-
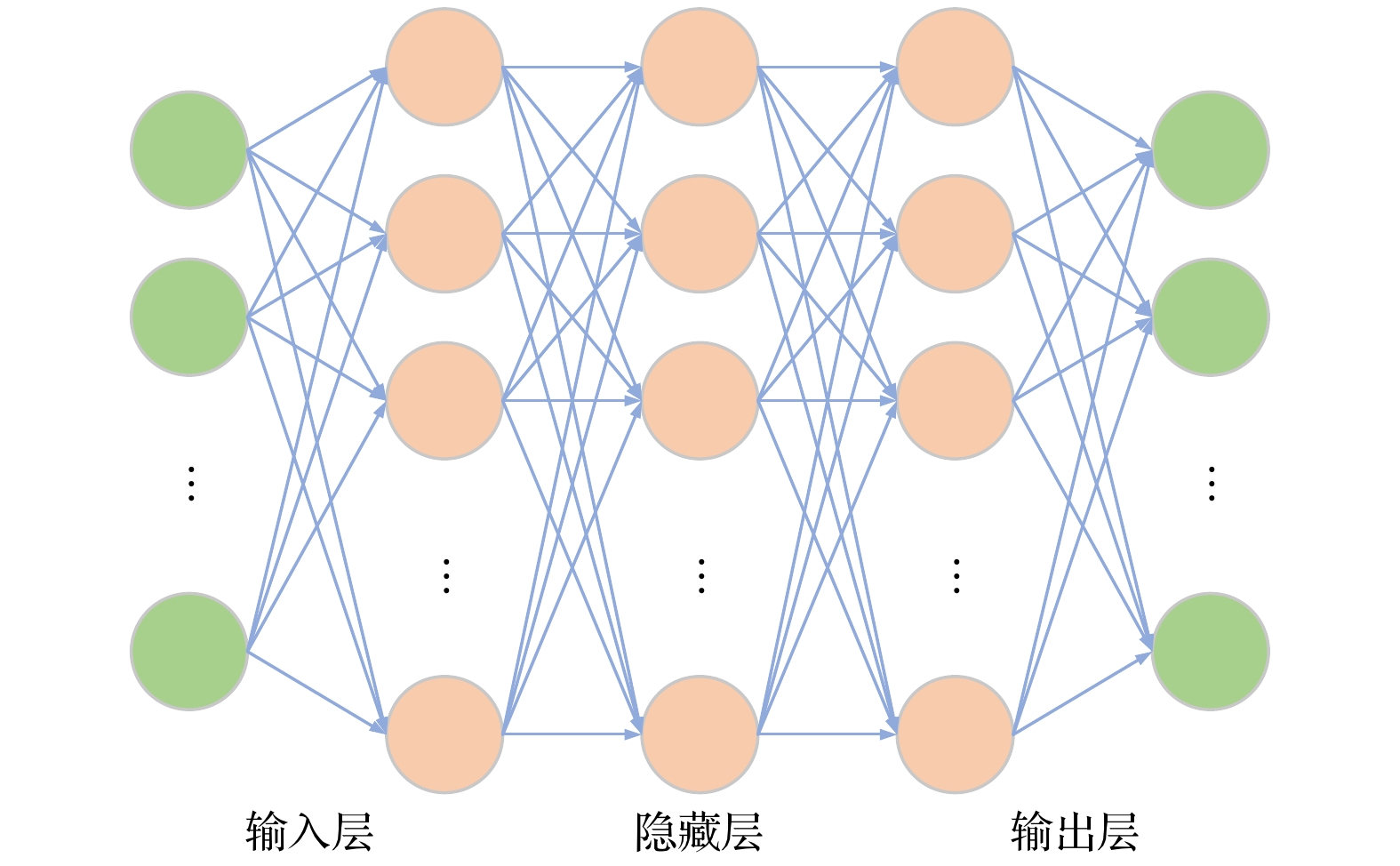
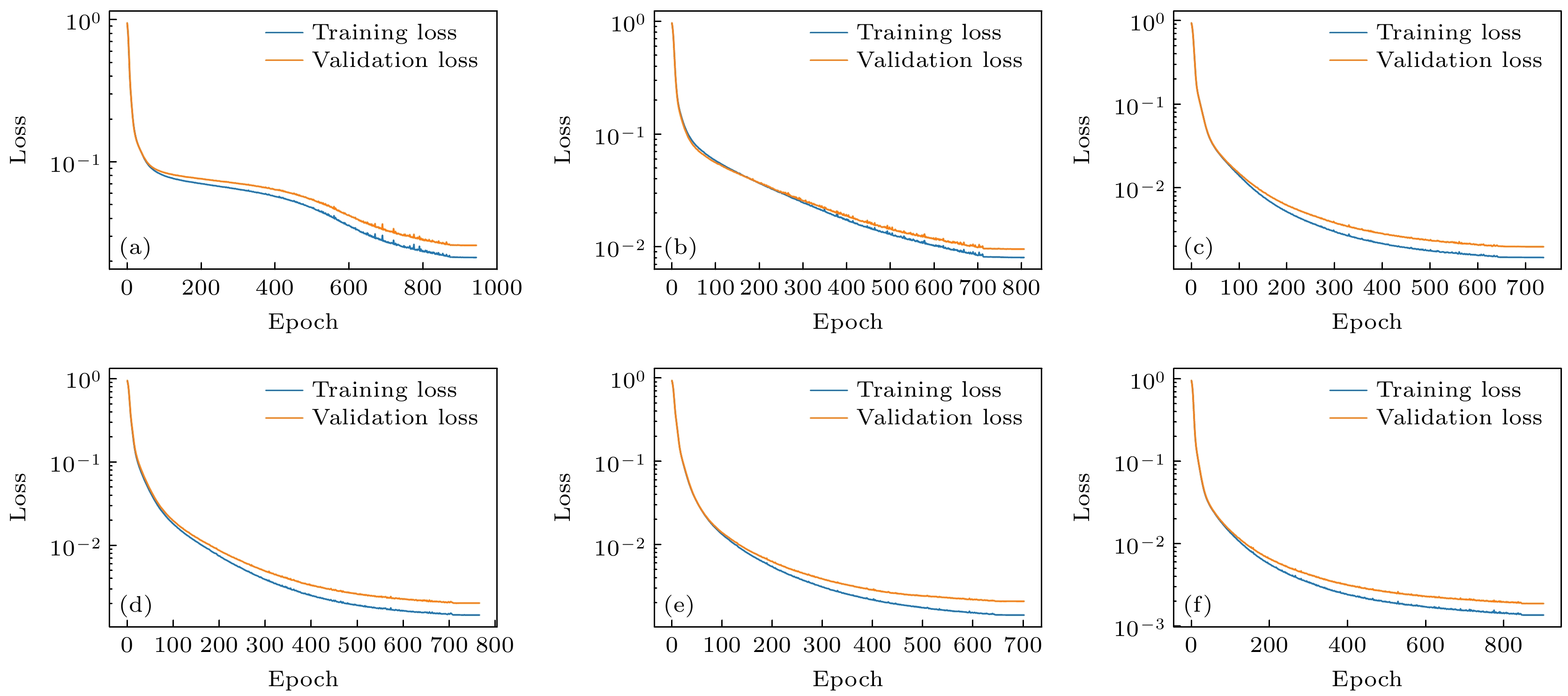
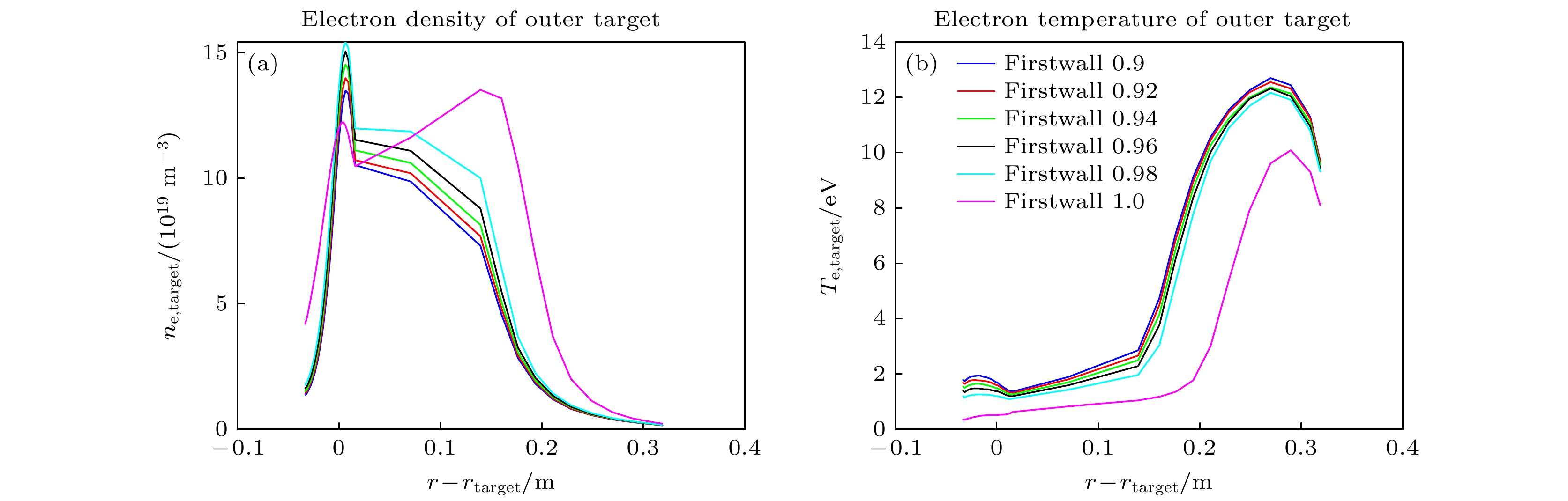
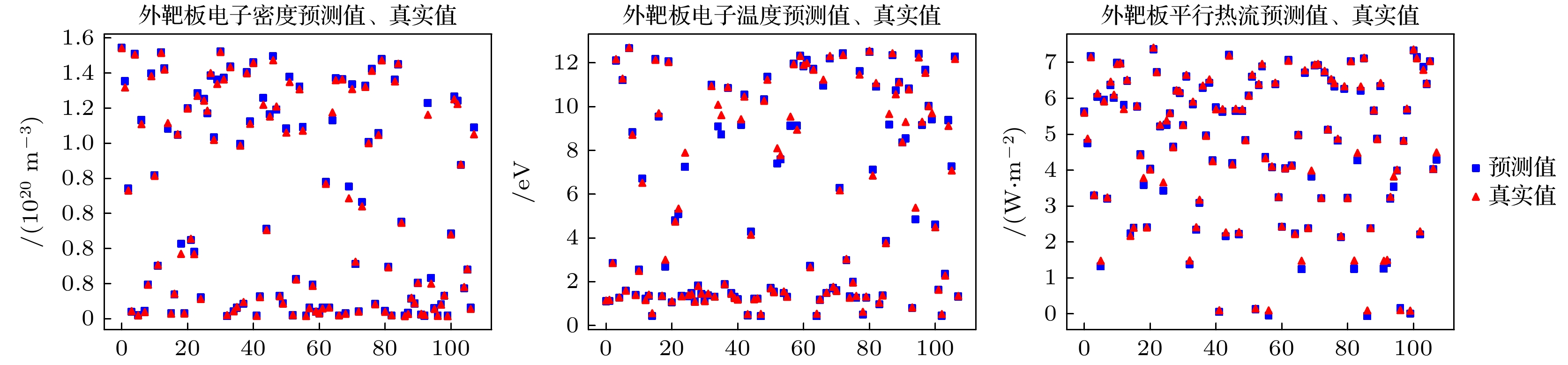
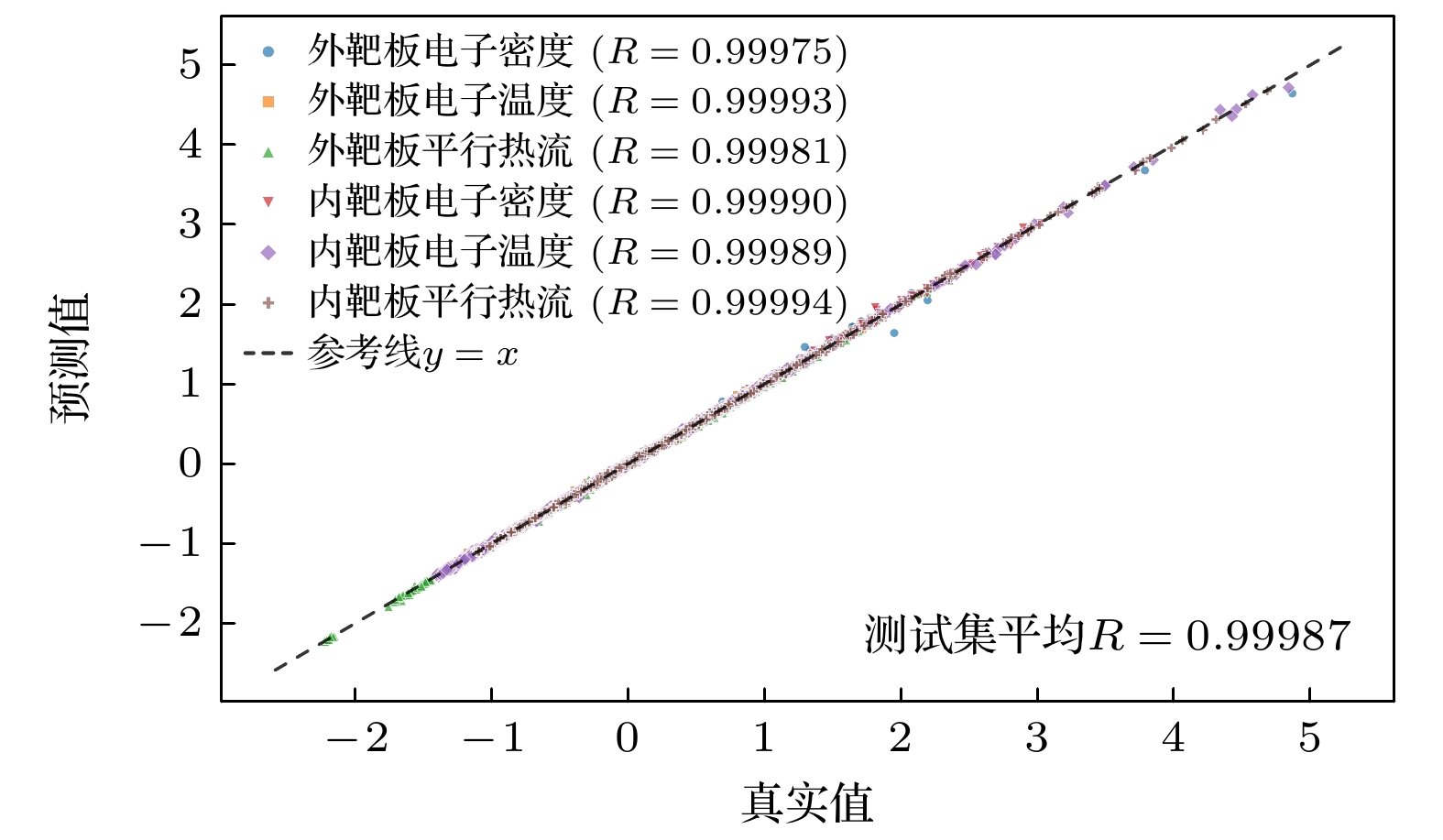
本文首次针对HL-3装置, 采用机器学习方法预测偏滤器靶板等离子体参数, 为未来快速预测大型聚变堆偏滤器热负荷奠定基础. 将机器学习应用于边缘等离子体物理中, 可以显著缩短大型边缘程序SOLPS-ITER模拟所需的时间, 从几周、几个月甚至半年缩短至毫秒级. 研究发现, 通过增加内外偏滤器区的辐射损失作为模型的输入参数, 能够明显提高预测精度(超过90%), 同时增强训练模型的适用性, 可以同时精确预测内外偏滤器靶板热流, 并验证了该特征参数与偏滤器靶板物理量之间的依赖关系. 该工作不仅为偏滤器物理研究提供了有效的方法, 也为未来跨装置预测偏滤器靶板参数提供了坚实的基础.
-
关键词:
- HL-3 /
- 机器学习 /
- 神经网络 /
- 偏滤器靶板热负荷 /
- SOLPS-ITER
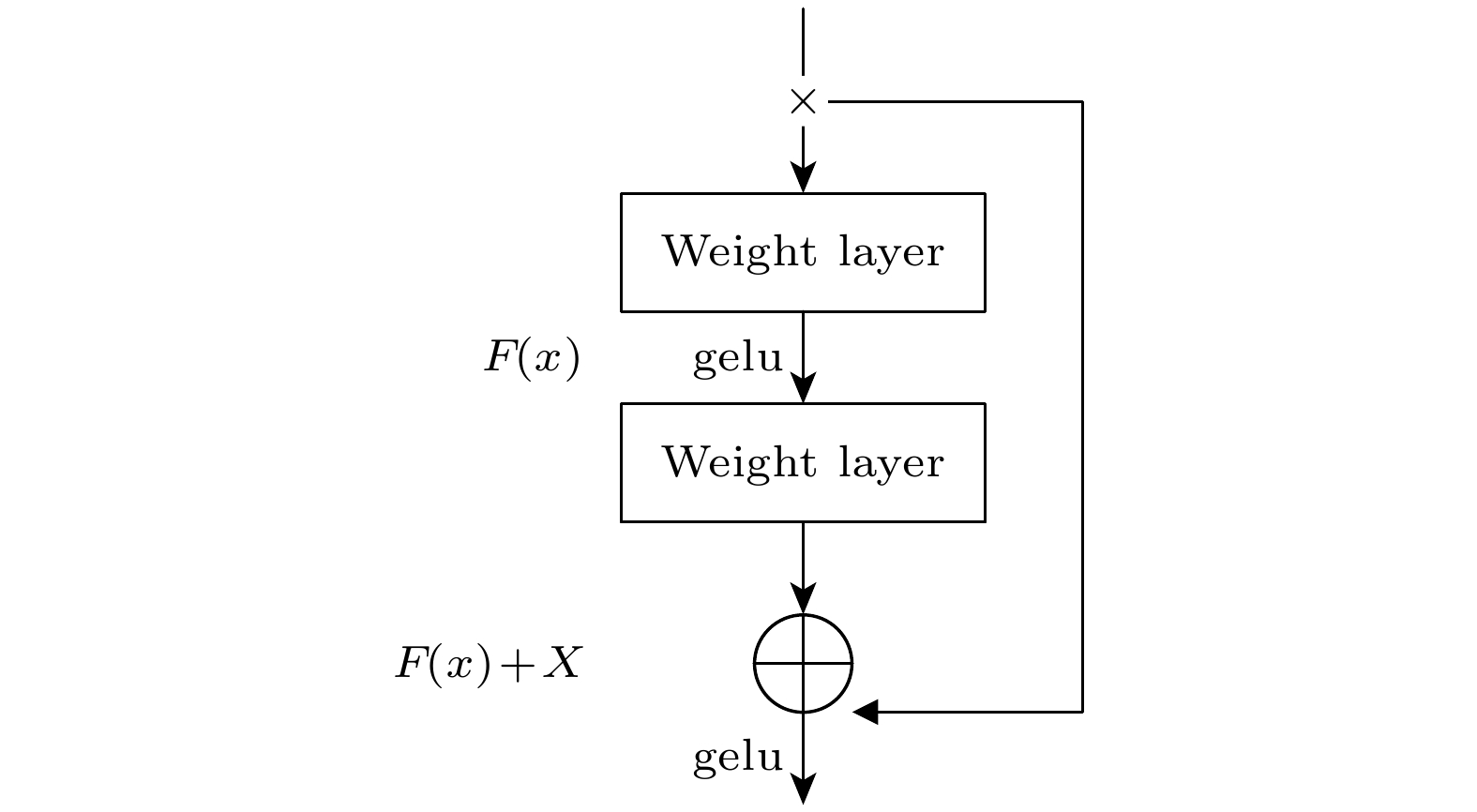
The SOLPS-ITER edge plasma simulation code has become a primary tool for designing divertor physics and predicting target plate heat load in fusion research. However, SOLPS-ITER-based divertor design requires not only substantial computational time but also intensive hardware resources, which fundamentally limits its application in advancing divertor optimization, particularly in large-scale fusion reactor divertor design. In this work, the machine learning method is used for the first time to predict the plasma parameters of the divertor target plate for HL-3, which provides a theoretical basis for predicting the heat load of divertor in large fusion reactor in the future. Based on the simulation of the edge plasma code SOLPS-ITER, we first build a database of HL-3 edge plasma parameters, including the upstream inner/outer midplane region and divertor target region. Then, we use the machine learning method and combine with the database to develop an artificial neural network model. Finally, the artificial neural network is used to train a model by using the boundary plasma parameters of the HL-3 device, and the heat load of the divertor target plate is predicted by the given upstream plasma parameters. This work can effectively shorten the time of simulating edge plasma by SOLPS-ITER code from weeks, months or even half a year to several milliseconds. In this work, a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) model is established with different input parameters to predict the electron temperature, density, and parallel heat fluxes of the inner and outer divertor target plates. It is found that reasonably increasing upstream plasma parameters as inputs to the model can not only improve the model’s generalization ability and the accuracy of prediction (both reaching over 90%), but also verify the correlation between upstream plasma parameters and divertor target physical quantities. In addition, a more stable ResMLP model is established on the basis of MLP. This work demonstrates the feasibility of using the neural networks to predict the heat load of the divertor target plate. -
Keywords:
- HL-3 /
- machine learning /
- neural network /
- divertor target heat load /
- SOLPS-ITER
-
表 1 模型的详细输入参数
Table 1. Detailed input parameters of the model.
-
[1] 高翔, 万元熙, 丁宁, 彭先觉 2018 中国工程科学 20 25
Gao X, Wan Y X, Ding N, Peng X J 2018 SSCAE 20 25
[2] Kuang A Q, Ballinger S, Brunner D, Canik J, Creely A J, Gray T, Greenwald M, Hughes J W, Irby J, LaBombard B, Lipschultz B, Lore J D, Reinke M L, Terry J L, Umansky M, Whyte D G, Wukitch S 2020 J. Plasma Phys. 86 865860505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Du H L, Li J X, Xue L, Bonnin X, Zheng G Y, Xiao G L, Fan D M, Tong R H, Xue M, Song X, Wang S, Wu N, Ji X Q, Chen W, Zhong W L 2025 Nucl. Fusion 65 036023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Shi B, Yang Z D , Zhang B, Yang C, Gan K F, Chen M W, Yang J H, Zhang H, Qi LJ L, Gong X Z, Zhang X D, Wang W H 2017 Chin. Phys. Lett. 34 095201
[5] Pitts R A, Kukushkin A, Loarte A, Martin A, Merola M, Kessel C E, Komarov V, Shimada M 2009 Phys. Scr. T 138 014001
[6] Hayashi Y, Masuzaki S, Kobayashi M, Kawamura G, Mukai K, Tanaka H, Murase T 2025 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 67 025010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 杜海龙, 桑超峰, 王亮, 孙继忠, 刘少承, 汪惠乾, 张凌, 郭后扬, 王德真 2013 62 245206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Du H L, Sang C F, Wang L, Sun J Z, Liu S C, Wang H Q, Zhang L, Guo H Y, Wang D Z 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 245206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Chen W T, Sun J Z, Gao F, Peng L, Wang D Z 2022 Chin. Phys. B 31 075204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wang M , Nie Q Y, Huang T, Wang X G, Zhang Y J 2024 Chin. Phys. B 33 035204
[10] Si H, Ding R, Senichenkov I, Rozhansky V, Molchanov P, Liu X J, Jia G Z, Sang C F, Mao S F, Chan V 2022 Nucl. Fusion 62 026031
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Peng L, Sun Z, Sun J Z, Maingi R, Gao F, Bonnin X, Chang H Y, Wang W K, Liu J Y 2024 Chin. Phys. B 33 115201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Moscheni M, Meineri C, Wigram M, Carati C, De Marchi E, Greenwald M, Innocente P, LaBombard B, Subba F, Wu H, Zanino R 2022 Nucl. Fusion 62 056009
[13] Coster D P 2016 Contrib. Plasma Phys. 56 790
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 马锐垚, 王鑫, 李树, 勇珩, 上官丹骅 2024 73 072802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma R Y, Wang X, Li S, Yong H, Shangguan D H 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 072802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Li H, Fu Y L, Li J Q, Wang Z X 2023 Chin. Phys. Lett 40 125201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 陈俊杰, 胡文慧, 肖建元, 郭笔豪, 肖炳甲 2020 计算机系统应用 29 21
Chen J J, Hu W H, Xiao J Y, Guo B H, Xiao B J 2020 Comput. Syst. Appl. 29 21
[17] Liu B, Wang Y X 2024 Chin. Phys. B 33 084401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Yan Z P, Wang Q Y, Yu X Q, Li J Z 2024 Chin. Phys. Lett. 41 098901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yue J C, Chen R K, Ma D K, Hu S Q 2025 Chin. Phys. Lett. 42 036301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Bonnin X, Dekeyser W, Pitts R, Coster D, Voskoboynikov S, Wiesen S 2016 Plasma Fusion Res. 11 1403102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Schneider R, Bonnin X, Borrass K, Coster D P, Kastelewicz H, Reiter D, Rozhansky V A, Braams B J 2006 Contrib. Plasma Phys. 46 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Sytova E, Senichenkov I, Kaveeva E, Rozhansky V, Veselova I, Voskoboynikov S, Coster D 2016 43rd EPS Conference on Plasma Physics Liege, Belgium, July 4–8, 2016 p1.054
[23] Stangeby P C, Sang C F 2017 Nucl. Fusion 57 056007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 马逐曦 2023 博士学位论文 (长沙: 中南大学)
Ma Z X 2023 PhD Dissertation (Changsha: Central South University
[25] Meha D, Manan S 2021 Clin. eHealth 4 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Naskath J, Sivakamasundari G, Begum A A S 2022 Wirel. Pers. Commun. 128 2913
[27] Glorot X, Bordes A, Bengio Y 2011 The 14th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, April 11–13, 2011 p315
[28] Nair V, Hinton G E 2010 The 27th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) Haifa, Israel, June 21—24, 2010 p807
[29] Hochreiter S 1998 Int. J. Uncertain. Fuzziness Knowl. Based Syst. 6 107
[30] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E 2017 Commun. ACM 60 84
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 任进军, 王宁 2018 甘肃高师学报 23 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ren J J, Wang N 2018 Gansu Gaoshi Xuebao 23 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Touvron H, Bojanowski P, Caron M, Cord M, El-Nouby A, Grave E, Izacard G, Joulin A, Synnaeve G, Verbeek J, Jégou H 2022 IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 45 5314
计量
- 文章访问数: 361
- PDF下载量: 6
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: