-
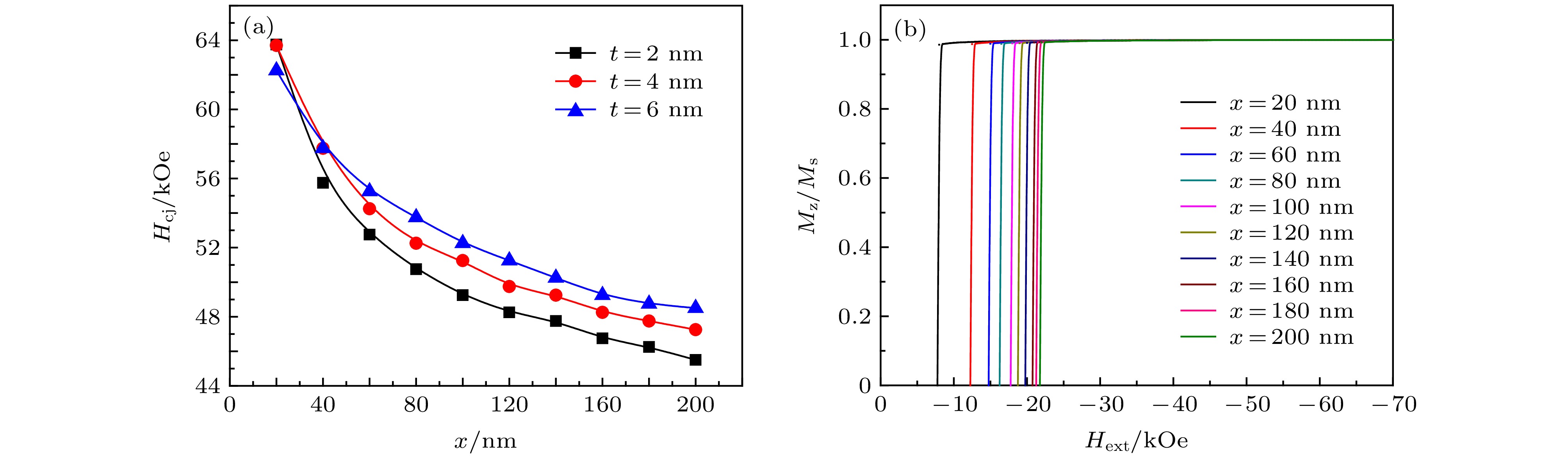
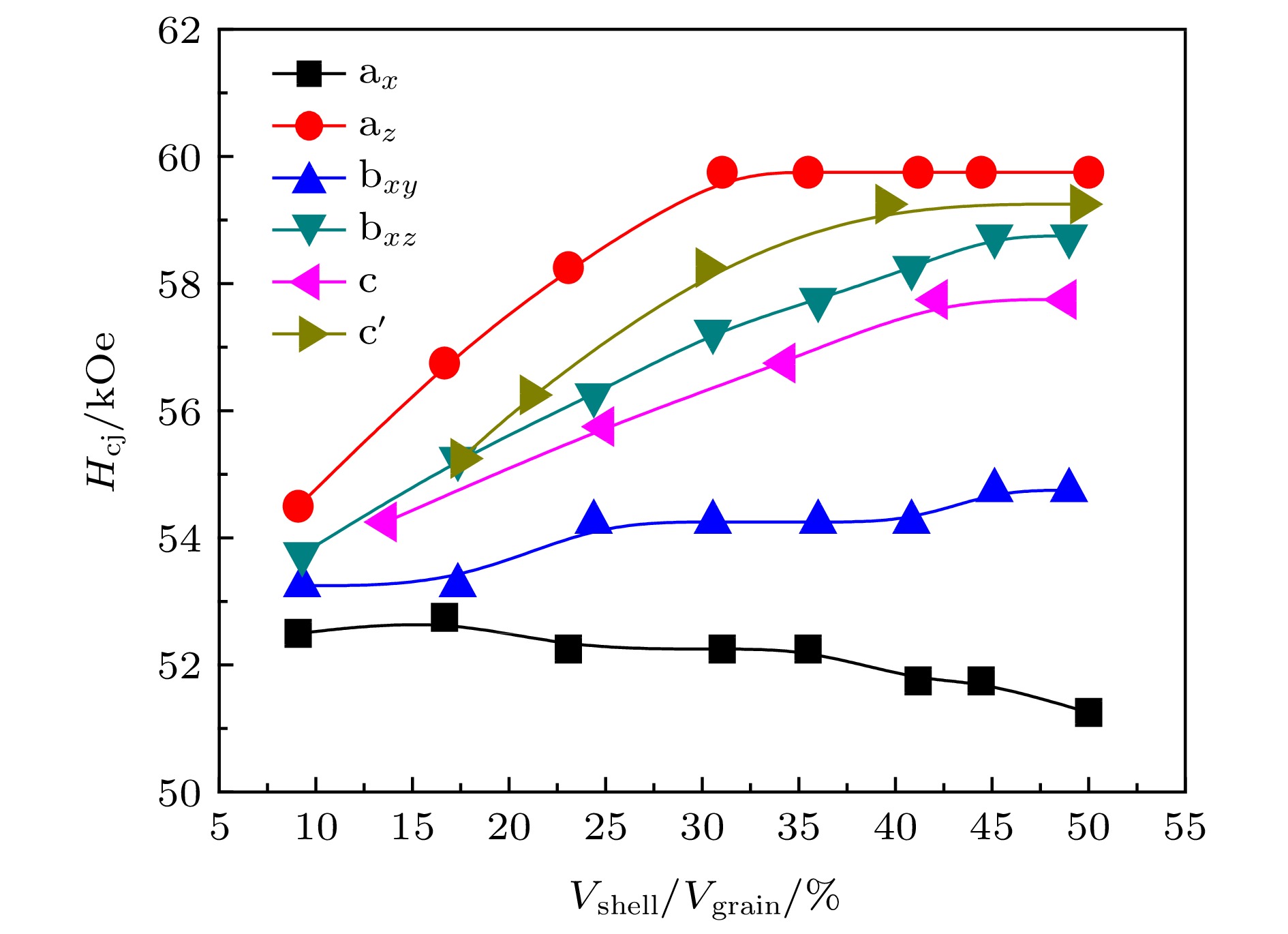
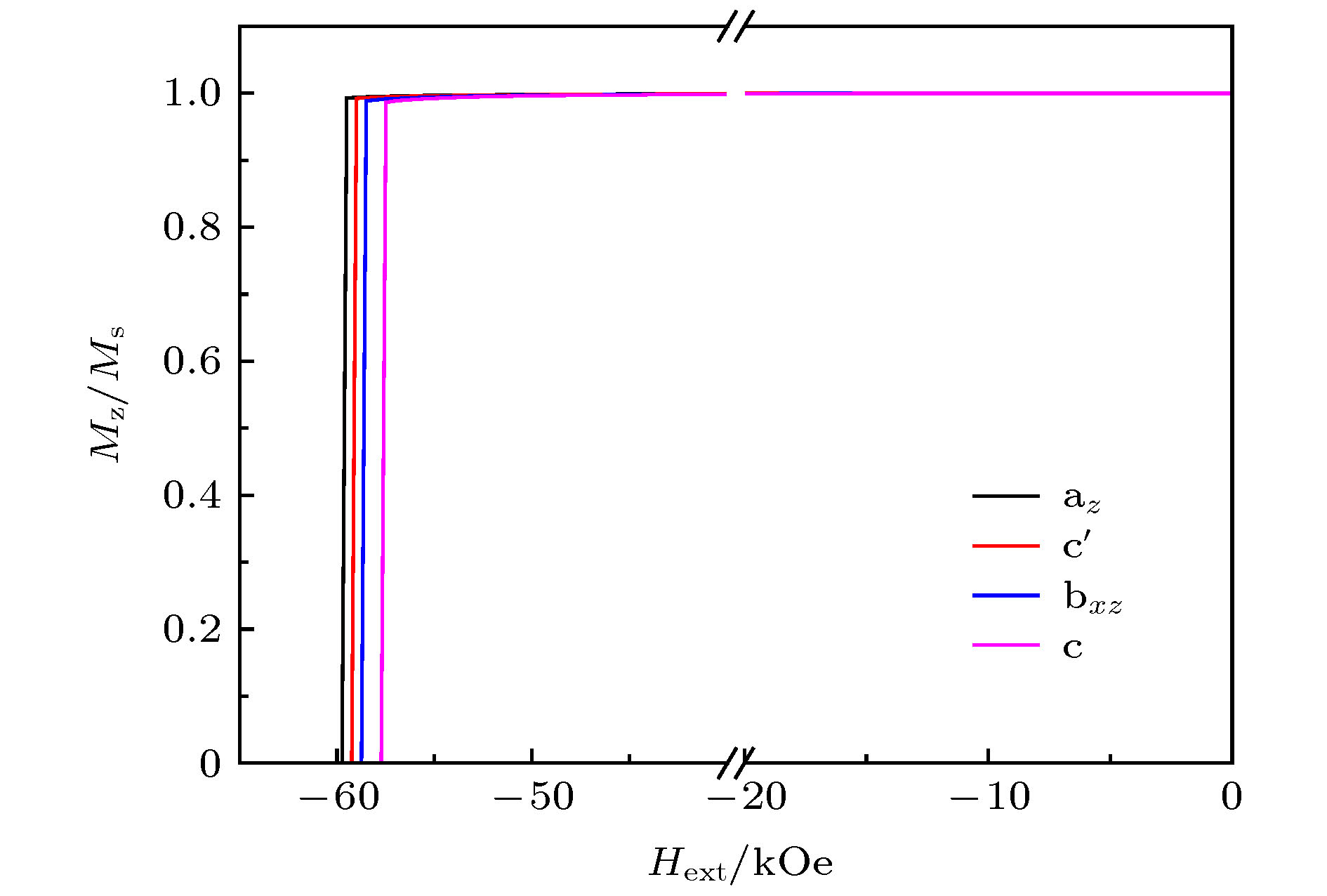
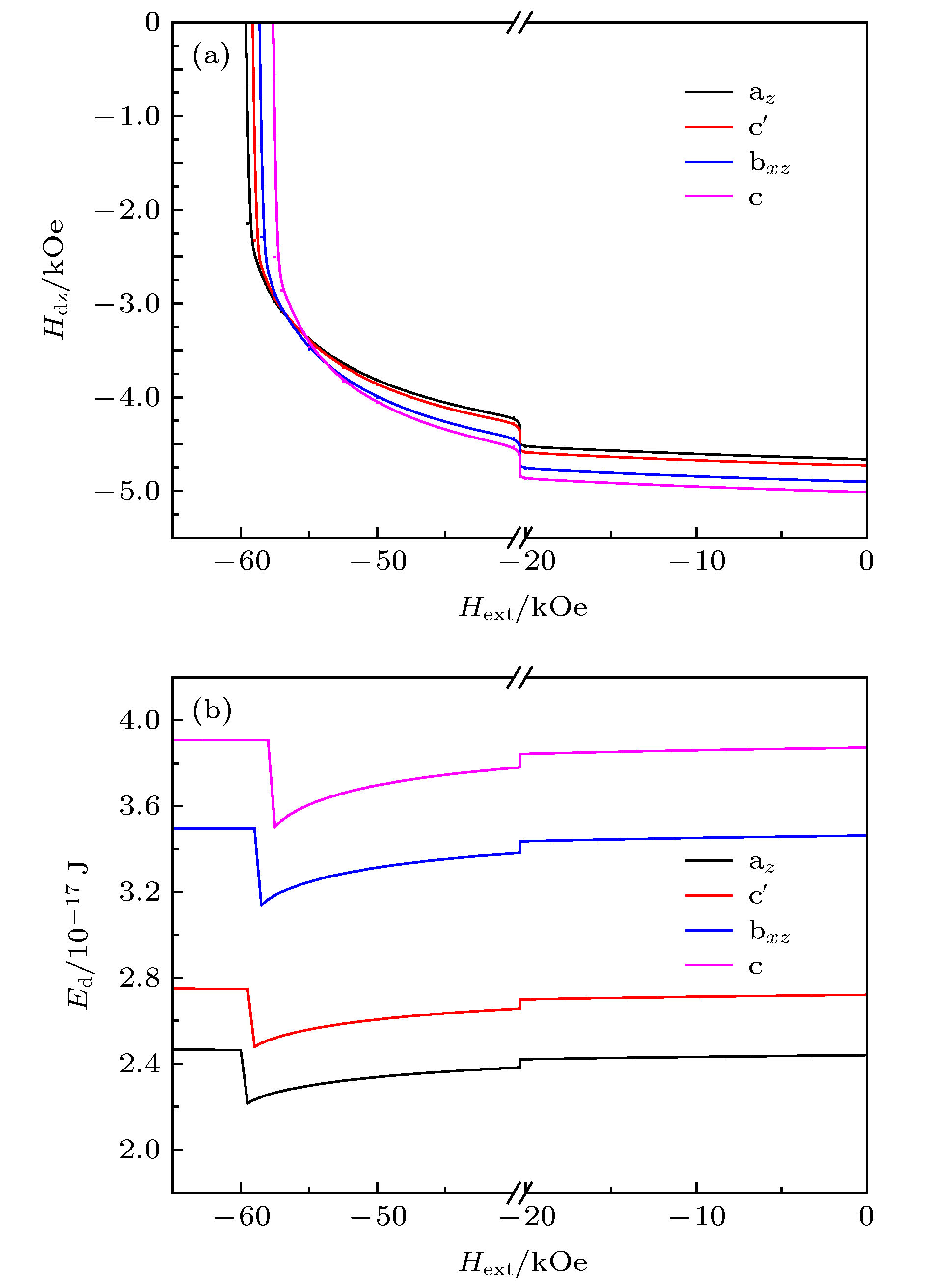
以核((Nd0.7,Ce0.3)2Fe14B)-壳(Nd2Fe14B)型晶粒为研究对象, 利用C++语言进行编程建模, 通过微磁学模拟软件OOMMF进行计算仿真, 系统讨论了核的尺寸、壳层厚度以及壳层分布对单晶粒磁体反磁化过程的影响. 对于核((Nd0.7,Ce0.3)2Fe14B)-壳(Nd2Fe14B)型晶粒, 当壳层厚度不变时, 矫顽力随核的尺寸增加而单调递减. 当核的尺寸不变时, 壳层厚度的增加使得矫顽力先增加后降低. 当核的尺寸不变, 壳层总体积也不变时, 壳层的不同分布会影响矫顽力的大小, 其中当壳层仅平均分布于核的z面(垂直于z轴的两个面)时, 矫顽力达到最大值.The effects of core size, shell thickness and shell distribution on the coercivity of single-grain core ((Nd0.7,Ce0.3)2Fe14B)-shell (Nd2Fe14B) magnets are studied by programming and modeling them through using the C++ language. All the micromagnetic simulations are carried out via object oriented micro magnetic framework (OOMMF). The results show that the coercivity decreases with the increase of core size when the shell thickness is constant. It is considered that for the grain, the increase in the size of the core leads the average magnetocrystalline anisotropy field to increase and the total demagnetization energy to increase, thereby contributing to the magnetization reversal occurring under a smaller external field. When the core size is unchanged, as the shell thickness increases gradually, the coercivity first increases and then decreases. The analysis of the position of the nucleation point shows that the reason why the coercivity increases in the early period is mainly that the nucleation point is located at the core-shell junction and belongs to the core. As the thickness of the shell increases, the exchange interaction effect between the magnetic moment of the shell and the one of the nucleation point is strengthened, so a larger external field is needed in the nucleation process. As for the decrease of the coercivity in the later period, the main reason is that the nucleation points are exactly the vertices of the shell (also the vertices of the grain), and the increase of the shell thickness conduces to increasing the total demagnetization energy, so the nucleation points can be formed under a smaller external magnetic field. With core size and shell volume kept unchanged, when the shell is distributed on the two easy-axis planes (i.e. the planes perpendicular to the easy axis) of the core, the coercivity of the magnet reaches a largest value. It is because that the nucleation points are located at the vertices of the shell (also the vertices of the grain), of which the magnetocrystalline anisotropy field is larger, and the demagnetization field is smaller. Via magnetocrystalline anisotropy field, the demagnetization energy, nucleation point, etc, the changes of coercivity in above cases can be explained.
-
Keywords:
- micromagnetic simulation /
- (Nd, Ce)-Fe-B magnets /
- core-shell structure /
- coercivity
[1] Skomski R, Coey J M D 2016 Scr. Mater. 112 112
[2] Sagawa M, Fujimura S, Togawa N, Yamamoto H, Matsuura Y 1984 J. Appl. Phys. 55 2083
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Hono K, Sepehri-Amin H 2012 Scr. Mater. 67 530
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Herbst J F, Meyer M S, Pinkerton F E 2012 J. Appl. Phys. 111 07A718
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhang H W, Zhao T Y, Rong C B, Zhang S Y, Han B S, Shen B G 2003 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 267 224
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Gutfleisch O, Willard M A, Brück E, Chen C H, Sankar S G, Liu J P 2011 Adv. Mater. 23 821
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Minowa T 2008 Resour. Geol. 58 414
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Niu E, Chen Z A, Chen G A, Zhao Y G, Zhang J, Rao X L, Hu B P, Wang Z X 2014 J. Appl. Phys. 115 113912
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Xing M Y, Han J Z, Lin Z, Wan F M, Li C, Liu S Q, Wang C S, Yang J B, Yang Y C 2013 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 331 140
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Boltich E B, Oswald E, Huang M Q, Hirosawa S, Wallace W E, Burzo E 1985 J. Appl. Phys. 57 4106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Zhou S X, Wang Y G, Hoier R 1994 J. Appl. Phys. 75 6268
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Okada M, Sugimoto S, Ishizaka C, Tanaka T, Homma M 1985 J. Appl. Phys. 57 4146
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li D, Bogatin Y 1991 J. Appl. Phys. 69 5515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Yan C J, Guo S, Chen R J, Lee D, Yan A R 2014 IEEE Trans. Magn. 50 2102605
[15] Zhu M G, Han R, Li W, Huang S L, Zheng D W, Song L W, Shi X N 2015 IEEE Trans. Magn. 51 2104604
[16] Zhu M G, Li W, Wang J D, Zheng L Y, Li Y F, Zhang K, Feng H B, Liu T 2014 IEEE Trans. Magn. 50 1000104
[17] Huang S L, Feng H B, Zhu M G, Li A H, Li Y F, Sun Y C, Zhang Y, Li W 2015 Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 22 417
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Li W, Li A H, Feng H B, Huang S L, Wang J D, Zhu M G 2015 IEEE Trans. Magn. 51 2103603
[19] Huang S L, Feng H B, Zhu M G, Li A H, Zhang Y, Li W 2014 AIP Adv. 4 10727
[20] Rong C B, Shen B G 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 117502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Shang R X, Xiong J F, Liu D, Zuo S L, Zhao X, Li R, Zuo W L, Zhao T Y, Chen R J, Sun J R, Shen B G 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 057502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Liu D, Zhao T Y, Li R, Zhang M, Shang R X, Xiong J F, Zhang J, Sun J R, Shen B G 2017 AIP Adv. 7 056201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Li R, Liu Y, Zuo S L, Zhao T Y, Hu F X, Sun J R, Shen B G 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 047501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Li L, Dong S Z, Chen H S, Jiang R J, Li D, Han R, Zhou D, Zhu M G, Wei Li W, Sun W 2019 Chin. Phys. B 28 037502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Sagawa M, Fujimura S, Yamamoto H, Matsuura T, Hirosawa S 1985 J. Appl. Phys. 57 4094
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Herbst J F 1991 Rev. Mod. Phys. 63 819
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
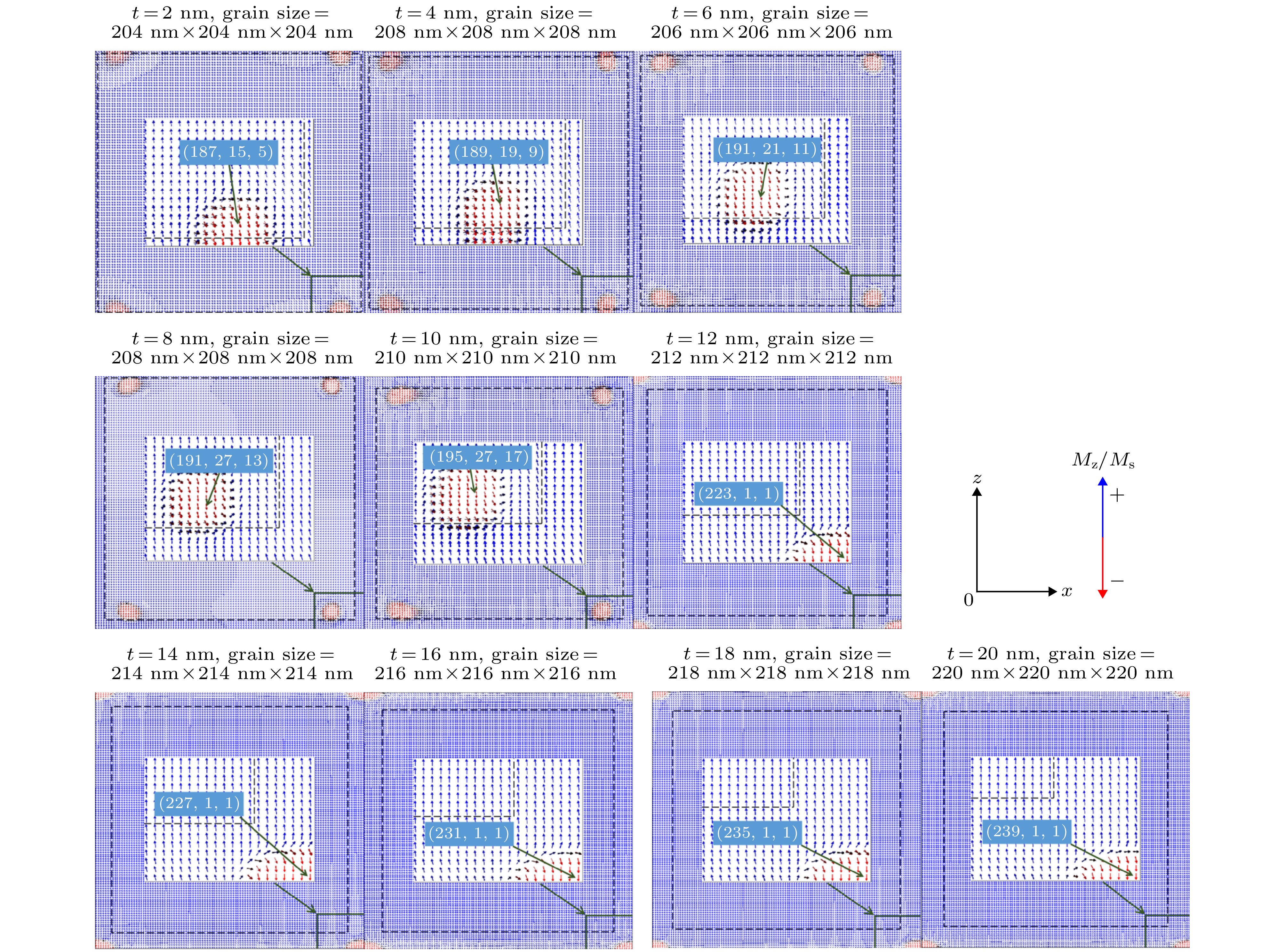
图 6 壳层厚度为2−20 nm时不同的形核点(x-z面视图)(虚线表示核与壳层的边界; 图中放大区域特别标出位置的点表示该模型的形核点; 蓝色箭头代表磁矩与初始磁化方向相同, 即磁矩未反生明显反转, 红色箭头磁矩已经发生反转)
Fig. 6. Illustration of the nucleation points for t = 2−20 nm (view of x-z plane) (The dotted lines represent the boundary between the core and the shelll; the point in the magnified area specifically indicates the nucleation point of the model; the blue arrow indicates that the magnetic moment is the same as the initial magnetization direction, that is, the magnetic moment is not reflected. Reversal, the magnetic moment of the red arrow has reversed).
图 7 外场为48.25 kOe (与矫顽力大小相同)时, t = 6 nm晶粒的磁化反转过程(x-z面视图, y = 21 nm)(虚线表示核与壳层的边界; 蓝色箭头代表磁矩与初始磁化方向相同, 即磁矩未反生明显反转, 红色箭头磁矩已经发生反转)
Fig. 7. The reversal process for t = 6 nm (view of x-z plane at y = 21 nm) under external field of 48.25 kOe (equal to the coercivity) (The dotted lines represent the boundary between the core and the shelll; the blue arrow indicates that the magnetic moment is the same as the initial magnetization direction, that is, the magnetic moment is not reflected. Reversal, the magnetic moment of the red arrow has reversed).
图 8 外场为50.25 kOe (与矫顽力大小相同)时, t = 16 nm晶粒的磁化反转过程(x-z面视图, y = 1 nm)(虚线表示核与壳层的边界; 蓝色箭头代表磁矩与初始磁化方向相同, 即磁矩未反生明显反转, 红色箭头磁矩已经发生反转)
Fig. 8. The reversal process for t =16 nm (view of x-z plane at y = 1 nm) under external field of 50.25 kOe (equal to the coercivity) (The dotted lines represent the boundary between the core and the shelll; the blue arrow indicates that the magnetic moment is the same as the initial magnetization direction, that is, the magnetic moment is not reflected. Reversal, the magnetic moment of the red arrow has reversed).
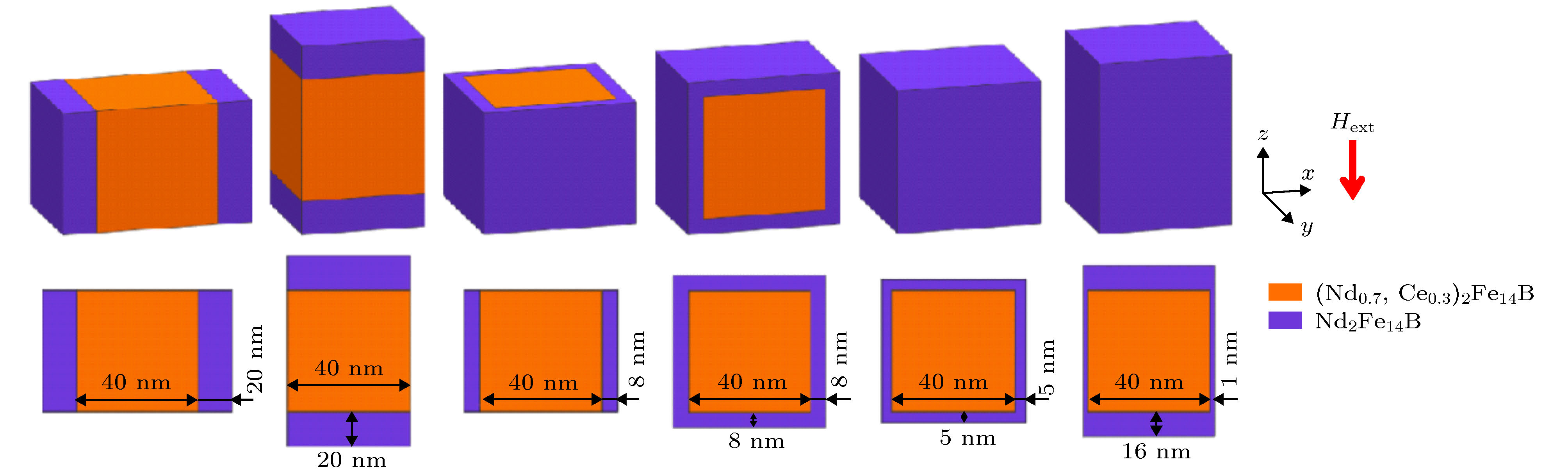
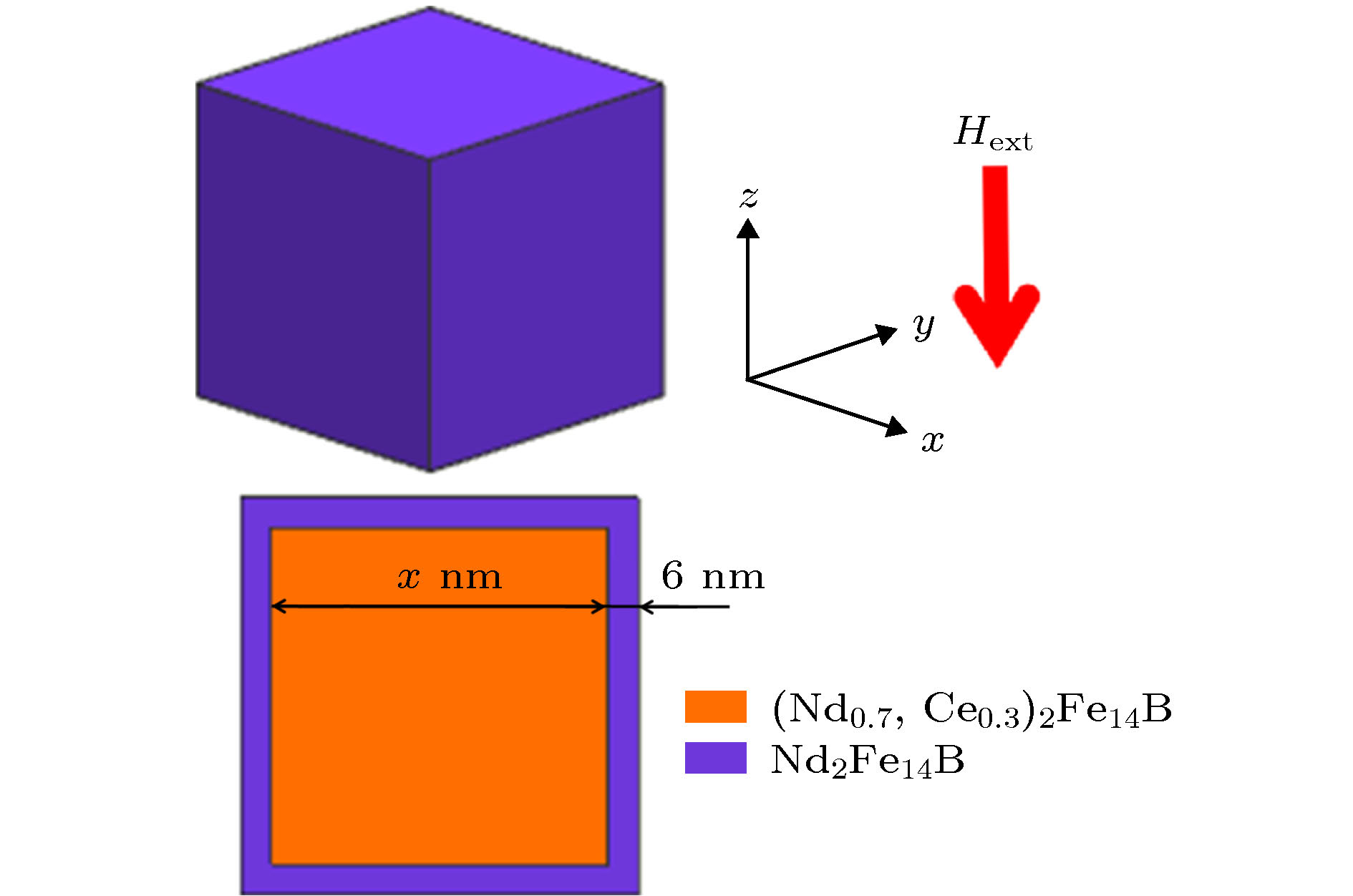
图 10 6种核((Nd0.7, Ce0.3)2Fe14B)-壳(Nd2Fe14B)模型, 从左到右: ax型, 壳层只分布在核的x面(即与x轴垂直的面), 两面各一半; az型, 壳层只分布在核的z面(即与z轴垂直的面), 两面各一半; bxy型, 壳层均匀分布在核的x面和y面; bxz型, 壳层均匀分布在核的x面和z面; c型, 壳层均匀分布在核的x面、y面、z面(即均匀包覆); c'型, 壳层在核的x面和y面的厚度均为1 nm, 在核的z面厚度随壳层总体积可变 (图中标示尺寸以Vshell/Vgrain ≈ 50%为例)
Fig. 10. Illustration of six types of core ((Nd0.7, Ce0.3)2Fe14B)-shell (Nd2Fe14B) model, from left to right: ax type, the shell is evenly distributed on the two x-planes (the plane perpendicular to the x-axis) of the core; az type, the shell is evenly distributed on the two z-planes (the plane perpendicular to the z-axis) of the core; bxy type, the shell is evenly distributed on the x-planes and the y-planes of the core; bxz type, the shell is evenly distributed on the x-planes and the z-planes of the core; c type, the shell is evenly distributed on the x-planes, y-planes and the z-planes of the core (evenly distributed around the core); c' type, both the shell thicknesses for the x-planes and the y-planes of the core are 1 nm, and the shell thickness for the z-planes of the core is variable with changing total shell volume (The size shown in the figure takes Vshell/Vgrain ≈ 50% as an example).
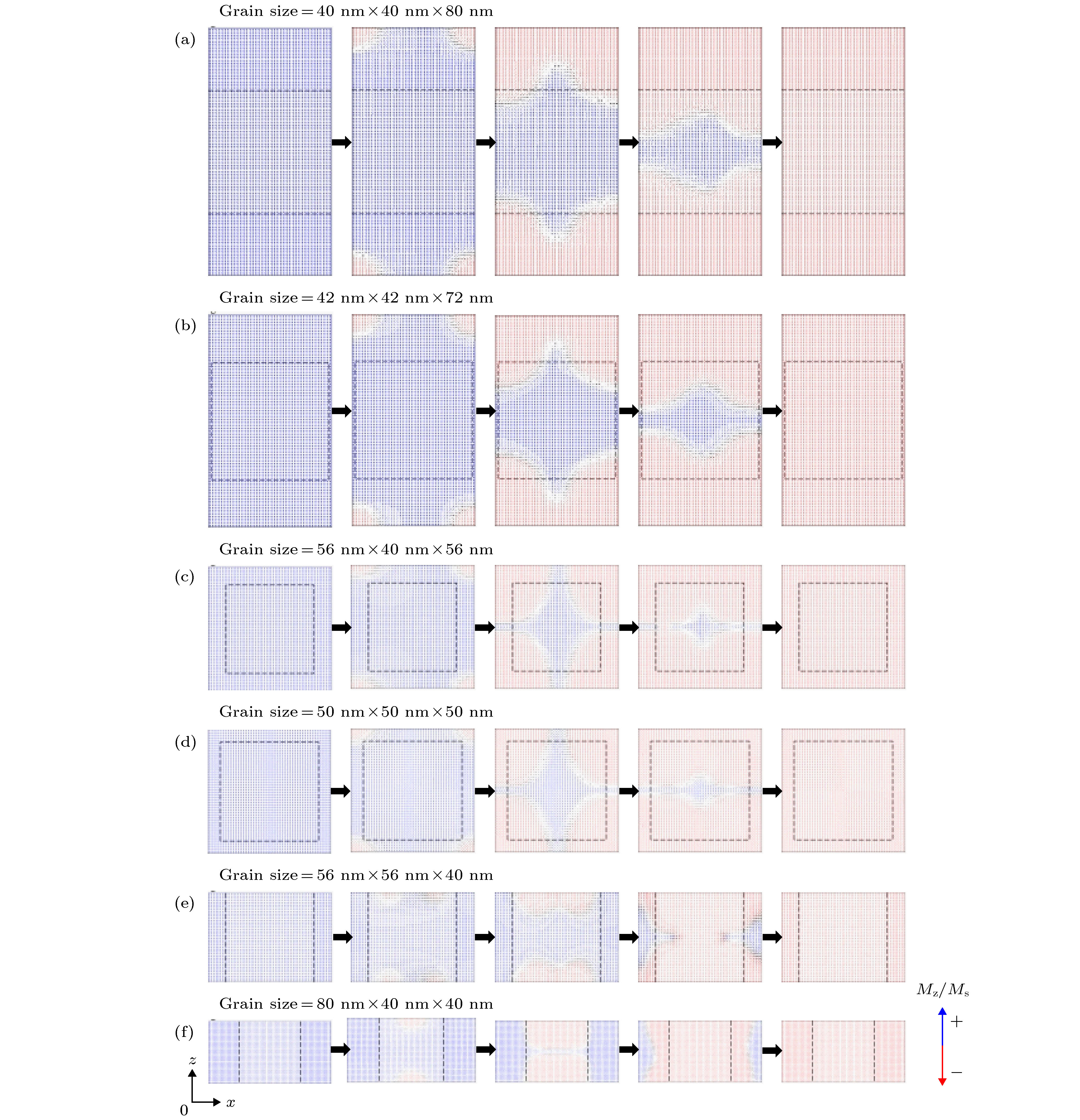
图 12 Vshell/Vgrain ≈ 50%时, 6种晶粒的磁化反转过程图(x-z面视图) (a) az型(x-z面位置: y = 0.5 nm; 外场为59.75 kOe, 与矫顽力大小相同); (b) c'型(x-z面位置: y = 0.5 nm; 外场为59.25 kOe, 与矫顽力大小相同); (c) bxz型(x-z面位置: y = 0.5 nm; 外场为58.75 kOe, 与矫顽力大小相同); (d) c型(x-z面位置: y = 0.5 nm; 外场为57.75 kOe, 与矫顽力大小相同); (e) bxy型(x-z面位置: y = 18.5 nm; 外场为54.75 kOe, 与矫顽力大小相同); (f) ax型(x-z面位置: y = 0.5 nm; 外场为51.25 kOe, 与矫顽力大小相同)
Fig. 12. The reversal magnetization processes of six types of grains when Vshell/Vgrain ≈ 50% (view of x-z plane): (a) az type (x-z plane position: y = 0.5 nm; external field is 59.75 kOe, same as coercive force); (b) c' type (x-z plane position: y = 0.5 nm; external field is 59.25 kOe, and the coercive force is the same); (c) bxz type (x-z plane position: y = 0.5 nm; the external field is 58.75 kOe, which is the same as the coercive force); (d) c type (x-z plane position: y = 0.5 nm; the external field is 57.75 kOe, which is the same as the coercive force; (e) bxy type (x-z plane position: y = 18.5 nm; the external field is 54.75 kOe, which is the same as the coercive force); (f) ax type (x-z plane position: y = 0.5 nm; the external field is 51.25 kOe, which is the same as the coercive force).
表 1 壳层厚度保持为6 nm时, 不同核尺寸(边长)的晶粒的总Ce含量及内禀磁性参数
Table 1. The total Ce content and intrinsic magnetic parameters of the grain with the same shell thickness 6 nm but different core size (side length).
Core size(x)/nm Total Ce content/at.% Average K1 /MJ·m–3 Average Ms /kA·m–1 Average HA /kA·m–1·kOe–1 20 7.32 4.28 1255.37 (5428.72)/(68.2) 40 13.65 4.09 1233.21 (5277.48)/(66.3) 60 17.36 3.98 1220.24 (5189.92)/(65.2) 80 19.73 3.91 1211.96 (5134.20)/(64.5) 100 21.35 3.86 1206.26 (5094.40)/(64.0) 120 22.54 3.82 1202.11 (5062.56)/(63.6) 140 23.44 3.80 1198.96 (5038.68)/(63.3) 160 24.15 3.78 1196.48 (5022.76)/(63.1) 180 24.72 3.76 1194.48 (5006.84)/(62.9) 200 25.19 3.74 1192.84 (4998.88)/(62.8) 表 2 核的尺寸保持为200 nm × 200 nm × 200 nm时, 不同壳层厚度t的晶粒的总Ce含量及内禀磁性参数
Table 2. The total Ce content and intrinsic magnetic parameters of the grain with the same core size 200 nm × 200 nm × 200 nm but different shell thicknesses t.
t/nm Total Ce content/at.% Average K1/MJ·m–3 Average Ms/kA·m–1 Average HA/kA·m–1·kOe–1 2 28.27 3.65 1182.06 (4919.28)/(61.8) 4 26.67 3.70 1187.66 (4959.08)/(62.3) 6 25.19 3.74 1192.84 (4998.88)/(62.8) 8 23.81 3.79 1197.65 (5030.72)/(63.2) 10 22.54 3.82 1202.11 (5062.56)/(63.6) 12 21.35 3.86 1206.26 (5094.40)/(64.0) 14 20.25 3.89 1210.13 (5118.28)/(64.3) 16 19.22 3.92 1213.73 (5150.12)/(64.7) 18 18.26 3.95 1217.09 (5174.00)/(65.0) 20 17.36 3.98 1220.24 (5189.92)/(65.2) -
[1] Skomski R, Coey J M D 2016 Scr. Mater. 112 112
[2] Sagawa M, Fujimura S, Togawa N, Yamamoto H, Matsuura Y 1984 J. Appl. Phys. 55 2083
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Hono K, Sepehri-Amin H 2012 Scr. Mater. 67 530
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Herbst J F, Meyer M S, Pinkerton F E 2012 J. Appl. Phys. 111 07A718
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhang H W, Zhao T Y, Rong C B, Zhang S Y, Han B S, Shen B G 2003 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 267 224
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Gutfleisch O, Willard M A, Brück E, Chen C H, Sankar S G, Liu J P 2011 Adv. Mater. 23 821
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Minowa T 2008 Resour. Geol. 58 414
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Niu E, Chen Z A, Chen G A, Zhao Y G, Zhang J, Rao X L, Hu B P, Wang Z X 2014 J. Appl. Phys. 115 113912
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Xing M Y, Han J Z, Lin Z, Wan F M, Li C, Liu S Q, Wang C S, Yang J B, Yang Y C 2013 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 331 140
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Boltich E B, Oswald E, Huang M Q, Hirosawa S, Wallace W E, Burzo E 1985 J. Appl. Phys. 57 4106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Zhou S X, Wang Y G, Hoier R 1994 J. Appl. Phys. 75 6268
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Okada M, Sugimoto S, Ishizaka C, Tanaka T, Homma M 1985 J. Appl. Phys. 57 4146
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li D, Bogatin Y 1991 J. Appl. Phys. 69 5515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Yan C J, Guo S, Chen R J, Lee D, Yan A R 2014 IEEE Trans. Magn. 50 2102605
[15] Zhu M G, Han R, Li W, Huang S L, Zheng D W, Song L W, Shi X N 2015 IEEE Trans. Magn. 51 2104604
[16] Zhu M G, Li W, Wang J D, Zheng L Y, Li Y F, Zhang K, Feng H B, Liu T 2014 IEEE Trans. Magn. 50 1000104
[17] Huang S L, Feng H B, Zhu M G, Li A H, Li Y F, Sun Y C, Zhang Y, Li W 2015 Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 22 417
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Li W, Li A H, Feng H B, Huang S L, Wang J D, Zhu M G 2015 IEEE Trans. Magn. 51 2103603
[19] Huang S L, Feng H B, Zhu M G, Li A H, Zhang Y, Li W 2014 AIP Adv. 4 10727
[20] Rong C B, Shen B G 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 117502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Shang R X, Xiong J F, Liu D, Zuo S L, Zhao X, Li R, Zuo W L, Zhao T Y, Chen R J, Sun J R, Shen B G 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 057502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Liu D, Zhao T Y, Li R, Zhang M, Shang R X, Xiong J F, Zhang J, Sun J R, Shen B G 2017 AIP Adv. 7 056201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Li R, Liu Y, Zuo S L, Zhao T Y, Hu F X, Sun J R, Shen B G 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 047501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Li L, Dong S Z, Chen H S, Jiang R J, Li D, Han R, Zhou D, Zhu M G, Wei Li W, Sun W 2019 Chin. Phys. B 28 037502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Sagawa M, Fujimura S, Yamamoto H, Matsuura T, Hirosawa S 1985 J. Appl. Phys. 57 4094
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Herbst J F 1991 Rev. Mod. Phys. 63 819
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 10456
- PDF下载量: 222
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: