-
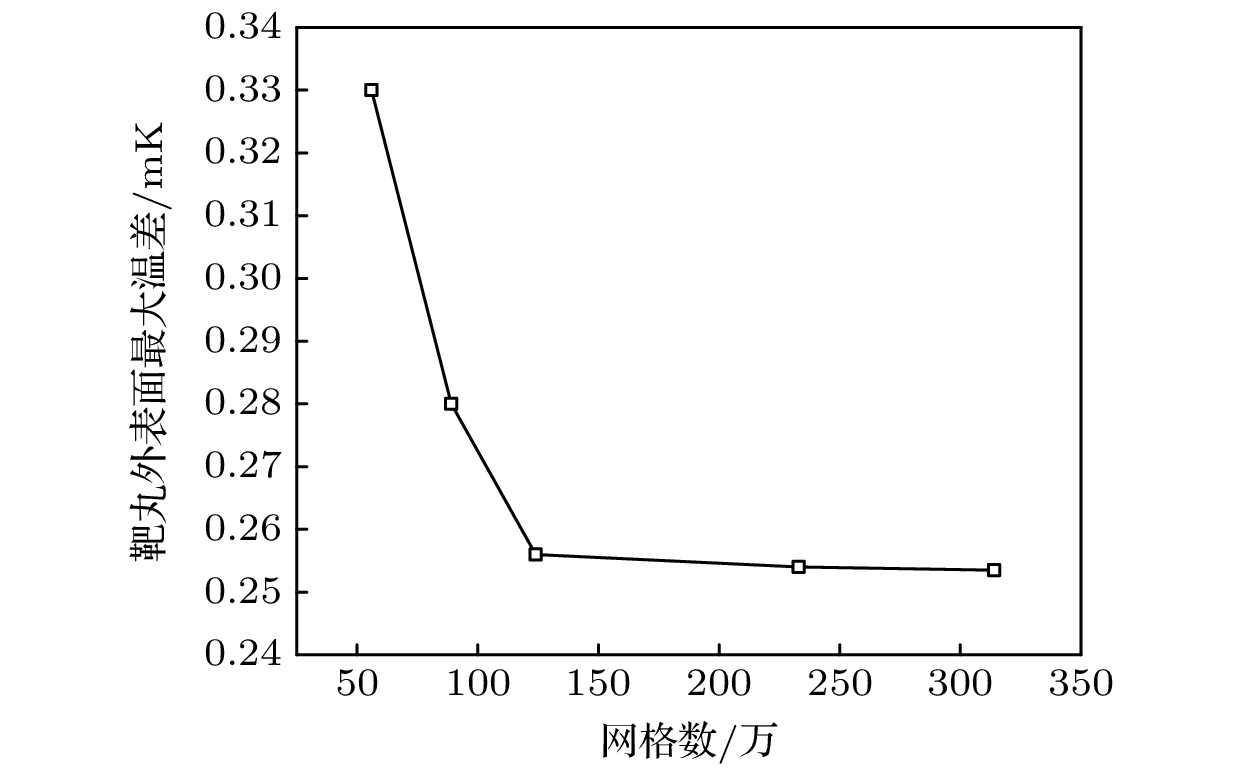
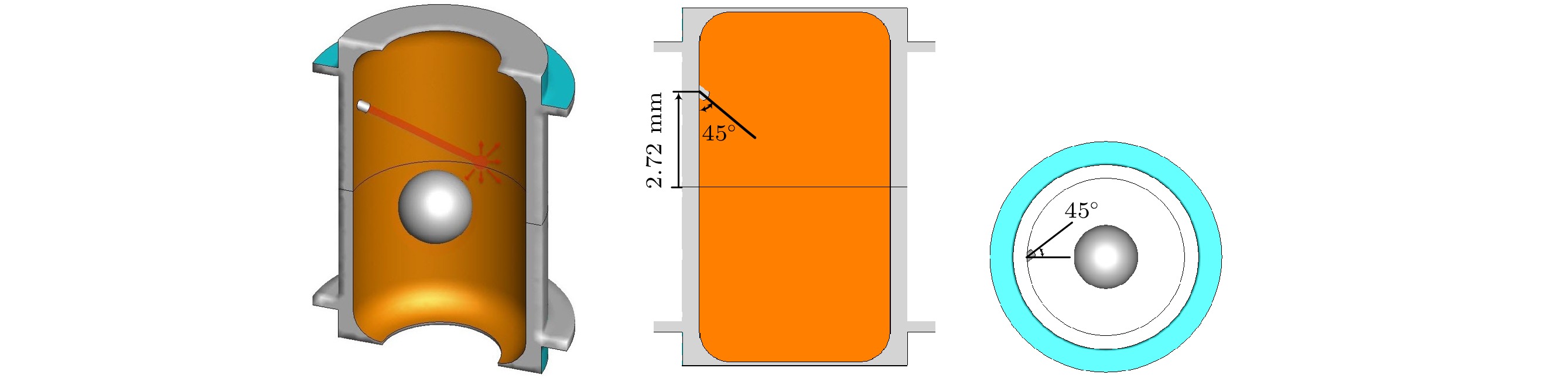
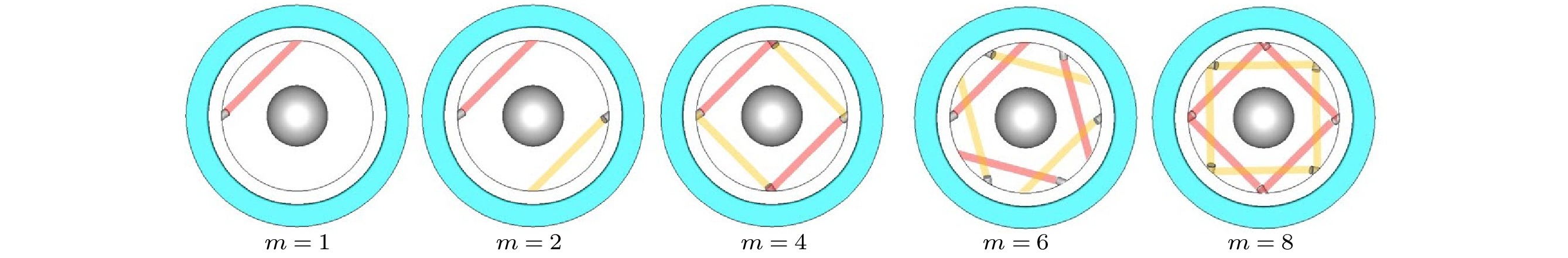
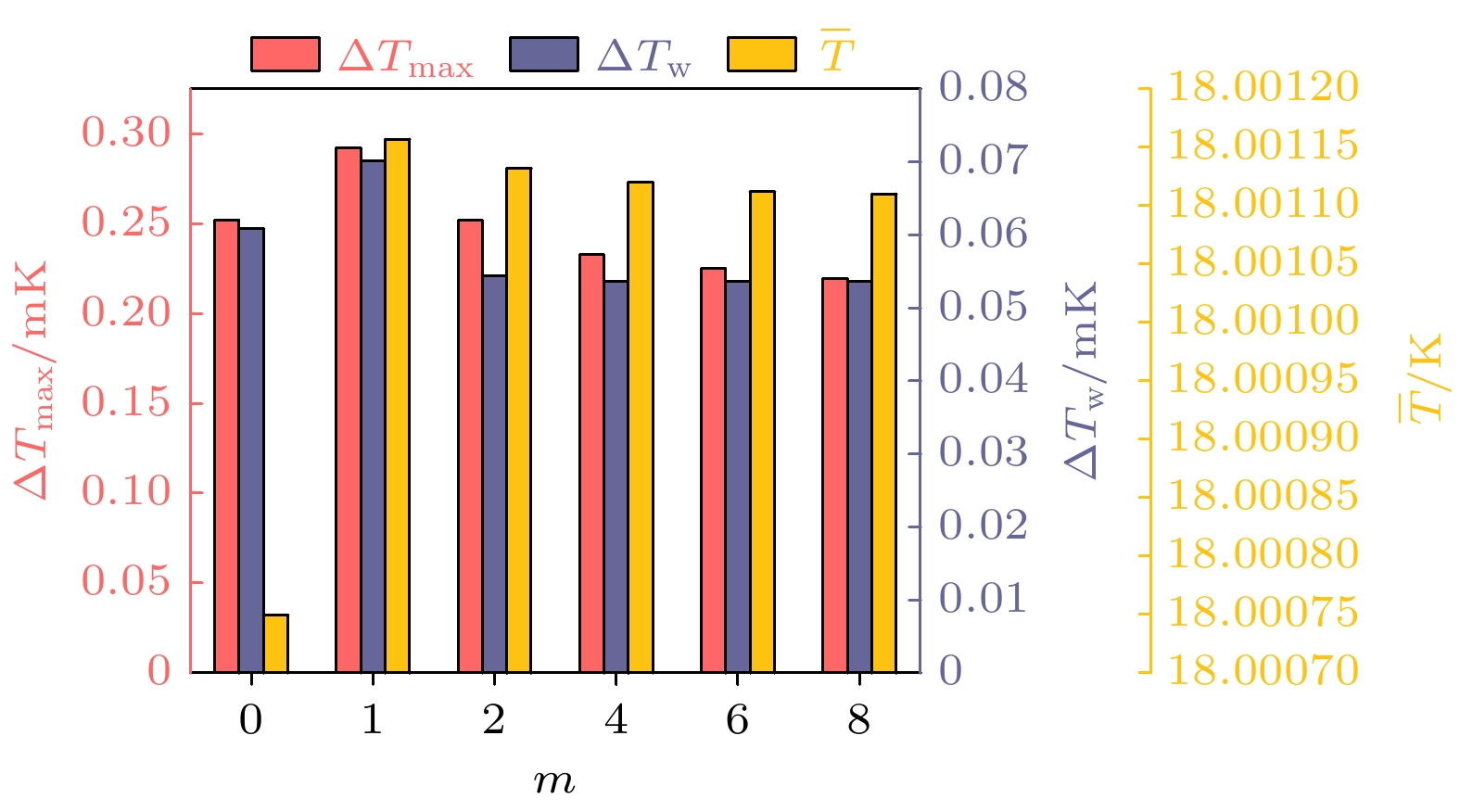
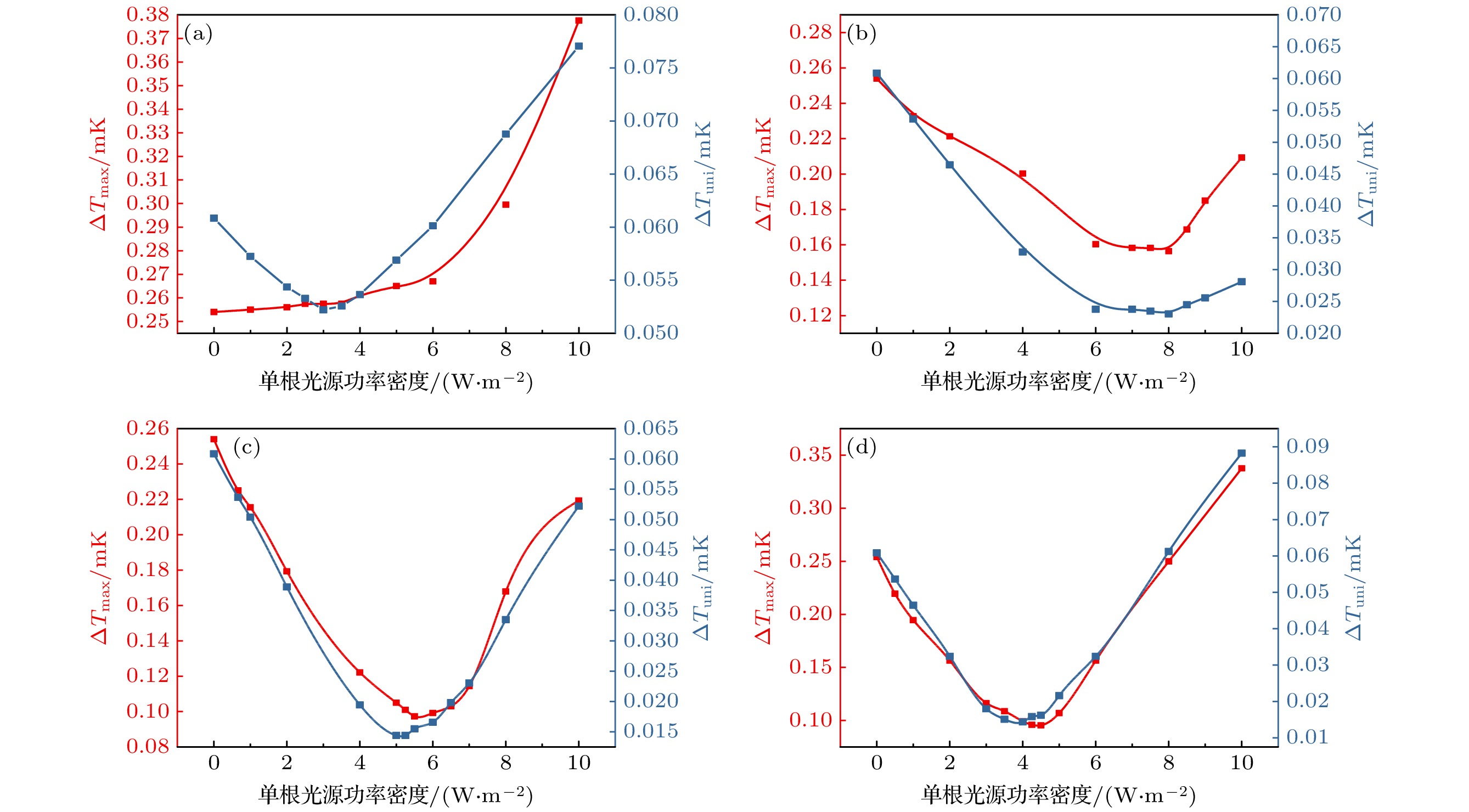
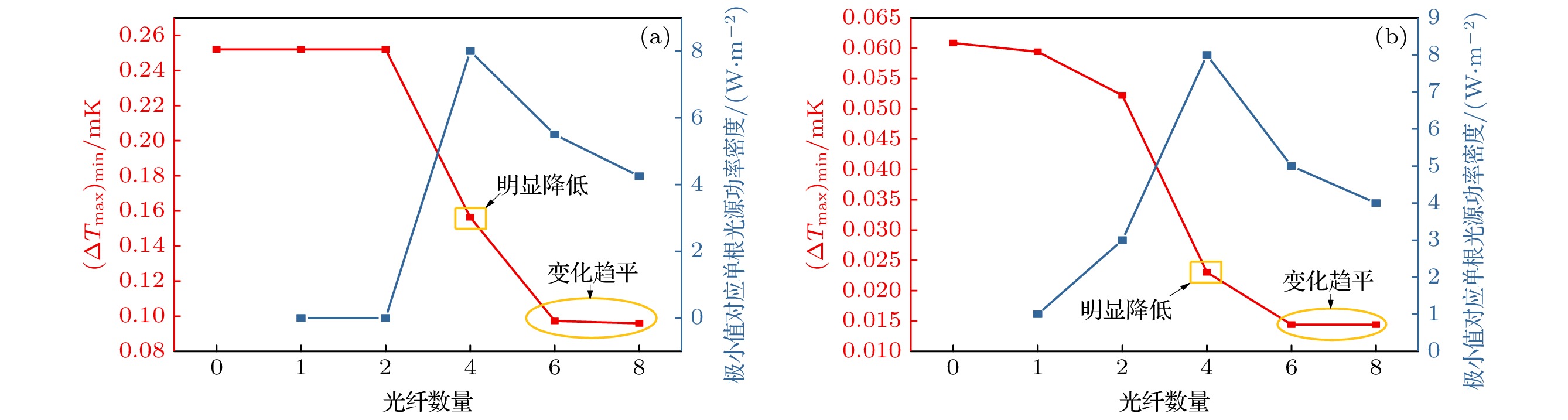
惯性约束核聚变成功的关键之一在于靶丸内要形成均匀的燃料冰层, 靶丸外表面温度特性对惯性约束聚变低温靶内形成均匀的燃料冰层有着决定性的影响. 为使得靶丸外表面温度场尽可能均匀, 需采用定向红外的方式对靶丸外表面温度进行局部调控. 采用全三维低温靶物理模型, 建立定向红外光路追踪与温度场计算耦合计算的光热耦合数值模型, 研究了定向红外条件下光纤布置形式及光源参数对低温靶温度场的影响规律. 结果表明: 在光纤总功率不变的前提下, 光纤数量越多, 靶丸外表面温度场均匀性越好. 光纤数量小于等于2时, 靶丸外表面温度场无法得到明显改善; 光纤数量大于2时, 靶丸外表面最大温差和加权温差降低幅值极限为61.94%和76.33%. 光纤投射的光斑向南北两极适量偏移可以改善靶丸外表面温度场均匀性, 其他的偏移方式会恶化温度场均匀性.For an inertial-confinement-fusion cryogenic target, the fusion ice layer inside the capsule should have a uniformity more than 99% and an inner surface roughness less than 1 μm (root mean square) to avoid Rayleigh-Taylor instabilities. And this highly smooth ice layer required for ignition is generated at the presence of volumetric heat and affected by the thermal environment around the capsule. For the D2 fuel targets, the volumetrically heating can be supplied by exposing the ice layer to IR radiation. A major challenge of IR-layering is a spherically uniform IR illumination of the capsule, particularly for capsules held in cylindrical hohlraums in indirect-drive targets. In the present study, a numerical study is conducted on the thermal environment of D2 fuel capsule under directional infrared radiation. A 3D simulation model coupling the photonic and thermal fields has been established based on the Monte Carlo ray tracing method. The influence of infrared optical fibers’ layouts and source power intensity on temperature characteristics outside the capsule have been studied. The results indicate that at constant total power of optical fibers, the more optical fibers set up, the lower the average temperature of the outer surface decreases, and the more uniform the capsule outer surface temperature turns to be. The temperature uniformity of capsule outer surface deteriorates with the two or less optical fibers, but improves with the number greater than 2 in which case ΔTmax and ΔTw can decrease by 61.94% and 76.33% at most. A proper offset of optical fiber spots towards the hohlraum poles can improve the temperature uniformity of capsule outer surface, while the other two optical fiber spot offset schemes deteriorate the temperature uniformity. The results are of guiding significance for determining the optical fibers layout in experiment and further design option for cryogenic targets.
-
Keywords:
- inertial confinement fusion /
- cryotarget /
- directional infrared irradiation /
- photothermal-coupling /
- numerical simulation
[1] 张歆, 章晓中, 谭新玉, 于奕, 万蔡华 2012 61 147303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X, Zhang X Z, Tan X Y, Yu Y, Wan C H 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 147303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 杨旭东, 陈汉, 毕恩兵, 韩礼元 2015 64 038404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang X D, Chen H, Bi E B, Han L Y 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 038404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Horvath A, Rachlew E 2016 Ambio 45 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Chen W M, Kim H, Yamaguchi H 2014 Energy Policy 74 31
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 张占文, 漆小波, 李波 2012 61 145204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Z W, Qi X B, Li B 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 145204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 黄鑫, 彭述明, 周晓松, 余铭铭, 尹剑, 温成伟 2015 64 215201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang X, Peng S M, Zhou X S, Yu M M, Yin J, Wen C W 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 215201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Tang J, Xie Z Y, Du A, Ye J J, Zhang Z H, Shen J, Zhou B 2016 J. Fusion Energ. 35 357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Holmlid L 2014 J. Fusion Energ. 33 348
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Lindl J D, Amendt P, Berger R L, Glendinning G, Glenzer S H, Haan S W, Kauffman R L, Landen O L, Suter L J 2004 Phys. Plasmas 11 339
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Baclet P, Bachelet F, Choux A, Fleury E, Jeannot L, Laffite S, Martin M, Moll G, Pascal G, Reneaume B, Theobald M 2006 Fusion Sci, Technol. 49 565
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 王凯, 谢瑞, 林伟, 刘元琼, 黎军, 漆小波, 唐永建, 雷海乐 2013 强激光与粒子束 25 3230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang K, Xie R, Lin W, Liu Y Q, Li J, Qi X B, Tang Y J, Lei H L 2013 High Power Laser and Particle Beams 25 3230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Hurricane O A, Callahan D A, Casey D T, Celliers P M, Cerjan C, Dewald E L, Dittrich T R, Doppner T, Hinkel D E, Berzak H L F, Kline J L, Le P S, Ma T, Macphee A G, Milovich J L, Pak A, Park H S, Patel P K, Remington B A, Salmonson J D, Springer P T, Tommasini R 2014 Nature 506 343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Lan K, He X T, Liu J 2014 Phys. Plasmas 21 052704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Harding D R, Ulreich J, Wittman M D 2018 Fusion Sci. Technol. 73 11
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 李翠, 陈洵, 厉彦忠 2019 西安交通大学学报 53 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li C, Chen X, LI Y Z 2019 Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University 53 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 林伟, 王凯, 毕鹏 2012 强激光与粒子束 25 2343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lin W, Wang K, BI P 2012 High Power Laser and Particle Beams 25 2343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] London R A, Kozioziemski B J, Marinak M M, Kerbel G D, Bittner D N 2006 Fusion Sci. Technol. 49 608
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Moll G, Baclet P, Martin M 2006 Fusion Sci. Technol. 49 574
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Moll G, Baclet P, Martin M 2007 Fusion Sci. Technol. 51 737
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Kozioziemski B J, London R A, McEachern R L, Bittner D N 2017 Fusion Sci. Technol. 45 262
[21] London R A, McEachern R L, Kozioziemski B J, Bittner D N 2017 Fusion Sci. Technol. 45 245
[22] 王凯, 林伟, 谢瑞, 刘元琼, 马坤全, 黎军, 唐永建, 雷海乐 2013 强激光与粒子束 25 4322
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang K, Lin W, Xie R, Liu Y Q, Ma K Q, Li J, Tang Y J, Lei H L 2013 High Power Laser and Particle Beams 25 4322
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Haan S W, Lindl D J, Callahan D A, Clark D S, Salmonson J D, Hammel B A, Atherton L J, Cook R C, Edwards M J, Glenzer S, Hamza A V 2011 Phys. Plasmas 18 051001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 陈鹏玮, 厉彦忠, 李翠, 代飞, 丁岚, 辛毅 2017 66 190702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen P W, Li Y Z, Li C, Dai F, Ding L, Xin Y 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 190702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 辛毅, 厉彦忠, 丁岚, 李翠 2019 原子能科学技术 53 6931
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xin Y, Li Y Z, Ding L, Li C 2019 Atomic Energy Science and Technology 53 6931
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Hong Y, Tao C Y, Gao S S, Qi X B, Jiang B B, Xie J, Liang J X, Zhang H J, Li G, Wei S, Tong W C, Yuan G H, Zhang Y J, Li X J 2020 Nuclear Fusion 60 026010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 不同材料在18 K环境下的物性参数
Table 1. Physical properties of different materials at 18 K
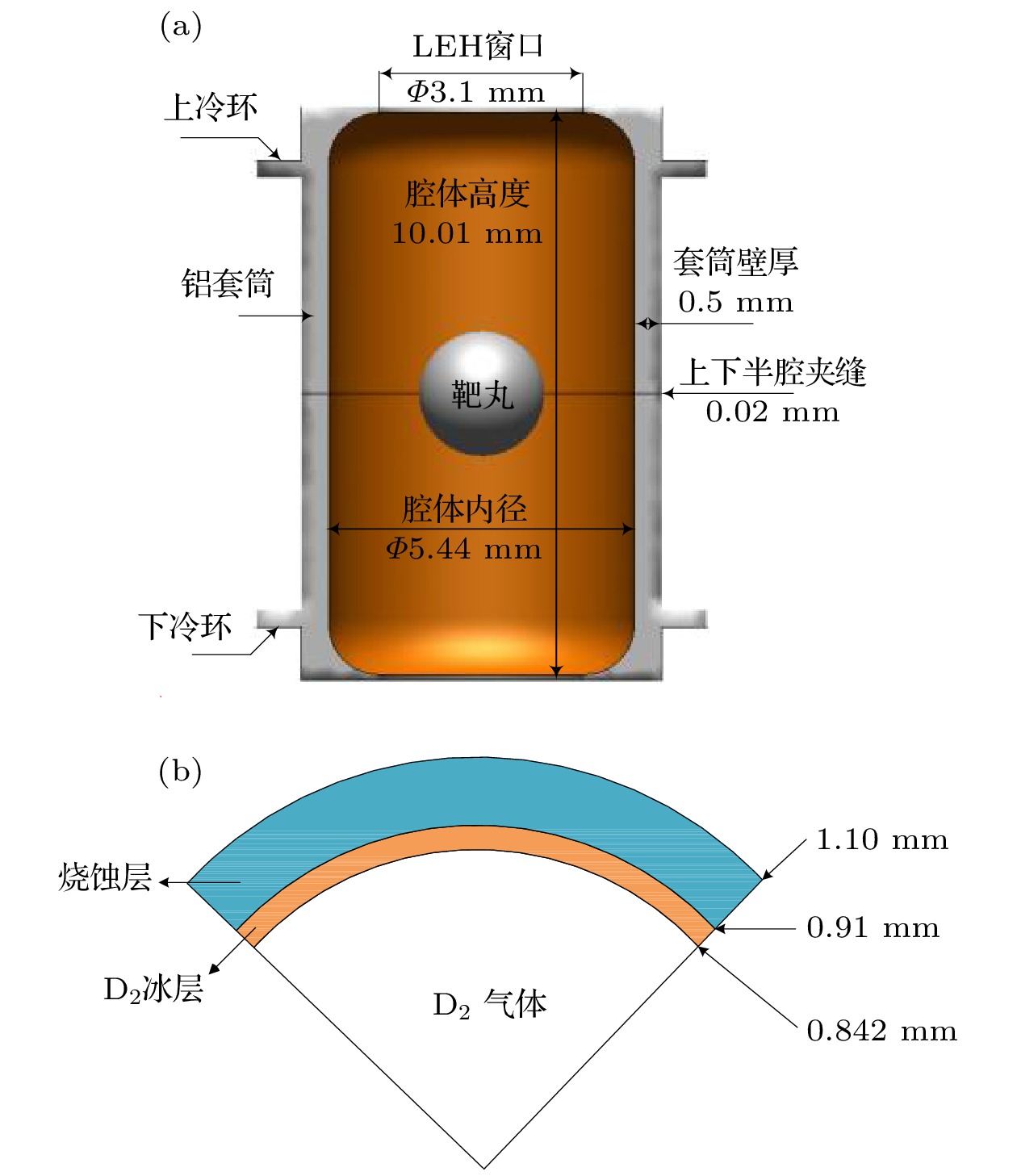
材料 密度ρ/ kg·m–3 热容cp/ J·kg–1·K–1 导热系数λ/ W·m–1·K–1 动力粘度μ/ kg·m–1·s–1 铝 2710 8.37 27 — 金 19320 14.66 1173.44 — 靶壳 1100 57.49 0.057 — He@1 kPa 0.3 5292.6 0.021 1.31 × 10–6 气态D2 0.025 5193.7 0.024 3.42 × 10–6 固态D2 260 5000 0.29 — (注: 本文不考虑气体对定向红外的影响, 因此氦气和氘气的吸收系数和散射系数均为0) 表 2 不同光纤数量下的每根光纤出射功率密度
Table 2. The power density of each optical fiber corresponding to optical fiber numbers
m 1 2 4 6 8 单根功率密度/(W·m–2) 4.00 2.00 1.00 0.67 0.50 -
[1] 张歆, 章晓中, 谭新玉, 于奕, 万蔡华 2012 61 147303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X, Zhang X Z, Tan X Y, Yu Y, Wan C H 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 147303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 杨旭东, 陈汉, 毕恩兵, 韩礼元 2015 64 038404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang X D, Chen H, Bi E B, Han L Y 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 038404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Horvath A, Rachlew E 2016 Ambio 45 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Chen W M, Kim H, Yamaguchi H 2014 Energy Policy 74 31
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 张占文, 漆小波, 李波 2012 61 145204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Z W, Qi X B, Li B 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 145204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 黄鑫, 彭述明, 周晓松, 余铭铭, 尹剑, 温成伟 2015 64 215201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang X, Peng S M, Zhou X S, Yu M M, Yin J, Wen C W 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 215201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Tang J, Xie Z Y, Du A, Ye J J, Zhang Z H, Shen J, Zhou B 2016 J. Fusion Energ. 35 357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Holmlid L 2014 J. Fusion Energ. 33 348
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Lindl J D, Amendt P, Berger R L, Glendinning G, Glenzer S H, Haan S W, Kauffman R L, Landen O L, Suter L J 2004 Phys. Plasmas 11 339
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Baclet P, Bachelet F, Choux A, Fleury E, Jeannot L, Laffite S, Martin M, Moll G, Pascal G, Reneaume B, Theobald M 2006 Fusion Sci, Technol. 49 565
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 王凯, 谢瑞, 林伟, 刘元琼, 黎军, 漆小波, 唐永建, 雷海乐 2013 强激光与粒子束 25 3230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang K, Xie R, Lin W, Liu Y Q, Li J, Qi X B, Tang Y J, Lei H L 2013 High Power Laser and Particle Beams 25 3230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Hurricane O A, Callahan D A, Casey D T, Celliers P M, Cerjan C, Dewald E L, Dittrich T R, Doppner T, Hinkel D E, Berzak H L F, Kline J L, Le P S, Ma T, Macphee A G, Milovich J L, Pak A, Park H S, Patel P K, Remington B A, Salmonson J D, Springer P T, Tommasini R 2014 Nature 506 343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Lan K, He X T, Liu J 2014 Phys. Plasmas 21 052704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Harding D R, Ulreich J, Wittman M D 2018 Fusion Sci. Technol. 73 11
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 李翠, 陈洵, 厉彦忠 2019 西安交通大学学报 53 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li C, Chen X, LI Y Z 2019 Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University 53 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 林伟, 王凯, 毕鹏 2012 强激光与粒子束 25 2343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lin W, Wang K, BI P 2012 High Power Laser and Particle Beams 25 2343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] London R A, Kozioziemski B J, Marinak M M, Kerbel G D, Bittner D N 2006 Fusion Sci. Technol. 49 608
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Moll G, Baclet P, Martin M 2006 Fusion Sci. Technol. 49 574
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Moll G, Baclet P, Martin M 2007 Fusion Sci. Technol. 51 737
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Kozioziemski B J, London R A, McEachern R L, Bittner D N 2017 Fusion Sci. Technol. 45 262
[21] London R A, McEachern R L, Kozioziemski B J, Bittner D N 2017 Fusion Sci. Technol. 45 245
[22] 王凯, 林伟, 谢瑞, 刘元琼, 马坤全, 黎军, 唐永建, 雷海乐 2013 强激光与粒子束 25 4322
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang K, Lin W, Xie R, Liu Y Q, Ma K Q, Li J, Tang Y J, Lei H L 2013 High Power Laser and Particle Beams 25 4322
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Haan S W, Lindl D J, Callahan D A, Clark D S, Salmonson J D, Hammel B A, Atherton L J, Cook R C, Edwards M J, Glenzer S, Hamza A V 2011 Phys. Plasmas 18 051001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 陈鹏玮, 厉彦忠, 李翠, 代飞, 丁岚, 辛毅 2017 66 190702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen P W, Li Y Z, Li C, Dai F, Ding L, Xin Y 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 190702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 辛毅, 厉彦忠, 丁岚, 李翠 2019 原子能科学技术 53 6931
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xin Y, Li Y Z, Ding L, Li C 2019 Atomic Energy Science and Technology 53 6931
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Hong Y, Tao C Y, Gao S S, Qi X B, Jiang B B, Xie J, Liang J X, Zhang H J, Li G, Wei S, Tong W C, Yuan G H, Zhang Y J, Li X J 2020 Nuclear Fusion 60 026010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 6663
- PDF下载量: 62
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: