-
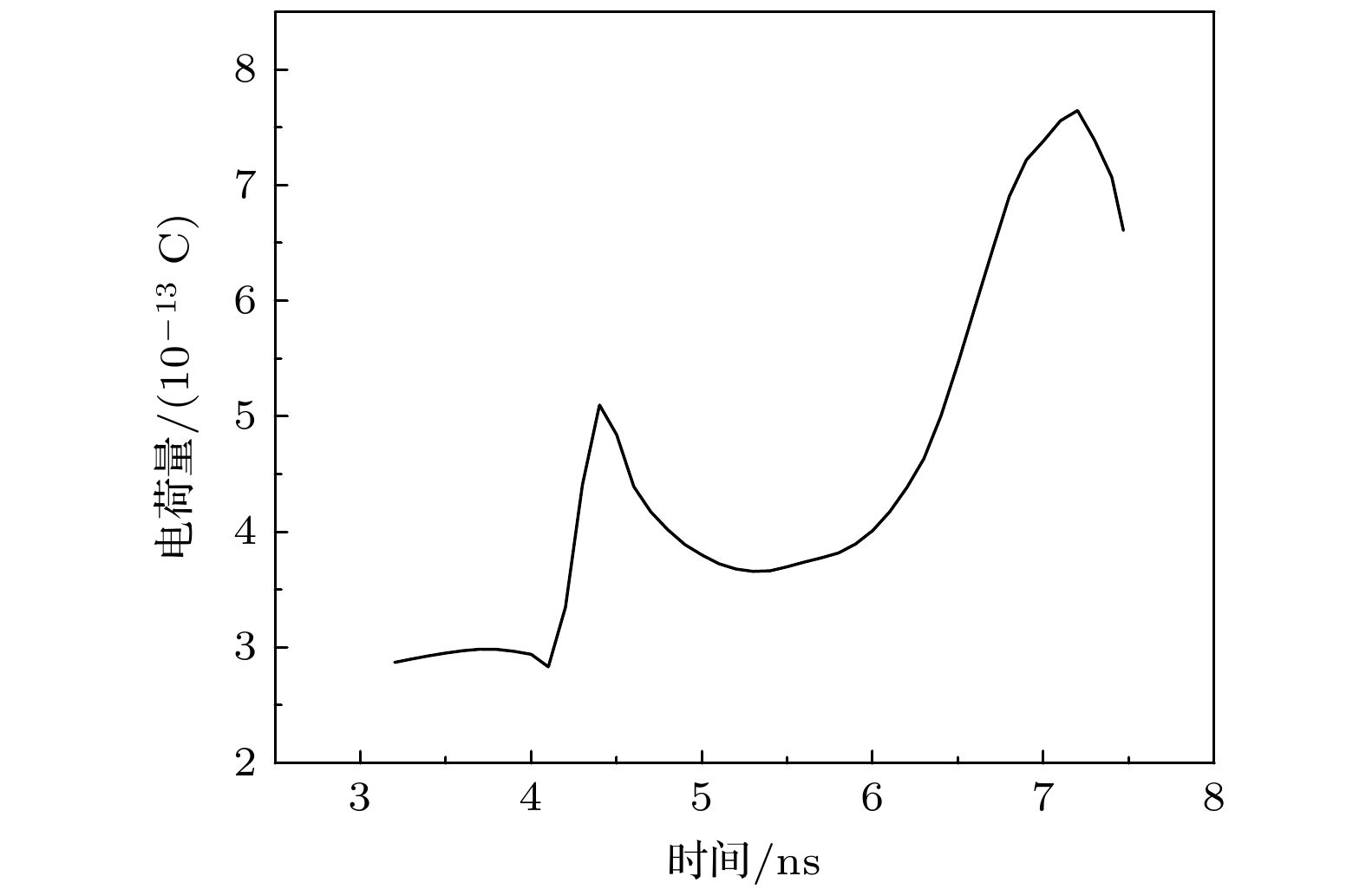
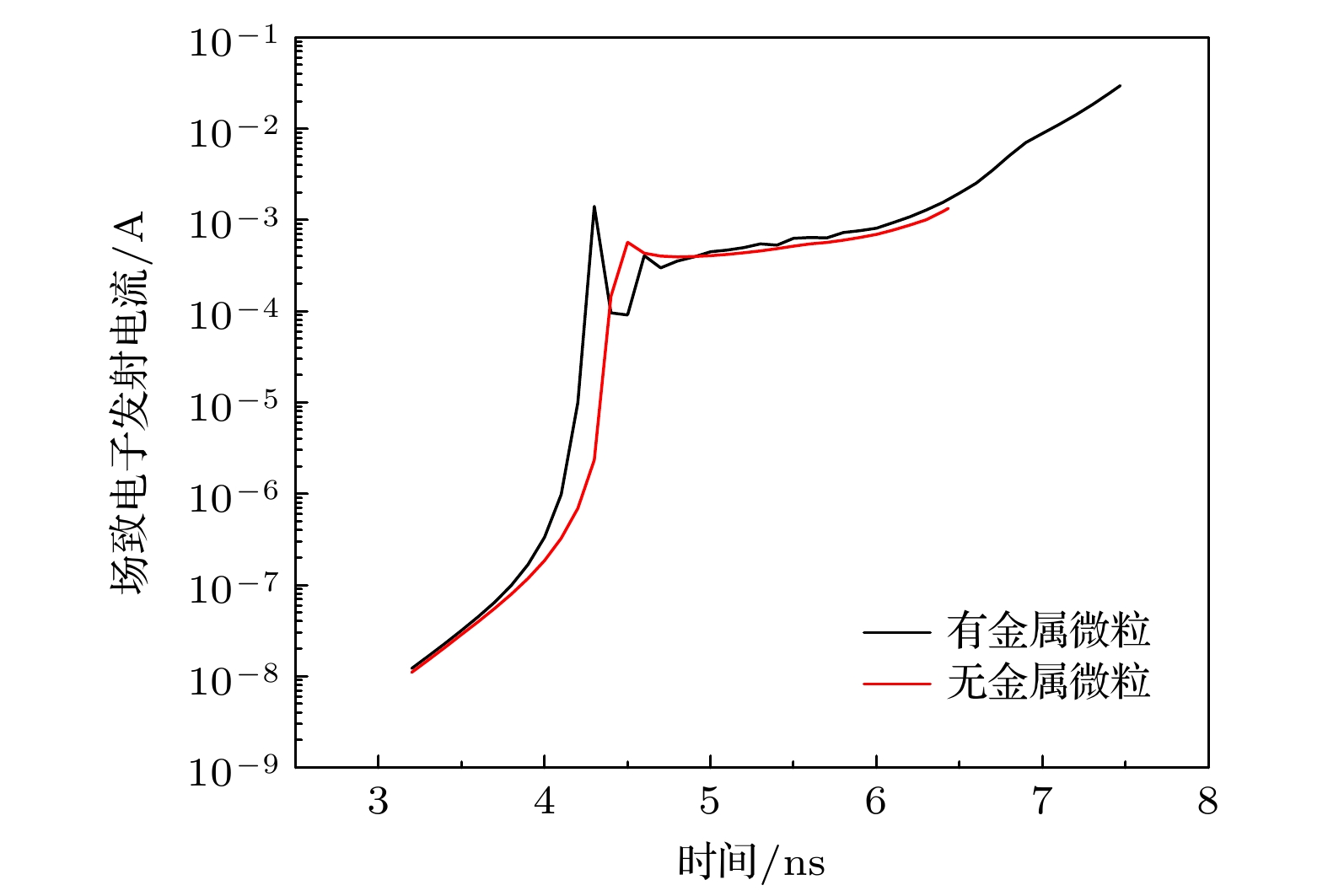
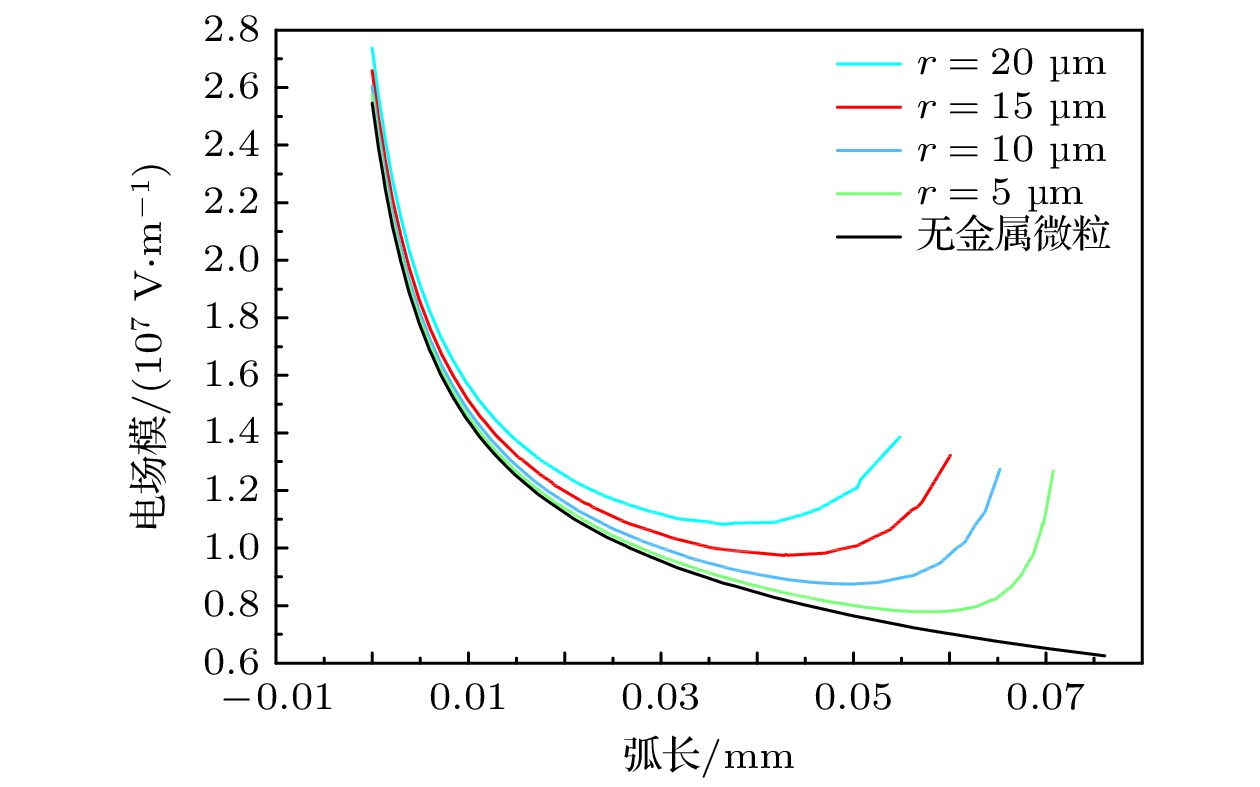
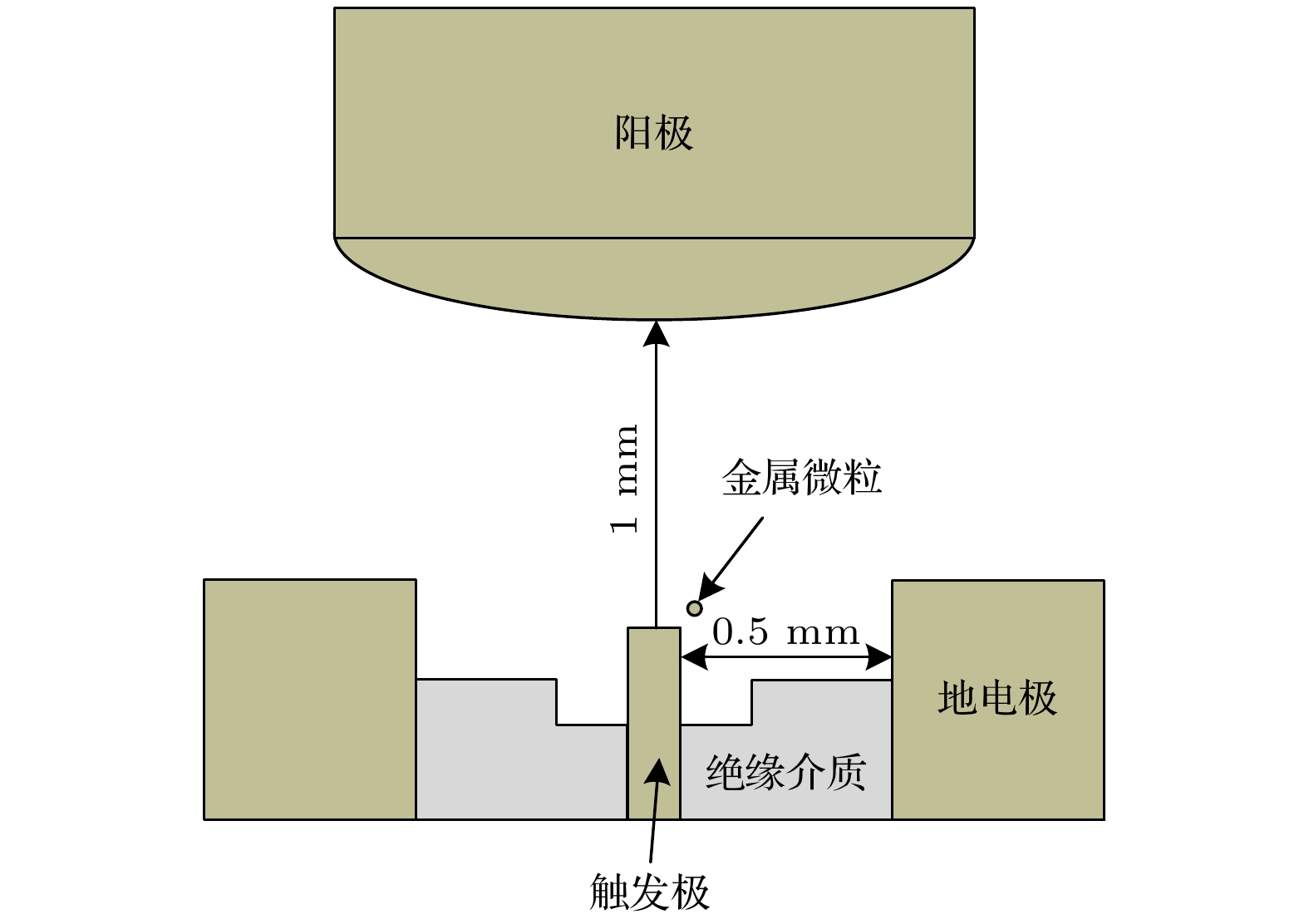
Compared with two-electrode gas spark switch, three-electrode gas spark switch has the advantages of lower operating voltage, higher reliability and less discharge jitter, so it has been widely used in pulse power systems. However, due to the characteristics of pulse power technology, the gas spark switch is easy to cause ablation on the electrode surface during use, and the metal particles generated by ablation will significantly affect the stability and reliability of the switch. In this work the discharge process of the three-electrode gas spark switch under atmospheric pressure nitrogen environment is simulated first. In this model, the ionization coefficient near the trigger electrode is modified to compensate for the shortcomings of the local field approximation, and the relevant mathematical derivation process is given. The formation of the initial electrons is described by the field electron emission phenomenon, and the development process of electron collapse into the streamer is obtained. The physical mechanism of switch on is investigated, and the development process of each stage of switch discharge is described in detail. Then, the discharge process of the switch is studied when there are metal particles near the trigger. The study shows that the presence of metal particles enhances the electric field near the trigger and accelerates the formation of the initial electron cloud. In addition, in the presence of metal particles, the metal particles and the trigger will first break down, forming a high-density plasma channel after the breakdown, and becoming the source of the subsequent flow development. At the same time, because the metal particles on the channel have an obstructing effect on the streamer development, the streamer generates a discharge branch after contacting metal particles. In the end, the influences of metal particles of different shapes and sizes on the discharge process are discussed. The results show that metal particles with sharp shapes have stronger electric field distortion, when the electric field intensity is large enough, it may cause field emission on the surface of metal particle. And it is also made clear that the size of metal particle is small, the obstruction of the development path of streamer is small, and the streamers quickly converge behind the particles.
-
Keywords:
- streamer discharge /
- gas spark switch /
- metal particle /
- field emission
[1] Golnabi H 2000 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 71 413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Yalandin M I, Sharypov K A, Shpak V G, Shunailov S A, Mesyats G A 2008 Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Power Modulators and High Voltage Conference, PMHVC Las Vegas, NV, USA, May 27–31, 2008 pp207–210
[3] 邵涛, 章程, 王瑞雪, 严萍, 任成燕 2016 高电压技术 42 685
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shao T, Zhang C, Wang R X, Yan P, Ren C Y 2016 High Voltage 42 685
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhong W, Zhang G L, Xu A 2019 AIP Adv. 9 045023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Li X A, Pei Z H, Wu Z C, Zhang Y Z, Liu X D, Li Y D, Zhang Q G 2018 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 89 035113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wang J, Li Q, Li B, Chen C, Liu S, Li C 2016 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 23 1951
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] You H, Zhang Q, Guo C, Xu P, Ma J, Qin Y, Wen T, Li Y 2017 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 24 876
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Cookson A H, Farish O, Sommerman G M L 1972 IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. PAS-91 1329
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Laghari J R, Qureshi A H 1981 IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul. EI-16 388
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Hara M, Akazaki M 1977 J. Electrost. 2 223
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 徐翱, 钟伟, 金大志, 陈磊, 谈效华 2019 真空科学与技术学报 39 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu A, Zhong W, Jin D Z, Chen L, Tan X H 2019 Chin. J. Vacuum Sci. Tech. 39 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhong W, Shi Y, Zhang C, Li X 2020 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 27 1095
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Sun Q, Zhou Q H, Yang W, Dong Y, Zhang H T, Song M M, Wu Y 2021 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 30 045001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 孙强, 周前红, 宋萌萌, 杨薇, 董烨 2021 70 015202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun Q, Zhou Q H, Song M M, Yang W, Dong Y 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 015202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Asiunin V I, Davydov S G, Dolgov A N, et al. 2018 Plasma Phys. Rep. 44 605
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 党腾飞, 尹佳辉, 孙凤举, 王志国, 姜晓峰, 曾江涛, 魏浩, 邱爱慈 2015 强激光与粒子束 27 065004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dang T F, Yin J H, Sun F J, Wang Z G, Jiang X F, Zeng J T, Wei H, Qiu A C 2015 High Power Laser Part. Beams 27 065004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 孙旭, 苏建仓, 张喜波, 王利民, 李锐 2012 强激光与粒子束 24 843
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun X, Su J C, Zhang X B, Wang L M, Li R 2012 High Power Laser Part. Beams 24 843
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Hagelaar G J M, Pitchford L C 2005 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 14 722
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Montijn C, Hundsdorfer W, Ebert U 2006 J. Comput. Phys. 219 801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Dhali S K, Williams P F 1987 J. Appl. Phys. 62 4696
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zhu Y F, Chen X C, Wu Y, Hao J B, Ma X G, Lu P F, Tardiveau P 2021 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 30 075025
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Soloviev V R, Krivtsov V M 2009 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 42 125208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Nefyodtsev E V 2014 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 21 892
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 杨初平, 耿屹楠, 王捷, 刘兴南, 时振刚 2021 70 135102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang C P, Geng Y N, Wang J, Liu X N, Shi Z G 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 135102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Forbes R G, Deane J H B 2007 Proc. R. Soc. A 463 2907
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 徐翱, 杨林, 钟伟, 刘云龙, 尚绍环, 金大志 2018 高电压技术 44 1922
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu A, Yang L, Zhong W, Liu Y L, Shang S H, Jin D Z 2018 High Voltage 44 1922
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Levko D, Arslanbekov R R, Kolobov V I 2020 J. Appl. Phys. 127 043301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 李伯男, 李熙, 黄磊峰, 刘洋, 吴益明, 吴鹏 2019 电力工程技术 38 123
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li B N, Li X, Huang L F, Liu Y, Wu Y M, Wu P 2019 Electric Power Eng. Tech. 38 123
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
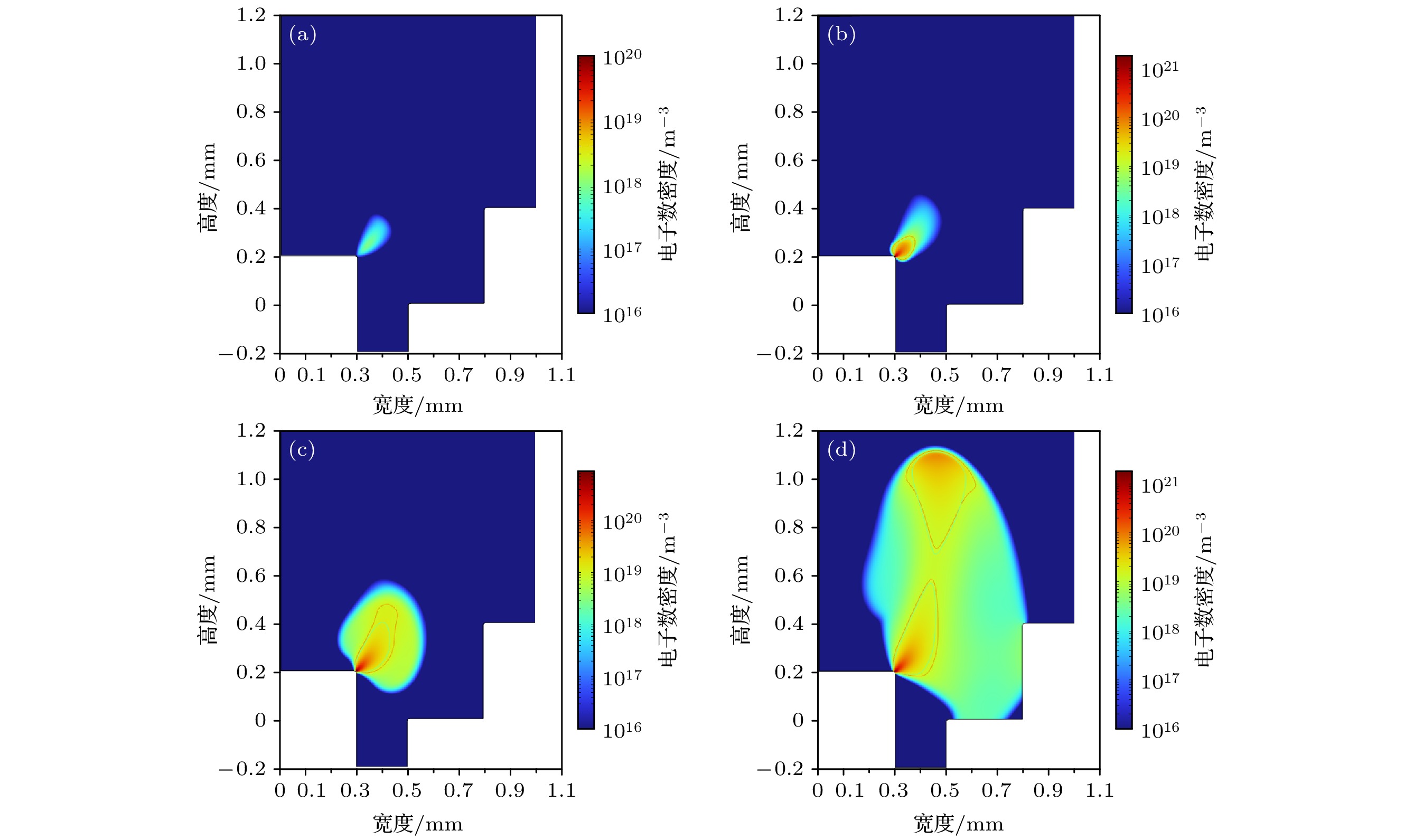
图 3 电子密度时空分布图, 其中绿色等高线为1×1019 m–3电子数密度等高线, 红色等高线为1×1019 m–3正离子数密度等高线 (a) 4.0 ns; (b) 4.5 ns; (c) 5.0 ns; (d) 6.3 ns
Figure 3. Spatial and temporal distribution of electron density, where the green contour is the 1×1019 m–3 electron number density contour and the red contour is the 1×1019 m–3 positive ion number density contour: (a) 4.0 ns; (b) 4.5 ns; (c) 5.0 ns; (d) 6.3 ns.
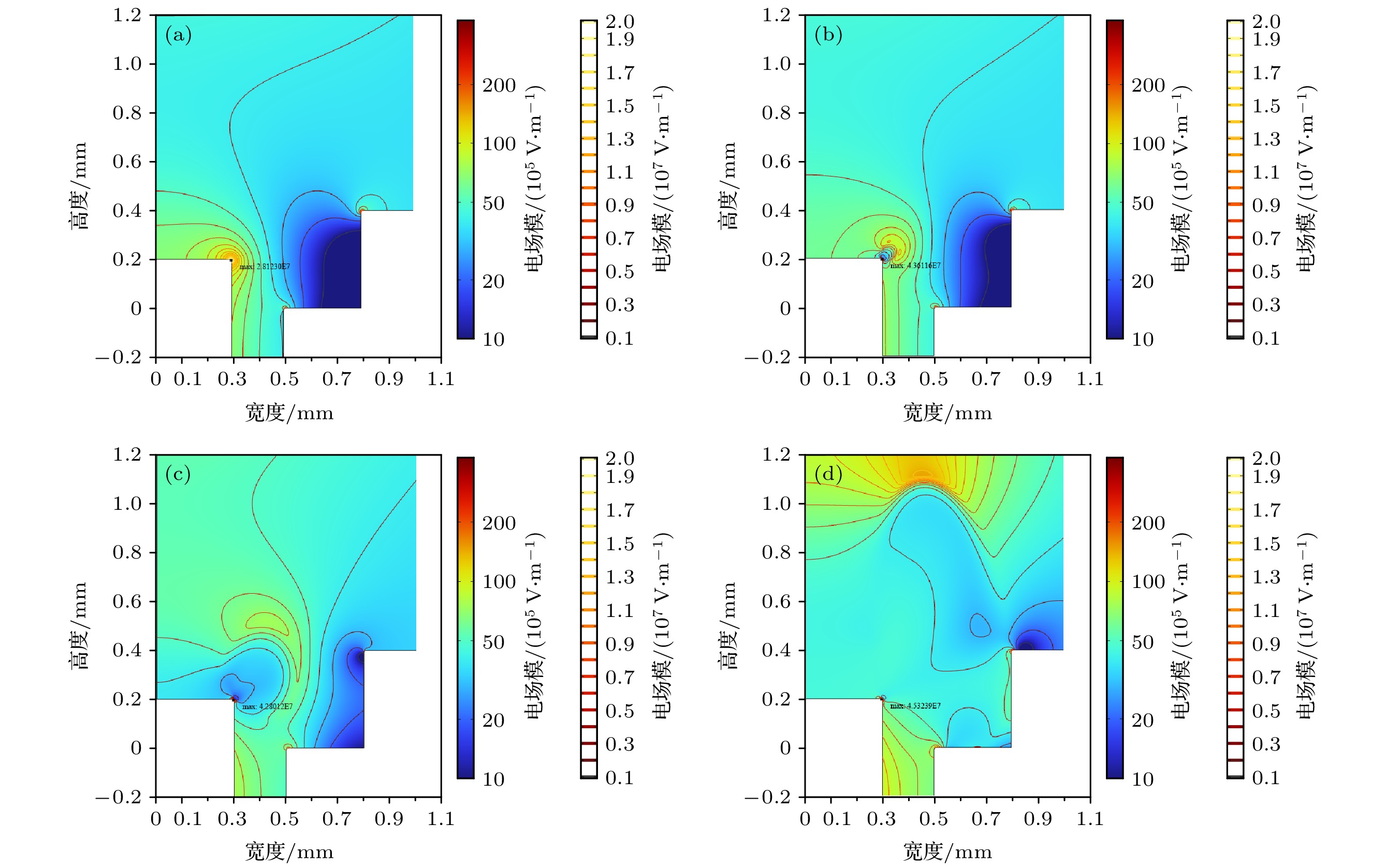
图 8 电子密度时空分布图, 其中绿色等高线为1×1019 m–3电子数密度等高线, 红色等高线为1×1019 m–3正离子数密度等高线 (a) 4.0 ns; (b) 4.5 ns; (c) 5.0 ns; (d) 6.3 ns
Figure 8. Spatial and temporal distribution of electron density, where the green contour is the 1×1019 m–3 electron number density contour and the red contour is the 1×1019 m–3 positive ion number density contour: (a) 4.0 ns; (b) 4.5 ns; (c) 5.0 ns; (d) 6.3 ns.
-
[1] Golnabi H 2000 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 71 413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Yalandin M I, Sharypov K A, Shpak V G, Shunailov S A, Mesyats G A 2008 Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Power Modulators and High Voltage Conference, PMHVC Las Vegas, NV, USA, May 27–31, 2008 pp207–210
[3] 邵涛, 章程, 王瑞雪, 严萍, 任成燕 2016 高电压技术 42 685
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shao T, Zhang C, Wang R X, Yan P, Ren C Y 2016 High Voltage 42 685
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhong W, Zhang G L, Xu A 2019 AIP Adv. 9 045023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Li X A, Pei Z H, Wu Z C, Zhang Y Z, Liu X D, Li Y D, Zhang Q G 2018 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 89 035113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wang J, Li Q, Li B, Chen C, Liu S, Li C 2016 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 23 1951
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] You H, Zhang Q, Guo C, Xu P, Ma J, Qin Y, Wen T, Li Y 2017 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 24 876
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Cookson A H, Farish O, Sommerman G M L 1972 IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. PAS-91 1329
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Laghari J R, Qureshi A H 1981 IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul. EI-16 388
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Hara M, Akazaki M 1977 J. Electrost. 2 223
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 徐翱, 钟伟, 金大志, 陈磊, 谈效华 2019 真空科学与技术学报 39 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu A, Zhong W, Jin D Z, Chen L, Tan X H 2019 Chin. J. Vacuum Sci. Tech. 39 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhong W, Shi Y, Zhang C, Li X 2020 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 27 1095
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Sun Q, Zhou Q H, Yang W, Dong Y, Zhang H T, Song M M, Wu Y 2021 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 30 045001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 孙强, 周前红, 宋萌萌, 杨薇, 董烨 2021 70 015202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun Q, Zhou Q H, Song M M, Yang W, Dong Y 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 015202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Asiunin V I, Davydov S G, Dolgov A N, et al. 2018 Plasma Phys. Rep. 44 605
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 党腾飞, 尹佳辉, 孙凤举, 王志国, 姜晓峰, 曾江涛, 魏浩, 邱爱慈 2015 强激光与粒子束 27 065004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dang T F, Yin J H, Sun F J, Wang Z G, Jiang X F, Zeng J T, Wei H, Qiu A C 2015 High Power Laser Part. Beams 27 065004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 孙旭, 苏建仓, 张喜波, 王利民, 李锐 2012 强激光与粒子束 24 843
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun X, Su J C, Zhang X B, Wang L M, Li R 2012 High Power Laser Part. Beams 24 843
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Hagelaar G J M, Pitchford L C 2005 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 14 722
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Montijn C, Hundsdorfer W, Ebert U 2006 J. Comput. Phys. 219 801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Dhali S K, Williams P F 1987 J. Appl. Phys. 62 4696
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zhu Y F, Chen X C, Wu Y, Hao J B, Ma X G, Lu P F, Tardiveau P 2021 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 30 075025
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Soloviev V R, Krivtsov V M 2009 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 42 125208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Nefyodtsev E V 2014 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 21 892
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 杨初平, 耿屹楠, 王捷, 刘兴南, 时振刚 2021 70 135102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang C P, Geng Y N, Wang J, Liu X N, Shi Z G 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 135102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Forbes R G, Deane J H B 2007 Proc. R. Soc. A 463 2907
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 徐翱, 杨林, 钟伟, 刘云龙, 尚绍环, 金大志 2018 高电压技术 44 1922
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu A, Yang L, Zhong W, Liu Y L, Shang S H, Jin D Z 2018 High Voltage 44 1922
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Levko D, Arslanbekov R R, Kolobov V I 2020 J. Appl. Phys. 127 043301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 李伯男, 李熙, 黄磊峰, 刘洋, 吴益明, 吴鹏 2019 电力工程技术 38 123
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li B N, Li X, Huang L F, Liu Y, Wu Y M, Wu P 2019 Electric Power Eng. Tech. 38 123
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
 1-20231283 补充材料.pdf
1-20231283 补充材料.pdf

Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 5324
- PDF Downloads: 83
- Cited By: 0
















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: