-
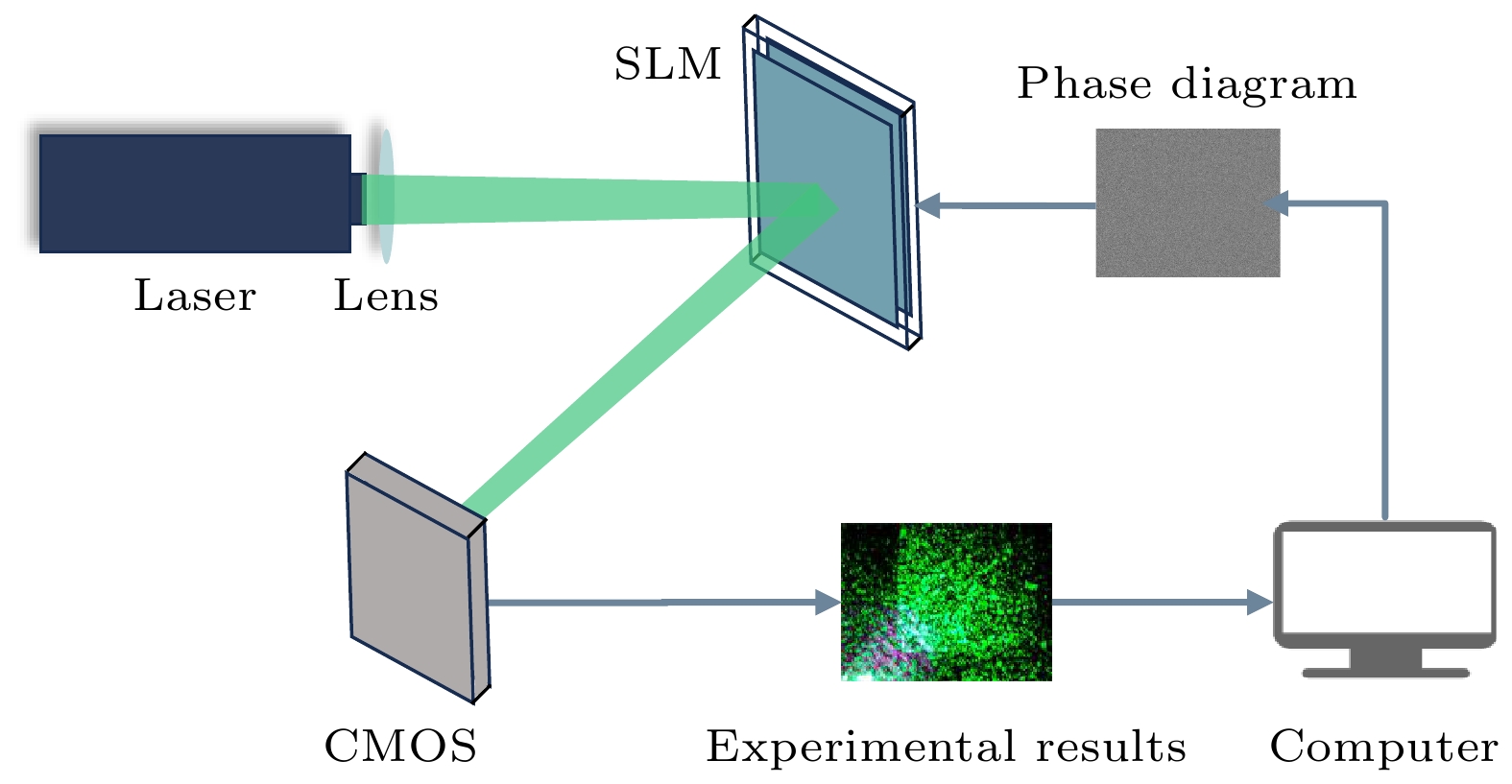
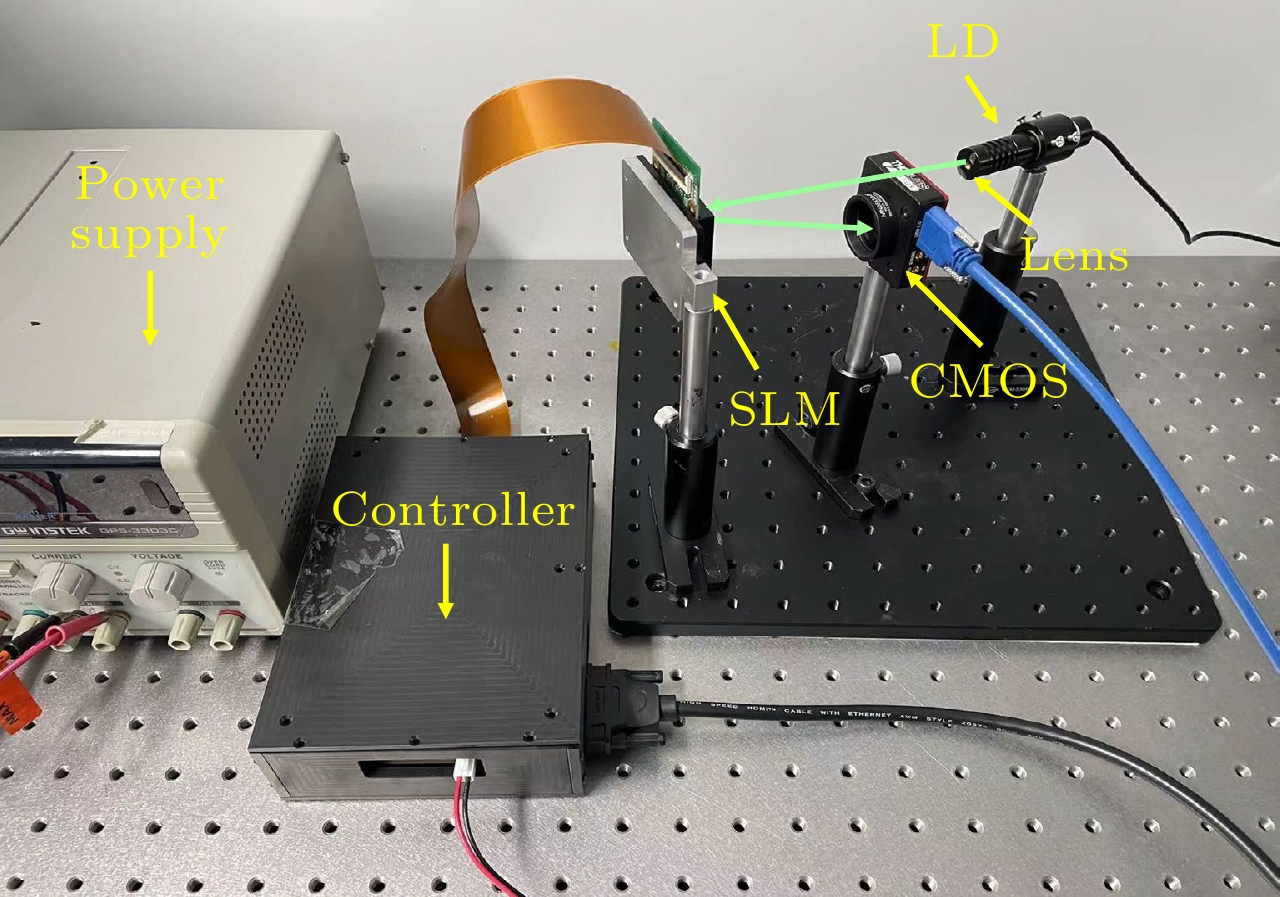
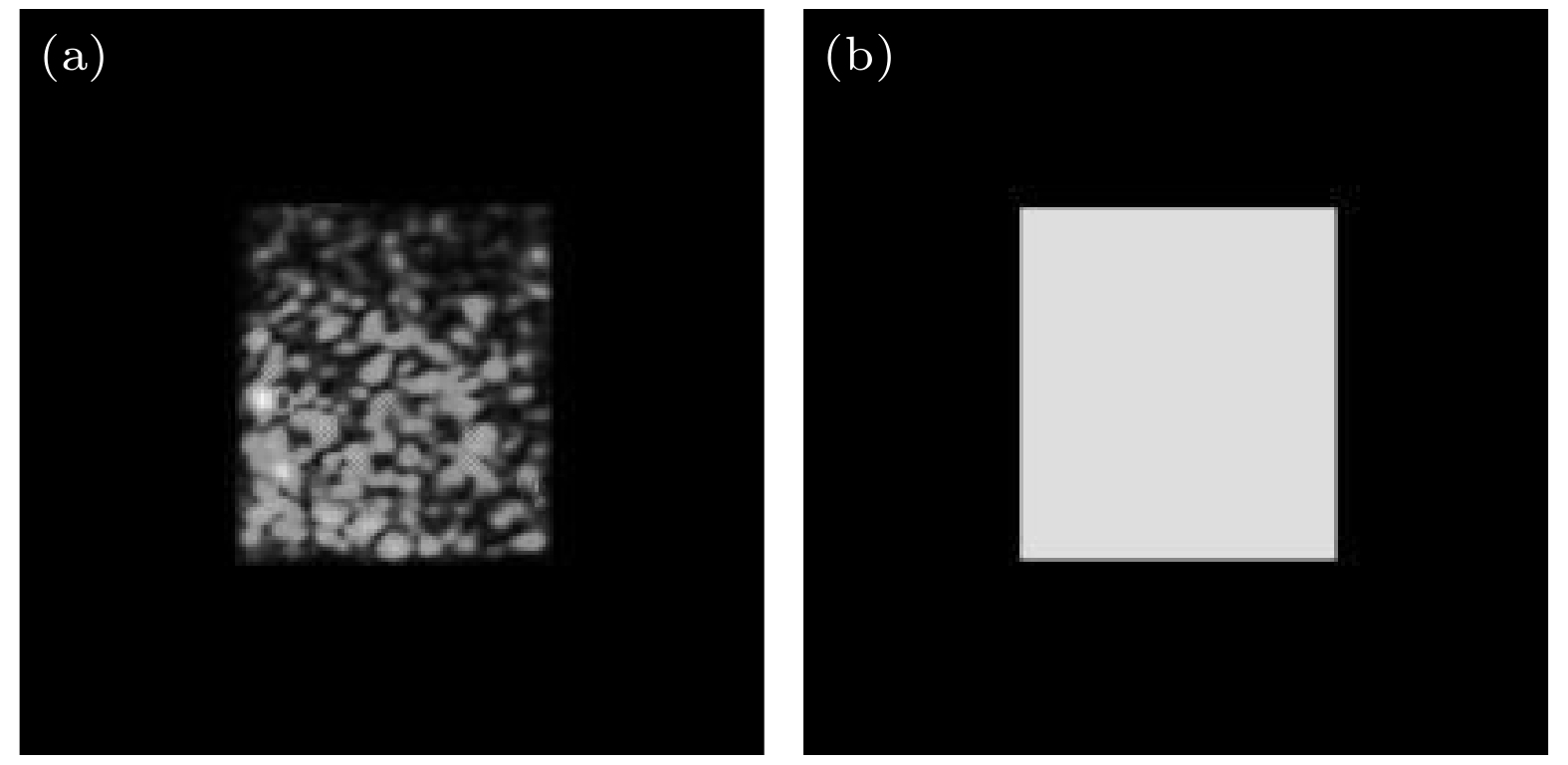
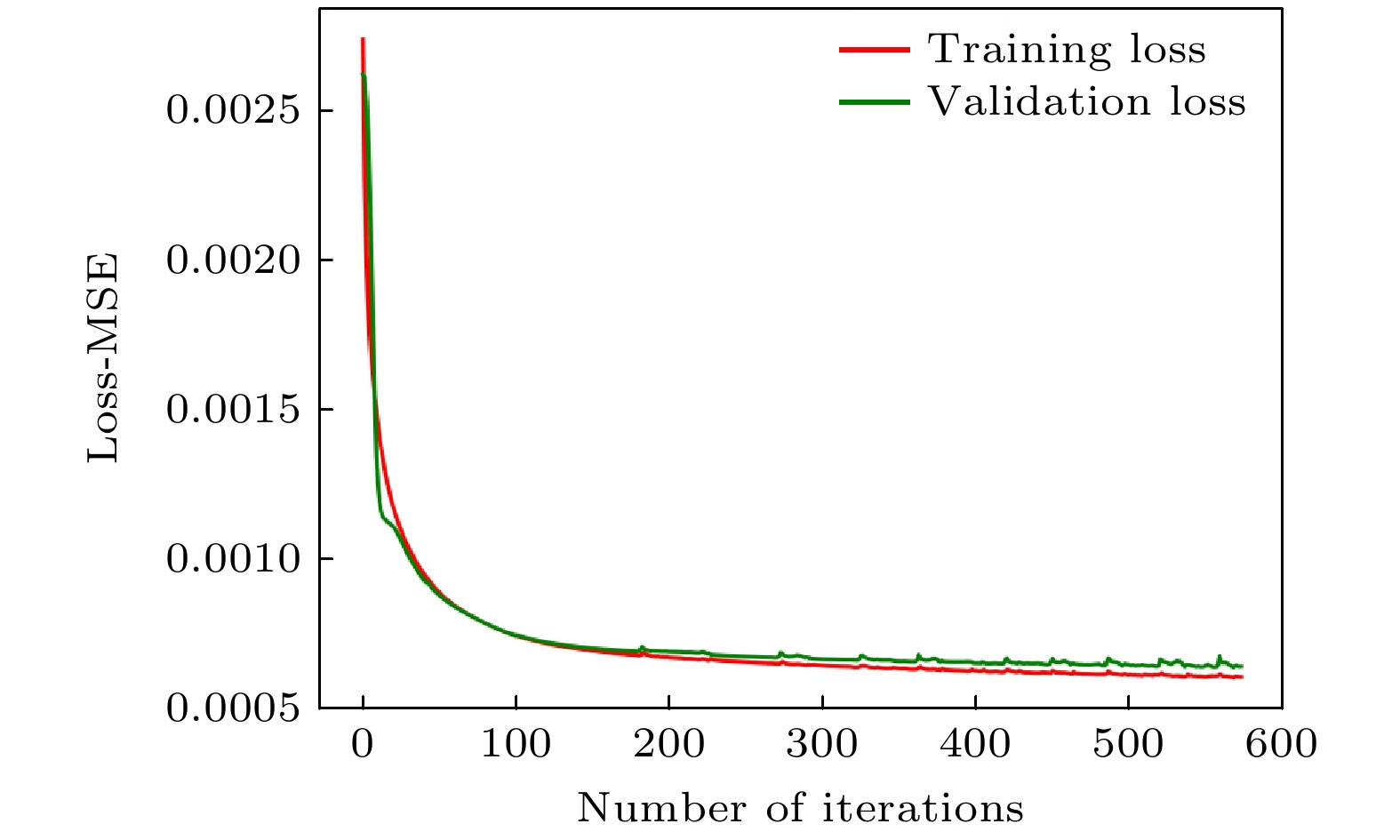
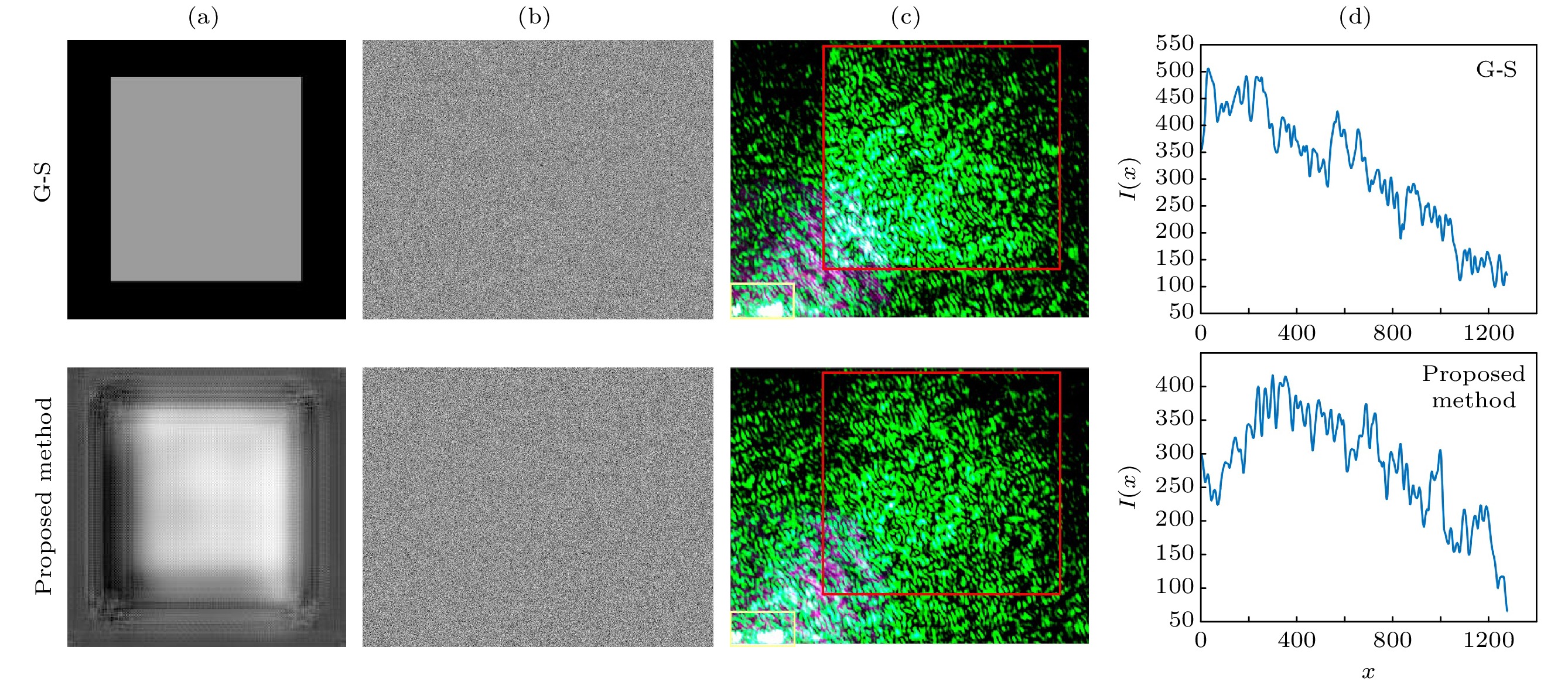
Laser is widely used in various fields such as laser processing, optical imaging, and optical trapping due to its high monochromaticity, directionality, and high energy density. However, the beam generated by the laser is a Gaussian beam with non-uniform distribution of optical energy, and this non-uniform distribution affects the interaction between the laser and the matter. Therefore, it is necessary to reshape the Gaussian beam into homogenized light spots with uniform distribution of optical energy. Laser beam homogenization method aims to change the spatial distribution of the Gaussian beam, precisely controlling the shape and intensity of the laser beam to achieve homogenized light spots. However, the existing laser beam homogenization methods encounter some problems such as complicated component preparation and poor flexibility. They also fail to address experimental errors caused by stray light and zero-order light interference, leading to discrepancies between the experimental results and the expected results. These limitations seriously restrict the widespread application of laser technology in various fields. A laser homogenization method based on machine learning is proposed for spatial light modulator (SLM) laser homogenization in this work. The preliminary approach to laser homogenization is to generate a phase hologram by using the Gerchberg-Saxton (G-S) algorithm and modulate the incident light beam into homogenized light spots by using an SLM. However, the inherent homogenization error of the SLM prevents laser homogenization from improving uniformity. The machine learning method is proposed as a means of compensating for homogenization errors, thereby improving the uniformity of the light spot. The corresponding supervised learning regression task on the experimental dataset establishes mapping relationships between the homogenization target images and the experimental detection images. The results of homogenization error compensation are validated through experiments. Compared with the traditional SLM laser homogenization methods, the proposed method reduces the non-uniformity of the light spot by 13%. The laser homogenization method based on machine learning is an efficient way to achieve laser beam homogenization. The proposed laser beam homogenization method can serve as a reference for machine learning-based method. This method possesses significant technical value for laser applications such as laser processing, optical imaging, and optical manipulation. Furthermore, it can provide guidance and reference for utilizing artificial intelligence in addressing optical problems. -
Keywords:
- laser beam homogenization /
- machine learning /
- error compensation /
- Gerchberg-Saxton algorithm
[1] Xue L, Pang Y, Liu W, Liu L, Pang H, Cao A X, Shi L, Fu Y, Deng Q L 2020 Micromachines 11 338
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Yuan W, Xue L, Cao A X, Pang H, Deng Q L 2021 Opt. Express 29 40878
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Yuan W, Xu C, Xue L, Pang H, Cao A X, Fu Y, Deng Q L 2021 Micromachines 12 673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yadav N K, ten Thije Boonkkamp J, Ijzerman W 2019 Opt. Commun. 439 251
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Bykov D A, Doskolovich L L, Byzov E V, Bezus E A, Kazanskiy N L 2021 Opt. Express 29 26304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wei S L, Zhu Z B, Fan Z C, Yan Y M, Ma D L 2019 Opt. Express 27 26757
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yan Y, Fan Z T, Sun G F, Tian K H 2023 Opt. Eng. 62 025103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Su P, Cai C, Song Y, Ma J, Tan Q 2020 Appl. Sci. 10 5485
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wu Y, Wang J, Chen C, Liu C J, Jin F M, Chen N 2021 Opt. Express 29 1412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Guo M, Lü G Q, Cai J H, Wang Z, Feng Q B 2022 Opt. Eng. 61 125103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Chen L Z, Tian S Z, Zhang H, Cao L C, Jin G F 2021 Opt. Express 29 11645
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Chen X, Fang X J, Ma D Y, Liu Y, Cao L, Zhai Y Y 2022 Appl. Opt. 61 C55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Chen W C, Yang T, Cheng D W, Wang Y T 2021 Opt. Express 29 27845
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Buske P, Völl A, Eisebitt M, Stollenwerk J, Holly C 2022 Opt. Express 30 22798
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Sun X H, Mu X Y, Xu C, Pang H, Deng Q L, Zhang K, Jiang H B, Du J L, Yin S Y, Du C L 2022 Opt. Express 30 2646
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Liu J S, Taghizadeh M R 2002 Opt. Lett. 27 1463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 周志华 2016 机器学习(北京: 清华大学出版社)第23—26页
Zhou Z H 2016 Micromachin Learning (Beijing: Tsinghua University Press) pp23–26
[18] Li P Z, Zheng Y B, Luo L 2020 J. Coast. Res. 104 255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Jeon W, Jeong W, Son K, Yang H 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 4240
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Eybposh M H, Caira N W, Atisa M, Chakravarthula P, Pégard N C 2020 Opt. Express 28 26636
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] Xue L, Pang Y, Liu W, Liu L, Pang H, Cao A X, Shi L, Fu Y, Deng Q L 2020 Micromachines 11 338
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Yuan W, Xue L, Cao A X, Pang H, Deng Q L 2021 Opt. Express 29 40878
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Yuan W, Xu C, Xue L, Pang H, Cao A X, Fu Y, Deng Q L 2021 Micromachines 12 673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yadav N K, ten Thije Boonkkamp J, Ijzerman W 2019 Opt. Commun. 439 251
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Bykov D A, Doskolovich L L, Byzov E V, Bezus E A, Kazanskiy N L 2021 Opt. Express 29 26304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wei S L, Zhu Z B, Fan Z C, Yan Y M, Ma D L 2019 Opt. Express 27 26757
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yan Y, Fan Z T, Sun G F, Tian K H 2023 Opt. Eng. 62 025103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Su P, Cai C, Song Y, Ma J, Tan Q 2020 Appl. Sci. 10 5485
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wu Y, Wang J, Chen C, Liu C J, Jin F M, Chen N 2021 Opt. Express 29 1412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Guo M, Lü G Q, Cai J H, Wang Z, Feng Q B 2022 Opt. Eng. 61 125103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Chen L Z, Tian S Z, Zhang H, Cao L C, Jin G F 2021 Opt. Express 29 11645
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Chen X, Fang X J, Ma D Y, Liu Y, Cao L, Zhai Y Y 2022 Appl. Opt. 61 C55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Chen W C, Yang T, Cheng D W, Wang Y T 2021 Opt. Express 29 27845
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Buske P, Völl A, Eisebitt M, Stollenwerk J, Holly C 2022 Opt. Express 30 22798
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Sun X H, Mu X Y, Xu C, Pang H, Deng Q L, Zhang K, Jiang H B, Du J L, Yin S Y, Du C L 2022 Opt. Express 30 2646
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Liu J S, Taghizadeh M R 2002 Opt. Lett. 27 1463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 周志华 2016 机器学习(北京: 清华大学出版社)第23—26页
Zhou Z H 2016 Micromachin Learning (Beijing: Tsinghua University Press) pp23–26
[18] Li P Z, Zheng Y B, Luo L 2020 J. Coast. Res. 104 255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Jeon W, Jeong W, Son K, Yang H 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 4240
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Eybposh M H, Caira N W, Atisa M, Chakravarthula P, Pégard N C 2020 Opt. Express 28 26636
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 3816
- PDF Downloads: 113
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: