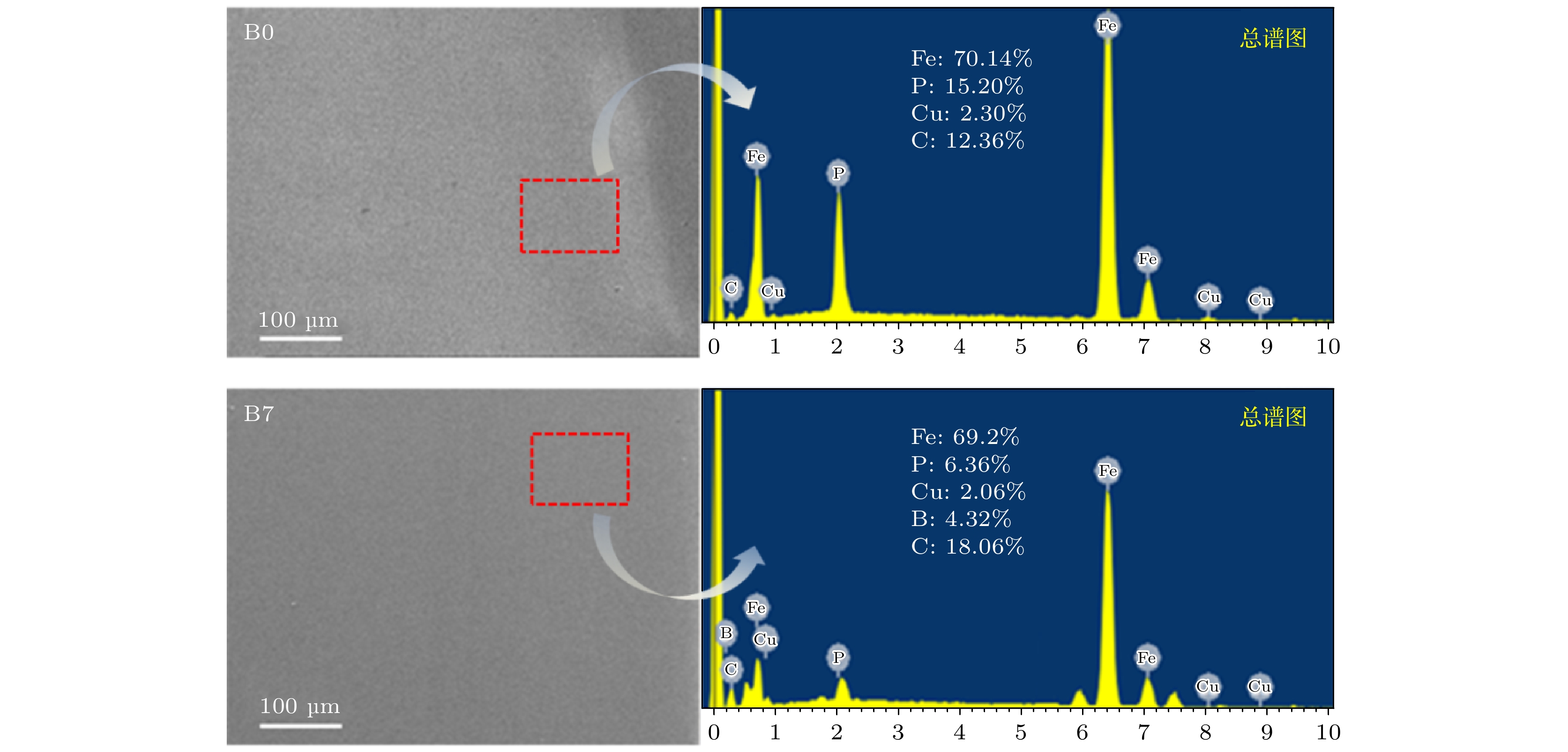
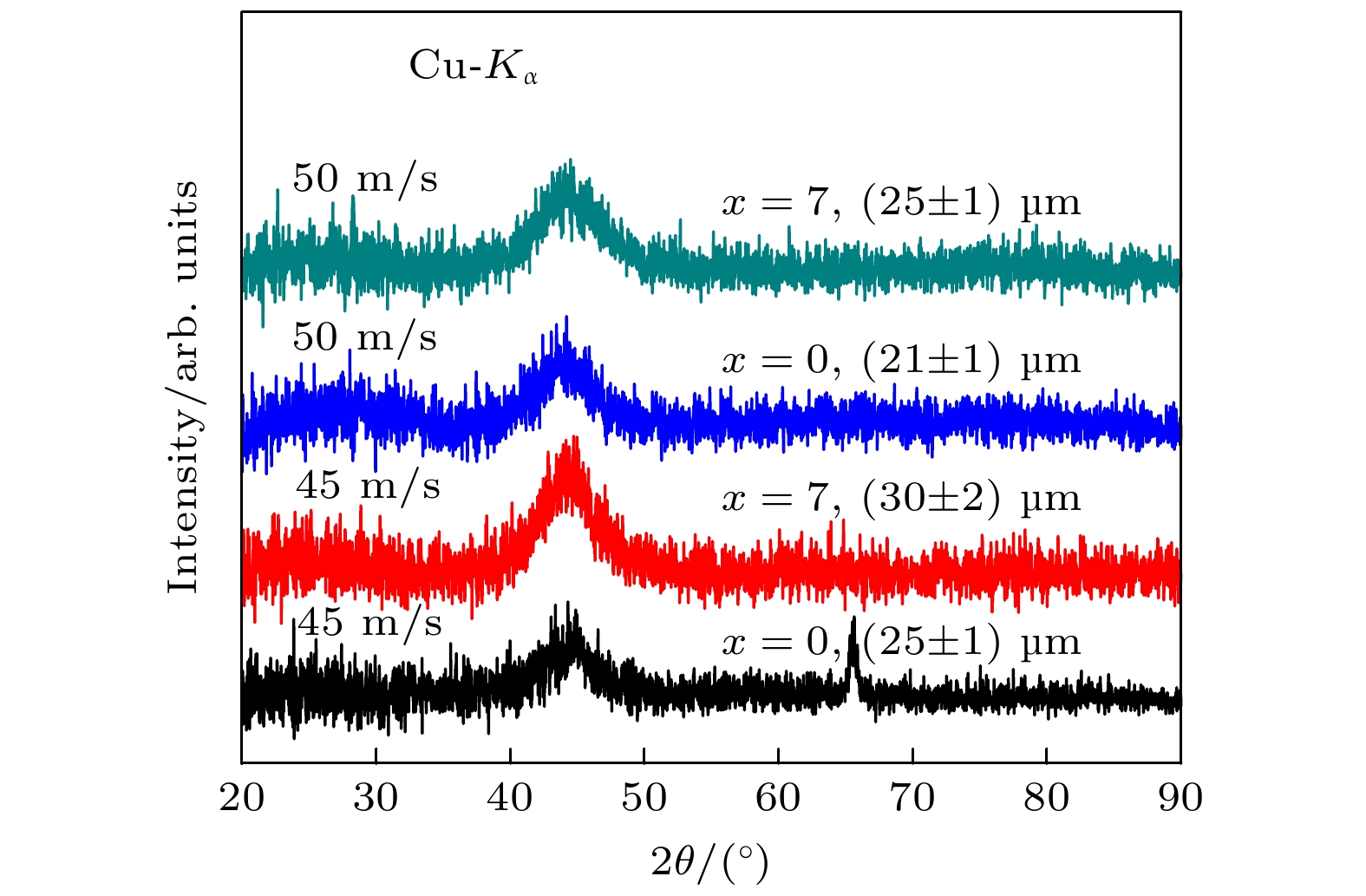
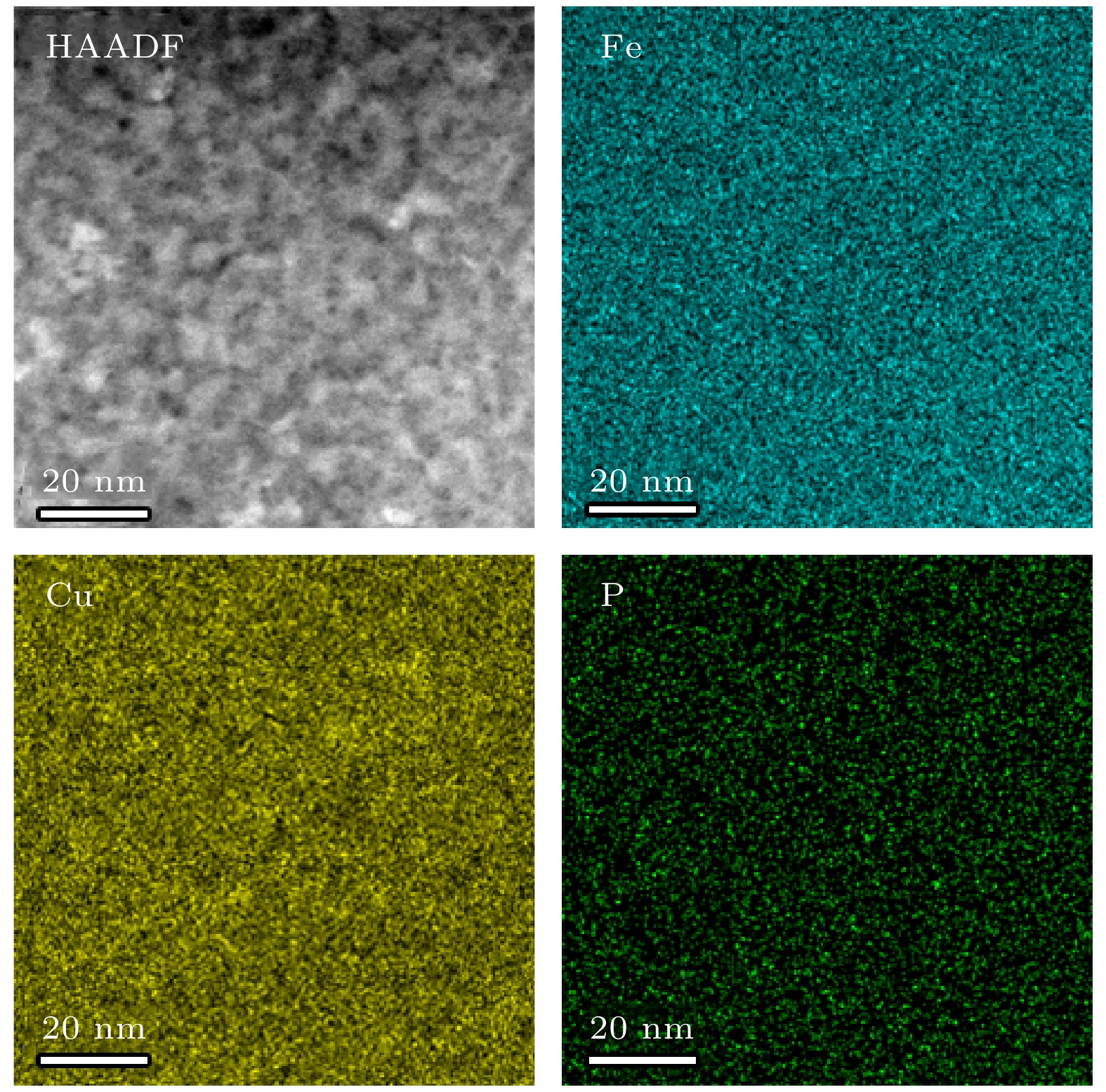
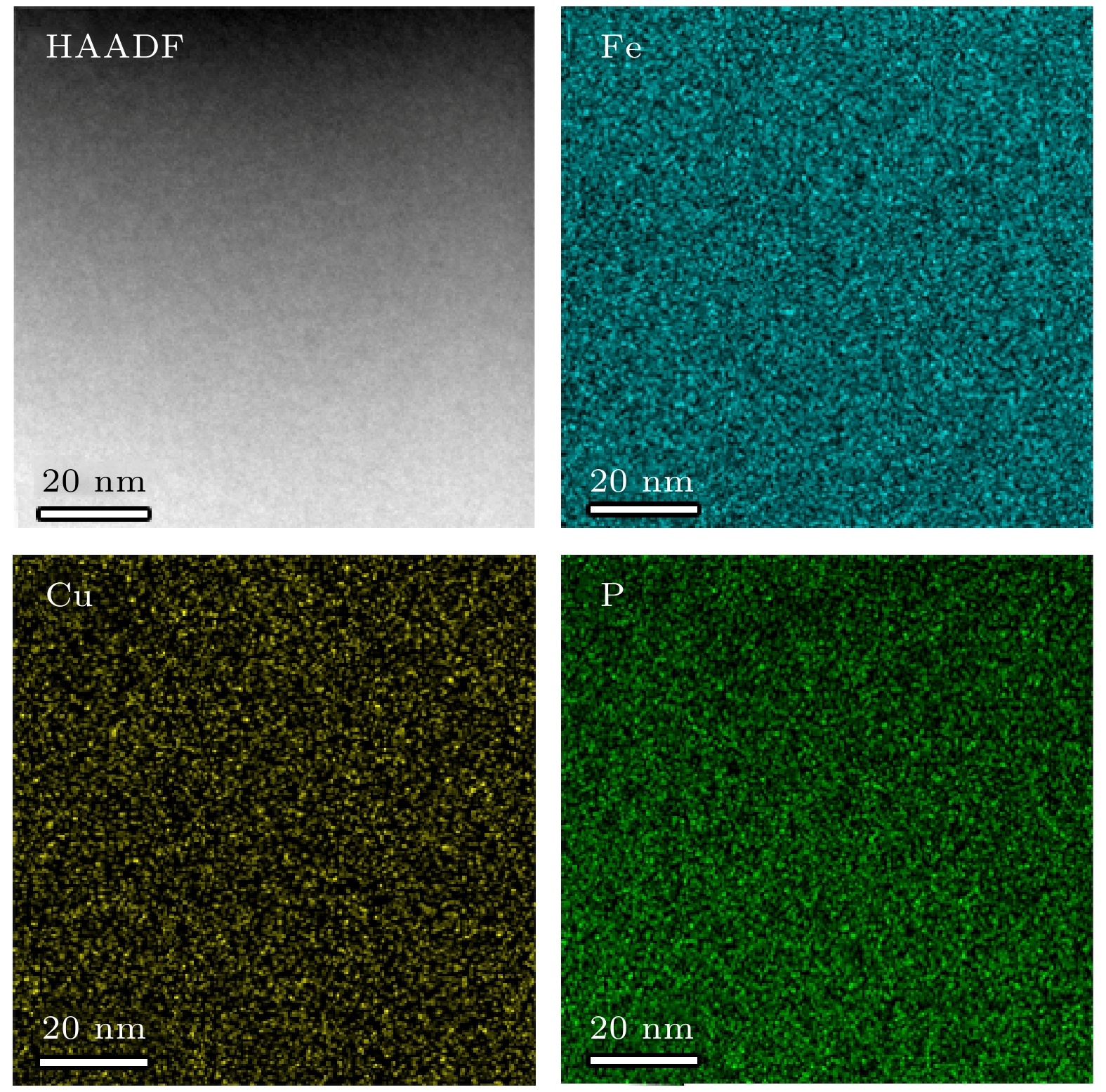
-
铁基非晶合金因其低矫顽力、高磁导率和低铁耗等被广泛应用于变压器、电抗器等电力电子领域, 然而, 较低的饱和磁感值限制了其进一步应用. 铁含量增大可有效提高合金的饱和磁感, 但相应非磁性元素含量的降低又将引起合金非晶形成能力的下降, 导致后续纳米晶带材的软磁性能及弯折韧性的恶化. 针对上述问题, 文章基于金属-类金属间的杂化作用, 通过原子百分比为7%的B替代P, 利用单辊甩带法制备了厚度约为25 μm的FePBCCu非晶薄带, 并研究了B添加对薄带非晶形成能力、磁性能和力学性能的影响. 热动力学行为揭示出小原子B添加能够降低合金结构的异质性, 有效提高非晶基体的热稳定性; 熔化与凝固曲线表明B元素能够促使合金系接近共晶成分且具有较大的过冷度. 因此合金的非晶形成能力显著提高, 其临界厚度从基体的约21 μm 提高到约30 μm. B添加促使合金系磁性原子有效磁矩的增大, 导致非晶薄带的饱和磁感值增大. 纳米压痕实验结果表明, B添加合金的约化模量值较大且在一个较小范围内波动, 这与合金的结构均匀性密切相关.Fe-based amorphous alloys are widely used in power electronics fields such as transformers and reactors due to their low coercivity, high permeability and low loss. However, the relatively low saturation magnetization (Bs) limits their further applications. Generally speaking, the adjustable magnetic Fe content as an effective strategy can ameliorate the magnetic properties, and the higher the Fe content, the higher the obtained Bs is, but the decrease of the corresponding non-magnetic element content will result in the drop of the ability of alloys to form amorphous phase, leading to the deterioration of the magnetic softness and bending ductility of nanocrystalline alloys. To address this critical issue, in this work, based on the metal-metalloid hybridization, the FePBCCu amorphous ribbons, each with a thickness of ~25 μm, are prepared by the single-roller melt spinning method via 7% (atomic percent) B substitution for P, and the effects of B element addition on the ability to form amorphous phase, magnetic properties and mechanical properties of ribbons are investigated. Thermodynamic behavior shows that the addition of small quantities of B element can reduce the structural heterogeneity of alloy and the crystallization driving force as well, thus effectively improving the thermal stability of the amorphous matrix. The melting and solidification curves show that the addition of B can promote alloy to approach to the eutectic composition, and there is a large degree of undercooling. As a result, the critical thickness of ribbons increases from ~21 μm for B-free alloy to ~30 μm for B-added alloy due to the micro-alloying effect. The addition of B increases the effective magnetic moment of magnetic atoms in alloy, resulting in the increase of the saturation magnetization. Furthermore, the results of nanoindentation tests show that the modulus value of the B-added alloy decreases greatlyr and fluctuates in a smaller range than that of the B-free alloy, which is closely associated with the structural uniformity of the alloy.
-
Keywords:
- Fe-based amorphous ribbon /
- amorphous forming ability /
- saturation magnetization /
- reduced modulus
[1] Inoue A, Shen B L, Chang C T 2004 Acta Mater. 52 4093
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Xu D D, Zhou B L, Wang Q Q, Zhou J, Yang W M, Yuan C C, Xue L, Fan X D, Ma L Q, Shen B L 2018 Corros. Sci. 138 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Li F C, Liu T, Zhang J Y, Shuang S, Wang Q, Wang A D, Wang J G, Yang Y 2019 Mater. Today Adv. 4 100027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] McHenry M E, Willard M A, Laughlin D E 1999 Prog. Mater. Sci. 44 291
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wang A D, Zhao C L, He A N, Men H, Chang C T, Wang X M 2016 J. Alloy. Compd. 656 729
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 姚可夫, 施凌翔, 陈双琴, 邵洋, 陈娜, 贾蓟丽 2018 67 016101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yao K F, Shi L X, Chen S Q, Shao Y, Chen N, Jia J L 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 016101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] McHenry M E, Laughlin D E 2014 hysical Metallurgy (5th Ed.) (Elsevier) p1881
[8] Hou L, Fan X D, Wang Q Q, Yang W M, Shen B L 2019 J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 35 1655
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Meng S Y, Ling H B, Li Q, Zhang J 2014 Scr. Mater. 81 24
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wang C J, He A N, Wang A D, Pang J, Ling X, Li Q, Chang C, Qiu K, Wang X 2017 Intermetallics 84 142
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Mizoguchi T 1976 AIP Conf. Proc. 34 286
[12] Xu J, Yang Y Z, Li W, Xie Z, Chen X 2017 Mater. Res. Bull. 97 452
[13] Shi L X, Qin X L, Yao K F 2020 Prog. Nat. Sci-Mater. 30 208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zuo M Q, Meng S Y, Li Q, Li H X, Chang C T, Sun Y F 2017 Intermetallics 83 83
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Jin Y L, Fan X D, He M, Liu X C, Shen B L 2012 Sci. China Technol. Sci. 55 3419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wang Q Q, Chen M X, Lin P H, Cui Z Q, Chu C L, Shen B L 2018 J. Mater. Chem. A 6 10686
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang Q Q, Yun L, Chen M X, Xu D D, Cui Z Q, Zeng Q S, Lin P H, Chu C L, Shen B L 2019 ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2 214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Jafari S, Beitollahi A, Eftekhari Yekta B, Ohkubo T, Budinsky V, Marsilius M, Herzer G, Hono K 2016 J. Alloy. Compd. 674 136
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Fan X D, Zhang T, Jiang M F, Yang W M, Shen B L 2019 J. Non-Cryst. Solid. 503 36
[20] Hou L, Yang W M, Luo Q, Fan X D, Liu H S, Shen B L 2020 J. Non-Cryst. Solid. 530 119800
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Li Y L, Dou Z X, Chen X M, Lv K, Li F S, Hui X D 2020 Mater. Sci. Eng. B 262 114740
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Hono K, Ping D H, Ohnuma M, Onodera H 1999 Acta Mater. 47 997
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Hu F, Yuan C C, Luo Q, Yang W M, Shen B L 2019 J. Alloy. Compd. 807 151675
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Ohnuma M, Ping D H, Abe T, Onodera H, Hono K, Yoshizawa Y 2003 J. Appl. Phys. 93 9186
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Yang W M, Li J W, Liu H S, Dun C C, Zhang H L, Huo J T, Xue L, Zhao Y C, Shen B L, Dou L M, Inoue A 2014 Intermetallics 49 52
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Lan S, Ren Y, Wei X Y, Wang B, Gilbert E P, Shibayama T, Watanabe S, Ohnuma M, Wang X L 2017 Nat. Commun. 8 14679
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Takeuchi A, Inoue A 2005 Mater. Trans. 46 2817
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 耿遥祥, 王英敏 2020 金属学报 56 1558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Geng Y X, Wang Y M 2020 Acta Metall. Sin. 56 1558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Fan X D, Jiang M F, Zhang T, Hou L, Wang C X, Shen B L 2020 J. Non-Cryst. Solid. 533 119941
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Hou L, Li M R, Jiang C, Fan X D, Luo Q, Chen S S, Song P D, Li W H 2021 J. Alloy. Compd. 853 157071
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 严密, 彭晓领 2011 磁学基础与磁性材料 (杭州: 浙江大学出版社)
Yan M, Peng X L 2011 Fundamentals of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials (Hangzhou: Zhejiang University Press) (in Chinese)
[32] Zhang J H, Chang C T, Wang A D Shen B L 2012 J. Non-Crystal. Solids 358 1443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Wang F, Inoue A, Han Y, Kong F L, Zhu S L, Shalaan E, Al-Marzouki F, Obaid A 2017 J. Alloy. Compd. 723 376
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Sun B R, Xin S W, Shen T D 2018 J. Mag. Magn. Mater. 466 130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Sarac B, Ivanov Y P, Chuvilin A, Schoberl T, Stoica M, Zhang Z L, Eckert J 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 1333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Liu Y H, Wang G, Wang R J, Zhao D Q, Pan, M X, Wang W H 2007 Science 315 1385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
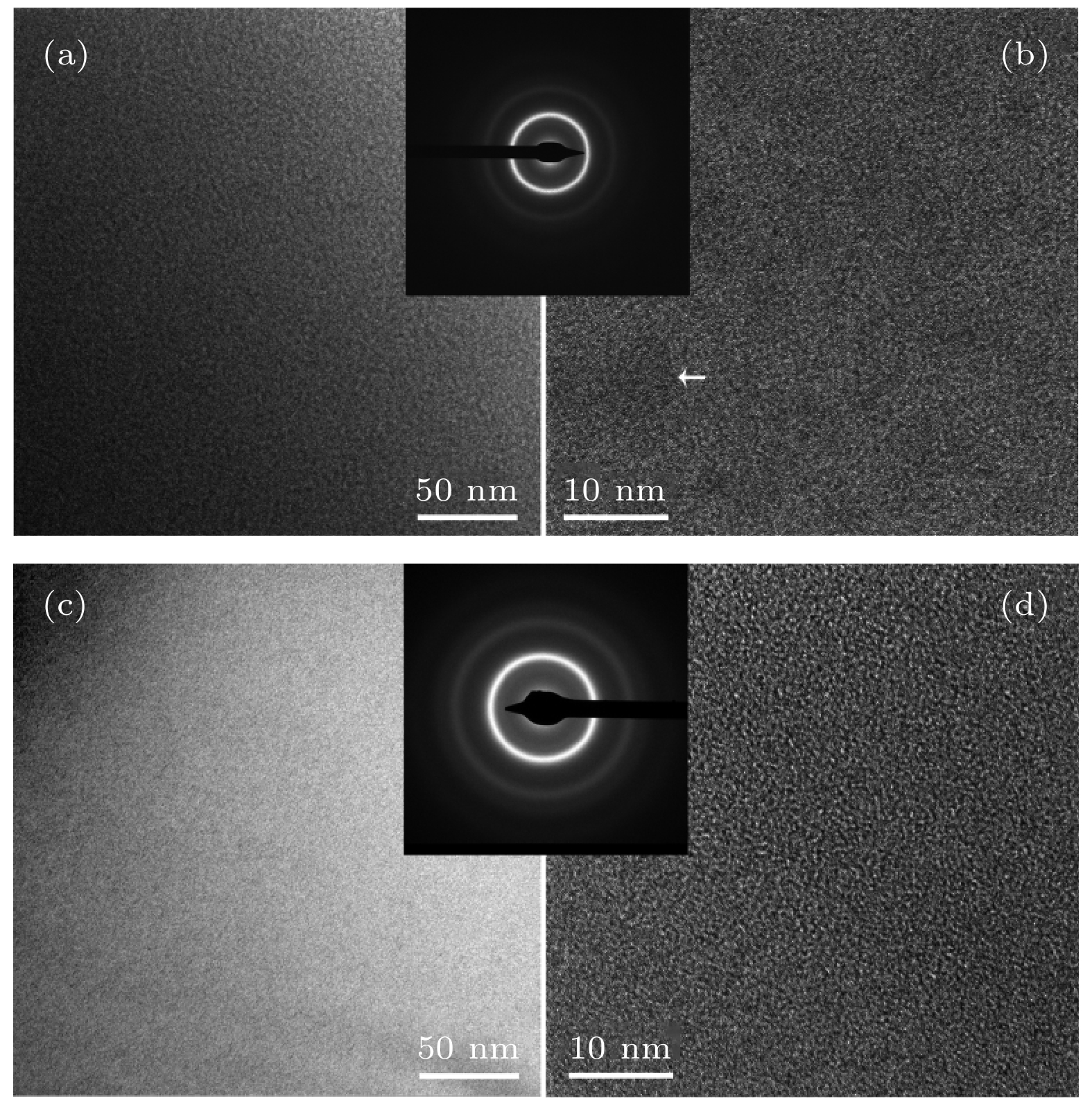
图 4 淬态Fe78.8P14–xBxC6Cu1.2非晶薄带的明场TEM图像 (a) x = 0; (b) (a)的局部放大图; (c) x = 7; (d) (c)的局部放大图. 插图分别为对应合金的SAED花样
Fig. 4. Bright-field TEM images of as-quenched Fe78.8P14–xBxC6Cu1.2 amorphous ribbons: (a) x = 0, (b) locally enlarged image in (a); (c) x = 7; (d) locally enlarged image in (c). The insets correspond to the SAED patterns, respectively.
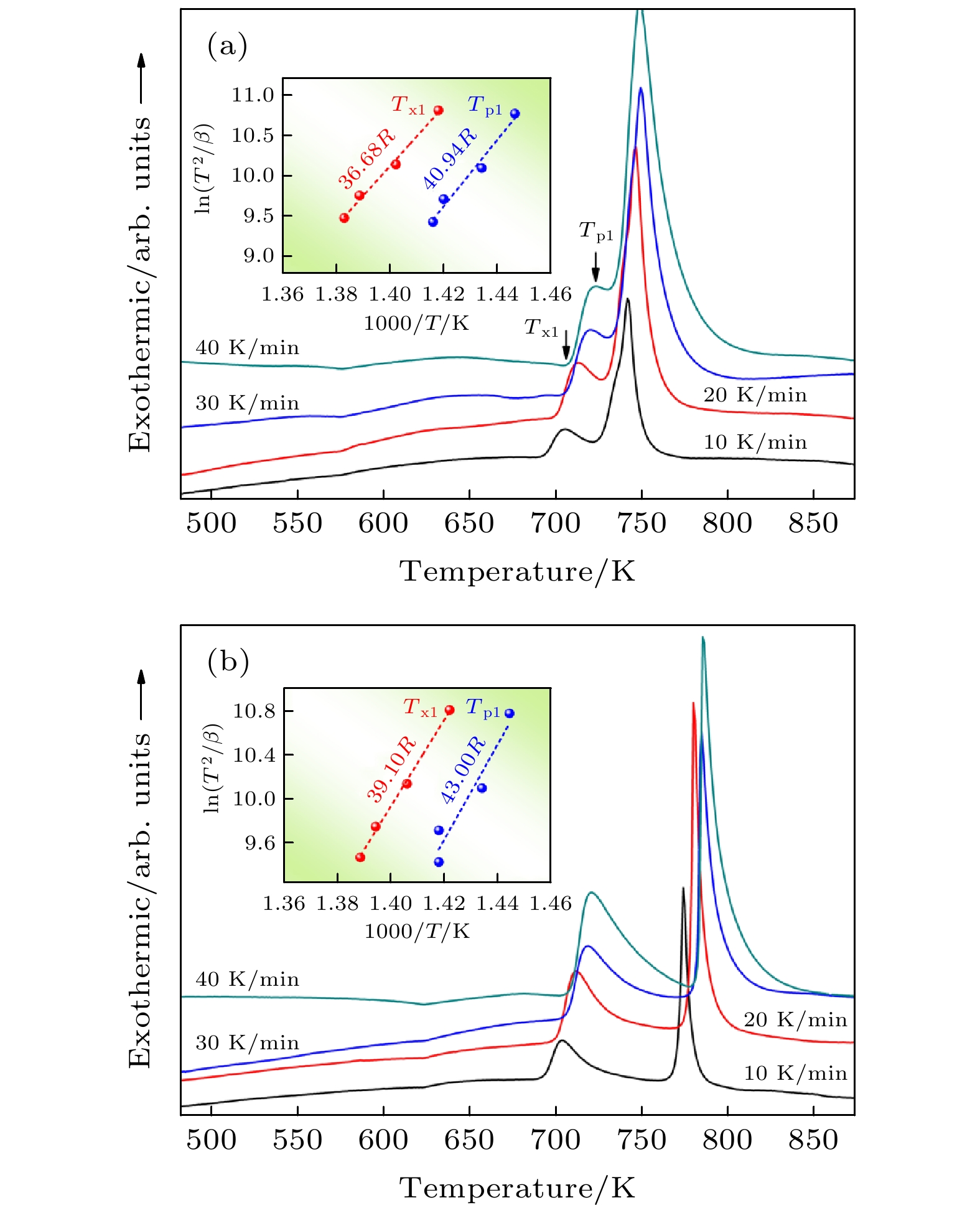
图 9 不同升温速率下的淬态Fe78.8P14–xBxC6Cu1.2 (x = 0, 7%)非晶薄带的DSC曲线 (a) x = 0; (b) x = 7. 插图分别为ln(T 2/β)与1000/T的线性关系
Fig. 9. The DSC curves of as-quenched Fe78.8P14–xBxC6Cu1.2 (x = 0, 7%) amorphous ribbons under the different heating rates: (a) x = 0; (b) x = 7. The insets correspond to the relationship of ln(T 2/β) and 1000/T, respectively.
图 10 淬态Fe78.8P14–xBxC6Cu1.2 (x = 0, 7%)非晶薄带的磁滞回线, 插图(左上)为局部放大的磁滞回线, 插图(右下)为磁性Fe与类金属B, P原子间的电子杂化机制图示
Fig. 10. Hysteresis loops of as-quenched Fe78.8P14–xBxC6Cu1.2 (x = 0, 7%) amorphous ribbons. The inset (top-left) is the locally enlarged hysteresis loops, and the inset (bottom-right) is the mechanism of electron hybridization between magnetic Fe and metalloid B, P atoms.
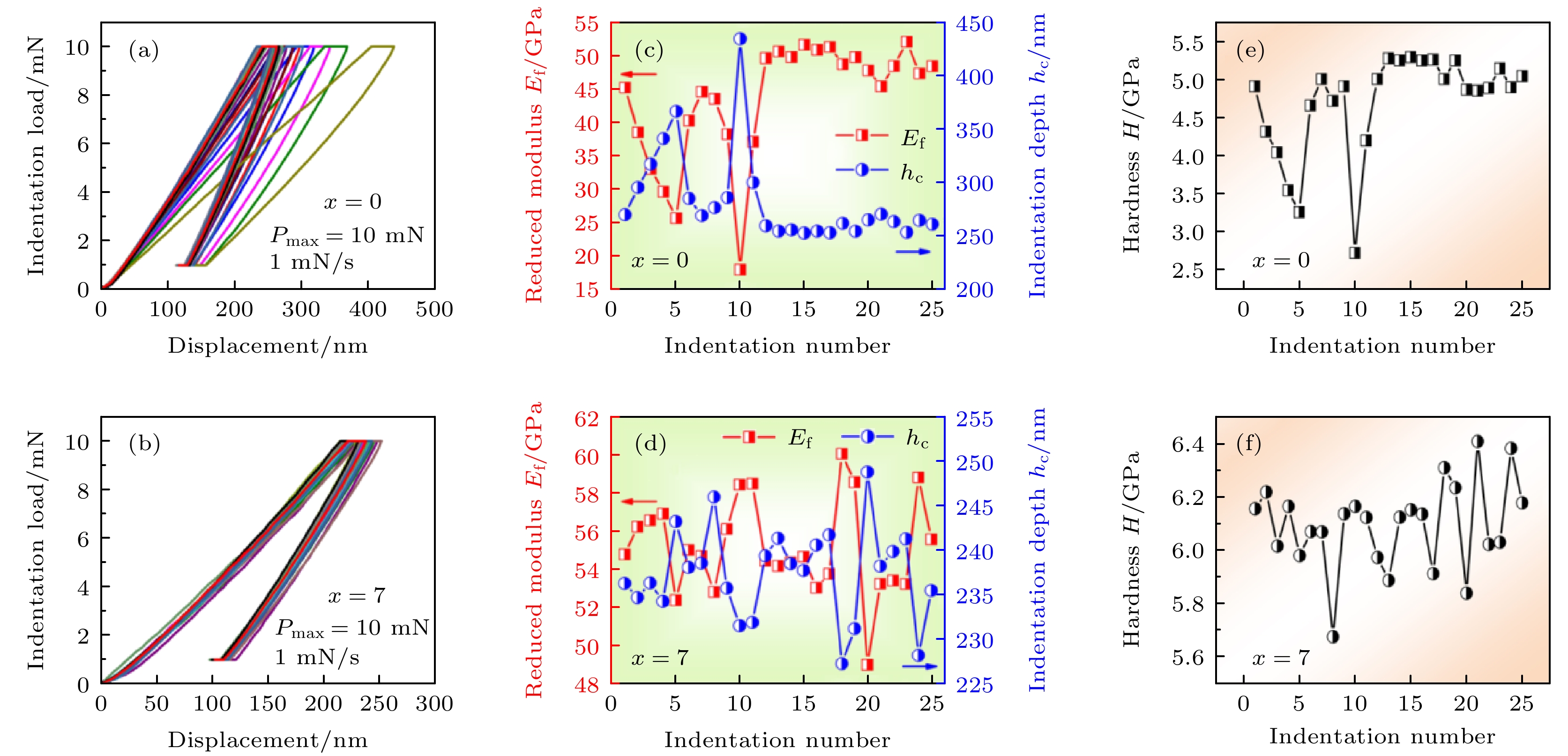
图 11 淬态Fe78.8P14–xBxC6Cu1.2 (x = 0, 7%)非晶薄带的纳米压痕实验 (a), (b) B0和B7合金的载荷-位移曲线; (c), (d) 合金的约化模量与压入深度值; (e), (f)合金的硬度变化值
Fig. 11. The nanoindentation tests of as-quenched Fe78.8P14–xBxC6Cu1.2 (x = 0, 7%) amorphous ribbons: (a) , (b) The load-displacement curves of B0 and B7 alloys, respectively; (c), (d) the reduced modulus and indentation depth of alloys, respectively; (e), (f) the variations in hardness of alloys, respectively
-
[1] Inoue A, Shen B L, Chang C T 2004 Acta Mater. 52 4093
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Xu D D, Zhou B L, Wang Q Q, Zhou J, Yang W M, Yuan C C, Xue L, Fan X D, Ma L Q, Shen B L 2018 Corros. Sci. 138 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Li F C, Liu T, Zhang J Y, Shuang S, Wang Q, Wang A D, Wang J G, Yang Y 2019 Mater. Today Adv. 4 100027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] McHenry M E, Willard M A, Laughlin D E 1999 Prog. Mater. Sci. 44 291
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wang A D, Zhao C L, He A N, Men H, Chang C T, Wang X M 2016 J. Alloy. Compd. 656 729
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 姚可夫, 施凌翔, 陈双琴, 邵洋, 陈娜, 贾蓟丽 2018 67 016101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yao K F, Shi L X, Chen S Q, Shao Y, Chen N, Jia J L 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 016101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] McHenry M E, Laughlin D E 2014 hysical Metallurgy (5th Ed.) (Elsevier) p1881
[8] Hou L, Fan X D, Wang Q Q, Yang W M, Shen B L 2019 J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 35 1655
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Meng S Y, Ling H B, Li Q, Zhang J 2014 Scr. Mater. 81 24
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wang C J, He A N, Wang A D, Pang J, Ling X, Li Q, Chang C, Qiu K, Wang X 2017 Intermetallics 84 142
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Mizoguchi T 1976 AIP Conf. Proc. 34 286
[12] Xu J, Yang Y Z, Li W, Xie Z, Chen X 2017 Mater. Res. Bull. 97 452
[13] Shi L X, Qin X L, Yao K F 2020 Prog. Nat. Sci-Mater. 30 208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zuo M Q, Meng S Y, Li Q, Li H X, Chang C T, Sun Y F 2017 Intermetallics 83 83
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Jin Y L, Fan X D, He M, Liu X C, Shen B L 2012 Sci. China Technol. Sci. 55 3419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wang Q Q, Chen M X, Lin P H, Cui Z Q, Chu C L, Shen B L 2018 J. Mater. Chem. A 6 10686
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang Q Q, Yun L, Chen M X, Xu D D, Cui Z Q, Zeng Q S, Lin P H, Chu C L, Shen B L 2019 ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2 214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Jafari S, Beitollahi A, Eftekhari Yekta B, Ohkubo T, Budinsky V, Marsilius M, Herzer G, Hono K 2016 J. Alloy. Compd. 674 136
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Fan X D, Zhang T, Jiang M F, Yang W M, Shen B L 2019 J. Non-Cryst. Solid. 503 36
[20] Hou L, Yang W M, Luo Q, Fan X D, Liu H S, Shen B L 2020 J. Non-Cryst. Solid. 530 119800
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Li Y L, Dou Z X, Chen X M, Lv K, Li F S, Hui X D 2020 Mater. Sci. Eng. B 262 114740
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Hono K, Ping D H, Ohnuma M, Onodera H 1999 Acta Mater. 47 997
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Hu F, Yuan C C, Luo Q, Yang W M, Shen B L 2019 J. Alloy. Compd. 807 151675
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Ohnuma M, Ping D H, Abe T, Onodera H, Hono K, Yoshizawa Y 2003 J. Appl. Phys. 93 9186
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Yang W M, Li J W, Liu H S, Dun C C, Zhang H L, Huo J T, Xue L, Zhao Y C, Shen B L, Dou L M, Inoue A 2014 Intermetallics 49 52
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Lan S, Ren Y, Wei X Y, Wang B, Gilbert E P, Shibayama T, Watanabe S, Ohnuma M, Wang X L 2017 Nat. Commun. 8 14679
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Takeuchi A, Inoue A 2005 Mater. Trans. 46 2817
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 耿遥祥, 王英敏 2020 金属学报 56 1558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Geng Y X, Wang Y M 2020 Acta Metall. Sin. 56 1558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Fan X D, Jiang M F, Zhang T, Hou L, Wang C X, Shen B L 2020 J. Non-Cryst. Solid. 533 119941
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Hou L, Li M R, Jiang C, Fan X D, Luo Q, Chen S S, Song P D, Li W H 2021 J. Alloy. Compd. 853 157071
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 严密, 彭晓领 2011 磁学基础与磁性材料 (杭州: 浙江大学出版社)
Yan M, Peng X L 2011 Fundamentals of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials (Hangzhou: Zhejiang University Press) (in Chinese)
[32] Zhang J H, Chang C T, Wang A D Shen B L 2012 J. Non-Crystal. Solids 358 1443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Wang F, Inoue A, Han Y, Kong F L, Zhu S L, Shalaan E, Al-Marzouki F, Obaid A 2017 J. Alloy. Compd. 723 376
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Sun B R, Xin S W, Shen T D 2018 J. Mag. Magn. Mater. 466 130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Sarac B, Ivanov Y P, Chuvilin A, Schoberl T, Stoica M, Zhang Z L, Eckert J 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 1333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Liu Y H, Wang G, Wang R J, Zhao D Q, Pan, M X, Wang W H 2007 Science 315 1385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 8390
- PDF下载量: 130
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: