-
网络的电输运性能优化, 不仅有助于理解网络的结构与功能关系, 而且对于提升电气工程技术也有着非常重要的意义. 从信息的角度看待网络, 寻求影响网络电输运性能的信息结构测度是解决这一问题的有效途径. 最近的研究表明, 复杂网络的通信序列熵可以有效地量化网络的整体结构信息. 本文将探讨其表征网络电输运性能的能力, 其中主要研究了小世界网络、无标度网络、关联无标度网络、 社团网络以及IEEE57等节点网络的通信序列熵和电输运性能之间的关联特性. 研究结果表明, 对于以上这些网络, 它们的电输运性能是关于通信序列熵的单调递增函数, 与通信序列熵成正关联特性. 该规律的发现为设计高传输效率的电力网络提供了一个有效的策略, 即可以通过提高网络的通信序列熵来优化其电输运性能.Optimization of the network’s electrical transport properties not only conduces to understanding the relationship between structure and network function, but also can improve the electrical engineering technology. The effective way to solve this problem is to treat the network from the information viewpoint and seek the information structure measure which affects crucially the network electrical transport performance. Recent studies have shown that the communicability sequence entropy of complex networks can effectively quantify the global structural information of networks. Based on this measure, the difference between networks can be quantified effectively, and the connotation of communicability sequence entropy is explained. In this paper, we predict that the electrical transport performance of complex networks has a strong correlation with the communicability sequence entropy. For this reason, we mainly study the correlation characteristics of the electrical transport performance and communicability sequence entropy of small-world networks, scale-free networks, degree-correlated scale-free networks, community networks, and IEEE57 and other electrical node networks. The results show that the electrical transport performances of these networks are all a monotonically increasing function of communicability sequence entropy, namely, the communicability sequence entropy, and the electrical transport properties have a positive correlation. Specifically, in the process evolving from a regular network to a small-world network, the communicability sequence entropy and electrical transport performance of the network increase gradually. For scale-free networks, in the process of increasing degree distribution exponent, communicability sequence entropy and electrical transport performance of the network increase gradually. For degree-correlated scale-free networks, during the evolution from assortative to disassortative topology, communicability sequence entropy and electrical transport performance both decrease gradually. For networks with community structure, the communicability sequence entropy and electrical transport performance decrease with the increase of the number of communities. Finally, the correlation between communicability sequence entropy and electrical transport performance of two classical node power supply networks and corresponding randomization network models are also studied. The results show that as the order of d increases, both communicability sequence entropy and electrical transport performance decrease. And both are getting closer to the original network's communicability sequence entropy and electrical transport performance. The rule is beneficial to providing an effective strategy for designing a high transmission efficiency of the power network, that is, we can optimize the electrical transport performance by improving the network communicability sequence entropy.
-
Keywords:
- complex network /
- electrical transport performance /
- communicability sequence entropy /
- positive correlation
[1] Dorogovtsev S N, Mendes J F F 2003 Evolution of Networks: From Biological Nets to the Internet and WWW (Oxford: Oxford University Press) p2
[2] 汪小帆, 李翔, 陈关荣 2006 复杂网络理论及其应用(北京: 清华大学出版社) 第1页
Wang X F, Li X, Chen G R 2006 Complex Network Theory and Application (Beijing: Tsinghua University Press) p1 (in Chinese)
[3] Barabási A L 2016 Network Science (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) p5
[4] Albert R, Barabási A L 2002 Rev. Mod. Phys. 74 47
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Boccaletti S, Latora V, Moreno Y, Chavez M, Hwang D U 2006 Phys. Rep. 424 175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Watts D J, Strogatz S H 1998 Nature 393 440
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Barabási A L, Albert R 1999 Science 286 509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Cohen R, Havlin S 2010 Complex Networks: Structure, Robustness and Function (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) p26, p181
[9] Newman M E J 2010 Networks: An Introduction (Oxford: Oxford University Press) p23
[10] Kleinberg J M 2000 Nature 406 845
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Roberson M R, Ben-Avraham D 2006 Phys. Rev. E 74 017101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Li G, Reis S D S, Moreira A A, Havlin S, Stanley H E, Andrade J S 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 018701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li G, Reis S D S, Moreira A A, Havlin S, Stanley H E, Andrade J S 2013 Phys. Rev. E 87 042810
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Pan G J, Niu R W 2016 Physica A 463 509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Niu R W, Pan G J 2016 Physica A 461 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Lopez E, Buldyrev S V, Havlin S, Stanley H E 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 248701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lopez E, Carmib S, Havlin S, Buldyrev S V, Stanley H E 2006 Physica D 224 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Carmi1 S, Wu Z, Lopez E, Havlin S, Stanley H E 2007 Eur. Phys. J. B 57 165
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Baba A O, Bamaarouf O, Rachadi A, Ez-Zahraouy H 2017 Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 28 1750064
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Xue Y H, Wang J, Li L, He D, Hu B 2010 Phys. Rev. E 81 037101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Asztalos A, Sreenivasan S, Szymanski B K, Korniss G 2012 Eur. Phys. J. B 85 288
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Oliveira C L N, Morais P A, Moreira A A, Andrade J S 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 112 148701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 蔡萌, 杜海峰, 任义科, 费尔德曼 M 2011 60 110513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cai M, Du H F, Ren Y K, Feldman M 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 110513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Hu Y, Wang Y, Li D, Havlin S, Di Z 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 106 108701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 李勇军, 尹超, 于会, 刘尊 2016 65 020501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y J, Yin C, Yu H, Liu Z 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 020501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 黄丽亚, 霍宥良, 王青, 成谢锋 2019 68 018901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang L Y, Huo Y L, Wang Q, Cheng X F 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 018901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Wang B, Tang H W, Guo C H, Xiu Z L 2006 Physica A 363 591
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 吴俊, 谭跃进, 郑宏钟, 朱大智 2007 系统工程理论与实践 27 101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu J, Tan Y J, Zheng H Z, Zhu D Z 2007 System Eng. Theor. Prac. 27 101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 蔡萌, 杜海峰, 费尔德曼 M 2014 63 060504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cai M, Du H F, Feldman M W 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 060504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Cai M, Cui Y, Stanley H E 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 9340
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Braunstein S L, Ghosh S, Severini S 2006 Ann. Comb. 10 291
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] de Domenico M, Biamonte J 2016 Phys. Rev. X 6 041062
[33] Chen D, Shi D D, Qin M, Xu S M, Pan G J 2018 Phys. Rev. E 98 012319
[34] Estrada E, Hatano N 2008 Phys. Rev. E 77 036111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Estrada E, Hatano N, Benzi M 2012 Phys. Rep. 514 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Estrada E 2012 Linear Algebra Appl. 436 4317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Wu J J, Gao Z Y, Sun H J 2006 Phys. Rev. E 74 066111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Gao J, Barzel B, Barabási A L 2016 Nature 530 307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Newman M E J 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 208701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Johnson S, Torres J, Marro J, Munñoz M A 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 108702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Erdös P, Rényi A 1959 Publ. Math. Debrecen 6 290
[42] Orsini C, Dankulov M M, Colomer-de-Simón P, Jamakovic A, Mahadevan P, Vahdat A, Bassler K E, Toroczkai Z, Boguñá M, Caldarelli G, Fortunato S, Krioukov D 2015 Nat. Commun. 6 8627
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
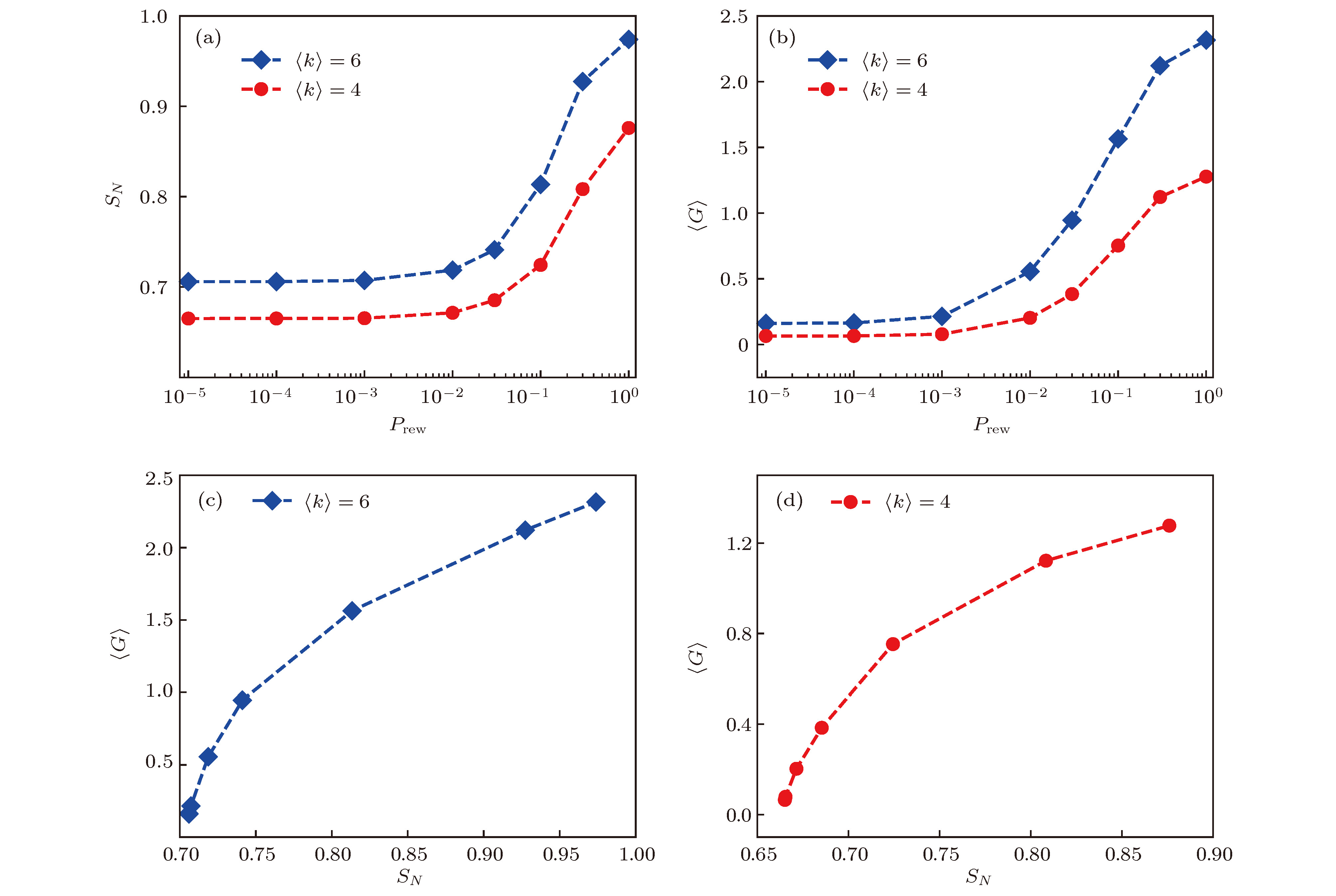
图 2 WS小世界网络的(a)通信序列熵
$S_N$ 和(b) 平均全局电导$\left\langle G \right\rangle$ 与重连概率$P_{\rm rew}$ 的依赖关系; (c), (d)相应的$S_N$ 与$\left\langle G \right\rangle$ 之间的关系Fig. 2. Dependence of (a) communicability sequence entropy
$S_N$ and (b) mean global conductance$\left\langle G \right\rangle$ on rewiring probability of WS small-world network; (c) , (d) the relation between$S_N$ and$\left\langle G \right\rangle$ of WS small-world network.图 3 无标度网络的(a)通信序列熵
$S_N$ 和(b)平均全局电导$\left\langle G \right\rangle$ 与度分布指数$\gamma$ 的依赖关系; (c), (d) 将$\left\langle G \right\rangle$ 与$S_N$ 映射在同一坐标系下的结果Fig. 3. The dependence of (a) communicability sequence entropy
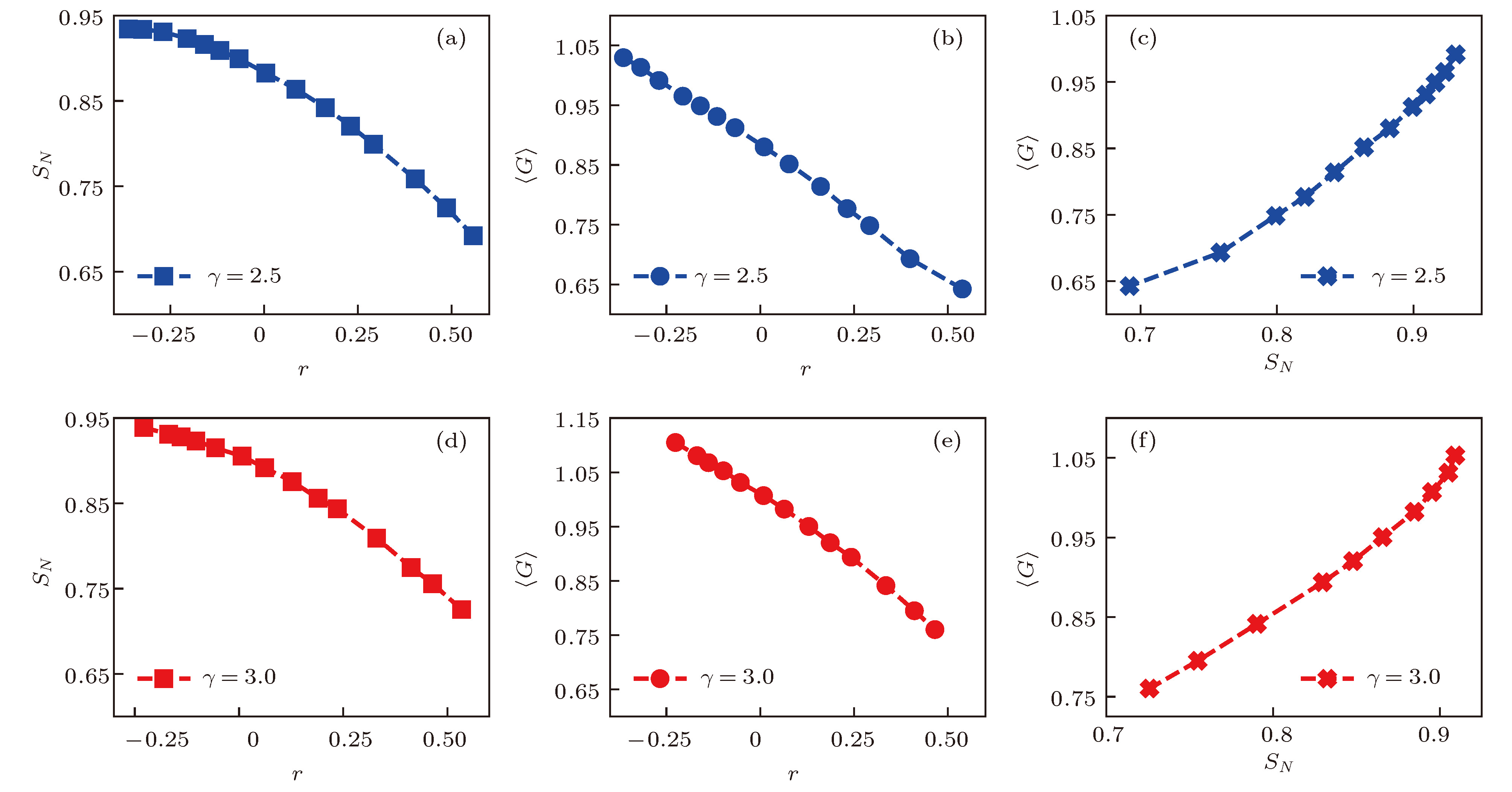
$S_N$ and (b) mean global conductance$\left\langle G \right\rangle$ on degree distribution exponent$\gamma$ of scale-free network; (c), (d) the results of mapping$\left\langle G \right\rangle$ with$S_N$ in the same coordinate system.图 4 度分布指数
$\gamma$ 分别等于(a) 2.5和(d) 3.0时的关联无标度网络的通信序列熵$S_N$ 与度-度关联系数$r$ 的依赖关系; 相应的平均全局电导$\left\langle G \right\rangle$ 与关联系数$r$ 的依赖关系,$\gamma$ 分别等于(b) 2.5和(e) 3.0; (c), (f)$\left\langle G \right\rangle$ 与$S_N$ 的关系曲线Fig. 4. Dependence of communicability sequence entropy
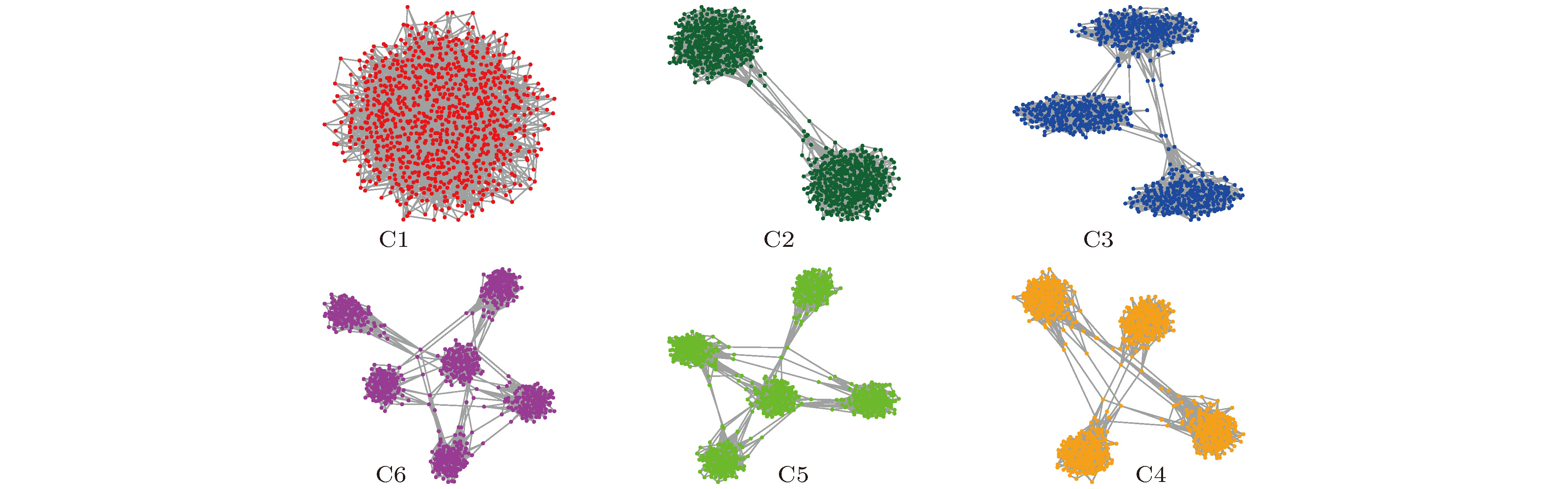
$S_N$ of the scale-free network on the degree-degree correlation coefficient$r$ , here, the degree distribution exponent$\gamma$ is equal to (a) 2.5 and (d) 3.0, respectively; (b), (e) the dependence of the mean global conductance$\left\langle G \right\rangle$ on the correlation coefficient$r$ ; (c), (f) the$\left\langle G \right\rangle$ and$S_N$ relation curve.图 5 以BA网络为例构建的社团网络可视化图, 社团个数为1—6, 分别表示为C1—C6. 图中每一个网络中社团网络的生成方式都是按照文献[7]的方法生成. 网络规模
$N = 900$ , 网络边数$E \approx 2700$ . 具体算法如下: 1)首先生成一个含有900个节点, 2700条边的BA网络(图C1); 2)生成两个含有450个节点、1350条边的BA网络, 然后在每个社团中随机断开少量的边, 并将这些断开的边连接到其他社团中断开的边的端点上, 形成一个含有两个社团的网络C2; 3)以此类推, 便可生成含有3, 4, 5, 6个社团的BA网络C3, C4, C5, C6Fig. 5. A visualization of the community network based on the BA network. The number of communities is 1 to 6, which are denoted as C1 to C6. The generation method of the community network in each network in the figure is generated according to the method of Ref. [7]. The network size is
$N = 900$ , the number of network edges is$E \approx 2700$ . The specific algorithm is as follows: 1) First, a BA network with 900 nodes and 2700 edges is generated, as shown in figure C1; 2) two BA networks containing 450 nodes and 1350 edges are generated, and then a small number of edges are randomly disconnected in each community, and these disconnected edges are connected to the endpoints of the interrupted edges of other communities to form a network C2 containing two communities; 3) in this way, BA network C3, C4, C5 and C6 containing 3, 4, 5 and 6 communities can be generated.ntaining 3, 4, 5 and 6 communities can be generated.表 1 含有社团结构的网络[BA (左), ER (右)]通信序列熵
$S_N$ 、平均全局电导$\left\langle G \right\rangle$ 与社团个数的关系Table 1. Relationship between communicability sequence entropy
$S_N$ , mean global conductance$\left\langle G \right\rangle$ and number of communities in networks [BA (left), ER (right)] containing communities.BA $S_N$ $\left\langle G \right\rangle$ ER $S_N$ $\left\langle G \right\rangle$ 1(C1) 0.9363 1.9380 1 0.9704 2.2106 2 (C2) 0.8925 1.6168 2 0.9256 1.8006 3 (C3) 0.8703 1.5026 3 0.9010 1.6625 4 (C4) 0.8512 1.4401 4 0.8832 1.5728 5 (C5) 0.8440 1.3929 5 0.8704 1.5203 6 (C6) 0.8409 1.3653 6 0.8642 1.4813 表 2 电力供需网络以及对应的随机化参考模型的
$S_N$ 和平均电导$\left\langle G \right\rangle$ , IEEE57 (左), IEEE118 (右)Table 2. Power supply network and corresponding randomized reference model
$S_N$ and mean global conductance$\left\langle G \right\rangle$ , IEEE57 (left), IEEE118 (right).IEEE57 $S_N$ $\left\langle G \right\rangle$ IEEE118 $S_N$ $\left\langle G \right\rangle$ 0阶 0.8744 0.6404 0阶 0.8884 0.7418 1阶 0.8502 0.6302 1阶 0.8692 0.7388 2阶 0.8391 0.6225 2阶 0.8689 0.7086 原始 0.8116 0.5616 原始 0.8029 0.4981 -
[1] Dorogovtsev S N, Mendes J F F 2003 Evolution of Networks: From Biological Nets to the Internet and WWW (Oxford: Oxford University Press) p2
[2] 汪小帆, 李翔, 陈关荣 2006 复杂网络理论及其应用(北京: 清华大学出版社) 第1页
Wang X F, Li X, Chen G R 2006 Complex Network Theory and Application (Beijing: Tsinghua University Press) p1 (in Chinese)
[3] Barabási A L 2016 Network Science (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) p5
[4] Albert R, Barabási A L 2002 Rev. Mod. Phys. 74 47
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Boccaletti S, Latora V, Moreno Y, Chavez M, Hwang D U 2006 Phys. Rep. 424 175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Watts D J, Strogatz S H 1998 Nature 393 440
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Barabási A L, Albert R 1999 Science 286 509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Cohen R, Havlin S 2010 Complex Networks: Structure, Robustness and Function (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) p26, p181
[9] Newman M E J 2010 Networks: An Introduction (Oxford: Oxford University Press) p23
[10] Kleinberg J M 2000 Nature 406 845
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Roberson M R, Ben-Avraham D 2006 Phys. Rev. E 74 017101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Li G, Reis S D S, Moreira A A, Havlin S, Stanley H E, Andrade J S 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 018701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li G, Reis S D S, Moreira A A, Havlin S, Stanley H E, Andrade J S 2013 Phys. Rev. E 87 042810
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Pan G J, Niu R W 2016 Physica A 463 509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Niu R W, Pan G J 2016 Physica A 461 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Lopez E, Buldyrev S V, Havlin S, Stanley H E 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 248701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lopez E, Carmib S, Havlin S, Buldyrev S V, Stanley H E 2006 Physica D 224 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Carmi1 S, Wu Z, Lopez E, Havlin S, Stanley H E 2007 Eur. Phys. J. B 57 165
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Baba A O, Bamaarouf O, Rachadi A, Ez-Zahraouy H 2017 Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 28 1750064
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Xue Y H, Wang J, Li L, He D, Hu B 2010 Phys. Rev. E 81 037101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Asztalos A, Sreenivasan S, Szymanski B K, Korniss G 2012 Eur. Phys. J. B 85 288
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Oliveira C L N, Morais P A, Moreira A A, Andrade J S 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 112 148701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 蔡萌, 杜海峰, 任义科, 费尔德曼 M 2011 60 110513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cai M, Du H F, Ren Y K, Feldman M 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 110513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Hu Y, Wang Y, Li D, Havlin S, Di Z 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 106 108701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 李勇军, 尹超, 于会, 刘尊 2016 65 020501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y J, Yin C, Yu H, Liu Z 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 020501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 黄丽亚, 霍宥良, 王青, 成谢锋 2019 68 018901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang L Y, Huo Y L, Wang Q, Cheng X F 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 018901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Wang B, Tang H W, Guo C H, Xiu Z L 2006 Physica A 363 591
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 吴俊, 谭跃进, 郑宏钟, 朱大智 2007 系统工程理论与实践 27 101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu J, Tan Y J, Zheng H Z, Zhu D Z 2007 System Eng. Theor. Prac. 27 101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 蔡萌, 杜海峰, 费尔德曼 M 2014 63 060504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cai M, Du H F, Feldman M W 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 060504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Cai M, Cui Y, Stanley H E 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 9340
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Braunstein S L, Ghosh S, Severini S 2006 Ann. Comb. 10 291
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] de Domenico M, Biamonte J 2016 Phys. Rev. X 6 041062
[33] Chen D, Shi D D, Qin M, Xu S M, Pan G J 2018 Phys. Rev. E 98 012319
[34] Estrada E, Hatano N 2008 Phys. Rev. E 77 036111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Estrada E, Hatano N, Benzi M 2012 Phys. Rep. 514 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Estrada E 2012 Linear Algebra Appl. 436 4317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Wu J J, Gao Z Y, Sun H J 2006 Phys. Rev. E 74 066111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Gao J, Barzel B, Barabási A L 2016 Nature 530 307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Newman M E J 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 208701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Johnson S, Torres J, Marro J, Munñoz M A 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 108702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Erdös P, Rényi A 1959 Publ. Math. Debrecen 6 290
[42] Orsini C, Dankulov M M, Colomer-de-Simón P, Jamakovic A, Mahadevan P, Vahdat A, Bassler K E, Toroczkai Z, Boguñá M, Caldarelli G, Fortunato S, Krioukov D 2015 Nat. Commun. 6 8627
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 8439
- PDF下载量: 108
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: