-
Optical cavity is a fundamental device of modern optics and has a wide range of applications in the fields of laser generation, nonlinear optical conversion, and optical sensors. A major aspect of the properties of optical cavity is the stability analysis. According to different geometric losses, these optical cavities can be divided into three types: stable cavity, critical cavity, and unstable cavity. The determination of the stability of the optical cavity is the basic problem of a classic system, but the research and analysis of this point have been much insufficient in the past. In this paper, by extending the definition domain of the inverse trigonometric function, the propagation matrices of the symmetric confocal cavity and the asymmetric confocal cavity are solved. The sudden change of stability with the change of geometric parameters is explained by algebraic analysis and optical ray topology.The mathematical analysis shows that the stability catastrophe of confocal cavity is due to the sudden change in the value of inverse cosine function at the critical point of the traditional domain of definition. From the perspective of geometric topology, we define the topological charge of the cavities according to the geometric propagation path of light in the cavity. Only the cavities with zero topological charge are found to be stable, and the change of topological charge is quantized, which explains the sudden change of confocal cavity stability. Finally, we build a coupled stable cavity consisting of two unstable cavities with the same parameters. The quality factors of the coupled stable cavity and the unstable cavity are analyzed by the finite difference time domain method, which further verifies the origin of the sudden change in the stability of the confocal cavity. We propose that the coupled unstable dual cavities with opposite topological charges are able to be stable, and we also find that there are new modes in the coupled cavities which are not found in the corresponding single cavity. These findings suggest a new method for controlling microcavity loss, which has a certain value for studying the new micro-nano lasers, on-chip nonlinear devices, and non-Hermitian optical sensors.
-
Keywords:
- confocal cavity /
- stability analysis /
- topological structure
[1] 周炳琨, 高以智, 陈倜嵘 2009 激光原理 (北京: 国防工业出版社) 第33−39页
Zhou B K, Gao Y Z, Chen T R 2009 Principles of Lasers (Vol.6) (Beijing: National Defense Industry Press) pp33−39 (in Chinese)
[2] Svelto O, Hanna D C 2010 Principles of Lasers (New York: Springer)
[3] Boyd R W 2003 Nonlinear Optics (Oxford: Elsevier) pp108−115
[4] Matsko A B, Savchenkov A A, Strekalov D 2005 IPN Progress Report 42 162
[5] Bravo-Abad J, Rodriguez A, Bermel P 2007 Opt. express 15 24
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Smolyaninov I I, Davis C C 2004 Phys. Rev. B 69 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Hsu C W, Zhen B, Stone A D 2016 Nat. Rev. Mater. 1 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kockum A F, Miranowicz A, De Liberato S 2019 Nat. Rev. Phys. 1 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Li M, Cushing S K, Wu N 2015 Analyst 140 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Vollmer F, Yang L 2012 Nanophotonics 1 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Jing H, Ozdemir S K, Lu X Y, Zhang J, Yang L, Nori F 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 113 053604
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Vahala K J 2003 Nature 424 6950
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 王阳, 崔碧峰, 房天啸 2017 光电子 7 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y, Cui B F, Fang T X 2017 Optoelectron. 7 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Liu Z Z, Yang J, Du J, Hu Z P, Shi T C, Zhang Z Y, Liu Y Q, Tang X S, Leng Y X, Li R 2018 ACS Nano 12 5923
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Wang K Y, Sun W Z, Li J K, Gu Z Y, Xiao S M, Song Q H 2016 ACS Photonics 3 1125
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 杨建勇, 陈华俊 2019 68 246302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang Y, Chen H J 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 246302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Chen W J, Ozdemir S K, Zhao G M, Wiersig J, Yang L 2017 Nature 548 192
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 陈华俊, 方贤文, 陈昌兆, 李洋 2019 65 194205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen H J, Fang W X, Chen C Z, Li Y 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 194205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Angelo B, Sara P, Francesco D A 2017 Analyst 142 883
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Chang L, Jiang X S, Hua S Y, Yang C, Wen J M, Jiang L, Li G Y, Wang G Z, Xiao M 2014 Nature Photon. 8 524
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Peng B, Ozdemir S K, Lei F C, Monifi F, Gianfreda M, Long G L, Fan S H, Nori F, Bender C M, Yang L 2014 Nature Phys. 10 394
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 1 腔的稳定性分析 (a)谐振腔的示意图及参数, O1和O2代表腔镜的球心, R1和R2分别表示两腔镜的半径, L表示腔长; (b)稳定图, 白色的区域表示稳定腔, 坐标轴和双曲线上的点表示临界腔, 灰色的区域表示非稳腔
Fig. 1. Stability analysis of the cavity: (a) Schematic diagram and parameters of the resonator cavity: O1 and O2 represent the spherical center of the cavity mirror, R1 and R2 represent the radius of the two mirrors, L represents the cavity length; (b) stability diagram, the white area represents the stable cavity, the coordinate axis and the hyperbola point represents the critical cavity, and the gray area represents the unstable cavity.
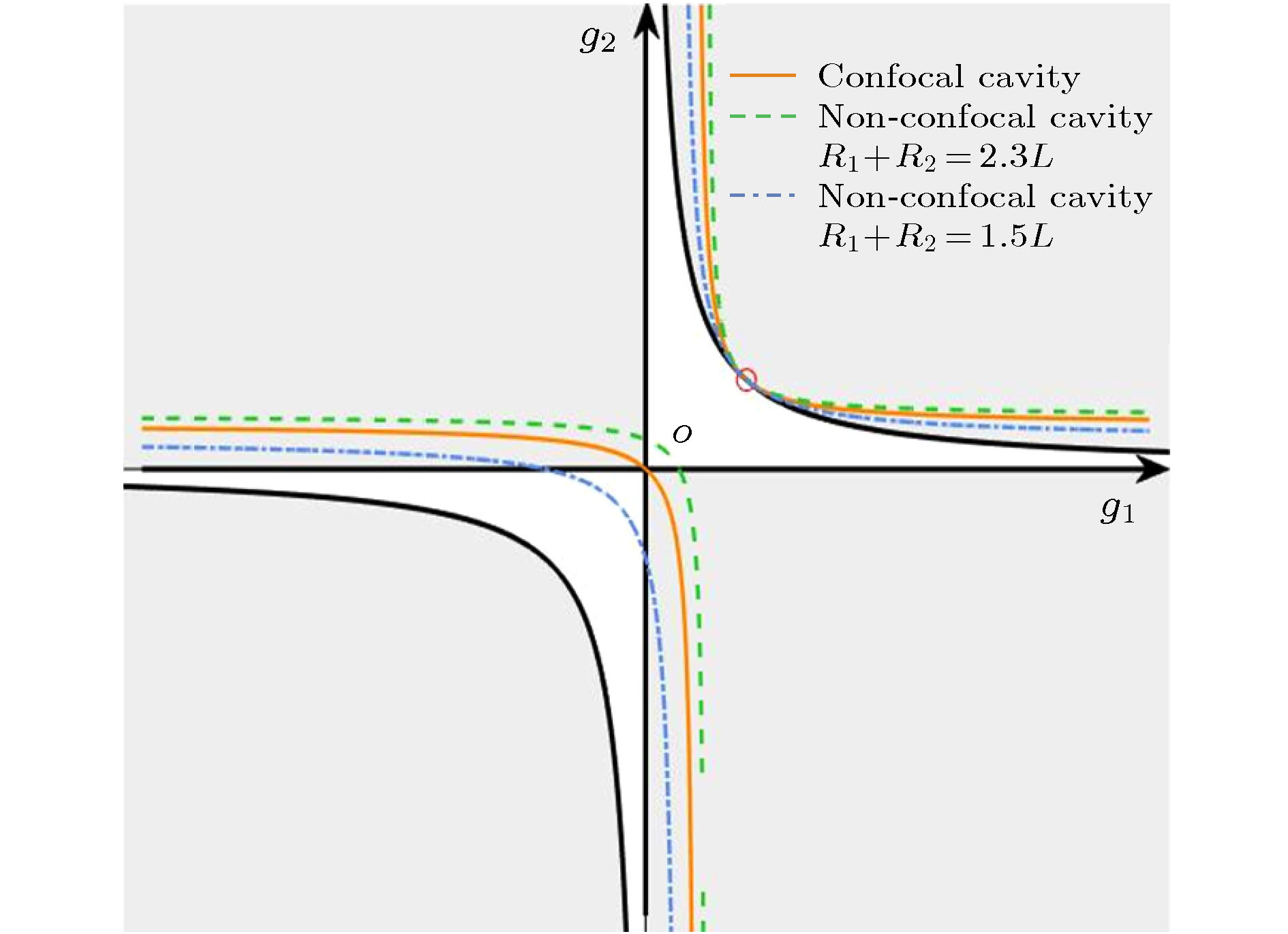
图 2 共焦腔和几种非共焦腔对应的曲线, 实线表示共焦腔, 虚线表示满足
$ {R}_{1}+{R}_{2}=2.3 L $ 的非共焦腔, 点划线表示满足$ {R}_{1}+{R}_{2}=1.5 L $ 的非共焦腔(红色圆圈除外)Fig. 2. Stability curves corresponding to the confocal cavity and non-confocal cavities. The solid line represents the confocal cavity, the dotted line represents the non-confocal cavity satisfying
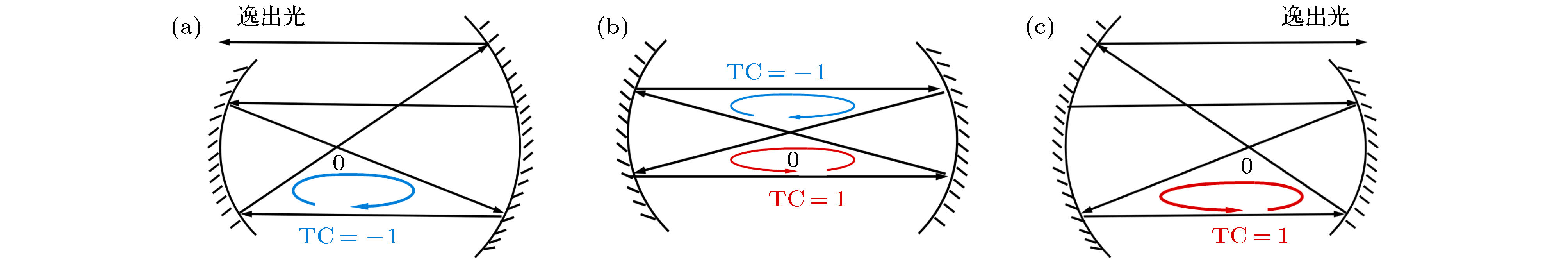
$ {R}_{1}+{R}_{2}=2.3 L $ , and the dash dot line represents the non-confocal cavity satisfying${R}_{1}+ {R}_{2}=1.5 L$ .(except for the red circle).图 3 对称和非对称共焦腔的拓扑荷分析 光线在 (a)稳定图上第二象限的非对称共焦腔(
$ {R}_{1} < {R}_{2} $ ); (b)对称共焦腔; (c)第四象限的非对称共焦腔($ {R}_{1}>{R}_{2} $ )内的传播路径图Fig. 3. Topological charge analysis of symmetric and asymmetric confocal cavities. The propagation path diagram of light in: (a) the asymmetric confocal cavity in the second quadrant (
$ {R}_{1} < {R}_{2} $ ); (b) the symmetric confocal cavity; (c) the asymmetric confocal cavity in the fourth quadrant ($ {R}_{1}>{R}_{2} $ ).表 1 腔的稳定性与
$ {g}_{1}{g}_{2} $ 的关系Table 1. Relationship between the stability of the cavity and the factors.
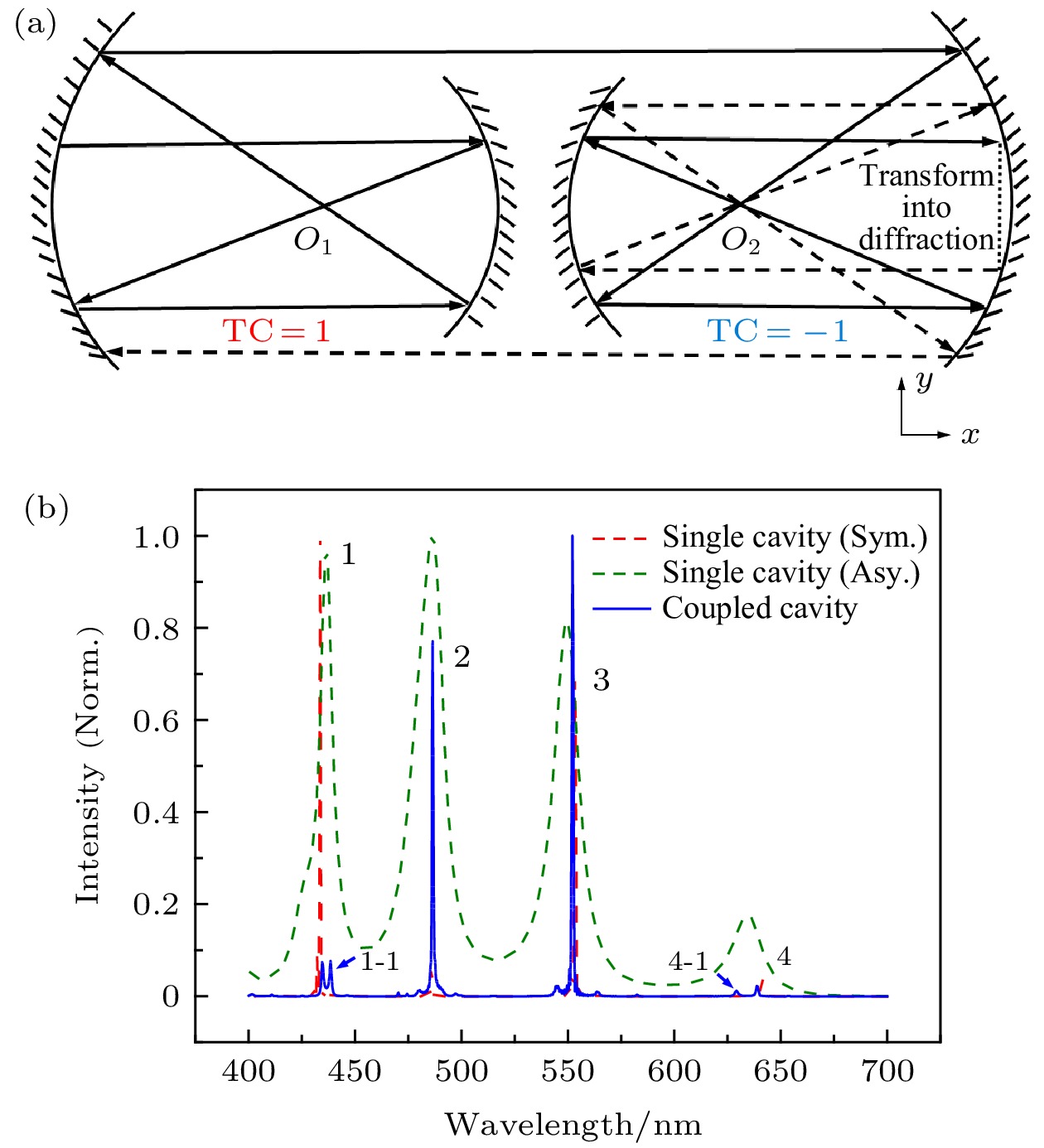
稳定性 $ {g}_{1}{g}_{2} $的取值范围 稳定腔 $ 0<{g}_{1}{g}_{2}<1 $ 临界腔 $ {g}_{1}{g}_{2}=0 $ 或 $ {g}_{1}{g}_{2}=1 $ 非稳腔 $ {g}_{1}{g}_{2}<0 $ 或 $ {g}_{1}{g}_{2}>1 $ 表 2 对称、非对称共焦腔及耦合腔内模式的Q值
Table 2. Q factor of modes in symmetric, asymmetric and coupled confocal cavities.
模式
Q 值1 1-1 2 3 4 4-1 对称共焦腔 666.2 555.6 505.6 427.5 非对称共焦腔 40.4 23.5 28.9 27.4 耦合腔 274.1 276.6 491.2 494.1 406.2 248.7 -
[1] 周炳琨, 高以智, 陈倜嵘 2009 激光原理 (北京: 国防工业出版社) 第33−39页
Zhou B K, Gao Y Z, Chen T R 2009 Principles of Lasers (Vol.6) (Beijing: National Defense Industry Press) pp33−39 (in Chinese)
[2] Svelto O, Hanna D C 2010 Principles of Lasers (New York: Springer)
[3] Boyd R W 2003 Nonlinear Optics (Oxford: Elsevier) pp108−115
[4] Matsko A B, Savchenkov A A, Strekalov D 2005 IPN Progress Report 42 162
[5] Bravo-Abad J, Rodriguez A, Bermel P 2007 Opt. express 15 24
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Smolyaninov I I, Davis C C 2004 Phys. Rev. B 69 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Hsu C W, Zhen B, Stone A D 2016 Nat. Rev. Mater. 1 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kockum A F, Miranowicz A, De Liberato S 2019 Nat. Rev. Phys. 1 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Li M, Cushing S K, Wu N 2015 Analyst 140 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Vollmer F, Yang L 2012 Nanophotonics 1 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Jing H, Ozdemir S K, Lu X Y, Zhang J, Yang L, Nori F 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 113 053604
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Vahala K J 2003 Nature 424 6950
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 王阳, 崔碧峰, 房天啸 2017 光电子 7 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y, Cui B F, Fang T X 2017 Optoelectron. 7 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Liu Z Z, Yang J, Du J, Hu Z P, Shi T C, Zhang Z Y, Liu Y Q, Tang X S, Leng Y X, Li R 2018 ACS Nano 12 5923
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Wang K Y, Sun W Z, Li J K, Gu Z Y, Xiao S M, Song Q H 2016 ACS Photonics 3 1125
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 杨建勇, 陈华俊 2019 68 246302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang Y, Chen H J 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 246302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Chen W J, Ozdemir S K, Zhao G M, Wiersig J, Yang L 2017 Nature 548 192
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 陈华俊, 方贤文, 陈昌兆, 李洋 2019 65 194205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen H J, Fang W X, Chen C Z, Li Y 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 194205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Angelo B, Sara P, Francesco D A 2017 Analyst 142 883
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Chang L, Jiang X S, Hua S Y, Yang C, Wen J M, Jiang L, Li G Y, Wang G Z, Xiao M 2014 Nature Photon. 8 524
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Peng B, Ozdemir S K, Lei F C, Monifi F, Gianfreda M, Long G L, Fan S H, Nori F, Bender C M, Yang L 2014 Nature Phys. 10 394
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 11851
- PDF下载量: 153
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: