-
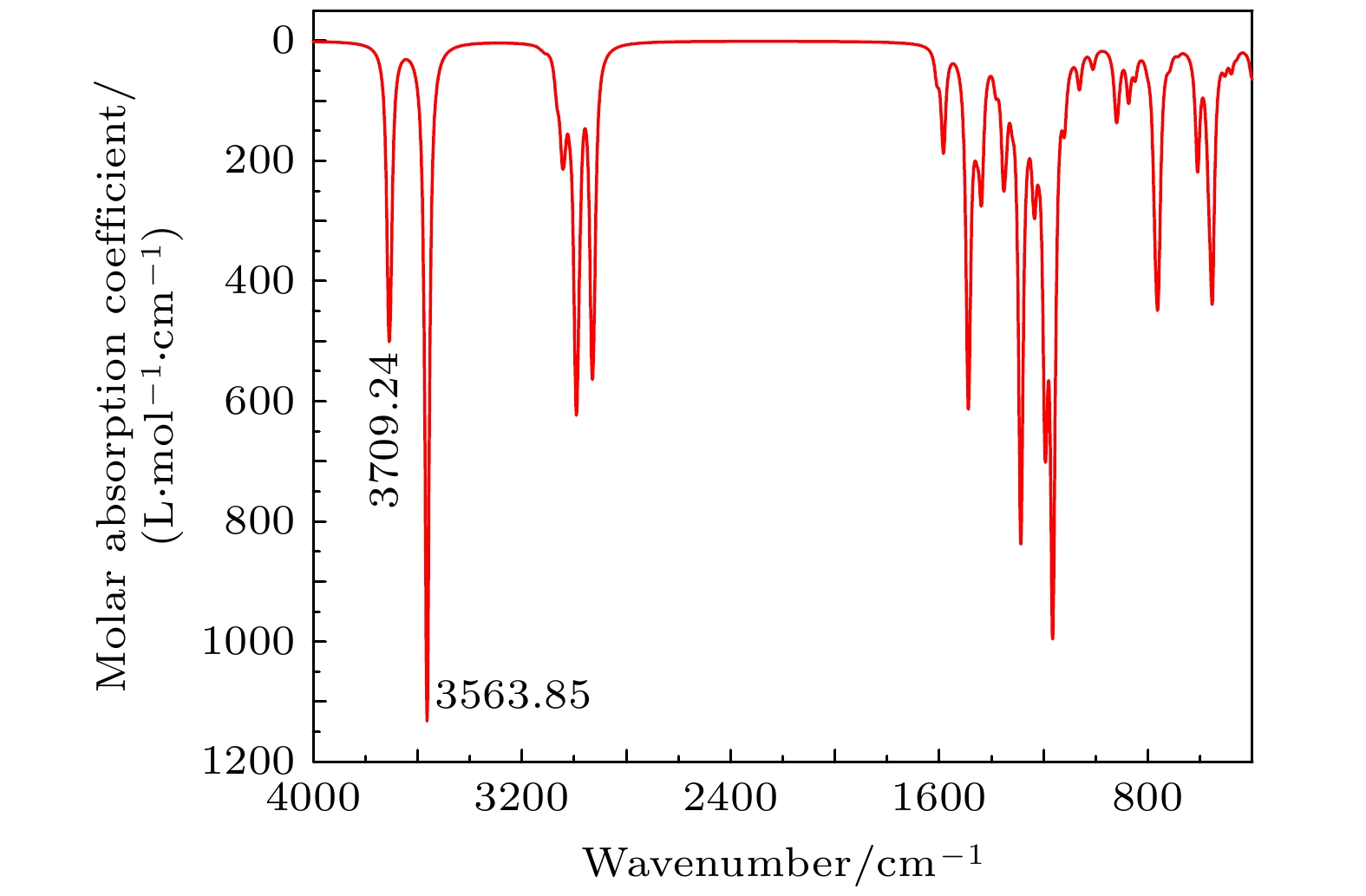
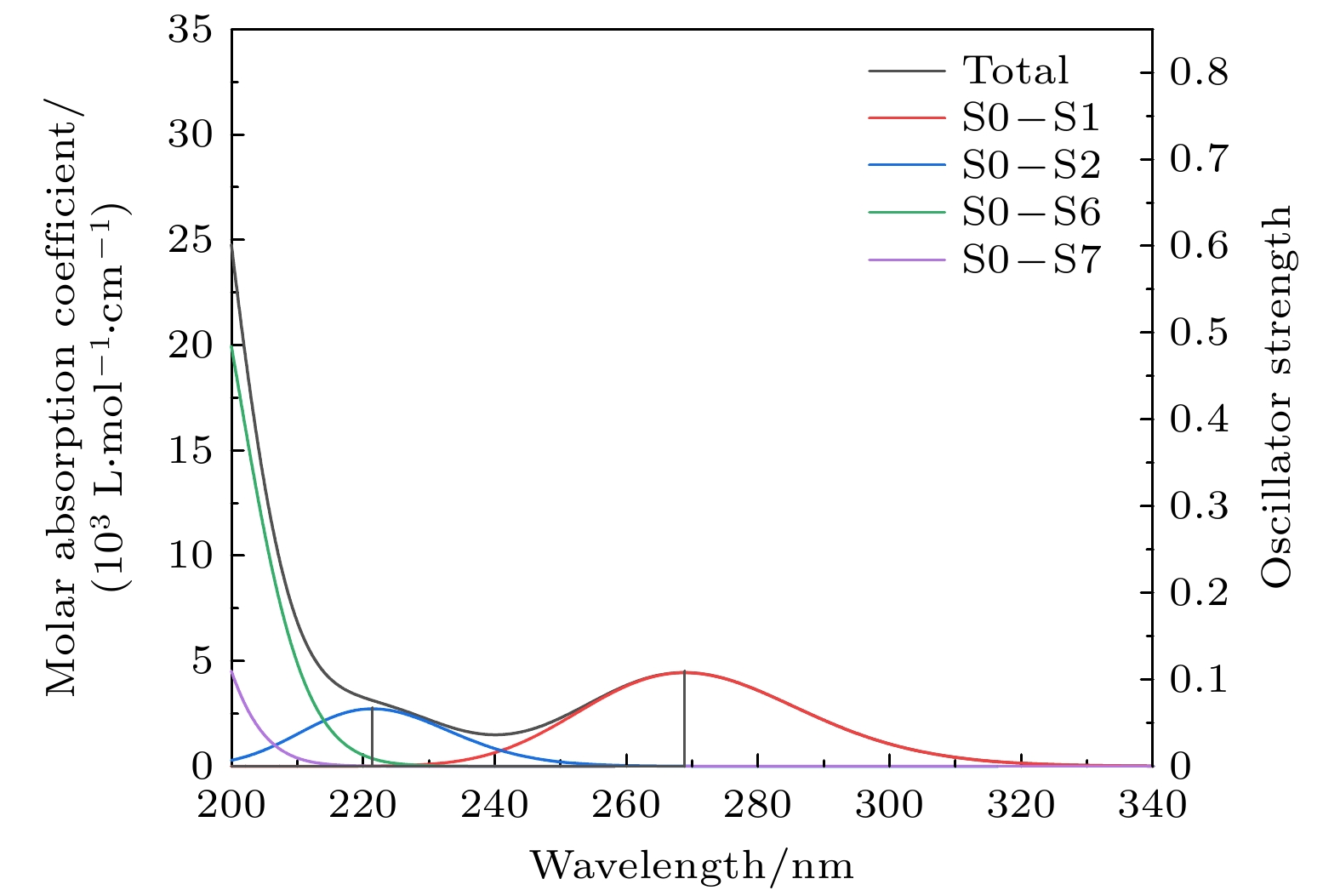
特丁基对苯二酚是重要的食品抗氧化剂. 理论上, 基于密度泛函理论, 采用B3LYP泛函及6-311G(d,p)基组在气相环境下优化分子的结构并进行频率计算. 在此基础上, 基于含时密度泛函理论, 选用SMD (solvation model based on density)溶剂模型, 利用B3LYP泛函并结合def2-TZVP基组计算分子在无水乙醇溶剂中的前50个激发态. 再通过Multiwfn软件对红外光谱做振动分析并考察分子间相互作用对红外光谱的影响, 对紫外光谱做分子轨道和电子空穴分析. 实验上, 通过KBr压片法, 利用傅里叶红外变换光谱仪测定样品红外光谱. 采用液相法, 以乙醇为溶剂, 利用紫外可见分光光度计测定样品紫外光谱. 通过对比分析可知, 理论光谱与实验光谱总体吻合较好. 红外光谱各基团的特征吸收峰都较为明显且较好吻合, 特丁基对苯二酚二聚体存在氢键作用, 这使得O—H键的强度被削弱, 导致吸收频率降低并在3670—3070 cm–1处出现一个宽峰. 紫外光谱主要由基态跃迁至第1, 2, 6, 7激发态形成, 最大吸收峰位于200 nm以下, 为π→π*和σ→π*跃迁形成, 268.8 nm和221.4 nm处的吸收峰均为n→π*和π→π*跃迁形成. 由电子空穴图可知, 这4个主要激发均为电子局域激发.Tert-butylhydroquinone (TBHQ) is an important food antioxidant. Based on density functional theory, the B3LYP functional is used to optimize the geometric configuration and calculate the frequency of TBHQ molecule in gas phase at a level of 6-311g (d, p) basis set. On this basis, based on the time-dependent density functional theory, SMD implicit solvent model is selected, and the first 50 excited states of molecule in ethanol solvent are calculated by using B3LYP functional and def2-TZVP basis set. Multiwfn software is used to analyze the vibration of IR spectrum, the influence of interaction among molecules on IR spectrum and the molecular orbital and electron-hole of UV spectrum. Experimentally, Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FTIR) is used to measure the IR spectrum of TBHQ sample by KBr tablet method. The UV spectrum of the sample determined in the ethanol solvent by ultraviolet visible spectrophotometer. By comparative analysis, it can be seen that the theoretical spectra are in good agreement with the experimental spectra. The characteristic absorption peaks of each group in the IR spectra are obvious, and the theoretical peaks are in good agreement with the positions of the measured peaks. The hydrogen bonding of dimers and polymers in the TBHQ sample can weaken the O—H bond strength of a single molecule, thus weakening the vibration frequency of the O—H bond and resulting in a wide peak at 3670–3070 cm–1 in the experimental IR spectrum. The UV spectra are mainly formed from the ground state to the first, second, sixth and seventh excited state. The maximum absorption peak in the UV spectrum is below 200 nm and is formed by the transitions of π→π* and σ→π*. The absorption peaks at 268.8 nm and 221.4 nm are formed by the transitions of n→π* and π→π*. It can be seen from the electron-hole distribution diagram that these four excitations are all electron local excitation. This study may play a certain role in understanding the molecular structure and excitation properties of TBHQ, as well as the formation mechanism of its IR and UV spectra, and also conduce to understanding its antioxidant properties.
-
Keywords:
- tert-butylhydroquinone /
- IR spectra /
- UV spectra /
- density functional theory
[1] Comert E D, Gokmen V 2018 Food Res. Int. 105 76
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zeb A 2020 J. Food Biochem. 44 e13394
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Martinez M L, Penci M C, Ixtaina V, Ribotta P D, Maestri D 2013 LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 51 44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Xu X L, Bi Y L, Wang H Y, Li J, Xu Z Y 2019 Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 121 1800510
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Gharavi N, Haggarty S, El-Kadi A O S 2007 Curr. Drug Metab. 8 1
[6] Alamed J, Chaiyasit W, McClements D J, Decker E A 2009 J. Agric. Food Chem. 57 2969
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 逯美红, 雷海英, 王志军, 张洁 2017 光谱学与光谱分析 37 2087
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lu M H, Lei H Y, Wang Z J, Zhang J 2017 Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 37 2087
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Rode J E, Kaczorek D, Wasiewicz A, Kawecki R, Jawiczuk M, Dobrowolski J C 2018 J. Mol. Spectrosc. 354 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Snehalatha M, Ravikumar C, Joe I H, Sekar N, Jayakumar V S 2009 Spectrochim. Acta A 72 654
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Frisch M J, Trucks G W, Schlegel H B, et al. 2016 Gaussian 16 (Rev. A.03). Gaussian: Inc., Wallingford CT
[11] Stephens P J, Devlin F J, Chabalowski C F, Frisch M J 1994 J. Phys. Chem. 98 11623
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 于建成, 唐延林, 常瑞, 魏晓楠, 袁荔, 袁园 2019 光谱学与光谱分析 39 1846
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu J C, Tang Y L, Chang R, Wei X N, Yuan L, Yuan Y 2019 Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 39 1846
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Lu T, Chen F W 2012 J. Comput. Chem. 33 580
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Weigend F, Ahlrichs R 2005 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 7 3297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 彭婕, 张嗣杰, 王苛, Dove Martin 2020 69 023101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Peng J, Zhang S J, Wang K, Dove M 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 023101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Liu Z Y, Lu T, Chen Q X 2020 Carbon 165 461
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Marenich A V, Cramer C J, Truhlar D G 2009 J. Phys. Chem. B 113 6378
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Lu T 2020 molclus program Version 1.9.6 http://www.keinsci.com/research/molclus.html [2020-7-25]
[19] Grimme S, Antony J, Ehrlich S, Krieg H 2010 J. Chem. Phys. 132 154104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Lu T, Chen F W 2013 J. Mol. Model. 19 5387
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Chai J D, Head-Gordon M 2008 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 10 6615
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhao Y, Truhlar D G 2008 Theor. Chem. Acc. 120 215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Multiwfn Manual Version 3.7, Lu T http://sobereva.com/multiwfn/ [2020-9-17]
[24] Johnson E R, Keinan S, Mori-Sanchez P, Contreras-Garcia J, Cohen A J, Yang W T 2010 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132 6498
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 赵明文, 夏曰源, 马玉臣, 刘向东, 英敏菊 2002 51 2440
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao M W, Xia Y Y, Ma Y C, Liu X D, Ying M J 2002 Acta Phys. Sin. 51 2440
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K 1996 J. Mol. Graphics 14 33
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Emamian S, Lu T, Kruse H, Emamian H 2019 J. Comput. Chem. 40 2868
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 8 分子轨道波函数等值面图 (a) 第44轨道; (b) 第45轨道; (c) 第45轨道(等值面为0.18); (d) 第46轨道; (e) 第47轨道; (f) 第47轨道(等值面为0.14)
Fig. 8. Isosurface of molecular orbital wavefunction: (a) The 44th molecular orbital; (b) the 45th molecular orbital; (c) the 45th molecular orbital (isosurface = 0.18); (d) the 46th molecular orbital; (e) the 47th molecular orbital; (f) the 47 th molecular orbital (isosurface = 0.14).
表 1 TBHQ分子几何结构优化参数
Table 1. Optimized geometry structure parameters of TBHQ.
Maximum force/a.u. RMS force/a.u. Maximum displacement/a.u. Root mean square displacement/a.u. 0.000006 0.000001 0.000193 0.000036 表 2 TBHQ分子主要键长、键角、二面角
Table 2. The main bond length, bond angle, and dihedral angle of TBHQ.
键长 R(2, 23) 0.13725 nm R(4, 10) 0.15417 nm R(5, 25) 0.13791 nm 键角 A(2, 23, 24) 109.0769º A(5, 25, 26) 108.6475º A(4, 10, 11) 111.9551º 二面角 D(3, 4, 10, 11) 0.0003º 表 3 TBHQ分子红外光谱振动分析
Table 3. Vibration analysis of IR spectra of TBHQ.
序号 计算光谱/cm–1 实验光谱/cm–1 振动分析 1 3709.24 3288.54 酚羟基的O—H伸缩振动 2 3034.34 3001.16 苯环上C—H伸缩振动 3 2989.00 2962.58 丁基上C—H伸缩振动 4 1581.86 1589.30 苯环的环伸缩振动 5 1483.16 1485.15 苯环的环伸缩振动及C—H弯曲振动 6 1440.48 1442.72 C—H弯曲振动 7 1284.43 1309.63 C—O伸缩振动及C—H弯曲振动 8 1169.72 1184.26 O—H面内弯曲振动及C—H面内弯曲振动 9 917.64 933.52 C—H弯曲振动 10 757.59 771.51 苯环上C—H面外弯曲振动 表 4 TBHQ分子的激发性质
Table 4. Excited state properties of TBHQ.
理论吸收峰值 实验吸收峰值 激发态 激发能/eV 波长/nm 振子强度 轨道跃迁 贡献权重/% 221.4 nm
268.8 nm229.1 nm
293.7 nm1 4.6118 268.84 0.1100 45→46
44→4791.91
7.862 5.6003 221.39 0.0676 45→47
44→4678.65
20.576 6.4329 192.73 0.6902 44→46
45→4777.09
20.077 6.7109 184.75 0.5669 44→47
45→4689.30
7.24表 5 电子空穴相关参数
Table 5. Electron-hole distribution related parameters of TBHQ.
Sr/a.u D/nm H/nm t/nm HDI EDI S0—S1 0.789 0.0075 0.2115 –0.1259 9.63 8.81 S0—S2 0.917 0.0034 0.2130 –0.1292 8.81 8.72 S0—S6 0.913 0.0271 0.2139 –0.1134 8.00 7.88 S0—S7 0.762 0.0223 0.2127 –0.1179 8.63 9.39 -
[1] Comert E D, Gokmen V 2018 Food Res. Int. 105 76
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zeb A 2020 J. Food Biochem. 44 e13394
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Martinez M L, Penci M C, Ixtaina V, Ribotta P D, Maestri D 2013 LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 51 44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Xu X L, Bi Y L, Wang H Y, Li J, Xu Z Y 2019 Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 121 1800510
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Gharavi N, Haggarty S, El-Kadi A O S 2007 Curr. Drug Metab. 8 1
[6] Alamed J, Chaiyasit W, McClements D J, Decker E A 2009 J. Agric. Food Chem. 57 2969
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 逯美红, 雷海英, 王志军, 张洁 2017 光谱学与光谱分析 37 2087
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lu M H, Lei H Y, Wang Z J, Zhang J 2017 Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 37 2087
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Rode J E, Kaczorek D, Wasiewicz A, Kawecki R, Jawiczuk M, Dobrowolski J C 2018 J. Mol. Spectrosc. 354 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Snehalatha M, Ravikumar C, Joe I H, Sekar N, Jayakumar V S 2009 Spectrochim. Acta A 72 654
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Frisch M J, Trucks G W, Schlegel H B, et al. 2016 Gaussian 16 (Rev. A.03). Gaussian: Inc., Wallingford CT
[11] Stephens P J, Devlin F J, Chabalowski C F, Frisch M J 1994 J. Phys. Chem. 98 11623
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 于建成, 唐延林, 常瑞, 魏晓楠, 袁荔, 袁园 2019 光谱学与光谱分析 39 1846
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu J C, Tang Y L, Chang R, Wei X N, Yuan L, Yuan Y 2019 Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 39 1846
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Lu T, Chen F W 2012 J. Comput. Chem. 33 580
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Weigend F, Ahlrichs R 2005 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 7 3297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 彭婕, 张嗣杰, 王苛, Dove Martin 2020 69 023101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Peng J, Zhang S J, Wang K, Dove M 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 023101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Liu Z Y, Lu T, Chen Q X 2020 Carbon 165 461
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Marenich A V, Cramer C J, Truhlar D G 2009 J. Phys. Chem. B 113 6378
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Lu T 2020 molclus program Version 1.9.6 http://www.keinsci.com/research/molclus.html [2020-7-25]
[19] Grimme S, Antony J, Ehrlich S, Krieg H 2010 J. Chem. Phys. 132 154104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Lu T, Chen F W 2013 J. Mol. Model. 19 5387
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Chai J D, Head-Gordon M 2008 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 10 6615
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhao Y, Truhlar D G 2008 Theor. Chem. Acc. 120 215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Multiwfn Manual Version 3.7, Lu T http://sobereva.com/multiwfn/ [2020-9-17]
[24] Johnson E R, Keinan S, Mori-Sanchez P, Contreras-Garcia J, Cohen A J, Yang W T 2010 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132 6498
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 赵明文, 夏曰源, 马玉臣, 刘向东, 英敏菊 2002 51 2440
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao M W, Xia Y Y, Ma Y C, Liu X D, Ying M J 2002 Acta Phys. Sin. 51 2440
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K 1996 J. Mol. Graphics 14 33
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Emamian S, Lu T, Kruse H, Emamian H 2019 J. Comput. Chem. 40 2868
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 9259
- PDF下载量: 113
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: