-
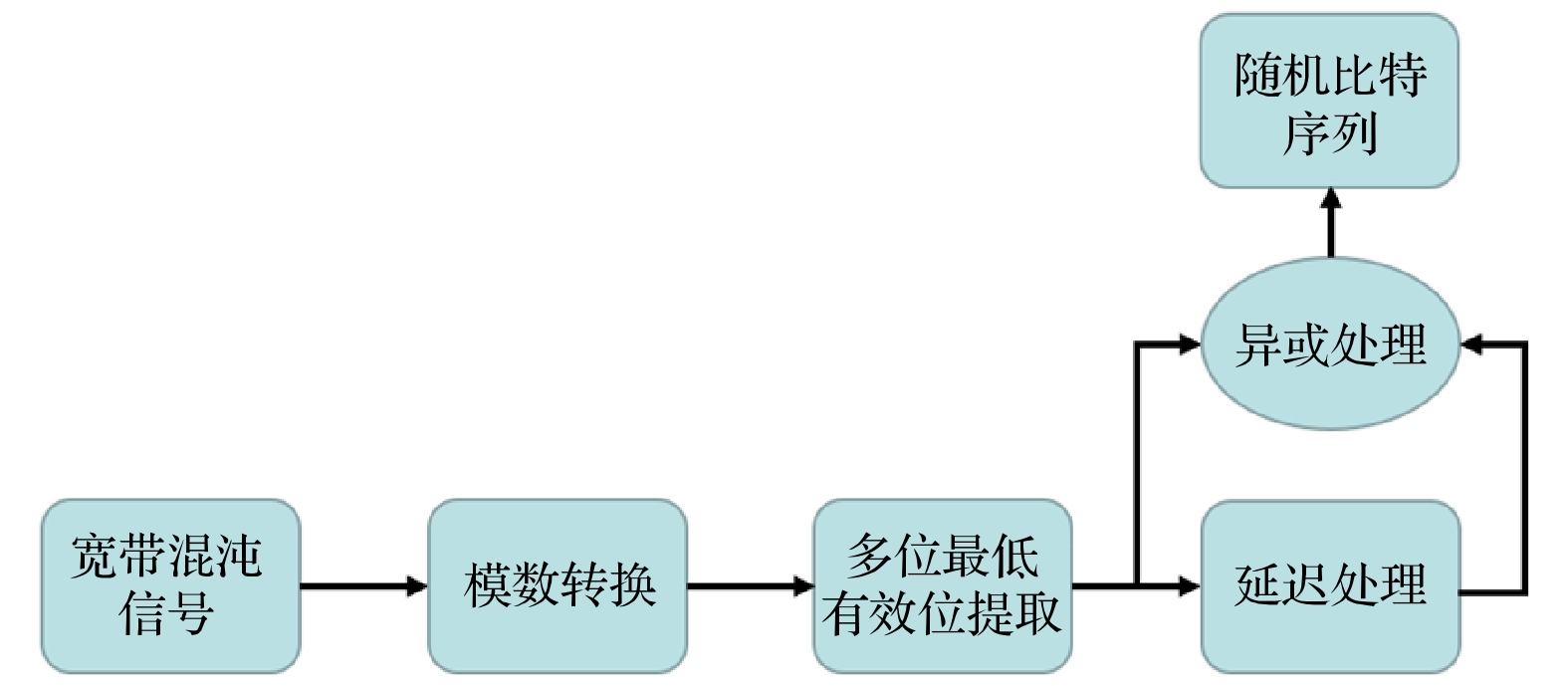
本文提出并实验证明了一种利用具有单滤波器光反馈的半导体激光器产生带宽增强混沌信号的方案. 为了获得高品质的混沌信号, 方案中讨论了滤波器失谐频率和反馈功率等关键参数对混沌信号带宽和平坦度的影响. 结果表明, 通过选择合适的参数, 可以获得带宽为24.4 GHz、平坦度为5.7 dB的混沌信号. 将这种混沌信号作为熵源, 采用8位模数转换采样量化和多位最低有效位异或提取处理实现了320 Gbit/s的随机比特生成并采用国际公认的随机数行业测试标准(NIST SP 800-22)来检验产生的序列, 结果表明, 通过单滤波器光反馈半导体激光器后处理的混沌熵源所获取的随机数序列具有均匀的分布特性, 可以成功通过NIST SP 800-22的全部测试.
Chaotic lasers feature wide spectrum and noise-like features, and extensively used in various fields, such as secure communications and random bit generation (RBG). Since the physical RBG using optical chaos was demonstrated first by Uchida et al., the optical chaos has been widely investigated in terms of chaos bandwidth and flatness, which determines the rate and randomness of RBG. Owing to the natural stability of semiconductor lasers, external perturbation is required to generate chaotic signals, such as optical injection, current modulation, and optical feedback. Among them, a semiconductor laser with optical feedback has attracted wide attention because of its simple structure and rich dynamic behaviors. Nonetheless, this configuration suffers the influence of the relaxation oscillation, which results in a limited bandwidth (a few GHz) and an uneven power spectrum. To obtain broad-spectrum chaotic signals, considerable efforts have been made in recent years. However, these solutions are associated with complex structures that require delicate manipulation because multiple parameters should be matched, so the cost of some of these schemes in terms of the system complexity can potentially outweigh the benefits. In this work, we incorporate an optical filter and an amplifier into the feedback loop of a conventional optical feedback system to generate broadband chaotic signals. The effects of the filter detuning frequency and feedback power on the bandwidth and flatness of the chaotic output are investigated experimentally. The experimental results demonstrate that by appropriately adjusting the feedback power and detuning frequency, both the low-frequency components and the high-frequency components of the chaotic output power spectrum can be increased, and the maximum chaotic bandwidth can reach 24.4 GHz with a flatness of 5.7 dB. This phenomenon is attributed to the physical process of beating between the filtered mode and the internal modes of the laser. Furthermore, the optimized chaotic output is processed by retaining the 4 least significant bits and implementing the delayed exclusive-OR (XOR) operation. Our scheme is capable of generating physical random number of the bit rate of 320 Gbit/s, and successfully passes the standard randomness test, i.e. the NIST test (NIST SP 800-22). -
Keywords:
- semiconductor laser /
- chaos /
- filter feedback /
- random bits generation
[1] Li H Y, Yang Y, Huang C M, Dai L Q, Cheng M F, Xiong X, Yang Q, Tang M, Liu D M, Deng L 2022 Opt, Lett. 47 118
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ke J X, Yi L L, Yang Z, Yang Y P, Zhuge Q B, Chen Y P, Hu W S 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 5776
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Li N Q, Kim B, Chizhevsky V N, Locquet A, Bloch M, Citrin D S, Pan W 2014 Opt. Express 22 6634
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Uchida A, Amano K, Inoue M, Hirano K, Naito S, Someya H, Oowada I, Kurashige T, Shiki M, Yoshimori S, Yoshimura K, Davis P 2008 Nat. Photonics 2 728
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Cheng C H, Chen C Y, Chen J D, Pan D K, Ting K T, Lin F Y 2018 Opt. Express 26 12230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhang M J, Liu H, Zhang J Z, Liu Y, Liu R X 2017 IEEE Photon. J. 9 1600610
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 钟东洲, 曾能, 杨华, 徐喆 2021 70 074206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhong D Z, Zeng N, Yang H, Xu Z 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 074206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Chai M M, Qiao L J, Zhang M J, Wang A B, Yang Q, Zhang J Z, Wang T, Gao S H 2020 IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 56 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Han H, Zhang M J, Shore K A 2019 IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 55 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Yin X M, Zhong Z Q, Zhao L J, Lu D, Qiu H Y, Xia G Q, Wu Z M 2015 Opt. Commun. 355 551
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Chen J J, Wu Z M, Tang X, Deng T, Fan L, Zhong Z Q, Xia G Q 2015 Opt. Express 23 7173
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Hong Y H, Spencer P S, Shore K A 2014 IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 50 236
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 陈俊, 陈建军, 吴正茂, 蒋波, 夏光琼 2016 65 164204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen J, Chen J J, Jiang B, Xia G Q 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 164204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Chan S C, Tang W K S 2009 Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 19 3417
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zeng Y, Zhou P, Huang Y, Li N Q 2021 Appl. Optics 60 7963
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Ruan J, Chan S C 2022 Opt. Lett. 47 858
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hao Y Z, Ma C G, Shen Z Z, Li J C, Xiao J L, Yang Y D, Huang Y Z 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 2115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Chang D, Zhong Z, Tang J, Spencer P S, Hong Y 2020 Opt. Express 28 39076
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhao A K, Jiang N, Liu S Q, Xue C P, Tang J M, Qiu K 2019 Opt. Express 27 12336
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Jiang N, Zhao A K, Liu S Q, Xue C P, Wang B Y, Qiu K 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 5359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Bouchez G, Uy C H, Macias B, Wolfersberger D, Sciamanna M 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 975
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Schires K, Gomez S, Gallet A, Duan G H, Grillot F 2017 IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. 23 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Yang Q, Qiao L J, Zhang M J, Zhang J Z, Wang T, Gao S H, Chai M M, Mohiuddin P M 2020 Opt. Lett. 45 1750
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Jiang N, Wang Y J, Zhao A K, Liu S Q, Zhang Y Q, Chen L, Li B C, Qiu K 2020 Opt. Express 28 1999
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Guo Y, Liu W, Huang Y, Sun Y, Zinsou R, He Y, Zhang R 2022 Opt. Express 30 3148
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhong Z Q, Lin G R, Wu Z M, Yang J Y, Chen J J, Yi L L, Xia G Q 2017 IEEE Photonic. Tech. L 29 1506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Wang L S, He Q Q, Wang A B, Wang Y C 2022 IEICE Nonlin. Theory Appl. 13 36
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Li P, Cai Q, Zhang J G, Xu B J, Liu Y M, Bogris A, Shore K A, Wang Y C 2019 Opt. Express 27 17859
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Yang Q, Qiao L J, Wei X J, Zhang B X, Chai M M, Zhang J Z, Zhang M J 2021 J. Lightwave Technol. 39 6246
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Zhao A K, Jiang N, Peng J F, Liu S Q, Zhang Y Q, Qiu K 2022 Opto-Electron Adv. 5 200026
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Ma C G, Xiao J L, Xiao Z X, Yang Y D, Huang Y Z 2022 Light Sci. Appl. 11 187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Lin F Y, Liu J M 2003 Opt. Commun. 221 173
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Hong Y H, Chen X F, Spencer P S, Shore K A 2015 IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 51 1200106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Hart J D, Terashima Y, Uchida A, Baumgartner G B, Murphy T E, Roy R 2017 APL Photonics 2 090901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Chizhevsky V N 2010 Phys. Rev. E 82 050101
[36] Reidler I, Aviad Y, Rosenbluh M, Kanter I 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 024102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Li X Z, Chan S C 2013 IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 49 829
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 1 宽带混沌信号产生的实验装置, 其中DFB-LD为分布反馈半导体激光器; CIR为循环器; OC为光耦合器; EDFA为掺铒光纤放大器; VOA为可变光衰减器; PC为偏振控制器; OSA为光谱分析仪; PD为光电探测器; EC为电耦合器; ESA为电频谱分析仪; OSC为示波器
Fig. 1. Experimental setup for the generation of a broadband chaotic signal. DFB-LD: distributed feedback laser diode; CIR: circulator; OC: optical coupler; EDFA: erbium-doped fiber amplifier; VOA: variable optical attenuator; PC: polarization controller; OSA: optical spectrum analyzer; PD: photoelectric detector; EC: electrical coupler; ESA: electrical spectrum analyzer; OSC: oscilloscope.
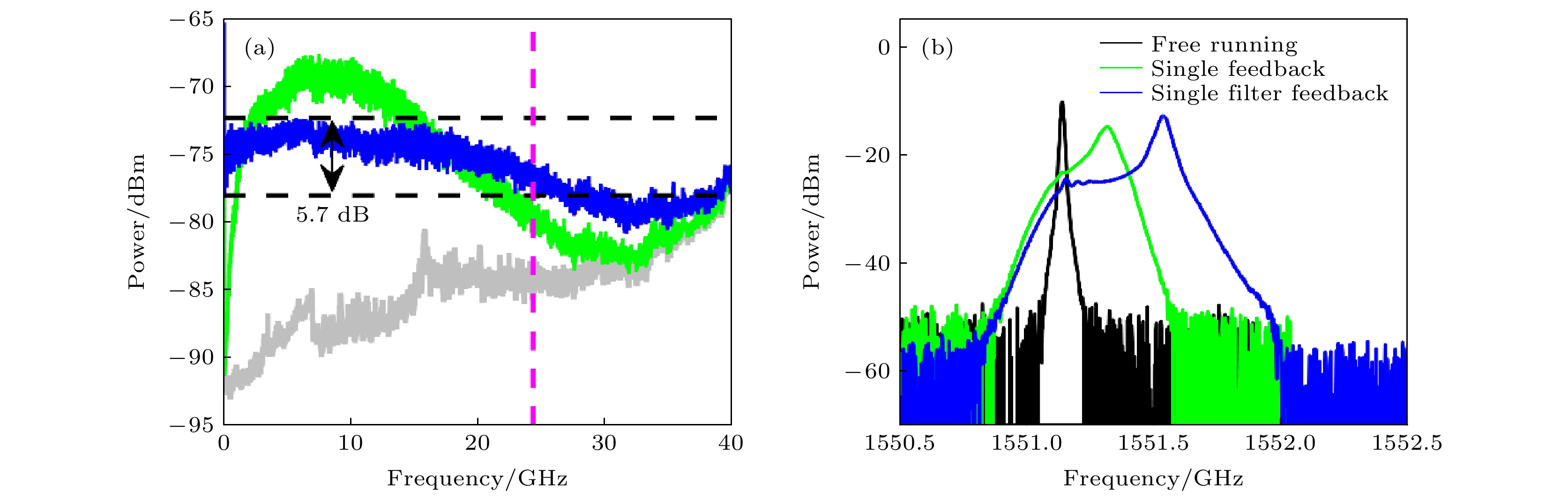
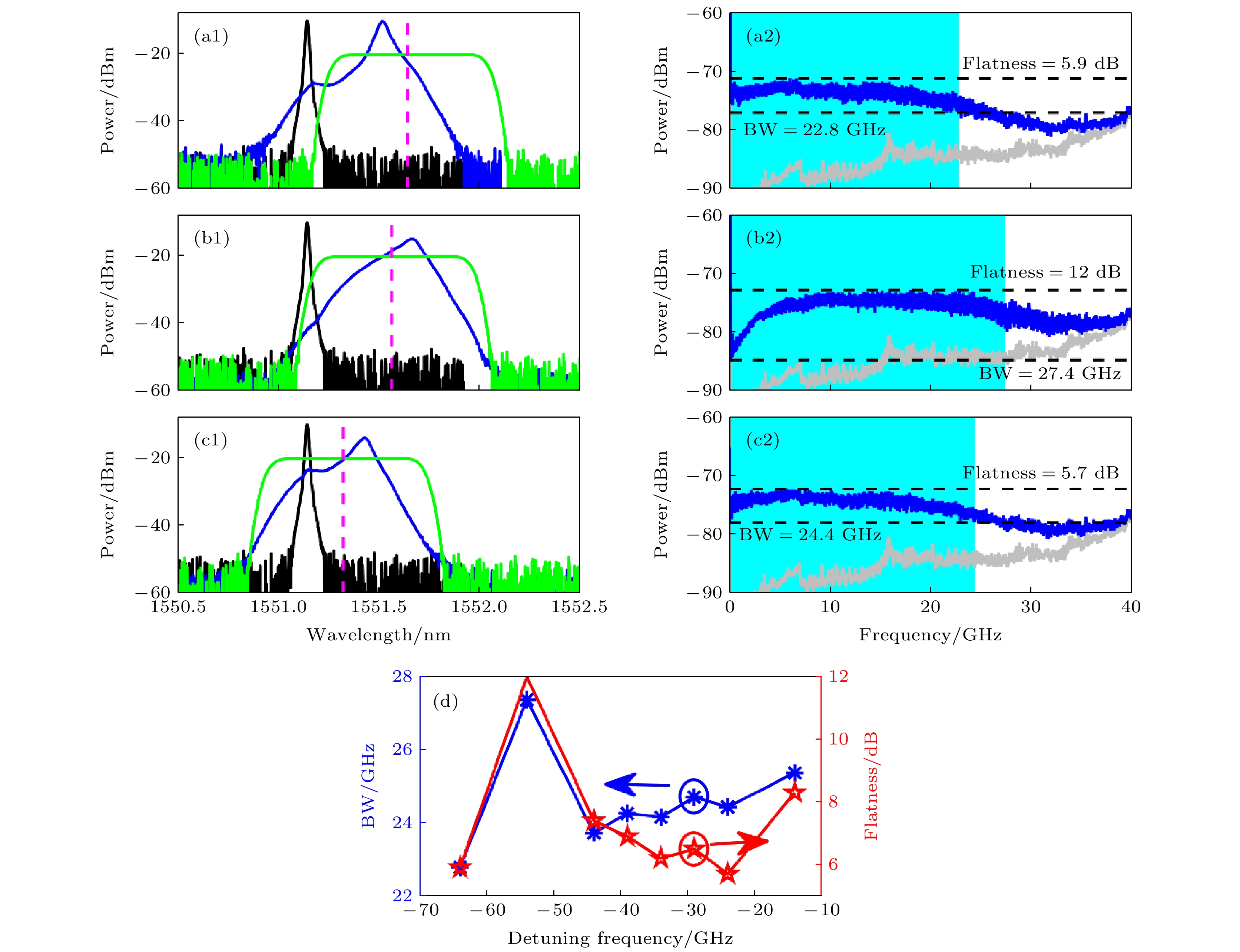
图 3 频率失谐Δν对混沌输出的影响. 光谱(左列), 功率谱(右列), 其中 (a1), (a2)
${\Delta } {\nu }=$ –64 GHz; (b1), (b2)${\Delta } {\nu }=$ –54 GHz; (c1), (c2)${\Delta } {\nu }=$ –24 GHz; (d) 混沌带宽和平坦度随频率失谐的演化情况Fig. 3. The effects of filter frequency detuning
${\Delta } {\nu }$ on the output of chaos. The optical spectra (left column) and corresponding power spectra (right column) of chaos generated with the filter frequency detuning (a1) (a2)${\Delta } {\nu }=$ –64 GHz; (b1) (b2) –54 GHz; (c1) (c2) –24 GHz ; (d) the BW and flatness of chaos as functions of filter frequency detuning.图 4 滤波反馈功率对混沌输出的影响. 光谱(左列), 功率谱(右列), 其中反馈功率
$ {P}_{\rm{f}} $ (a1) (a2) 0.718 mW; (b1) (b2) 1.486 mW; (c1) (c2) 3 mW; (d) 混沌带宽和平坦度随反馈功率的演化情况Fig. 4. The effects of filter feedback power on the output of chaos. optical spectra (left column) and corresponding power spectra (right column) of chaos generated from the filter feedback scheme, where the feedback power
$ {P}_{\rm{f}} $ (a1) (a2) 0.718 mW; (b1) (b2) 1.486 mW; (c1) (c2) 3 mW; (d) the BW and flatness of chaos as functions of the filter feedback power. -
[1] Li H Y, Yang Y, Huang C M, Dai L Q, Cheng M F, Xiong X, Yang Q, Tang M, Liu D M, Deng L 2022 Opt, Lett. 47 118
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ke J X, Yi L L, Yang Z, Yang Y P, Zhuge Q B, Chen Y P, Hu W S 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 5776
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Li N Q, Kim B, Chizhevsky V N, Locquet A, Bloch M, Citrin D S, Pan W 2014 Opt. Express 22 6634
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Uchida A, Amano K, Inoue M, Hirano K, Naito S, Someya H, Oowada I, Kurashige T, Shiki M, Yoshimori S, Yoshimura K, Davis P 2008 Nat. Photonics 2 728
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Cheng C H, Chen C Y, Chen J D, Pan D K, Ting K T, Lin F Y 2018 Opt. Express 26 12230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhang M J, Liu H, Zhang J Z, Liu Y, Liu R X 2017 IEEE Photon. J. 9 1600610
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 钟东洲, 曾能, 杨华, 徐喆 2021 70 074206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhong D Z, Zeng N, Yang H, Xu Z 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 074206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Chai M M, Qiao L J, Zhang M J, Wang A B, Yang Q, Zhang J Z, Wang T, Gao S H 2020 IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 56 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Han H, Zhang M J, Shore K A 2019 IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 55 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Yin X M, Zhong Z Q, Zhao L J, Lu D, Qiu H Y, Xia G Q, Wu Z M 2015 Opt. Commun. 355 551
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Chen J J, Wu Z M, Tang X, Deng T, Fan L, Zhong Z Q, Xia G Q 2015 Opt. Express 23 7173
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Hong Y H, Spencer P S, Shore K A 2014 IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 50 236
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 陈俊, 陈建军, 吴正茂, 蒋波, 夏光琼 2016 65 164204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen J, Chen J J, Jiang B, Xia G Q 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 164204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Chan S C, Tang W K S 2009 Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 19 3417
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zeng Y, Zhou P, Huang Y, Li N Q 2021 Appl. Optics 60 7963
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Ruan J, Chan S C 2022 Opt. Lett. 47 858
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hao Y Z, Ma C G, Shen Z Z, Li J C, Xiao J L, Yang Y D, Huang Y Z 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 2115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Chang D, Zhong Z, Tang J, Spencer P S, Hong Y 2020 Opt. Express 28 39076
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhao A K, Jiang N, Liu S Q, Xue C P, Tang J M, Qiu K 2019 Opt. Express 27 12336
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Jiang N, Zhao A K, Liu S Q, Xue C P, Wang B Y, Qiu K 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 5359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Bouchez G, Uy C H, Macias B, Wolfersberger D, Sciamanna M 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 975
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Schires K, Gomez S, Gallet A, Duan G H, Grillot F 2017 IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. 23 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Yang Q, Qiao L J, Zhang M J, Zhang J Z, Wang T, Gao S H, Chai M M, Mohiuddin P M 2020 Opt. Lett. 45 1750
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Jiang N, Wang Y J, Zhao A K, Liu S Q, Zhang Y Q, Chen L, Li B C, Qiu K 2020 Opt. Express 28 1999
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Guo Y, Liu W, Huang Y, Sun Y, Zinsou R, He Y, Zhang R 2022 Opt. Express 30 3148
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhong Z Q, Lin G R, Wu Z M, Yang J Y, Chen J J, Yi L L, Xia G Q 2017 IEEE Photonic. Tech. L 29 1506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Wang L S, He Q Q, Wang A B, Wang Y C 2022 IEICE Nonlin. Theory Appl. 13 36
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Li P, Cai Q, Zhang J G, Xu B J, Liu Y M, Bogris A, Shore K A, Wang Y C 2019 Opt. Express 27 17859
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Yang Q, Qiao L J, Wei X J, Zhang B X, Chai M M, Zhang J Z, Zhang M J 2021 J. Lightwave Technol. 39 6246
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Zhao A K, Jiang N, Peng J F, Liu S Q, Zhang Y Q, Qiu K 2022 Opto-Electron Adv. 5 200026
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Ma C G, Xiao J L, Xiao Z X, Yang Y D, Huang Y Z 2022 Light Sci. Appl. 11 187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Lin F Y, Liu J M 2003 Opt. Commun. 221 173
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Hong Y H, Chen X F, Spencer P S, Shore K A 2015 IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 51 1200106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Hart J D, Terashima Y, Uchida A, Baumgartner G B, Murphy T E, Roy R 2017 APL Photonics 2 090901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Chizhevsky V N 2010 Phys. Rev. E 82 050101
[36] Reidler I, Aviad Y, Rosenbluh M, Kanter I 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 024102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Li X Z, Chan S C 2013 IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 49 829
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 7594
- PDF下载量: 135
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: