-
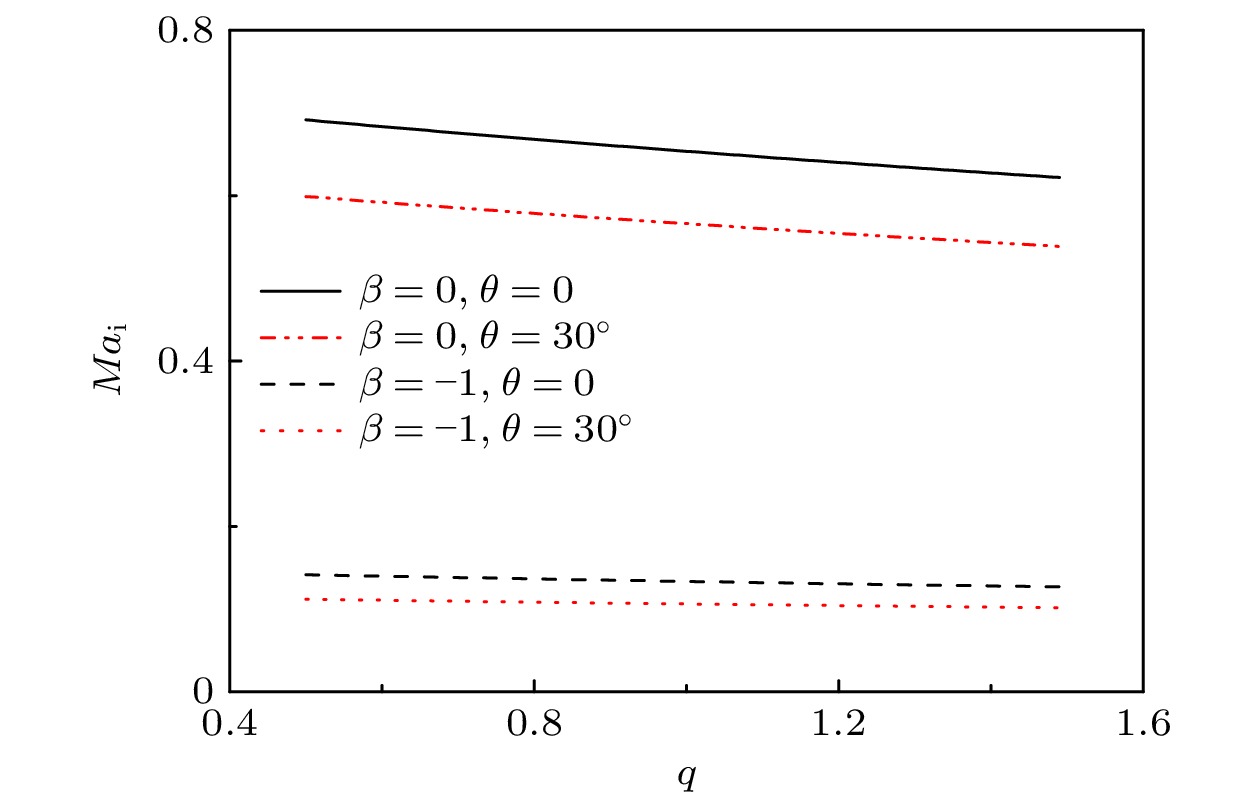
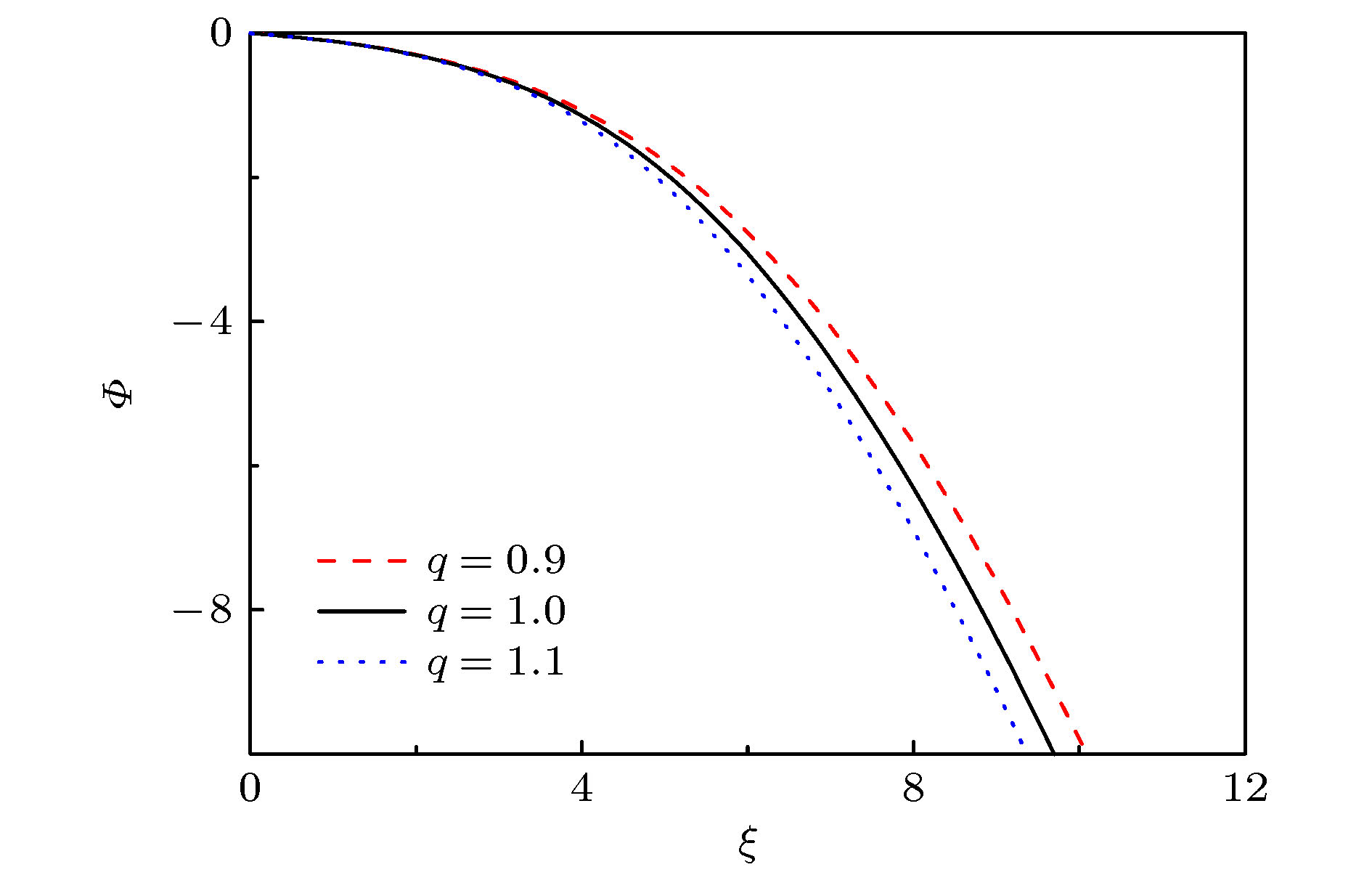
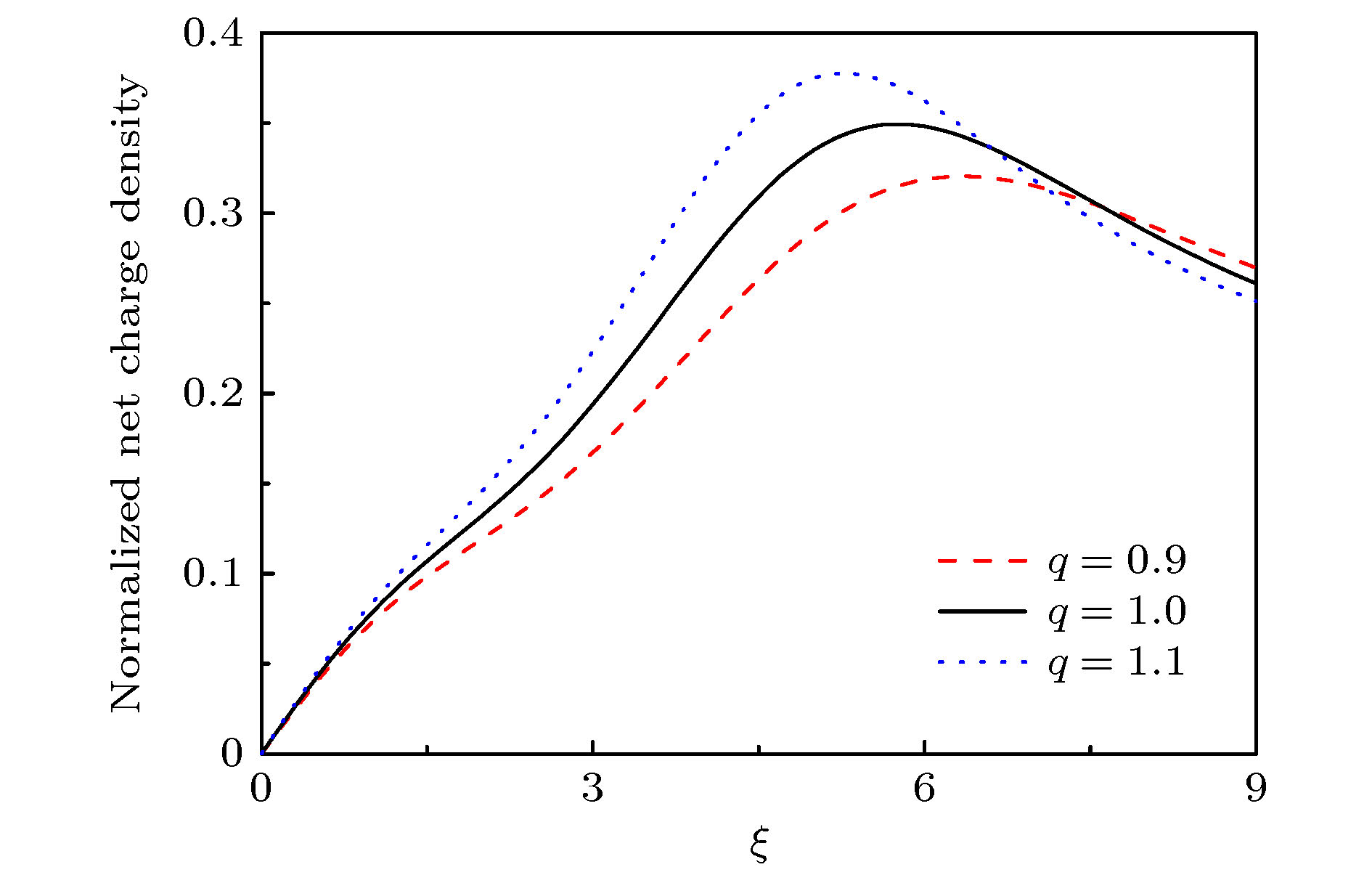
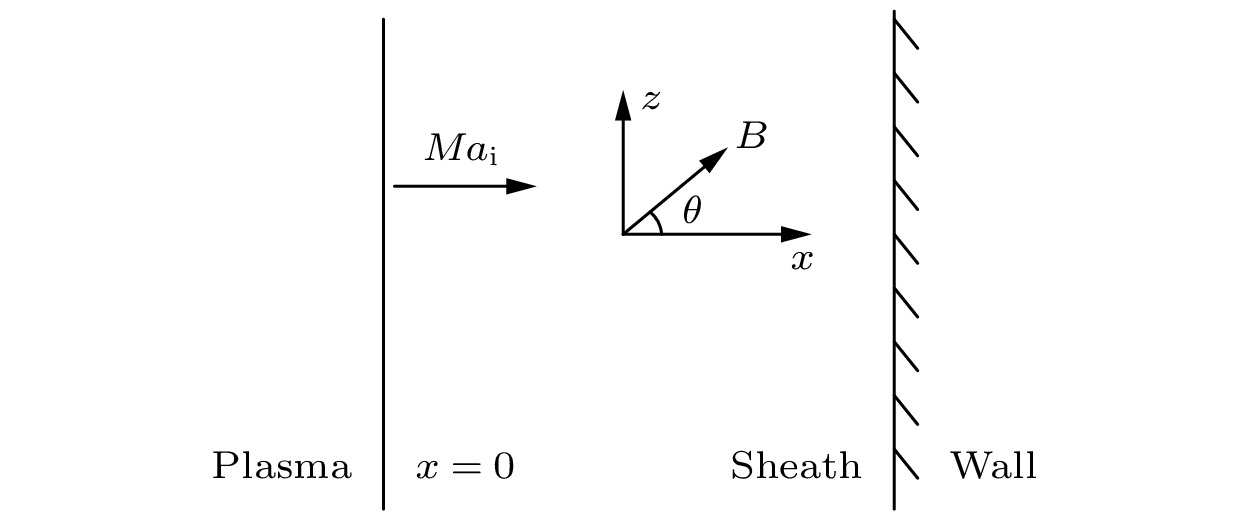
很多关于等离子体鞘层的研究工作都是基于电子满足经典的麦克斯韦速度分布函数, 而等离子体中的粒子具有长程电磁相互作用, 使用Tsallis提出的非广延分布来描述电子更为恰当. 本文建立一个具有非广延分布电子的碰撞等离子体磁鞘模型, 理论推导出受非广延参数q影响的玻姆判据, 离子马赫数的下限数值会随着参数q的增大而减小. 经过数值模拟, 发现与具有麦克斯韦分布(q = 1)电子的碰撞等离子体磁鞘对比, 具有超广延分布(q < 1)和亚广延分布(q > 1)电子的碰撞等离子体磁鞘的结构各有不同, 包括空间电势分布、离子电子密度分布、空间电荷密度分布. 模拟结果显示非广延分布的参数q对碰撞等离子体磁鞘的结构具有不可忽略的影响. 希望这些结论对相关的天体物理、等离子体边界问题的研究有参考价值.Many previous researches on the plasma sheath were based on the fact that the electrons satisfy the classical Maxwell velocity distribution function, while the particles in the plasma have long-range electromagnetic interactions. It is more appropriate to use the non-extensive distribution proposed by Tsallis to describe the electrons. In this paper, a collisional magnetized plasma sheath model with non-extensive distribution of electrons is established. Bohm criterion is derived theoretically. With the ion drift motion in the plasma pre-sheath region taken into consideration, the ion Mach number is only related to the angle of the magnetic field, the collision parameters, the electric field at the sheath edge, and non-extensive parameter
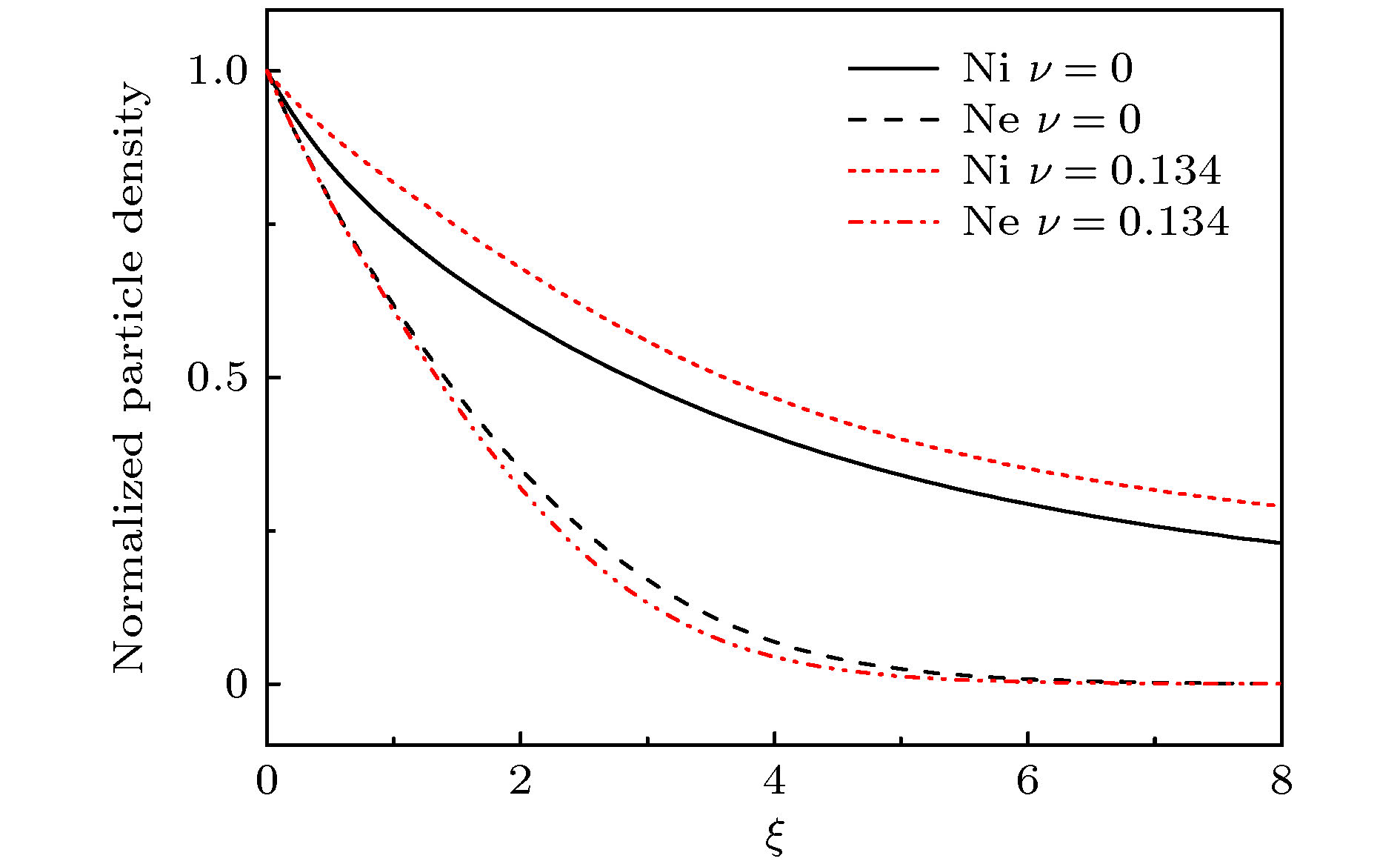
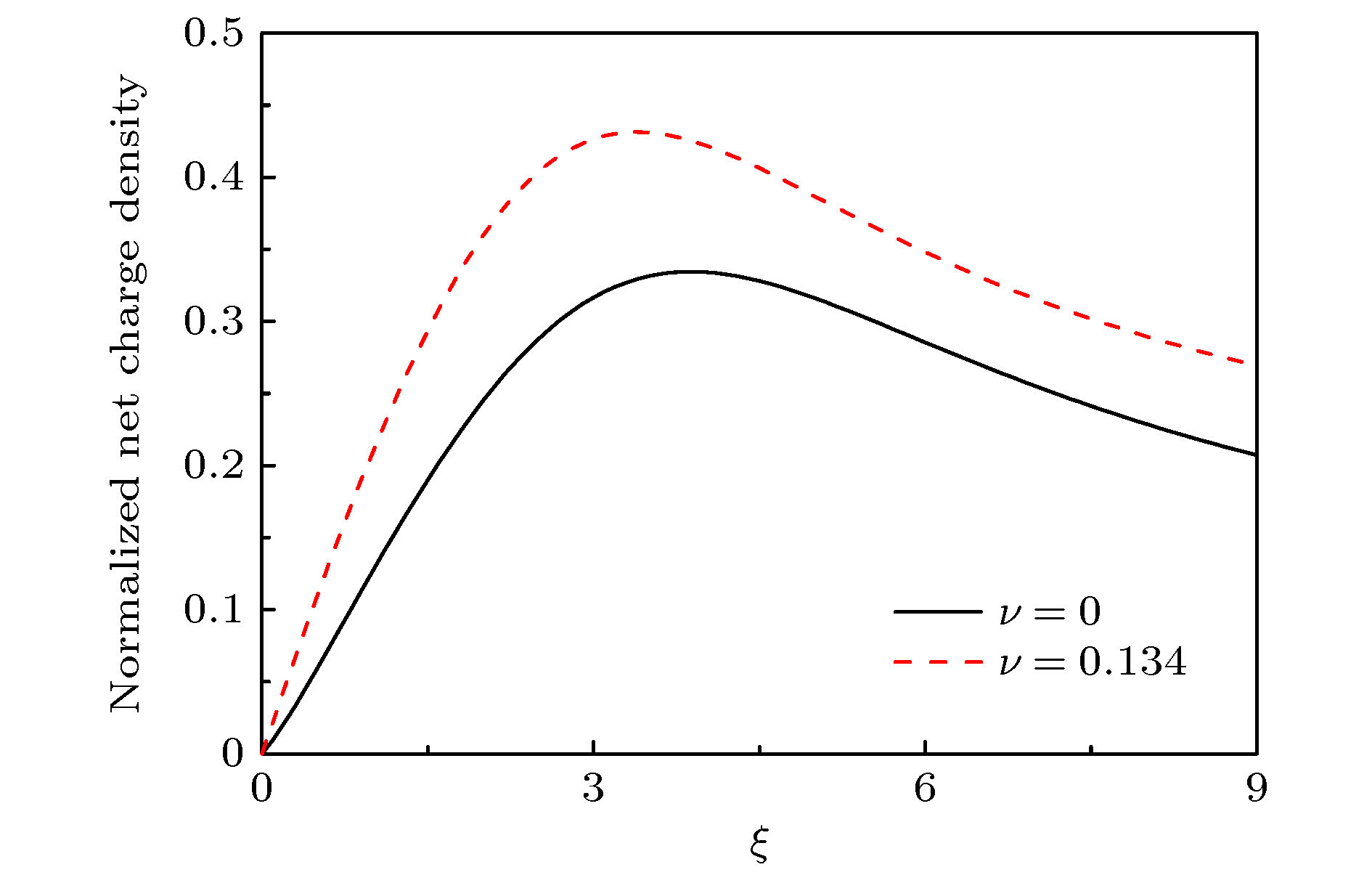
$ q $ . The influence of parameter$ q $ on the criterion is discussed in this paper. The lower limit of the ion Mach number changes with the value of parameter$ q $ . The lower limit of the ion Mach number increases for$ q < 1 $ . And the lower limit of the ion Mach number decreases for$ q>1 $ . With the increase of$ q $ , the number of electrons with lower speed increases, ions need less kinetic energy to enter into the sheath and thus enter into the sheath more easily. Through numerical simulation, it is found that compared with the structure of the plasma magnetized sheath with Maxwell distribution ($ q=1 $ ), the structure of the plasma magnetized sheath with super-extensive distribution ($ q < 1 $ ) and that with sub-extensive ($ q>1 $ ) are different, including the distribution of the space potential, the ion density, the electron density, and the space charge density. When$ q < 1 $ , the space potential, the electron density and the ion density fall more slowly, and the peak of the space charge density curve is closer to the wall. When$ q>1 $ , the space potential and the ion electron density fall faster, especially the electron density drops to zero faster, and the peak of the space charge density curve is far away from the wall. The simulation results show that the non-extensive parameter$ q $ has a significant influence on the structure of collisional plasma magnetized sheath. The influence of the collision on the magnetized plasma sheath with non-extensive distribution is similar to that with the Maxwell distribution. These conclusions may be useful in solving the problems of plasma boundary.-
Keywords:
- non-extensive distribution /
- plasma /
- sheath
[1] Chodura R 1982 Phys. Fluid 25 1628
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Riemann K U 1994 Phys. Plasmas 1 552
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Stangeby P C 1995 Phys. Plasmas 2 702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ahedo E 1997 Phys. Plasmas 4 4419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Liu J Y, Wang Z X, Wang X G 2003 Phys. Plasmas 10 3032
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Liu J Y, Wang Z X, Wang X G, Zhang Q, Zou X 2003 Phys. Plasmas 10 3507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 王正汹, 刘金远, 邹秀, 刘悦, 王晓刚 2004 53 0793
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Z X, Liu J Y, Zou X, Liu Y, Wang X G 2004 Acta Phys. Sin. 53 0793
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 邹秀, 刘金远, 王正汹 2004 53 3409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zou X, Liu J Y, Wang Z X 2004 Acta Phys. Sin. 53 3409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Masoudi S F 2007 Vacuum 81 871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 邹秀, 刘惠平, 谷秀娥 2008 57 5111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zou X, Liu H P, Gu X E 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 5111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 刘惠平, 邹秀, 邹滨雁, 邱明辉 2016 65 245201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu H P, Zou X, Zou B Y, Qiu M H 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 245201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 邹秀, 籍延坤, 邹滨雁 2010 59 1902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zou X, Ji Y K, Zou B Y 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 1902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 刘惠平, 邹秀 2020 69 025201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu H P, Zou X 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 025201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hatami M M 2015 Phys. Plasmas 22 013508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Hatami M M 2015 Phys. Plasmas 22 023506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Hatami M M, Tribeche M, Mamun A A 2018 Phys. Plasmas 25 094502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Borgohain D R, Saharia K, Goswami K S 2016 Phys. Plasmas 23 122113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Borgohain D R, Saharia K 2018 Phys. Plasmas 25 032122
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 赵晓云, 张丙开, 王春晓, 唐义甲 2019 68 185204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao X Y, Zhang B K, Wang C X, Tang Y J 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 185204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Liu Y, Liu S Q, Xu K 2012 Phys. Plasmas 19 073702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Liu Y, Liu S Q, Zhou L 2013 Phys. Plasmas 20 043702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Tantawy S A E, Tribeche M, Moslem W M 2012 Phys. Plasmas 19 032104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Emamuddin M, Yasmin S, Asaduzzaman M, Mamun A A 2013 Phys. Plasmas 20 083708
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Safa N N, Ghomi H, Niknam A R 2014 Phys. Plasmas 21 082111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Mehdipoor M, Mohsenpour T 2015 Phys. Plasmas 22 112110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Gougam L A, Triceche M 2011 Phys. Plasmas 18 062102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Liu J Y, Wang F, Sun J Z 2011 Phys. Plasmas 18 013506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Ou J, Yang J H 2012 Phys. Plasmas 19 113504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Li J J, Ma J X, Wei Z A 2013 Phys. Plasmas 20 063503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Wang T T, Ma J X, Wei Z A 2015 Phys. Plasmas 22 093505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Tsallis C 1988 J. Stat. Phys. 52 479
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
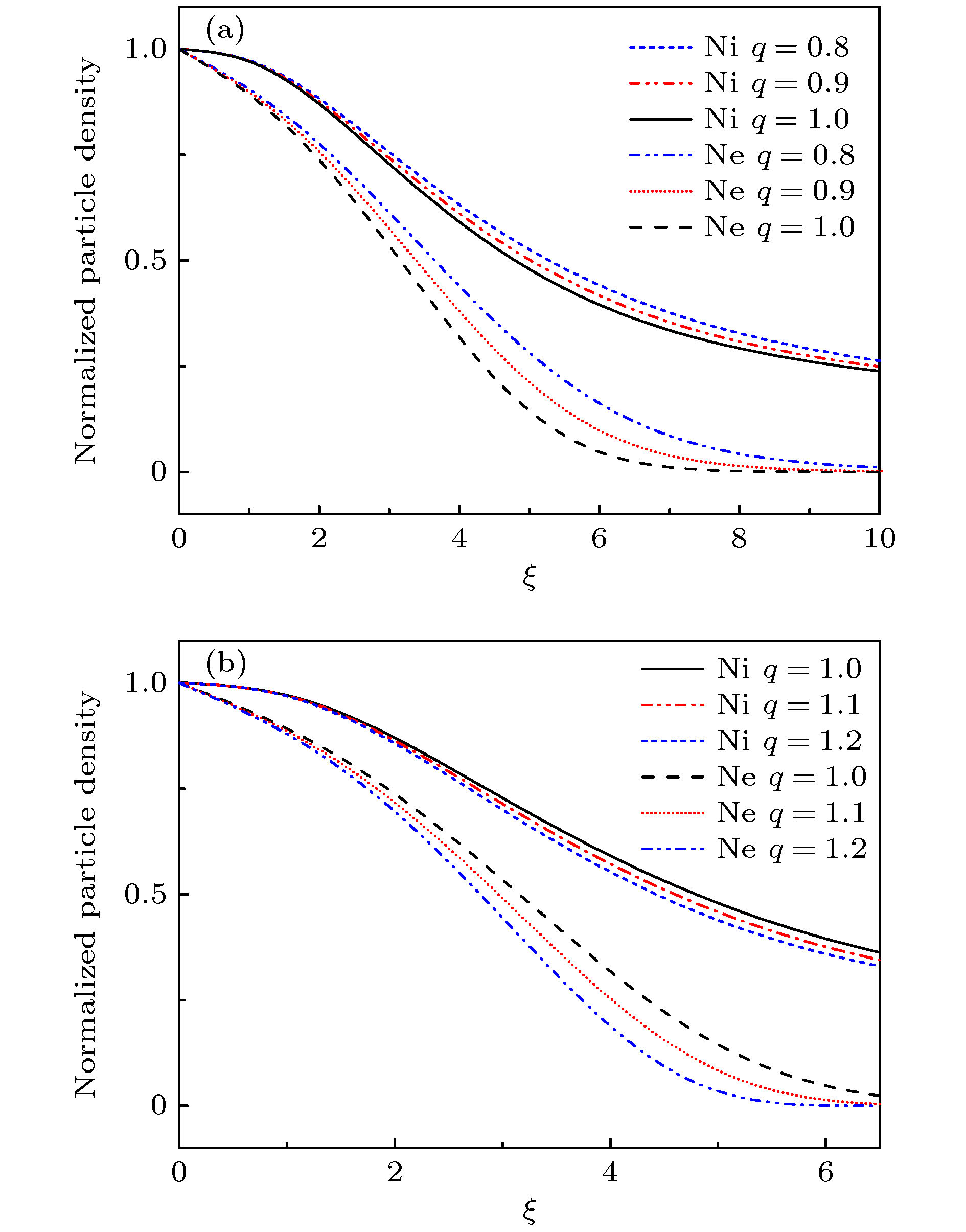
图 4 具有不同参数
$ q $ 值的离子电子密度分布($B=0.3~\mathrm{T}$ ,$ \theta =15° $ ,$ {E}_{0}=0.1 $ ,$ \beta =0 $ ) (a)$ q < 1 $ ; (b$ )q>1 $ Fig. 4. Normalized density of ions and electrons for different values of non-extensive parameter
$ q $ ($B=0.3~\mathrm{T}$ ,$ \theta =15° $ ,$ {E}_{0}=0.1 $ ,$ \beta =0 $ ): (a)$ q < 1 $ ; (b)$ q>1 $ -
[1] Chodura R 1982 Phys. Fluid 25 1628
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Riemann K U 1994 Phys. Plasmas 1 552
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Stangeby P C 1995 Phys. Plasmas 2 702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ahedo E 1997 Phys. Plasmas 4 4419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Liu J Y, Wang Z X, Wang X G 2003 Phys. Plasmas 10 3032
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Liu J Y, Wang Z X, Wang X G, Zhang Q, Zou X 2003 Phys. Plasmas 10 3507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 王正汹, 刘金远, 邹秀, 刘悦, 王晓刚 2004 53 0793
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Z X, Liu J Y, Zou X, Liu Y, Wang X G 2004 Acta Phys. Sin. 53 0793
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 邹秀, 刘金远, 王正汹 2004 53 3409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zou X, Liu J Y, Wang Z X 2004 Acta Phys. Sin. 53 3409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Masoudi S F 2007 Vacuum 81 871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 邹秀, 刘惠平, 谷秀娥 2008 57 5111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zou X, Liu H P, Gu X E 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 5111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 刘惠平, 邹秀, 邹滨雁, 邱明辉 2016 65 245201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu H P, Zou X, Zou B Y, Qiu M H 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 245201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 邹秀, 籍延坤, 邹滨雁 2010 59 1902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zou X, Ji Y K, Zou B Y 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 1902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 刘惠平, 邹秀 2020 69 025201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu H P, Zou X 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 025201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hatami M M 2015 Phys. Plasmas 22 013508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Hatami M M 2015 Phys. Plasmas 22 023506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Hatami M M, Tribeche M, Mamun A A 2018 Phys. Plasmas 25 094502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Borgohain D R, Saharia K, Goswami K S 2016 Phys. Plasmas 23 122113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Borgohain D R, Saharia K 2018 Phys. Plasmas 25 032122
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 赵晓云, 张丙开, 王春晓, 唐义甲 2019 68 185204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao X Y, Zhang B K, Wang C X, Tang Y J 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 185204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Liu Y, Liu S Q, Xu K 2012 Phys. Plasmas 19 073702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Liu Y, Liu S Q, Zhou L 2013 Phys. Plasmas 20 043702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Tantawy S A E, Tribeche M, Moslem W M 2012 Phys. Plasmas 19 032104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Emamuddin M, Yasmin S, Asaduzzaman M, Mamun A A 2013 Phys. Plasmas 20 083708
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Safa N N, Ghomi H, Niknam A R 2014 Phys. Plasmas 21 082111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Mehdipoor M, Mohsenpour T 2015 Phys. Plasmas 22 112110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Gougam L A, Triceche M 2011 Phys. Plasmas 18 062102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Liu J Y, Wang F, Sun J Z 2011 Phys. Plasmas 18 013506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Ou J, Yang J H 2012 Phys. Plasmas 19 113504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Li J J, Ma J X, Wei Z A 2013 Phys. Plasmas 20 063503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Wang T T, Ma J X, Wei Z A 2015 Phys. Plasmas 22 093505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Tsallis C 1988 J. Stat. Phys. 52 479
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 6547
- PDF下载量: 75
- 被引次数: 0

















 下载:
下载: