-
磁电电压可调电感器(ME-VTI)是基于磁电效应实现电场对电感的调控. 与其他可调电感器相比, 具有能耗低、体积小、可调性大且连续等特点. 而以往对ME-VTI的研究主要针对结构和磁致伸缩材料, 致使电感器制备工艺复杂或可调性提高不大. 本文通过构建理论模型, 着眼于压电材料场致应变对电感可调性的影响. 采用磁电复合材料Metglas/PMN-PT单晶/Metglas作为磁芯制备ME-VTI. 在1 kHz时可调性高达680%, 相当于选用Metglas/PZT/Metglas磁芯的2.4倍. 前者品质因子达到15.6, 相对于后者提高了2.8倍. 本文提出的基于PMN-PT单晶的ME-VTI为器件集成化、小型化的发展提供了新的思路, 在电力电子领域有重要的应用前景.Magnetoelectric voltage tunable inductor (ME-VTI) realizes the modulation of electric field to inductance based on magnetoelectric effect. Compared with other adjustable inductors, it has the advantages of low energy consumption, small volume, large tunability and continuity. However, previous reports on ME-VTI mainly focused on structure and magnetostrictive materials, resulting in the complexity of inductor structure and slight improvement of tunability. This study focuses on the influence of field-induced strain in piezoelectric materials on inductance tunability by constructing a theoretical model. The magnetoelectric laminate of Metglas/ PMN-PT single crystal /Metglas is employed as a magnetic core to design ME-VTI. The tunability is as high as 680% at 1 kHz, which is over 2.4 times larger than that of the Metglas/PZT/Metglas magnetic core. The quality factor of the PMN-PT based ME laminate reaches 15.6, which is 2.8 times higher than that of the PZT-based one. The proposed PMN-PT based ME-VTI provides an alternative approach for developing the integrated and miniaturized devices, and has an important prospect of application in the field of power electronics.
-
Keywords:
- tunable inductor /
- magnetoelectric effect /
- field-induced strain /
- piezoelectric single crystal
[1] Yan Y K, Geng L W D, Tan Y H, Ma J H, Zhang L J, Sanghadasa M, Ngo K, Ghosh A W, Wang Y U, Priya S 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 4998
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Peng B, Zhang C, Yan Y, Liu M 2017 Phys. Rev. Appl. 7 044015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhang J, Chen D, Filippov D A, Li K, Zhang Q, Jiang L, Zhu W, Cao L, Srinivasan G 2018 Appl. Phys. Lett. 113 113502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhang J, Chen D, Filippov D A, Zhang Q, Li K, Hang X, Ge B, Cao L, Srinivasan G 2019 IEEE Trans. Magn. 55 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Liu G, Zhang Y, Ci P, Dong S 2013 J. Appl. Phys. 114 064107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 杨娜娜, 陈轩, 汪尧进 2018 67 157508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang N N, Chen X, Wang Y J 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 157508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 俞斌, 胡忠强, 程宇心, 彭斌, 周子尧, 刘明 2018 67 157507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu B, Hu Z Q, Cheng Y X, Peng B, Zhou Z Y, Liu M 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 157507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Lin H, Lou J, Gao Y, Hasegawa R, Liu M, Howe B, Jones J, Brown G, Sun N X 2015 IEEE Trans. Magn. 51 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Yan Y, Geng L, Zhang L, Tu C, Sri Ramdas R M, Liu H, Li X, Sanghadasa M, Ngo K D T, Wang Y U, Priya S 2020 IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 12 44981
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Lou J, Reed D, Liu M, Sun N X 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 94 112508 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 94 112508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Liu G, Cui X, Dong S 2010 J. Appl. Phys. 108 094106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Geng L, Yan Y, Priya S, Wang Y U 2020 ACS Applied Mater. Interfaces 12 44981
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Geng L W D, Yan Y K, Priya S, Wang Y U 2017 Acta Mater. 140 97
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Geng L D, Yan Y, Priya S, Wang Y U 2019 Acta Mater. 166 493
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Geng L D, Yan Y, Priya S, Wang Y U 2020 Phys. Rev. B 101 054422
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Ma F D, Jin Y M, Wang Y U, Kampe S L, Dong S 2014 Acta Mater. 70 45
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang Y, Wang Z, Ge W, Luo C, Li J, Viehland D, Chen J, Luo H 2014 Phys. Rev. B 90 134107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wang Y, Wen X, Jia Y, Huang M, Wang F, Zhang X, Bai Y, Yuan G, Wang Y 2020 Nat. Commun. 11 1328
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 李飞, 张树君, 徐卓 2020 69 217703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li F, Zhang S J, Xu Z 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 217703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Chu Z, Shi H, Shi W, Liu G, Wu J, Yang J, Dong S 2017 Adv Mater. 29 1606022
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wang Y J, Gray D, Berry D, Gao J Q, Li M H, Li J F, Viehland D 2011 Adv. Mater. 23 4111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Liu G, Ci P, Dong S 2014 Appl. Phys. Lett. 104 032908
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chu Z, PourhosseiniAsl M, Dong S 2018 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 51 243001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wang Y, Li J, Viehland D 2014 Mater. Today 17 269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Chu Z, Dong C, Tu C, He Y, Liang X, Wang J, Wei Y, Chen H, Gao X, Lu C, Zhu Z, Lin Y, Dong S, McCord J, Sun N X 2019 Phys. Rev. Appl. 12 044001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 王慧, 徐萌, 郑仁奎 2020 69 017301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H, Xu M, Zheng R K 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 017301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Li M, Wang Y, Hasanyan D, Li J, Viehland D 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 100 132904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wang Y, Wang D, Yuan G, Ma H, Xu F, Li J, Viehland D, Gehring P M 2016 Phys. Rev. B 94 174103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Wang D, Yuan G, Luo H, Li J, Viehland D, Wang Y 2017 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 100 4938
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Yan Y K, Geng L W D, Zhang L J, Gao X Y, Gollapudi S, Song H C, Dong S X, Sanghadasa M, Ngo K, Wang Y U, Priya S 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 16008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
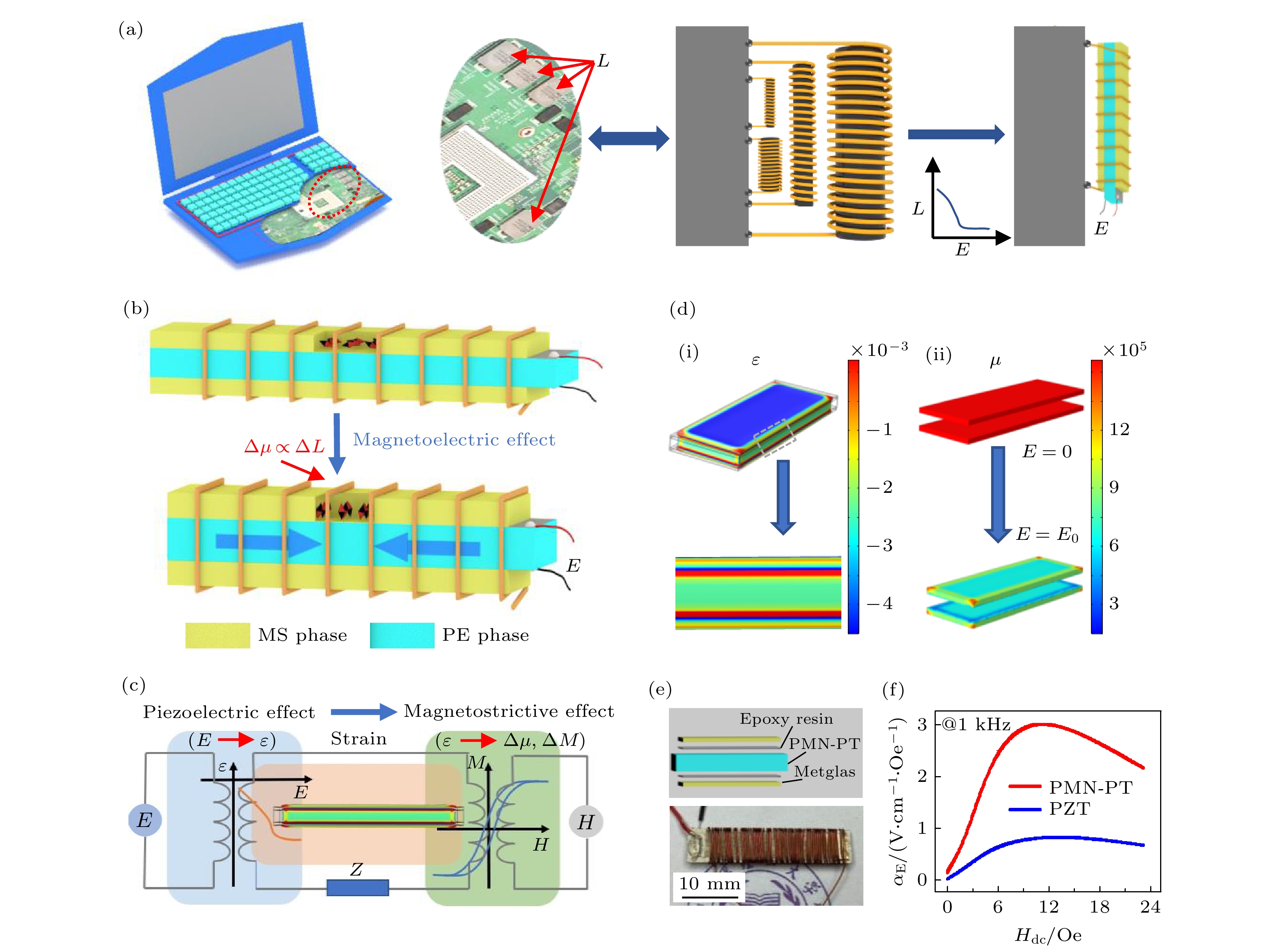
图 1 磁电电压可调电感器 (a) 应用示意图; (b) 结构示意图; (c) 逆磁电效应原理图; (d) (i)和(ii) 分别为电场作用时应变和磁导率的变化图; (e) 实物图; (f) PMN-PT基和PZT基磁电系数随偏置磁场的变化
Fig. 1. Magnetoelectric voltage tunable inductor (ME-VTI): (a) Potential application and (b) structure of ME-VTI; (c) principle of inverse magnetoelectric effect; (d) the variation of (i) strain and (ii) permeability under electric field; (e) photo for a ME-VTI; (f) the ME voltage coefficient of the Metglas/PMN-PT/Metglas and Metglas/PZT/Metglas.
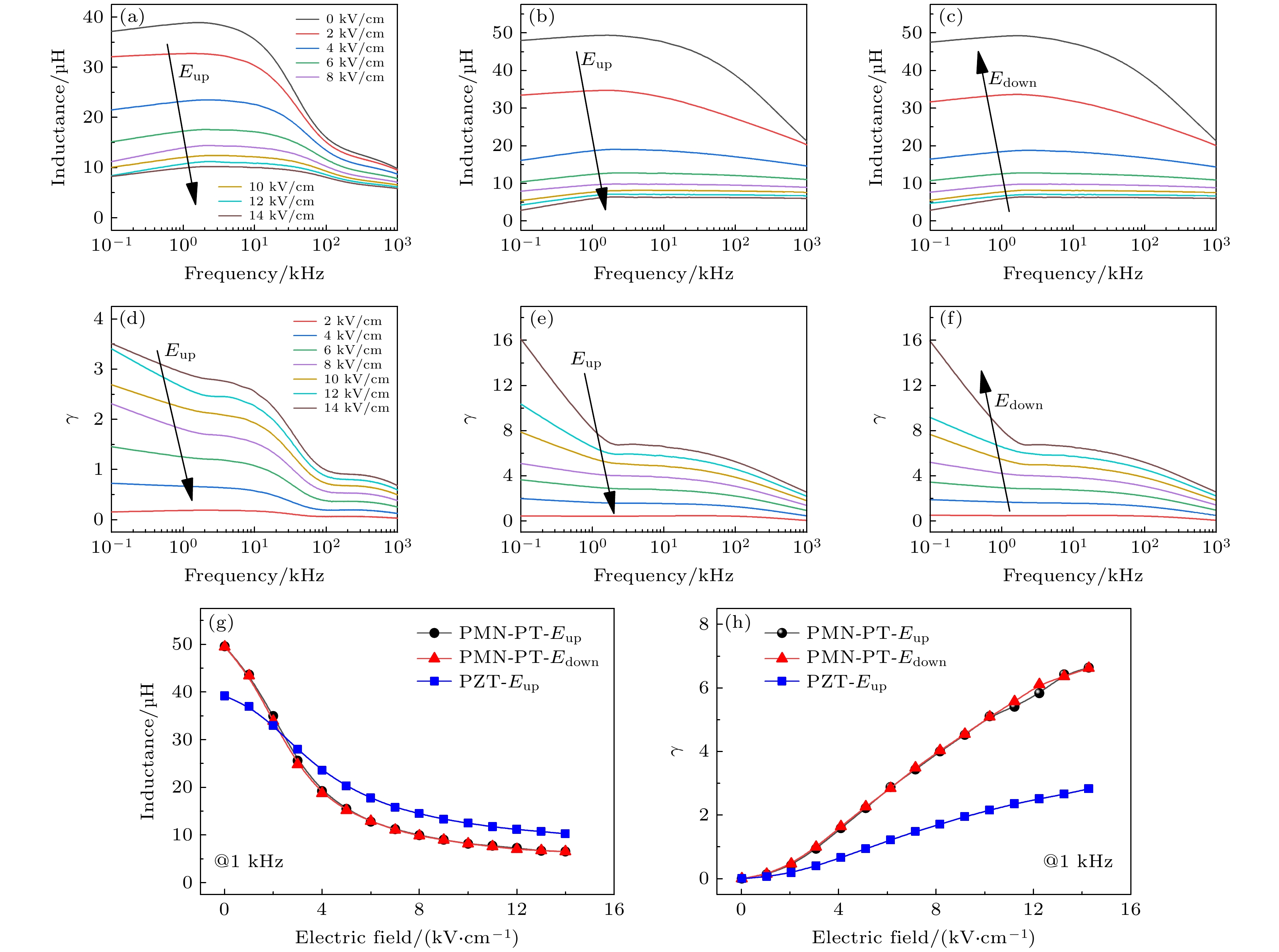
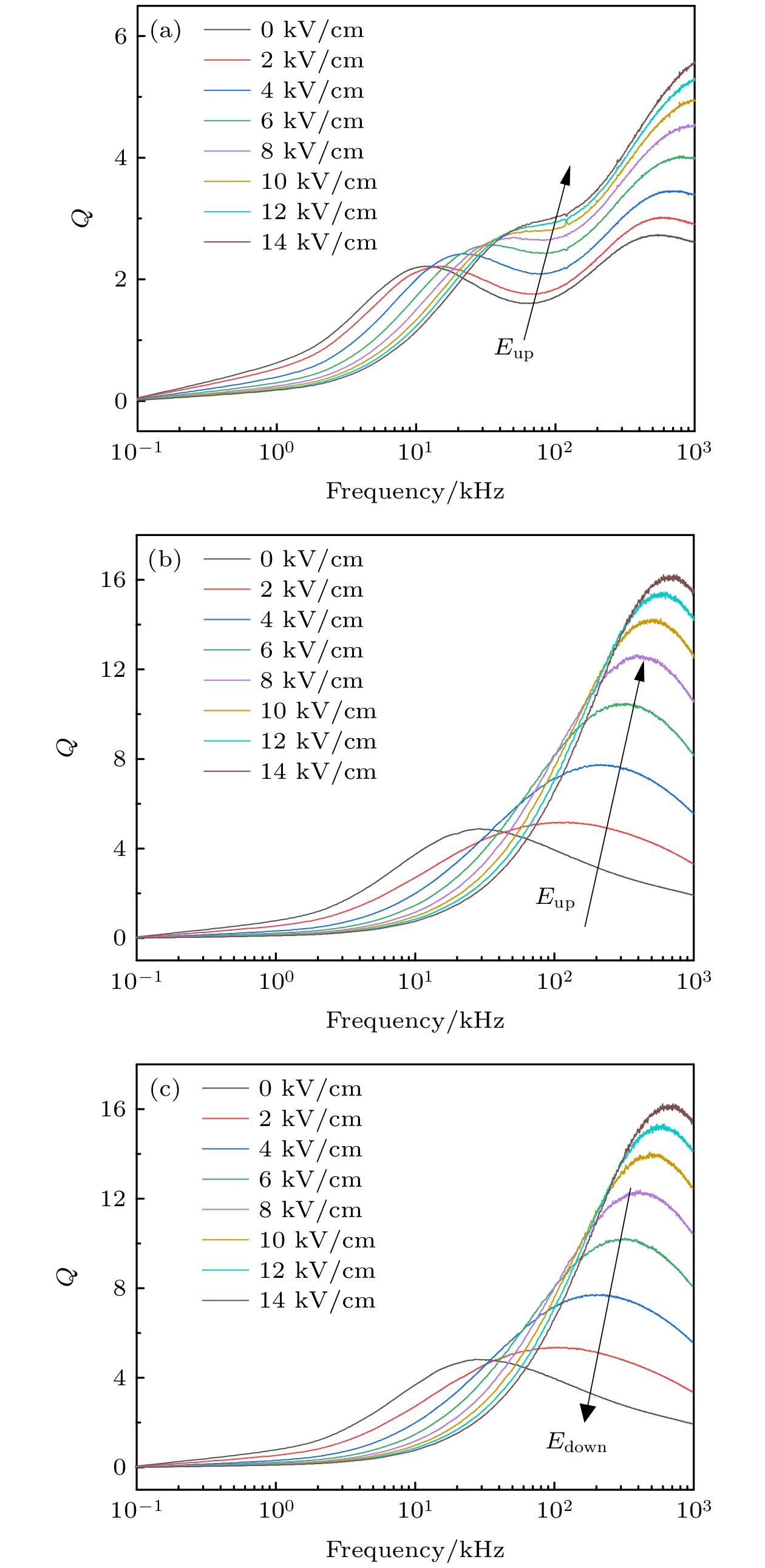
图 3 (a)−(c)和(d)−(f) 分别为磁电电压可调电感器PZT基 (E-field up)、PMN-PT基(E-field up)、PMN-PT基 (E-field down)的电感频谱图和可调性频谱图; (g) 1 kHz时直流电场对PZT基和PMN-PT基电感的影响; (h) 1 kHz时PZT基和PMN-PT基的电感可调性
Fig. 3. (a)−(c) Inductance and (d)−(f) tunable spectra of PZT based (E-field up), PMN-PT based (E-field up) and PMN-PT based (E-field down) ME-VTI, respectively; (g) inductance of PZT based and PMN-PT based ME-VTI as a function of the applied dc voltage at 1 kHz; (h) tunability γ of PZT based and PMN-PT based ME-VTI at 1 kHz.
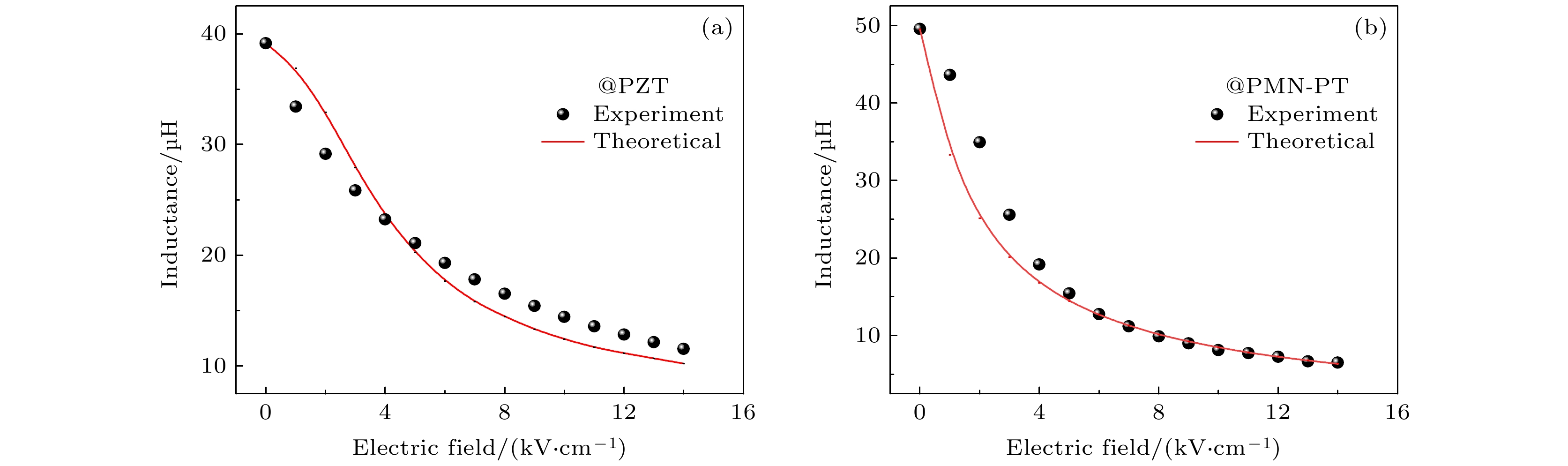
图 6 (a) 各频率下PMN-PT基电压可调电感器电场对可调性的影响; (b) 1 kHz下PMN-PT基电压可调电感器电场对电感和可调性的影响; (c), (d) 分别为电场对应力和磁导率影响的模拟图
Fig. 6. Influence of electric field of PMN-PT based ME-VTI on (a) tunability at various frequencies; (b) influence of electric field of PMN-PT based ME-VTI on inductance and tunability at 1 kHz; simulation of electric field dependent (c) stress and (d) permeability, respectively.
-
[1] Yan Y K, Geng L W D, Tan Y H, Ma J H, Zhang L J, Sanghadasa M, Ngo K, Ghosh A W, Wang Y U, Priya S 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 4998
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Peng B, Zhang C, Yan Y, Liu M 2017 Phys. Rev. Appl. 7 044015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhang J, Chen D, Filippov D A, Li K, Zhang Q, Jiang L, Zhu W, Cao L, Srinivasan G 2018 Appl. Phys. Lett. 113 113502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhang J, Chen D, Filippov D A, Zhang Q, Li K, Hang X, Ge B, Cao L, Srinivasan G 2019 IEEE Trans. Magn. 55 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Liu G, Zhang Y, Ci P, Dong S 2013 J. Appl. Phys. 114 064107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 杨娜娜, 陈轩, 汪尧进 2018 67 157508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang N N, Chen X, Wang Y J 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 157508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 俞斌, 胡忠强, 程宇心, 彭斌, 周子尧, 刘明 2018 67 157507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu B, Hu Z Q, Cheng Y X, Peng B, Zhou Z Y, Liu M 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 157507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Lin H, Lou J, Gao Y, Hasegawa R, Liu M, Howe B, Jones J, Brown G, Sun N X 2015 IEEE Trans. Magn. 51 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Yan Y, Geng L, Zhang L, Tu C, Sri Ramdas R M, Liu H, Li X, Sanghadasa M, Ngo K D T, Wang Y U, Priya S 2020 IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 12 44981
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Lou J, Reed D, Liu M, Sun N X 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 94 112508 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 94 112508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Liu G, Cui X, Dong S 2010 J. Appl. Phys. 108 094106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Geng L, Yan Y, Priya S, Wang Y U 2020 ACS Applied Mater. Interfaces 12 44981
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Geng L W D, Yan Y K, Priya S, Wang Y U 2017 Acta Mater. 140 97
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Geng L D, Yan Y, Priya S, Wang Y U 2019 Acta Mater. 166 493
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Geng L D, Yan Y, Priya S, Wang Y U 2020 Phys. Rev. B 101 054422
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Ma F D, Jin Y M, Wang Y U, Kampe S L, Dong S 2014 Acta Mater. 70 45
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang Y, Wang Z, Ge W, Luo C, Li J, Viehland D, Chen J, Luo H 2014 Phys. Rev. B 90 134107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wang Y, Wen X, Jia Y, Huang M, Wang F, Zhang X, Bai Y, Yuan G, Wang Y 2020 Nat. Commun. 11 1328
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 李飞, 张树君, 徐卓 2020 69 217703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li F, Zhang S J, Xu Z 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 217703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Chu Z, Shi H, Shi W, Liu G, Wu J, Yang J, Dong S 2017 Adv Mater. 29 1606022
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wang Y J, Gray D, Berry D, Gao J Q, Li M H, Li J F, Viehland D 2011 Adv. Mater. 23 4111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Liu G, Ci P, Dong S 2014 Appl. Phys. Lett. 104 032908
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chu Z, PourhosseiniAsl M, Dong S 2018 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 51 243001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wang Y, Li J, Viehland D 2014 Mater. Today 17 269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Chu Z, Dong C, Tu C, He Y, Liang X, Wang J, Wei Y, Chen H, Gao X, Lu C, Zhu Z, Lin Y, Dong S, McCord J, Sun N X 2019 Phys. Rev. Appl. 12 044001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 王慧, 徐萌, 郑仁奎 2020 69 017301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H, Xu M, Zheng R K 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 017301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Li M, Wang Y, Hasanyan D, Li J, Viehland D 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 100 132904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wang Y, Wang D, Yuan G, Ma H, Xu F, Li J, Viehland D, Gehring P M 2016 Phys. Rev. B 94 174103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Wang D, Yuan G, Luo H, Li J, Viehland D, Wang Y 2017 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 100 4938
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Yan Y K, Geng L W D, Zhang L J, Gao X Y, Gollapudi S, Song H C, Dong S X, Sanghadasa M, Ngo K, Wang Y U, Priya S 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 16008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 7117
- PDF下载量: 184
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: