-
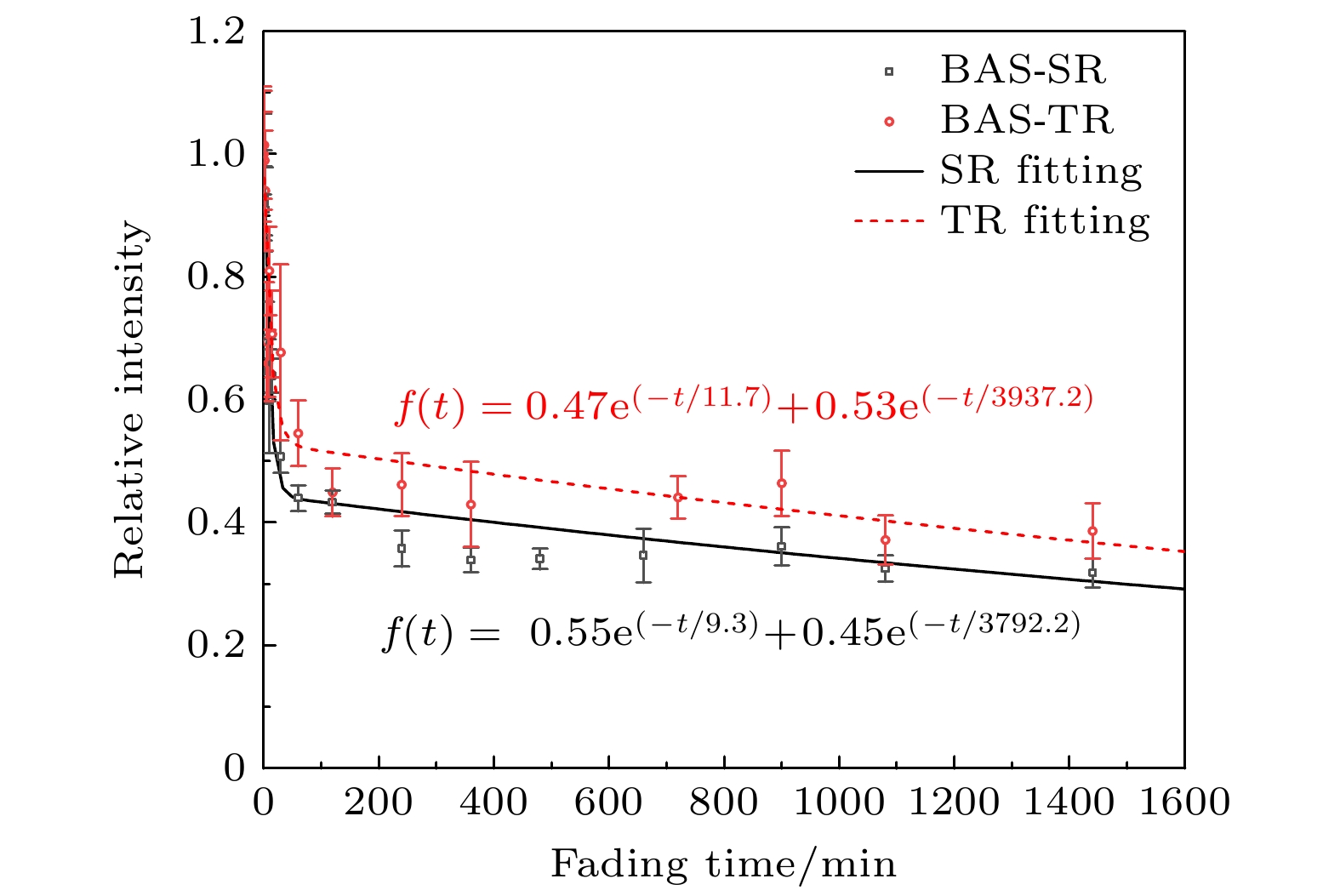
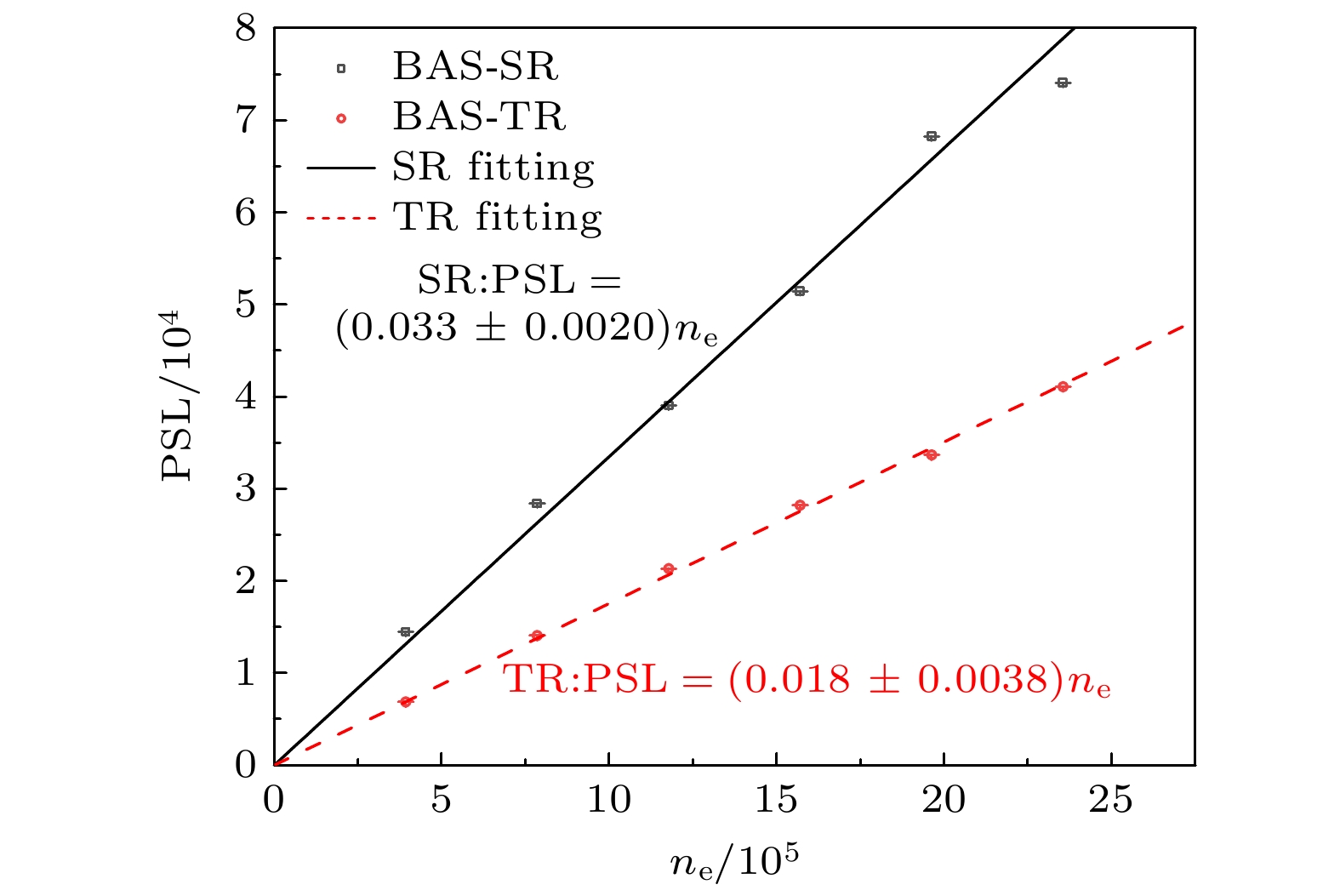
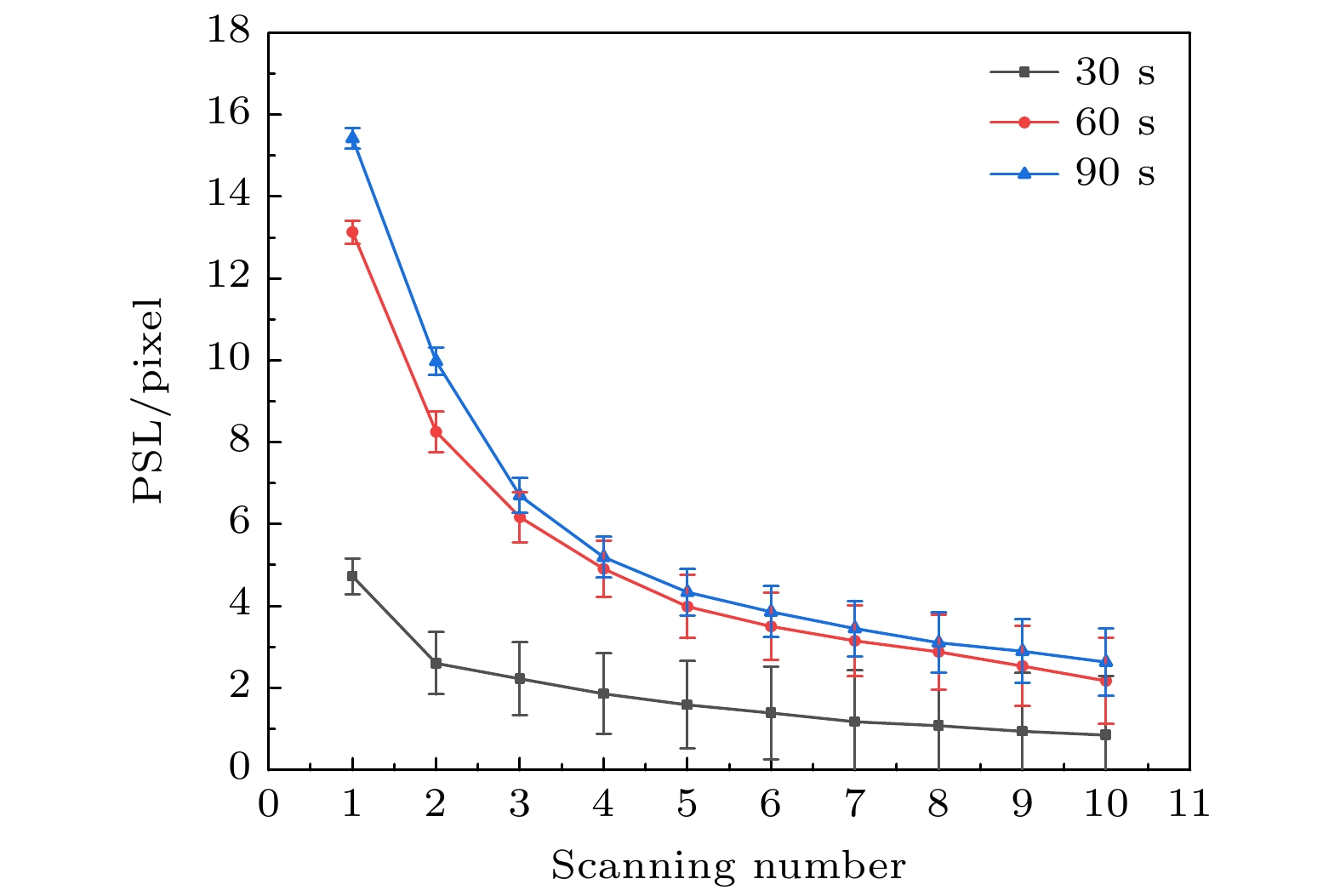
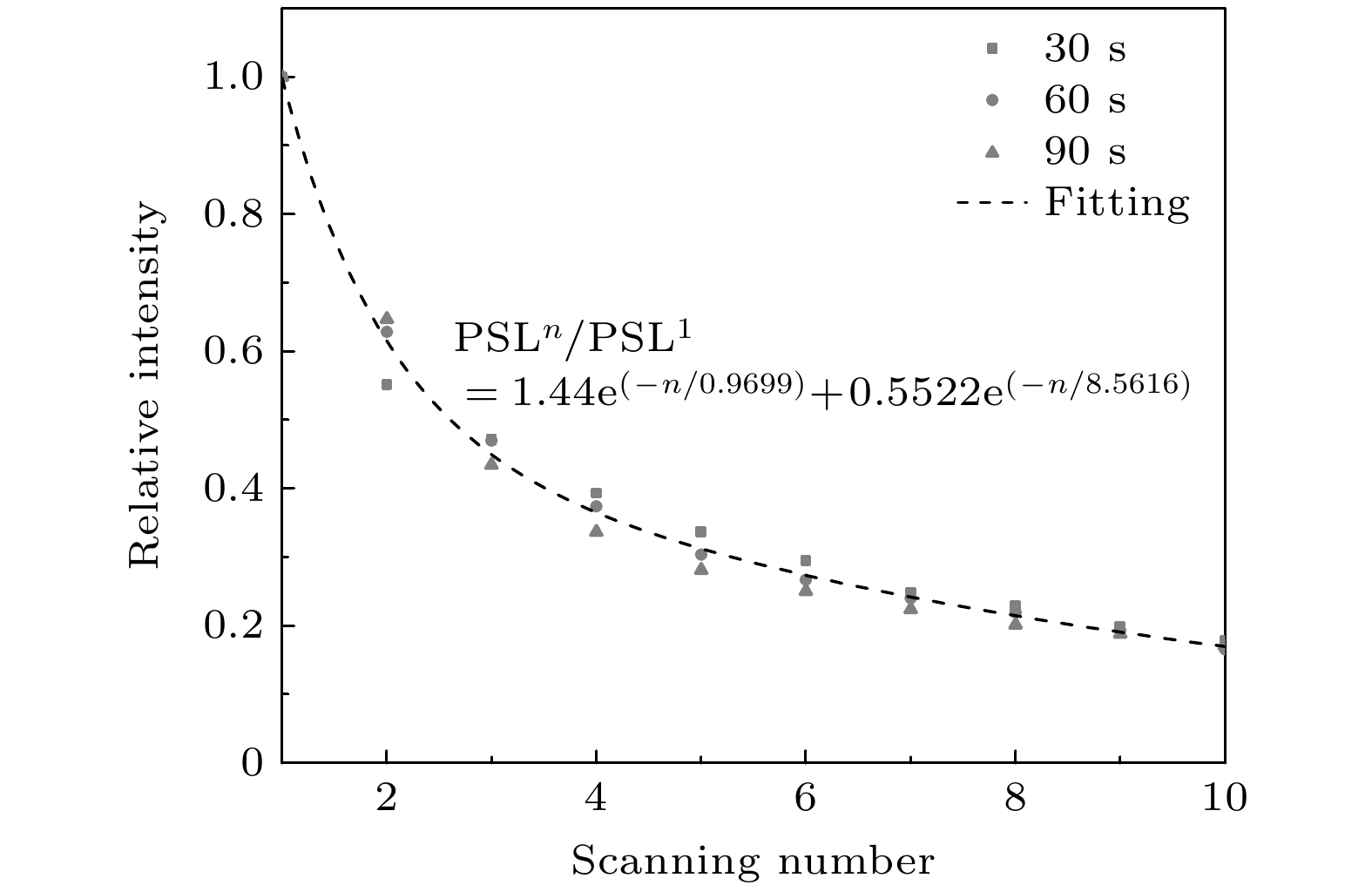
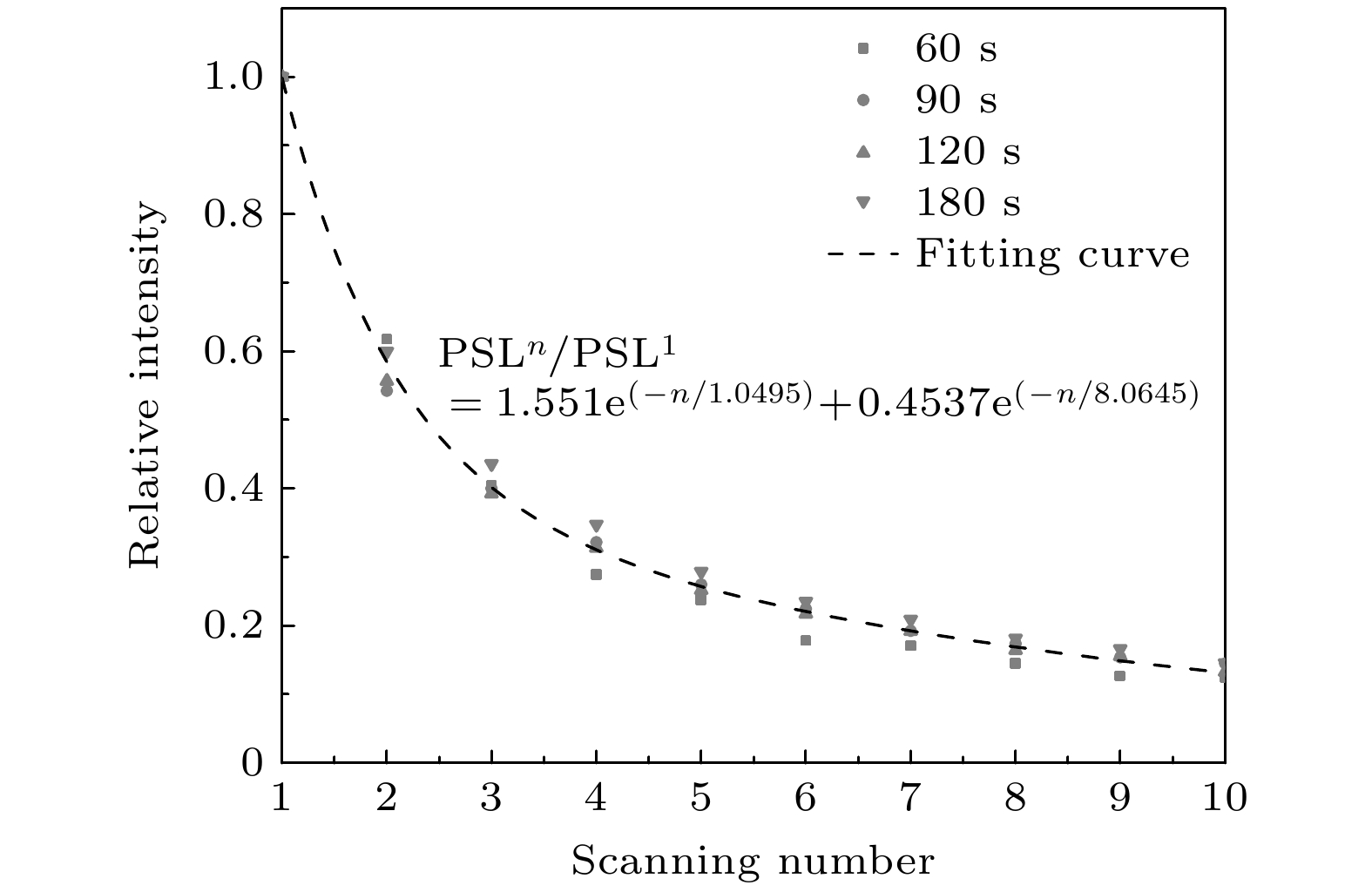
由于成像板(imaging plate, IP)对电磁辐射场不敏感, 因而作为探测介质被广泛应用于激光驱动的辐射粒子诊断设备中, 在使用前需要对其特性和物理机制进行研究. 利用90Sr/90Y电子源测量BAS-SR和BAS-TR两种IP板的时间衰减曲线, 同时对长时间辐照的衰减曲线进行修正; 刻度了 BAS-SR和BAS-TR两种IP板对90Sr/90Y电子源的绝对灵敏度, 其分别为(0.033±0.002) PSL/e和(0.0180±0.0038) PSL/e (photostimulated light, PSL), 与国际上大部分电子绝对刻度的结果基本相符, IP板对辐射粒子的绝对刻度依赖于IP板的类型、扫描设备和实验环境. 此外对BAS-SR和BAS-TR两种IP板辐照后进行多次连续扫描, 研究了信号强度变化趋势的规律. 建立了用于描述辐射粒子在IP板荧光层中沉积能量、存储信息和信息读取微观物理过程的光激励发光模型, 结合光激励发光模型建立的数学模型有效地阐释了IP板探测辐射粒子物理机制与其表现的特性之间的关系. 这些研究可以为后续开展IP板应用于激光等离子体诊断实验提供一定的数据基础.The imaging plate (IP) is a reusable detector for detecting radiation particles in a complex electromagnetic field environment, and it is widely used as a detection medium in laser-accelerated particle beam diagnostic equipment. Therefore, it is necessary to study the performance characteristics and physical mechanism of IP. An electron source with known activity is used to explore the performance characteristics of IP. A 90Sr/90Y electron source is used to measure the time attenuation curve, calibrate the absolute sensitivity, and study the law of multiple scanning of BAS-SR and BAS-TR. In the case of a longer irradiation, the fading cannot be neglected, and the attenuation curves are modified. The time attenuation characteristics indicate that the IP should be cooled after irradiation, and the scanning should be carried out in the slow decay process to reduce the influence of the reading error in the decay process. The absolute sensitivity of BAS-SR and BAS-TR to 90Sr/90Y source are (0.033±0.002) PSL/e and (0.018±0.0038) PSL/e (photostimulated light, PSL), respectively, which are consistent with the results of most absolute sensitivity. The absolute sensitivity is closely related to the type of IP, scanning equipment, and experimental environment. In addition, the energy spectrum integral effect of the broad spectrum β source has a significant influence on the absolute sensitivity. This method is only suitable for the rough evaluation of the sensitivity characteristic parameters of the IP. Multiple scanning approximately satisfies the double exponential function distribution, which is consistent with the physical model. The characteristics of IP are determined by its storage principle. The fluorescence layer of IP is composed of typical electron trapping materials MFX (M = Ca, Sr, Ba; X = C1, Br, I) alkaline earth metal fluorhalide BaFBr. When the IP is irradiated, a large number of free electron-hole pairs are excited by the deposited energy in the material, and the free electrons will be captured by the electron trap, so the fluorescence layer of the IP records the radiation particles’ information through the energy deposited. In this paper, we study three kinds of models. Based on the models, a photo-stimulated luminescence model is proposed to describe the electron transfer process. The photo-stimulated luminescence model describes the physical mechanism of energy deposition, information storage, and information scanning of radiation particles. The relationship between the physical mechanism and characteristics is explained effectively by combining the microscopic mathematical model with the macroscopic physical phenomenon. It provides a specific data basis for the subsequent application of IPs in laser plasma diagnostic experiments.
-
Keywords:
- imaging plate /
- characteristics /
- photo-stimulated luminescence
[1] Danson C N, Haefner C, Bromage J 2019 High Power Laser Sci. 7 54
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Esarey E, Schroeder C B, Leemans W P 2009 Rev. Mod. Phys. 81 1229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 黄建微, 李德红, 党永乐, 吴笛, 王乃彦, 郝艳梅 2017 核电子学与探测技术 37 559
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang J W, Li D H, Dang Y L, Wu D, Wang N Y, Hao Y M 2017 Nucl. Electron. Detect. Technol. 37 559
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zeil K, Kraft S D, Jochmann A, Kroll F, Jahr W, Schramm U, Karsch L, Pawelke J, Hidding B, Pretzler G 2010 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 81 013307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Gales S G, Bentley C D 2004 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 75 4001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Busold1 S, Philipp K, Otten A, Roth M 2014 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85 113306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 孙力, 王永生, 董金凤, 何志毅, 徐征 2001 激光与红外 31 269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun L, Wang Y S, Dong J F, He Z Y, Xu Z 2001 Laser Infrared 31 269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bonnet T, Comet M, Denis-Petit D, Gobet F, Hannachi F, Tarisien M, Versteegen M, Aléonard M M 2013 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 84 103510
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Bonnet T, Comet M, Denis-Petit D, Gobet F, Hannachi F, Tarisien M, Versteegen M, Aleonard M M 2013 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 84 103508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Williams G, Jackson M, Brian R, Chen H, Kojima S 2014 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85 11E604
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ohuchi H, Yamadera A, Nakamura T 2000 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 450 343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tanaka K A, Yabuuchi T, Sato T, Kodama R, Kitagawa Y, Takahashi T, Ikeda T, Honda Y, Okuda S 2005 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 76 013507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Chen H, Back N L, Bartal T, Beg F N, Eder D C, Link A J, MacPhee A G, Ping Y, Song P M, Throop A, Van Woerkom L 2008 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 79 033301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Rabhi N, Bohacek K, Batani D, Boutoux G, Ducret J E, Guillaume E, Jakubowska K, Thaury C, Thfoin I 2016 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 87 053306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Singh S, Slavicek T, Hodak R, Versaci R, Pridal P, Kumar D 2017 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 88 075105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Takahashi K, Kohda K, Miyahara J 1984 J. Lumi. 31 266
[17] Von Seggern H, Voigt T, Knüpfer W, Lange G 1988 J. Appl. Phys. 64 1405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Von Seggern H 1999 Brazilian J. Phys. 29 254
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 赵辉, 王永生, 徐征, 侯延冰, 徐叙 1998 47 333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao H, Wang Y S, Xu Z, Hou Y B, Xu X 1998 Acta Phys. Sin. 47 333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Golovin D O, Mirfayzi S R, Shokita S, Abe Y, Lanl Z, Arikawa Y, Morace A, Pikuz T A, Yogo A 2021 J. Instrum. 16 T02005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Qi J M, Zhang F Q, Chen J C, Xie H W 2014 Chin. Phys. C 38 016001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 IP板衰退效应时间函数的参数以及文献中对应参数[4,9,20,21]
Table 1. Parameters of fading time effect for IPs and corresponding parameters [4,9,20,21].
IP $ {A}_{1} $ $ {B}_{1} $/min $ {A}_{2} $ $ {B}_{2} $/min BAS-SR 0.55 9.3 0.45 3792.2 BAS-TR 0.47 11.7 0.53 3937.2 BAS-SR[4] 0.27 36.0 0.33 1338 BAS-MS[4] 0.18 36.0 0.17 288 BAS-MS[9] 0.26 37.6 0.74 2604 BAS-TR[9] 0.49 17.9 0.51 1482 BAS-SR[9] 0.49 11.9 0.51 1390 BAS-MS[21] 0.12 49.0 0.27 335 BAS-TR[21] 0.31 48.0 0.25 295 BAS-TR[20] 0.36 33.0 0.64 2041 表 2 衰退时间效应对IP板读数信号强度的影响
Table 2. Signal intensity decreases with fading time.
冷却
时间BAS-SR BAS-TR 衰减剩余/% 衰减速率/% 衰减剩余/% 衰减速率/% B1 65.12 2.19 62.16 1.49 2B1 52.22 0.81 51.09 0.56 3B1 47.41 0.31 46.94 0.21 4B1 45.57 0.12 45.33 0.09 5B1 44.82 0.05 44.65 0.05 -
[1] Danson C N, Haefner C, Bromage J 2019 High Power Laser Sci. 7 54
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Esarey E, Schroeder C B, Leemans W P 2009 Rev. Mod. Phys. 81 1229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 黄建微, 李德红, 党永乐, 吴笛, 王乃彦, 郝艳梅 2017 核电子学与探测技术 37 559
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang J W, Li D H, Dang Y L, Wu D, Wang N Y, Hao Y M 2017 Nucl. Electron. Detect. Technol. 37 559
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zeil K, Kraft S D, Jochmann A, Kroll F, Jahr W, Schramm U, Karsch L, Pawelke J, Hidding B, Pretzler G 2010 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 81 013307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Gales S G, Bentley C D 2004 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 75 4001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Busold1 S, Philipp K, Otten A, Roth M 2014 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85 113306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 孙力, 王永生, 董金凤, 何志毅, 徐征 2001 激光与红外 31 269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun L, Wang Y S, Dong J F, He Z Y, Xu Z 2001 Laser Infrared 31 269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bonnet T, Comet M, Denis-Petit D, Gobet F, Hannachi F, Tarisien M, Versteegen M, Aléonard M M 2013 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 84 103510
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Bonnet T, Comet M, Denis-Petit D, Gobet F, Hannachi F, Tarisien M, Versteegen M, Aleonard M M 2013 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 84 103508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Williams G, Jackson M, Brian R, Chen H, Kojima S 2014 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85 11E604
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ohuchi H, Yamadera A, Nakamura T 2000 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 450 343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tanaka K A, Yabuuchi T, Sato T, Kodama R, Kitagawa Y, Takahashi T, Ikeda T, Honda Y, Okuda S 2005 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 76 013507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Chen H, Back N L, Bartal T, Beg F N, Eder D C, Link A J, MacPhee A G, Ping Y, Song P M, Throop A, Van Woerkom L 2008 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 79 033301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Rabhi N, Bohacek K, Batani D, Boutoux G, Ducret J E, Guillaume E, Jakubowska K, Thaury C, Thfoin I 2016 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 87 053306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Singh S, Slavicek T, Hodak R, Versaci R, Pridal P, Kumar D 2017 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 88 075105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Takahashi K, Kohda K, Miyahara J 1984 J. Lumi. 31 266
[17] Von Seggern H, Voigt T, Knüpfer W, Lange G 1988 J. Appl. Phys. 64 1405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Von Seggern H 1999 Brazilian J. Phys. 29 254
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 赵辉, 王永生, 徐征, 侯延冰, 徐叙 1998 47 333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao H, Wang Y S, Xu Z, Hou Y B, Xu X 1998 Acta Phys. Sin. 47 333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Golovin D O, Mirfayzi S R, Shokita S, Abe Y, Lanl Z, Arikawa Y, Morace A, Pikuz T A, Yogo A 2021 J. Instrum. 16 T02005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Qi J M, Zhang F Q, Chen J C, Xie H W 2014 Chin. Phys. C 38 016001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 6362
- PDF下载量: 79
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: