-
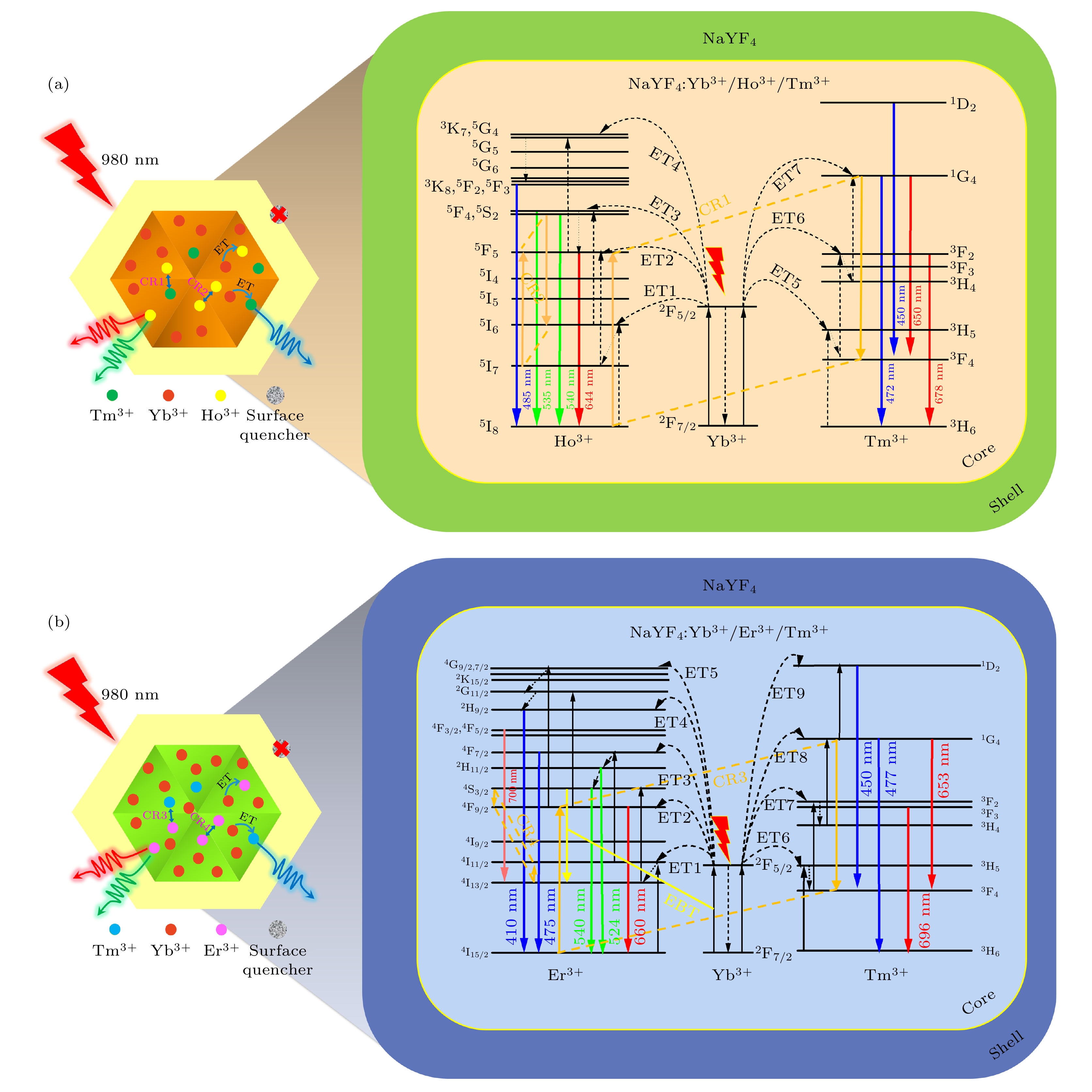
上转换白光材料在固态照明、液晶显示器和生物成像等领域展现出其他光源无法比拟的优势, 倍受研究者们广泛关注. 为此, 本文采用水热法合成了一系列掺杂不同离子浓度的NaYF4∶Yb3+/Re3+/Tm3+ (Re3+ = Ho3+, Er3+)微米晶体. 在980 nm近红外光激发下, 通过调控掺杂离子的浓度, 研究Ho3+/Tm3+及Er3+/Tm3+共掺杂单颗粒NaYF4微米晶体的白光发射特性. 研究表明: 在NaYF4∶Yb3+/Ho3+/Tm3+微米晶体中, 通过调控Yb3+离子的掺杂浓度易于实现其白光发射; 而在NaYF4∶Yb3+/Er3+/Tm3+微米晶体中, 通过调控Er3+离子的掺杂浓度易于实现其白光发射. 根据不同掺杂体系中微米晶体的发光特性, 揭示了白光发射调控的物理机理, 即主要是借助掺杂离子间交叉弛豫及能量反向传递过程而实现. 同时, 通过包覆NaYF4惰性壳进一步有效增强了微米棒上转换白光发射. 结果表明,通过离子掺杂技术及构建核壳结构不仅可实现微米棒的上转换白光发射, 且可为进一步增强微米棒发光特性提供重要的实验参考, 拓展微米晶体在显示、光电子技术及防伪等领域中的应用.White upconversion (UC) luminescent materials have shown incomparable advantages over other light sources in the fields of solid-state lighting, liquid crystal display, and bioimaging, and received extensive attention from researchers. In this work, a series of microcrystals doped with different ion concentrations is synthesized by hydrothermal method, such as NaYF4: Yb3+/Ho3+/Tm3+ and NaYF4: Yb3+/Ho3+/Tm3+, and their corresponding micron core-shell (CS) structures are constructed based on epitaxial growth technology. The structure and morphology of the prepared microcrystals are characterised by X-ray diffractometer (XRD) and scanning electron microscope (SEM), showing that the microcrystal has a pure hexagonal-phase crystal structure with a rod-like shape. Under the excitation of 980 nm near-infrared laser, the white UC luminescence characteristics of Ho3+/Tm3+ and Er3+/Tm3+ co-doped single-particle NaYF4 microcrystals are systematically studied by modulating the concentration of the doping ions. The study shows that in Ho3+/Tm3+ co-doped NaYF4 microcrystals, white UC luminescence can be easily achieved by modulating the concentration of Yb3+ ions, while in the Er3+/Tm3+ co-doped NaYF4 microcrystal, the white UC luminescence can be effectively achieved by modulating the concentration of Er3+ ions. According to the luminescence characteristics of the microncrystals in different doping systems, the physical mechanism of white light emission regulation is revealed, which is mainly due to the interaction between the doped ions, including cross relaxation (CR) process and energy back transfer (EBT) process. Meanwhile, an effective enhancement of the white UC luminescence on CS microrod is achieved by coating the NaYF4 inert shell. Therefore, ion doping technique and the construction of CS structure can not only realize the white UC luminescence of microrods, but also provide important experimental reference for further enhancing the luminescence characteristics of microrods, and expand the applications of microcrystals in the fields of display, optoelectronics and anti-counterfeiting.
-
Keywords:
- white upconversion luminescence /
- micron core-shell structure /
- ion doping /
- single particle /
- luminescence mechanism
[1] Shao L, Liu D, Lyu J, Zhou D, Ding N, Sun R, Xu W, Wang N, Xu S, Dong B, Song H 2021 Mater. Today Phys. 21 100495
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Hao S, Shang Y F, Hou Y D, Chen T, Lv W Q, Hu P G, Yang C H 2021 Sol. Energy 224 563
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Liu H L, Xu J H, Wang H, Liu Y J, Ruan Q F, Wu Y M, Liu X G, Yang J K W 2019 Adv. Mater. 31 1807900
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Gao L X, Shan X C, Xu X X, Liu Y T, Liu B L, Li S Q, Wen S H, Ma C S, Jin D Y, Wang F 2020 Nanoscale 12 18595
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Liang H Z, Lei W C, Liu S X, Zhang P, Luo Z W, Lu A X 2021 Opt. Mater. 119 111320
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Du P, Bharat L K, Yu J S 2015 J. Alloys Compd. 633 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Ray S K, Joshi B, Ramani S, Park S, Hur J 2022 J. Alloys Compd. 892 162101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bao S, Yu H Y, Gao G Y, Zhu H Y, Wang D S, Zhu P F, Wang G F 2021 Nano Res. 15 3594
[9] Li G G, Tian Y, Zhao Y, Lin J 2015 Chem. Soc. Rev. 44 8688
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Luitel H N, Chand R, Watari T 2016 Displays 42 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Vinodkumar P, Panda S, Jaiganesh G, Padhi R K, Madhusoodanan U, Panigrahi B S 2021 Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 253 119560
[12] Meng Z P, Zhang S F, Wu S L 2020 J. Lumin. 227 117566
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Long S W, Ma D C, Zhu Y Z, Yang M M, Lin S P, Wang B 2017 J. Lumin. 192 728
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Mehrdel B, Nikbakht A, Aziz A A, Jameel M S, Dheyab M A, Khaniabadi P M 2021 Nanotechnology 33 082001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Shi F, Wang J S, Zhai X S, Zhao D, Qin W P 2011 CrystEngComm 13 3782
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Lin H, Xu D K, Teng D D, Yang S H, Zhang Y L 2015 Luminescence 30 723
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Pathak T K, Kumar A, Erasmus L J B, Pandey A, Coetsee E, Swart H C, Kroon R E 2018 Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 207 23
[18] Hassairi M A, Hernandez A G, Dammak M, Zambon D, Chadeyron G, Mahiou R 2018 J. Lumin. 203 707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Xiao P, Ye S, Liao H Z, Shi Y L, Wang D P 2019 J. Solid State Chem. 275 63
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Ju D D, Song F, Han Y D, Zhang J, Song F F, Zhou A H, Huang W, Zadkov V 2019 J. Alloys Compd. 787 1120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ju D D, Gao X L, Zhang S C, Li Y, Cui W J, Yang Y H, Luo M Y, Liu S J 2021 CrystEngComm 23 3892
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 高伟, 孙泽煜, 郭立淳, 韩珊珊, 陈斌辉, 韩庆艳, 严学文, 王勇凯, 刘继红, 董军 2022 71 034207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao W, Sun Z Y, Guo L C, Han S S, Chen B H, Han Q Y, Yan X W, Wang Y K, Liu J H, Dong J 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 034207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 高伟, 王博扬, 孙泽煜, 高露, 张晨雪, 韩庆艳, 董军 2020 69 034207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao W, Wang B Y, Sun Z Y, Gao L, Zhang C X, Han Q Y, Dong J 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 034207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Gao W, Zhang C X, Han Q Y, Lu Y R, Yan X W, Wang Y K, Yang Y, Liu J H, Dong J 2022 J. Lumin. 241 118501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Bao H Q, Wang W, Li X, et al. 2021 Adv. Opt. Mater. 10 2101702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Tong L M, Lu E, Pichaandi J, Zhao G Y, Winnik M A 2016 J. Phys. Chem. C 120 6269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Tang J F, Li G N, Yang C, Gou J, Luo D H, He H 2015 CrystEngComm 17 9048
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Sun J Y, Xue B, Du H Y 2013 Mat. Sci. Eng. B 178 822
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Wu Y F S, Lai F Q, Liu B, Li Z B, Liang T X, Qiang Y C, Huang J H, Ye X Y, You W X 2020 J. Rare Earths 38 130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Zhang C M, Ma P A, Li C X, Li G G, Huang S S, Yang D M, Shang M M, Kang X J, Lin J 2011 J. Mater. Chem. 21 717
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Gao W, Sun Z Y, Han Q Y, Han S S, Cheng X T, Wang Y K, Yan X W, Dong J 2021 J. Alloys Compds. 857 157578
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Kuang Y, Xu J, Wang C, Li T Y, Gai S L, He F, Yang P P, Lin J 2019 Chem. Mater. 31 7898
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Yu Z C, Zhou H F, Zhou G J, et al. 2017 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19 31675
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Gao W, Kong X Q, Han Q Y, Chen Y, Zhang J, Zhao X, Yan X W, Liu J H, Shi J, Dong J 2018 J. Lumin. 202 381
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Wu Q X, Xu Z, Wageh S, Al-Ghamdia A, Zhao S L 2022 J. Alloys Compd. 891 162067
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Huo L L, Zhou J J, Wu R Z, Ren J F, Zhang S J, Zhang J J, Xu S Q 2016 Opt. Mater. Express 6 1056
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Pang T, Cao W H, Xing M M, Luo X X, Yang X F 2011 Opt. Mater. 33 485
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Gao D L, Zhang X Y, Chong B, Xiao G Q, Tian D P 2017 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19 4288
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Jeong S H, Kshetri Y K, Kim S H, Cho S H, Lee S W 2019 Prog. Nat. Sci. 29 549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Pollnau M, Gamelin D R, Lüthi S R, Güdel H U 2000 Phys. Rev. B 61 3337
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Gao W, Zheng H R, Han Q Y, He E J, Wang R B 2014 CrystEngComm 16 6697
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
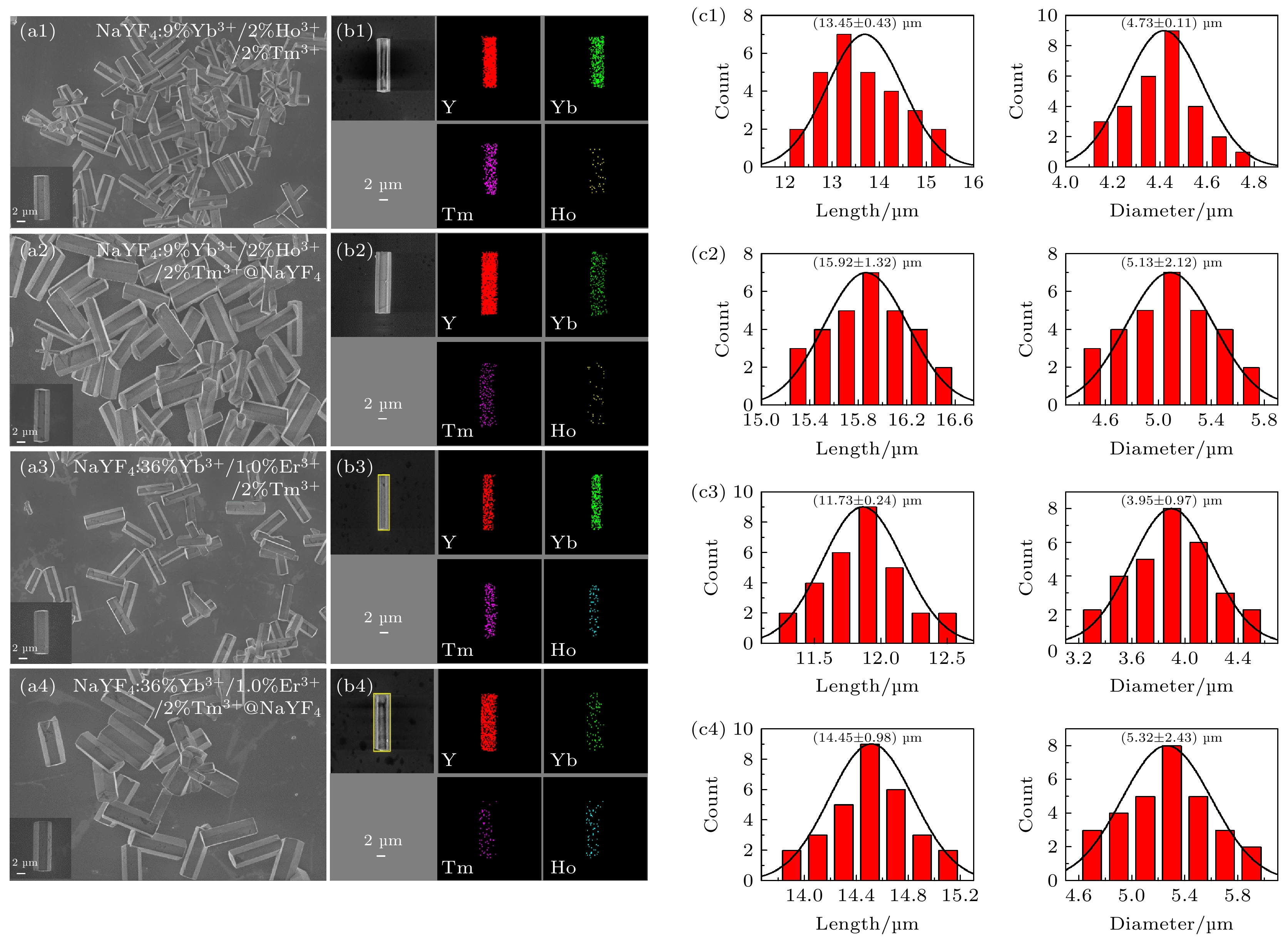
图 2 NaYF4: 9% Yb3+/2% Ho3+/2% Tm3+, NaYF4 : 36% Yb3+/1.0% Er3+/2% Tm3+微米晶体及其核壳微米棒的(a1)—(a4) SEM图像, (b1)—(b4)元素映射图, (c1)—(c4)尺寸分布图
Fig. 2. (a1)–(a4) SEM images, (b1)–(b4) element maps and (c1)–(c4) size distribution of NaYF4: 9% Yb3+/2% Ho3+/2% Tm3+ and NaYF4 : 36% Yb3+/1.0% Er3+/2% Tm3+ microcrystals and their core-shell microcrystals.
图 4 在980 nm激光激发下, 单颗粒NaYF4 : x% Yb3+/2% Ho3+/2% Tm3+ (x = 6, 7, 8, 9)微米棒的(a)上转换发射光谱, (b)红光、绿光和蓝光的发射峰面积, (c)红绿比、蓝绿比和(d) CIE色度坐标图
Fig. 4. (a) The UC emission spectra, (b) the peak area of the bule, green and red emission intensity, (c) R/G ratio, B/G ratio and (d) CIE chromaticity coordinates of single-particle NaYF4 : x% Yb3+/2% Ho3+/2% Tm3+ (x = 6, 7, 8, 9) microrods under the excitation of 980 nm NIR laser.
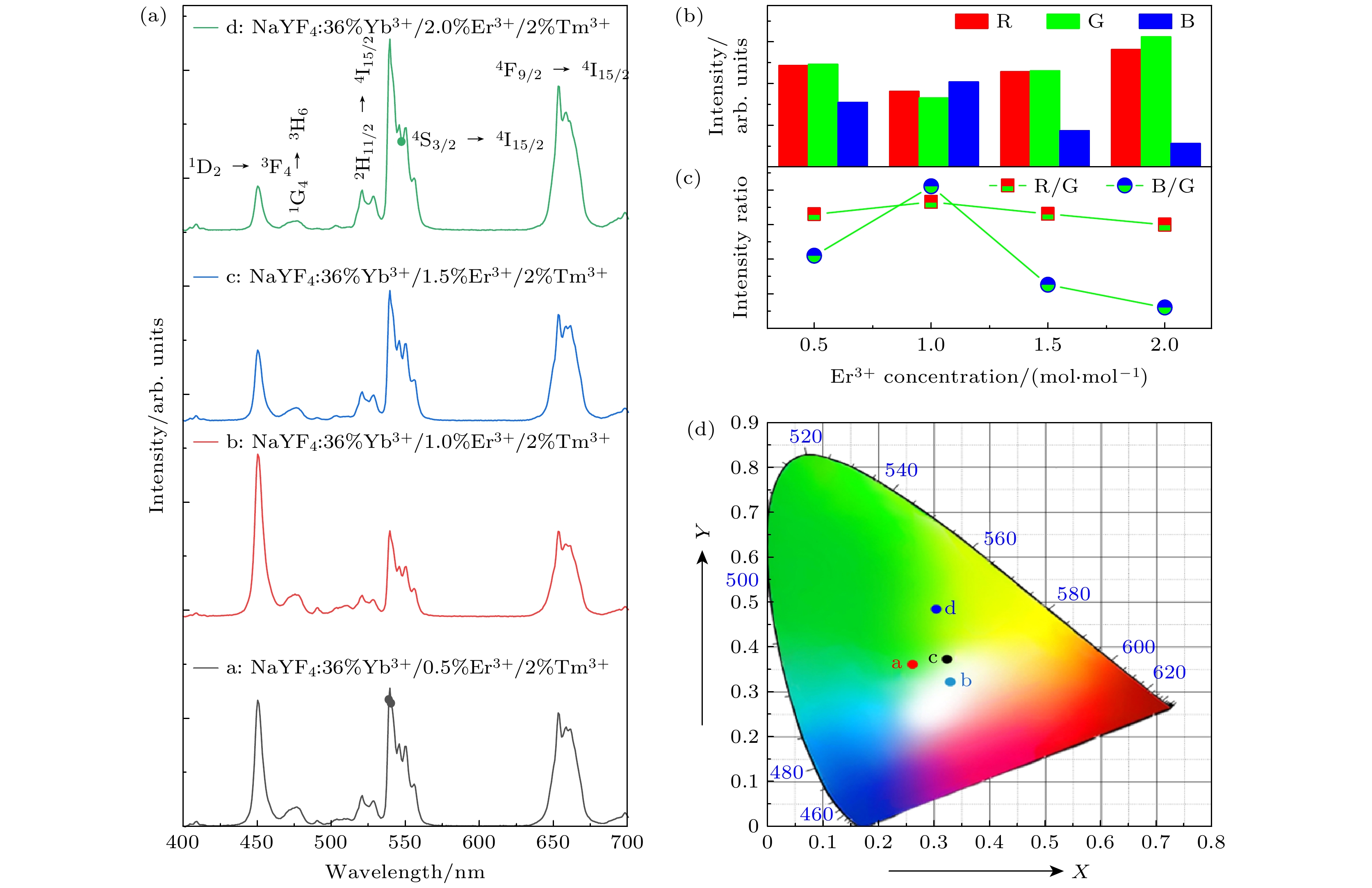
图 5 在980 nm激光激发下, 单颗粒NaYF4 : 36% Yb3+/x% Er3+/2% Tm3+ (x = 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0)微米棒的(a)上转换发射光谱; (b)红光、绿光和蓝光的发射峰面积; (c)红绿比、蓝绿比以及(d) CIE色度坐标图
Fig. 5. (a) The UC emission spectra, (b) the peak area of the bule, green and red emission intensity, (c) R/G ratio, B/G ratio and (d) CIE chromaticity coordinates of single-particle NaYF4 : 36% Yb3+/x% Er3+/2% Tm3+ (x = 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0) microrods under the excitation of 980 nm NIR laser.
图 6 在980 nm激光激发下, 单颗粒(a) NaYF4 : 9% Yb3+/2% Ho3+/2% Tm3+, (b) NaYF4 : 36% Yb3+/1.0% Er3+/2% Tm3+微米棒及其惰性核壳结构的发射光谱, (c), (e)红光、绿光和蓝光的发射峰面积和(d), (f)增强倍数
Fig. 6. (a)(b) The UC emission spectra, (c)(e) the peak area of the bule, green and red emission intensity and (d)(f) enhancement of single-particle NaYF4 : 9% Yb3+/2% Ho3+/2% Tm3+, NaYF4 : 36% Yb3+/1.0% Er3+/2% Tm3+ and its inert core-shell microrods under the excitation of 980 nm NIR laser.
图 8 在不同功率980 nm激光激发下, 单颗粒NaYF4 : 9% Yb3+/2% Ho3+/2% Tm3+及NaYF4 : 36% Yb3+/1.0% Er3+/2% Tm3+微棒的(a)(d)发射光谱, (b)(e) 红光、绿光和蓝光的发射峰面积(插图为对应的R/G比值、B/G比值), 及(c)(f) 泵浦功率依赖关系
Fig. 8. (a)(d) The UC emission spectra, (b)(e) the peak area of the bule, green and red emission intensity (insets show the corresponding R/G ratio, B/G ratio) and (c)(f) pump power dependences of single-particle NaYF4 : 9% Yb3+/2% Ho3+/2% Tm3+, NaYF4 : 36% Yb3+/1.0% Er3+/2% Tm3+.
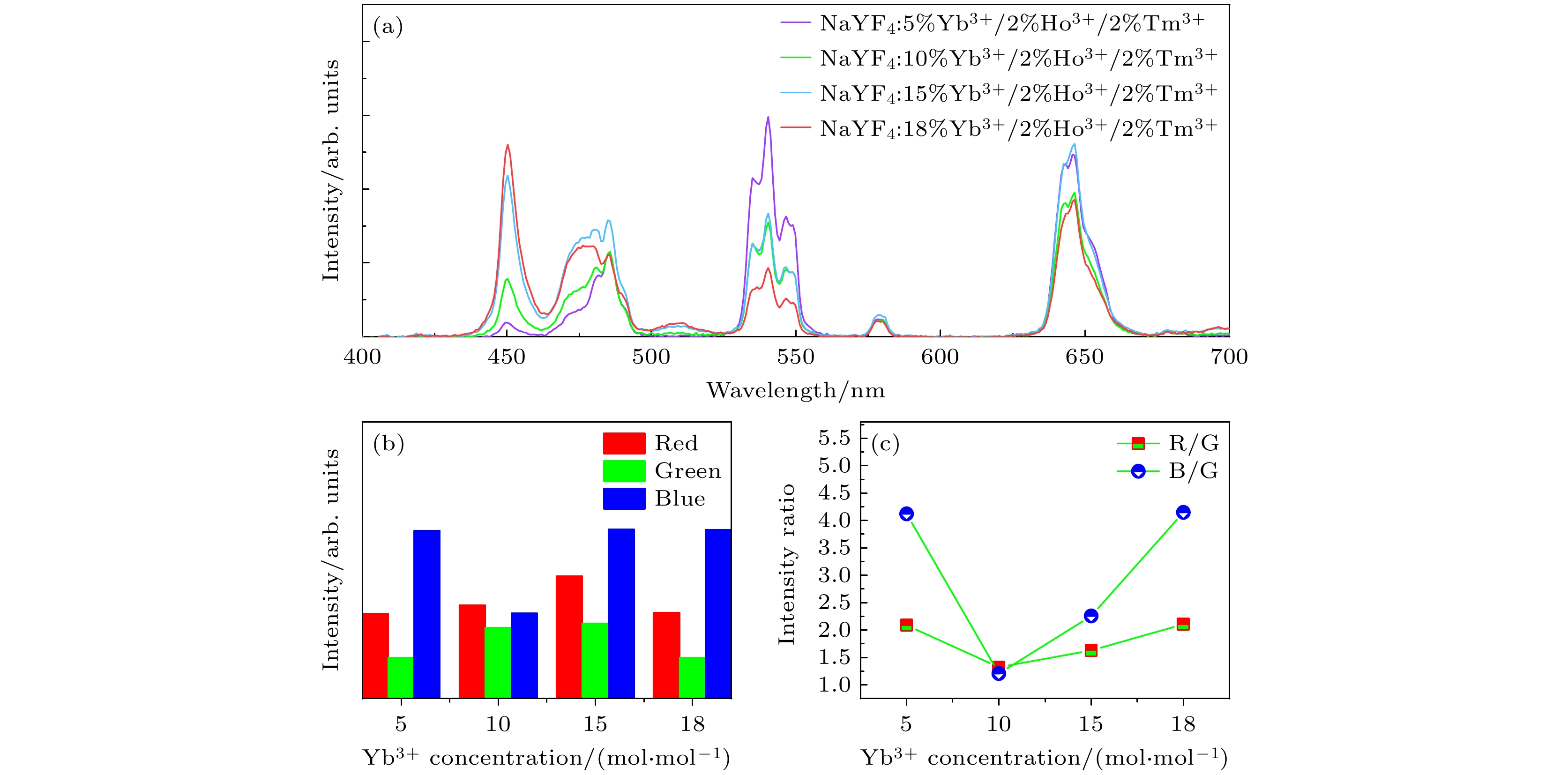
图 A1 980 nm激光激发下, 单颗粒NaYF4:x% Yb3+/2% Ho3+/2% Tm3+(x = 5, 10, 15, 18)微米棒的(a)上转换发射光谱, (b)红光、绿光、蓝光发射峰面积以及(c)红绿比、蓝绿比
Fig. A1. (a) The UC emission spectra, (b) the peak area of the bule, green and red emission intensity, (c) R/G ratio, B/G ratio of single-particle NaYF4: x% Yb3+/2% Ho3+/2% Tm3+ (x = 5, 10, 15, 18) microrods under the excitation of 980 nm NIR laser.
图 A2 980 nm激光激发下, 单颗粒NaYF4:x% Yb3+/2% Er3+/2% Tm3+(x = 10, 20, 30, 40, 45, 50)微米棒的(a)上转换发射光谱, (b)红光、绿光、蓝光发射峰面积以及(c)红绿比、蓝绿比
Fig. A2. (a) The UC emission spectra, (b) the peak area of the bule, green and red emission intensity and (c) R/G ratio, B/G ratio of single-particle NaYF4:x% Yb3+/2% Er3+/2% Tm3+(x = 10, 20, 30, 40, 45, 50) microrods under the excitation of 980 nm NIR laser.
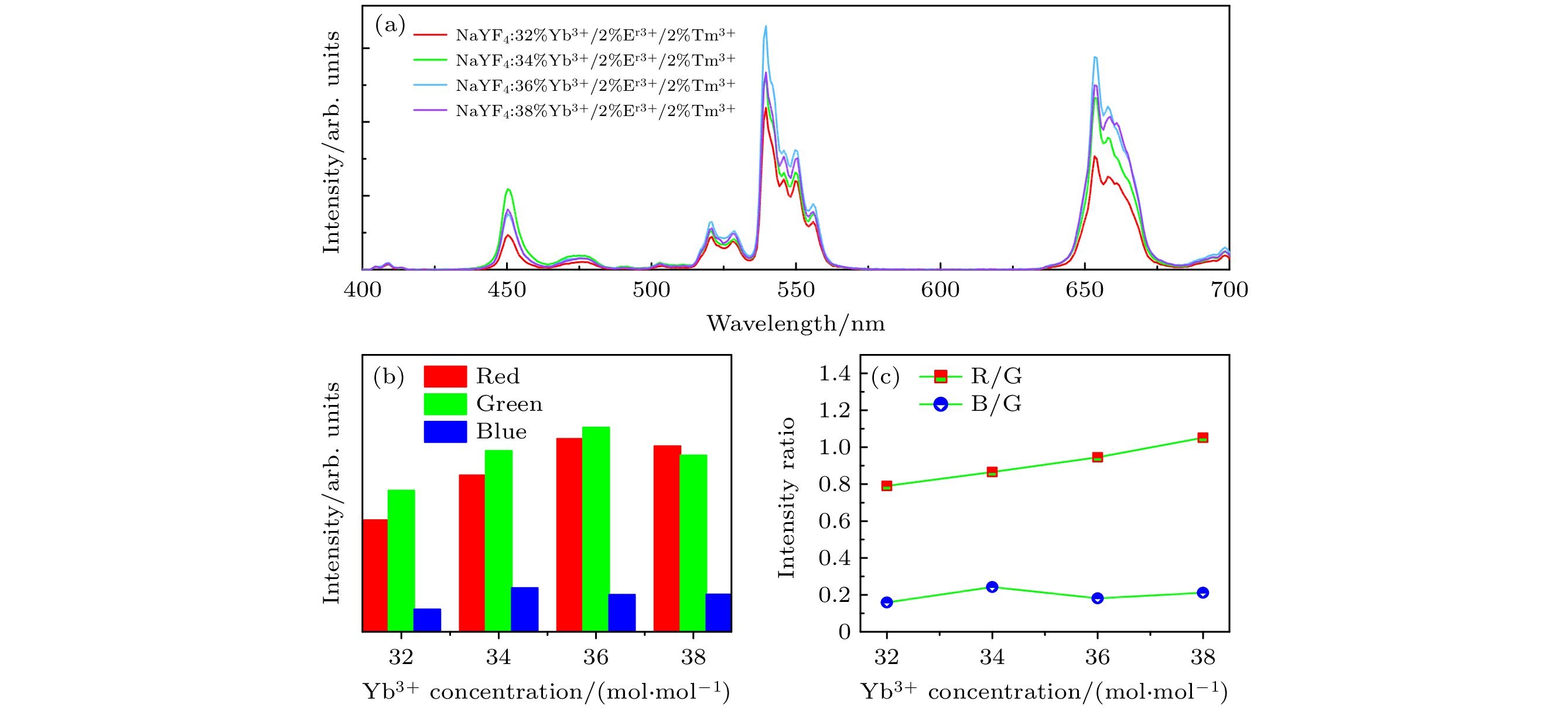
图 A3 980 nm激光激发下, 单颗粒NaYF4:x% Yb3+/2% Er3+/2% Tm3+ (x = 32, 34, 36, 38)微米棒的(a)上转换发射光谱, (b)红光、绿光、蓝光发射峰面积以及(c)红绿比、蓝绿比
Fig. A3. (a) The UC emission spectra, (b) the peak area of the bule, green and red emission intensity and (c) R/G ratio, B/G ratio of single-particle NaYF4:x% Yb3+/2% Er3+/2% Tm3+ (x = 32, 34, 36, 38) microrods under the excitation of 980 nm NIR laser.
表 1 水热法制备微米晶体所需药品的详细参数
Table 1. Detailed parameters of medicines for the preparation of the microcrystals by hydrothermal method.
样品 核体积/mL EDTA-2Na/g Re(NO3)3/mL NaF/mL NH4HF2/mL NaYF4:Yb3+/Ho3+/Tm3+ — 0.282 1.50 5.00 6.00 NaYF4:Yb3+/Er3+/Tm3+ — 0.282 1.50 5.00 6.00 NaYF4:Yb3+/Ho3+/Tm3+@NaYF4 5 0.282 1.50 5.00 6.00 NaYF4:Yb3+/Er3+/Tm3+@NaYF4 5 0.282 1.50 5.00 6.00 注: Re(NO3)3, NaF和NH4HF2溶液浓度均为0.5 mol/L. 表 2 单个NaYF4 : x% Yb3+/2% Ho3+/2% Tm3+(x = 6, 7, 8, 9)微米棒的CIE色度坐标
Table 2. CIE coordinates of single-particle NaYF4 : x% Yb3+/2% Ho3+/2% Tm3+ (x = 6, 7, 8, 9) microrods.
Samples CIE chromaticity coordinate x y NaYF4 : 6% Yb3+/2% Ho3+/2% Tm3+ 0.3123 0.3824 NaYF4 : 7% Yb3+/2% Ho3+/2% Tm3+ 0.3215 0.3456 NaYF4 : 8% Yb3+/2% Ho3+/2% Tm3+ 0.3383 0.3932 NaYF4 : 9% Yb3+/2% Ho3+/2% Tm3+ 0.3284 0.3401 表 3 单个NaYF4 : 36% Yb3+/x% Er3+/2% Tm3+ (x = 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0)微米棒的CIE色度坐标
Table 3. CIE coordinates of single-particle NaYF4 : 36% Yb3+/x% Er3+/2% Tm3+ (x = 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0) microrods.
Samples CIE chromaticity coordinate x y NaYF4 : 36% Yb3+/0.5% Er3+/2% Tm3+ 0.2604 0.3661 NaYF4 : 36% Yb3+/1.0% Er3+/2% Tm3+ 0.3281 0.3204 NaYF4 : 36% Yb3+/1.5% Er3+/2% Tm3+ 0.3216 0.3748 NaYF4 : 36% Yb3+/2.0% Er3+/2% Tm3+ 0.3018 0.4854 -
[1] Shao L, Liu D, Lyu J, Zhou D, Ding N, Sun R, Xu W, Wang N, Xu S, Dong B, Song H 2021 Mater. Today Phys. 21 100495
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Hao S, Shang Y F, Hou Y D, Chen T, Lv W Q, Hu P G, Yang C H 2021 Sol. Energy 224 563
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Liu H L, Xu J H, Wang H, Liu Y J, Ruan Q F, Wu Y M, Liu X G, Yang J K W 2019 Adv. Mater. 31 1807900
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Gao L X, Shan X C, Xu X X, Liu Y T, Liu B L, Li S Q, Wen S H, Ma C S, Jin D Y, Wang F 2020 Nanoscale 12 18595
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Liang H Z, Lei W C, Liu S X, Zhang P, Luo Z W, Lu A X 2021 Opt. Mater. 119 111320
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Du P, Bharat L K, Yu J S 2015 J. Alloys Compd. 633 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Ray S K, Joshi B, Ramani S, Park S, Hur J 2022 J. Alloys Compd. 892 162101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bao S, Yu H Y, Gao G Y, Zhu H Y, Wang D S, Zhu P F, Wang G F 2021 Nano Res. 15 3594
[9] Li G G, Tian Y, Zhao Y, Lin J 2015 Chem. Soc. Rev. 44 8688
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Luitel H N, Chand R, Watari T 2016 Displays 42 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Vinodkumar P, Panda S, Jaiganesh G, Padhi R K, Madhusoodanan U, Panigrahi B S 2021 Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 253 119560
[12] Meng Z P, Zhang S F, Wu S L 2020 J. Lumin. 227 117566
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Long S W, Ma D C, Zhu Y Z, Yang M M, Lin S P, Wang B 2017 J. Lumin. 192 728
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Mehrdel B, Nikbakht A, Aziz A A, Jameel M S, Dheyab M A, Khaniabadi P M 2021 Nanotechnology 33 082001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Shi F, Wang J S, Zhai X S, Zhao D, Qin W P 2011 CrystEngComm 13 3782
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Lin H, Xu D K, Teng D D, Yang S H, Zhang Y L 2015 Luminescence 30 723
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Pathak T K, Kumar A, Erasmus L J B, Pandey A, Coetsee E, Swart H C, Kroon R E 2018 Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 207 23
[18] Hassairi M A, Hernandez A G, Dammak M, Zambon D, Chadeyron G, Mahiou R 2018 J. Lumin. 203 707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Xiao P, Ye S, Liao H Z, Shi Y L, Wang D P 2019 J. Solid State Chem. 275 63
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Ju D D, Song F, Han Y D, Zhang J, Song F F, Zhou A H, Huang W, Zadkov V 2019 J. Alloys Compd. 787 1120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ju D D, Gao X L, Zhang S C, Li Y, Cui W J, Yang Y H, Luo M Y, Liu S J 2021 CrystEngComm 23 3892
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 高伟, 孙泽煜, 郭立淳, 韩珊珊, 陈斌辉, 韩庆艳, 严学文, 王勇凯, 刘继红, 董军 2022 71 034207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao W, Sun Z Y, Guo L C, Han S S, Chen B H, Han Q Y, Yan X W, Wang Y K, Liu J H, Dong J 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 034207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 高伟, 王博扬, 孙泽煜, 高露, 张晨雪, 韩庆艳, 董军 2020 69 034207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao W, Wang B Y, Sun Z Y, Gao L, Zhang C X, Han Q Y, Dong J 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 034207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Gao W, Zhang C X, Han Q Y, Lu Y R, Yan X W, Wang Y K, Yang Y, Liu J H, Dong J 2022 J. Lumin. 241 118501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Bao H Q, Wang W, Li X, et al. 2021 Adv. Opt. Mater. 10 2101702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Tong L M, Lu E, Pichaandi J, Zhao G Y, Winnik M A 2016 J. Phys. Chem. C 120 6269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Tang J F, Li G N, Yang C, Gou J, Luo D H, He H 2015 CrystEngComm 17 9048
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Sun J Y, Xue B, Du H Y 2013 Mat. Sci. Eng. B 178 822
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Wu Y F S, Lai F Q, Liu B, Li Z B, Liang T X, Qiang Y C, Huang J H, Ye X Y, You W X 2020 J. Rare Earths 38 130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Zhang C M, Ma P A, Li C X, Li G G, Huang S S, Yang D M, Shang M M, Kang X J, Lin J 2011 J. Mater. Chem. 21 717
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Gao W, Sun Z Y, Han Q Y, Han S S, Cheng X T, Wang Y K, Yan X W, Dong J 2021 J. Alloys Compds. 857 157578
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Kuang Y, Xu J, Wang C, Li T Y, Gai S L, He F, Yang P P, Lin J 2019 Chem. Mater. 31 7898
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Yu Z C, Zhou H F, Zhou G J, et al. 2017 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19 31675
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Gao W, Kong X Q, Han Q Y, Chen Y, Zhang J, Zhao X, Yan X W, Liu J H, Shi J, Dong J 2018 J. Lumin. 202 381
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Wu Q X, Xu Z, Wageh S, Al-Ghamdia A, Zhao S L 2022 J. Alloys Compd. 891 162067
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Huo L L, Zhou J J, Wu R Z, Ren J F, Zhang S J, Zhang J J, Xu S Q 2016 Opt. Mater. Express 6 1056
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Pang T, Cao W H, Xing M M, Luo X X, Yang X F 2011 Opt. Mater. 33 485
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Gao D L, Zhang X Y, Chong B, Xiao G Q, Tian D P 2017 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19 4288
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Jeong S H, Kshetri Y K, Kim S H, Cho S H, Lee S W 2019 Prog. Nat. Sci. 29 549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Pollnau M, Gamelin D R, Lüthi S R, Güdel H U 2000 Phys. Rev. B 61 3337
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Gao W, Zheng H R, Han Q Y, He E J, Wang R B 2014 CrystEngComm 16 6697
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 5836
- PDF下载量: 84
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: