-
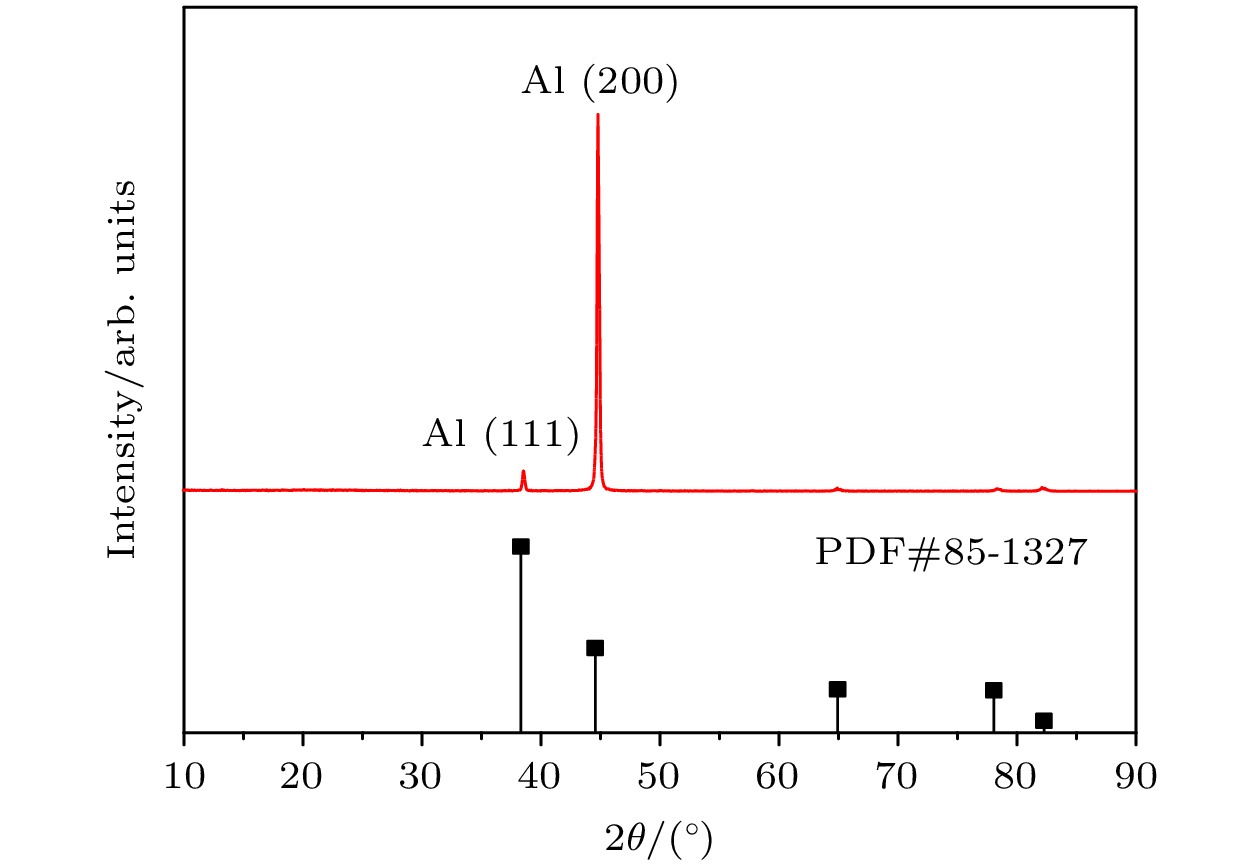
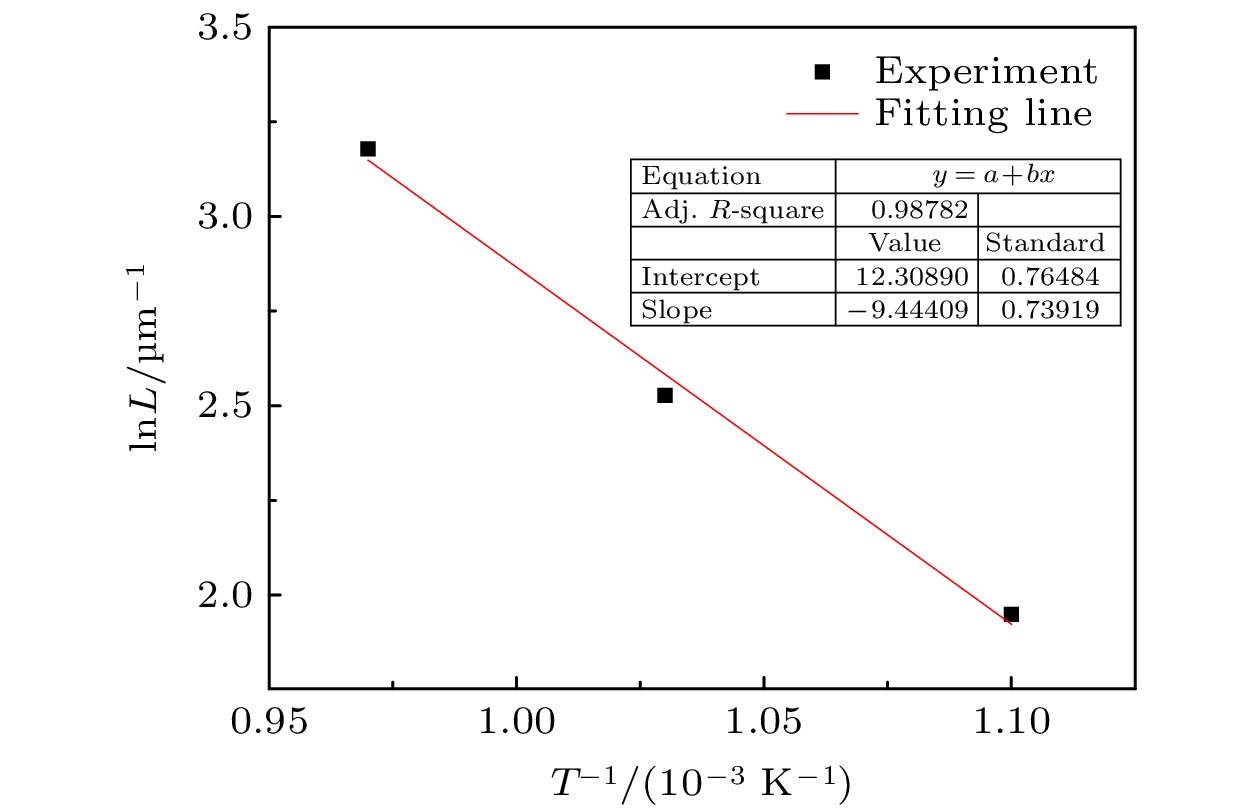
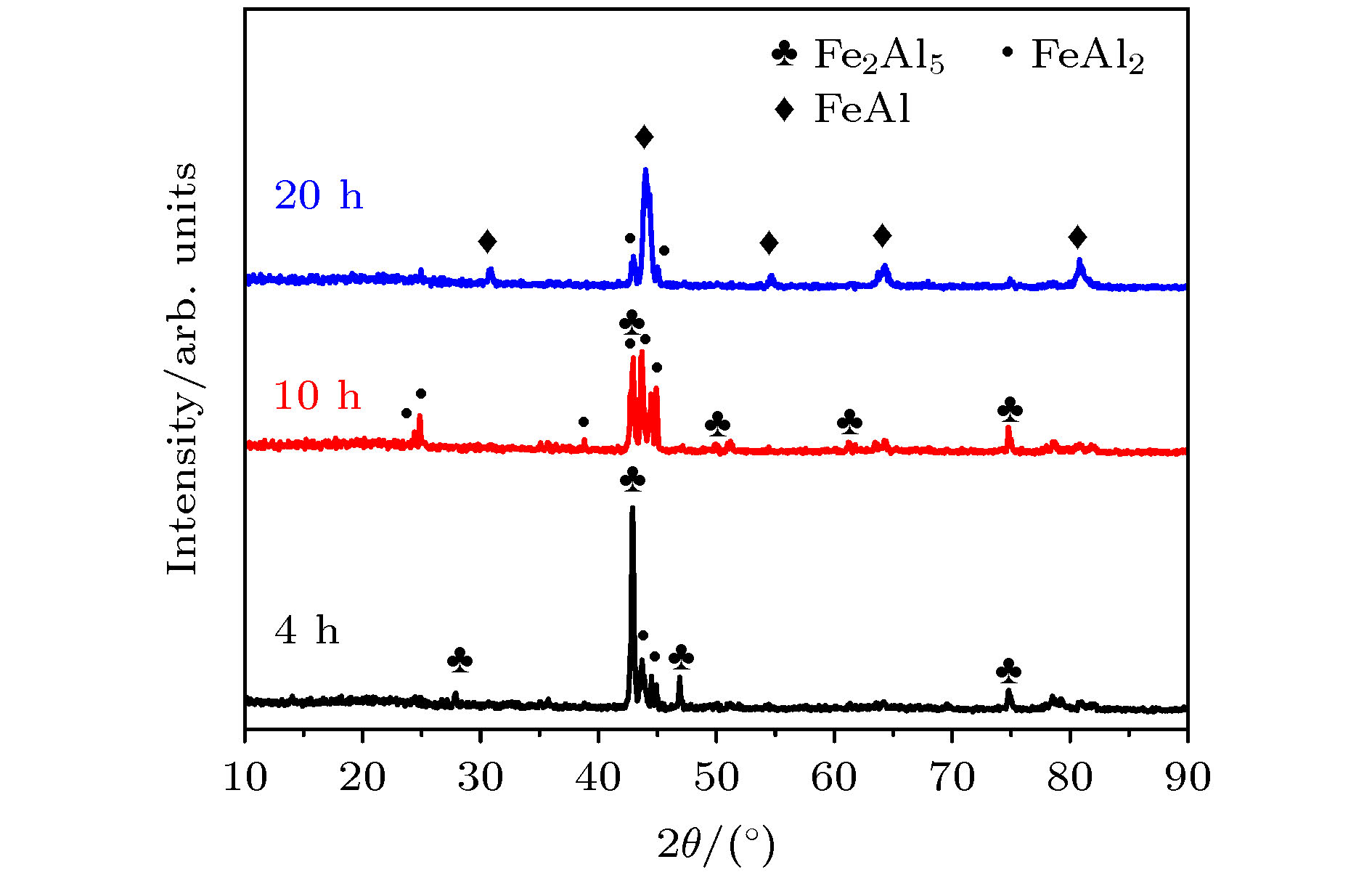
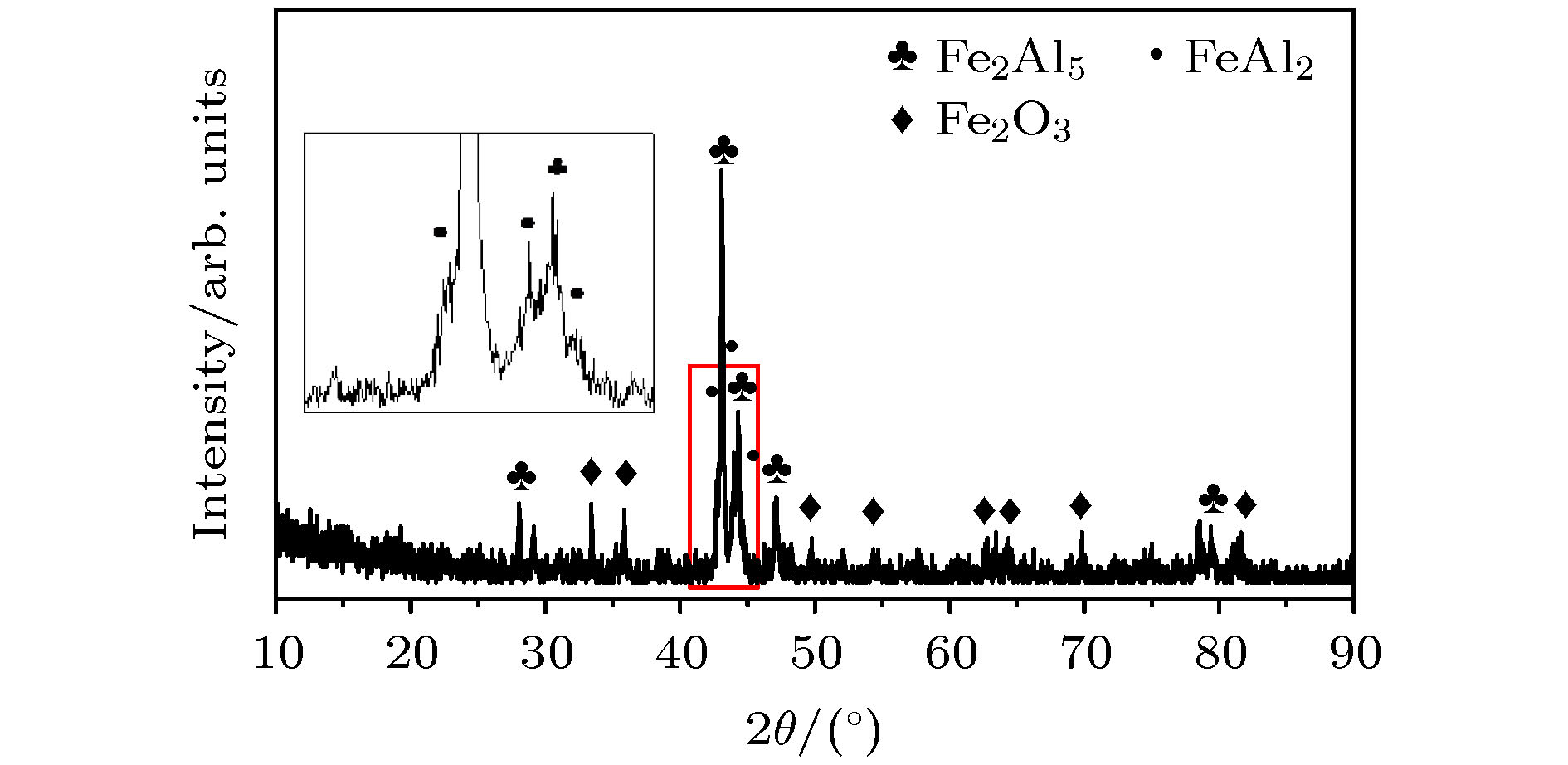
FeAl/Al2O3阻氚涂层具有高阻氚因子、耐腐蚀和耐高温等优良性能, 是ITER首选的阻氚涂层. Fe-Al合金渗层对Al2O3膜层的形成质量有重要的影响. 本文采用了AlCl3-EMIC离子液体电镀法在CLAM钢表面镀铝, 然后利用热处理使Al与基体相互扩散制备Fe-Al合金渗层. 采用X射线衍射仪、扫描电子显微镜和能量散射谱仪研究了热处理时间和温度对渗层组织结构的影响. 结果表明: 渗层厚度随着热处理温度和时间的提升而增大, 试样表面逐渐由富铝相向贫铝相转化. 在不同热处理条件下获得的渗层与CLAM钢基体结合紧密, 无孔洞等缺陷. 热处理时间一定时, 热处理温度对渗层生长速率的影响符合Arrhenius关系, 拟合计算出CLAM钢的渗铝Arrhenius活化能为78.48 kJ/mol. 在640 ℃和760 ℃时, 渗层中金属间化合物的生长受晶界扩散速率与体扩散速率的共同影响. 在综合考虑合理的渗层厚度、表面Fe-Al合金相、热处理成本的情况下, 较优的热处理工艺为700 ℃/10 h.Reduced activation ferritic/martensitic steel is one of the candidate materials for tritium breeding module in the fusion reactor. In order to control the permeability of tritium in an acceptable range, coating with low hydrogen isotope permeability, known as tritium permeation barrier, is usually prepared on the surface of such structural materials. The FeAl/Al2O3 is the first choice of tritium permeation barrier for many countries, because of its fine performance of high permeation reduction factor, corrosion resistance and high-temperature resistance. The surface morphology and microstructure of Fe-Al infiltrated layer have important influence on the quality of Al2O3 coating. In this study, Al coating on the surface of CLAM steel is prepared by electroplating of aluminum from AlCl3-EMIC. Then the Fe-Al infiltrated layer is obtained by diffusion between Al and substrate by annealing. The effects of annealing time and temperature on the microstructure of Fe-Al infiltrated layer are studied by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscope and energy dispersive spectrometer. The results show that 20-μm-thick aluminum coating is obtained on the CLAM steel surface by electroplating. The Al coating is uniform and compact, and the size of its surface columnar grain decreases with electroplating current density increasing. Annealing results show that neither hole nor gap is observed between the Fe-Al infiltrated layer and the substrate. In addition, the infiltrated layer is found to be tightly bound to the substrate with a thickness ranging from 7 μm to 45 μm, depending on the annealing parameters. At the initial stage of annealing, Cr enriched Fe-Al alloy is formed evidently. However, such a Cr enrichment disappears at higher annealing temperature or longer annealing time due to diffusion. The surface of infiltrated layer changes from aluminum-rich phase to aluminum-poor phase, and its thickness increases with annealing time or temperature rising. The temperature dependence of the growth rate of Fe-Al infiltrated layer can be described by Arrhenius equation. At this time, the Arrhenius activation energy of aluminization on CLAM steel is calculated to be 78.48 kJ/mol. At 640 ℃ and 760 ℃, the growth of Fe-Al infiltrated layer is controlled by the grain boundary as well as the volume diffusion. When the reasonable thickness and microstructure of Fe-Al alloy layer are used and annealing time or temperature keeps as low as possible, the optimal annealing temperature and time are 700 ℃/10 h, respectively.
-
Keywords:
- Fe-Al infiltrated layer /
- annealing /
- aluminum electrodeposition /
- CLAM steel
[1] Jitsukawa S, Kimura A, Kohyama A, Klueh R L, Tavassoli A A, van der Schaaf B, Odette G R, Rensman J W, Victoria M, Petersen C 2004 J. Nucl. Mater. 329 39
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Kumar E R, Vyas K N, Jayakumar T 2016 Fusion Eng. Des. 109 1522
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 丁兆楠, 杨义涛, 宋银, 张丽卿, 缑洁, 张崇宏, 罗广南 2017 66 112501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ding Z N, Yang Y T, Song Y, Zhang L Q, Gou J, Zhang C H, Luo G N 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 112501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Krauss W, Konys J, Wulf S E 2014 J. Nucl. Mater. 455 522
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 范东军 2018 硕士学位论文 (绵阳: 中国工程物理研究院)
Fan D J 2018 M. S. Thesis (Mianyang: China Academy of Engineering Physics) (in Chinese)
[6] Trinkaus H, Singh B N 2003 J. Nucl. Mater. 323 229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yang H G, Zhan Q, Zhao W W, Yuan X M, Hu Y, Han Z B 2011 J. Nucl. Mater. 417 1237
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Xiang X, Wang X L, Zhang G K, Tang T, Lai X C 2015 Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 40 3697
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Purushothaman J, Ramaseshan R, Albert S K, Rajendran, R, Gowrishankar N, Ramasubbu V, Murugesan S, Dasgupta A, Jayakumar T 2015 Fusion Eng. Des. 101 154
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 张桂凯, 向鑫, 杨飞龙 2015 核化学与放射化学 37 310
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang G K, Xiang X, Yang F L 2015 J. Nuclear Radiochem. 37 310
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 袁晓明, 杨洪广, 赵崴巍 2015 材料导报 29 66
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yuan X M, Yang H G, Zhao W W 2015 Mater. Rev. 29 66
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Purushothaman J, Ramaseshan R, Albert S K, Rajendran R, Murugesan N, Ramesh C, Gowrishankar N 2017 Surf. Coat. Tech. 325 697
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Chen J, Li X F, Hua P, Wang C Y, Chen K, Wu Y C, Zhou W 2017 Fusion Eng. Des. 125 57
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wulf S E, Holstein N, Krauss W, Konys J 2013 Fusion Eng. Des. 88 2530
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhang G K, Li J, Chen C A, Dou S P, Ling G P 2011 J. Nucl. Mater. 417 1245
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhang G K, Chen C A, Luo D L, Wang X L 2012 Fusion Eng. Des. 87 1370
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 张胜涛 2011 电镀实用技术 (北京: 中国纺织出版社) 第32页
Zhang S T 2011 Practical Technology of Electroplating (Beijing: China Textile & Apparel Press) p32 (in Chinese)
[18] 张桂凯, 李炬, 陈长安, 向鑫, 凌国平 2010 稀有金属材料与工程 39 81
Zhang G K, Li J, Chen C A, Xiang X, Ling G P 2010 Rare Metal Mat. Eng. 39 81
[19] 王兴庆, 隋永江, 吕海波 1998 上海大学学报 4 661
Wang X Q, Sui Y J, Lv H B 1998 J. Shanghai Univ. 4 661
[20] Xiang Z D, Datta P K 2004 Surf. Coat. Tech. 184 108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Mita M, Miura K, Takenaka T, Kajihara M, Kurakawa N, Sakamoto K 2006 Mat. Sci. Eng. B 126 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 胡林华, 戴松元, 王孔嘉 2003 52 2135
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu L H, Dai S Y, Wang K J 2003 Acta Phys. Sin. 52 2135
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 张桂凯 2010 硕士学位论文(绵阳: 中国工程物理研究院)
Zhang G K 2010 M. S. Thesis (Mianyang: China Academy of Engineering Physics) (in Chinese)
[24] 张桂凯, 李炬, 陈长安 2009 金属学报 45 983
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang G K, Li J, Chen C A 2009 Acta Metall. Sin. 45 983
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 李亚江, 王娟, U. A. Puskov, 马海军 2007 材料科学与工艺 15 469
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y J, Wang J, Puskov U A, Ma H J 2007 Mater. Sci. Technol. 15 469
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 刘宗昌, 任慧平, 计云萍 2015 固态相变原理新论 (北京: 科学出版社) 第56页
Liu Z C, Ren H P, Ji Y P 2015 New Theory of Solid Phase Transition (Beijing: Science Press) p56 (in Chinese)
[27] Tanaka Y, Kajihara M, Watanabe Y 2007 Mat. Sci. Eng. A 445 355
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zhang Z G, Gesmundo F, Hou P Y, Niu Y 2006 Corro. Sci. 48 741
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Tanigawa H, Gaganidze E, Hirose T, Ando M, Zinkle S J, Lindau R, Diegele E 2017 Nucl. Fusion 57 092004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Ravikirana, Mythili R, Raju S, Saibaba S, Paneerselvam G, Jayakumar T, Rajendrakumar E 2014 Bull. Mater. Sci. 37 1453
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
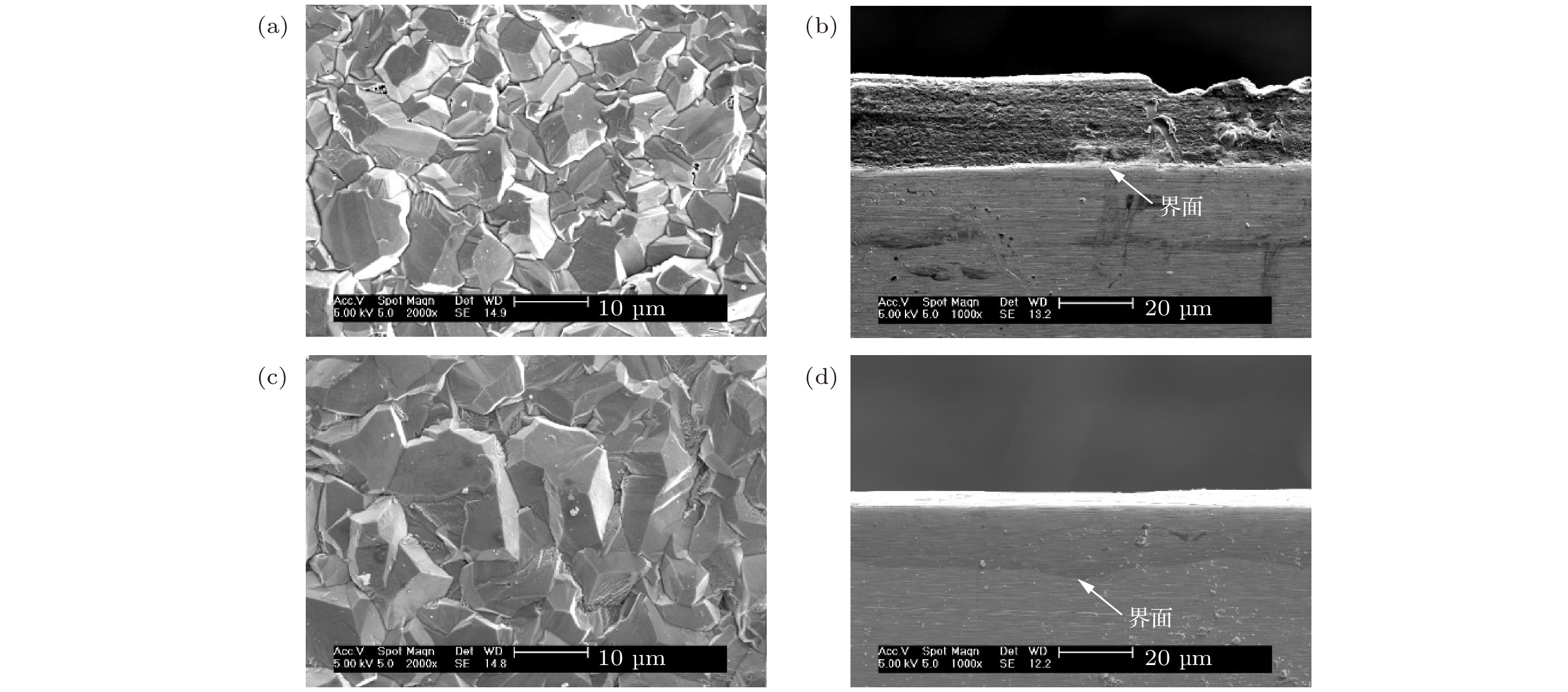
图 1 不同电镀参数下铝镀层表面(a), (c)及截面(b), (d)形貌 (a), (b)电流密度为15 mA/cm2, 68 min; (c), (d) 电流密度为10 mA/cm2, 96 min
Fig. 1. Surface (a), (c) and cross-sectional (b), (d) SEM micrographs of aluminum coatings under different electroplating parameters: (a), (b) Current density is 15 mA/cm2, 68 min; (c), (d) current density is 10 mA/cm2, 96 min.
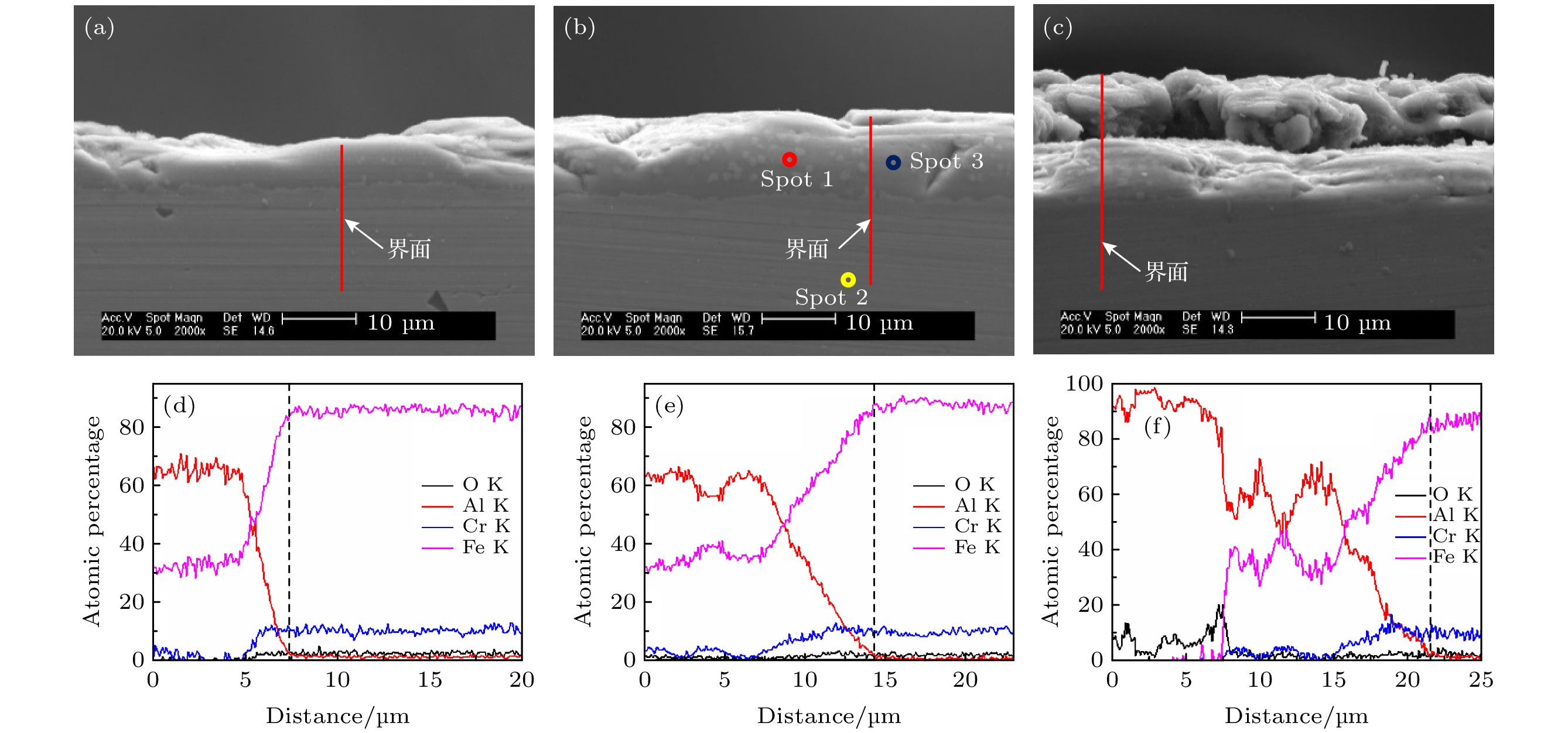
图 4 不同温度下热处理4 h后试样SEM截面形貌及EDS元素分析结果, 其中SEM截面图中红线为线扫描位置, 白色箭头指示了相应EDS曲线图中虚线位置 (a), (d)温度为640 ℃; (b), (e) 温度为700 ℃; (c), (f) 温度为760 ℃
Fig. 4. Cross-sectional SEM micrographs and EDS element analysis of samples after annealing for 4 h at different temperature. The red lines in the cross-sectional SEM micrographs are scanning lines, and the white arrows indicate the position of the dotted line in the corresponding EDS graphs. (a), (d) The temperature is 640 ℃; (b), (e) the temperature is 700 ℃; (c), (f) the temperature is 760 ℃
图 7 640 ℃热处理不同时间后试样SEM截面形貌及EDS元素分析结果, 其中SEM截面图中红线为线扫描位置, 白色箭头指示了相应EDS曲线图中虚线位置 (a), (d)处理时间为4 h; (b), (e) 处理时间为20 h; (c), (f) 处理时间为50 h
Fig. 7. Cross-sectional SEM micrographs and EDS element analysis of samples after annealing at 640 ℃ for different time. The red lines in the cross-sectional SEM micrographs are scanning lines, and the white arrows indicate the position of the dotted line in the corresponding EDS graphs: (a), (d) Heating time is 4 h; (b), (e) heating time is 20 h; (c), (f) heating time is 50 h.
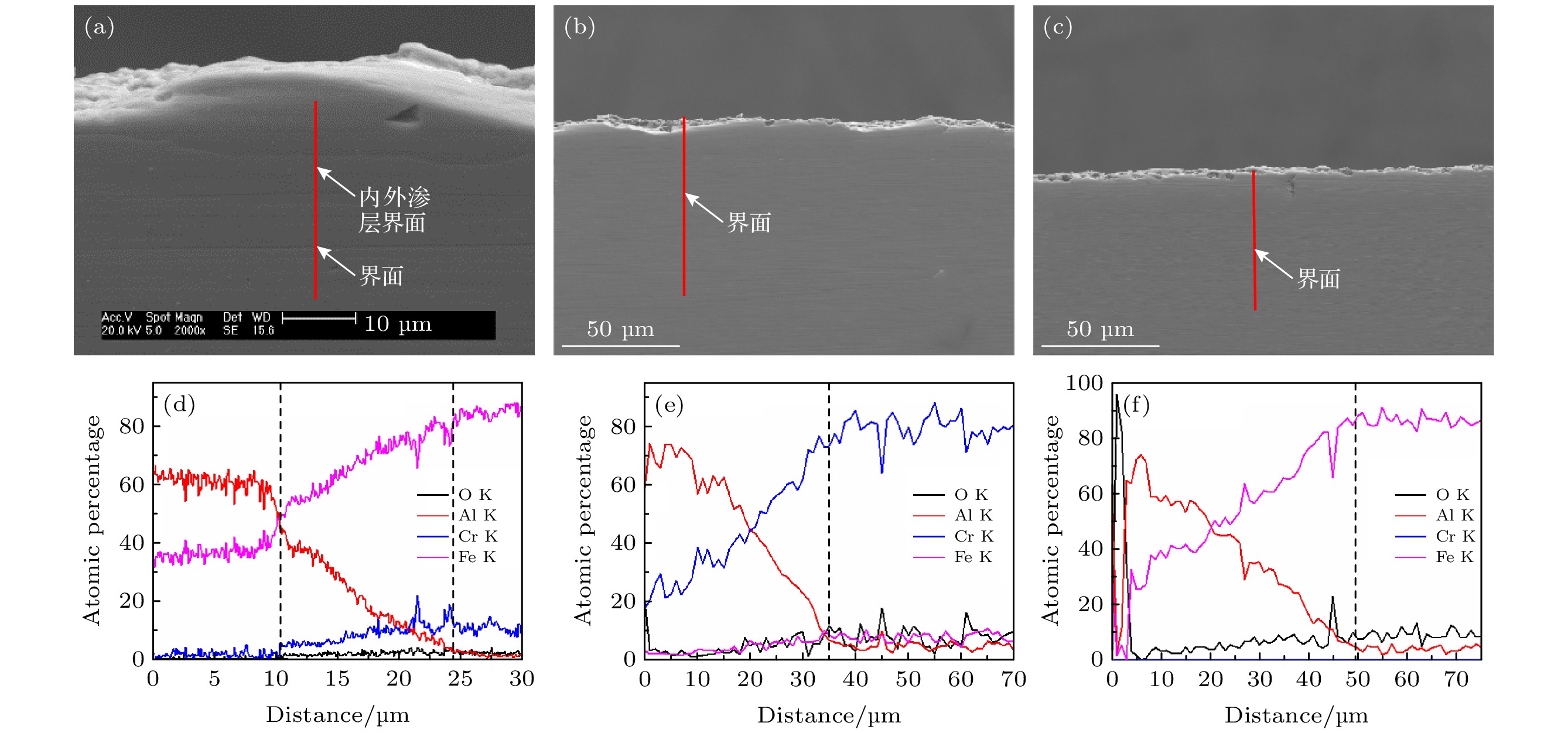
图 9 760 ℃热处理不同时间后试样SEM截面形貌及EDS元素分析结果, 其中SEM截面图中红线为线扫描位置, 白色箭头指示了相应EDS曲线图中虚线位置 (a), (d)处理时间为4 h; (b), (e) 处理时间为10 h; (c), (f) 处理时间为20 h
Fig. 9. Cross-sectional SEM micrographs and EDS element analysis of samples after annealing at 760 ℃ for different time. The red lines in the cross-sectional SEM micrographs are scanning lines, and the white arrows indicate the position of the dotted line in the corresponding EDS graphs. (a), (d) Heating time is 4 h; (b), (e) heating time is 10 h; (c), (f) heating time is 20 h.
表 1 CLAM钢的化学成分(wt%)
Table 1. Chemical composition of CLAM steel (wt%).
Cr W V Ta Mn C Si Fe 9.00 1.50 0.20 0.07 0.45 0.10 0.01 Bal 表 2 热处理条件
Table 2. Annealing condition.
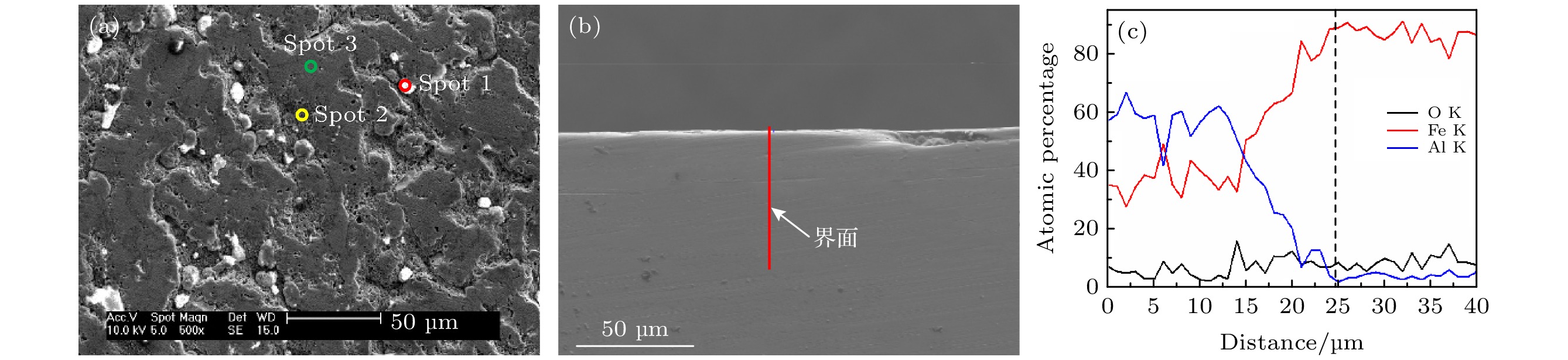
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Temperature/℃ 640 640 640 700 700 760 760 760 Annealing time/h 4 20 50 4 10 4 10 20 表 3 640 ℃/20 h下试样表面EDS能谱分析(at%)
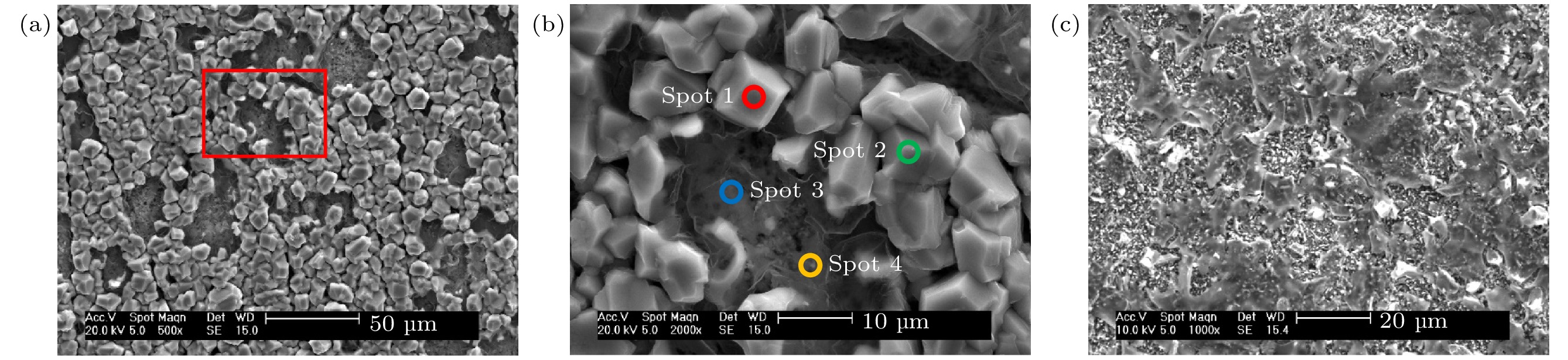
Table 3. EDS elemental analysis of sample surface at 640 ℃ for 4 h (at%).
Spot Al K Fe K Cr K O K Possible 1 95.74 — — 4.26 Al, Al2O3 2 89.82 — — 10.18 Al, Al2O3 3 58.81 16.72 1.56 22.92 — 4 57.38 16.69 — 25.93 — 表 4 640 ℃/20 h下试样截面EDS能谱分析(at%)
Table 4. EDS elemental analysis of sample cross section at 640 ℃ for 20 h (at%).
Spot Al K Fe K Cr K O K 1 (白点) 62.81 32.87 4.33 — 2 (基体) — 79.68 8.32 2.35 3 (渗层) 67.53 24.26 1.26 6.95 表 5 700 ℃/10 h试样表面EDS结果
Table 5. EDS elemental analysis of sample surface at 700 ℃ for 10 h (at%).
Spot Al K Fe L O K 1 — 25.16 74.84 2 20.37 12.46 67.17 3 71.45 14.00 14.55 -
[1] Jitsukawa S, Kimura A, Kohyama A, Klueh R L, Tavassoli A A, van der Schaaf B, Odette G R, Rensman J W, Victoria M, Petersen C 2004 J. Nucl. Mater. 329 39
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Kumar E R, Vyas K N, Jayakumar T 2016 Fusion Eng. Des. 109 1522
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 丁兆楠, 杨义涛, 宋银, 张丽卿, 缑洁, 张崇宏, 罗广南 2017 66 112501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ding Z N, Yang Y T, Song Y, Zhang L Q, Gou J, Zhang C H, Luo G N 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 112501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Krauss W, Konys J, Wulf S E 2014 J. Nucl. Mater. 455 522
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 范东军 2018 硕士学位论文 (绵阳: 中国工程物理研究院)
Fan D J 2018 M. S. Thesis (Mianyang: China Academy of Engineering Physics) (in Chinese)
[6] Trinkaus H, Singh B N 2003 J. Nucl. Mater. 323 229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yang H G, Zhan Q, Zhao W W, Yuan X M, Hu Y, Han Z B 2011 J. Nucl. Mater. 417 1237
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Xiang X, Wang X L, Zhang G K, Tang T, Lai X C 2015 Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 40 3697
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Purushothaman J, Ramaseshan R, Albert S K, Rajendran, R, Gowrishankar N, Ramasubbu V, Murugesan S, Dasgupta A, Jayakumar T 2015 Fusion Eng. Des. 101 154
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 张桂凯, 向鑫, 杨飞龙 2015 核化学与放射化学 37 310
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang G K, Xiang X, Yang F L 2015 J. Nuclear Radiochem. 37 310
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 袁晓明, 杨洪广, 赵崴巍 2015 材料导报 29 66
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yuan X M, Yang H G, Zhao W W 2015 Mater. Rev. 29 66
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Purushothaman J, Ramaseshan R, Albert S K, Rajendran R, Murugesan N, Ramesh C, Gowrishankar N 2017 Surf. Coat. Tech. 325 697
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Chen J, Li X F, Hua P, Wang C Y, Chen K, Wu Y C, Zhou W 2017 Fusion Eng. Des. 125 57
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wulf S E, Holstein N, Krauss W, Konys J 2013 Fusion Eng. Des. 88 2530
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhang G K, Li J, Chen C A, Dou S P, Ling G P 2011 J. Nucl. Mater. 417 1245
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhang G K, Chen C A, Luo D L, Wang X L 2012 Fusion Eng. Des. 87 1370
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 张胜涛 2011 电镀实用技术 (北京: 中国纺织出版社) 第32页
Zhang S T 2011 Practical Technology of Electroplating (Beijing: China Textile & Apparel Press) p32 (in Chinese)
[18] 张桂凯, 李炬, 陈长安, 向鑫, 凌国平 2010 稀有金属材料与工程 39 81
Zhang G K, Li J, Chen C A, Xiang X, Ling G P 2010 Rare Metal Mat. Eng. 39 81
[19] 王兴庆, 隋永江, 吕海波 1998 上海大学学报 4 661
Wang X Q, Sui Y J, Lv H B 1998 J. Shanghai Univ. 4 661
[20] Xiang Z D, Datta P K 2004 Surf. Coat. Tech. 184 108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Mita M, Miura K, Takenaka T, Kajihara M, Kurakawa N, Sakamoto K 2006 Mat. Sci. Eng. B 126 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 胡林华, 戴松元, 王孔嘉 2003 52 2135
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu L H, Dai S Y, Wang K J 2003 Acta Phys. Sin. 52 2135
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 张桂凯 2010 硕士学位论文(绵阳: 中国工程物理研究院)
Zhang G K 2010 M. S. Thesis (Mianyang: China Academy of Engineering Physics) (in Chinese)
[24] 张桂凯, 李炬, 陈长安 2009 金属学报 45 983
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang G K, Li J, Chen C A 2009 Acta Metall. Sin. 45 983
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 李亚江, 王娟, U. A. Puskov, 马海军 2007 材料科学与工艺 15 469
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y J, Wang J, Puskov U A, Ma H J 2007 Mater. Sci. Technol. 15 469
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 刘宗昌, 任慧平, 计云萍 2015 固态相变原理新论 (北京: 科学出版社) 第56页
Liu Z C, Ren H P, Ji Y P 2015 New Theory of Solid Phase Transition (Beijing: Science Press) p56 (in Chinese)
[27] Tanaka Y, Kajihara M, Watanabe Y 2007 Mat. Sci. Eng. A 445 355
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zhang Z G, Gesmundo F, Hou P Y, Niu Y 2006 Corro. Sci. 48 741
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Tanigawa H, Gaganidze E, Hirose T, Ando M, Zinkle S J, Lindau R, Diegele E 2017 Nucl. Fusion 57 092004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Ravikirana, Mythili R, Raju S, Saibaba S, Paneerselvam G, Jayakumar T, Rajendrakumar E 2014 Bull. Mater. Sci. 37 1453
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 7461
- PDF下载量: 98
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: