-
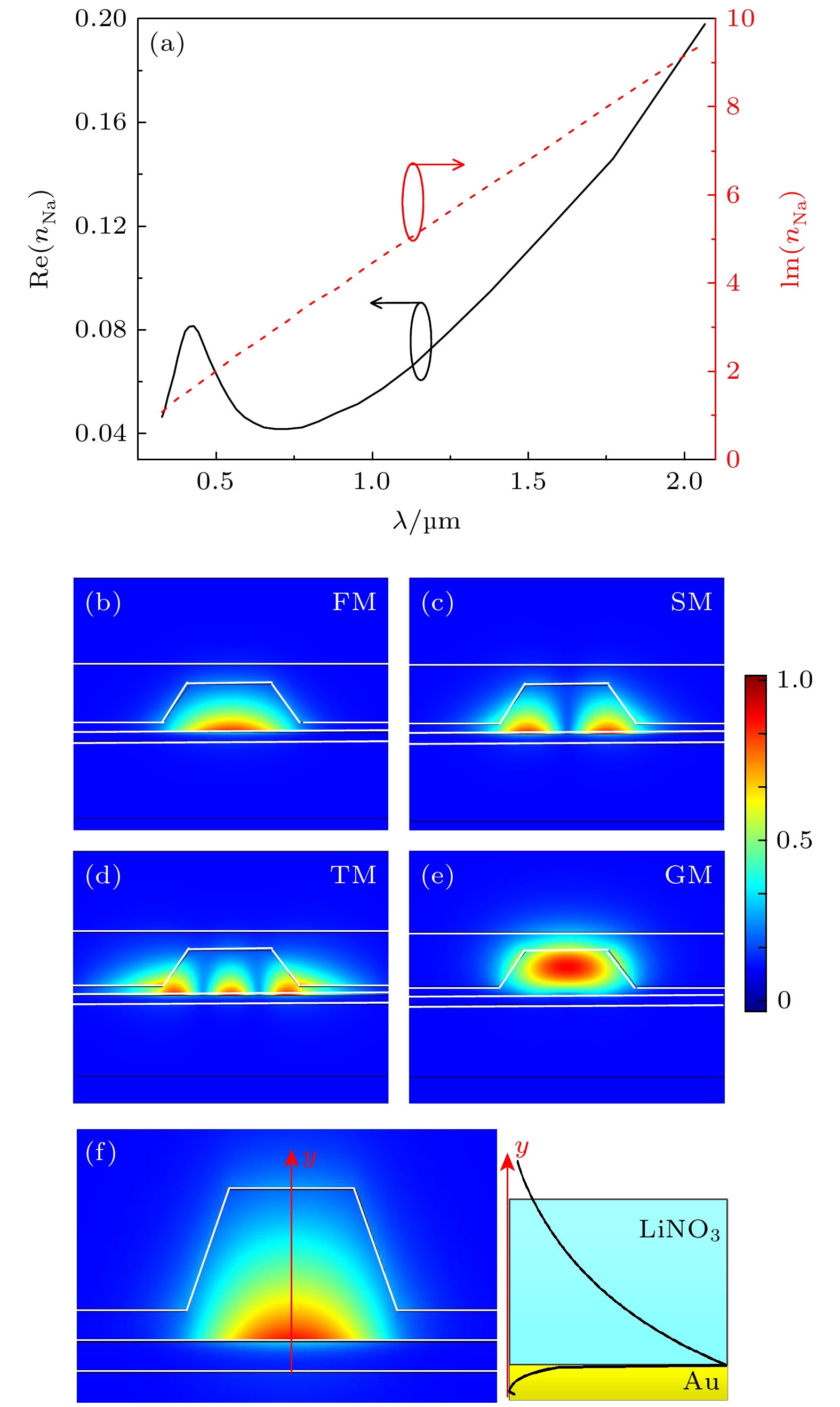
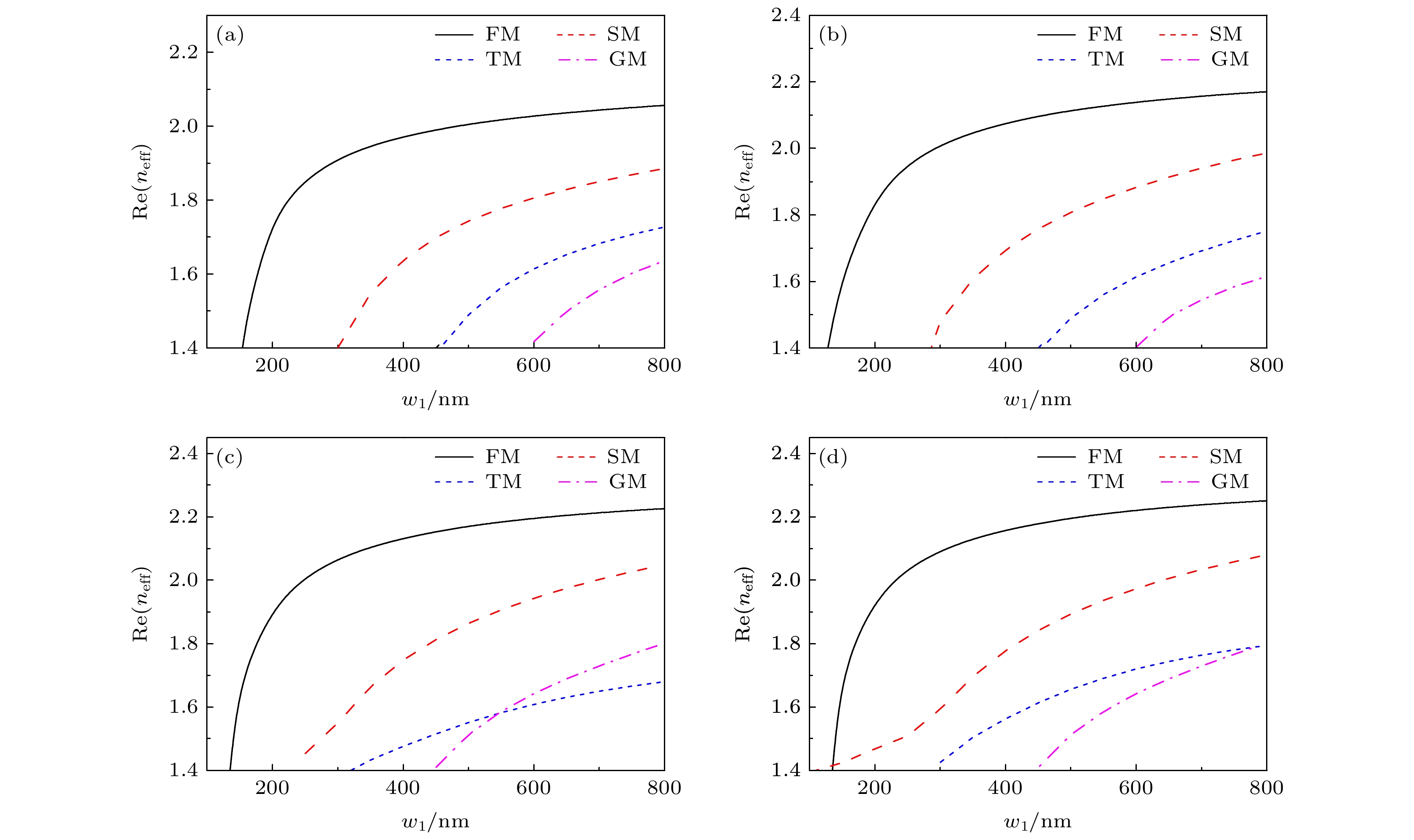
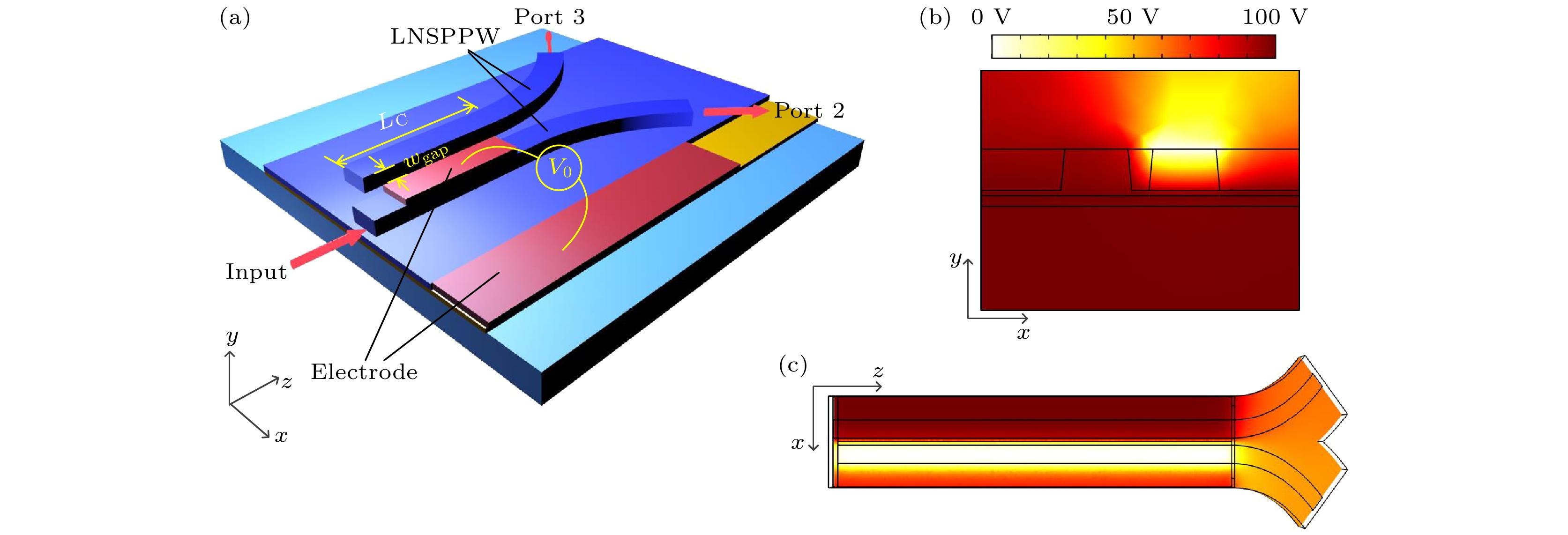
为了满足日益增加的集成光子器件设计的需求, 本文研究了一种铌酸锂/钠表面等离子体波导(LiNbO3/Na surface plasmonic waveguide, LNSPW), 并利用LNSPW构成电光可调的定向耦合器(directional coupling, DC). 利用有限元方法(finite element method, FEM)对波导的模式特性和耦合器的耦合特性进行了分析. 结果表明, 随着波导尺寸的增大, 传播长度可达约200 μm, 归一化有效模场面积小于0.4. 通过调节耦合间距(Wgap)、耦合长度(LC)和工作波长(λ)等参数, 铌酸锂钠表面等离子体波导构建的定向耦合结构可实现3 dB耦合. 当Wgap = 100 nm和LC = 17 μm时, DC在V0 = 53 V时可实现3 dB耦合, 且具有较好的方向性和隔离度. LNSPW的研究为实现可调的DC提供了一种可行的方案, 在集成电光可调器件研究领域有潜在的应用前景. 除此之外, LNSPW还可广泛应用于非线性光学、光信号处理及光全息存储等领域.To meet the increasing demand of integrated photonic device design, a LiNbO3/Na surface plasmonic waveguide (LNSPW) is demonstrated, and a directional coupler (DC) based on the LNSPW is also studied. The mode characteristics of the LNSPW and the coupling performances of the DC are simulated by the finite element method (FEM). There are four modes in the LNSPW when its width (w1) and the thickness (h1) are less than 600 nm and 400 nm, respectively. The number of the modes in the LNSPW increases with waveguide size increasing. To achieve the single-mode propagation, w1 and h1 are chosen to be 300 nm and 200 nm, respectively. The effective refractive index (neff), propagation length (Lp), and normalized effective mode area (Aeff/A0) are analyzed with different dimensional parameters of the LNSPW. The value of Lp is ~200 μm, and Aeff/A0 is less than 0.4. In order to demonstrate the electro-optic tunable performance, the normalized output power (Pnorm) values of the DC are calculated based on the LNSPWs with different values of coupling interval (Wgap), coupling length (LC), and operating wavlength (λ). The Pnorm values of the output ports (port 2 and port 3) vary with Wgap and LC. Owing to the electro-optic effect of LiNbO3 (LN), Pnorm of the DC can be adjusted by changing the applied electrostatic voltage (V0). The influence of V0 on Pnorm increases when Wgap is larger than 100 nm and LC is greater than 12 μm. The larger the value of LC and Wgap, the stronger the effect of V0 on Pnorm is, but Pnorm values from two output ports decrease with Wgap and LC increasing. A 3 dB coupler can be achieved by changing V0 to 53 V when Wgap = ~100 nm, LC = ~17 μm, and λ = 1.55 μm, and has good directivity and isolation. The LNSPW provides a feasible scheme to realize the tunable DC, and has potential applications in integratable electro-optic tuanble devices, nonlinear optics, optical signal processing, and optical holographic storage.
-
Keywords:
- LiNbO3 waveguide /
- electro-optical device /
- surface plasmonic /
- directional coupler
[1] Zhang Q, Li M, Xu J, Lin Z J, Yu H F, Wang M, Fang Z W, Cheng Y, Gong Q H, Li Y 2019 Photonics Res. 7 503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 刘时杰, 郑远林, 陈险峰 2021 光学学报 41 0823013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu S J, Zheng Y L, Chen X F 2021 Acta Opt. Sin. 41 0823013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wang C, Zhang M, Chen X, Bertrand M, Shams-Ansari A, Chandrasekhar S, Winzer P, Lončar M 2018 Nature 562 101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Kues M, Reimer C, Roztocki P, Cortés L R, Sciara S, Wetzel B, Zhang Y B, Cino A, Chu S T, Little B E, Moss D J, Caspani L, Azaña J, Morandotti R 2017 Nature 546 622
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Janner D, Tulli D, García-Granda M, Belmonte M, Pruneri V 2009 Laser Photonics Rev. 3 301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 李庚霖, 贾曰辰, 陈峰 2020 69 157801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li G L, Jia Y C, Chen F 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 157801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Poberaj G, Hu H, Sohler W, Günter P 2012 Laser Photonics Rev. 6 488
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Levy M, Osgood R M, Liu R, Cross L E, Cargill G S, Kumar A, Bakhru H 1998 Appl. Phys. Lett. 73 2293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wang C, Burek M J, Lin Z, Atikian H A, Venkataraman V, Huang I C, Stark P, Lončar M 2014 Opt. Express 22 30924
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang M, Wang C, Cheng R, Shams-Ansari A, Lončar M 2017 Optica 4 1536
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Lin J T, Xu Y X, Fang Z W, Wang M, Wang N W, Qiao L L, Fang W, Cheng Y 2015 Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 58 114209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wu R B, Zhang J H, Yao N, Fang W, Qiao L L, Chai Z F, Lin J T, Cheng Y 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 4116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 乔玲玲, 汪旻, 伍荣波, 方致伟, 林锦添, 储蔚, 程亚 2021 光学学报 41 0823012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qiao L L, Wang M, Wu R B, Fang Z W, Lin J T, Chu W, Cheng Y 2021 Acta Opt. Sin. 41 0823012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wu R B, Wang M, Xu J, Qi J, Chu W, Fang Z W, Zhang J H, Zhou J X, Qiao L L, Chai Z F, Lin J T, Cheng Y 2018 Nanomaterials 8 910
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Lin J T, Yao N, Hao Z Z, Zhang J H, Mao W B, Wang M, Chu W, Wu R B, Fang Z W, Qiao L L, Fang W, Bo F, Cheng Y 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. 122 173903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Jia Y C, Wang L, Chen F 2021 Appl. Phys. Rev. 8 011307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yang L K, Li P, Wang H C, Li Z P 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 094216
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Boltasseva A, Atwater H A 2011 Science 331 290
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Khurgin J B 2015 Nat. Nanotechnol. 10 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Naik G V, Shalaev V M, Boltasseva A 2013 Adv. Mater. 25 3264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Prucha E J, Palik E D 1998 Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids II (London: Academic Press) p354
[22] Wang Y, Yu J Y, Mao Y F, Chen J, Wang S, Chen H Z, Zhang Y, Wang S Y, Chen X J, Li T, Zhou L, Ma R M, Zhu S N, Cai W S, Zhu J 2020 Nature 581 401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Tsilipakos O, Yioultsis T V, Kriezis E E 2009 J. Hazard Mater. 106 93109
[24] Jiang A Q, Geng W P, Lv P, Hong J W, Jiang J, Wang C, Chai X J, Lian J W, Zhang Y, Huang R, Zhang D W, Scott J F, Hwang C S 2020 Nat. Mater. 19 1188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] Zhang Q, Li M, Xu J, Lin Z J, Yu H F, Wang M, Fang Z W, Cheng Y, Gong Q H, Li Y 2019 Photonics Res. 7 503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 刘时杰, 郑远林, 陈险峰 2021 光学学报 41 0823013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu S J, Zheng Y L, Chen X F 2021 Acta Opt. Sin. 41 0823013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wang C, Zhang M, Chen X, Bertrand M, Shams-Ansari A, Chandrasekhar S, Winzer P, Lončar M 2018 Nature 562 101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Kues M, Reimer C, Roztocki P, Cortés L R, Sciara S, Wetzel B, Zhang Y B, Cino A, Chu S T, Little B E, Moss D J, Caspani L, Azaña J, Morandotti R 2017 Nature 546 622
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Janner D, Tulli D, García-Granda M, Belmonte M, Pruneri V 2009 Laser Photonics Rev. 3 301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 李庚霖, 贾曰辰, 陈峰 2020 69 157801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li G L, Jia Y C, Chen F 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 157801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Poberaj G, Hu H, Sohler W, Günter P 2012 Laser Photonics Rev. 6 488
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Levy M, Osgood R M, Liu R, Cross L E, Cargill G S, Kumar A, Bakhru H 1998 Appl. Phys. Lett. 73 2293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wang C, Burek M J, Lin Z, Atikian H A, Venkataraman V, Huang I C, Stark P, Lončar M 2014 Opt. Express 22 30924
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang M, Wang C, Cheng R, Shams-Ansari A, Lončar M 2017 Optica 4 1536
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Lin J T, Xu Y X, Fang Z W, Wang M, Wang N W, Qiao L L, Fang W, Cheng Y 2015 Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 58 114209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wu R B, Zhang J H, Yao N, Fang W, Qiao L L, Chai Z F, Lin J T, Cheng Y 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 4116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 乔玲玲, 汪旻, 伍荣波, 方致伟, 林锦添, 储蔚, 程亚 2021 光学学报 41 0823012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qiao L L, Wang M, Wu R B, Fang Z W, Lin J T, Chu W, Cheng Y 2021 Acta Opt. Sin. 41 0823012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wu R B, Wang M, Xu J, Qi J, Chu W, Fang Z W, Zhang J H, Zhou J X, Qiao L L, Chai Z F, Lin J T, Cheng Y 2018 Nanomaterials 8 910
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Lin J T, Yao N, Hao Z Z, Zhang J H, Mao W B, Wang M, Chu W, Wu R B, Fang Z W, Qiao L L, Fang W, Bo F, Cheng Y 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. 122 173903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Jia Y C, Wang L, Chen F 2021 Appl. Phys. Rev. 8 011307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yang L K, Li P, Wang H C, Li Z P 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 094216
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Boltasseva A, Atwater H A 2011 Science 331 290
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Khurgin J B 2015 Nat. Nanotechnol. 10 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Naik G V, Shalaev V M, Boltasseva A 2013 Adv. Mater. 25 3264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Prucha E J, Palik E D 1998 Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids II (London: Academic Press) p354
[22] Wang Y, Yu J Y, Mao Y F, Chen J, Wang S, Chen H Z, Zhang Y, Wang S Y, Chen X J, Li T, Zhou L, Ma R M, Zhu S N, Cai W S, Zhu J 2020 Nature 581 401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Tsilipakos O, Yioultsis T V, Kriezis E E 2009 J. Hazard Mater. 106 93109
[24] Jiang A Q, Geng W P, Lv P, Hong J W, Jiang J, Wang C, Chai X J, Lian J W, Zhang Y, Huang R, Zhang D W, Scott J F, Hwang C S 2020 Nat. Mater. 19 1188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 7751
- PDF下载量: 138
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: