-
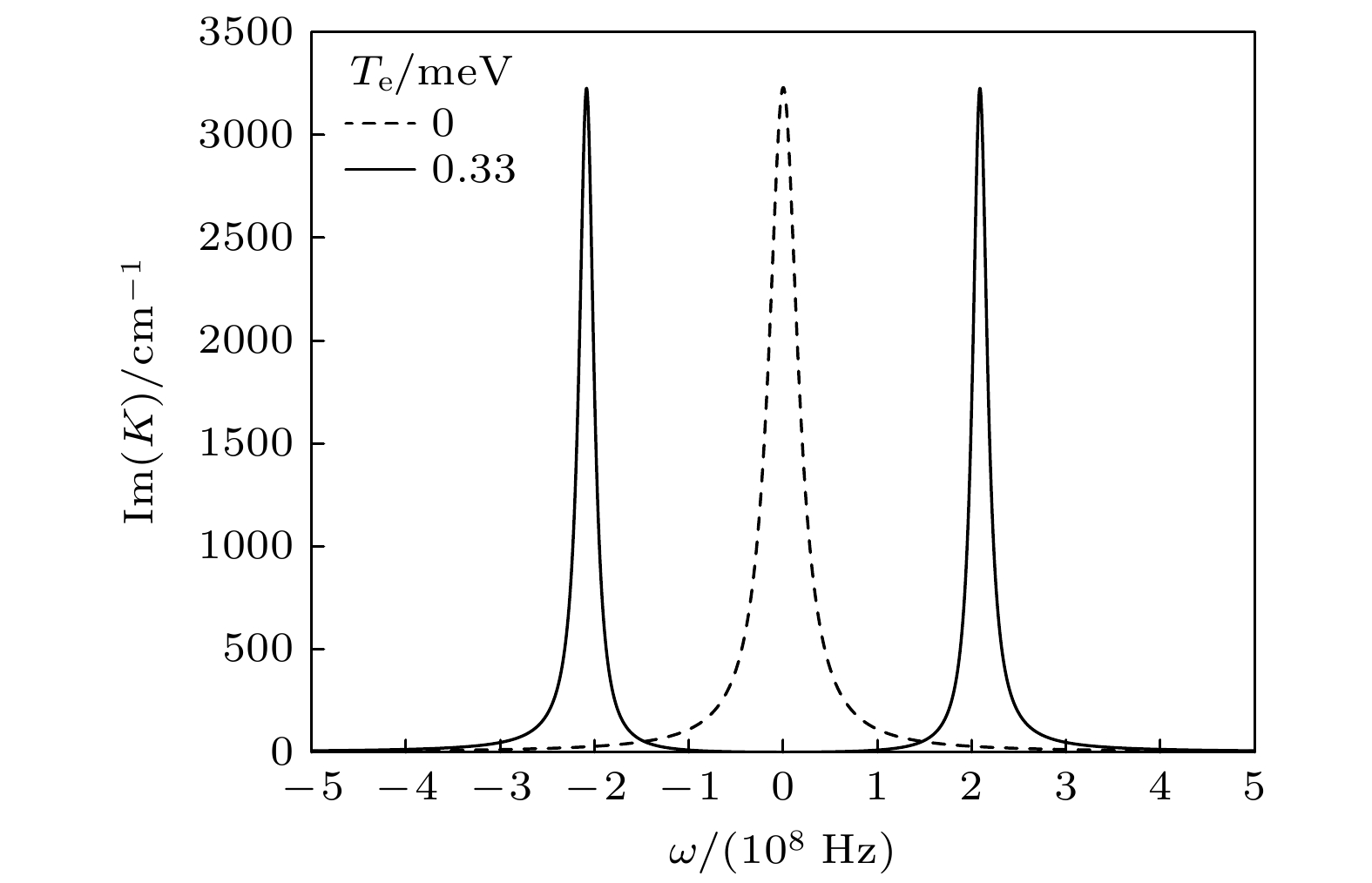
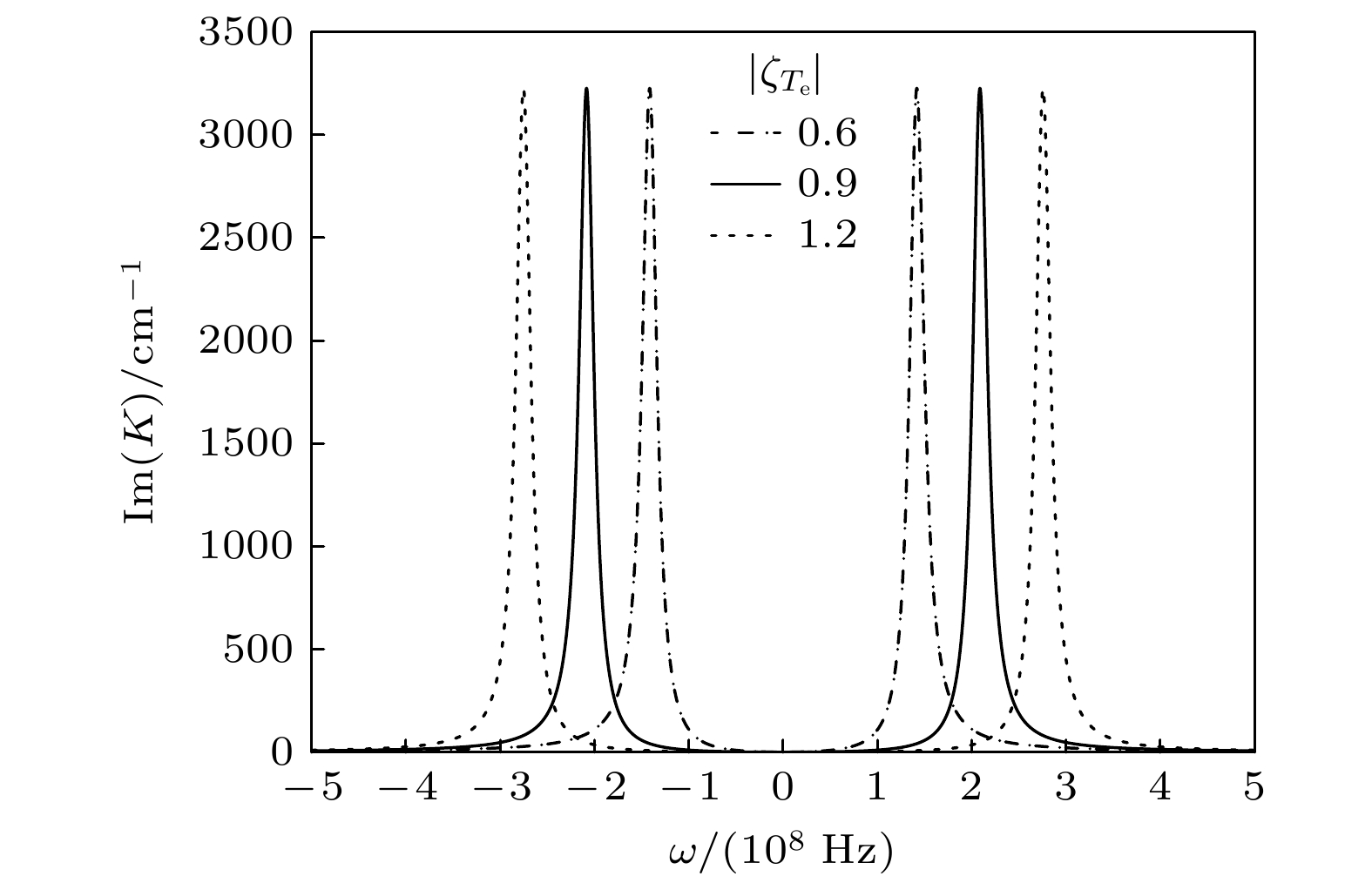
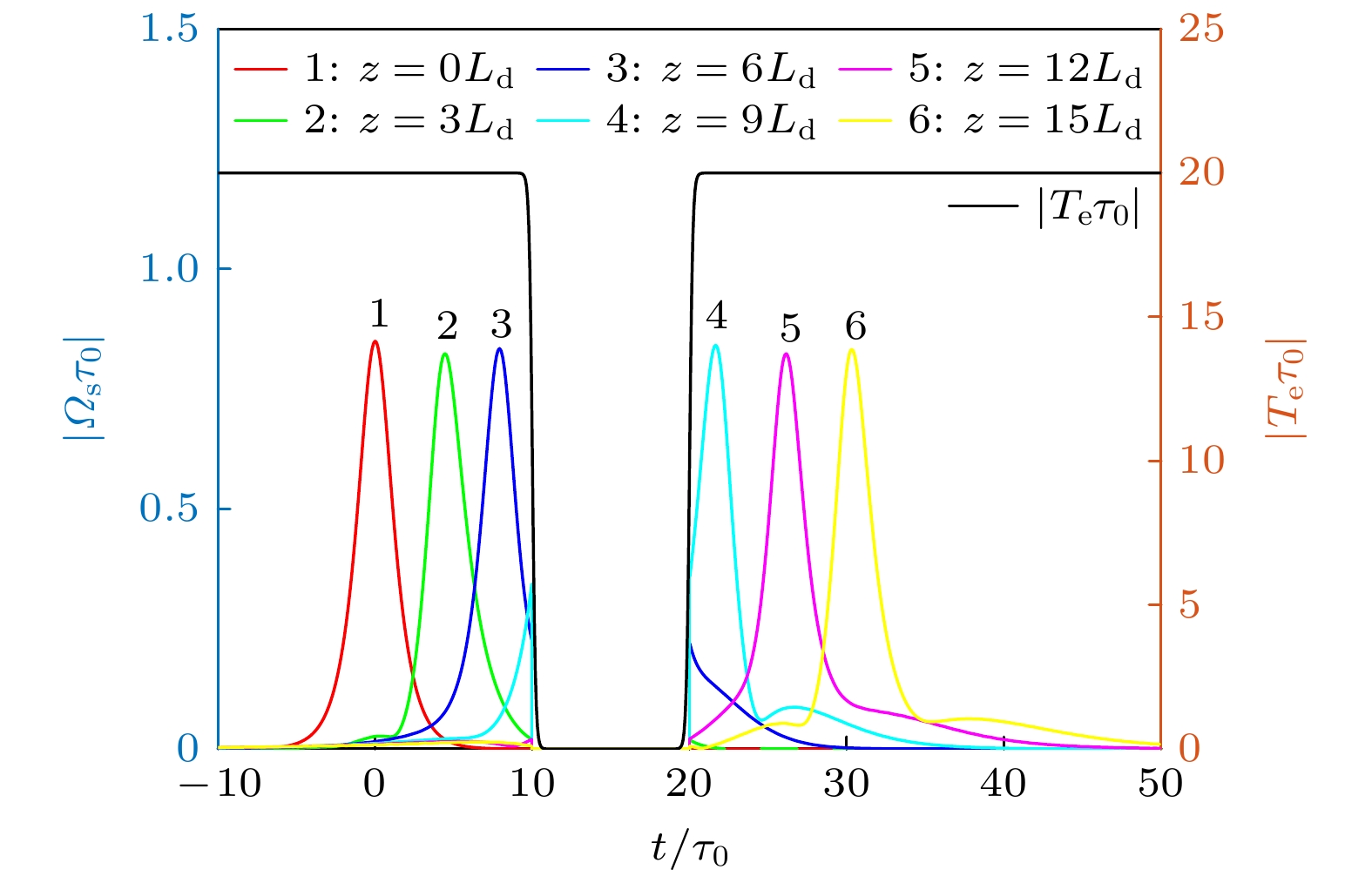
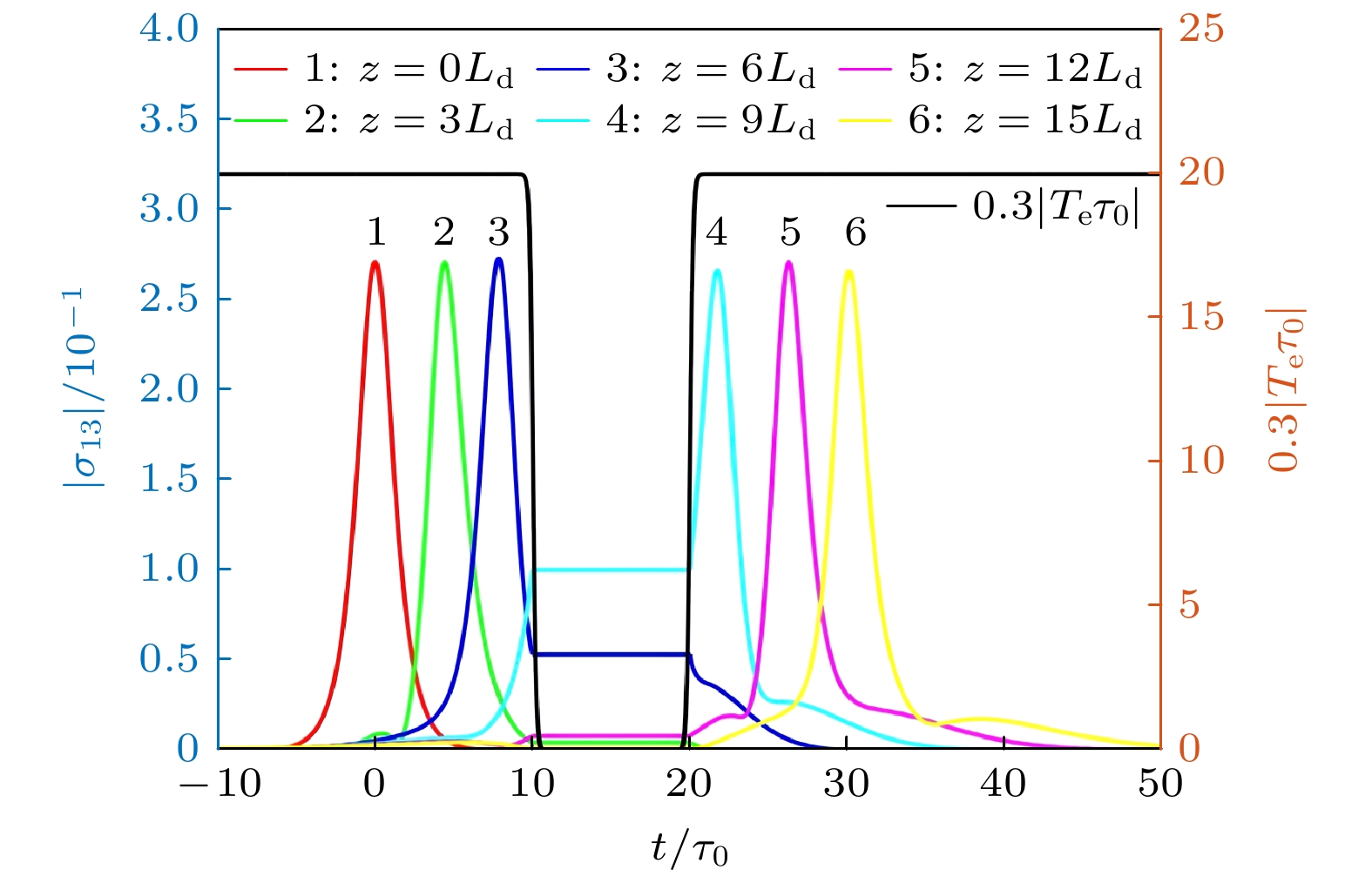
The best carrier for quantum information transmission is light signal, which has a fast propagation speed and can carry a large amount of information. However, during the propagation of light, dispersion effect and diffraction effect can cause quantum information to be distorted to a certain extent. On the contrary, optical solitons are formed due to the balance between the system’s dispersion (diffraction) effect and nonlinear effect, and they exhibit very high stability and fidelity. Therefore, they have received widespread attention in electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT) media with ultracold atoms. However, cold atomic gas media require extremely low operating temperatures, and the performances of the materials are difficult to control precisely. These factors are unfavorable for the miniaturization and integration of future information devices, thus significantly limiting their practical applications. Semiconductor quantum dot media, on the other hand, possess advantages such as discrete energy level structures and spectral properties similar to those of cold atomic gases, longer decoherence times, larger electric dipole moments, more significant nonlinear optical effects, and easy integration, making them an ideal alternative to cold atomic media. In this work, semiconductor quantum dots are coupled with optical fibers, the most common carrier in optical communication, to explore the formation, storage, and retrieval of temporal optical solitons in the coupled system. The results show that due to the tunneling-induced transparency effect between dots in semiconductor quantum dot molecules, light absorption in the system is greatly suppressed. At the same time, the transverse confinement of the nanofiber can enhance the interaction between light and the system, and the enhanced nonlinear response of the system can balance the dispersion effect, resulting in stable temporal optical solitons. Further research indicates that by turning on and off the inter-dot tunneling coupling, the high-efficiency and high-fidelity storage and retrieval of optical solitons can be realized in the system. These findings have certain guiding significance and potential application value for the processing all-optical information in solid quantum materials.
-
Keywords:
- tunneling induced transparency /
- the storage and retrieval of the optical solitons /
- semiconductor quantum dot /
- nanofiber
[1] Harris S E, Field J E, Imamoğlu A 1990 Phys. Rev. Lett. 64 1107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Huang G X, Hang C, Deng L 2008 Phys. Rev. A 77 011803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wu Y, Deng L 2004 Opt. Lett. 29 2064
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wu Y, Deng L 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 93 143904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Fleischhauer M, Lukin M D 2000 Phys. Rev. Lett. 84 5094
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Mohapatra A K, Jackson T R, Adams C S 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 113003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Chen Y, Bai Z Y, Huang G X 2014 Phys. Rev. A 89 023835
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Chen Y, Chen Z M, Huang G X 2015 Phys. Rev. A 91 023820
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Xu D T, Chen Z M, Huang G X 2017 Opt. Express 25 19094
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Shou C, Huang G X 2020 Opt. Lett. 45 6787
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Shou C, Zhang Q, Luo W C, Huang G X 2021 Opt. Express 29 9772
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Chen H X, Durrant A V, Marangos J P, Vaccaro J A 1998 Phys. Rev. A 58 1545
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Boon J R, Zekou E, Fulton D J, Dunn M H 1998 Phys. Rev. A 57 1323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Sprague M R, Michelberger P S, Champion T F M, England D G, Nunn J, Jin X M, Kolthammer W S, Abdolvand A, Russell P St J, Walmsley I A 2014 Nat. Photonics 8 287
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Xu D T, Bai Z Y, Huang G X 2016 Phys. Rev. A 94 063857
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Maxwell D, Szwer D J, Barato D P, Busche H, Pritchard J D, Gauguet A, Weatherill K J, Jones M P A, Adams C S 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 103001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Gouraud B, Maxein D, Nicolas A, Morin O, Laurat J 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 180503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Sayrin C, Clausen C, Albrecht B, Schneeweiss P, Rauschenbeutel A 2015 Optica 2 353
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wang Z P, Yu B L 2013 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 30 2915
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Yang W, Chen A, Lee R, Wu Y 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 013835
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] She Y C, Zheng X J, Wang D L, Zhang W X 2013 Opt. Express 21 17392
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Yuan C H, Zhu K D 2006 Appl. Phys. Lett. 89 052115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Tian S C, Wan R G, Tong C Z, Fu X H, Cao J S, Ning Y Q 2015 Laser Phys. Lett. 12 125203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wang J Y, Huang S Y, Huang G Y, Pan D, Zhao J H, Xu H Q 2017 Nano Lett. 17 4158
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 任波, 佘彦超, 徐小凤, 叶伏秋 2021 70 224205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ren B, She Y C, Xu X F, Ye F Q 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 224205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 杨璇, 王胤, 王登龙, 丁建文 2020 69 174203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang X, Wang Y, Wang D L, Ding J W 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 174203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Ku P C, Chang-Hasnain C J, Chuang S L 2002 Electron. Lett. 38 1581
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Chang-Hasnain C J, Ku P C, Kim J 2003 Proc. IEEE 91 1884
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhou Y, Yi C, Liu Q, Wang C K, Tan C H 2020 Opt. Express 28 34730
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Tan C H, Huang G X 2014 Phys. Rev. A 89 033860
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Tan C H, Huang G X 2015 Phys. Rev. A 91 023803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Liu Q, Li N, Tan C H 2020 Phys. Rev. A 101 023818
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Zorgabad S A, Bonabi R S, Sanders B C 2018 Phys. Rev. A 98 013825
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Zorgabad S A, Berini P, Sanders B C 2019 Phys. Rev. A 99 051802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Liu M, Luo A P, Luo Z C, Xu W C 2017 Opt. Lett. 42 330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Chen Z M, Xie H Q, Li Q, Huang G X 2019 Phys. Rev. A 100 013827
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
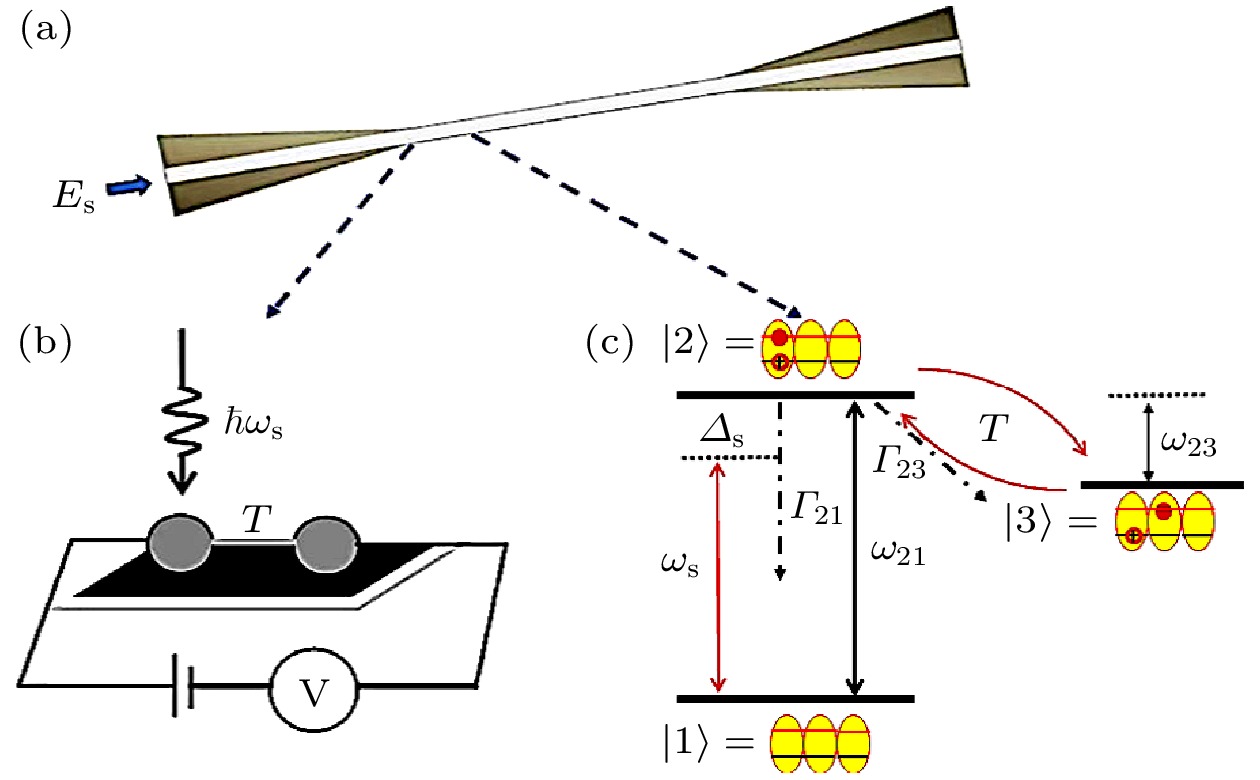
图 1 纳米光纤-半导体量子点分子耦合系统物理模型 (a)模型平面示意图, 纳米光纤引导信号光脉冲; (b)量子点分子原理图; (c)非对称双量子点模型能级图
Figure 1. Physical model of nanofiber-semiconductor quantum dot molecule coupling system: (a) Schematic diagram of the model plane, nanofiber guiding signal light pulses; (b) schematic diagram of quantum dot molecule; (c) energy level diagram of asymmetric double quantum dot model.
-
[1] Harris S E, Field J E, Imamoğlu A 1990 Phys. Rev. Lett. 64 1107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Huang G X, Hang C, Deng L 2008 Phys. Rev. A 77 011803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wu Y, Deng L 2004 Opt. Lett. 29 2064
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wu Y, Deng L 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 93 143904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Fleischhauer M, Lukin M D 2000 Phys. Rev. Lett. 84 5094
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Mohapatra A K, Jackson T R, Adams C S 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 113003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Chen Y, Bai Z Y, Huang G X 2014 Phys. Rev. A 89 023835
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Chen Y, Chen Z M, Huang G X 2015 Phys. Rev. A 91 023820
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Xu D T, Chen Z M, Huang G X 2017 Opt. Express 25 19094
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Shou C, Huang G X 2020 Opt. Lett. 45 6787
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Shou C, Zhang Q, Luo W C, Huang G X 2021 Opt. Express 29 9772
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Chen H X, Durrant A V, Marangos J P, Vaccaro J A 1998 Phys. Rev. A 58 1545
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Boon J R, Zekou E, Fulton D J, Dunn M H 1998 Phys. Rev. A 57 1323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Sprague M R, Michelberger P S, Champion T F M, England D G, Nunn J, Jin X M, Kolthammer W S, Abdolvand A, Russell P St J, Walmsley I A 2014 Nat. Photonics 8 287
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Xu D T, Bai Z Y, Huang G X 2016 Phys. Rev. A 94 063857
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Maxwell D, Szwer D J, Barato D P, Busche H, Pritchard J D, Gauguet A, Weatherill K J, Jones M P A, Adams C S 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 103001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Gouraud B, Maxein D, Nicolas A, Morin O, Laurat J 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 180503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Sayrin C, Clausen C, Albrecht B, Schneeweiss P, Rauschenbeutel A 2015 Optica 2 353
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wang Z P, Yu B L 2013 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 30 2915
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Yang W, Chen A, Lee R, Wu Y 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 013835
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] She Y C, Zheng X J, Wang D L, Zhang W X 2013 Opt. Express 21 17392
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Yuan C H, Zhu K D 2006 Appl. Phys. Lett. 89 052115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Tian S C, Wan R G, Tong C Z, Fu X H, Cao J S, Ning Y Q 2015 Laser Phys. Lett. 12 125203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wang J Y, Huang S Y, Huang G Y, Pan D, Zhao J H, Xu H Q 2017 Nano Lett. 17 4158
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 任波, 佘彦超, 徐小凤, 叶伏秋 2021 70 224205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ren B, She Y C, Xu X F, Ye F Q 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 224205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 杨璇, 王胤, 王登龙, 丁建文 2020 69 174203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang X, Wang Y, Wang D L, Ding J W 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 174203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Ku P C, Chang-Hasnain C J, Chuang S L 2002 Electron. Lett. 38 1581
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Chang-Hasnain C J, Ku P C, Kim J 2003 Proc. IEEE 91 1884
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhou Y, Yi C, Liu Q, Wang C K, Tan C H 2020 Opt. Express 28 34730
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Tan C H, Huang G X 2014 Phys. Rev. A 89 033860
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Tan C H, Huang G X 2015 Phys. Rev. A 91 023803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Liu Q, Li N, Tan C H 2020 Phys. Rev. A 101 023818
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Zorgabad S A, Bonabi R S, Sanders B C 2018 Phys. Rev. A 98 013825
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Zorgabad S A, Berini P, Sanders B C 2019 Phys. Rev. A 99 051802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Liu M, Luo A P, Luo Z C, Xu W C 2017 Opt. Lett. 42 330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Chen Z M, Xie H Q, Li Q, Huang G X 2019 Phys. Rev. A 100 013827
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 3951
- PDF Downloads: 66
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: