-
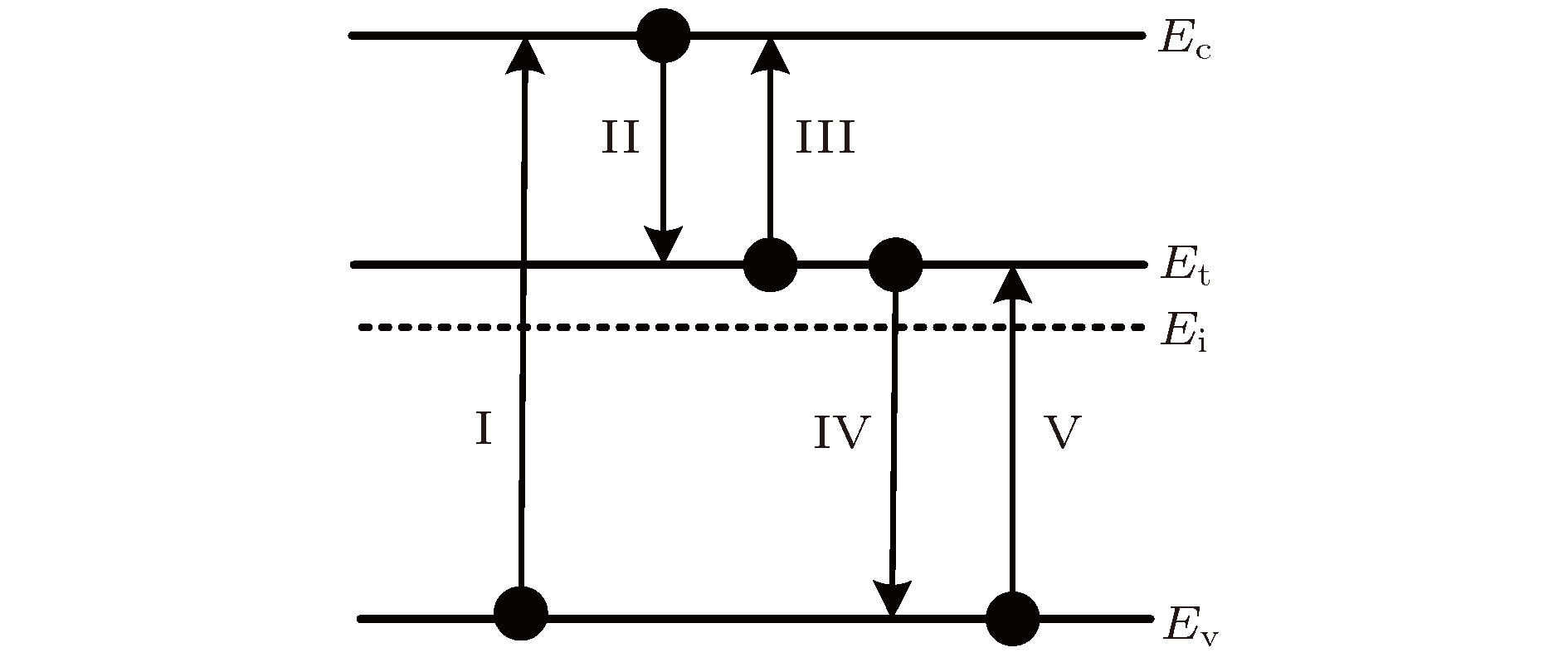
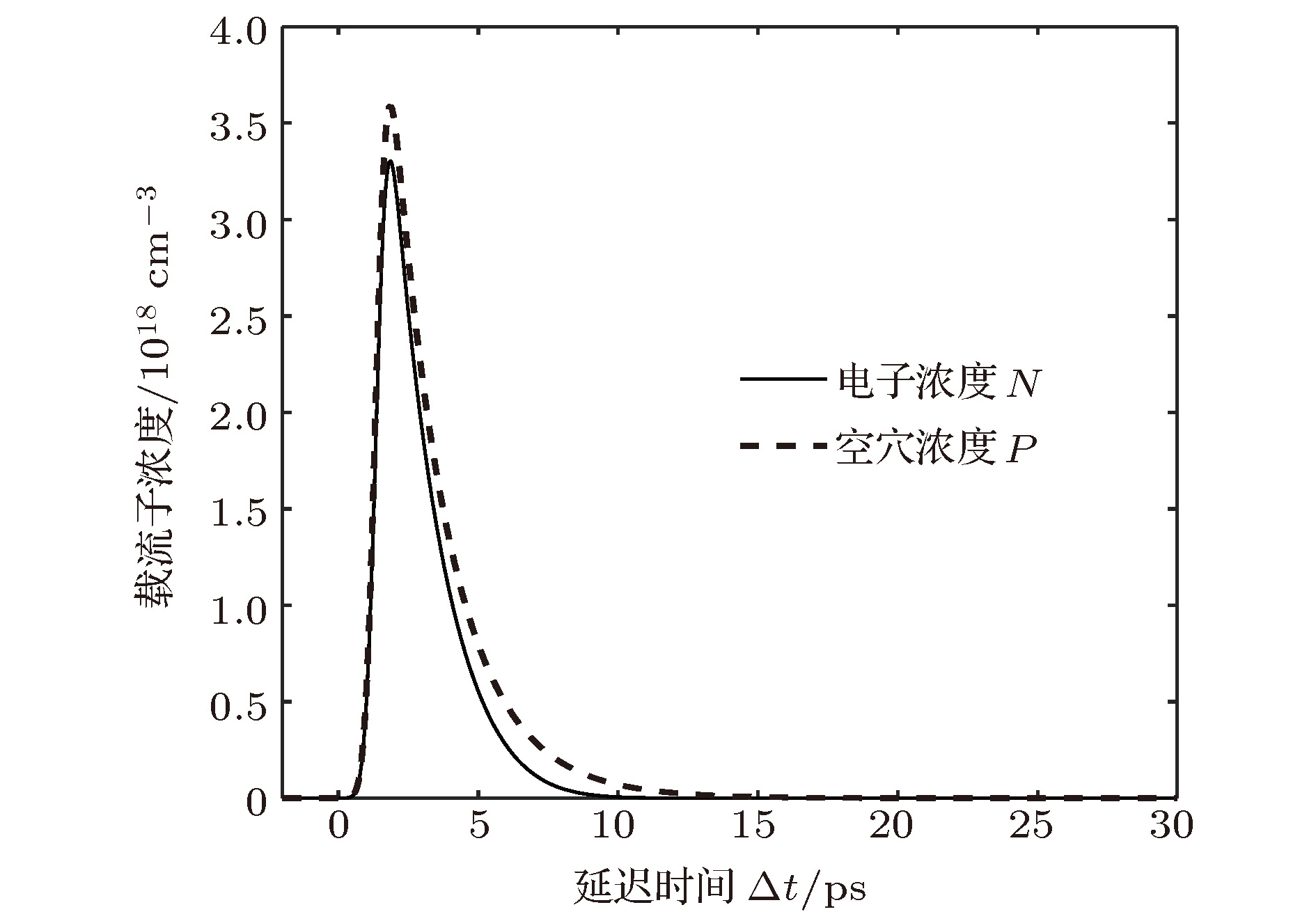
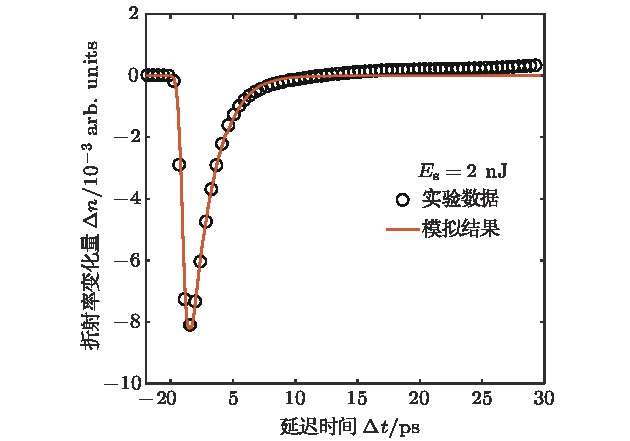
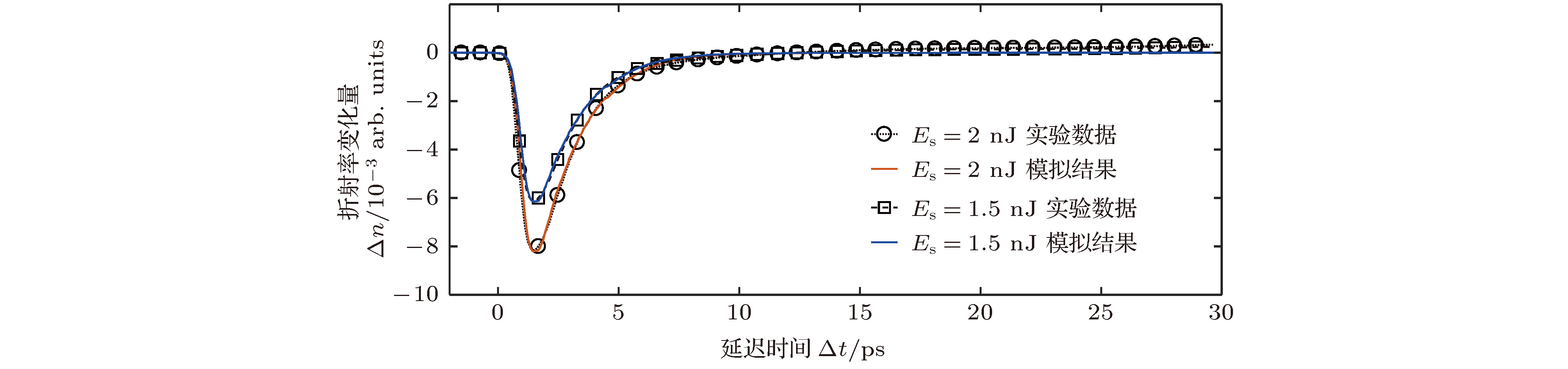
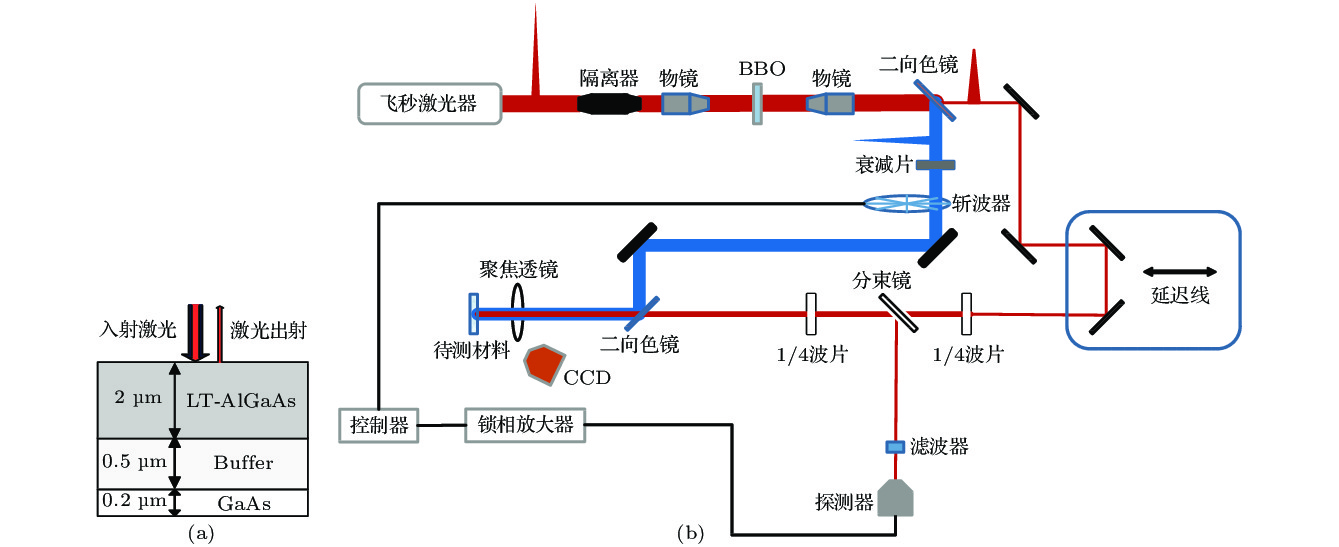
三元化合物铝镓砷(AlGaAs)是一种可用于全光固体超快诊断技术的重要材料.基于低温外延技术的AlGaAs材料不仅具有低温生长砷化镓(low-temperature grown GaAs, LT-GaAs)超短载流子寿命的特点, 并且可以调整材料的禁带宽度, 为超快诊断系统的设计增加了极大的灵活性. 泵浦-探测实验结果表明, 低温外延生长可以有效加速AlGaAs材料的非平衡载流子复合, 非平衡载流子弛豫时间小于300 fs, 而非平衡载流子的复合时间低至2.08 ps. 由于经过特殊的钝化工艺处理, 极大地降低了表面复合对载流子衰退过程的影响, 而低温外延生长引入的As原子团簇, 形成了深能级缺陷, 是加速载流子复合的主要因素. 基于单复合中心的间接复合理论, 建立LT-AlGaAs载流子演化模型, 获得与复合速率相关的关键物理参量: 载流子俘获面积σe = 6.6×10—14 cm2, σh = 4.7×10—15 cm2, 计算结果与实验相符. 该方法可用于半导体材料载流子演化特性定量分析, 有助于推进超快响应半导体材料的优化改进.The ternary compound aluminum gallium arsenide is an important material that can be used in all-optical solid-state ultrafast diagnostic technology. The low-temperature-epitaxially-grown AlGaAs (LT-AlGaAs) not only has the characteristics of ultra-short carrier lifetime of low-temperature-grown gallium arsenide (LT-GaAs), but also possesses the advantage of adjustability of band gap, which will provide great flexibility for the design of ultra-fast diagnostic systems. We use low-temperature epitaxial growth technology to grow AlGaAs on a GaAs substrate. The low-temperature-grown AlGaAs can effectively absorb 400 nm pump light to generate excess carrier. Therefore, we use a femtosecond laser with a wavelength of 800 nm and a pulse width of 200 fs as a light source to generate 400-nm pump light after passing through the BBO crystal, and 800 nm light without frequency doubling as the probe light. Using such a light source, we build a pump probe experimental platform to test the LT-AlGaAs. We normalize the experimental results and deconvolute it with the normalized laser pulses to obtain the response function of the semiconductor to the pump light. Therefore, we know that the nonequilibrium carrier relaxation time is less than 300 fs, and the nonequilibrium carrier recombination time is 2.08 ps. Due to the special passivation process, the effect of surface recombination on the carrier decay process is greatly reduced. The As clusters introduced by low-temperature epitaxial growth form deep level defects are the main factor for accelerating carrier recombination. In order to understand the complex process of photogenerated nonequilibrium carriers in depth, we use the indirect recombination theory of single recombination center to calculate the carrier recombination process, and establish an LT-AlGaAs carrier evolution model. Thus we obtain the key physical parameter related to the recombination rate, which is the carrier trapping area. We also use a theoretical model of carrier-regulated refractive index to calculate the effect of carrier concentration on the amount of change in refractive index. Combining our AlGaAs carrier evolution model, we simulate the refractive index change process of LT-AlGaAs after being illuminated by pump light. The simulation results are in good agreement with the experimental results. The method can be used for the quantitative analysis of carrier evolution characteristics of semiconductor materials, and it can conduce to the optimization and improvement of ultra-fast response semiconductor materials.
-
Keywords:
- photorefractive effect /
- AlGaAs /
- pump-probe /
- carrier lifetime
[1] 顾礼, 宗方轲, 李翔, 张敬金, 张驰, 杨勤劳 2015 强激光与粒子束 27 062011
Gu L, Zong F K, Li X, Zhang J J, Zhang C, Yang Q L 2015 High Pow. Las. Part. Beam 27 062011
[2] 潘京生, 亓鲁, 肖洪亮, 张蓉, 周建勋, 蒲冬冬, 吕景文 2012 61 194211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pan J S, Qi L, Xiao H L, Zhang R, Zhou J X, Pu D D, Lü J W 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 194211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Bradley D K, Bell P M, Landen O L, Kilkenny J D, Oertel J 1995 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 66 716
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Baker K L, Stewart R E, Steele P T, Vernon S P, Hsing W W, Remington B A 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 103 151111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 梁玲亮, 田进寿, 汪韬, 李福利, 高贵龙, 王俊锋, 王超, 卢裕, 徐向晏, 曹希斌, 温文龙, 辛丽伟, 刘虎林, 王兴 2014 63 060702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang L L, Tian J S, Wang T, Li F L, Gao G L, Wang J F, Wang C, Lu Y, Xu X Y, Cao X B, Wen W L, Xin L W, Liu H L, Wang X 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 060702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 王博, 白永林, 曹伟伟, 徐鹏, 刘百玉, 缑永胜, 朱炳利, 候洵 2015 64 200701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang B, Bau Y L, Cao W W, Xu P, Liu B Y, Gou Y S, Zhu B L, Hou X 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 200701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Gao G, He K, Tian J, Zhang C, Zhang J, Wang T, Chen S, Jia H, Yuan F, Liang L, Yan X, Li S, Wang C, Yin F 2017 Opt. Express 25 8721
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bennett B R, Soref R A, Alamo J A D 1990 IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 26 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Vurgaftman I, Meyer J R, Ram-Mohan L R 2001 J. Appl. Phys. 89 5815
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Dankowski S U, Streb D, Ruff M, Kiesel P, Kneissl M, Knüpfer B, Döhler G H, Keil U D, Sørensen C B, Verma A K 1996 Appl. Phys. Lett. 68 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Lochtefeld A J, Melloch M R, Chang J C P, Harmon E S 1996 Appl. Phys. Lett. 69 1465
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Fleischer S, Beling C D, Fung S, Nieveen W R, Squire J E, Zheng J Q, Missous M 1997 J. Appl. Phys. 81 190
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Khanna V K 2005 Progress in Quantum Electronics 29 59
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 夏宁, 方铉, 容天宇, 王登魁, 房丹, 唐吉龙, 王新伟, 王晓华, 李永峰, 姚斌, 魏志鹏 2018 中国激光 45 0603002
Xia N, Gang X, Rong T Y, Wan D K, Fang D, Tang J lL, Wang X W, Wang X H, Li Y F, Yao B, Wei Z P 2018 Chin. J. Las. 45 0603002
[15] Aspnes D E, Kelso S M, Logan R A, Bhat R 1986 J. Appl. Phys. 60 754
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 吕铁铮, 王韬, 钱列加, 鲁欣, 魏志义, 张杰 2002 51 1268
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lü T Z, Wang T Q, Qian L J, Lu X, Wei Z Y, Zhang J 2002 Acta Phys. Sin. 51 1268
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Vernon S P, Lowry M E, Baker K L, Bennett C V, Celeste J R, Cerjan C, Haynes S, Hernandez V J, Hsing W W, Lacaille G A 2012 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 83 193
[18] Lasher G, Stern F 1964 Phys. Rev. 133 553
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Nilsson N G 1978 Appl. Phys. Lett. 33 653
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wolff P A 1962 Phys. Rev. 126 405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Moss T S, Burrell G J, Ellis B, Omar M A 1973 Semiconductor Opto‐Electronics (London: Butterworths) pp48-94
[22] 沈学础 2002 半导体光谱和光学性质(北京: 科学出版社)第20页
Shen X C 2002 Semiconductor Spectroscopy and Optical Properties (Beijing: Science Press) p20 (in Chinese)
[23] Alig R C, Bloom S 1975 Phys. Rev. Lett. 35 1522
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 刘恩科, 朱秉升, 罗晋生 2011 半导体物理学(第7版) (北京: 电子工业出版社)第47页
Liu E K, Zhu B S, Luo J S 2011 The Physics of Semiconductors (Version 7) p47 (in Chinese)
[25] Fang Z Q, Schlesinger T E, Milnes A G 1987 J. Appl. Phys. 61 5047
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 实验激光参量
Table 1. Laser parameters in experiment.
参量 数值 单脉冲泵浦光能量Es/nJ 2 泵浦光斑直径dpump/μm 75 泵浦光入射深度l/nm 20 探测光斑直径dprobe/μm 70 表 2 实验数据的拟合结果
Table 2. Fitting results of experimental data.
物理参量 数值 A 0.0082 t0/ps 0.5 τin/ps 0.44 τre/ps 2.08 表 3 LT-AlGaAs载流子浓度导致折射率变化的相关参量
Table 3. Parameters related to carrier-mediated refractive index change in LT-AlGaAs.
物理参量 数值 物理参量 数值 me/m0 0.088 Eg/eV 1.79 mlh/m0 0.102 C/cm–1·s–1/2 4.6 × 1012 mhh/m0 0.59 Clh/cm–1·s–1/2 1.5 × 1012 μelh/m0 0.047 Chh/cm–1·s–1/2 3.1 × 1012 μehh/m0 0.076 εs 12 表 4 电子与空穴的俘获系数和发射系数
Table 4. Capture and emission coefficients of electrons and holes.
物理参量 数值 re/cm3·s–1 2.6 × 10–6 rh/cm3·s–1 7.2 × 10–8 se/cm3·s–1 640 sh/cm3·s–1 1400 -
[1] 顾礼, 宗方轲, 李翔, 张敬金, 张驰, 杨勤劳 2015 强激光与粒子束 27 062011
Gu L, Zong F K, Li X, Zhang J J, Zhang C, Yang Q L 2015 High Pow. Las. Part. Beam 27 062011
[2] 潘京生, 亓鲁, 肖洪亮, 张蓉, 周建勋, 蒲冬冬, 吕景文 2012 61 194211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pan J S, Qi L, Xiao H L, Zhang R, Zhou J X, Pu D D, Lü J W 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 194211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Bradley D K, Bell P M, Landen O L, Kilkenny J D, Oertel J 1995 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 66 716
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Baker K L, Stewart R E, Steele P T, Vernon S P, Hsing W W, Remington B A 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 103 151111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 梁玲亮, 田进寿, 汪韬, 李福利, 高贵龙, 王俊锋, 王超, 卢裕, 徐向晏, 曹希斌, 温文龙, 辛丽伟, 刘虎林, 王兴 2014 63 060702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang L L, Tian J S, Wang T, Li F L, Gao G L, Wang J F, Wang C, Lu Y, Xu X Y, Cao X B, Wen W L, Xin L W, Liu H L, Wang X 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 060702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 王博, 白永林, 曹伟伟, 徐鹏, 刘百玉, 缑永胜, 朱炳利, 候洵 2015 64 200701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang B, Bau Y L, Cao W W, Xu P, Liu B Y, Gou Y S, Zhu B L, Hou X 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 200701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Gao G, He K, Tian J, Zhang C, Zhang J, Wang T, Chen S, Jia H, Yuan F, Liang L, Yan X, Li S, Wang C, Yin F 2017 Opt. Express 25 8721
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bennett B R, Soref R A, Alamo J A D 1990 IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 26 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Vurgaftman I, Meyer J R, Ram-Mohan L R 2001 J. Appl. Phys. 89 5815
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Dankowski S U, Streb D, Ruff M, Kiesel P, Kneissl M, Knüpfer B, Döhler G H, Keil U D, Sørensen C B, Verma A K 1996 Appl. Phys. Lett. 68 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Lochtefeld A J, Melloch M R, Chang J C P, Harmon E S 1996 Appl. Phys. Lett. 69 1465
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Fleischer S, Beling C D, Fung S, Nieveen W R, Squire J E, Zheng J Q, Missous M 1997 J. Appl. Phys. 81 190
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Khanna V K 2005 Progress in Quantum Electronics 29 59
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 夏宁, 方铉, 容天宇, 王登魁, 房丹, 唐吉龙, 王新伟, 王晓华, 李永峰, 姚斌, 魏志鹏 2018 中国激光 45 0603002
Xia N, Gang X, Rong T Y, Wan D K, Fang D, Tang J lL, Wang X W, Wang X H, Li Y F, Yao B, Wei Z P 2018 Chin. J. Las. 45 0603002
[15] Aspnes D E, Kelso S M, Logan R A, Bhat R 1986 J. Appl. Phys. 60 754
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 吕铁铮, 王韬, 钱列加, 鲁欣, 魏志义, 张杰 2002 51 1268
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lü T Z, Wang T Q, Qian L J, Lu X, Wei Z Y, Zhang J 2002 Acta Phys. Sin. 51 1268
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Vernon S P, Lowry M E, Baker K L, Bennett C V, Celeste J R, Cerjan C, Haynes S, Hernandez V J, Hsing W W, Lacaille G A 2012 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 83 193
[18] Lasher G, Stern F 1964 Phys. Rev. 133 553
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Nilsson N G 1978 Appl. Phys. Lett. 33 653
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wolff P A 1962 Phys. Rev. 126 405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Moss T S, Burrell G J, Ellis B, Omar M A 1973 Semiconductor Opto‐Electronics (London: Butterworths) pp48-94
[22] 沈学础 2002 半导体光谱和光学性质(北京: 科学出版社)第20页
Shen X C 2002 Semiconductor Spectroscopy and Optical Properties (Beijing: Science Press) p20 (in Chinese)
[23] Alig R C, Bloom S 1975 Phys. Rev. Lett. 35 1522
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 刘恩科, 朱秉升, 罗晋生 2011 半导体物理学(第7版) (北京: 电子工业出版社)第47页
Liu E K, Zhu B S, Luo J S 2011 The Physics of Semiconductors (Version 7) p47 (in Chinese)
[25] Fang Z Q, Schlesinger T E, Milnes A G 1987 J. Appl. Phys. 61 5047
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 15422
- PDF下载量: 117
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: