-
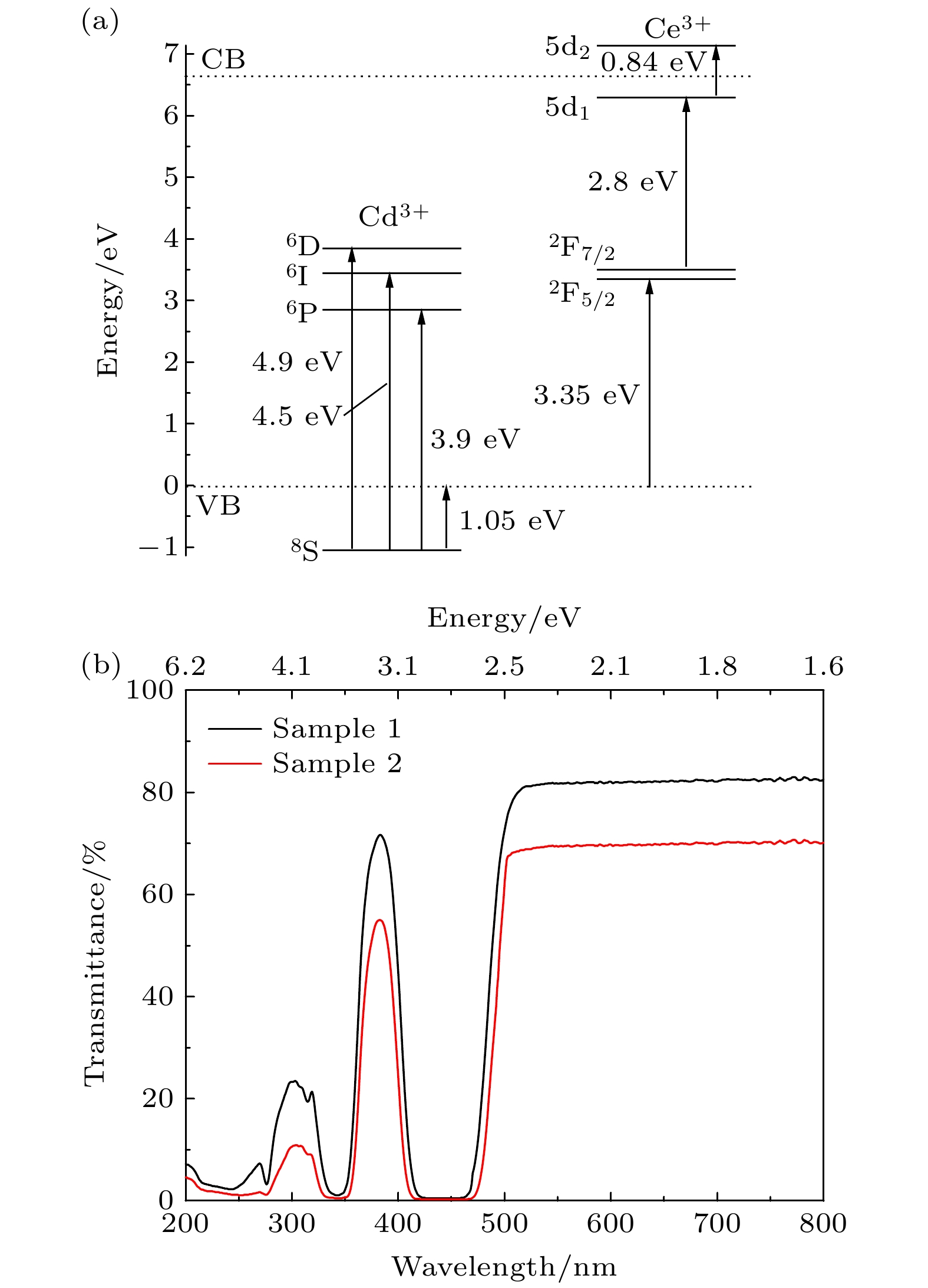
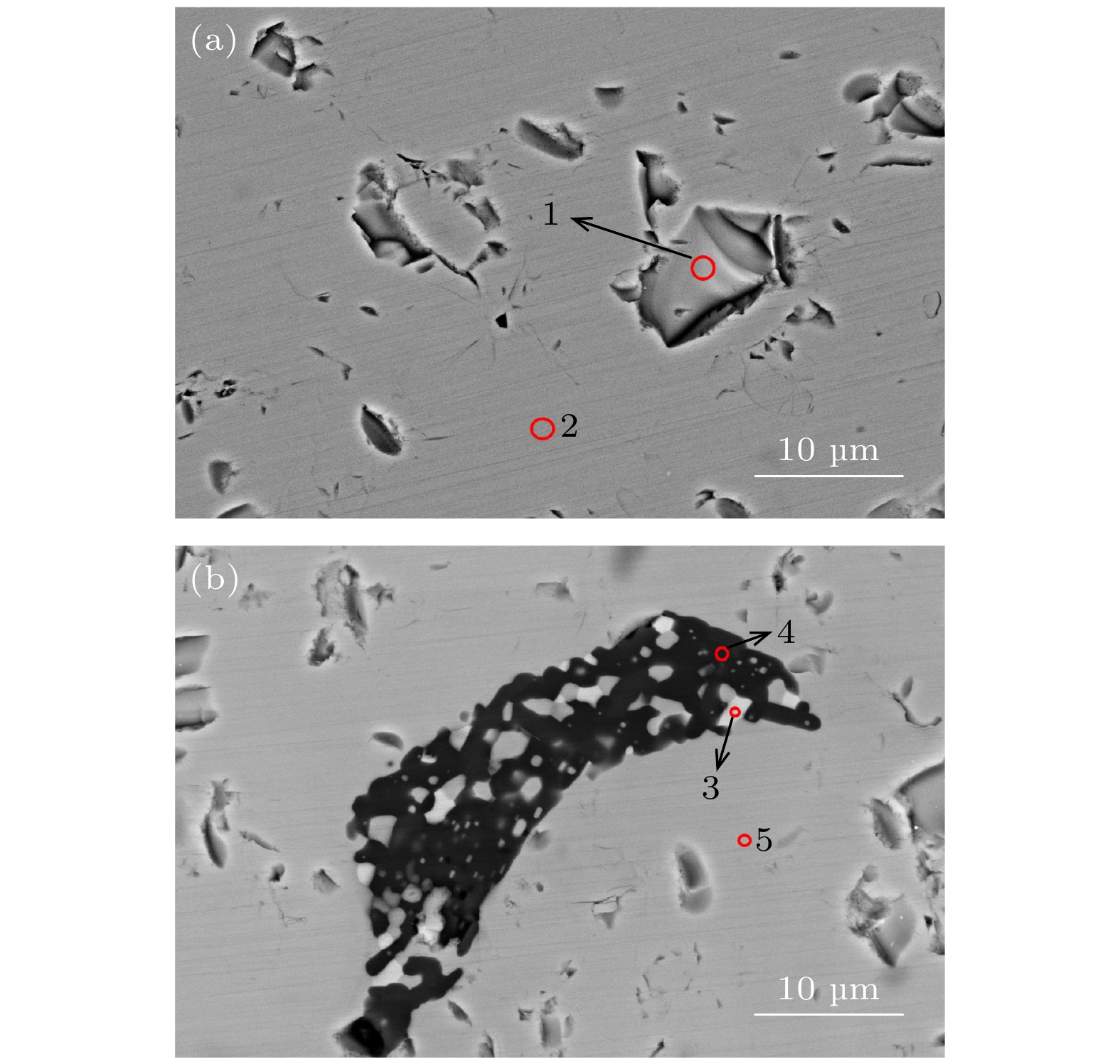
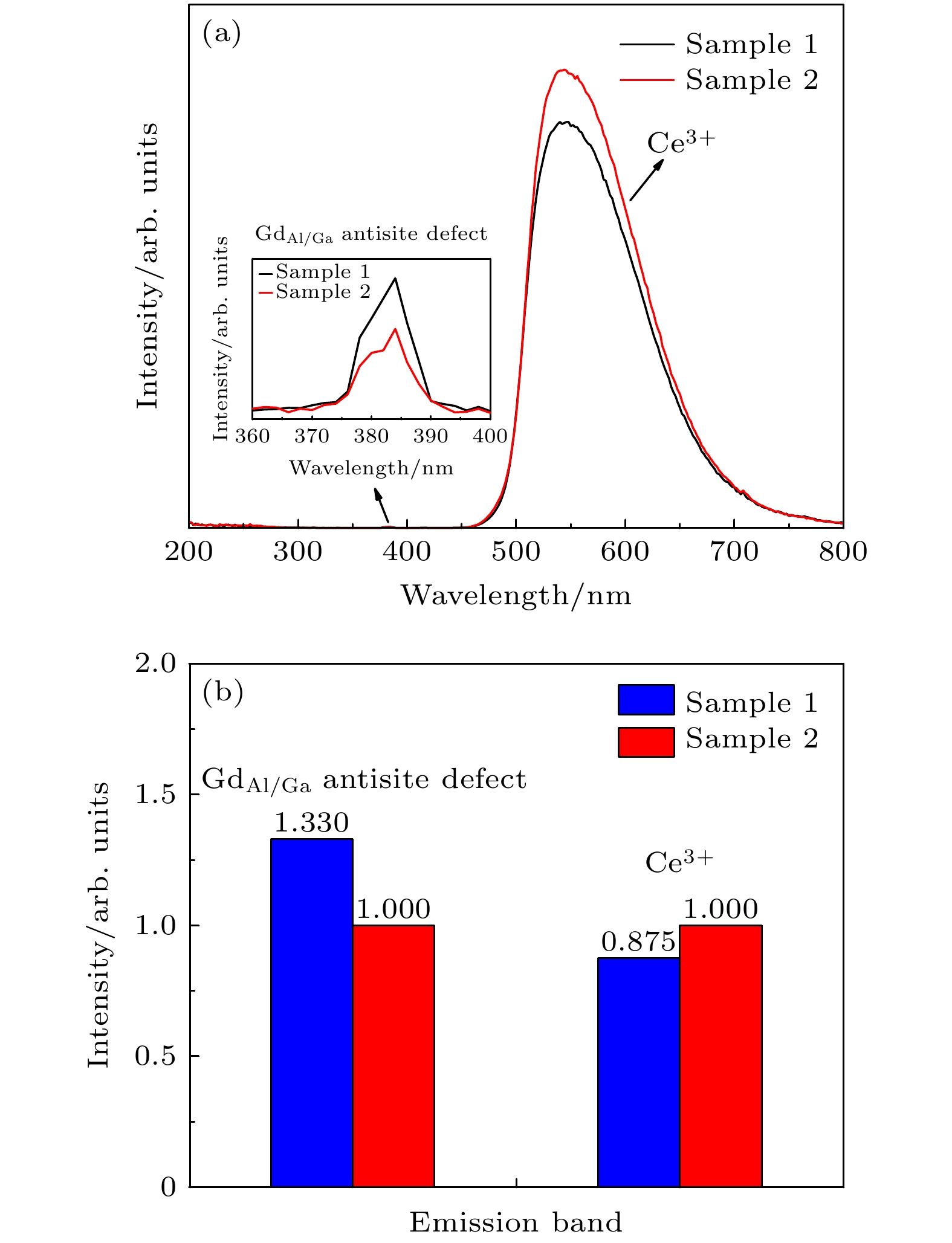
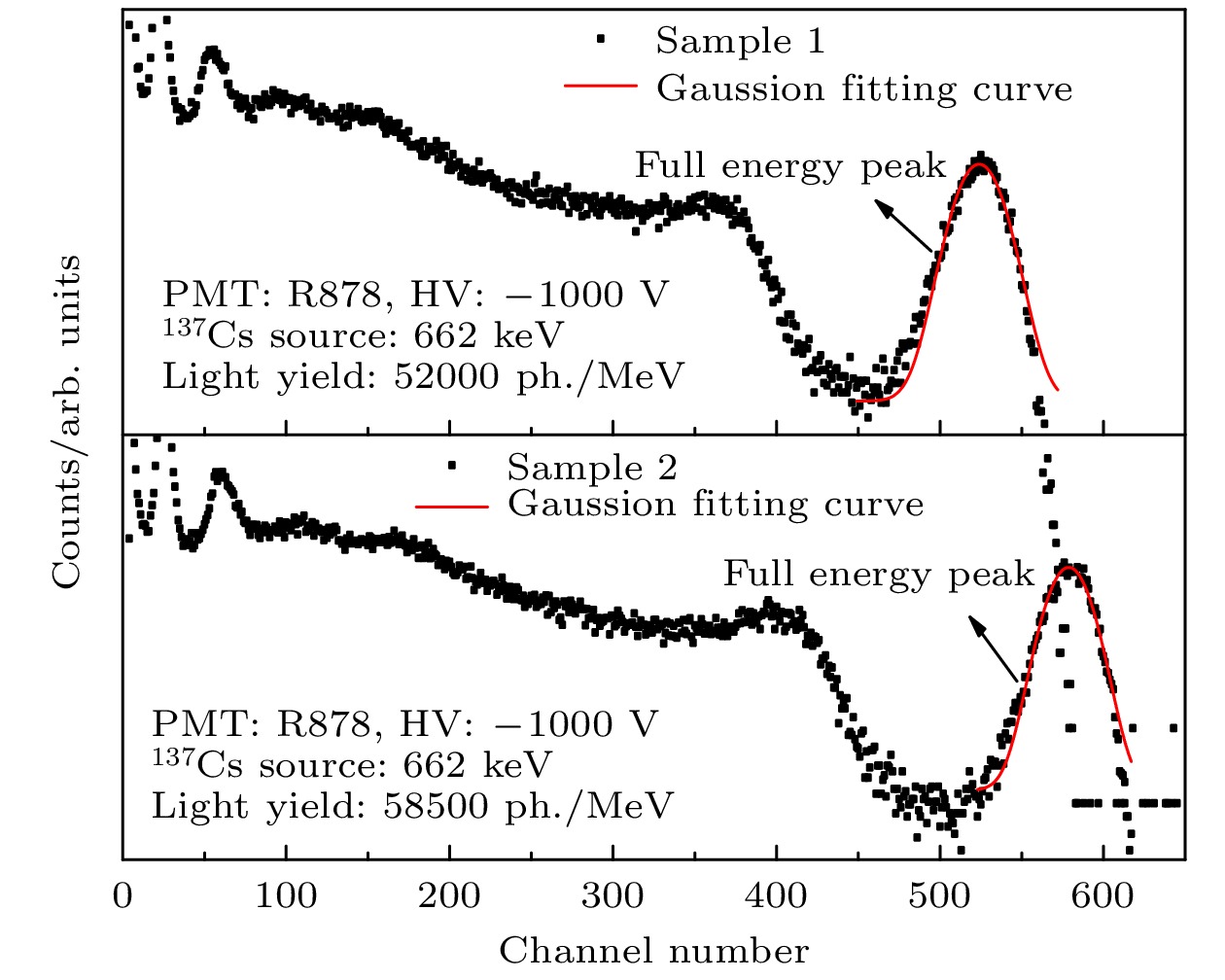
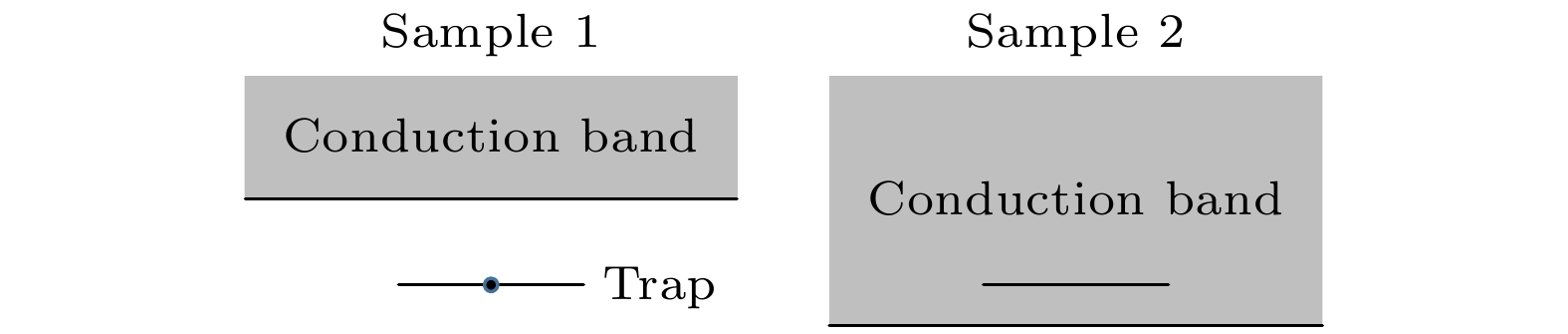
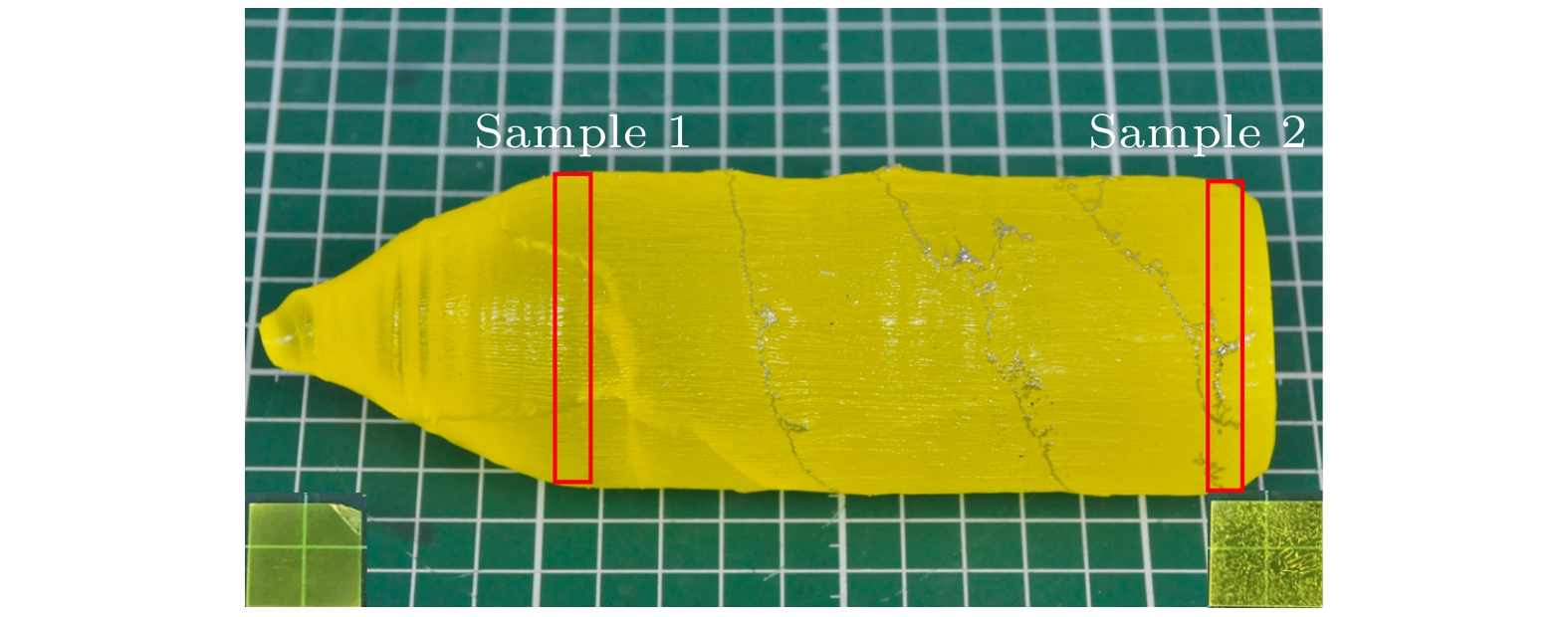
新型闪烁晶体Gd3(Al,Ga)5O12:Ce (GAGG:Ce)在制备过程中易出现包裹体及反格位缺陷等问题, 严重影响晶体的性能. 为了抑制这些缺陷以得到大尺寸高质量的GAGG:Ce晶体, 本文以Gd3(Al,Ga)5O12为基质、Ce3+为掺杂离子, 采用提拉法生长得到了GAGG:Ce晶体, 并对不同晶体部位的物相结构、微区成分、透光性质、发光及时间性能进行了测试和对比分析. 结果表明, GAGG:Ce晶体的透过谱中存在340和440 nm两处Ce3+特征吸收带, 且位于550 nm处的直线透过率为82%. 晶体尾部因杂相包裹体等宏观缺陷的影响, 导致其透过率下降至70%左右. 微区成分分析进一步表明GAGG:Ce晶体中存在三种类型的包裹体, 分别为富Gd相、富Ce相及(Al,Ga)2O3相. GAGG:Ce晶体的X射线激发发射谱中在550 nm附近存在Ce3+宽发射带, 且380 nm处还存在GdAl/Ga反格位缺陷引起的发射. 晶体中存在的杂相包裹体及GdAl/Ga反格位缺陷等因素导致Ce3+在GAGG基质的发光强度下降12.5%; GdAl/Ga反格位离子与近邻Ce的隧穿效应使得GAGG:Ce晶体的衰减时间由117.7 ns延长至121.9 ns, 且慢分量比例由16%增加至17.2%.There are many problems during the preparation of the scintillation crystal Gd3(Al,Ga)5O12:Ce (abbreviated as GAGG:Ce), such as inclusions and antisite-defect. In order to inhibit these defects and obtain large-size and high-quality GAGG:Ce crystal, this study uses Gd3(Al,Ga)5O12 as the matrix and Ce3+ as the doping ions to grow the GAGG:Ce crystal by the Czochralski method. The phase structure, micro-region composition, optical and scintillation properties of GAGG:Ce are tested and compared. It is found that tipical Ce3+ absorption bands are at 340 nm and 440 nm, and the linear transmittance at 550 nm is 82%. The transmittance of the crystal tail drops to about 70% due to the macroscopic defects such as inclusions. The micro-region composition analysis shows that the three types of inclusions in GAGG:Ce crystal are Gd-rich phase, Ce-rich phase, and (Al,Ga)2O3 phase. The Ce3+ ion emission wavelength of GAGG:Ce crystal is about 550 nm excited by the X-ray, and there is also an emission wavelength caused by the GdAl/Ga antisite-defect at 380 nm. The emission intensity of GdAl/Ga antisite-defect in the lack of (Al,Ga) component is higher than that in the excess (Al,Ga) component. The inclusions and GdAl/Ga antisite-defect make the luminous efficiency of GAGG:Ce crystal decrease by 12.5% and the corresponding light yield decreases from 58500 to 52000 photon/MeV. The tunneling effect between GdAl/Ga antisite-defect ions and neighboring Ce3+ ions makes the decay time of the GAGG:Ce crystal extend from 117.7 to 121.9 ns, and the ratio of slow component increases from 16% to 17.2%. The migration of energy along the Gd3+ sublattice makes the rise time of the GAGG:Ce crystal extend from 8.6 to 10.7 ns. The above conclusions further deepen the understanding of the source of inclusions and the relationship between the GdAl/Ga antisite-defect and crystal composition, and provide a theoretical basis for restraining the defects and improving the crystal properties.
-
Keywords:
- GAGG:Ce /
- light yield /
- energy resolution /
- decay time /
- antisite-defect /
- inclusions
[1] 何伟, 张约品, 王金浩, 王实现, 夏海平 2011 60 042901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
He W, Zhang Y P, Wang J H, Wang S X, Xia H P 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 042901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 孟猛, 祁强, 丁栋舟, 赫崇君, 施俊杰, 任国浩 2019 人工晶体学报 48 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Meng M, Qi Q, Ding D Z, He C J, Shi J J, Ren G H 2019 J. Synth. Cryst. 48 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Sakthong O, Chewpraditkul W, Wanarak C, Kamada K, Yoshikawa A, Prusa P, Nikl M 2014 Nucl. Instrum. Methosds Phys. Res. A 751 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Tamagawa Y, Inukai Y, Ogawa I, Kobayashi M 2015 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 795 192
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Kochurikhin V, Kamada K, Kim J, Ivanov M, Yoshikawa A 2020 J. Cryst. Growth 531 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 冯大建, 丁雨憧, 刘军, 李和新, 付昌禄, 胡少勤 2016 压电与声光 38 430
Feng D J, Ding Y C, Liu J, Li H X, Fu C L, Hu S Q 2016 Piezoelectrics Acoustooptics 38 430
[7] Kamada K, Takayuki A, Yanagida T, Endo T, Tsutumi K, Usuki Y, Nikl M, Fujimoto Y, Fukabori A, Yoshikawa A 2012 J. Cryst. Growth 352 88
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wang C, Wu Y T, Ding D Z, Li H Y, Chen X F, Shi J, Ren G H 2016 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 820 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Chewpraditkul W, Panek D, Bruza P, Chewpraditkul W, Wanarak C, Pattanaboonmee N, Babin V, Bartosiewicz K, Kamada K, Yoshikawa A, Nikl M 2014 J. Appl. Phys. 116 083505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Kitaura M, Watanabe S, Kamada K, Kim J K, Yoshino M, Kurosawa S, Yagihashi T, Ohnishi A, Hara K 2018 Appl. Phys. Lett. 113 041906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 丁栋舟, 李焕英, 秦来顺, 卢胜, 潘尚可, 任国浩 2010 无机材料学报 25 1021
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ding D Z, Li H Y, Qin L S, Lu S, Pan S K, Ren G H 2010 J. Inorg. Mater. 25 1021
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 孟猛, 祁强, 丁栋舟, 赫崇君, 赵书文, 万博, 陈露, 施俊杰, 任国浩 2020 无机材料学报
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Meng M, Qi Q, Ding D Z, He C J, Zhao S W, Wan B, Chen L, Shi J J, Ren G H 2020 J. Inorg. Mater.
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 鲁万成, 张庆礼, 罗建乔, 丁守军, 窦仁勤, 彭方, 张会丽, 王小飞, 孙贵花, 孙敦陆 2017 66 154204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lu W C, Zhang Q L, Luo J Q, Ding S J, Dou R Q, Peng F, Zhang H L, Wang X F, Sun G H, Sun D L 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 154204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Kurosawa S, Shoji Y, Yokota Y, Kamada K, Chani V, Yoshikawa A 2014 J. Cryst. Growth 393 134
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Etiennette A, Ramunas A, Andrei F, Georgy D, Larisa G, Vidmantas G, Merry K, Marco L, Charles M, Saulius L, Gintautas T, Augustas V, Aleksejs Z, Mikhail K 2018 Phys. Status Solidi A 215 1700798
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Mares J A, Nikl M, Beitlerova A, Solovieva N, Ambrosio C, Blazek K, Maly P, Nejezchle K, Fabeni P, Pazzi P 2005 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 537 271
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Stanek C R, McClellana C J, Levyb M R, Milanese C, Grimes R W 2007 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 579 27
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 杨新波, 石云, 李红军, 毕群玉, 苏良碧, 刘茜, 潘裕柏, 徐军 2009 58 8050
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang X B, Shi Y, Li H J, Bi Q Y, Su L B, Liu Q, Pan Y B, Xu J 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 8050
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yoshino M, Kamada K, Shoji Y, Yamaji A, Kurosawa S, Kurosawa Y, Ohashi Y, Yoshikawa A, Chani V 2017 J. Cryst. Growth 468 420
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Kamada K, Kurosawa S, Prusa P, Nikl M, Kochurikhin V, Endo T, Tsutumi K, Sato H, Yokota K, Y, Sugiyama K, Yoshikawa A 2014 Opt. Mater. 36 1942
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 杨斌, 张约品, 徐波, 来飞, 夏海平, 赵天池 2012 61 192901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang B, Zhang Y P, Xu B, Lai F, Xia H P, Zhao T C 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 192901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zorenko Y 2005 Phys. Status Solidi C 26 375
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 GAGG:Ce晶体的EDS成分分析
Table 1. Composition analysis data by EDS of GAGG:Ce crystal.
Sample Gd Al Ga Al + Ga ion ratio 1 3.034 2.274 2.692 4.966 2 2.985 2.213 2.802 5.015 Theoretical value 3 2.3 2.7 5 表 2 GAGG:Ce晶体的晶胞参数
Table 2. Lattice parameters of GAGG:Ce crystal at different positions.
Sample 1 2 Diffractive angle (2θ)/(°) 32.8 32.73 Lattice parameters/nm 12.2492 12.2516 表 3 GAGG:Ce晶体的EDS能谱微区成分分析数据
Table 3. Micro-region composition analysis data by EDS of GAGG:Ce crystal.
取样点 Gd Ce Al Ga Al + Ga O (Gd + Ce)∶(Al + Ga)∶O Atomic percentage 离子数之比 1 17.61 — 10.33 12.06 22.39 60 3.5∶4.5∶12 2 14.97 — 11.11 13.92 25.03 60 3∶5∶12 3 3.71 20.57 4.45 11.26 15.71 60 4.9∶3.1∶12 4 1.19 — 17.9 20.91 38.81 60 0.06∶2∶3 5 15.06 — 10.63 14.31 24.94 60 3∶5∶12 -
[1] 何伟, 张约品, 王金浩, 王实现, 夏海平 2011 60 042901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
He W, Zhang Y P, Wang J H, Wang S X, Xia H P 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 042901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 孟猛, 祁强, 丁栋舟, 赫崇君, 施俊杰, 任国浩 2019 人工晶体学报 48 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Meng M, Qi Q, Ding D Z, He C J, Shi J J, Ren G H 2019 J. Synth. Cryst. 48 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Sakthong O, Chewpraditkul W, Wanarak C, Kamada K, Yoshikawa A, Prusa P, Nikl M 2014 Nucl. Instrum. Methosds Phys. Res. A 751 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Tamagawa Y, Inukai Y, Ogawa I, Kobayashi M 2015 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 795 192
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Kochurikhin V, Kamada K, Kim J, Ivanov M, Yoshikawa A 2020 J. Cryst. Growth 531 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 冯大建, 丁雨憧, 刘军, 李和新, 付昌禄, 胡少勤 2016 压电与声光 38 430
Feng D J, Ding Y C, Liu J, Li H X, Fu C L, Hu S Q 2016 Piezoelectrics Acoustooptics 38 430
[7] Kamada K, Takayuki A, Yanagida T, Endo T, Tsutumi K, Usuki Y, Nikl M, Fujimoto Y, Fukabori A, Yoshikawa A 2012 J. Cryst. Growth 352 88
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wang C, Wu Y T, Ding D Z, Li H Y, Chen X F, Shi J, Ren G H 2016 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 820 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Chewpraditkul W, Panek D, Bruza P, Chewpraditkul W, Wanarak C, Pattanaboonmee N, Babin V, Bartosiewicz K, Kamada K, Yoshikawa A, Nikl M 2014 J. Appl. Phys. 116 083505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Kitaura M, Watanabe S, Kamada K, Kim J K, Yoshino M, Kurosawa S, Yagihashi T, Ohnishi A, Hara K 2018 Appl. Phys. Lett. 113 041906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 丁栋舟, 李焕英, 秦来顺, 卢胜, 潘尚可, 任国浩 2010 无机材料学报 25 1021
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ding D Z, Li H Y, Qin L S, Lu S, Pan S K, Ren G H 2010 J. Inorg. Mater. 25 1021
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 孟猛, 祁强, 丁栋舟, 赫崇君, 赵书文, 万博, 陈露, 施俊杰, 任国浩 2020 无机材料学报
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Meng M, Qi Q, Ding D Z, He C J, Zhao S W, Wan B, Chen L, Shi J J, Ren G H 2020 J. Inorg. Mater.
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 鲁万成, 张庆礼, 罗建乔, 丁守军, 窦仁勤, 彭方, 张会丽, 王小飞, 孙贵花, 孙敦陆 2017 66 154204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lu W C, Zhang Q L, Luo J Q, Ding S J, Dou R Q, Peng F, Zhang H L, Wang X F, Sun G H, Sun D L 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 154204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Kurosawa S, Shoji Y, Yokota Y, Kamada K, Chani V, Yoshikawa A 2014 J. Cryst. Growth 393 134
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Etiennette A, Ramunas A, Andrei F, Georgy D, Larisa G, Vidmantas G, Merry K, Marco L, Charles M, Saulius L, Gintautas T, Augustas V, Aleksejs Z, Mikhail K 2018 Phys. Status Solidi A 215 1700798
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Mares J A, Nikl M, Beitlerova A, Solovieva N, Ambrosio C, Blazek K, Maly P, Nejezchle K, Fabeni P, Pazzi P 2005 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 537 271
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Stanek C R, McClellana C J, Levyb M R, Milanese C, Grimes R W 2007 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 579 27
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 杨新波, 石云, 李红军, 毕群玉, 苏良碧, 刘茜, 潘裕柏, 徐军 2009 58 8050
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang X B, Shi Y, Li H J, Bi Q Y, Su L B, Liu Q, Pan Y B, Xu J 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 8050
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yoshino M, Kamada K, Shoji Y, Yamaji A, Kurosawa S, Kurosawa Y, Ohashi Y, Yoshikawa A, Chani V 2017 J. Cryst. Growth 468 420
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Kamada K, Kurosawa S, Prusa P, Nikl M, Kochurikhin V, Endo T, Tsutumi K, Sato H, Yokota K, Y, Sugiyama K, Yoshikawa A 2014 Opt. Mater. 36 1942
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 杨斌, 张约品, 徐波, 来飞, 夏海平, 赵天池 2012 61 192901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang B, Zhang Y P, Xu B, Lai F, Xia H P, Zhao T C 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 192901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zorenko Y 2005 Phys. Status Solidi C 26 375
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 9345
- PDF下载量: 151
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: