-
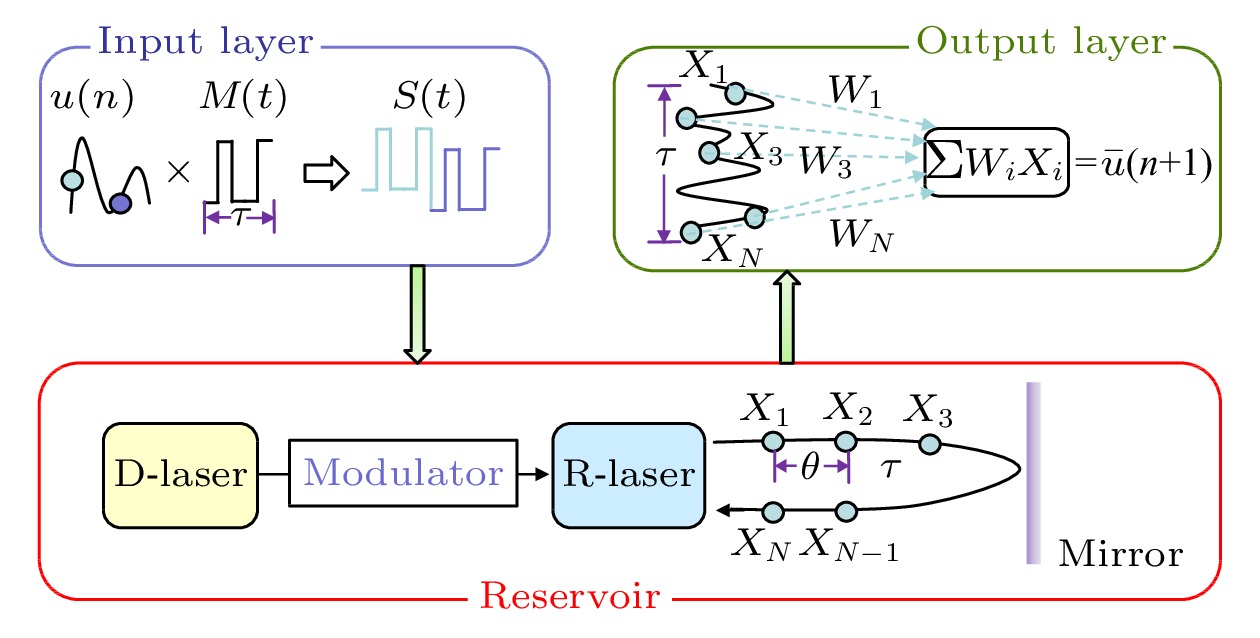
Prediction of chaotic laser has a wide prospect of applications, such as retrieving lost data, providing assists for data analysis, testing data encryption security in cryptography based on chaotic synchronization of lasers. We propose and demonstrate a new method of using time delayed photonic reservoir computing (RC) to forecast the continuous dynamical evolution of chaotic laser from previous measurements. Specifically, the time delayed photonic RC based on semiconductor laser with optical injection and feedback structure is established as a prediction system. Chaotic laser, as input signal, is generated by semiconductor laser with external disturbance. The time delayed photonic RC used in this stage is a novel implementation, which consists of three parts: the input layer, the reservoir and the output layer. In the input layer, the chaos laser from the semiconductor with an optical feedback needs to preprocess and multiply by a mask signal. The reservoir is the master-slave configuration consisting of a response laser with the optical feedback and light injection. In the feedback loop, there are N virtual nodes at each interval θ with a delay time of τ (N = τ/θ). The reservoir performs the mapping of the input signal onto a high-dimensional state space. In the output layer, the output of the reservoir is a linear combination of the reservoir state and the output weight. The output weight is optimized by minimizing the mean-square error between target value and output value through using the ridge regression algorithm. The results demonstrate that time delayed photonic RC based on semiconductor laser can forecast the trajectory of chaotic laser in about 2 ns. Moreover, we also investigate the influence of critical parameters on prediction result, including the type of the mask, the quantity of the virtual nodes, the length of the training data, the input gain, the feedback strength, the injection strength, the ridge parameter and the leakage rate. The method used here in this work has many attractive advantages, such as simple configuration, low training cost and eminently suitable for hardware implementation. Although the prediction length is limited, the significant innovation using time delayed photonic RC based on semiconductor lasers as the prediction system of chaotic laser presents a new opportunity for further developing a technique for predicting chaotic laser. -
Keywords:
- reservoir computing /
- prediction /
- chaotic laser /
- machine learning
[1] Amil P, Soriano M C, Masoller C 2019 Chaos 29 113111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Cunillera A, Soriano M C, Fischer I 2019 Chaos 29 113113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Meng Q F, Peng Y H 2007 Phys. Lett. A 370 465
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Lin X W, Yang Z H, Song Y X 2009 Expert Syst. Appl. 36 7313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Pathak J, Wikner A, Fussell R, Chandra S, Hunt B R, Girvan M, Ott E 2018 Chaos 28 041101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Pathak J, Hunt B, Girvan M, Lu Z X, Ott E 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 120 024102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Covas E, Benetos E 2019 Chaos 29 063111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Appeltant L, Soriano M C, Van d S G, Danckaert J, Massar S, Dambre J, Schrauwen B, Mirasso C R, Fischer I 2011 Nat. Commun. 2 468
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Hicke K, Escalona-Moran M A, Brunner D, Soriano M C, Fischer I, Mirasso C R 2013 IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 19 4
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Paquot Y, Duport F, Smerieri A, Dambre J, Schrauwen B, Haelterman M, Massar S 2012 Sci. Rep. 2 287
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Duport F, Schneider B, Smerieri A, Haelterman M, Massar S 2012 Opt. Express 20 A20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Martinenghi R, Rybalko S, Jacquot M, Chembo Y K, Larger L 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 244101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Larger L, Soriano M C, Brunner D, Appeltant L, Gutierrez J M, Pesquera L, Mirasso C R, Fischer I 2012 Opt. Express 20 3241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Dejonckheere A, Duport F, Smerieri A, Fang L, Oudar J L, Haelterman M, Massar S 2014 Opt. Express 22 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Appeltant L, Sande G V D, Danckaert J, Fischer I 2014 Sci. Rep. 4 3629
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Nguimdo R M, Verschaffelt G, Danckaert J, Van der Sande G 2014 Opt. Express 22 8672
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Nguimdo R M, Verschaffelt G, Danckaert J, Van der Sande G 2015 IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 26 3301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Vinckier Q, Duport F, Smerieri A, Vandoorne K, Bienstman P, Haelterman M, Massar S 2015 Optica 2 438
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Larger L, Baylón-Fuentes A, Martinenghi R, Udaltsov V S, Chembo Y K, Jacquot M 2017 Phys. Rev. X 7 011015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Takano K, Sugano C, Inubushi M, Yoshimura K, Sunada S, Kanno K, Uchida A 2018 Opt. Express 26 29424
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Vatin J, Rontani D, M Sciamanna 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 4497
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Vatin J, Rontani D, M Sciamanna 2019 Opt. Express 27 018579
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Tan X S, Hou Y S, Wu Z M, Xia G Q 2019 Opt. Express 27 026082
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Guo X X, Xiang S Y, Zhang Y H, Lin L, Wen A J, Hao Y 2019 IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 26 1700109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Li P, Cai Q, Zhang J, Xu B, Wang Y 2019 Opt. Express 27 017859
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Nakayama J, Kanno K, Uchida A 2016 Opt. Express 24 8679
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Lang R, Kobayashi K 1980 IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 16 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wieczorek S, Krauskopf B, Simpson T B, Lenstra D 2005 Phys. Rep. 416 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Hoerl A E, Kennard R W 1970 Technometrics 12 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Lukosevicius M, Jaeger H 2009 Comput. Sci. Rev. 3 127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
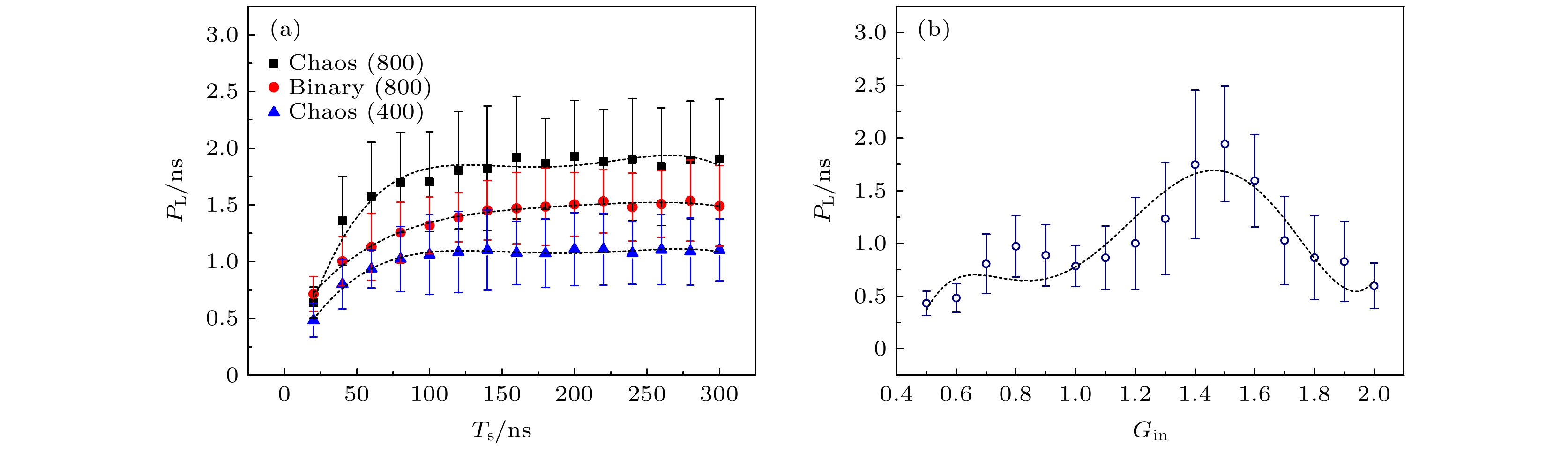
图 3 (a) 在不同掩模类型和不同节点数的情况下, 预测长度(PL)随训练长度(Ts)变化的趋势图; (b) 在使用混沌掩模信号且节点数为800的情况下, 预测长度(PL)随输入增益(Gin)变化的趋势图; 虚线为拟合曲线
Fig. 3. (a) PL as a function of the length of the training data (Ts) under different type of masks and the number of nodes; (b) PL as a function of the input gain (Gin) under N = 800 with the chaos mask signal. The dotted lines represent the associated fitting curves.
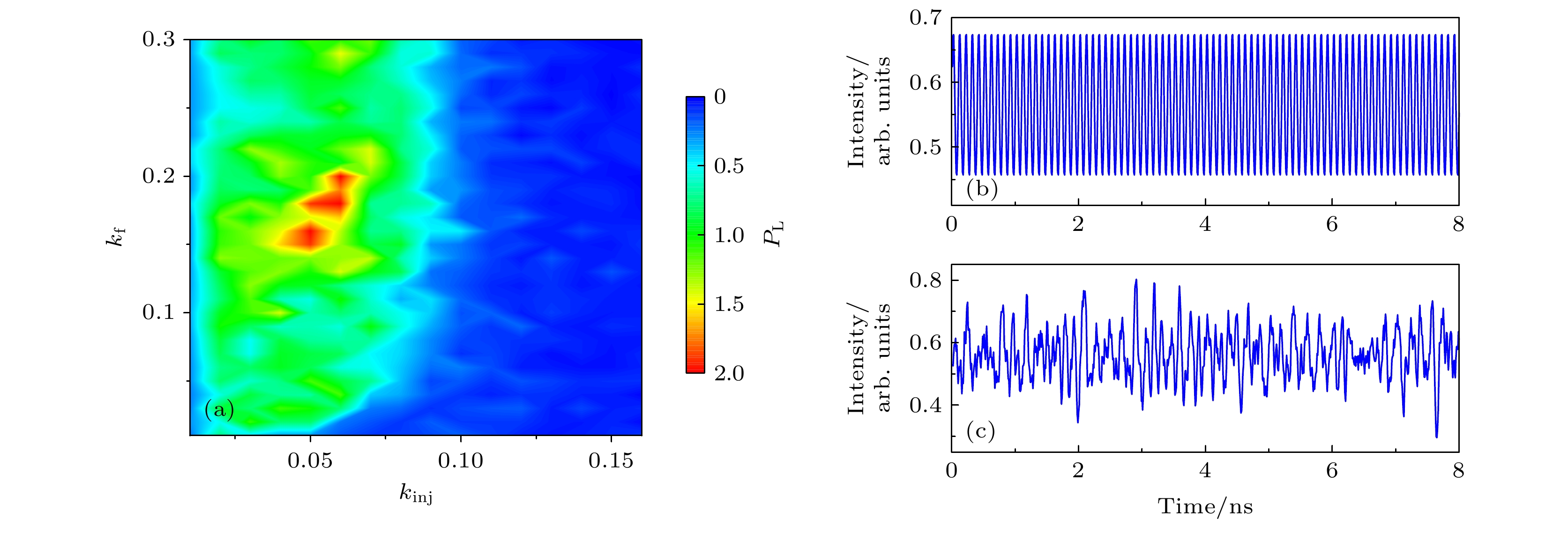
图 4 (a)预测系统在不同反馈强度(kf)和注入强度(kinj)的参数空间中PL值的二维图; (b), (c) 在(kinj, kf) = (0.06, 0.18)的条件下, 无调制信号和有调制信号时R-laser的输出强度时序
Fig. 4. (a) Two-dimensional map of the PL values of prediction system in the parameter space of the different feedback strength (kf) and the injection strength (kinj); (b), (c) temporal traces of the R-laser under (kinj, kf) = (0.06, 0.18) without and with modulated input data.
表 1 数值模拟中使用的激光器参数值
Table 1. Laser parameter values used in numerical simulations.
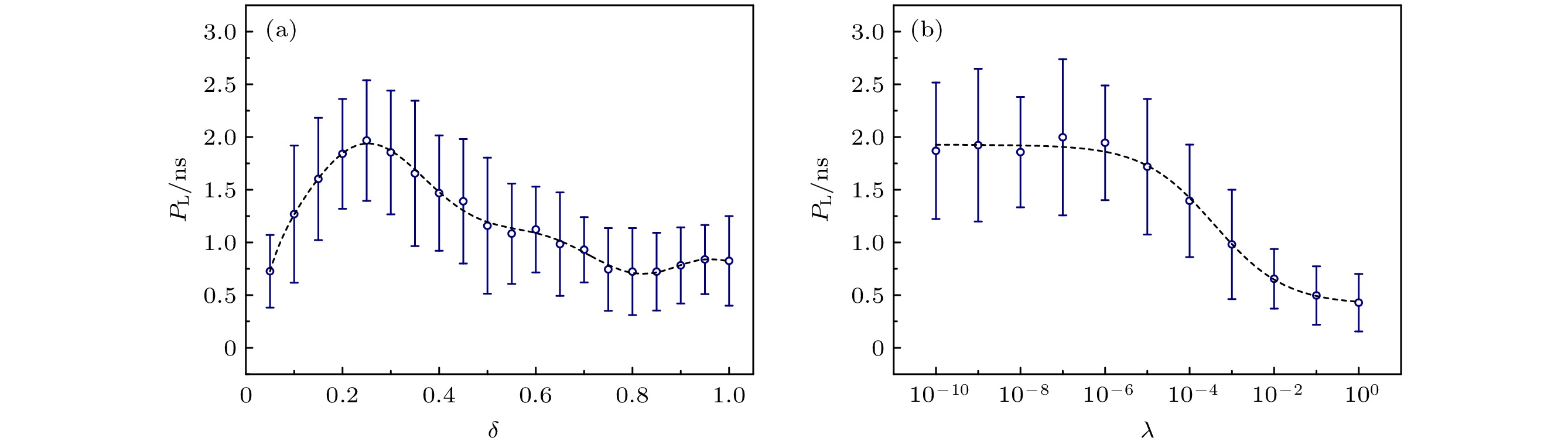
符号 参数 参考值 q/C 电子电荷量 1.6 × 10–19 α 线宽增强因子 5.0 g/(m3·s–1) 微分增益 1.414 × 10–12 N0/ m-3 透明载流子密度 1.4 × 1024 ε 增益饱和系数 5.0 × 10–23 τp/ps 光子寿命 1.92 τs/ns 载流子寿命 2.04 τin/ps 内腔往返时间 7.38 kf 反馈强度 0.18 kinj 注入强度 0.06 ∆ν/GHz 频率失谐 –10 τ/ns 外腔反馈延时 8 (N = 800) θ/ns 节点间隔 0.01 Id/Ith D-laser的归一化偏置电流 1.2 Ir/Ith R-laser的归一化偏置电流 1.25 Gin 输入增益 1.5 λ 岭参数 10–6 δ 泄漏率 0.25 -
[1] Amil P, Soriano M C, Masoller C 2019 Chaos 29 113111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Cunillera A, Soriano M C, Fischer I 2019 Chaos 29 113113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Meng Q F, Peng Y H 2007 Phys. Lett. A 370 465
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Lin X W, Yang Z H, Song Y X 2009 Expert Syst. Appl. 36 7313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Pathak J, Wikner A, Fussell R, Chandra S, Hunt B R, Girvan M, Ott E 2018 Chaos 28 041101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Pathak J, Hunt B, Girvan M, Lu Z X, Ott E 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 120 024102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Covas E, Benetos E 2019 Chaos 29 063111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Appeltant L, Soriano M C, Van d S G, Danckaert J, Massar S, Dambre J, Schrauwen B, Mirasso C R, Fischer I 2011 Nat. Commun. 2 468
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Hicke K, Escalona-Moran M A, Brunner D, Soriano M C, Fischer I, Mirasso C R 2013 IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 19 4
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Paquot Y, Duport F, Smerieri A, Dambre J, Schrauwen B, Haelterman M, Massar S 2012 Sci. Rep. 2 287
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Duport F, Schneider B, Smerieri A, Haelterman M, Massar S 2012 Opt. Express 20 A20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Martinenghi R, Rybalko S, Jacquot M, Chembo Y K, Larger L 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 244101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Larger L, Soriano M C, Brunner D, Appeltant L, Gutierrez J M, Pesquera L, Mirasso C R, Fischer I 2012 Opt. Express 20 3241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Dejonckheere A, Duport F, Smerieri A, Fang L, Oudar J L, Haelterman M, Massar S 2014 Opt. Express 22 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Appeltant L, Sande G V D, Danckaert J, Fischer I 2014 Sci. Rep. 4 3629
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Nguimdo R M, Verschaffelt G, Danckaert J, Van der Sande G 2014 Opt. Express 22 8672
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Nguimdo R M, Verschaffelt G, Danckaert J, Van der Sande G 2015 IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 26 3301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Vinckier Q, Duport F, Smerieri A, Vandoorne K, Bienstman P, Haelterman M, Massar S 2015 Optica 2 438
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Larger L, Baylón-Fuentes A, Martinenghi R, Udaltsov V S, Chembo Y K, Jacquot M 2017 Phys. Rev. X 7 011015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Takano K, Sugano C, Inubushi M, Yoshimura K, Sunada S, Kanno K, Uchida A 2018 Opt. Express 26 29424
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Vatin J, Rontani D, M Sciamanna 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 4497
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Vatin J, Rontani D, M Sciamanna 2019 Opt. Express 27 018579
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Tan X S, Hou Y S, Wu Z M, Xia G Q 2019 Opt. Express 27 026082
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Guo X X, Xiang S Y, Zhang Y H, Lin L, Wen A J, Hao Y 2019 IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 26 1700109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Li P, Cai Q, Zhang J, Xu B, Wang Y 2019 Opt. Express 27 017859
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Nakayama J, Kanno K, Uchida A 2016 Opt. Express 24 8679
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Lang R, Kobayashi K 1980 IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 16 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wieczorek S, Krauskopf B, Simpson T B, Lenstra D 2005 Phys. Rep. 416 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Hoerl A E, Kennard R W 1970 Technometrics 12 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Lukosevicius M, Jaeger H 2009 Comput. Sci. Rev. 3 127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 8982
- PDF下载量: 212
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: