-
提出了一种基于Pancharatnam-Berry相位和动力学相位操控纵向光子自旋霍尔效应的方法. 理论分析表明: 当光场通过一个由Pancharatnam-Berry相位透镜和动力学相位透镜构成的透镜组时, 透镜组会存在两个自旋相关的焦点. 首先, 当左旋和右旋圆偏振光通过微结构相位延迟为
${\text{π}}$ 的Pancharatnam-Berry相位透镜时, 由于Pancharatnam-Berry相位的自旋相关性, 两个圆偏振分量会获得符号相反的Pancharatnam-Berry相位而导致其中一个被聚焦而另一个发散. 然后, 在Pancharatnam-Berry相位透镜后再插入普通透镜引入动力学相位调制, 由于动力学相位是自旋无关, 使得这一透镜组可以在合适的条件下使不同自旋态的光子分别聚焦于纵向上不同焦点处. 纵向自旋分裂由两透镜焦距及间距共同决定, 因此可以通过改变两个透镜的焦距及其间距获得任意的纵向自旋分裂值. 最后, 搭建了一套实验装置, 所得实验结果与理论结果一致.-
关键词:
- 光子自旋霍尔效应 /
- Pancharatnam-Berry相位 /
- 琼斯矩阵
Photonic spin Hall effect is generally described as a spin-dependent splitting. Previous studies have focused on the transverse spin-dependent splitting of light field. In this work, a method of manipulating the longitudinal photonic spin Hall effect which is based on dynamic and Pancharatnam-Berry phase is proposed. The theoretical analysis demonstrates that the lens group consisting of a Pancharatnam-Berry phase lens and a dynamic lens has two spin-dependent foci. Firstly, because Pancharatnam-Berry phase is spin-dependent, the left- and right-handed circularly polarized component can respectively acquire a Pancharatnam-Berry phase with opposite sign when a linearly polarized light beam passes through the Pancharatnam-Berry phase lens with phase retardation${\text{π}}$ . It leads one circularly polarized component to be focused and the other diverged. This is essentially the spin-dependent splitting of light field in momentum space, which is caused by Pancharatnam-Berry phase. And then, an ordinary lens is inserted behind the Pancharatnam-Berry phase lens to introduce a dynamic phase modulation. Due to dynamic phase being spin-independent, the constructed lens group can focus the photons with different spin states at different focal points longitudinally under the appropriate conditions. In other words, the lens group has two spin-dependent focal points. The two focal points split the photons with different spin states in the longitudinal direction. The longitudinal spin-dependent splitting is dependent on the focal lengths of the two lens and the distance between the two lenses. By changing the three parameters, arbitrary longitudinal spin-dependent splitting can be obtained. Lastly, an experimental system is set up to verify the theoretical results. The relationship between the spin-dependent splitting and the distance between the two lenses is measured. By introducing a Glan laser polarizer and a quarter wave-plate, the circularly polarized chirality of the light field at the focal point is also measured. These experimental results are all in good agreement with the theoretical analyses. These results are helpful in understanding the physical origin of photonic spin Hall effect and developing novel photonic devices based on photonic spin Hall effect.-
Keywords:
- photonic spin Hall effect /
- Pancharatnam-Berry phase /
- Jones matrix
[1] Onoda M, Murakami S, Nagaosa N 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 93 083901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Hosten O, Kwiat P 2008 Science 319 787
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Bliokh K Y, Niv A, Kleiner V, Hasman E 2008 Nature Photon. 2 748
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Bliokh K Y, Bliokh Y P 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 96 073903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Luo H, Wen S, Shu W, Tang Z, Zou Y, Fan D 2009 Phys. Rev. A 80 043810
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Qin Y, Li Y, He H, Gong Q 2009 Opt. Lett. 34 2551
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Qin Y, Li Y, Feng X, Liu Z, He H, Xiao Y, Gong Q 2010 Opt. Express 18 16832
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Luo H, Zhou X, Shu W, Wen S, Fan D 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 043806
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wang H, Zhang X 2011 Phys. Rev. A 83 053820
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhu W, She W 2015 Opt. Lett. 40 2961
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Tang T, Li J, Zhang Y, Li C, Luo L 2016 Opt. Express 24 28113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Xiang Y, Jiang X, You Q, Guo J, Dai X 2017 Photon. Res. 5 467
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhang W, Wu W, Chen S, Zhang J, Ling X, Shu W, Luo H, Wen S 2018 Photon. Res. 6 511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhou X, Xiao Z, Luo H, Wen S 2012 Phys. Rev. A 85 043809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhou X, Ling X, Luo H, Wen S 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 101 251602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kang M, Chen J, Li S, Gu B, Li Y, Wang H 2011 Opt. Lett. 36 3942
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Shitrit N, Yulevich I, Maguid E, Ozeri D, Veksler D, Kleiner V, Hasman E 2013 Science 340 724
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ling X, Zhou X, Yi X, Shu W, Liu Y, Chen S, Luo H, Wen S, Fan D 2015 Light: Sci. Appl. 4 e290
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Shao Z, Zhu J, Chen Y, Zhang Y, Yu S 2018 Nature Commun. 9 926
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 万婷, 罗朝明, 闵力, 陈敏, 肖磊 2018 67 064201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wan T, Luo Z M, Min L, Chen M, Xiao L 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 064201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Khorasaninejad M, Chen W, Devlin R, Oh J, Zhu A, Capasso F 2016 Science 352 1190
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Ke Y, Liu Y, Zhou J, Liu Y, Luo H, Wen S 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 108 101102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Shu W, Ke Y, Liu Y, Ling X, Luo H, Yin X 2016 Phys. Rev. A 93 013839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 陈敏, 罗朝明, 万婷, 刘靖 2017 光学学报 37 0226002
Chen M, Luo Z M, Wan T, Liu J 2017 Acta Opt. Sin. 37 0226002
[25] 徐兆鑫, 黄修章, 黄攀立, 艾余前, 张晨, 陈欢, 易煦农 2018 光子学报 47 0126002
Xu Z X, Huang X Z, Huang P L, Ai Y Q, Zhang C, Chen H, Yi X N 2018 Acta Photon. Sin. 47 0126002
[26] Marrucci L, Manzo C, Paparo D 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 96 163905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Yi X, Liu Y, Ling X, Zhou X, Ke Y, Luo H, Wen S, Fan D 2015 Phys. Rev. A 91 023801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Beresna M, Gecevičius M, Kazansky P G, Gertus T 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 98 201101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Beresna M, Gecevičius M, Kazansky P G 2011 Opt. Mater. Express 1 783
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
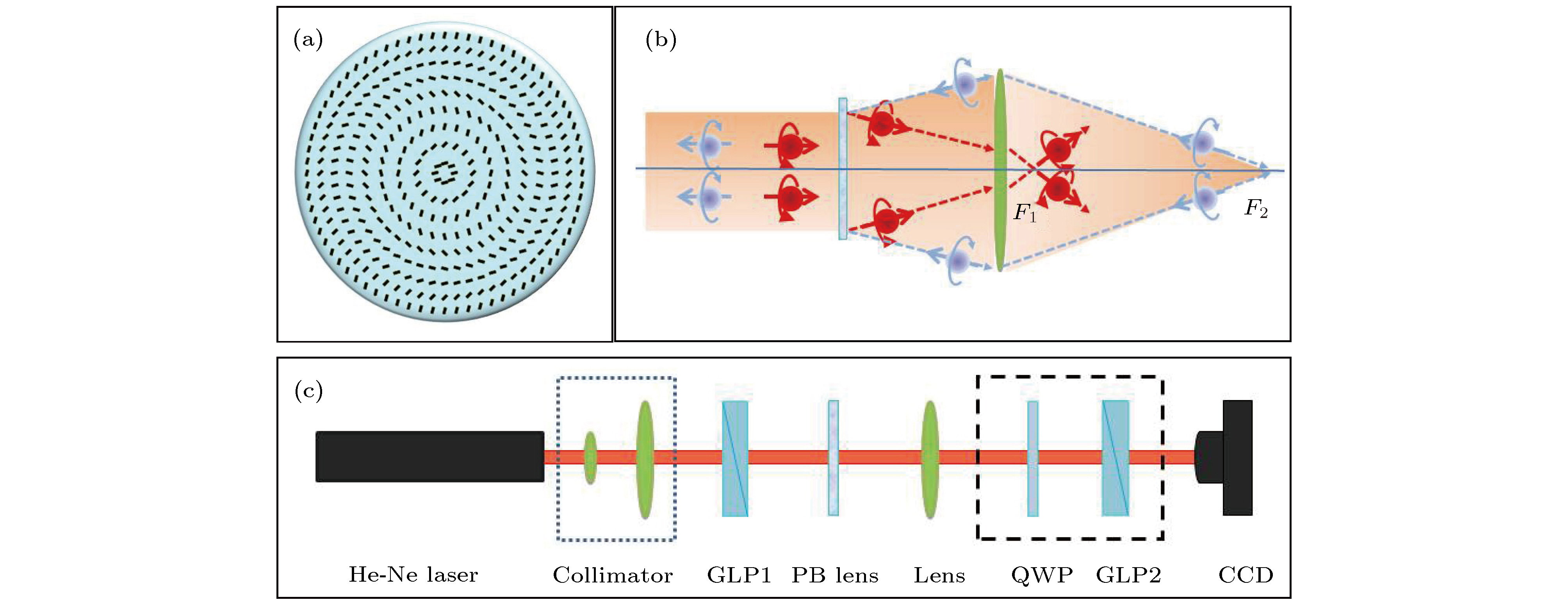
图 1 (a) PB相位透镜的光轴分布示意图; (b)当线偏振光通过PB相位透镜与普通透镜构成的透镜组时, 不同自旋态光子的光路示意图; (c)实验装置示意图(GLP, 格兰激光偏振镜; PB lens, PB相位透镜; Lens, 普通透镜; QWP, 四分之一波片)
Fig. 1. (a) Schematic illustration of optical axis spatial distribution of the PB phase lens; (b) optical pathway diagram of photon with different spin states when a linearly polarized light beam passes through the lens group consisting of a PB phase lens and a ordinary lens; (c) diagram of experimental setup (GLP, Glan laser polarizer; PB lens, PB phase lens; Lens, ordinary lens, QWP, quarter-wave plate).
图 2 透镜组的焦点位置及纵向自旋分裂与两透镜之间的距离
$d$ 的关系曲线 (a1)—(a3)分别为当${f_{{\rm{PB}}}} = 200\;{\rm{mm}}$ ,${f_{\rm{C}}} = 175\;{\rm{mm}}$ 时, 透镜组的左旋圆偏振光焦点位置、右旋圆偏振光焦点位置及纵向自旋分裂与两透镜之间的距离$d$ 的关系曲线, (a3)中的实线为理论计算结果, 方形离散点为实验测得的结果; (b1)—(b3)为${f_{{\rm{PB}}}} = 200\;{\rm{mm}}$ ,${f_{\rm{C}}} = 100\;{\rm{mm}}$ 时对应的结果Fig. 2. Focus position of the lens group and longitudinal spin splitting change with the distance of the PB lens and the ordinary lens, when (a1)−(a3)
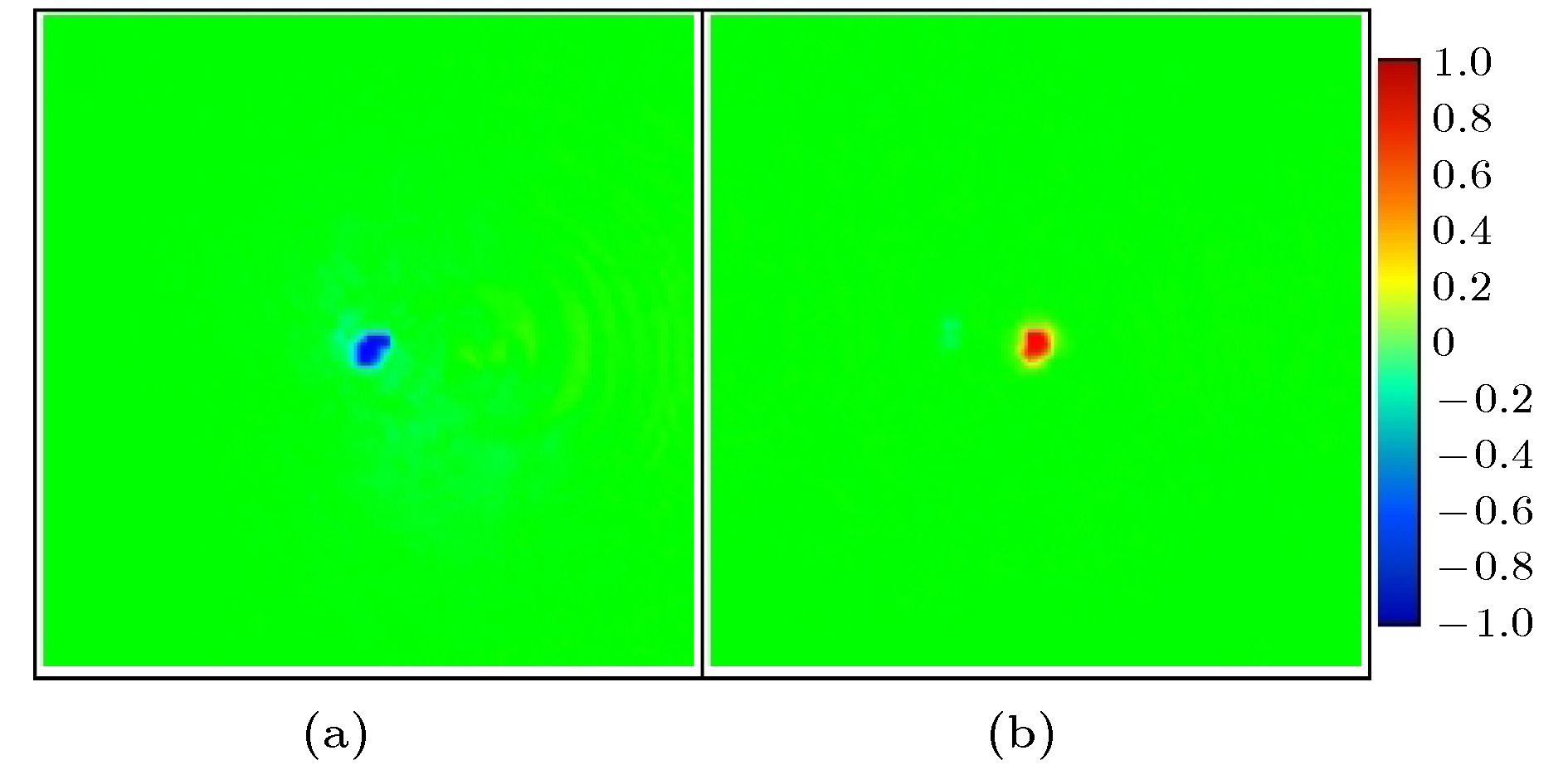
${f_{{\rm{PB}}}} = 200\;{\rm{mm}}$ ,${f_{\rm{C}}} = 175\;{\rm{mm}}$ ; (b1)−(b3) the corresponding case, when${f_{{\rm{PB}}}} = 200\;{\rm{mm}}$ ,${f_{\rm{C}}} = 100$ mm图 3 透镜组焦点处光场的归一化斯托克斯
${s_3}$ 参数 (a)焦点${F_1}$ 处光场的斯托克斯${s_3}$ 参数; (b)焦点${F_2}$ 处光场的斯托克斯${s_3}$ 参数Fig. 3. Normalized Stokes parameter
${s_3}$ of the optical field at the focus: (a) The Stokes parameter${s_3}$ of the optical field at the focus${F_1}$ ; (b) the Stokes parameter${s_3}$ of the optical field at the focus${F_2}$ . -
[1] Onoda M, Murakami S, Nagaosa N 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 93 083901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Hosten O, Kwiat P 2008 Science 319 787
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Bliokh K Y, Niv A, Kleiner V, Hasman E 2008 Nature Photon. 2 748
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Bliokh K Y, Bliokh Y P 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 96 073903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Luo H, Wen S, Shu W, Tang Z, Zou Y, Fan D 2009 Phys. Rev. A 80 043810
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Qin Y, Li Y, He H, Gong Q 2009 Opt. Lett. 34 2551
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Qin Y, Li Y, Feng X, Liu Z, He H, Xiao Y, Gong Q 2010 Opt. Express 18 16832
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Luo H, Zhou X, Shu W, Wen S, Fan D 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 043806
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wang H, Zhang X 2011 Phys. Rev. A 83 053820
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhu W, She W 2015 Opt. Lett. 40 2961
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Tang T, Li J, Zhang Y, Li C, Luo L 2016 Opt. Express 24 28113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Xiang Y, Jiang X, You Q, Guo J, Dai X 2017 Photon. Res. 5 467
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhang W, Wu W, Chen S, Zhang J, Ling X, Shu W, Luo H, Wen S 2018 Photon. Res. 6 511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhou X, Xiao Z, Luo H, Wen S 2012 Phys. Rev. A 85 043809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhou X, Ling X, Luo H, Wen S 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 101 251602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kang M, Chen J, Li S, Gu B, Li Y, Wang H 2011 Opt. Lett. 36 3942
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Shitrit N, Yulevich I, Maguid E, Ozeri D, Veksler D, Kleiner V, Hasman E 2013 Science 340 724
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ling X, Zhou X, Yi X, Shu W, Liu Y, Chen S, Luo H, Wen S, Fan D 2015 Light: Sci. Appl. 4 e290
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Shao Z, Zhu J, Chen Y, Zhang Y, Yu S 2018 Nature Commun. 9 926
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 万婷, 罗朝明, 闵力, 陈敏, 肖磊 2018 67 064201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wan T, Luo Z M, Min L, Chen M, Xiao L 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 064201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Khorasaninejad M, Chen W, Devlin R, Oh J, Zhu A, Capasso F 2016 Science 352 1190
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Ke Y, Liu Y, Zhou J, Liu Y, Luo H, Wen S 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 108 101102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Shu W, Ke Y, Liu Y, Ling X, Luo H, Yin X 2016 Phys. Rev. A 93 013839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 陈敏, 罗朝明, 万婷, 刘靖 2017 光学学报 37 0226002
Chen M, Luo Z M, Wan T, Liu J 2017 Acta Opt. Sin. 37 0226002
[25] 徐兆鑫, 黄修章, 黄攀立, 艾余前, 张晨, 陈欢, 易煦农 2018 光子学报 47 0126002
Xu Z X, Huang X Z, Huang P L, Ai Y Q, Zhang C, Chen H, Yi X N 2018 Acta Photon. Sin. 47 0126002
[26] Marrucci L, Manzo C, Paparo D 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 96 163905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Yi X, Liu Y, Ling X, Zhou X, Ke Y, Luo H, Wen S, Fan D 2015 Phys. Rev. A 91 023801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Beresna M, Gecevičius M, Kazansky P G, Gertus T 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 98 201101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Beresna M, Gecevičius M, Kazansky P G 2011 Opt. Mater. Express 1 783
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 13207
- PDF下载量: 250
- 被引次数: 0















 下载:
下载: