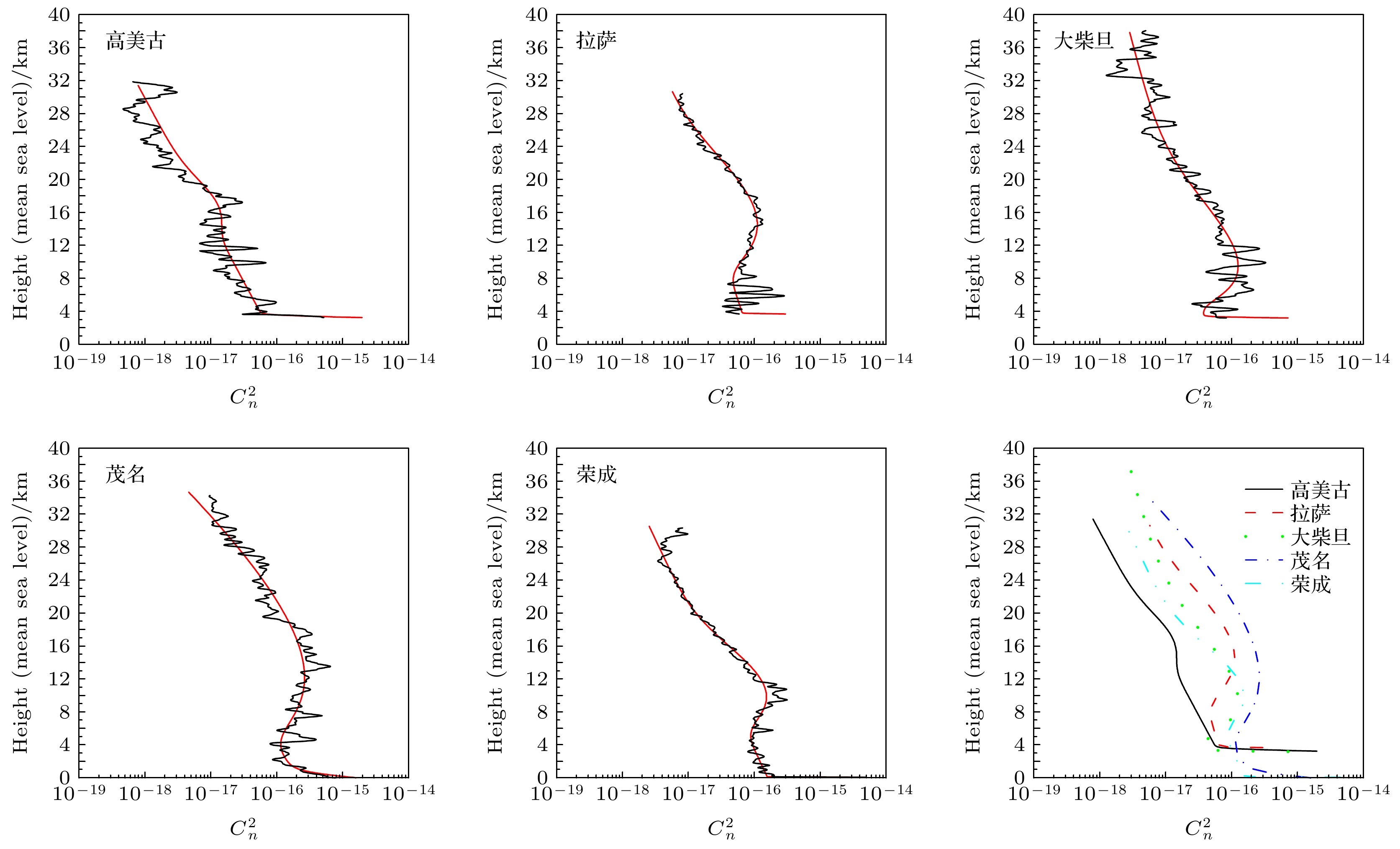
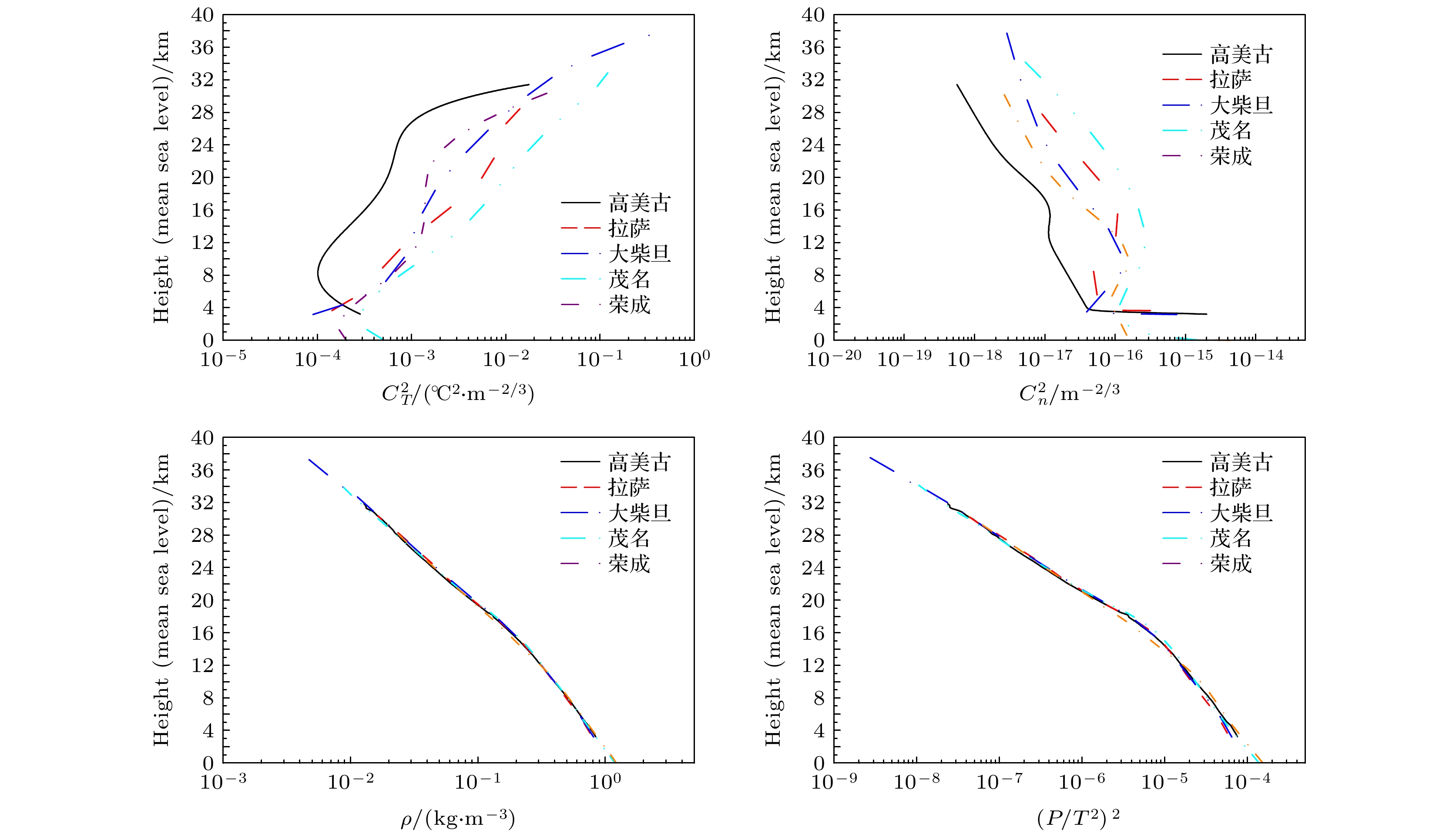
-
由于大气湍流的存在, 当光束在大气中传播时会发生相位起伏、光强闪烁等一系列湍流效应现象, 严重制约光电系统的性能, 是造成天文观测困难的主要原因. 大气折射率结构常数
$C_n^2$ 廓线是评估大气湍流效应的重要参数. 本文归纳了几种有代表性的$ C_n^2 $ 廓线模式, 提出了修正的CLEAR I夜晚模式; 分析了高美古、拉萨、大柴旦、茂名、荣成等5个实验点探空测量数据, 给出了5个实验点算术平均拟合的$ C_n^2 $ 廓线公式; 计算了各模式和测量数据在波长为0.5 μm时的大气相干长度$ {r_0} $ 、视宁度$ {\varepsilon _{{\text{FWHM}}}} $ 、等晕角$ {\theta _0} $ 、相干时间$ {\tau _0} $ 、等效高度$ \overline h $ 和等效风速$ \overline V $ 等大气光学参数以及各大气层$ C_n^2 $ 递减率和不同大气层湍流贡献百分比. 重点对H-V(5/7)模式的存疑、$ C_n^2 $ 廓线模式采用的平均方法、低平流层$ C_n^2 $ 是否具有统一的递减率等问题进行讨论并给出答案.-
关键词:
- 大气光学湍流 /
- 修正的CLEAR I夜晚模式 /
- 5个实验点$ C_n^2 $廓线公式 /
- H-V(5/7)模式的存疑
Owing to the existence of atmospheric turbulence, a series of turbulence effects such as phase fluctuation and light intensity scintillation will occur when the electromagnetic waves propagates through the atmosphere, which seriously affects the performance of the electro-optic system, resulting in the difficulty of astronomical observation. The atmospheric refractive index structure constant ($ C_n^2 $ ) profile is an important parameter to evaluate the turbulence effects. This paper summarizes several representative$ C_n^2 $ profile models and analyzes the data using balloon-borne microthermal probes at five sites i.e. Gaomeigu, Lhasa, Dachaidan, Maoming, and Rongcheng. The atmospheirc optical parameters are calculated, such as coherence length, seeing, isoplanatie angle, coherence time, equivalent height, equivalent wind speed, drop-off rate and integrated contribution from each atmosphere layer. The formulas of five sites are developed by fitting the arithmetic average of measurements. Several troubling basic problems such as suspicion the H-V (5/7) model, the model developed by arithmetic average or geometric average, the problem whether there is a uniform lapse rate in the low stratosphere, are discussed and solved. The modified CLEAR I night model is given.-
Keywords:
- atmospheric optical turbulence /
- modified CLEAR I night model /
- $ C_n^2 $ profile model of 5 field test site /
- suspicion of the H-V(5/7) model
[1] 饶瑞中 2022 红外与激光工程 51 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Rao R Z 2022 Infrared Laser Eng. 51 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] [3] 吴晓庆, 曾宗泳, 马成胜, 翁宁泉, 肖黎明 1996 量子电子学报 13 385
Wu X Q, Zeng Z Y, Ma C S, Weng N Q, Xiao L M 1996 Chin. J. Quantum Electron. 13 385
[4] Coulman C, Vernin J, Coqueugniot Y, Caccia J 1988 Appl. Opt. 27 155
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Dewan E M, Good R E, Beland B, Brown J 1993 A Model for Cn2 Profiles Using Radiosonde Rata (Phillips Laboratory, Hansom Air Force Base) PL-TR-93-2043
[6] Trinquet H, Vernin J 2007 Environ. Fluid Mech. 7 397
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Tatarski V I 1961 Wave Propagation in a Turbulent Medium (New York: McGraw-Hill)
[8] Jumper G Y, Beland R R 2000 31st AIAA Plasmadynamics and Lasers Conference Denver, CO, USA, June 19–22, 2000, AIAA-2000-2355
[9] Parenti R R, Sasiela R J 1994 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 11 288
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Battles F P, Murphy E A, Noonan J P 1988 Phys. Scripta 37 151
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 吴晓庆, 钱仙妹, 黄宏华, 汪平, 崔朝龙, 青春 2014 天文学报 55 144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu X Q, Qian X M, Huang H H, Wang P, Cui C L, Qing C 2014 Acta Astron. Sin. 55 144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Good R, Beland R, Murphy E, Brown J, Dewan E 1988 SPIE 928 165
[13] 蔡俊, 李学彬, 詹国伟, 武鹏飞, 徐春燕, 青春, 吴晓庆 2018 67 014206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cai J, Li X B, Zhan G W, Wu P F, Xu C Y, Qing C, Wu X Q 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 014206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Han Y J, Wu X Q, Luo T, Qing C, Yang Q K, JinX M, Liu N N, Wu S, Su C D 2020 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 37 995
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Beland R R, Brown J H, Good R E, Murphy E A 1985 Optical Turbulence Characterization of AMOS Report AFGL-TR-88-xxxx
[16] Tyson R K 1996 Appl. Opt. 35 3640
[17] 程知, 侯再红, 靖旭, 李菲, 陆茜茜, 于龙昆 2013 红外与激光工程 42 1562
Cheng Z, Hou Z H, Jing X, Li F, Lu Q Q, Yu L K 2013 Infrared Laser Eng. 42 1562
[18] Cheng Z, Tan F F, Jing X, He F, Qin L A, Hou Z H 2017 Chin. Opt. Lett. 15 020101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Balaley B, Peterson V L 1981 J. Appl. Meteor. 20 266
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 几种有代表性的
$ C_n^2 $ 廓线模式简介Table 1. Brief introduction of several typical
$ C_n^2 $ profile models.模式名称 模式种类 海拔高度/km 有效高度/km 平均方式 数据来源 代表性 夜晚 白天 日出 SLC 有 有 无 3.06 20 (相对高度) 几何平均 光闪烁 亚热带海洋
大气湍流AFGL AMOS 有 有 有 3.06 30 (海拔高度) 算术平均 探空 亚热带海洋
大气湍流H-V(5/7) 含有高空风速的$ C_n^2 $参数公式 实际海拔
高度/km24 (海拔高度) 算术平均 光闪烁、探空 中纬度大气湍流 CLEAR I 有 无 无 1.24 30 (海拔高度) 算术平均 探空 低对流层风速
下沙漠型湍流表 2 模式廓线计算的
$ {r_0} $ ,$ {\varepsilon _{{\text{FWHM}}}} $ ,$ {\theta _0} $ ,$ {\tau _0} $ ,$ \overline h $ 和$ \overline V $ Table 2. The
$ {r_0} $ ,$ {\varepsilon _{{\text{FWHM}}}} $ ,$ {\theta _0} $ ,$ {\tau _0} $ ,$ \overline h $ and$ \overline V $ calculated by$ C_n^2 $ models.$ {r_0} $/cm $ {\varepsilon _{{\text{FWHM}}}} $/μrad $ {\theta _0} $/μrad $ {\tau _0} $/ms $ \overline h $/m (AGL) $ \overline V $/(m·s–1) AFGL night 8.9 5.52 12.2 5.7 2260.7 4.9 AFGL day 7.3 6.71 4.4 3.5 5191.4 6.5 AFGL sunrise 15.3 3.21 5.3 5.3 9016.9 9.1 H-V (5/7) 5.0 9.84 6.9 1.9 2271.9 8.4 CLEAR I night 11.3 4.33 8.5 14.8 4179.1 2.4 修正CLEAR I 5.6 8.77 6.5 8.2 2684.2 2.1 表 3 模式中各大气层
$ {r_0} $ (i)对整层$ {r_0} $ 贡献占比Table 3. Integrated contribution of coherence length from each atmosphere layer.
AFGL night AFGL day AFGL sunrise H-V (5/7) CLEAR I night SL/% BL/% FA/% SL/% BL/% FA/% SL/% BL/% FA/% SL/% BL/% FA/% SL/% BL/% FA/% 11.0 81.3 7.7 40.3 36.7 22.9 3.3 43.8 52.9 30.4 58.6 10.9 50.4 12.1 37.4 表 4 模式中各大气层等晕角
$ {\theta _0} $ (i)对整层等晕角$ {\theta _0} $ 贡献占比Table 4. Integrated contribution of isoplanatic angle from each atmosphere layer.
AFGL night AFGL day AFGL sunrise H-V (5/7) CLEAR I night SL/% BL/% FA/% SL/% BL/% FA/% SL/% BL/% FA/% SL/% BL/% FA/% SL/% BL/% FA/% 0.0 6.5 93.5 0.0 0.4 99.6 0.0 0.7 99.3 0.0 3.3 96.6 0.4 1.7 97.4 表 5 修正的CLEAR I夜晚模式表达式
Table 5. Modified CLEAR I night model.
边界层内 $ \lg (C_n^2)= a + bh + c{h^2} $ 对流层内 $ \lg (C_n^2)= a + bh + c{h^2} $ 低平流层下 $\lg (C_n^2)= a + bh + c{h^2} + d\exp \big\{ { - 0.5 { {[{ {(h - e)} }/{f}]}^2} } \big\}$ CLEAR I night模式/km 修正CLEAR I night模式/km 1.23 < h ≤ 2.13 2.13 < h ≤ 10.34 10.34 < h ≤ 30 1.23 < h ≤ 2.13 2.13 < h ≤ 10.34 10.34 < h ≤ 30 a = –10.7025 a = –16.2897 a = –17.0577 a = –9.7025 a = –16.0897 a = –16.6577 b = –4.3507 b = 0.0335 b = –0.0449 b = –4.3507 b = 0.0435 b = –0.0449 c = 0.8141 c = –0.0134 c = –0.0005 c = 0.6541 c = –0.0134 c = –0.0005 d = 0.6181 d = 0.1981 e = 15.5617 e = 15.5617 f = 3.4666 f = 3.4666 表 6 湍流模式各大气层
$ C_T^2 $ ,$ C_n^2 $ ,$ \rho $ 与$(P/T^2)^2$ 的递减率Table 6. Drop-off rate of
$ C_T^2 $ ,$ C_n^2 $ ,$ \rho $ and$(P/T^2)^2$ in each atmosphere layer.$ {\text{DR}}(C_T^2) $ $ {\text{DR}}(C_n^2) $ $ {\text{DR}}(\rho ) $ ${\text{DR} }((P/T^2)^2)$ SL BL FA SL BL FA SL BL FA SL BL FA AFGL night 9.62 11.37 –0.61 10.30 12.05 0.85 0.43 0.44 0.70 0.68 0.69 1.46 AFGL day 67.15 14.84 –0.88 67.83 15.53 0.58 0.43 0.44 0.70 0.68 0.69 1.46 AFGL sunrise 5.01 5.28 –0.54 5.69 5.97 0.92 0.43 0.44 0.70 0.68 0.69 1.46 H-V (5/7) 41.98 10.77 0.76 42.62 11.42 2.16 0.42 0.43 0.69 0.64 0.65 1.40 CLEAR I 17.36 1.72 –0.69 17.93 2.26 0.76 0.39 0.39 0.69 0.57 0.54 1.45 修正 CLEAR I 22.39 3.22 –0.72 22.96 3.76 0.73 0.39 0.39 0.69 0.57 0.54 1.45 表 7 外场探空实验基本信息
Table 7. Basic information of field thermosonde.
地点 经纬度 海拔高度/m 平均最大探测
海拔高度/km早晨有效
探空数夜晚有效
探空数总有效
探空数高美古 26.41°N, 100.01°E 3237 32.45 1 7 8 拉萨 29.39°N, 91.08°E 3660 31.19 4 7 11 大柴旦 37.44°N, 95.20°E 3183 37.00 12 13 25 茂名 21.27°N, 111.18°E 11 35.56 7 4 11 荣成 36.46°N, 122.11°E 80 31.37 7 6 13 表 8 5个测量点算术平均拟合的
$ C_n^2 $ 廓线公式系数Table 8. Coefficient of
$ C_n^2 $ formula fitted by arithmetic average of five sites.a b c d f i g 高美古 $ 1 \times {10^{ - 40}} $ 33.31 0.393 $ 6.2 \times {10^{ - 17}} $ 6.45 $ 1.95 \times {10^{ - 15}} $ 0.0871 拉萨 $ 2.29 \times {10^{ - 22}} $ 9.10 1.227 $ 6.62 \times {10^{ - 17}} $ 10.468 $ 2.50 \times {10^{ - 16}} $ 0.0247 大柴旦 $ 4.45 \times {10^{ - 18}} $ 3.59 1.81 $ 3.88 \times {10^{ - 17}} $ 13.24 $ 7.14 \times {10^{ - 16}} $ 0.0459 茂名 $ 5.65 \times {10^{ - 20}} $ 5.46 2.31 $ 2.12 \times {10^{ - 16}} $ 5.02 $ 1.4 \times {10^{ - 15}} $ 0.305 荣成 $ 3.24 \times {10^{ - 24}} $ 13.20 0.767 $ 1.58 \times {10^{ - 16}} $ 7.37 $ 5.68 \times {10^{ - 15}} $ 0.0073 表 9 实测
$ C_n^2 $ 廓线的校正后拟合决定系数(Radj-Square)Table 9. Adjusted R square of fitting
$ C_n^2 $ profile.高美古 拉萨 大柴旦 茂名 荣成 $ C_n^2/{m^{ - 2/3}} $ 0.773 0.798 0.834 0.704 0.874 表 10 5实验点算术平均和几何平均廓线计算的
$ {r_0} $ ,$ {\varepsilon _{{\text{FWHM}}}} $ ,$ {\theta _0} $ ,$ {\tau _0} $ ,$ \overline h $ 和$ \overline V $ Table 10. The
$ {r_0} $ ,$ {\varepsilon _{{\text{FWHM}}}} $ ,$ {\theta _0} $ ,$ {\tau _0} $ ,$ \overline h $ and$ \overline V $ calculated by$ C_n^2 $ profiles from arithmetic average and geometric average in five sites.$ {r_0} $/cm $ {\varepsilon _{{\text{FWHM}}}} $/μrad $ {\theta _0} $/μrad $ {\tau _0} $/ms $ \overline h $/km (AGL) $ \overline V $/(m·s–1) 算术 几何 算术 几何 算术 几何 算术 几何 算术 几何 算术 几何 高美古 11.0 18.2 4.5 2.7 5.2 10.9 1.6 3.0 6.674 5.268 22.2 19.1 拉萨 6.4 9.8 7.7 5.1 1.7 2.8 1.7 2.7 11.533 11.063 11.9 11.5 大柴旦 6.6 14.9 7.5 3.3 2.0 4.8 0.9 2.2 10.172 9.659 22.2 21.8 茂名 3.1 7.6 15.7 6.5 0.8 2.0 0.6 1.5 12.993 11.775 17.3 15.9 荣成 5.3 9.1 9.2 5.4 1.8 3.5 0.7 1.5 9.454 8.179 23.0 19.7 表 11 5实验点各大气层
$ C_T^2 $ ,$ C_n^2 $ 以及$ \rho $ 与$(P/T^2)^2$ 廓线的递减率Table 11. Drop-off rate of
$ C_T^2 $ ,$ C_n^2 $ ,$ \rho $ and$(P/T^2)^2$ in each atmosphere layer of five sites.算术平均 $ {\text{DR}}(C_T^2) $ $ {\text{DR}}(C_n^2) $ $ {\text{DR}}(\rho ) $ ${\text{DR} }((P/T^2)^2)$ SL BL FA SL BL FA SL BL FA SL BL FA 高美古 5.46 3.01 –0.71 6.23 3.72 0.95 0.41 0.46 0.77 0.61 0.72 1.66 拉萨 9.95 –0.80 –0.61 10.65 –0.18 0.99 0.40 0.41 0.74 0.56 0.59 1.60 大柴旦 21.49 0.03 –0.67 22.87 0.61 0.97 0.41 0.40 0.76 0.64 0.55 1.64 茂名 18.07 2.94 –0.91 19.21 3.80 0.79 0.43 0.47 0.77 0.70 0.85 1.70 荣成 63.52 0.88 –0.48 66.59 1.71 0.99 0.44 0.47 0.71 0.71 0.82 1.47 表 12 模式廓线和实测廓线在低平流层的递减率
Table 12. Drop-off rate of model profile and measured profile in low stratosphere.
Model AFGL night AFGL day AFGL sunrise H-V(5/7) CLEAR I 修正CLEAR 高美古 拉萨 大柴旦 茂名 荣成 ASL/km 25—29 25—29 25—29 17—23 25—29 25—29 18—26 18—26 18—26 18—26 18—26 DR($ C_n^2 $) 0.85 0.58 0.92 2.16 0.76 0.73 0.95 0.99 0.97 0.79 0.99 DR($ C_T^2 $) –0.61 –0.88 –0.54 0.76 –0.69 –0.72 –0.71 –0.61 –0.67 –0.91 –0.48 DR($ \rho $) 0.70 0.70 0.70 0.69 0.69 0.69 0.77 0.74 0.76 0.77 0.71 ${\text{DR} } \big(\big(P/T^2\big)^2\big)$ 1.46 1.46 1.46 1.40 1.45 1.45 1.66 1.60 1.64 1.70 1.47 -
[1] 饶瑞中 2022 红外与激光工程 51 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Rao R Z 2022 Infrared Laser Eng. 51 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] [3] 吴晓庆, 曾宗泳, 马成胜, 翁宁泉, 肖黎明 1996 量子电子学报 13 385
Wu X Q, Zeng Z Y, Ma C S, Weng N Q, Xiao L M 1996 Chin. J. Quantum Electron. 13 385
[4] Coulman C, Vernin J, Coqueugniot Y, Caccia J 1988 Appl. Opt. 27 155
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Dewan E M, Good R E, Beland B, Brown J 1993 A Model for Cn2 Profiles Using Radiosonde Rata (Phillips Laboratory, Hansom Air Force Base) PL-TR-93-2043
[6] Trinquet H, Vernin J 2007 Environ. Fluid Mech. 7 397
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Tatarski V I 1961 Wave Propagation in a Turbulent Medium (New York: McGraw-Hill)
[8] Jumper G Y, Beland R R 2000 31st AIAA Plasmadynamics and Lasers Conference Denver, CO, USA, June 19–22, 2000, AIAA-2000-2355
[9] Parenti R R, Sasiela R J 1994 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 11 288
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Battles F P, Murphy E A, Noonan J P 1988 Phys. Scripta 37 151
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 吴晓庆, 钱仙妹, 黄宏华, 汪平, 崔朝龙, 青春 2014 天文学报 55 144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu X Q, Qian X M, Huang H H, Wang P, Cui C L, Qing C 2014 Acta Astron. Sin. 55 144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Good R, Beland R, Murphy E, Brown J, Dewan E 1988 SPIE 928 165
[13] 蔡俊, 李学彬, 詹国伟, 武鹏飞, 徐春燕, 青春, 吴晓庆 2018 67 014206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cai J, Li X B, Zhan G W, Wu P F, Xu C Y, Qing C, Wu X Q 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 014206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Han Y J, Wu X Q, Luo T, Qing C, Yang Q K, JinX M, Liu N N, Wu S, Su C D 2020 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 37 995
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Beland R R, Brown J H, Good R E, Murphy E A 1985 Optical Turbulence Characterization of AMOS Report AFGL-TR-88-xxxx
[16] Tyson R K 1996 Appl. Opt. 35 3640
[17] 程知, 侯再红, 靖旭, 李菲, 陆茜茜, 于龙昆 2013 红外与激光工程 42 1562
Cheng Z, Hou Z H, Jing X, Li F, Lu Q Q, Yu L K 2013 Infrared Laser Eng. 42 1562
[18] Cheng Z, Tan F F, Jing X, He F, Qin L A, Hou Z H 2017 Chin. Opt. Lett. 15 020101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Balaley B, Peterson V L 1981 J. Appl. Meteor. 20 266
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 8442
- PDF下载量: 151
- 被引次数: 0

































 下载:
下载: