-
非晶合金因具有独特的无序结构、优异或独特的各种性能以及良好的应用前景, 而受到专家学者的广泛关注. 其中, 制备过程中的冷却速率对非晶的结构与性能起着非常重要的调控作用. 本文采用分子动力学的模拟方法, 分别以4种冷却速率获得相同尺寸的Zr48Cu45Al7三元非晶合金的制备态原子结构模型, 并模拟了各制备态模型的压缩变形过程. 在此基础上系统地研究冷却速率对非晶微观结构及其变形行为的影响. 研究表明: 在施加大冷却速率时, 非晶合金保留更多高温液态的结构特征, 如五次对称性低的团簇数量较多, 原子堆积较为松散, 自由体积含量更多, 并存在更多的“类液区”. 上述大冷却速率所对应的结构特征导致了非晶发生变形时, 屈服强度降低, 表现出软化行为, 同时降低了剪切带形成与发生局域化变形的概率, 从而提高了非晶的塑性.Since the discovery of the first metallic glass (MG) in 1960, vast efforts have been devoted to the understanding of the structural mechanisms of unique properties, in particular, mechanical properties in MGs, which is helpful for the applications of such novel alloys. As is well known, the cooling rate during the quenching as well as the sample size, significantly affects the mechanical properties in MGs. In order to study the effect of cooling rate on microstructure and deformation behavior in MG by excluding the size effect, Zr48Cu45Al7 ternary composition with good glass-forming ability is selected as a research prototype in this work. The classical molecular dynamics simulation is utilized to construct four structural MG models with the same size under different cooling rates, and the uniaxial compressive deformation for each model is also simulated. It is found that an MG model prepared at a lower cooling rate has a higher yield strength and is more likely to form shear bands that lead the strain to be localized, resulting in a lower plasticity. The Voronoi tessellation, together with atomic packing efficiency and free volume algorithms that have been designed by ourselves, is used to analyze the four as-constructed models and high-temperature liquid model. It is found that the as-constructed model, which is prepared by quenching metallic melt at a higher cooling rate, can preserve more structural characteristics of the high-temperature liquid. In other words, the higher cooling rate leads to more clusters with relatively low five-fold symmetry, loose atomic packing and large fraction of free volumes in MG. By calculating the distribution of the free volumes, a new computational approach to detecting liquid-like regions in MG models is adopted. It is found that there are more liquid-like regions in the as-constructed model which is prepared by quenching metallic melt at a relatively high cooling rate. This should be the structural origin of the effect of cooling rate on the deformation behavior, in particular, the yield strength and the plasticity. This work provides an understanding of how the cooling rate during quenching affects the microstructure and deformation behavior, and will shed light on the development of new MGs with relatively large plasticity.
-
Keywords:
- amorphous alloy /
- cooling rates /
- microstructures and mechanical properties /
- molecular dynamics simulation
[1] Jung H Y, Choi S J, Prashanth K G, Stoica M, Scudino S, Yi S, Kühn U, Kim D H, Kim K B, Eckert J 2015 Mater. Des. 86 703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Reichel L, Schultz L, Pohl D, Oswald S, Fahler S, Werwinski M, Edstrom A, Delczeg-Czirjak E K, Rusz J 2015 J. Phys-Condens Mat. 27 476002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhang C, Guo R Q, Yang Y, Wu Y, Liu L 2011 Electrochim. Acta 56 6380
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Schuh C, Hufnagel T, Ramamurty U 2007 Acta Mater. 55 4067
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wang W H, Dong C, Shek C H 2004 Mater. Sci. Eng., R 44 45
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Yang L, Guo G Q, Chen L Y, LaQua B, Jiang J Z 2014 Intermetallics 44 94
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Liu Y, Bei H, Liu C T, George E P 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett. 90 071909
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Liu Z Y, Yang Y, Guo S, Liu X J, Lu J, Liu Y H, Liu C T 2011 J. Alloys Compd. 509 3269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Hu Y, Yan H H, Yan Z J, Wang X G 2018 Aip. Adv. 8 105002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Li C, Kou S, Zhao Y, Liu G, Ding Y 2012 Prog. Nat. Sci. 22 21
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Yokoyama Y, Yamano K, Fukaura K, Sunada H, Inoue A 2001 Scr. Mater. 44 1529
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Conner R D, Johnson W L, Paton N E, Nix W D 2003 J. Appl. Phys. 94 904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Lin X H, Johnson W L 1995 J. Appl. Phys. 78 6514
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Liao W, Zhao Y, He J, Zhang Y 2013 J. Alloys Compd. 555 357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Jiang W H, Liu F X, Wang Y D, Zhang H F, Choo H, Liaw P K 2006 Mat. Sci. Eng., A 430 350
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Huang Y J, Shen J, Sun J F 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett. 90 081919
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yang L, Guo G Q, Chen L Y, Wei S H, Jiang J Z, Wang X D 2010 Scr. Mater. 63 879
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 郭古青, 杨亮, 张国庆 2011 60 016103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo G Q, Yang L, Zhang G Q 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 016103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Cheng Y Q, Ma E, Sheng H W 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 102 245501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zeng Q, Sheng H, Ding Y, Wang L, Yang W, Jiang J Z, Mao W L, Mao H K 2011 Science 332 1404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Cheng Y Q, Cao A J, Sheng H W, Ma E 2008 Acta Mater. 56 5263
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Park K W, Fleury E, Seok H K, Kim Y C 2011 Intermetallics 19 1168
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Ghidelli M, Idrissi H, Gravier S, Blandin J J, Raskin J P, Schryvers D, Pardoen T 2017 Acta Mater. 131 246
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Lewandowski J J, Greer A L 2006 Nat. Mater. 5 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Feng S D, Chan K C, Zhao L, Pan S P, Qi L, Wang L M, Liu R P 2018 Mater. Des. 158 248
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 汪卫华 2014 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 44 396
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang W H 2014 Sci. China: Phys. Mech. Astron. 44 396
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 管鹏飞, 王兵, 吴义成, 张珊, 尚宝双, 胡远超, 苏锐, 刘琪 2017 66 176112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guan P F, Wang B, Wu Y C, Zhang S, Shang B S, Hu Y C, Su R, Liu Q 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 176112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wang W H 2012 J. Appl. Phys. 111 123519
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Miracle D B 2004 Nat. Mater. 3 697
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Cheng Y Q, Ma E 2011 Prog. Mater Sci. 56 379
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Peng H L, Li M Z, Wang W H 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 106 135503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 郭古青, 吴诗阳, 蔡光博, 杨亮 2016 65 096402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo G Q, Wu S Y, Cai G B, Yang L 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 096402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] 李茂枝 2017 66 176107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li M Z 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 176107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Yang L, Guo G Q, Chen L Y, Huang C L, Ge T, Chen D, Liaw P K, Saksl K, Ren Y, Zeng Q S, LaQua B, Chen F G, Jiang J Z 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 105502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Cohen M H, Turnbull D 1959 J. Chem. Phys. 31 1164
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Turnbull D, Cohen M H 1961 J. Chem. Phys. 34 120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Turnbull D, Cohen M H 1970 J. Chem. Phys. 52 3038
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Sietsma J, Thijsse B J 1995 Phys. Rev. B 52 3248
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Zhang Y, Hahn H 2011 J. Non-Cryst. Solids 357 1420
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Li F, Liu X J, Hou H Y, Chen G, Chen G L, Li M 2009 Intermetallics 17 98
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Liao B, Wu S Y, Yang L 2017 Aip Adv 7 105101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Qi L, Zhang H F, Hu Z Q 2004 Intermetallics 12 1191
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Wakeda M, Shibutani Y, Ogata S, Park J 2007 Intermetallics 15 139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Da W, Wang P W, Wang Y F, Li M F, Yang L 2018 Materials 12 98
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
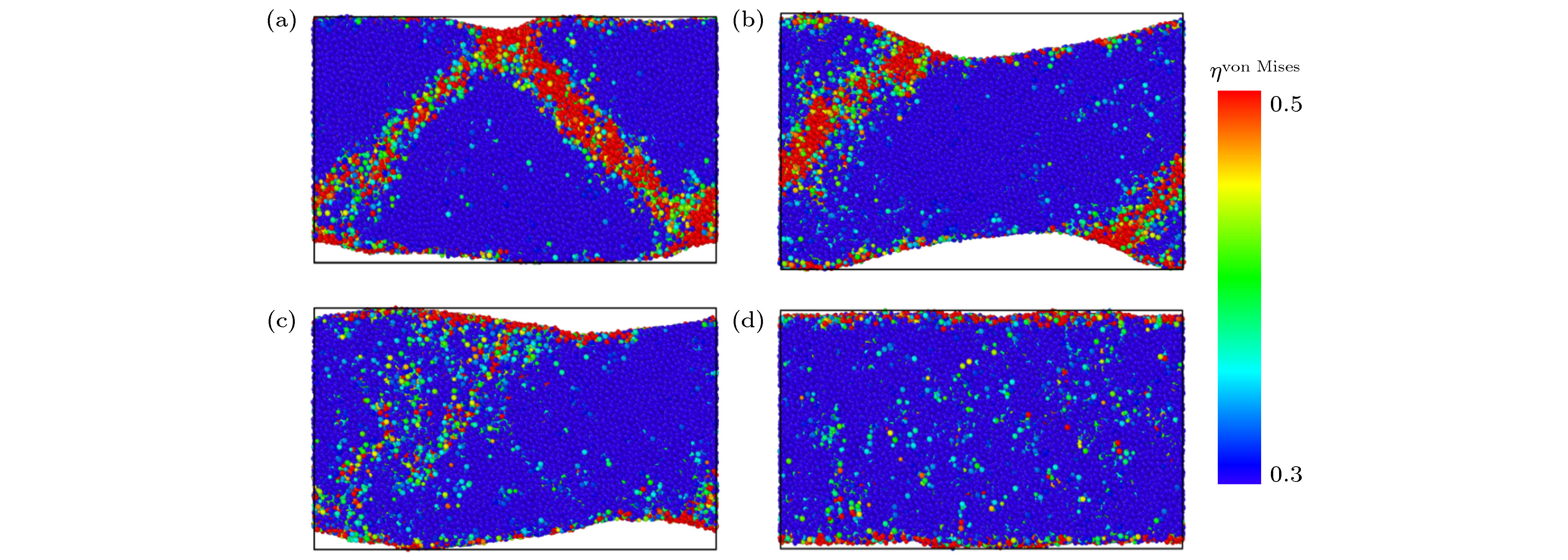
图 3 压缩变形过程中应变量为20%时, 不同冷却速率获得的Zr48Cu45Al7非晶合金模型的原子剪切应变图 (a) 1010 K/s; (b) 1011 K/s; (c) 1012 K/s; (d) 1013 K/s
Fig. 3. Distributions of atomic local shear strains of Zr48Cu45Al7 amorphous alloy models at macrostrain of 20% during the compressive deformation, including those prepared with different cooling rates: (a) 1010 K/s; (b) 1011 K/s; (c) 1012 K/s; (d) 1013 K/s.
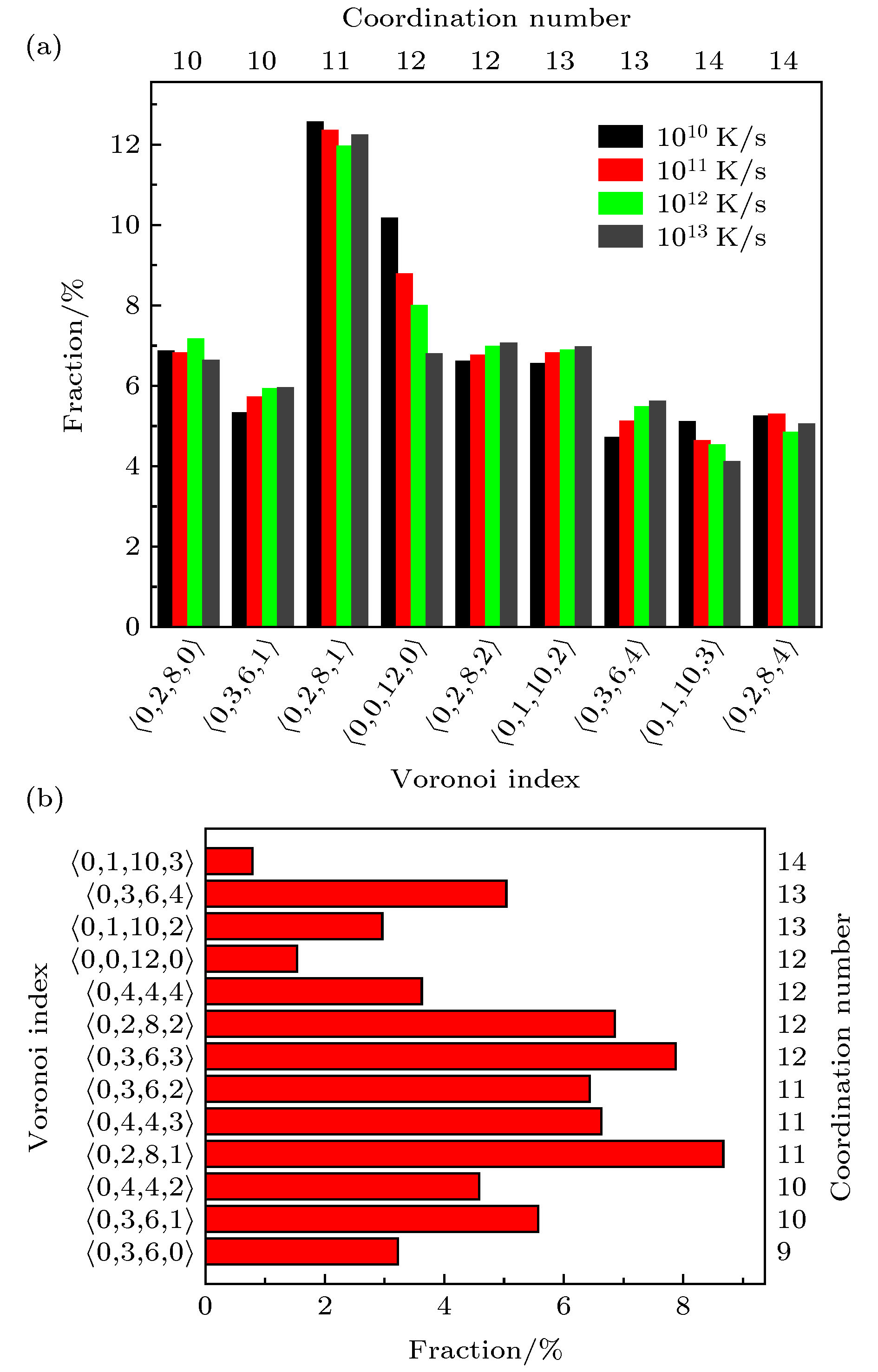
图 4 Voronoi团簇类型及含量分布 (a) 不同冷却速率的Zr48Cu45Al7非晶合金制备态模型(列出了含量超过4%的Voronoi团簇); (b) 2000 K时Zr48Cu45Al7液体结构模型(列出了含量较多与五次对称性较高的几种Voronoi团簇)
Fig. 4. Distributions of major Voronoi clusters in (a) The as-constructed models of Zr48Cu45Al7 amorphous alloy with different cooling rate (Note only Voronoi clusters possessing a weight larger than 4% are selected), and (b) a liquid model of Zr48Cu45Al7 with a temperature of 2000 K (Note only Voronoi clusters with highest fractions and relatively higher five-fold symmetry are selected).
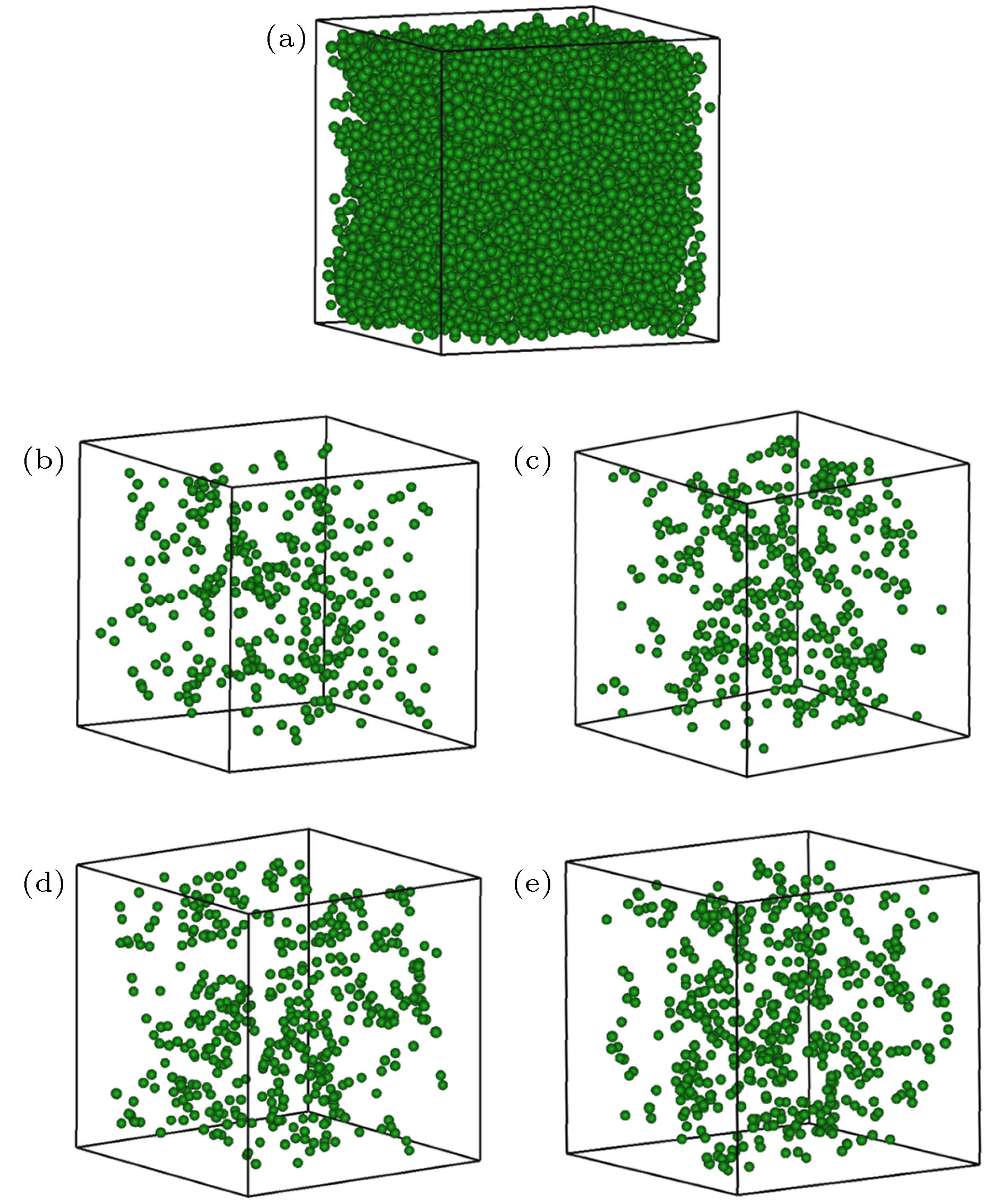
图 5 LFV原子分布图 (a) 2000 K液体模型; (b) 1010 K/s制备态模型; (c) 1011 K/s制备态模型; (d) 1012 K/s制备态模型; (e) 1013 K/s制备态模型
Fig. 5. 3 D distributions of LFV atoms in (a) a liquid model at 2000 K, and those as-constructed models prepared by using with cooling rates of (b) 1010 K/s, (c) 1011 K/s, (d) 1012 K/s, and (e) 1013 K/s.
表 1 不同冷速制备态模型与2000 K液体模型的原子堆积效率η
Table 1. The atomic packing efficiencies, η, in the as-constructed models prepared by using different cooling rates and a liquid model with a temperature of 2000 K.
1010 K/s 1011 K/s 1012 K/s 1013 K/s 2000 K η/% 70.547 70.473 70.399 70.320 63.983 表 2 Zr48Cu45Al7非晶合金不同冷却速制备态模型和液体模型的自由体积大小与自由体积占总体积的比值
Table 2. The total free volume and fraction of free volume in the as-constructed models prepared by using different cooling rates and a liquid model with a temperature of 2000 K.
1010 K/s 1011 K/s 1012 K/s 1013 K/s 2000 K 总自由体积/Å 11117.05 11430.34 11758.24 12052.57 42825.75 自由体积占比/% 3.440 3.532 3.628 3.715 12.059 表 3 不同冷速制备态模型的LFV原子数
Table 3. The number of LFV atoms in the as-constructed models prepared by using different cooling rates.
1010 K/s 1011 K/s 1012 K/s 1013 K/s LFV原子数/个 317 404 437 485 -
[1] Jung H Y, Choi S J, Prashanth K G, Stoica M, Scudino S, Yi S, Kühn U, Kim D H, Kim K B, Eckert J 2015 Mater. Des. 86 703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Reichel L, Schultz L, Pohl D, Oswald S, Fahler S, Werwinski M, Edstrom A, Delczeg-Czirjak E K, Rusz J 2015 J. Phys-Condens Mat. 27 476002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhang C, Guo R Q, Yang Y, Wu Y, Liu L 2011 Electrochim. Acta 56 6380
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Schuh C, Hufnagel T, Ramamurty U 2007 Acta Mater. 55 4067
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wang W H, Dong C, Shek C H 2004 Mater. Sci. Eng., R 44 45
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Yang L, Guo G Q, Chen L Y, LaQua B, Jiang J Z 2014 Intermetallics 44 94
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Liu Y, Bei H, Liu C T, George E P 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett. 90 071909
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Liu Z Y, Yang Y, Guo S, Liu X J, Lu J, Liu Y H, Liu C T 2011 J. Alloys Compd. 509 3269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Hu Y, Yan H H, Yan Z J, Wang X G 2018 Aip. Adv. 8 105002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Li C, Kou S, Zhao Y, Liu G, Ding Y 2012 Prog. Nat. Sci. 22 21
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Yokoyama Y, Yamano K, Fukaura K, Sunada H, Inoue A 2001 Scr. Mater. 44 1529
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Conner R D, Johnson W L, Paton N E, Nix W D 2003 J. Appl. Phys. 94 904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Lin X H, Johnson W L 1995 J. Appl. Phys. 78 6514
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Liao W, Zhao Y, He J, Zhang Y 2013 J. Alloys Compd. 555 357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Jiang W H, Liu F X, Wang Y D, Zhang H F, Choo H, Liaw P K 2006 Mat. Sci. Eng., A 430 350
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Huang Y J, Shen J, Sun J F 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett. 90 081919
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yang L, Guo G Q, Chen L Y, Wei S H, Jiang J Z, Wang X D 2010 Scr. Mater. 63 879
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 郭古青, 杨亮, 张国庆 2011 60 016103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo G Q, Yang L, Zhang G Q 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 016103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Cheng Y Q, Ma E, Sheng H W 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 102 245501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zeng Q, Sheng H, Ding Y, Wang L, Yang W, Jiang J Z, Mao W L, Mao H K 2011 Science 332 1404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Cheng Y Q, Cao A J, Sheng H W, Ma E 2008 Acta Mater. 56 5263
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Park K W, Fleury E, Seok H K, Kim Y C 2011 Intermetallics 19 1168
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Ghidelli M, Idrissi H, Gravier S, Blandin J J, Raskin J P, Schryvers D, Pardoen T 2017 Acta Mater. 131 246
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Lewandowski J J, Greer A L 2006 Nat. Mater. 5 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Feng S D, Chan K C, Zhao L, Pan S P, Qi L, Wang L M, Liu R P 2018 Mater. Des. 158 248
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 汪卫华 2014 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 44 396
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang W H 2014 Sci. China: Phys. Mech. Astron. 44 396
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 管鹏飞, 王兵, 吴义成, 张珊, 尚宝双, 胡远超, 苏锐, 刘琪 2017 66 176112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guan P F, Wang B, Wu Y C, Zhang S, Shang B S, Hu Y C, Su R, Liu Q 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 176112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wang W H 2012 J. Appl. Phys. 111 123519
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Miracle D B 2004 Nat. Mater. 3 697
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Cheng Y Q, Ma E 2011 Prog. Mater Sci. 56 379
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Peng H L, Li M Z, Wang W H 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 106 135503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 郭古青, 吴诗阳, 蔡光博, 杨亮 2016 65 096402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo G Q, Wu S Y, Cai G B, Yang L 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 096402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] 李茂枝 2017 66 176107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li M Z 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 176107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Yang L, Guo G Q, Chen L Y, Huang C L, Ge T, Chen D, Liaw P K, Saksl K, Ren Y, Zeng Q S, LaQua B, Chen F G, Jiang J Z 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 105502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Cohen M H, Turnbull D 1959 J. Chem. Phys. 31 1164
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Turnbull D, Cohen M H 1961 J. Chem. Phys. 34 120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Turnbull D, Cohen M H 1970 J. Chem. Phys. 52 3038
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Sietsma J, Thijsse B J 1995 Phys. Rev. B 52 3248
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Zhang Y, Hahn H 2011 J. Non-Cryst. Solids 357 1420
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Li F, Liu X J, Hou H Y, Chen G, Chen G L, Li M 2009 Intermetallics 17 98
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Liao B, Wu S Y, Yang L 2017 Aip Adv 7 105101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Qi L, Zhang H F, Hu Z Q 2004 Intermetallics 12 1191
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Wakeda M, Shibutani Y, Ogata S, Park J 2007 Intermetallics 15 139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Da W, Wang P W, Wang Y F, Li M F, Yang L 2018 Materials 12 98
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 16781
- PDF下载量: 452
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: