-
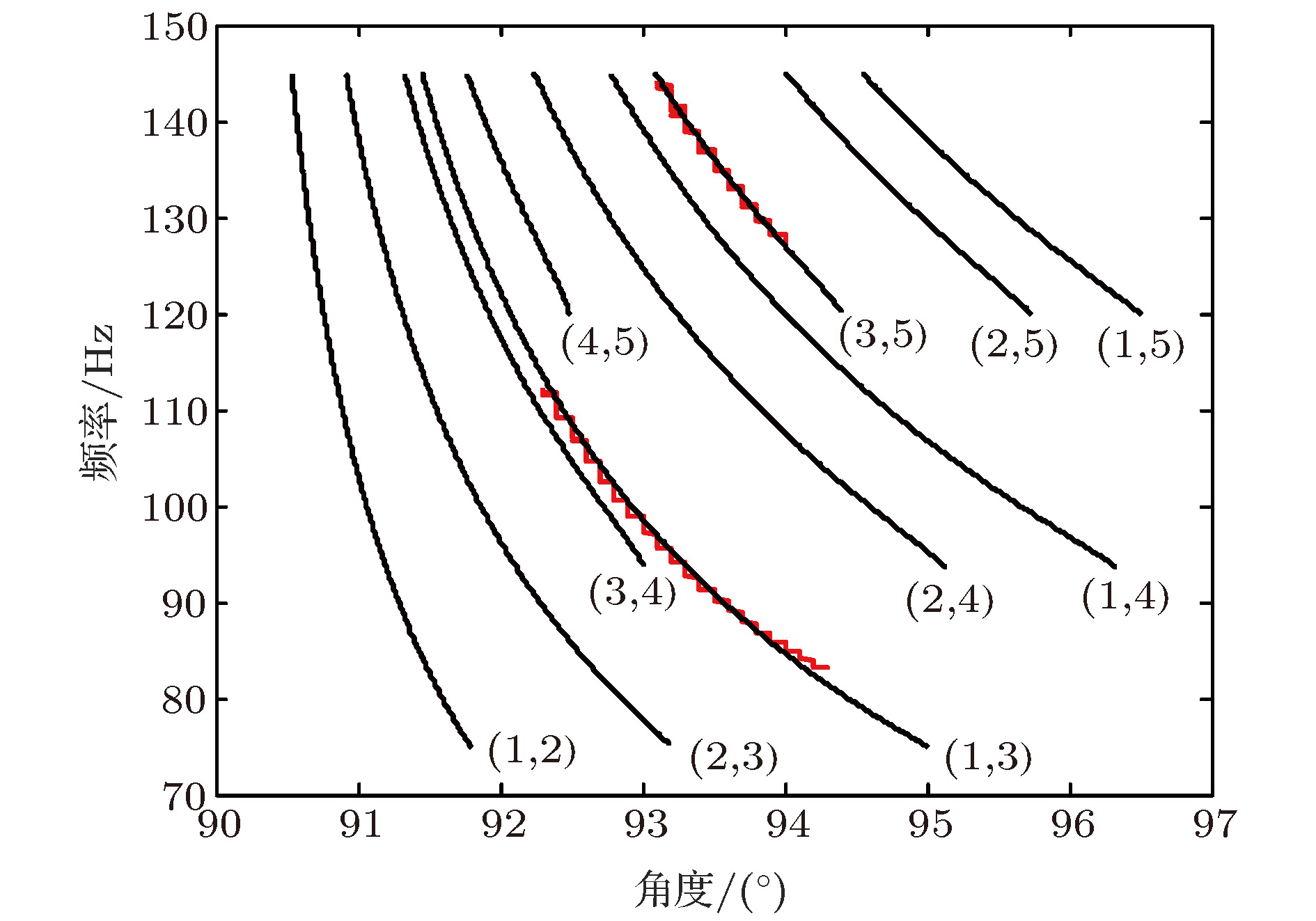
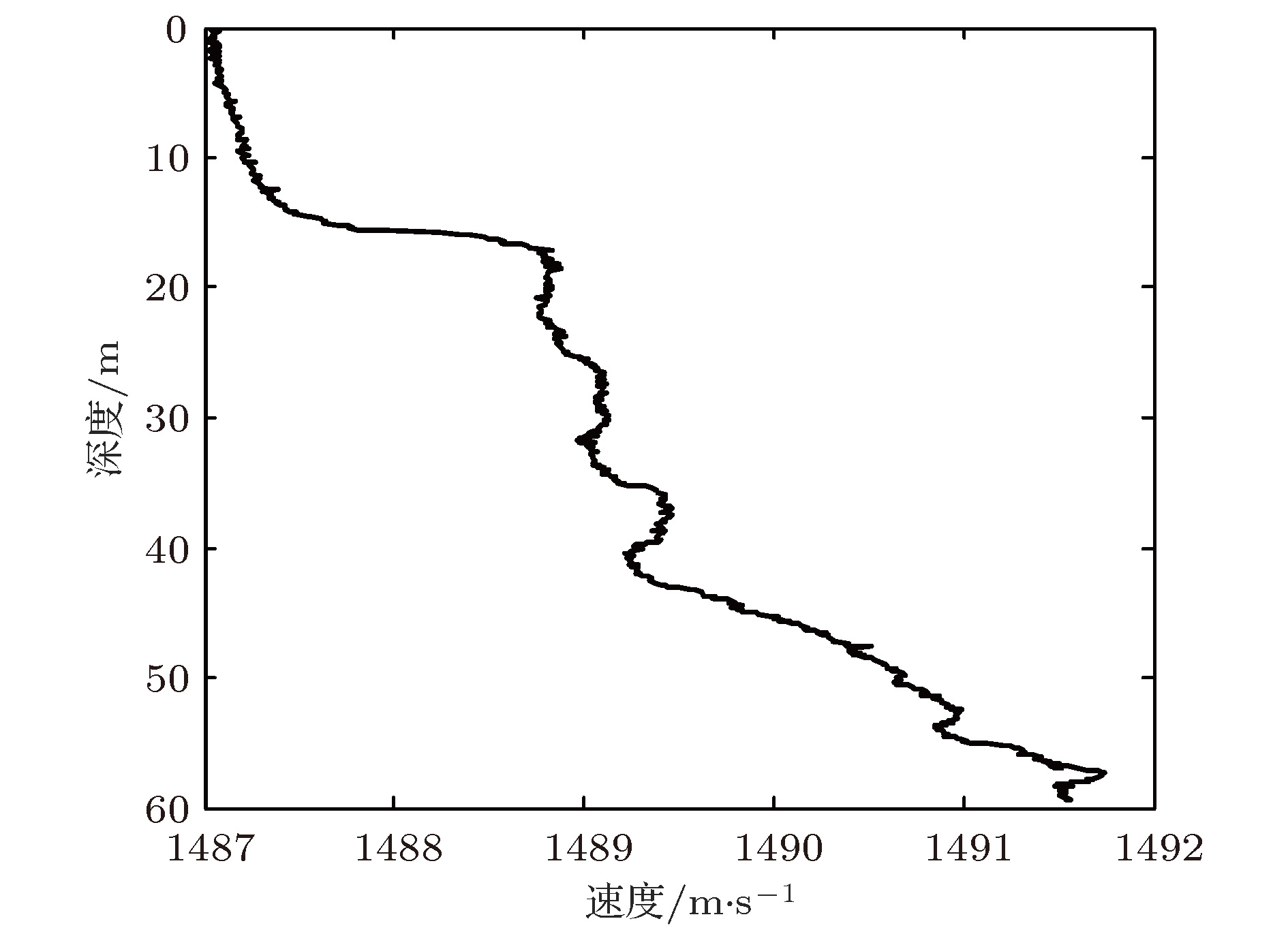
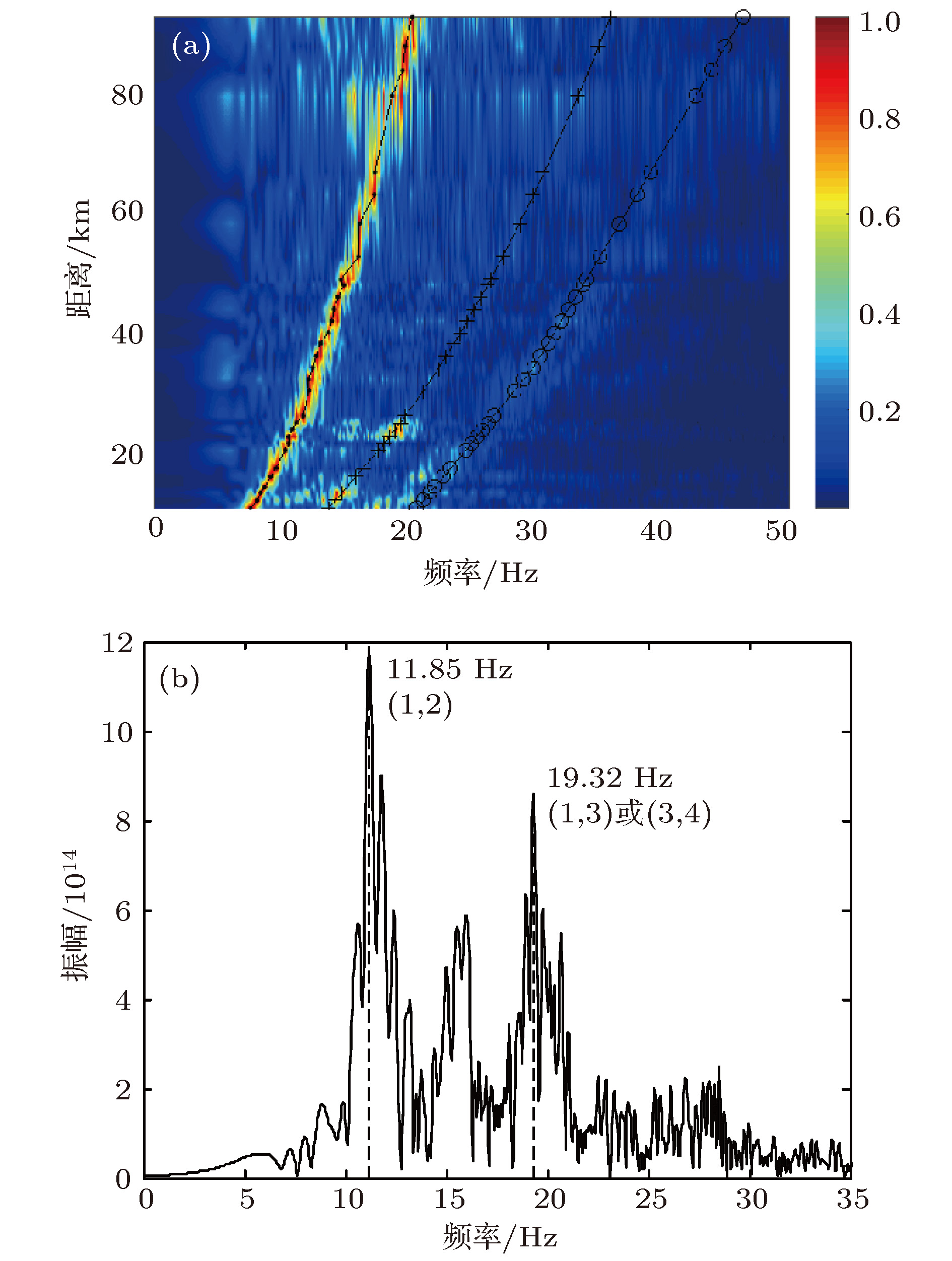
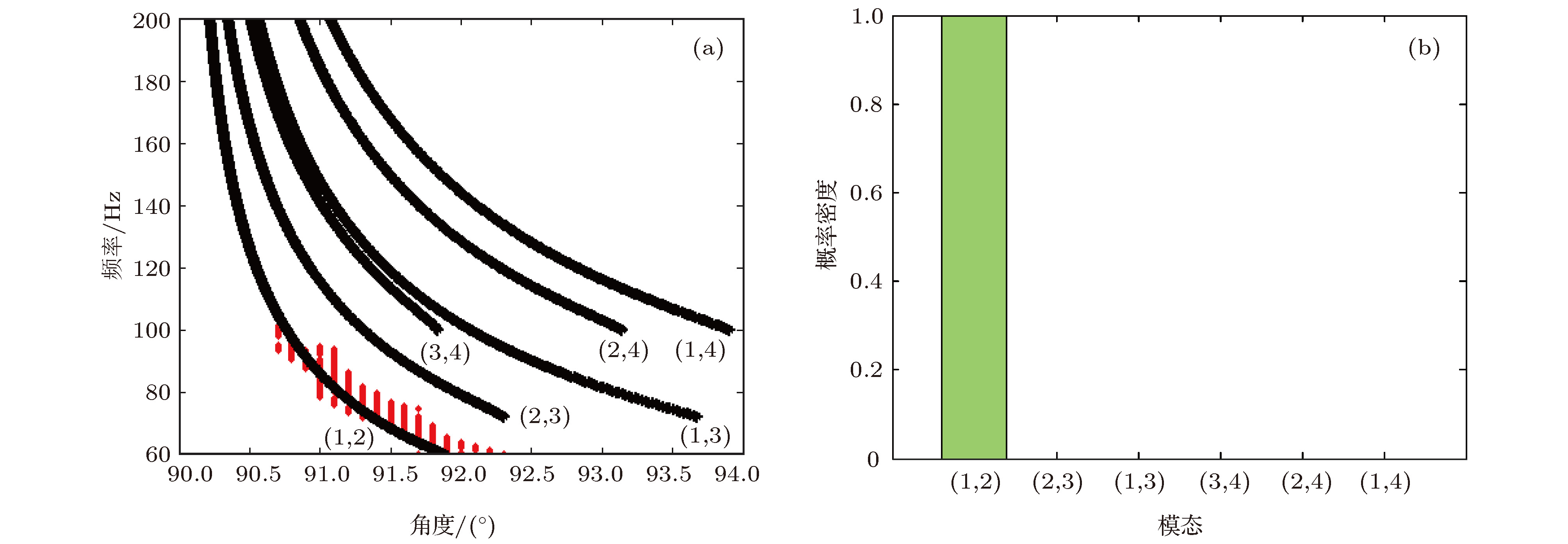
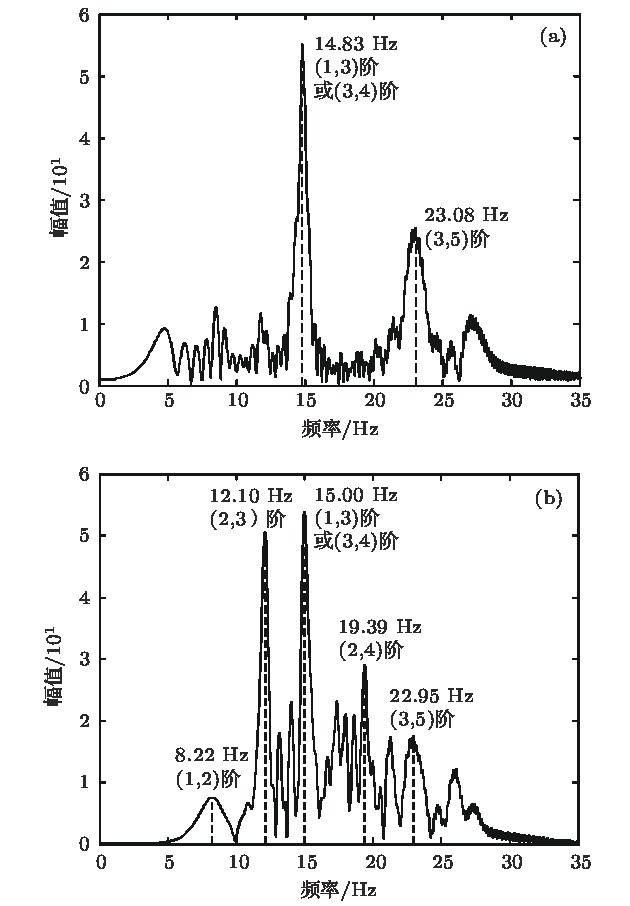
浅海波导中, 低频宽带声场中干涉简正模特性可用于声源定位和环境参数反演, 然而实际应用中由于存在声源位置不确知、某些简正模激发较弱、模型参数选取失配等因素的制约, 导致干涉简正模阶数的判别存在问题. 结合水平线列阵应用, 根据阵列接收信号中干涉简正模成分的波束输出角度与距离无关但与干涉简正模阶数和频率相关的波导固有频散特性, 提出了一种基于阵元域接收信号自相关函数WARPING变换过滤干涉简正模, 进而对其波束输出角度进行模基匹配判别简正模阶数的方法. 利用2011年北黄海海域声学实验中坐底布放的32元水平线列阵接收的爆炸声脉冲信号, 对方法进行了验证. 并由仿真数据分析了声速剖面、海底参数和水深等参数失配及信噪比对方法性能的影响. 结果表明水深变化14%以上对干涉简正模波束输出角度的提取值影响最大, 可引起方法失效; 声速剖面和海底参数在一定失配范围内对方法性能的影响可忽略; 方法要求单阵元信噪比大于2 dB.The interference characteristics of normal modes in low-frequency broadband sound can be applied to source localization and environmental parameter inversion in shallow water. However, the identification ambiguity of interference normal mode pairs generally occurs in practical applications due to unknown source position, some weakly-excited normal modes, mismatched environmental model, etc. For the applications of a horizontal line array, a model-based processing approach is proposed to determine the orders of the interference normal mode pairs based on the intrinsic dispersion characteristics of interference normal mode pairs in the received signals and the range-independent properties of the array beam output angles. Firstly, the normal mode pair filtering is achieved by using the WARPING transform of the signal autocorrelation function in the element domain of the horizontal line array. Then, the arrival angles of the filtered interference normal mode pairs are estimated by using array beamforming. Finally, the estimated beam output angles are matched with the replica values computed by sound field model. The approach is verified by using the explosive pulse signals received by the seafloor-deployed 32-element horizontal line array at the North Yellow Sea in 2011. Furthermore, some simulations are involved to analyze the effects of environmental parameter mismatches including water sound speed profile, sea bottom parameters and water depth on the identification performance of interference normal mode pairs. The results show that the water depth is a major factor influencing the extracted values of the beam output angles of interference normal mode pairs. The approach might fail when the water depth mismatch exceeds 14% of the practical value. However, the effects of water sound speed profile mismatch and sea bottom parameters mismatch are negligible. The effect of signal-to-noise ratio in the element domain on a horizontal line array is also simulated in order to analyze the limitation of identification performance, which shows that the required signal-to-noise ratio in the element domain should be more than 2 dB.
-
Keywords:
- shallow water waveguide /
- interference normal mode pair /
- WARPING transform /
- modal identification /
- horizontal line array
[1] Bonnel J, Nicolas B, Mars J I, Walker S C 2010 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 128 719
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Bonnel J, Chapman N R 2011 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 130 EL101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 牛海强, 何利, 李整林, 张仁和, 南明星 2014 声学学报 39 1
Niu H Q, He L, Li Z L, Zhang R H, Nan M X 2014 Acta Acoust. 39 1
[4] Li Z L, Zhang R H 2007 Chin. Phys. Lett. 24 471
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Li F H, Zhang B, Guo Y G 2014 Chin. Phys. Lett. 31 47
[6] Bonnel J, Ying-Tsong L, Eleftherakis D, Goff J A, Dosso S, Chapman R, Miller J H, Potty G R 2018 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 143 405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 李佳蔚, 鹿力成, 郭圣明, 马力 2017 66 204301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li J W, Lu L C, Guo S M, Ma L 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 204301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Lopatka M, Touzé G L, Nicolas B, Cristol X, Mars J I, Fattaccioli D 2010 J. Adv. Signal Proc. 2010 304103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 王冬, 郭良浩, 刘建军, 戚聿波 2016 65 104302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang D, Guo L H, Liu J J, Qi Y B 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 104302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Bonnel J, Thode A 2013 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 19 070066
[11] 戚聿波, 周士弘, 张仁和, 张波, 任云 2014 63 044303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi Y B, Zhou S H, Zhang R H, Zhang B, Ren Y 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 044303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 李晓曼, 张明辉, 张海刚, 朴胜春, 刘亚琴, 周建波 2017 66 094302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li X M, Zhang M H, Zhang H G, Piao S C, Liu Y Q, Zhou J B 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 094302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 李晓曼, 朴胜春, 张明辉, 刘亚琴, 周建波 2017 66 184301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li X M, Piao S C, Zhang M H, Liu Y Q, Zhou J B 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 184301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhou S H, Qi Y B, Ren Y 2014 Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 57 225
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Baraniuk R G, Jones D L 1995 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 43 2269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Touzé L, Nicolas B, Mars J I, Lacoume J L 2009 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 57 1783
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 戚聿波, 周士弘, 张仁和, 任云 2015 64 074301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi Y B, Zhou S H, Zhang R H, Ren Y 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 074301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 戚聿波, 周士弘, 张仁和 2016 65 134301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi Y B, Zhou S H, Zhang R H 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 134301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Jensen F B, Kuperman W A, Porter M B, Schmidt H 2011 Computational Ocean Acoustics (2nd Ed.) (NewYork: Springer) p408
[20] Bender C M, Orszag S A 1978 Advanced Mathematical Methods for Scientists and Engineers (New York: McGraw-Hill) p276
[21] 戚聿波, 周士弘, 任云, 刘建军, 王德俊, 冯希强 2015 声学学报 40 144
Qi Y B, Zhou S H, Ren Y, Liu J J, Wang D J, Feng X Q 2015 Acta Acoust. 40 144
[22] Porter M B 1991 The KRAKEN Normal Mode Program (La Spezia: SACLANT Undersea Research Centre) p1
-
表 1 海底底质参数选择
Table 1. Sea bottom parameters
海底声速/m·s–1 海底密度/g·cm–3 吸收系数/dB·λ–1 1530 1.20 0.30 1550 1.50 0.20 1606 1.65 0.09 1700 1.80 0.05 -
[1] Bonnel J, Nicolas B, Mars J I, Walker S C 2010 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 128 719
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Bonnel J, Chapman N R 2011 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 130 EL101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 牛海强, 何利, 李整林, 张仁和, 南明星 2014 声学学报 39 1
Niu H Q, He L, Li Z L, Zhang R H, Nan M X 2014 Acta Acoust. 39 1
[4] Li Z L, Zhang R H 2007 Chin. Phys. Lett. 24 471
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Li F H, Zhang B, Guo Y G 2014 Chin. Phys. Lett. 31 47
[6] Bonnel J, Ying-Tsong L, Eleftherakis D, Goff J A, Dosso S, Chapman R, Miller J H, Potty G R 2018 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 143 405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 李佳蔚, 鹿力成, 郭圣明, 马力 2017 66 204301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li J W, Lu L C, Guo S M, Ma L 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 204301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Lopatka M, Touzé G L, Nicolas B, Cristol X, Mars J I, Fattaccioli D 2010 J. Adv. Signal Proc. 2010 304103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 王冬, 郭良浩, 刘建军, 戚聿波 2016 65 104302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang D, Guo L H, Liu J J, Qi Y B 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 104302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Bonnel J, Thode A 2013 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 19 070066
[11] 戚聿波, 周士弘, 张仁和, 张波, 任云 2014 63 044303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi Y B, Zhou S H, Zhang R H, Zhang B, Ren Y 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 044303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 李晓曼, 张明辉, 张海刚, 朴胜春, 刘亚琴, 周建波 2017 66 094302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li X M, Zhang M H, Zhang H G, Piao S C, Liu Y Q, Zhou J B 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 094302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 李晓曼, 朴胜春, 张明辉, 刘亚琴, 周建波 2017 66 184301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li X M, Piao S C, Zhang M H, Liu Y Q, Zhou J B 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 184301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhou S H, Qi Y B, Ren Y 2014 Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 57 225
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Baraniuk R G, Jones D L 1995 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 43 2269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Touzé L, Nicolas B, Mars J I, Lacoume J L 2009 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 57 1783
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 戚聿波, 周士弘, 张仁和, 任云 2015 64 074301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi Y B, Zhou S H, Zhang R H, Ren Y 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 074301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 戚聿波, 周士弘, 张仁和 2016 65 134301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi Y B, Zhou S H, Zhang R H 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 134301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Jensen F B, Kuperman W A, Porter M B, Schmidt H 2011 Computational Ocean Acoustics (2nd Ed.) (NewYork: Springer) p408
[20] Bender C M, Orszag S A 1978 Advanced Mathematical Methods for Scientists and Engineers (New York: McGraw-Hill) p276
[21] 戚聿波, 周士弘, 任云, 刘建军, 王德俊, 冯希强 2015 声学学报 40 144
Qi Y B, Zhou S H, Ren Y, Liu J J, Wang D J, Feng X Q 2015 Acta Acoust. 40 144
[22] Porter M B 1991 The KRAKEN Normal Mode Program (La Spezia: SACLANT Undersea Research Centre) p1
计量
- 文章访问数: 14629
- PDF下载量: 118
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: