharyya K 1983 J. Phys. A 16 2993
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Huang J H, Hu L Y, Liu F Y 2020 Phys. Rev. A 102 062221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Campaioli F, Pollock F A, Binder F C, Modi K 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 120 060409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Huang J H, Qin L G, Chen G L, Hu L Y, Liu F Y 2022 Chin. Phys. B 31 110307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Levitin L B, Toffoli T 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 160502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Pires D P, Cianciaruso M, Celeri L C, Adesso G, Soares-Pinto D O 2016 Phys. Rev. X 6 021031
[25] Alberti A, Ness G, Sagi Y 2022 Phys. Rev. Lett. 129 140403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Shiraishi N, Funo K, Saito K 2019 New J. Phys. 21 013006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Hörnedal N, Allan D, Sönnerborn O 2022 New J. Phys. 24 055004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 田聪, 鹿翔, 张英杰, 夏云杰 2019 68 150301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tian C, Lu X, Zhang Y J, Xia Y J 2019 Acta. Phys. Sin. 68 150301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 刘天, 李宗良, 张延惠, 蓝康 2023 72 047301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu T, Li Z L, Zhang Y H, Lan K 2023 Acta. Phys. Sin. 72 047301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Ma Y J, Gao X C, Wu S X, Yu C S 2023 Chin. Phys. B 32 040308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 4331
- PDF下载量: 139
- 被引次数: 0






















 下载:
下载: